




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (7): 133-141.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0419
• ANIMAL AND PLANT HEALTH • Previous Articles
Yishuai YANG1( ), Lin TAN2, Li NIU1, Ping SHU1, Zihan SHI1, Jie FANG2, Qiulong HU1(
), Lin TAN2, Li NIU1, Ping SHU1, Zihan SHI1, Jie FANG2, Qiulong HU1( )
)
Received:2024-05-24
Accepted:2024-12-26
Online:2025-07-15
Published:2025-07-11
Contact:
Qiulong HU
杨艺帅1( ), 谭琳2, 牛丽1, 舒坪1, 史子涵1, 方洁2, 胡秋龙1(
), 谭琳2, 牛丽1, 舒坪1, 史子涵1, 方洁2, 胡秋龙1( )
)
通讯作者:
胡秋龙
作者简介:杨艺帅E-mail:519414001@qq.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yishuai YANG, Lin TAN, Li NIU, Ping SHU, Zihan SHI, Jie FANG, Qiulong HU. Biological Characteristics and Fungicides Screening in Laboratory of Fusarium cugenangense Causing Camellia sinensis Root Rot[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(7): 133-141.
杨艺帅, 谭琳, 牛丽, 舒坪, 史子涵, 方洁, 胡秋龙. 茶树根腐病菌生物学特征及室内药剂筛选[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(7): 133-141.
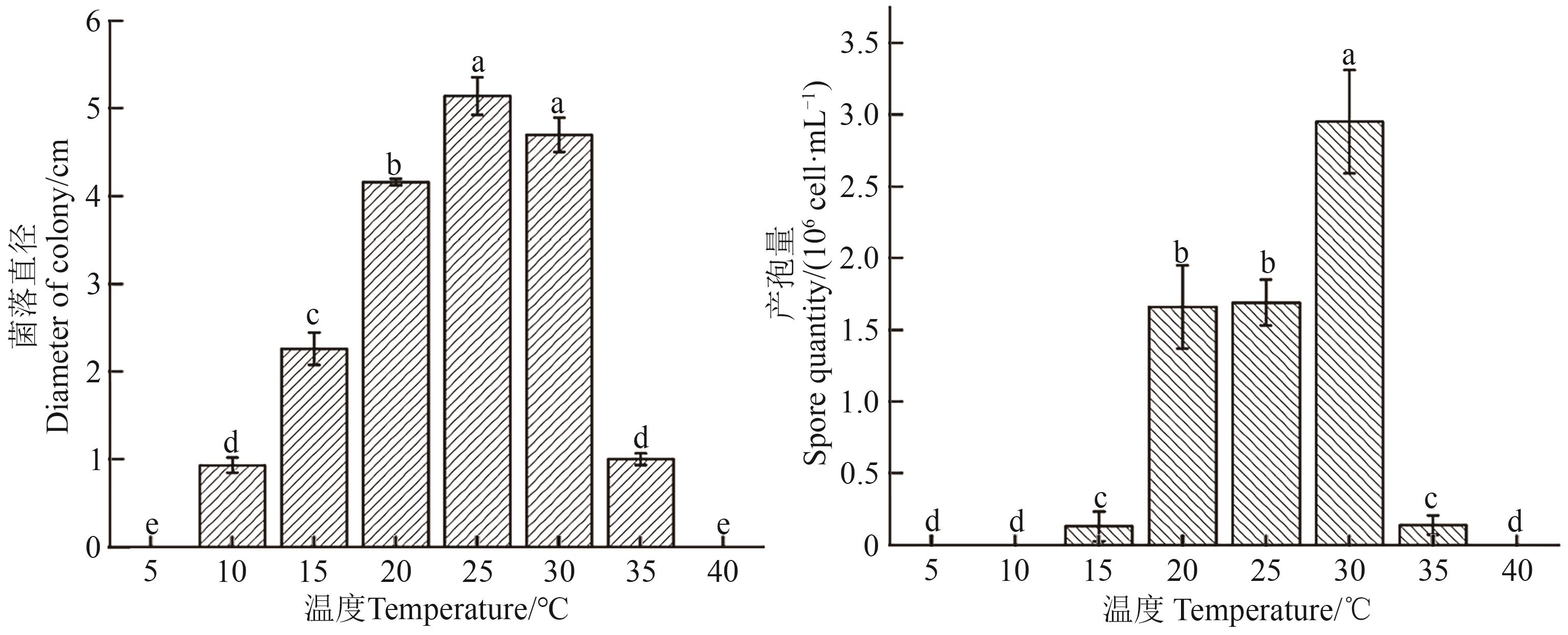
Fig. 1 Mycelial growth and sporulation of Fusarium cugenangense under different temperatureNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different temperatures at P<0.05 level.
