




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (3): 47-56.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0693
陈军1( ), 李静雯1(
), 李静雯1( ), 王立光1, 朱天地1, 陈琛1, 包奇军2, 欧巧明1
), 王立光1, 朱天地1, 陈琛1, 包奇军2, 欧巧明1
收稿日期:2021-08-13
接受日期:2021-11-19
出版日期:2023-03-15
发布日期:2023-05-22
通讯作者:
李静雯
作者简介:陈军 E-mail:chenjun004@126.com;
基金资助:
Jun CHEN1( ), Jingwen LI1(
), Jingwen LI1( ), Liguang WANG1, Tiandi ZHU1, Chen CHEN1, Qijun BAO2, Qiaoming OU1
), Liguang WANG1, Tiandi ZHU1, Chen CHEN1, Qijun BAO2, Qiaoming OU1
Received:2021-08-13
Accepted:2021-11-19
Online:2023-03-15
Published:2023-05-22
Contact:
Jingwen LI
摘要:
为探究氮肥施用量对低醇溶蛋白转基因大麦花后各营养器官氮素积累、分布及转运的影响,明确大麦花后至籽粒形成过程中氮素的变化规律,采用土培盆栽试验,利用前期筛选出已稳定遗传的低醇溶蛋白转基因大麦为试验材料,以其受体为对照,分析二者分别在不施氮、低氮(160 mg N·kg-1土)、正常氮(230 mg N·kg-1土)和高氮(300 mg N·kg-1土)4 个氮素处理下的籽粒产量、生物量及花后营养器官氮素积累及转运特性。结果表明,相同施氮量下,转基因大麦的籽粒产量和地上部生物量高于对照,而株高和千粒重较对照显著降低,有效穗数和每穗粒数较对照显著增加;即与受体相比,转基因大麦通过增加分蘖数和有效穗数补偿产量配给,实现增产。转基因大麦籽粒的蛋白含量显著低于对照,较对照降低0.58%~2.40%;且随着施氮量增加,籽粒蛋白含量逐渐增加。转基因大麦各营养器官的氮素含量表现为穗>叶>茎秆,且在穗中氮素含量在扬花期最高。不同时期植株地上部的氮素积累量表现为扬花期>灌浆期>成熟期,说明扬花期是影响大麦氮素再利用的关键时期,且转基因大麦的籽粒产量与扬花期穗氮素含量呈显著正相关。以上结果为大麦氮素转运的生理机制及生产施肥实践奠定了理论基础。
中图分类号:
陈军, 李静雯, 王立光, 朱天地, 陈琛, 包奇军, 欧巧明. 低醇溶蛋白转基因大麦氮素转移特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 47-56.
Jun CHEN, Jingwen LI, Liguang WANG, Tiandi ZHU, Chen CHEN, Qijun BAO, Qiaoming OU. Nitrogen Transfer Characteristics of Low Prolamin Transgenic Barley[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(3): 47-56.
材料 Material | 处理 Treatment | 株高 Plant height/cm | 有效穗数 Effective ear number | 每穗粒数 Number of grains per spike | 千粒重 1 000-grain weight/g | 单株籽粒产量 Grain yield per plant/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GP | N0 | 51.76±1.64 ab | 2.90±0.22 f | 14.07±0.61 c | 39.85±1.86 ab | 1.51±0.08 c |
| N160 | 52.06±2.85 ab | 3.46±0.33 def | 18.64±1.15 ab | 44.63±1.96 a | 2.35±0.19 bc | |
| N230 | 50.81±0.09 ab | 3.29±0.19 ef | 16.22±0.01 bc | 42.96±0.57 a | 3.09±0.08 ab | |
| N300 | 54.62±3.36 a | 4.57±0.19 bcd | 17.96±2.15 abc | 43.99±1.22 a | 3.37±0.01 a | |
| T | N0 | 45.69±1.71 b | 4.29±0.04 cde | 17.50±1.83 abc | 37.96±1.27 ab | 2.11±0.33 c |
| N160 | 46.90±0.20 b | 5.85±0.89 a | 20.58±0.05 a | 31.55±1.37 b | 3.92±0.31 a | |
| N230 | 45.93±0.13 b | 5.09±0.11 abc | 19.09±1.39 ab | 31.81±1.76 b | 3.32±0.22 a | |
| N300 | 47.45±0.88 b | 5.54±0.04 ab | 21.19±0.65 a | 32.93±0.50 b | 3.79±0.03 a |
表1 不同处理下大麦的产量构成及籽粒产量
Table 1 Yield composition and grain yield of barley in different treatments
材料 Material | 处理 Treatment | 株高 Plant height/cm | 有效穗数 Effective ear number | 每穗粒数 Number of grains per spike | 千粒重 1 000-grain weight/g | 单株籽粒产量 Grain yield per plant/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GP | N0 | 51.76±1.64 ab | 2.90±0.22 f | 14.07±0.61 c | 39.85±1.86 ab | 1.51±0.08 c |
| N160 | 52.06±2.85 ab | 3.46±0.33 def | 18.64±1.15 ab | 44.63±1.96 a | 2.35±0.19 bc | |
| N230 | 50.81±0.09 ab | 3.29±0.19 ef | 16.22±0.01 bc | 42.96±0.57 a | 3.09±0.08 ab | |
| N300 | 54.62±3.36 a | 4.57±0.19 bcd | 17.96±2.15 abc | 43.99±1.22 a | 3.37±0.01 a | |
| T | N0 | 45.69±1.71 b | 4.29±0.04 cde | 17.50±1.83 abc | 37.96±1.27 ab | 2.11±0.33 c |
