













中国农业科技导报 ›› 2022, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (3): 166-175.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2020.0545
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
董林林1( ), 查金芳2, 沈明星1, 王海候1, 施林林1, 陶玥玥1, 周新伟1, 陆长婴1(
), 查金芳2, 沈明星1, 王海候1, 施林林1, 陶玥玥1, 周新伟1, 陆长婴1( )
)
收稿日期:2020-06-21
接受日期:2020-09-14
出版日期:2022-03-15
发布日期:2022-03-14
通讯作者:
陆长婴
作者简介:董林林E-mail:jinjindoudou2005@163.com;
基金资助:
Linlin DONG1( ), Jinfang ZHA2, Mingxing SHEN1, Haihou WANG1, Linlin SHI1, Yueyue TAO1, Xinwei ZHOU1, Changying LU1(
), Jinfang ZHA2, Mingxing SHEN1, Haihou WANG1, Linlin SHI1, Yueyue TAO1, Xinwei ZHOU1, Changying LU1( )
)
Received:2020-06-21
Accepted:2020-09-14
Online:2022-03-15
Published:2022-03-14
Contact:
Changying LU
摘要:
为研究长期秸秆还田对太湖地区稻麦轮作土壤有机碳(soil organic carbon, SOC)含量的影响,依托10 a田间定位试验,以无秸秆还田为对照(CK),设置稻秸秆不还田+麦秸秆全量还田(W)、稻秸秆全量还田+麦秸秆不还田(R)、稻麦秸秆均半量还田(HRW)、稻麦秸秆均全量还田(ARW)4个秸秆还田处理,分析5种处理下SOC含量及其组分构成。结果表明,秸秆类型和还田量对SOC含量及其组分有显著影响。与2007年相比,2017年各处理SOC、重组分有机碳(heavy fraction organic carbon,HFOC)和轻组分有机碳(light fraction organic carbon,LFOC)含量的增速分别为0.18~0.46、0.15~0.42和-0.03~0.02 g·kg-1·a-1;R、HRW和ARW处理下SOC和HFOC含量显著增加;所有处理轻组分有机质中的碳含量均显著下降,其中,ARW处理的降幅最大;HFOC占比均大于80%,是SOC的主要组分,其中,W和HRW处理HFOC占比增加,其他处理HFOC占比下降;秸秆还田降低了SOC及其组分含量与水稻产量的相关性,LFOC对水稻产量影响更大。综上所述,稻麦秸秆均全量还田可增加SOC含量及稳定性,是太湖地区较为理想的秸秆还田模式。
中图分类号:
董林林, 查金芳, 沈明星, 王海候, 施林林, 陶玥玥, 周新伟, 陆长婴. 长期秸秆还田对稻麦轮作区土壤有机碳组分构成的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(3): 166-175.
Linlin DONG, Jinfang ZHA, Mingxing SHEN, Haihou WANG, Linlin SHI, Yueyue TAO, Xinwei ZHOU, Changying LU. Effect of Long-term Straw Returning on Soil Organic Carbon Fractions Composition in Rice-Wheat Rotation Ecosystem[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(3): 166-175.
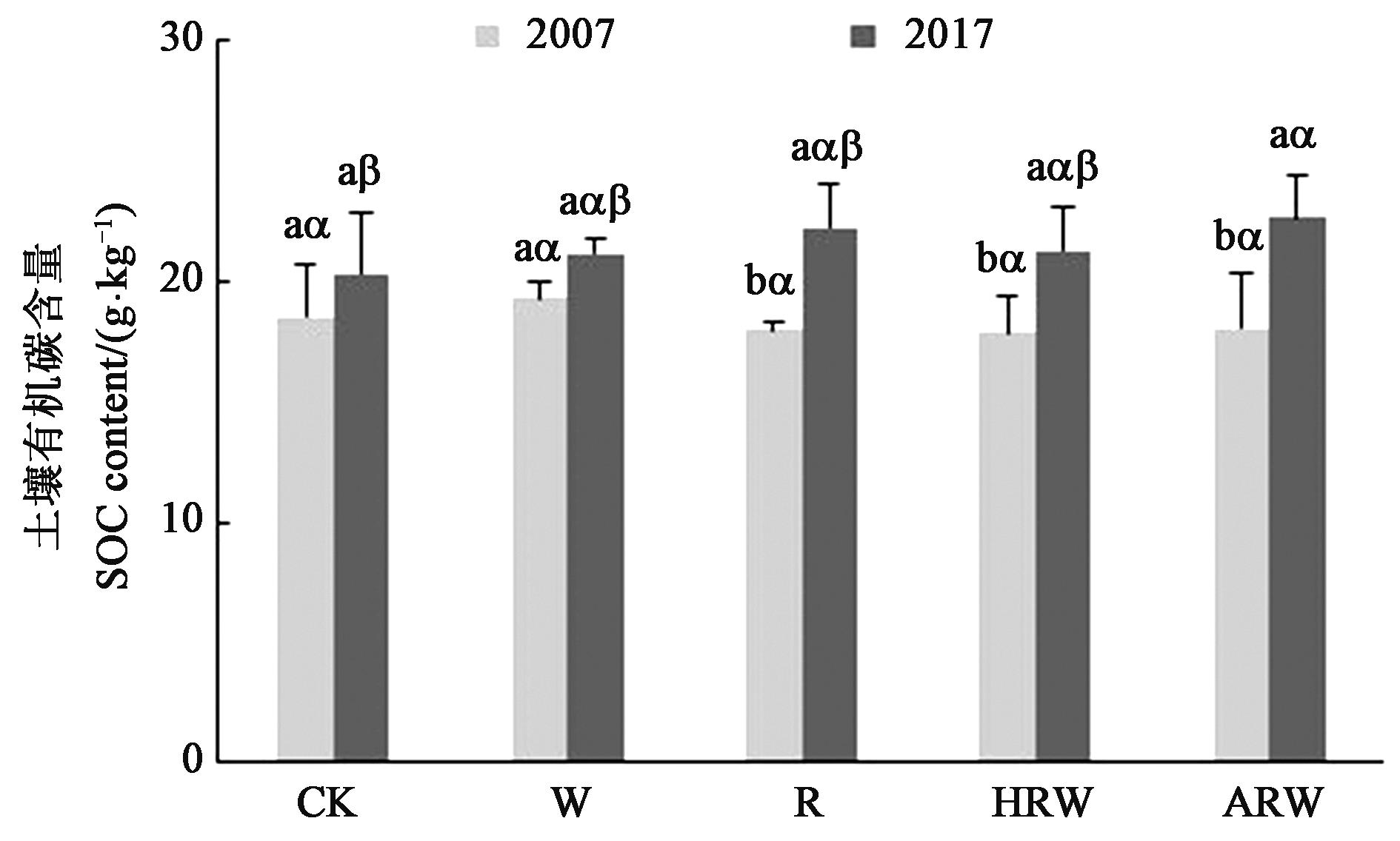
图1 不同处理下土壤有机碳含量注:不同英文字母表示同一处理不同年份间差异在P<0.05水平显著;不同希腊字母表示同一年份不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 1 Soil organic carbon content under different treatmentsNote: Different English letters indicate significant differences between 2007 and 2017 of the same treatment at P<0.05 level; different Greek letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in same year at P<0.05 level.