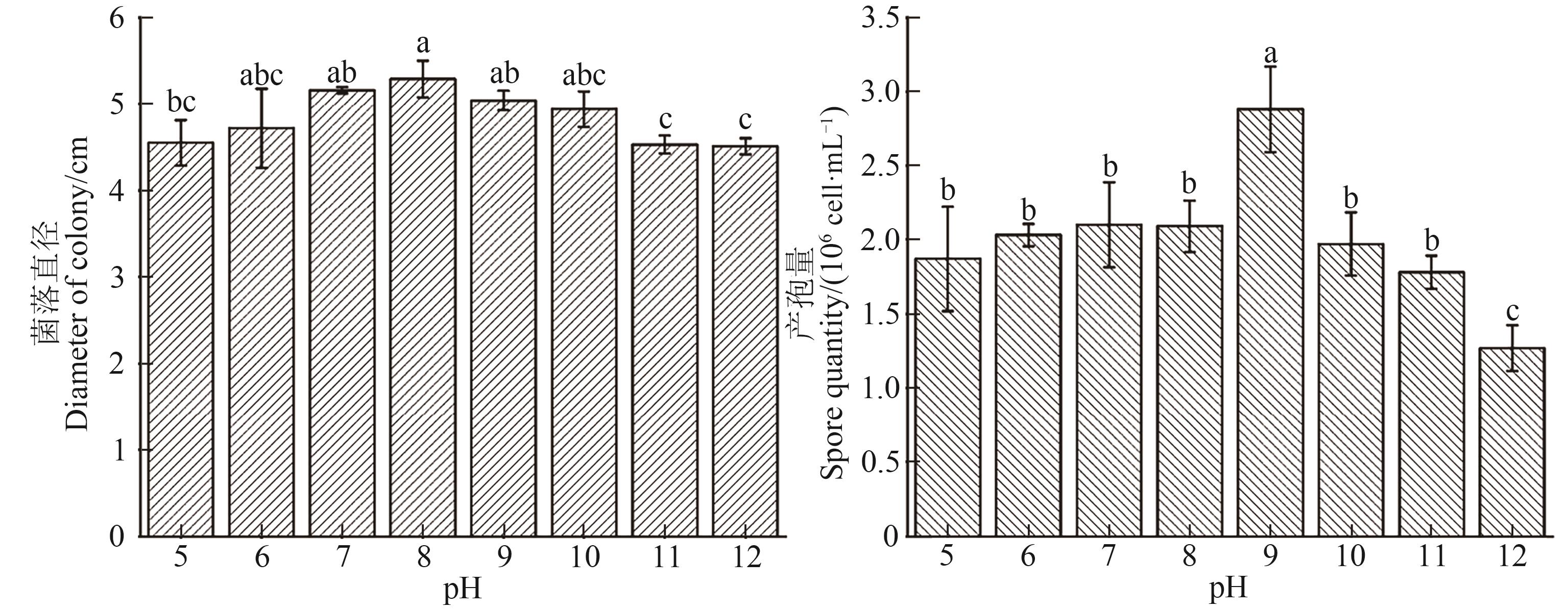
Fig. 2 Mycelial growth and sporulation of Fusarium cugenangense under different pH treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different pH treatments at P<0.05 level.

Fig. 3 Mycelial growth and sporulation of Fusarium cugenangense under different light conditionsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different light conditions at P<0.05 level.

Fig. 4 Mycelial growth and sporulation of Fusarium cugenangense under different carbon sourcesNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different carbon sources at P<0.05 level.