| N160 | 46.90±0.20 b | 5.85±0.89 a | 20.58±0.05 a | 31.55±1.37 b | 3.92±0.31 a | |
| N230 | 45.93±0.13 b | 5.09±0.11 abc | 19.09±1.39 ab | 31.81±1.76 b | 3.32±0.22 a | |
| N300 | 47.45±0.88 b | 5.54±0.04 ab | 21.19±0.65 a | 32.93±0.50 b | 3.79±0.03 a |
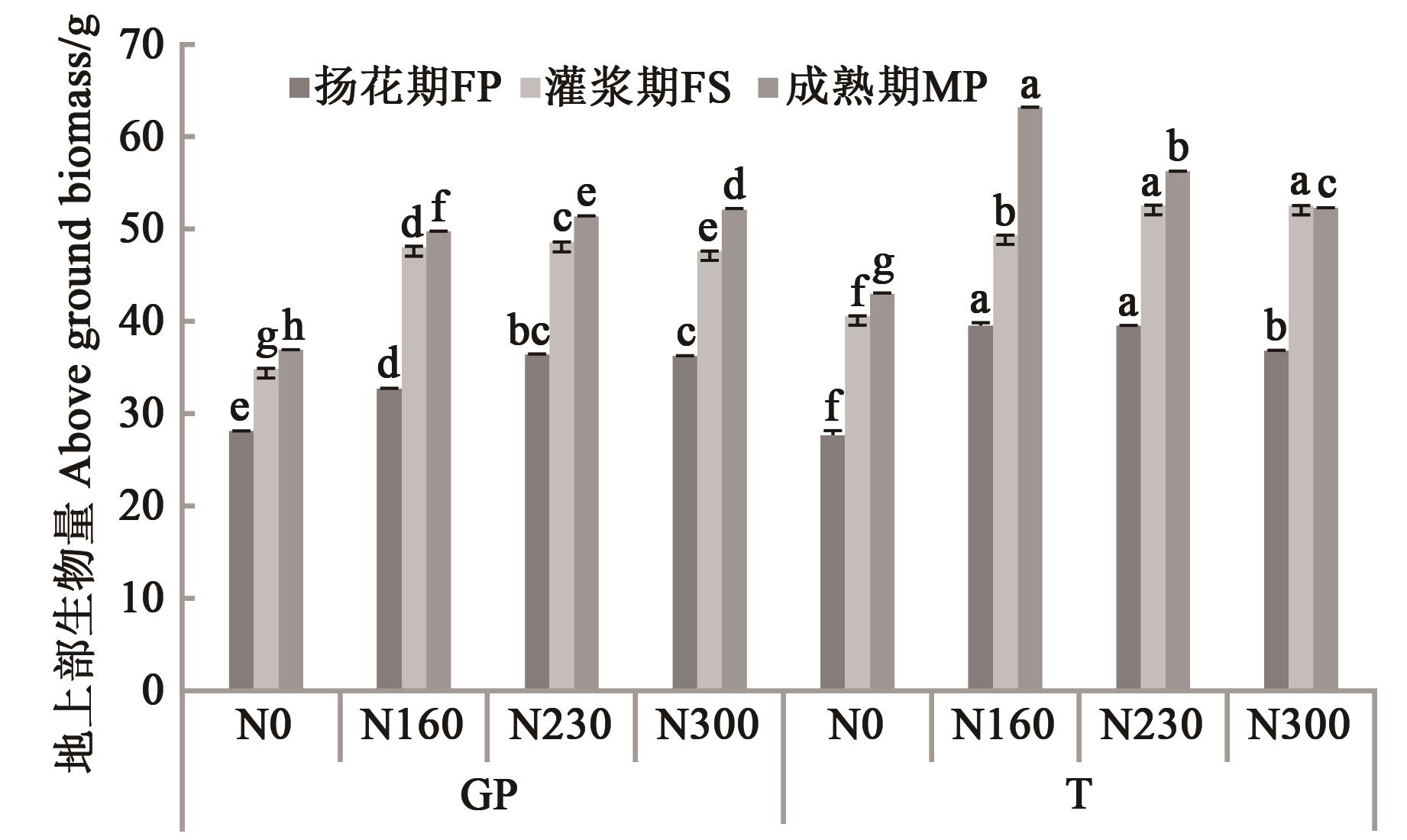
图1 不同生育期地上部生物量注:同一时期不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 1 Aboveground biomass in different growth periodsNote:Different lowercase letters in same period indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
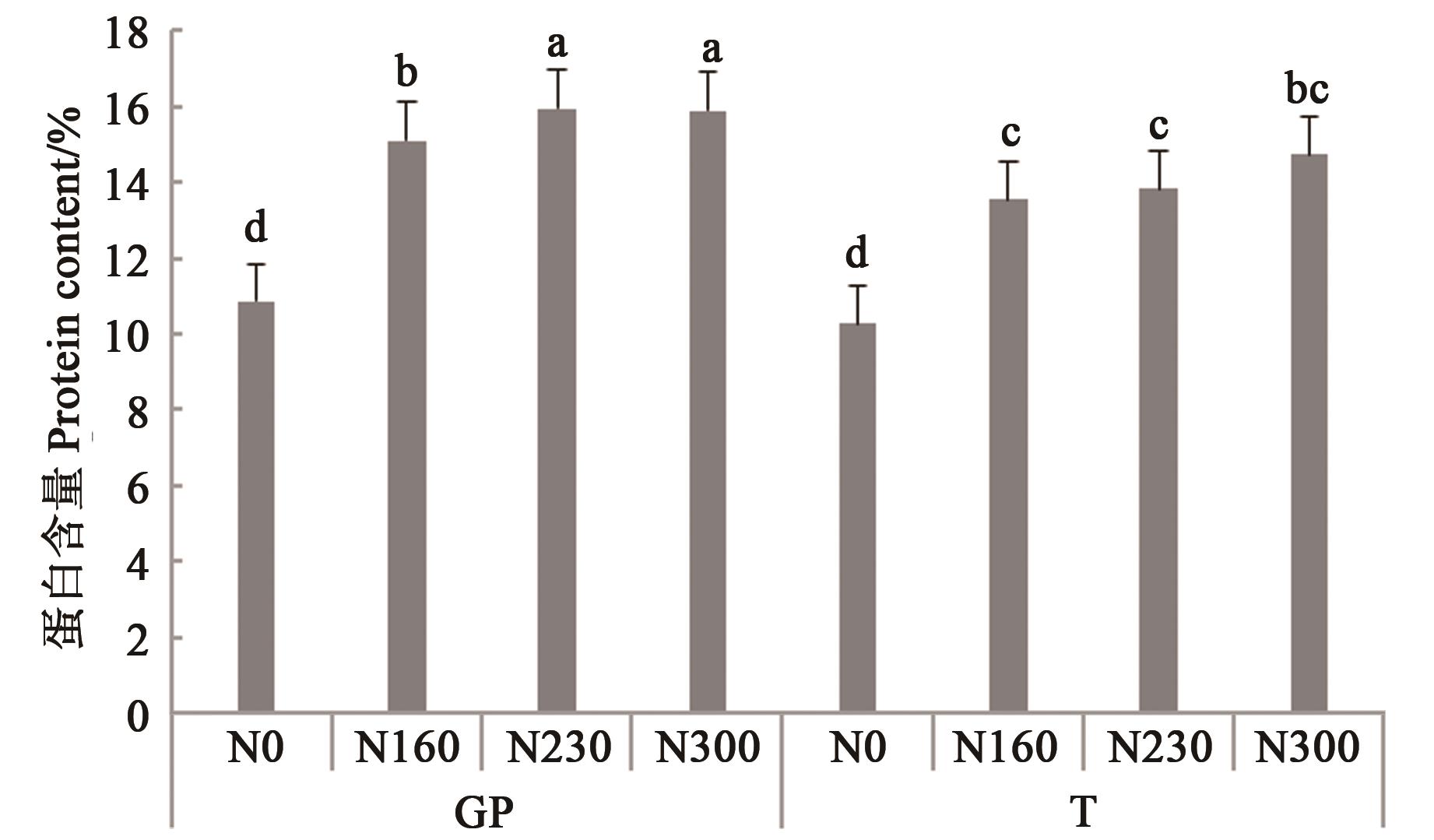
图2 籽粒蛋白含量注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 2 Grain protein contentNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.

图 3 穗、叶和茎秆中氮素含量注:同一时期不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 3 Nitrogen contents of ear, leaf and stemNote:Different lowercase letters in same period indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 材料Material | 处理Treatment | 穗 Ear | 叶 Leaf | 茎秆 Stem | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 扬花期FP | 灌浆期FS | 成熟期MP | 扬花期FP | 灌浆期FS | 成熟期MP | 扬花期FP | 灌浆期FS | 成熟期MP | |||||||||||
| 氮积 累量 NA/mg | 比例Proportion/% | 氮积 累量 NA/mg | 比例Proportion/% | 氮积 累量 NA/mg | 比例Proportion/% | 氮积 累量 NA/mg | 比例Proportion/% | 氮积 累量NA/mg | 比例Proportion/% | 氮积 累量 NA/mg | 比例Proportion/% | 氮积 累量 NA/mg | 比例Proportion/% | 氮积 累量 NA/mg | 比例Proportion/% | 氮积 累量 NA/mg | 比例Proportion/% | ||
| GP | N0 | 16.87±0.64 d | 37.56 | 40.55±0.75 a | 69.99 | 28.31±1.10 e | 63.30 | 17.62±0.42 e | 39.23 | 4.75±0.51 e | 8.21 | 11.00±0.12 g | 24.61 | 10.43±0.25 e | 23.21 | 12.63±0.42 f | 21.81 | 5.41±0.11 e | 12.10 |
| N160 | 21.18±0.68 c | 23.59 | 37.72±0.57 c | 35.62 | 34.10±1.42 d | 38.27 | 41.93±0.53 d | 46.69 | 26.06±0.18 c | 24.61 | 24.64±0.11 e | 27.65 | 26.68±0.82 c | 29.72 | 42.11±0.76 c | 39.77 | 30.37±0.13 b | 34.08 | |
| N230 | 33.31±0.84 a | 27.39 | 33.76±0.68 d | 33.93 | 40.37±1.23 c | 36.50 | 54.75±0.52 b | 45.01 | 32.39±0.63 b | 32.55 | 34.75±0.11 b | 31.42 | 33.57±0.21 a | 27.60 | 33.36±0.15 d | 33.53 | 35.49±0.43 a | 32.08 | |
| N300 | 33.73±0.25 a | 28.11 | 48.51±1.22 bc | 49.84 | 50.79±0.32 b | 51.23 | 52.37±0.80 c | 43.65 | 25.21±0.82 c | 25.90 | 22.88±0.18 f | 23.08 | 33.88±0.43 a | 28.24 | 23.62±0.12 e | 24.27 | 25.46±0.94 c | 25.69 | |
| T | N0 | 22.20±0.18 c | 44.00 | 27.63±0.34 e | 63.63 | 31.06±0.55 e | 68.01 | 17.66±0.82 e | 35.00 | 6.70±0.61 d | 15.43 | 8.44±0.16 h | 18.49 | 9.09±0.30 e | 20.94 | 10.6±0.11 g | 21.00 | 6.16±1.01 f | 13.49 |
| N160 | 31.34±0.20 b | 25.35 | 41.50±1.10 b | 31.04 | 54.45±1.85 a | 50.65 | 60.33±1.02 a | 48.81 | 37.63±0.86 a | 28.15 | 31.33±0.44 c | 29.15 | 31.95±0.33 b | 25.84 | 54.56±0.51 b | 40.81 | 21.71±0.76 d | 20.20 | |
| N230 | 34.05±0.82 a | 28.78 | 50.82±0.56 a | 47.16 | 54.07±1.55 a | 51.89 | 59.13±1.11 a | 49.98 | 32.99±0.65 b | 30.61 | 28.16±0.42 d | 27.02 | 23.95±0.39 d | 21.24 | 25.13±0.64 e | 22.23 | 21.97±0.19 d | 21.09 | |
| N300 | 31.33±0.22 b | 27.24 | 41.42±0.50 b | 31.08 | 49.17±0.65 b | 44.07 | 51.71±0.85 c | 44.96 | 32.69±0.27 b | 24.52 | 36.44±0.32 a | 32.67 | 31.98±0.47 b | 27.80 | 59.18±0.84 a | 44.40 | 25.94±1.09 c | 23.25 | |