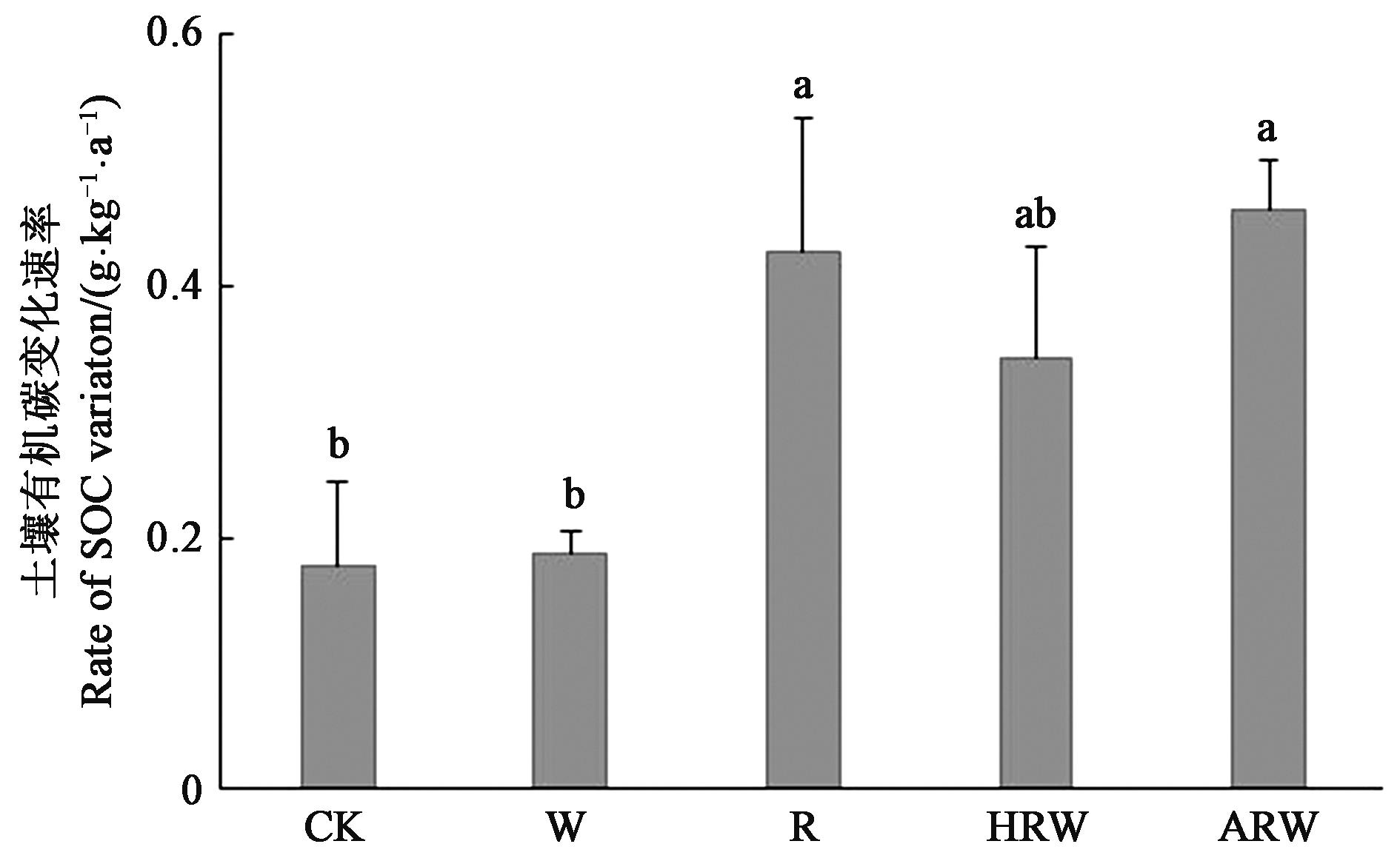
图2 不同处理的土壤有机碳变化速率注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 2 Variation of soil organic carbon under different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
处理 Treatment | LFOC /% | HFOC /% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | 2017 | 2007 | 2017 | |
| CK | 11.44±2.16 aα | 15.69±4.56 aβ | 88.56±2.16 aα | 84.31±4.56 aαβ |
| W | 11.92±0.65 aα | 10.96±1.67 aαβ | 88.08±0.65 aα | 89.00±1.67 aβ |
| R | 10.22±0.71 aα | 11.36±2.18 aαβ | 89.78±0.71 aα | 88.64±2.18 aαβ |
| HRW | 14.25±3.54 aα | 13.70±2.88 aαβ | 85.75±3.54 aα | 86.30±2.88 aαβ |
| ARW | 11.47±1.79 bα | 17.37±1.62 aα | 93.41±3.33 aα | 82.63±1.62 bα |
表1 不同处理下土壤有机碳的构成
Table 1 Composition of soil organic carbon components under different treatments