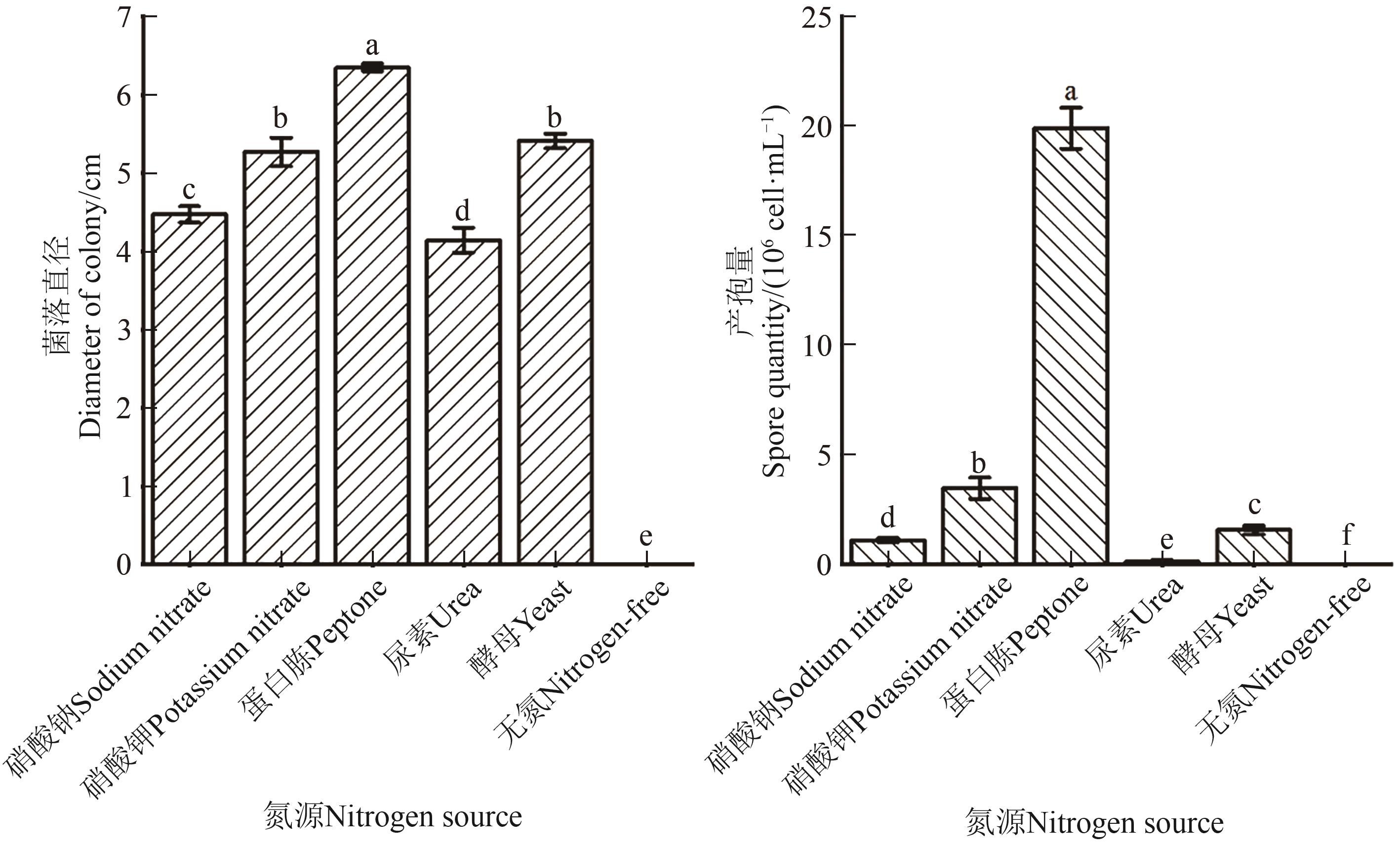
Fig. 5 Mycelial growth and sporulation of Fusarium cugenangense under different nitrogen resourcesNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different nitrogen sources at P<0.05 level.