表2 穗、叶、茎秆氮素积累量及占比
Table 2 Accumulation and proportion of nitrogen in ears, leaves and stems
| 材料Material | 处理Treatment | 穗 Ear | 叶 Leaf | 茎秆 Stem | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 扬花期FP | 灌浆期FS | 成熟期MP | 扬花期FP | 灌浆期FS | 成熟期MP | 扬花期FP | 灌浆期FS | 成熟期MP | |||||||||||
| 氮积 累量 NA/mg | 比例Proportion/% | 氮积 累量 NA/mg | 比例Proportion/% | 氮积 累量 NA/mg | 比例Proportion/% | 氮积 累量 NA/mg | 比例Proportion/% | 氮积 累量NA/mg | 比例Proportion/% | 氮积 累量 NA/mg | 比例Proportion/% | 氮积 累量 NA/mg | 比例Proportion/% | 氮积 累量 NA/mg | 比例Proportion/% | 氮积 累量 NA/mg | 比例Proportion/% | ||
| GP | N0 | 16.87±0.64 d | 37.56 | 40.55±0.75 a | 69.99 | 28.31±1.10 e | 63.30 | 17.62±0.42 e | 39.23 | 4.75±0.51 e | 8.21 | 11.00±0.12 g | 24.61 | 10.43±0.25 e | 23.21 | 12.63±0.42 f | 21.81 | 5.41±0.11 e | 12.10 |
| N160 | 21.18±0.68 c | 23.59 | 37.72±0.57 c | 35.62 | 34.10±1.42 d | 38.27 | 41.93±0.53 d | 46.69 | 26.06±0.18 c | 24.61 | 24.64±0.11 e | 27.65 | 26.68±0.82 c | 29.72 | 42.11±0.76 c | 39.77 | 30.37±0.13 b | 34.08 | |
| N230 | 33.31±0.84 a | 27.39 | 33.76±0.68 d | 33.93 | 40.37±1.23 c | 36.50 | 54.75±0.52 b | 45.01 | 32.39±0.63 b | 32.55 | 34.75±0.11 b | 31.42 | 33.57±0.21 a | 27.60 | 33.36±0.15 d | 33.53 | 35.49±0.43 a | 32.08 | |
| N300 | 33.73±0.25 a | 28.11 | 48.51±1.22 bc | 49.84 | 50.79±0.32 b | 51.23 | 52.37±0.80 c | 43.65 | 25.21±0.82 c | 25.90 | 22.88±0.18 f | 23.08 | 33.88±0.43 a | 28.24 | 23.62±0.12 e | 24.27 | 25.46±0.94 c | 25.69 | |
| T | N0 | 22.20±0.18 c | 44.00 | 27.63±0.34 e | 63.63 | 31.06±0.55 e | 68.01 | 17.66±0.82 e | 35.00 | 6.70±0.61 d | 15.43 | 8.44±0.16 h | 18.49 | 9.09±0.30 e | 20.94 | 10.6±0.11 g | 21.00 | 6.16±1.01 f | 13.49 |
| N160 | 31.34±0.20 b | 25.35 | 41.50±1.10 b | 31.04 | 54.45±1.85 a | 50.65 | 60.33±1.02 a | 48.81 | 37.63±0.86 a | 28.15 | 31.33±0.44 c | 29.15 | 31.95±0.33 b | 25.84 | 54.56±0.51 b | 40.81 | 21.71±0.76 d | 20.20 | |
| N230 | 34.05±0.82 a | 28.78 | 50.82±0.56 a | 47.16 | 54.07±1.55 a | 51.89 | 59.13±1.11 a | 49.98 | 32.99±0.65 b | 30.61 | 28.16±0.42 d | 27.02 | 23.95±0.39 d | 21.24 | 25.13±0.64 e | 22.23 | 21.97±0.19 d | 21.09 | |
| N300 | 31.33±0.22 b | 27.24 | 41.42±0.50 b | 31.08 | 49.17±0.65 b | 44.07 | 51.71±0.85 c | 44.96 | 32.69±0.27 b | 24.52 | 36.44±0.32 a | 32.67 | 31.98±0.47 b | 27.80 | 59.18±0.84 a | 44.40 | 25.94±1.09 c | 23.25 | |
| 材料Material | 处理 Treatment | 干物质转运量DMT/g | 干物质转运率 DMTR/% | 营养器官氮素 转运量 NT/g | 营养器官氮素 转运率 NTR/% | 氮素转运量对穗的贡献率CRNTE/% | 氮肥农学利用率 NAE/% | 氮肥偏生产力 NPP | 氮转 移量 NT/g | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 穗 Ear | 叶 Leaf | 茎秆Stem | |||||||||
| GP | N0 | 9.21±0.02 | 0.97±0.03 | 0.06±0.00 | 3.86±0.01 | 3.84±0.02 h | 7.60± 0.07 d | 12.68±0.01 f | 0.83±0.01 h | ||
| N160 | 9.85±0.01 | 1.84±0.04 | 4.58±0.04 | 23.04±0.08 | 3.93±0.04 g | 4.51± 0.04 f | 11.51±0.07 g | 2.49±0.01 f | 7.04±0.05 c | 2.85±0.04 f | |
| N230 | 10.48±0.04 | 1.34±0.04 | 3.90± 0.03 | 17.40±0.06 | 5.70± 0.07 e | 4.90± 0.07 e | 14.13±0.04 e | 3.44±0.02 b | 6.78±0.04 d | 9.13±0.04 d | |
| N300 | 13.96±0.01 | 2.23±0.02 | 6.12±0.04 | 12.37±0.04 | 22.76±0.01 a | 19.93±0.04 a | 52.83±0.16 a | 3.21±0.02 c | 5.85±0.05 f | 20.84±0.04a | |