处理 Treatment | LFOC /% | HFOC /% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | 2017 | 2007 | 2017 | |
| CK | 11.44±2.16 aα | 15.69±4.56 aβ | 88.56±2.16 aα | 84.31±4.56 aαβ |
| W | 11.92±0.65 aα | 10.96±1.67 aαβ | 88.08±0.65 aα | 89.00±1.67 aβ |
| R | 10.22±0.71 aα | 11.36±2.18 aαβ | 89.78±0.71 aα | 88.64±2.18 aαβ |
| HRW | 14.25±3.54 aα | 13.70±2.88 aαβ | 85.75±3.54 aα | 86.30±2.88 aαβ |
| ARW | 11.47±1.79 bα | 17.37±1.62 aα | 93.41±3.33 aα | 82.63±1.62 bα |
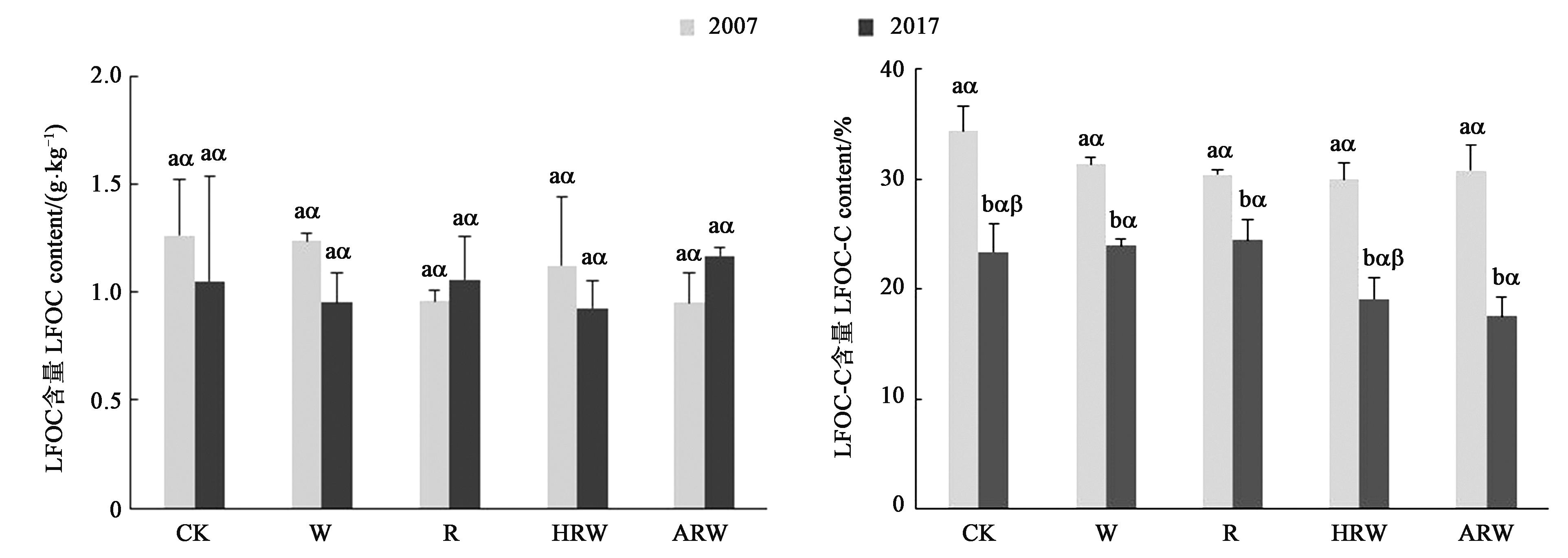
图3 不同处理下土壤LFOC及LFOM?C含量注:不同英文字母表示同一处理不同年份间差异在P<0.05水平显著;不同希腊字母表示同一年份不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 3 LFOC and LFOM?C content under different treatmentsNote: Different English letters indicate significant differences between 2007 and 2017 of the same