| 药剂名称Agent name | 菌落直径Colony diameter/cm | 抑菌率Inhibition rate/% |
|---|---|---|
| 噁霉灵Hymexazol | 1.30±0.00 e | 80.97 a |
| 氟氯氰菊酯Cyfluthrin | 3.00±0.20 d | 56.08 b |
| 甲霜·噁霉灵Metalaxyl·hymexazol | 3.25±0.18 cd | 52.42 bc |
| 精甲·咯·嘧菌Metalaxyl-M·fludioxonil·azoxystrobin | 3.50±0.10 cd | 48.76 bc |
| 多菌灵Sanmate | 4.53±0.25 c | 33.63 c |
| 宁南霉Ningnanmycin | 5.37±0.21 bc | 21.43 cd |
| 氯溴异氰尿酸Chloroisobromine cyanuric acid | 5.68±0.49 abc | 16.79 cd |
| 氟菌·霜霉威Fluomycetes downomycetes | 6.17±0.15 ab | 9.71 d |
| 对照Control | 6.83±0.15 a | — |
Table 1 Inhibition rates of test agents
| 药剂名称Agent name | 菌落直径Colony diameter/cm | 抑菌率Inhibition rate/% |
|---|---|---|
| 噁霉灵Hymexazol | 1.30±0.00 e | 80.97 a |
| 氟氯氰菊酯Cyfluthrin | 3.00±0.20 d | 56.08 b |
| 甲霜·噁霉灵Metalaxyl·hymexazol | 3.25±0.18 cd | 52.42 bc |
| 精甲·咯·嘧菌Metalaxyl-M·fludioxonil·azoxystrobin | 3.50±0.10 cd | 48.76 bc |
| 多菌灵Sanmate | 4.53±0.25 c | 33.63 c |
| 宁南霉Ningnanmycin | 5.37±0.21 bc | 21.43 cd |
| 氯溴异氰尿酸Chloroisobromine cyanuric acid | 5.68±0.49 abc | 16.79 cd |
| 氟菌·霜霉威Fluomycetes downomycetes | 6.17±0.15 ab | 9.71 d |
| 对照Control | 6.83±0.15 a | — |
药剂名称 Agents name | 剂量 Dosage/(g·L-1) | 菌落直径 Colony diameter/cm | 抑菌率 Inhibition rate/% | 产孢数 Sporulation count/(cell·mL-1) | 毒力回归方程 Virulence regression equation | EC50/ (g·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
噁霉灵 Hymexazol | 0.1 | 3.45±0.15 | 49.12 | 2.75×107 | y=0.855x+0.889 | 0.109 |
| 0.2 | 2.88±0.09 | 57.52 | 2.23×107 | |||
| 0.3 | 2.23±0.06 | 67.11 | 1.87×107 | |||
| 0.4 | 2.13±0.09 | 68.58 | 1.26×107 | |||
| 0.5 | 1.89±0.08 | 72.12 | 5.12×106 | |||
氟氯氰菊酯 Cyfluthrin | 0.1 | 4.54±0.15 | 33.04 | 7.84×107 | y=0.659x+0.227 | 0.452 |
| 0.2 | 3.94±0.27 | 41.89 | 6.85×107 | |||
| 0.3 | 3.76±0.14 | 44.54 | 5.29×107 | |||
| 0.4 | 3.54±0.25 | 47.79 | 4.99×107 | |||
| 0.5 | 3.26±0.09 | 51.92 | 3.54×107 | |||
| 对照组Control | — | 6.78±0.08 | — | 1.23×108 | — | — |
Table 2 Inhibition rate of oxamethrin and cyfluthrin at different dosages
药剂名称 Agents name | 剂量 Dosage/(g·L-1) | 菌落直径 Colony diameter/cm | 抑菌率 Inhibition rate/% | 产孢数 Sporulation count/(cell·mL-1) | 毒力回归方程 Virulence regression equation | EC50/ (g·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
噁霉灵 Hymexazol | 0.1 | 3.45±0.15 | 49.12 | 2.75×107 | y=0.855x+0.889 | 0.109 |
| 0.2 | 2.88±0.09 | 57.52 | 2.23×107 | |||
| 0.3 | 2.23±0.06 | 67.11 | 1.87×107 | |||
| 0.4 | 2.13±0.09 | 68.58 | 1.26×107 | |||
| 0.5 | 1.89±0.08 | 72.12 | 5.12×106 | |||
氟氯氰菊酯 Cyfluthrin | 0.1 | 4.54±0.15 | 33.04 | 7.84×107 | y=0.659x+0.227 | 0.452 |
| 0.2 | 3.94±0.27 | 41.89 | 6.85×107 | |||
| 0.3 | 3.76±0.14 | 44.54 | 5.29×107 | |||
| 0.4 | 3.54±0.25 | 47.79 | 4.99×107 | |||
| 0.5 | 3.26±0.09 | 51.92 | 3.54×107 | |||
| 对照组Control | — | 6.78±0.08 | — | 1.23×108 | — | — |
| [1] | WEI C L, YANG H, WANG S B, et al.. Draft genome sequence of Camellia sinensis var. sinensis provides insights into the evolution of the tea genome and tea quality [J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2018, 115(18):4151-4158. |
| [2] | 黄华,张建,苏东,等.2017—2019年信阳市茶树病虫害发生种类调查及绿色防控技术探讨[J].中国植保导刊,2020,40(10):79-82. |