| T | N0 | 13.06±0.02 | 0.67±0.03 | 1.38±0.02 | 9.09± 0.02 | 8.04±0.03 d | 15.51±0.04 c | 31.91±0.07 d | 5.26±0.02 e | ||
| N160 | 14.77±0.02 | 1.43±0.02 | -6.00± 0.03 | 13.40±0.03 | 17.97±0.01 c | 15.48±0.06 c | 35.11±0.08 c | 5.42±0.02 a | 11.74±0.06 a | 10.84±0.03 c | |
| N230 | 15.59±0.01 | 1.77±0.04 | 4.09±0.02 | 6.92±0.03 | 21.61±0.04 b | 19.04±0.04 b | 43.95±0.12 b | 2.65±0.01 e | 7.28±0.04 b | 18.92±0.04 b | |
| N300 | 12.63±0.01 | 0.76±0.03 | 3.07±0.04 | 12.37±0.04 | 4.61±0.01 f | 4.20± 0.04 f | 10.80± 0.04 g | 2.92±0.01 d | 6.58±0.02 e | 1.69±0.03 g | |
表3 不同大麦营养器官的氮素转运量、转运率、干物质转运量、转运率及氮肥农学利用率和氮肥偏生产力
Table 3 Nitrogen transfer rate, transfer rate, dry matter transfer rate, transfer rate, agronomic utilization rate of nitrogen fertilizer, partial productivity of nitrogen fertilizer in different barley vegetative organs
| 材料Material | 处理 Treatment | 干物质转运量DMT/g | 干物质转运率 DMTR/% | 营养器官氮素 转运量 NT/g | 营养器官氮素 转运率 NTR/% | 氮素转运量对穗的贡献率CRNTE/% | 氮肥农学利用率 NAE/% | 氮肥偏生产力 NPP | 氮转 移量 NT/g | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 穗 Ear | 叶 Leaf | 茎秆Stem | |||||||||
| GP | N0 | 9.21±0.02 | 0.97±0.03 | 0.06±0.00 | 3.86±0.01 | 3.84±0.02 h | 7.60± 0.07 d | 12.68±0.01 f | 0.83±0.01 h | ||
| N160 | 9.85±0.01 | 1.84±0.04 | 4.58±0.04 | 23.04±0.08 | 3.93±0.04 g | 4.51± 0.04 f | 11.51±0.07 g | 2.49±0.01 f | 7.04±0.05 c | 2.85±0.04 f | |
| N230 | 10.48±0.04 | 1.34±0.04 | 3.90± 0.03 | 17.40±0.06 | 5.70± 0.07 e | 4.90± 0.07 e | 14.13±0.04 e | 3.44±0.02 b | 6.78±0.04 d | 9.13±0.04 d | |
| N300 | 13.96±0.01 | 2.23±0.02 | 6.12±0.04 | 12.37±0.04 | 22.76±0.01 a | 19.93±0.04 a | 52.83±0.16 a | 3.21±0.02 c | 5.85±0.05 f | 20.84±0.04a | |
| T | N0 | 13.06±0.02 | 0.67±0.03 | 1.38±0.02 | 9.09± 0.02 | 8.04±0.03 d | 15.51±0.04 c | 31.91±0.07 d | 5.26±0.02 e | ||
| N160 | 14.77±0.02 | 1.43±0.02 | -6.00± 0.03 | 13.40±0.03 | 17.97±0.01 c | 15.48±0.06 c | 35.11±0.08 c | 5.42±0.02 a | 11.74±0.06 a | 10.84±0.03 c | |
| N230 | 15.59±0.01 | 1.77±0.04 | 4.09±0.02 | 6.92±0.03 | 21.61±0.04 b | 19.04±0.04 b | 43.95±0.12 b | 2.65±0.01 e | 7.28±0.04 b | 18.92±0.04 b | |
| N300 | 12.63±0.01 | 0.76±0.03 | 3.07±0.04 | 12.37±0.04 | 4.61±0.01 f | 4.20± 0.04 f | 10.80± 0.04 g | 2.92±0.01 d | 6.58±0.02 e | 1.69±0.03 g | |
材料 Material | 器官 Organ | 生育期 Period | 单株产量Yield per plant | 氮素含量 Nitrogen content | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 穗 Ear | 叶 Leaf | 茎秆 Stem | 地上部 Above ground | ||||||||||||
| 扬花期FP | 灌浆期 GP | 成熟期 MP | 扬花期 FP | 灌浆期 GP | 成熟期MP | 扬花期FP | 灌浆期GP | 成熟期MP | 扬花期 FP | 灌浆期GP | 成熟期MP | ||||
| GP | 穗 Ear | 扬花期FP | 0.567 | ||||||||||||
| 灌浆期GP | 0.516 | 0.147 | |||||||||||||
| 成熟期MP | 0.575 | 0.991** | 0.221 | ||||||||||||
| 叶 Leaf | 扬花期FP | 0.661 | 0.783 | 0.300 | 0.853 | ||||||||||
| 灌浆期GP | 0.712 | 0.858 | 0.218 | 0.911 | 0.989* | ||||||||||
| 成熟期MP | 0.223 | 0.653 | 0.719 | 0.740 | 0.879 | 0.831 | |||||||||
| 茎秆 Stem | 扬花期FP | 0.810 | 0.838 | 0.071 | 0.885 | 0.968* | 0.989* | 0.743 | |||||||
| 灌浆期GP | 0.630 | 0.079 | -0.038 | 0.180 | 0.643 | 0.566 | 0.439 | 0.609 | |||||||
| 成熟期MP | 0.604 | 0.532 | 0.321 | 0.632 | 0.943 | 0.889 | 0.843 | 0.873 | 0.836 | ||||||