treatment at P<0.05 level; different Greek letters indicate significantly differences between different treatments in same year at P<0.05 level.
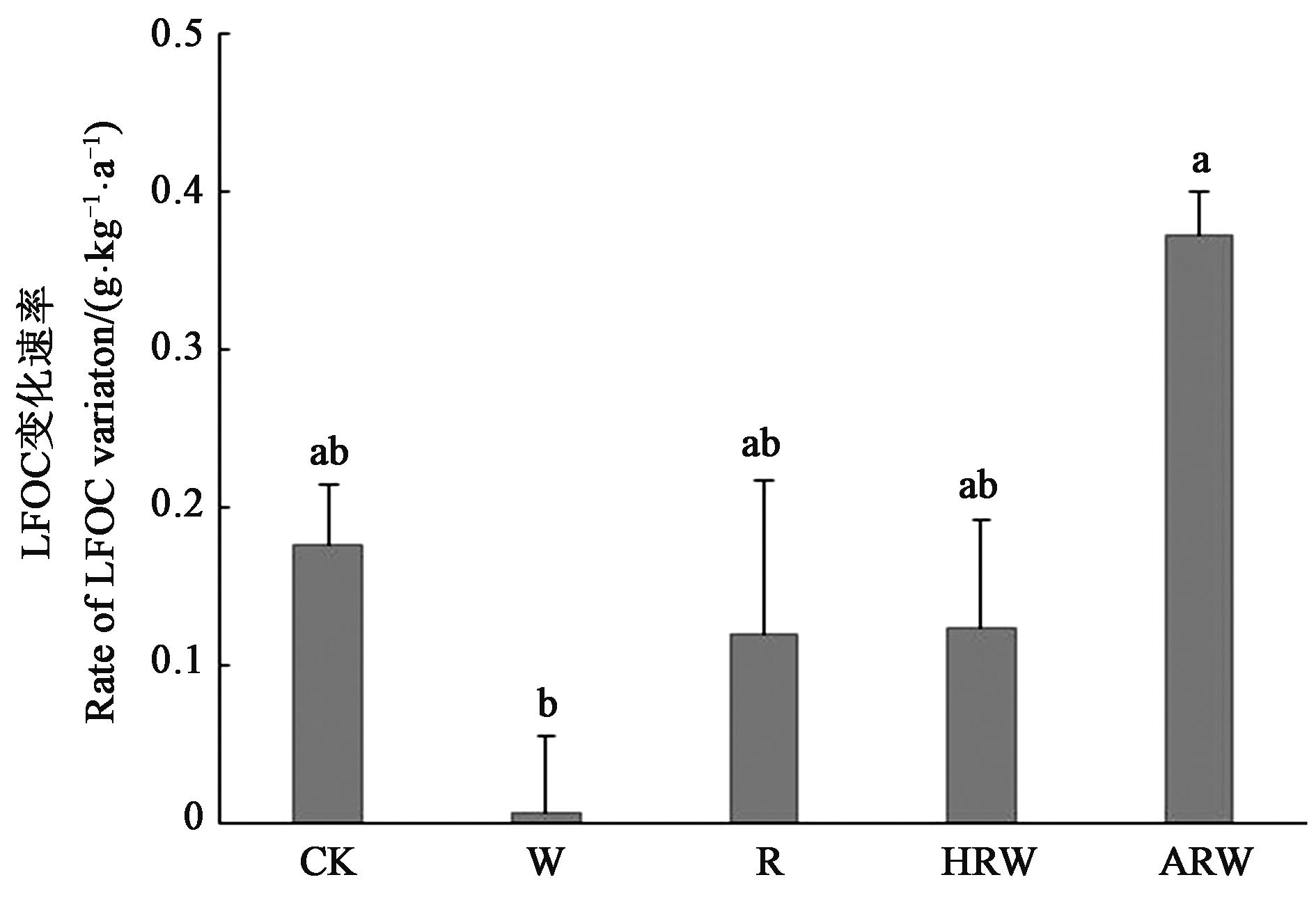
图4 不同处理的LFOC变化速率注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 4 Variation of LFOC under different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
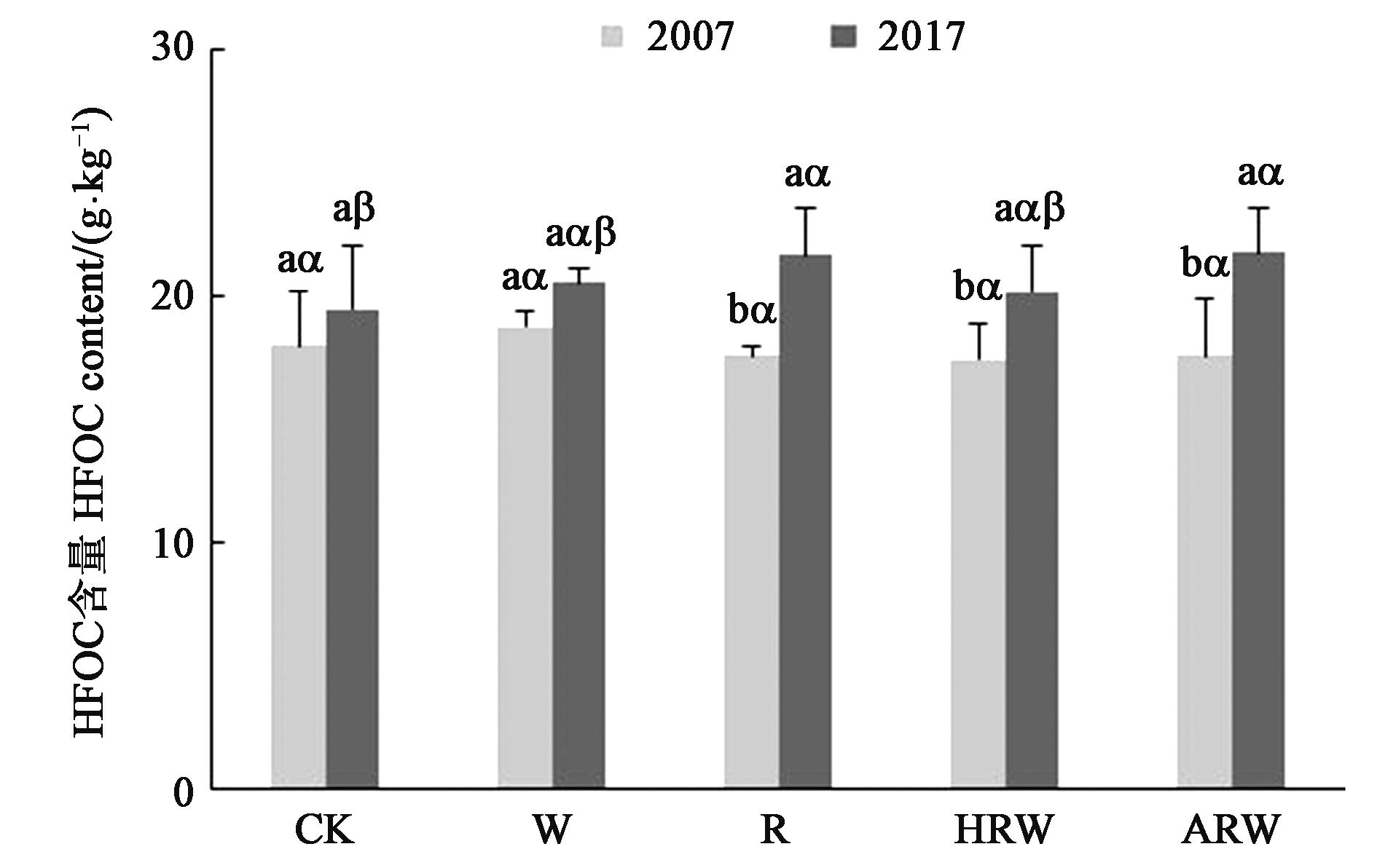
图5 不同处理下土壤HFOC含量注:不同英文字母表示同一处理不同年份间差异在P<0.05水平显著;不同希腊字母表示同一年份不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 5 HFOC content under different treatmentsNote: Different English letters indicate significant differences between 2007 and 2017 of the same treatment at P<0.05 level; different Greek letters indicate significantly differences between different treatments in same year at P<0.05 level.