| [3] | 杨艺帅,杨学宇,王玉生,等.气候变化背景下茶角胸叶甲潜在适生区预测[J].湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版),2023,49(5):581-587. |
| YANG Y S, YANG X Y, WANG Y S, et al.. Prediction of the potential adaptive areas of Basilepta melanopus under climate change scenarios [J]. J. Hunan Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2023, 49(5):581-587. | |
| [4] | HU Y Q, ZHANG M T, LU M Q, et al.. Salicylic acid carboxyl glucosyl transferase UGT87E7 regulates disease resistance in Camellia sinensis [J]. Plant Physiol., 2021, 188(3):1507-1520. |
| [5] | LING H M, TANG X X, ZHENG C Q, et al.. First report of leaf spot caused by Clonostachys rosea on tea (Camellia sinensis) in China [J/OL]. Plant Dis., 2023, 107(8):2537 [2024-04-20]. . |
| [6] | WANG X, YIN Q X, JIANG S L, et al.. First report of Didymella bellidis causing tea leaf spot in China [J/OL]. Plant Dis., 2020, 104(4):1254 [2024-04-20]. . |
| [7] | YIN Q X, AN X L, WU X, et al.. First report of Alternaria longipes causing leaf spot on tea in China [J/OL]. Plant Dis., 2021, 105(12):4167 [2024-04-20]. . |
| [8] | BAO X T, DHARMASENA D S P, LI D X, et al.. First report of Epicoccum sorghinum causing leaf spot on tea in China [J/OL]. Plant Dis., 2019, 103(12):3282 [2024-04-20]. . |
| [9] | TANG Z, ZHU J, SONG Q, et al.. Identification and pathogenicity of Fusarium spp . associated with tea wilt in Zhejiang province, China [J/OL]. BMC Microbiol., 2024, 24(1):38 [2024-04-20]. . |
| [10] | 叶正凡,张觉晚,钟世芳,等.湖南茶树病虫害防治研究的回顾与展望[J].茶叶通讯,1991(1):7-10. |
| [11] | 张觉晚,谭济才,袁通政,等.湖南茶园病虫区系特点及区域性防治[J].茶叶通讯,1998(3):21-23. |
| [12] | KOLANDASAMY M, PONNUSAMY P. Expression of phenolics and defence-related enzymes in relation to red root rot disease of tea plants [J]. Arch. Phytopathol., 2013, 46(4):451-462. |
| [13] | MORANG P, DEVI S P, JHA D K, et al.. Tea root brown-rot fungus disease reduction and yield recovery with rhizobacteria inoculation in both nursery and field trials [J]. Rhizosphere, 2018, 6:89-97. |
| [14] | SINNIAH G D, SENANAYAKE P D. Microbial technologies in pest and disease management of tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) //[M]. (1st Eds). BHATT P, GANGALA S, UDAYANGA D, et al.. Microbial Technology for Sustainable Environment. Singapore: Springer, 2021:325-345. |
| [15] | YANG Y S, YANG X Y, ZHANG Y D, et al.. First report of Fusarium cugenangense causing root rot of tea plants (Camellia sinensis) in China [J/OL]. Plant Dis., 2024, 108(1):214 [2024-04-20]. . |
| [16] | CHERUIYOT H. Armillaria root rot (Armillaria mellea) of tea: biology, pathogenicity, symptoms and control [J]. Tea, 2014, 35(3):7-30. |
| [17] | 赖宝春,姚锦爱.福建蜜柚炭疽病菌的生物学特性及高效防治药剂筛选[J].福建农业学报,2022,37(6):789-793. |
| LAI B C, YAO J A. Biological characteristics of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides and fungicides for disease control on honey pomelo in Fujian [J]. Fujian J. Agric. Sci., 2022, 37(6):789-793. | |
| [18] | 黄玉凤,李菲,汪汉成,等.烟草镰刀菌根腐病病原生物学特性及其优势种的代谢表型特征[J].江苏农业科学,2024,52(7):124-132. |