| 地上部 Above ground | 扬花期FP | 0.672 | 0.935 | 0.219 | 0.970* | 0.952* | 0.984* | 0.807 | 0.966* | 0.412 | 0.797 | ||||
| 灌浆期GP | 0.473 | 0.597 | 0.495 | 0.696 | 0.953* | 0.898 | 0.939 | 0.853 | 0.712 | 0.977* | 0.829 | ||||
| 成熟期MP | 0.578 | 0.810 | 0.395 | 0.879 | 0.992** | 0.981* | 0.921 | 0.944 | 0.564 | 0.918 | 0.958* | 0.954* | |||
| T | 地上部 Above ground | 成熟期MP | 0.606 | 0.720 | 0.215 | 0.863 | 0.873 | 0.893 | 0.301 | 0.680 | 0.413 | 0.868 | 0.958* | 0.954* | |
| 灌浆期GP | 0.622 | 0.733 | 0.375 | 0.788 | 0.816 | 0.819 | 0.033 | 0.580 | 0.326 | 0.740 | 0.829 | ||||
| 扬花期FP | 0.586 | 0.687 | 0.094 | 0.889 | 0.881 | 0.913 | 0.551 | 0.757 | 0.510 | 0.938 | |||||
| 茎秆 Stem | 成熟期MP | 0.795 | 0.851 | 0.338 | 0.980* | 0.968* | 0.982* | 0.687 | 0.936 | 0.777 | |||||
| 灌浆期GP | 0.908 | 0.861 | 0.666 | 0.816 | 0.800 | 0.778 | 0.706 | 0.947 | |||||||
| 扬花期FP | 0.923 | 0.926 | 0.572 | 0.956* | 0.944 | 0.936 | 0.708 | ||||||||
| 叶 Leaf | 成熟期MP | 0.407 | 0.390 | -0.057 | 0.577 | 0.525 | 0.556 | ||||||||
| 灌浆期GP | 0.866 | 0.921 | 0.476 | 0.998** | 0.997** | ||||||||||
| 扬花期FP | 0.900 | 0.948 | 0.542 | 0.998** | |||||||||||
| 穗 Ear | 成熟期MP | 0.890 | 0.936 | 0.511 | |||||||||||
| 灌浆期GP | 0.836 | 0.780 | |||||||||||||
| 扬花期FP | 0.988* | ||||||||||||||
表4 不同大麦单株产量与不同时期各营养器官的氮素含量相关性
Table 4 Correlation between the yield per plant of different barley and the nitrogen content of various vegetative organs in different periods
材料 Material | 器官 Organ | 生育期 Period | 单株产量Yield per plant | 氮素含量 Nitrogen content | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 穗 Ear | 叶 Leaf | 茎秆 Stem | 地上部 Above ground | ||||||||||||
| 扬花期FP | 灌浆期 GP | 成熟期 MP | 扬花期 FP | 灌浆期 GP | 成熟期MP | 扬花期FP | 灌浆期GP | 成熟期MP | 扬花期 FP | 灌浆期GP | 成熟期MP | ||||
| GP | 穗 Ear | 扬花期FP | 0.567 | ||||||||||||
| 灌浆期GP | 0.516 | 0.147 | |||||||||||||
| 成熟期MP | 0.575 | 0.991** | 0.221 | ||||||||||||
| 叶 Leaf | 扬花期FP | 0.661 | 0.783 | 0.300 | 0.853 | ||||||||||
| 灌浆期GP | 0.712 | 0.858 | 0.218 | 0.911 | 0.989* | ||||||||||
| 成熟期MP | 0.223 | 0.653 | 0.719 | 0.740 | 0.879 | 0.831 | |||||||||
| 茎秆 Stem | 扬花期FP | 0.810 | 0.838 | 0.071 | 0.885 | 0.968* | 0.989* | 0.743 | |||||||
| 灌浆期GP | 0.630 | 0.079 | -0.038 | 0.180 | 0.643 | 0.566 | 0.439 | 0.609 | |||||||
| 成熟期MP | 0.604 | 0.532 | 0.321 | 0.632 | 0.943 | 0.889 | 0.843 | 0.873 | 0.836 | ||||||
| 地上部 Above ground | 扬花期FP | 0.672 | 0.935 | 0.219 | 0.970* | 0.952* | 0.984* | 0.807 | 0.966* | 0.412 | 0.797 | ||||
| 灌浆期GP | 0.473 | 0.597 | 0.495 | 0.696 | 0.953* | 0.898 | 0.939 | 0.853 | 0.712 | 0.977* | 0.829 | ||||
| 成熟期MP | 0.578 | 0.810 | 0.395 | 0.879 | 0.992** | 0.981* | 0.921 | 0.944 | 0.564 | 0.918 | 0.958* | 0.954* | |||
| T | 地上部 Above ground | 成熟期MP | 0.606 | 0.720 | 0.215 | 0.863 | 0.873 | 0.893 | 0.301 | 0.680 | 0.413 | 0.868 | 0.958* | 0.954* | |
| 灌浆期GP | 0.622 | 0.733 | 0.375 | 0.788 | 0.816 | 0.819 | 0.033 | 0.580 | 0.326 | 0.740 | 0.829 | ||||
| 扬花期FP | 0.586 | 0.687 | 0.094 | 0.889 | 0.881 | 0.913 | 0.551 | 0.757 | 0.510 | 0.938 | |||||
| 茎秆 Stem | 成熟期MP | 0.795 | 0.851 | 0.338 | 0.980* | 0.968* | 0.982* | 0.687 | 0.936 | 0.777 | |||||
| 灌浆期GP | 0.908 | 0.861 | 0.666 | 0.816 | 0.800 | 0.778 | 0.706 | 0.947 | |||||||