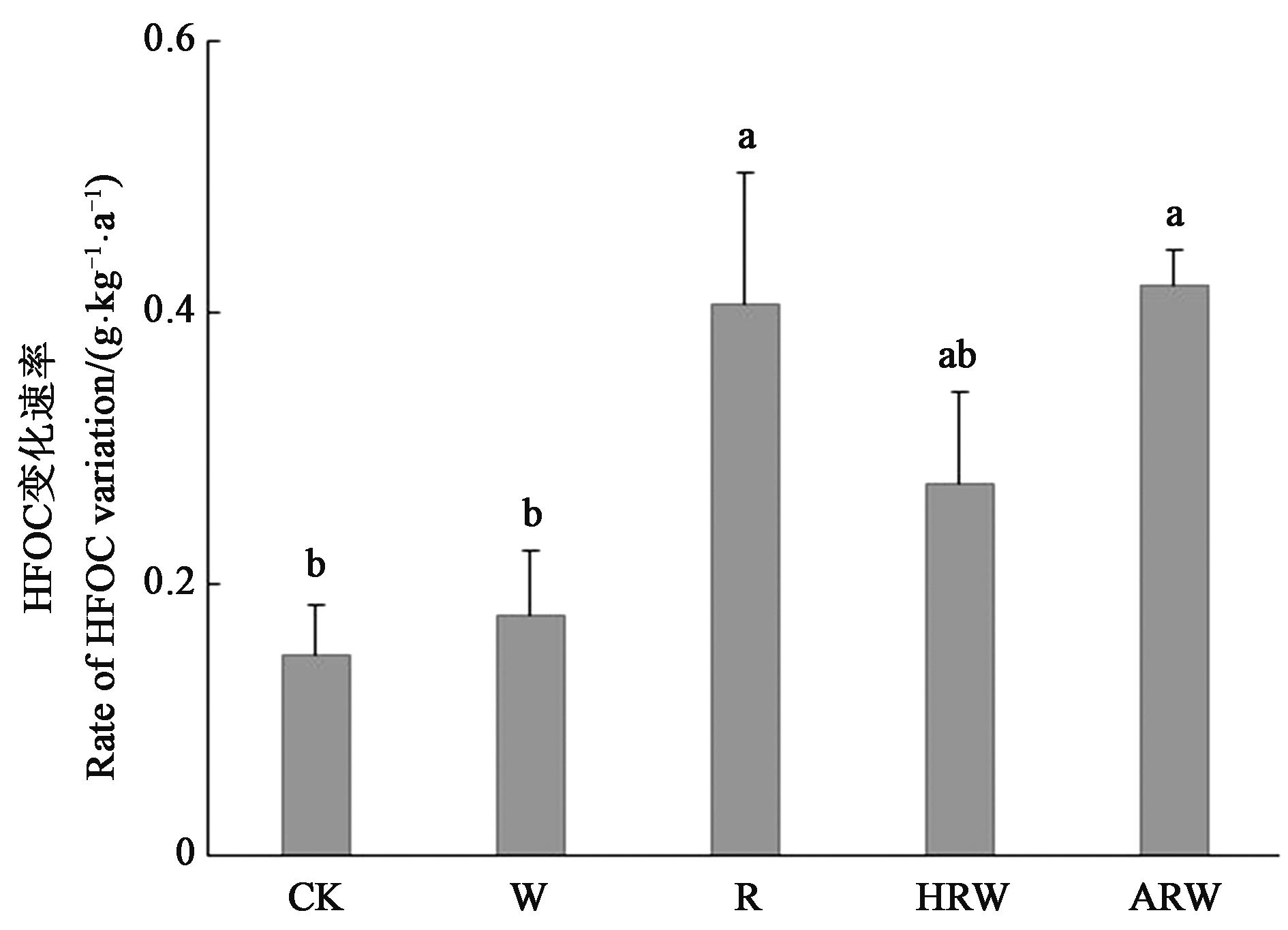
图6 不同处理的HFOC变化速率注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 6 Variation of HFOC under different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
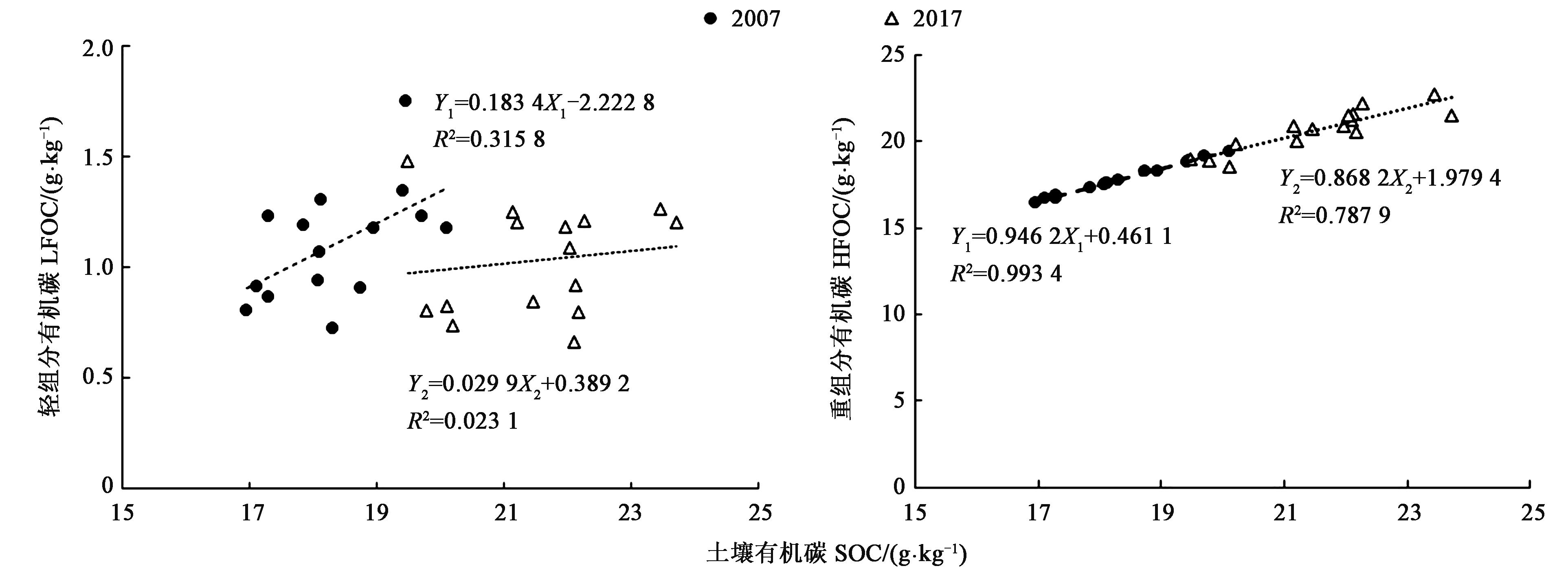
图7 土壤有机碳与碳组分之间的关系注:X1和Y1代表2007年数据;X2和Y2代表2017年数据。
Fig.7 Relationship between the contents of soil organic carbon and its fractionsNote:X1 and Y1represent data of 2007;X2 and Y2 represent data of 2017.