| [19] | 代毅,杨文睿,吐逊艾力·艾孜提力,等.新疆甘草根腐病病原鉴定及生物学特性测定[J].北方园艺,2021(20):111-118. |
| DAI Y, YANG W R, Aizitili Tusunaili, et al.. Pathogen identification and biological characteristics of licorice root rot in Xinjiang [J]. Northern Hortic., 2021 (20):111-118. | |
| [20] | 张海珊.麦冬炭疽菌的生物学特性及有效药剂筛选[D].合肥:安徽农业大学,2009. |
| ZHANG H S. Biological characteristics and effective fungicide selection of anthracnose pathogen of Ophiopogon japonicus [D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2009. | |
| [21] | 王美琴,陈俊美,李新凤.不同碳、氮源对番茄两种内生真菌菌丝生长的影响研究[J].山西农业科学,2008 (11):75-77. |
| WANG M Q, CHEN J M, LI X F. Study on mycelia growth of two tomato endophytic fungi in different carbon and nitrogen medium [J]. J. Shanxi Agric. Sci., 2008(11):75-77. | |
| [22] | 周利,郭明明.茶园农药的合理选用和使用[J].中国茶叶,2022,44(9):1-7. |
| ZHOU L, GUO M M. Rational selection and application of pesticides in tea gardens [J]. China Tea, 2022, 44(9):1-7. | |
| [23] | LEON M E, SCHINASI L H, LEBAILLY P, et al.. Pesticide use and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoid malignancies in agricultural cohorts from France, Norway and the USA: a pooled analysis from the AGRICOH consortium [J]. Int. J. Epidemiol., 2019, 48(5):1519-1535. |
| [24] | 张志鹏,程庆华,谢靖康,等.小檗碱对不同茶树炭疽菌的抑菌活性及作用机制[J].茶叶科学,2022,42(3):367-375. |
| ZHANG Z P, CHEN Q H, XIE J K, et al.. The antifungal effect and mechanism of berberine on different Colletotrichum species causing tea brown blight disease [J]. J. Tea Sci., 2022, 42(3):367-375. | |
| [25] | 张玉丹,谭琳,刘仲华,等.茶树炭疽病菌拮抗链霉菌的筛选及其抑菌特性研究[J].茶叶科学,2024, 44(2):283-298. |
| ZHANG Y D, TAN L, LIU Z H, et al.. Identification of antagonistic Streptomycetes against anthracnose pathogen of tea plants and determination of their inhibitory properties [J]. J. Tea Sci., 2024, 44(2):283-298. | |
| [26] | 王志坤.武夷菌素对茶树主要叶部病害的控制作用[D].重庆:西南大学,2008. |
| WANG Z K. Suppression effects of wuyiencin on tea foliar diseases and their pathogens [D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2008. | |
| [27] | MYRESIOTIS K, KARAOGLANIDIS G S, VRYZAS Z, et al.. Evaluation of plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria, acibenzolar-S-methyl and hymexazol for integrated control of Fusarium crown and root rot on tomato [J]. Pest Manag. Sci., 2012, 68(3):404-411. |
| [28] | ROBERTS T R, HUSTSON D H. Metabolic pathways of agrochemicals. part 2: insecticides and fungicides [J/OL]. R. Soc. Chem. 1999, 13:75 [2024-04-20]. . |
| [29] | FAN Y, GAO R H, XIAO X, et al.. Inclusion complexes of hymexazol with three different cucurbit[n]uril: preparation, and physicochemical and antifungal characterization [J]. Israel J. Chem., 2018, 58:466-471. |
| [30] | 焦鹏,贾变桃,孙颖,等.6种杀菌剂对兰花枯萎病菌抑制作用比较[J].山西农业大学学报(自然科学版),2012,32(2):154-157. |
| JIAO P, YAO B T, SUN Y, et al.. Conparison of inhibition of six fungicides against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Cattleyae [J]. J. Shanxi Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2012, 32(2):154-157. | |
| [31] | 李艳春,陈志鹏,林伟伟,等.茶树连作障碍形成机制及调控措施研究进展[J].生态科学,2019,38(5):225-232. |