| 扬花期FP | 0.923 | 0.926 | 0.572 | 0.956* | 0.944 | 0.936 | 0.708 | ||||||||
| 叶 Leaf | 成熟期MP | 0.407 | 0.390 | -0.057 | 0.577 | 0.525 | 0.556 | ||||||||
| 灌浆期GP | 0.866 | 0.921 | 0.476 | 0.998** | 0.997** | ||||||||||
| 扬花期FP | 0.900 | 0.948 | 0.542 | 0.998** | |||||||||||
| 穗 Ear | 成熟期MP | 0.890 | 0.936 | 0.511 | |||||||||||
| 灌浆期GP | 0.836 | 0.780 | |||||||||||||
| 扬花期FP | 0.988* | ||||||||||||||
| 1 | 魏胜文,乔德华,张东伟.甘肃农业发展研究报告(2011—2015)[R].北京:社会科学出版社,2016. |
| WEI S W, QIAO D H, ZHANG D W. Gansu agricultural development research report (2011—2015) [R]. Beijing: Social Science Press, 2016. | |
| 2 | 杨建明,林峰,尚毅,等.2009—2010年大麦产业技术现状与发展趋势[J].浙江农业学报,2010,22(5):683-688. |
| YANG J M, LIN F, SHANG Y, et al.. The status and development trend of barley industry technology from 2009 to 2010 [J]. Zhejiang Agric. Sci., 2010, 22(5):683-688. | |
| 3 | JONASSEN I B, INGVERSEN J, BRANDT A. Synthesis of SPII albumin, β-amylase and chymotrypsin inhibitor CI-1 on polysomes from the endoplasmic reticulum of barley endosperm [J]. Carlsberg Res. Comm., 1981, 46:175-181. |
| 4 | MASCHER M, GUNDLACH H, HIMMELBACH A, et al.. Achromosome conformation capture ordered sequence of thebarley genome [J]. Nature, 2017, 544(7651):427-433. |
| 5 | GRANT C A, GAURE L E, GEHL D T, et al.. Protein production and nitrogen utilization by barley cultivars in response to nitrogen fertilizer under varying moisture conditions [J]. Canadian J. Plant Sci., 1991, 71:997-1009. |
| 6 | PAPAKOSTA D K G A. Nitrogen and dry matter accumulation, remobilization, and losses for mediterranean wheat during grain filling [J]. Agron. J., 1991, 85(3):864-870. |
| 7 | 王健,韩金玲,杨敏,等.不同氮高效玉米品种对氮素的吸收转运和代谢研究[J].核农学报,2020,34(12):2800-2812. |
| WANG J, HAN J L, YANG M, et al.. Study on nitrogen absorption, transportation and metabolism of different nitrogen-efficient maize varieties [J]. Chin. J. Nucl. Agric., 2020, 34(12): 2800-2812. | |
| 8 | 王晓芸,马增科,孟亚雄.不同基因型大麦苗期氮素利用效率的评价分析[J].大麦与谷类科学,2018,35(3):5- 16. |
| WANG X Y, MA Z K, MENG Y X. Evaluation and analysis of nitrogen use efficiency of different genotypes of barley at seedling stage [J]. Barley Cereal Sci., 2018, 35(3):5-16. | |
| 9 | 潘永东,王效宗,包奇军,等.氮素肥料对啤酒大麦产量和麦芽品质的影响[[J].农业现代化研究,2007,28 (4):80-82 . |
| PAN Y D, WANG X Z, BAO Q J, et al.. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer on malting barley yield and malt quality [J]. Res.Agric. Mod., 2007, 28 (4):80-82. | |
| 10 | 李赢.大麦NRT2/3基因家族分析及其功能验证[D].扬州:扬州大学,2019. |
| LI Y. Barley NRT2/3 gene family analysis and functional verification [D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2019. | |
| 11 | 李静雯,张正英,令利军,等.利用RNAi 抑制B-hordein 合成降低大麦籽粒蛋白质含量[J].中国农业科学,2014,47(19):3746-3756. |
| LI J W, ZHANG Z Y, LING L J, et al.. Using RNAi to inhibit B-hordein synthesis and reduce the protein content of barley grains [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci., 2014, 47(19):3746-3756. | |
| 12 | 许明,封超年,李长亚,等.氮肥对啤酒大麦籽粒品质的影响[J].扬州大学学报,2004,25 (2):34-38. |
| XU M, FENG C N, LI C Y, et al.. The effect of nitrogen fertilizer on malting barley grain quality [J]. J. Yangzhou Univ., 2004, 25(2):34-38. | |