| 处理Treatment | 千粒重 Thousand seed weight/g | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 产量 Yield/(t·hm-2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | 2017 | 2007 | 2017 | 2007 | 2017 | |
| CK | 24.9±0.13 aα | 25.9±0.03 aα | 91.1±2.73 aα | 82.4±2.99 aα | 8.5±0.36 aα | 8.8±0.32 aαβ |
| W | 25.8±0.49 aα | 26.0±0.04 aα | 93.6±2.26 aα | 84.2±4.43 aα | 8.5±0.26 aα | 8.0±0.10 bβ |
| R | 25.5±0.20 aα | 26.0±0.20 aα | 95.4±1.34 aα | 79.3±3.42 aα | 8.1±0.17 aα | 8.90±0.23 aαβ |
| HRW | 25.2±0.17 aα | 26.0±0.03 aα | 92.8±1.29 aα | 81.2±3.27 aα | 8.4±0.17 aα | 8.53±0.13 bαβ |
| ARW | 24.8±0.56 aα | 25.7±0.20 aα | 94.6±0.31 aα | 76.7±1.82 aα | 8.1±035 aα | 9.03±0.25 aα |
表2 不同处理下水稻的产量
Table 2 Rice yield under different treatments
| 处理Treatment | 千粒重 Thousand seed weight/g | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 产量 Yield/(t·hm-2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | 2017 | 2007 | 2017 | 2007 | 2017 | |
| CK | 24.9±0.13 aα | 25.9±0.03 aα | 91.1±2.73 aα | 82.4±2.99 aα | 8.5±0.36 aα | 8.8±0.32 aαβ |
| W | 25.8±0.49 aα | 26.0±0.04 aα | 93.6±2.26 aα | 84.2±4.43 aα | 8.5±0.26 aα | 8.0±0.10 bβ |
| R | 25.5±0.20 aα | 26.0±0.20 aα | 95.4±1.34 aα | 79.3±3.42 aα | 8.1±0.17 aα | 8.90±0.23 aαβ |
| HRW | 25.2±0.17 aα | 26.0±0.03 aα | 92.8±1.29 aα | 81.2±3.27 aα | 8.4±0.17 aα | 8.53±0.13 bαβ |
| ARW | 24.8±0.56 aα | 25.7±0.20 aα | 94.6±0.31 aα | 76.7±1.82 aα | 8.1±035 aα | 9.03±0.25 aα |
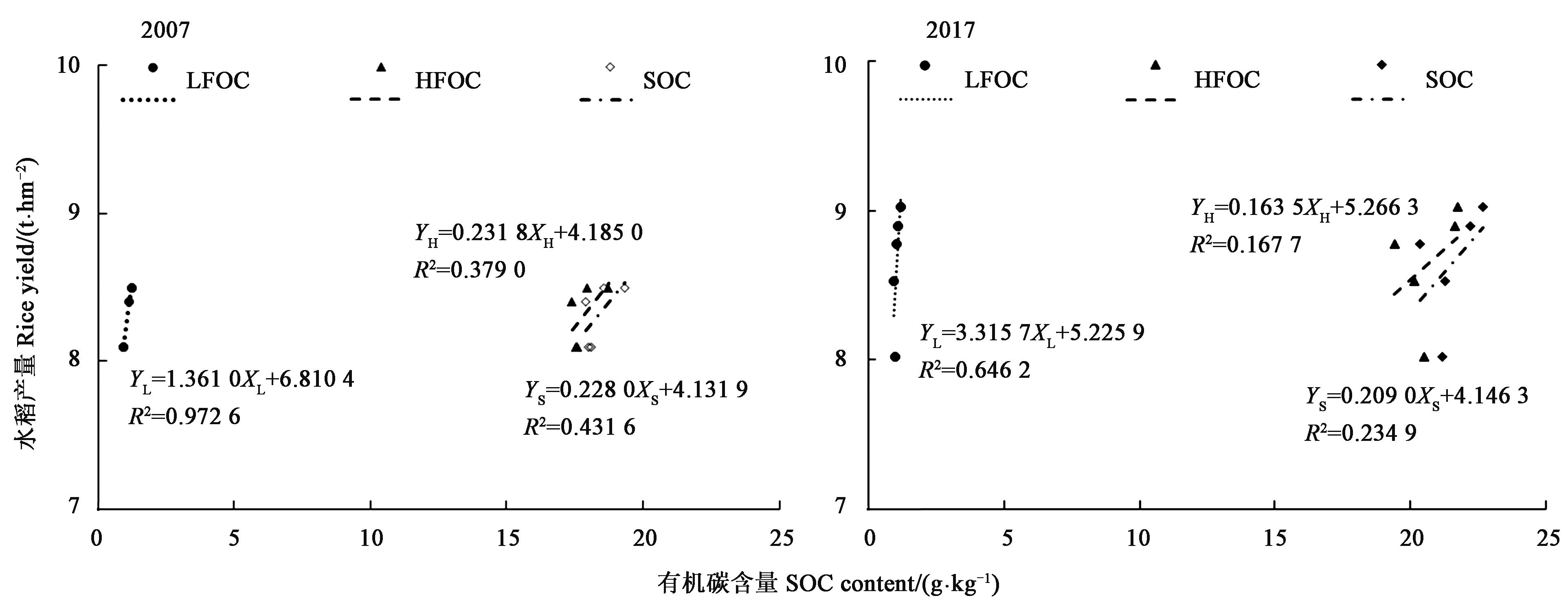
图8 土壤有机碳组分与水稻产量间的关系注:XL、XH和XS代表 LFOC,HFOC和SOC,YL、YH和YS代表由LFOC,HFOC和SOC拟合的水稻产量.
Fig.8 Relationship between the content of soil organic carbon fractions and rice yieldNote:XL, XH and XSrepresent contents of LFOC, HFOC and SOC, YL, YH and YS represent fitting data of rice yield from LFOC, HFOC and SOC.