| LI Y C, CHEN Z P, LIN W W, et al.. Research advances in mechanisms and preventions of continuous cropping obstacles of tea plants [J]. Ecol. Sci., 2019, 38(5):225-232. |
| [1] | Shifeng MU, Xiaolei WEN, Lina FENG, Dexuan ZHAO, Suhong GAO, Peng GAO, Huixia QI. Identification and Biological Characteristics of a Colletotrichum fructicola Causing Chestnut Internal Rot Disease [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(9): 122-128. |
| [2] | Dengyang LU, Panpan TONG, Min YAN, Jingkai BAO, Mingzhe LIU, Yilei XIA, Cuiyun WU. Identification and Evaluation of Korla Pear Bud Sport with Larger Fruit Size [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(5): 52-64. |
| [3] | Shiying ZHOU, Yanchen LIU, Yang ZHANG, Xuesong YANG, Weijun GUAN, Yang GAO. Isolational Culture and Biological Identification of Japanese Large Ear White Rabbit Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 96-105. |
| [4] | Xinci WANG, Junqiao LI, Chenqin LI, Tian TIAN, Junru QU. Identification and Biological Characteristics of a Thelonectria Pathogenic Fungi of Potentilla anserina L. [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(5): 87-95. |
| [5] | Xin XU, Kun MENG, Hongying CAI, Peilong YANG, Xianren JIANG. Research Progress on Application of Lactic Acid Bacteria in Pig Production [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(2): 19-26. |
| [6] | Hua SUN, Ning GUO, Xiaojuan ZHENG, Jie SHI, Lirong ZHANG, Hongfei YAN. Identification and Biological Characteristics Analysis of Fusarium andiyazi Causing Maize Ear Rot [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(2): 145-151. |
| [7] | ZHANG Nana§, LI Shuangmin§, WEN Xiaolei, FENG Lina, WANG Junfeng, YANG Wenjie, HUO Jiahuan, LAN Shuhui, SUN Weiming, QI Huixia. Identification and Biological Characteristics of the Pathogen Causing Pink Disease of Chestnut [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(7): 145-152. |
| [8] | WEN Xiaolei1,2, QI Huixia1*, SUN Weiming1, LIU Yijian1, FENG Lina1, MENG Tongyao2, HAN Zhiling1, CAO Jia1, WANG Junfeng1. Identification and Biological Characteristics of the Pathogen (Fusarium equiseti) Causing Shoot Blight of Atractylodes chinensis [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(5): 115-121. |
| [9] | LIANG Jun1, ZHANG Tao1*, LI Tingting2. Research on the Biological Characteristics of Liver Epithelioid Stem Cells in Beijing Duck [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 21(10): 107-114. |
| [10] | WANG Bao-lian1,2, FAN Qing-qi1, LI Yong-bo1, QU Zhi-cai2, CHU Xiu-sheng1. Research Progress on Mevalonate Kinase Genes [J]. , 2011, 13(3): 17-25. |
| [11] | TANG Hai-ming, TANG Wen-guang, XIAO Xiao-ping, TANG Hai-tao, YANG Guang-li. Effects of Different Winter Cover Plants on Biological Characteristics and Yield Traits of Rice in Southern China [J]. , 2010, 12(3): 108-113. |
| [12] | XI0NG Ge-sheng, CHEN Jin-xiang,TANG Hai-ming . Effects of Floatable Nursing Method of Cotton Seedling on its |Biological Characteristics and Yield Components |of Transplanted Cotton [J]. , 2007, 9(5): 105-109. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号