| 13 | 徐银萍.不同氮磷水平对啤酒大麦产量和品质及氮肥农学效率的影响[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2016,11(44):77-83. |
| XU Y P. The effect of different levels of nitrogen and phosphorus on the yield and quality of malting barley and the agronomic efficiency of nitrogen fertilizer [J]. J. Northwest A&F Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2016, 11(44):77-83. | |
| 14 | 刘盈盈,高晓阳,武季玲,等.甘啤大麦氮素运移模型模拟试验研究[J].中国农机化学报,2016,37(10):98-102. |
| LIU Y Y, GAO X Y, WU J L, et al.. Study on the simulation experiment of nitrogen transport model in sweet beer barley [J]. Chin. J. Agric. Mach. Chem., 2016, 37(10):98-102. | |
| 15 | 张金灿.种植密度和施氮量对啤用大麦生长、产量及品质的影响[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆农业大学,2016. |
| ZHANG J C. The effect of planting density and nitrogen application rate on the growth, yield and quality of beer barley [D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2016. | |
| 16 | 徐寿军,刘志萍,张凤英,等.氮肥水平对冬大麦产量、品质和氮肥利用效率的影响及其相关分析[J].扬州大学学报( 农业与生命科学版),2012,33(1):66-71. |
| XU S J, LIU Z P, ZHANG F Y, et al.. The effect of nitrogen fertilizer level on winter barley yield, quality and nitrogen fertilizer use efficiency and its correlation analysis [J]. J. Yangzhou Univ. (Agric. Life Sci.), 2012, 33(1):66-71. | |
| 17 | 沈会权,栾海业,陈和.施氮水平对啤酒大麦氮素吸收、转运及籽粒蛋白质含量的影响[J].江苏农业学报,2013,29(5):1034-1038. |
| SHEN H Q, LUAN H Y, CHEN H. Effects of nitrogen application level on nitrogen absorption, transport and grain protein content of malting barley [J]. J. Jiangsu Agric. Sci., 2013, 29(5):1034-1038. | |
| 18 | 蔡剑.氮钾肥对啤酒大麦籽粒产量和蛋白质形成的影响及其生理机制[D].南京:南京农业大学,2009. |
| CAI J. Effects of nitrogen and potassium fertilizers on the grain yield and protein formation of malting barley and its physiological mechanism [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2009. | |
| 19 | GAUFICHON L, REISDORF-CREN M, ROTHSTEIN S J, et al.. Biological functions of asparagine synthetase in plants [J]. Plant Sci., 2010, 179(3):141-153. |
| 20 | 李东方,李世清,张胜利.不同基因型冬小麦干物质运移及其对氮的反应[J].河南农业科学,2006 (8):34-36. |
| LI D F, LI S Q, ZHANG S L. Dry matter transport of different genotypes of winter wheat and its response to nitrogen [J]. Henan Agric. Sci., 2006(8):34-36. | |
| 21 | 丁锦峰,丁永刚,李福建,等.稻茬晚播小麦氮高效品种氮素积累、分配与利用特征[C]//2018中国作物学会学术年会论文摘要集.北京:中国农业科技出版社,2018. |
| 22 | 黄亿.氮高效利用基因型大麦筛选及氮素吸收转运特性[D].成都:四川农业大学,2014. |
| HUANG Y. Screening of genotypes of barley with high nitrogen utilization and characteristics of nitrogen absorption and transport [D]. Chengdu: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2014. | |
| 23 | 左青松,杨海燕,冷锁虎,等.施氮量对油菜氮素积累和运转及氮素利用率的影响[J].作物学报,2014,40(3):511-518 . |
| ZUO Q S, YANG H Y, LENG S H, et al.. Effects of nitrogen application rate on the accumulation and transfer of nitrogen and nitrogen utilization efficiency in rape [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2014, 40(3):511-518. | |
| 24 | 董桂春,王余龙,周娟,等.不同氮素籽粒生产效率类型籼稻品种氮素分配与运转的差异[J].作物学报,2009,35(1):149-155. |
| DONG G C, WANG Y L, ZHOU J, et al.. Differences in nitrogen distribution and translocation of indica rice varieties with different nitrogen grain production efficiency types [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2009, 35(1):149-155. | |