| 1 | 曹湛波,王磊,李凡,等.土壤呼吸与土壤有机碳对不同秸秆还田的响应及其机制[J].环境科学,2016,37(5):1908-1914. |
| CAO Z B, WANG L, LI F, et al.. Response of soil respiration and organic carbon to returning of different agricultural straws and its mechanism [J]. Environ. Sci., 2016, 37(5):1908-1914. | |
| 2 | WIGHT J P, ASHWORTH A J, ALLEN F L. Organic substrate, clay type, texture, and water influence on NIR carbon measurements [J]. Geoderma, 2016, 261:36-43. |
| 3 | MURGE E W, VORONEY P, BEYAERT R P. Turnover of carbon in the free light fraction with and without charcoal as determined using the 13C natural abundance method [J]. Geoderma, 2007, 138(1-2):133-143. |
| 4 | DONG L L, ZHANG H D, WANG L Q, et al.. Irrigation with sediment-laden river water affects the soil texture and composition of organic matter fractions in arid and semi-arid areas of Northwest China [J]. Geoderma, 2018, 328:10-19. |
| 5 | RAFFA D W, BOGDANSKI A, TITTONELL P. How does crop residue removal affect soil organic carbon and yield? A hierarchical analysis of management and environmental factors [J]. Biomas Bioenergy, 2015, 81:345-355. |
| 6 | 何振超,苏瑶,喻曼,等.秸秆碳对不同施肥水平低肥力土壤碳组分的影响[J].农业资源与环境学报,2019,36(3):304-312. |
| HE Z C, SU Y, YU M, et al.. Effect of straw-derived carbon on carbon component of the low fertility soil at different nitrogen application rates [J]. J. Agric. Res. Environ., 2019, 36(3):304-312. | |
| 7 | LIU Z, GAO T P, LIU W T, et al.. Effects of part and whole straw returning on soil carbon sequestration in C3-C4 rotation cropland [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci., 2019, 182(3):429-440. |
| 8 | 赵惠丽,董金琎,师江澜,等.秸秆还田模式对小麦-玉米轮作体系土壤有机碳固存的影响[J].土壤学报, 2021, 58(1):213-224. |
| ZHAO H L, DONG J J, SHI J L, et al.. Effect of straw returning mode on soil organic carbon sequestration [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2021, 58(1):213-224. | |
| 9 | 李昊昱,孟兆良,庞党伟,等.周年秸秆还田对农田土壤固碳及冬小麦—夏玉米产量的影响[J].作物学报,2019,45(6):893-903. |
| LI H Y, MENG Z L, PANG D W, et al.. Effect of annual straw return model on soil carbon sequestration and crop yields in winter wheat-summer maize rotation farmland [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2019, 45(6):893-903. | |
| 10 | 徐蒋来,胡乃娟,张政文,等.连续秸秆还田对稻麦轮作农田土壤养分及碳库的影响[J].土壤,2016,48(1):71-75. |
| XU J L, HU N J, ZHANG Z W, et al.. Effect of continuous straw returning on soil nutrients and carbon pool in rice-wheat rotation system [J]. Soils, 2016, 48(1):71-75. | |
| 11 | CHEN S, XU C M, YAN J X, et al.. The influence of the type of crop residue on soil organic carbon fractions: an 11-year field study of rice-based cropping systems in southeast China [J]. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ., 2016, 223:261-269. |
| 12 | 王虎,王旭东,田宵鸿.秸秆还田对土壤有机碳不同活性组分储量及分配的影响[J].应用生态学报,2014,25(12):3491-3498. |
| WANG H, WANG X D, TIAN X H. Effect of straw-returning on the storage and distribution of different active fractions of soil organic carbon [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2014, 25(12):3491-3498. | |
| 13 | PINHEIRO E F M, CAMPOS D V B D, BALIEIRO F D C, et al.. Tillage systems effects on soil carbon stock and physical fractions of soil organic matter [J]. Agric. Syst., 2015, 132:35-39. |
| 14 | 傅敏,郝敏敏,胡恒宇,等.土壤有机碳与微生物群落结构对多年不同耕作方式与秸秆还田的响应[J].应用生态学报,2019,30(9):3183-3194. |
| FU M, HAO M M, HU H Y, et al.. Response of soil organic carbon and microbial community structure to different tillage patterns and straw returning after many years [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2019, 30(9):3183-3194. | |
| 15 | 周延辉,朱新开,郭文善,等.中国地区小麦产量及产量要素对秸秆还田响应的整合分析[J].核农学报,2019,33(1):129-137. |
| ZHOU Y H, ZHU X K, GUO W S, et al.. Meta-analysis of the response of wheat yield and yield components to straw returning in China [J]. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci., 2019, 33(1):129-137. | |
| 16 | 郑继成,张刚,王德建,等.稻麦轮作下秸秆还田对稻麦产量和稻田可溶性有机碳含量的影响[J].中国生态农业学报,2019,27(3):431-440. |
| ZHENG J C, ZHANG G, WANG D J, et al.. Effects of straw incorporation on crop yield and dissolved organic carbon concentration at rice growing season in rice-wheat rotation cropping system [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2019, 27(3):431-440. | |
| 17 | 张雅洁,陈晨,陈曦,等.小麦-水稻秸秆还田对土壤有机质组成及不同形态氮含量的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2015,34(11):2155-2161. |
| ZHANG Y J, CHEN C, CHEN X, et al.. Effects of wheat and rice straw returning on soil organic matter composition and content of different nitrogen forms in soil [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2015, 34(11):2155-2161. | |
| 18 | 鲁如坤.土壤农业化学分析方法[M].北京:中国农业科技出版社,2000:85-96. |
| 19 | KÄTTERER T, BOLINDER M A, ANDRÉN O, et al.. Roots contribute more to refractory soil organic matter than above-ground crop residues, as revealed by a long-term field experiment [J]. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ., 2011, 141(1-2):184-192. |
| 20 | SYAM K D, WANG J J, DELAUNE R D. Characterization of labile organic carbon in coastal wetland soils of the Mississippi River deltaic plain: Relationships to carbon functionalities [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2012, 435-436:151-158. |
| 21 | 汤宏,沈健林,张杨珠,等.秸秆还田与水分管理对稻田土壤微生物量碳、氮及溶解性有机碳、氮的影响[J].水土保持学报,2013,27(1):240-246. |
| TANG H, SHEN J L, ZHANG Y Z, et al.. Effect of rice straw incorporation and water management on soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen and dissolved organic carbon, nitrogen in a rice paddy field [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2013, 27(1):240-246. | |
| 22 | SALAZAR O, BALLOA L, PERALTA K, et al.. Effect of cover crops on leaching of dissolved organic nitrogen and carbon in a maize-cover crop rotation in Mediterranean Central Chile [J]. Agric. Water Manage., 2019, 212:399-406. |
| 23 | 王海候,金梅娟,陆长婴,等.秸秆还田模式对农田土壤碳库特性及产量的影响[J].自然资源学报,2017,32(5):755-764. |
| WANG H H, JIN M J, LU C Y, et al.. Effects of patterns of returning straw to field on soil carbon pool and yield in rice-wheat double cropping systems [J]. J. Nat. Resour., 2017, 32(5):755-764. | |
| 24 | 陈鲜妮,岳西杰,葛玺祖,等.长期秸秆还田对塿土耕层土壤有机碳库的影响[J].自然资源学报,2012,27(1):25-32. |
| CHEN X N, YUE X J, GE X Z, et al.. Effect of long-term residue return on soil organic carbon storage [J]. J. Nat. Resour., 2012, 27(1):25-32. | |
| 25 | 张志毅,熊桂云,吴茂前,等.有机培肥与耕作方式对稻麦轮作土壤团聚体和有机碳组分的影响[J].中国生态农业学报,2020,28(3):405-412. |
| ZHANG Z Y, XIONG G Y, WU M Q, et al.. Effects of organic fertilization and tillage method on soil aggregates and organic carbon fractions in a wheat-rice system [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2020, 28(3):405-412. | |
| 26 | LIAO P, HUANG S, GESTEL N C V, et al.. Liming and straw retention interact to increase nitrogen uptake and grain yield in a double rice-cropping system [J]. Field Crops Res., 2018, 216:217-224. |
| 27 | 胡乃娟,韩新忠,杨敏芳,等.秸秆还田对稻麦轮作农田土壤活性有机碳组分含量、酶活性及产量的短期效应[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2015,21(2):371-377. |
| HU N J, HAN X Z, YANG M F, et al.. Short-term influence of straw return on the content of soil organic carbon fractions, enzyme activities and crop yields in rice-wheat rotation farmland [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2015, 21(2):371-377. | |
| 28 | 董林林,王海候,陆长婴,等.秸秆还田量和类型对土壤氮及氮组分构成的影响[J].应用生态学报,2019,30(4):1143-1150. |
| DONG L L, WANG H H, LU C Y, et al.. Effect of straw returning amount and type on soil nitrogen and its composition [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2019, 30(4):1143-1150. | |
| 29 | NIE J, ZHOU J M, WANG H Y, et al.. Effect of long-term rice straw return on soil glomalin, carbon and nitrogen [J]. Pedosphere, 2007, 17(3):295-302. |
| 30 | 张翰林,郑宪清,何七勇,等.不同秸秆还田年限对稻麦轮作土壤团聚体和有机碳的影响[J].水土保持学报,2016,30(4):216-220. |
| ZHANG H L, ZHENG X Q, HE Q Y, et al.. Effect of years of straw returning on soil aggregates and organic carbon in rice-wheat rotation systems [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2016, 30(4):216-220. | |
| 31 | XU Y H, CHEN Z M, FONTAINE S, et al.. Dominant effect of organic carbon chemistry on decomposition dynamics of crop residues in a Mollisol [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2017, 115:221-232. |
| 32 | CHEN Z M, WANG H Y, LIU X W, et al.. Changes in soil microbial community and organic carbon fractions under short-term straw return in a rice-wheat cropping system [J]. Soil Tillage Res., 2017,165:121-127. |
| 33 | 周运来,张振华,范如芹,等.秸秆还田方式对水稻田土壤理化性质及水稻产量的影响[J].江苏农业学报,2016,32(4):786-790. |
| ZHOU Y L, ZHANG Z H, FAN R Q, et al.. Effects of straw-returning modes on paddy soil properties and rice yield [J]. Jiangsu J. Agric. Sci., 2016, 32(4):786-790. | |
| 34 | 李新华,郭洪海,朱振林,等. 不同秸秆还田模式对土壤有机碳及其活性组分的影响[J].农业工程学报,2016,32(9):130-135. |
| LI X H, GUO H H, ZHU Z L, et al.. Effects of different straw return modes on contents of soil organic carbon and fractions of soil active carbon [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2016, 32(9):130-135. | |
| 35 | LIANG C, AMELUNG W, LEHMANN J, et al.. Quantitative assessment of microbial necromass contribution to soil organic matter [J]. Global Change Biol., 2019, 25(11):3578-3590. |
| 36 | 赵蒙蒙,姜曼,周祚万.几种农作物秸秆的成分分析[J].材料导报,2011,25(8):122-125 |
| ZHAO M M, JIANG M, ZHOU Z W. The components analysis of several kinds of agricultural residues [J]. Mater. Rev., 2011, 25(8):122-125. | |
| 37 | 单玉华,蔡祖聪,韩勇,等.淹水土壤有机酸积累与秸秆碳氮比及氮供应的关系[J].土壤学报,2006,43(6):941-947. |
| SHAN Y H, CAI Z C, HAN Y, et al.. Accumulation of organic acids in relation to C:N ratios of straws and N application in flooded soil [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2006, 43(6):941-947. |
| [1] | 齐天明, 李志坚, 秦培友, 任贵兴, 周帮伟. 藜麦栽培技术研究与应用展望[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(3): 157-165. |
| [2] | 许鑫, 马兆务, 熊淑萍, 马新明, 程涛, 李海洋, 赵锦鹏. 基于气候年型的河南省冬小麦产量预测[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 136-144. |
| [3] | 李宝石, 刘文科, 王奇, 邵明杰. 起垄内嵌基质栽培对日光温室夏季黄瓜根区温度、生长和产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 177-183. |
| [4] | 周旋, 杨嫔玲, 彭建伟, 柴慧清, 钟雪梅, 康兴蓉, 龙俊佑, 张慧茹. 功能菌型复合肥减施对结球甘蓝产量、品质及经济效益的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 184-192. |
| [5] | 陈昌婕, 马琳, 苗玉焕, 郭兰萍, 刘大会. 施用钾肥对蕲春蕲艾产量、出绒率及品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 201-209. |
| [6] | 王健, 许爱玲, 卫晓东, 席吉龙, 杨娜, 王珂, 席天元, 张建诚. 运城盆地不同播期小麦春季冻害风险评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 137-147. |
| [7] | 王志丹, 刘吉利, 吴娜. 粉垄耕作对甜高粱光合生理特性及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 148-156. |
| [8] | 黄渝岚§, 龙盛风§, 叶兴枝, 李艳英, 申章佑, 周佳, 周灵芝, 劳承英, 韦本辉. 木薯在湖北恩施的农艺性状及产量品质研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(9): 46-55. |
| [9] | 孙梦遥, 徐岚俊, 李小龙, 李传友, 陈华, 张传帅, 刘婞韬. 不同节水方式对油菜水分利用、分配及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(9): 138-143. |
| [10] | 李生梅, 张大伟, 迪丽拜尔·迪力买买提, 魏鑫, 芮存, 杨涛, 耿世伟, 高文伟. 减量灌溉对转ScALDH21基因棉花农艺性状、产量和品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(9): 152-159. |
| [11] | 李成晨, 索海翠, 罗焕明, 安康, 刘计涛, 王丽, 单建伟, 杨少海, 李小波. 化肥减施和施肥方式对马铃薯产量和块茎氮素积累的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(9): 173-182. |
| [12] | 李双, 张伟, 王丽, 李孝军, 崔俊涛. 秸秆还田对不同地力黑土培肥与茎腐病害发生的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(8): 80-90. |
| [13] | 吴子帅, 李虎, 黄秋要, 陈传华, 罗群昌, 周新明, 吴佳桔, 刘广林. 施氮量和栽插密度对桂育11号产量和稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(8): 154-162. |
| [14] | 翁文安, 程爽, 李绍平, 田晋钰, 陶钰, 胡群, 胡雅杰, 郭保卫, 魏海燕, 邢志鹏, 张洪程. 氮肥一次性基施对不同成穗方式下直播常规粳稻产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(8): 163-172. |
| [15] | 朱利霞, 陈居田, 徐思薇, 陈如冰, 李俐俐. 生物炭施用下土壤微生物量碳氮的动态变化[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(8): 193-200. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 72
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 962
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号