| 25 | 高润红,徐红卫,郭桂梅,等.两份大麦纯合突变体与其原始品种的氮素吸收利用差异[J].植物生理学报,2020,56 (4):863-870. |
| GAO R H, XU H W, GUO G M, et al.. Differences in nitrogen absorption and utilization between two homozygous barley mutants and their original varieties [J]. Acta Plant Physiol., 2020, 56(4):863-870. | |
| 26 | 德木其格.栽培措施对大麦淀粉与可溶性糖含量的影响[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古民族大学,2020. |
| DE M Q G. The effect of cultivation measures on the content of barley starch and soluble sugar [D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University for Nationalities, 2020. | |
| 27 | 苏丙华,徐炜,张娟,等. 施氮量对超高产小麦品种济麦22号产量和氮素利用效率的影响 [J].山东农业科学,2012,44(8):78-80. |
| SU B H, XU W, ZHANG J, et al.. Effects of nitrogen application rate on yield and nitrogen use efficiency of super high-yield wheat variety Jimai 22 [J]. Shandong Agric. Sci., 2012, 44(8):78-80. | |
| 28 | 张如标,王蓓蓓,丁焕新,等.氮肥对耐盐啤酒大麦产量、品质及光合功能的影响[J].麦类作物学报,2013,33(1):162-168. |
| ZHANG R B, WANG B B, DING H X, et al.. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer on the yield, quality and photosynthetic function of salt-tolerant malting barley [J]. Acta Triticeae Sin., 2013, 33(1):162-168. |
| [1] | 胡秀文, 邓波, 王金斌, 刘华, 唐雪明, 王宇, 曾海娟, 蒋玮, 李红. 基于RPA技术对转CP4-EPSPS基因产品的快速检测[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 227-233. |
| [2] | 陆国清, 马彩霞, 孙国清, 郭惠明, 程红梅. 抗除草剂棉花GV-2的分子特征和遗传稳定性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(1): 42-49. |
| [3] | 焦悦, 王智, 张振民, 彭萱子, 付海滨, 朱鹏宇, 黄春蒙, 张永江, 付伟. 基于转基因产品成分低水平混杂问题探究我国转基因阈值制度[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(3): 20-27. |
| [4] | 包奇军, 潘永东, 张华瑜, 柳小宁, 张东佳, 赵锋, 牛小霞, 陈军. 甘肃与欧洲、北美啤酒大麦品种农艺及品质性状比较分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(3): 57-66. |
| [5] | 邹俊杰, 徐妙云, 张兰, 罗彦忠, 刘源, 郑红艳, 王磊. 转基因抗虫、耐除草剂及品质改良复合性状玉米BBHTL8-1的分子特征及功能评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 77-85. |
| [6] | 周元成, 曹永立, 王镇, 贾志荣, 姚勇, 陈爱萍. 不同大麦品种抗旱性鉴定指标的筛选与评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 86-92. |
| [7] | 陈浩, 周菲, 林拥军. 我国作物新种质创制研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(12): 112-119. |
| [8] | 张健. 中国重要农作物生物育种产业化应用的展望[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(12): 15-24. |
| [9] | 徐彤晓, 贺晓云, 黄昆仑. 生物育种产品食用安全评价研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(12): 153-159. |
| [10] | 孙逸凡, 黄志磊, 李葆春, 姚立蓉, 汪军成, 司二静, 杨轲, 孟亚雄, 马小乐, 王化俊. 大麦种质资源抗叶斑病评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(11): 43-54. |
| [11] | 庄重, 赵龙, 白皓, 毕瑜林, 黄应权, 陈国宏, 常国斌. CRISPR/Cas9技术在家禽育种方面的应用[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 14-23. |
| [12] | 马小倩, 杨涛, 张全, 张洪亮. 水稻新型育种技术研究现状与展望[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 24-30. |
| [13] | 邹俊杰, 徐妙云, 张兰, 郑红艳, 王磊. 转基因复合抗虫耐除草剂玉米BFL4-1的分子特征及功能评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 31-37. |
| [14] | 黄耀辉, 焦悦, 付仲文. 国际转基因产品低水平混杂政策对我国的启示[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(9): 1-11. |
| [15] | 李生梅, 张大伟, 迪丽拜尔·迪力买买提, 魏鑫, 芮存, 杨涛, 耿世伟, 高文伟. 减量灌溉对转ScALDH21基因棉花农艺性状、产量和品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(9): 152-159. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号