




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (3): 119-131.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0284
• 动植物健康 • 上一篇
李小玲1( ), 周武先1(
), 周武先1( ), 蒋小刚1, 李大荣1, 黄大野2(
), 蒋小刚1, 李大荣1, 黄大野2( ), 张美德1(
), 张美德1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-04-11
接受日期:2022-05-10
出版日期:2023-03-15
发布日期:2023-05-22
通讯作者:
周武先,黄大野,张美德
作者简介:李小玲 E-mail:1411271284@qq.com
基金资助:
Xiaoling LI1( ), Wuxian ZHOU1(
), Wuxian ZHOU1( ), Xiaogang JIANG1, Darong LI1, Daye HUANG2(
), Xiaogang JIANG1, Darong LI1, Daye HUANG2( ), Meide ZHANG1(
), Meide ZHANG1( )
)
Received:2022-04-11
Accepted:2022-05-10
Online:2023-03-15
Published:2023-05-22
Contact:
Wuxian ZHOU,Daye HUANG,Meide ZHANG
摘要:
为研究微生物菌肥对川党参连作障碍及紫纹羽病的防控效果,以川党参为研究对象,探索重茬灵和新特锐菌对连作川党参生长及土壤酶活性的影响。结果表明,在施用重茬灵和新特锐菌2年后,与对照(CK)相比,川党参的种苗存活率分别提高了42.3%和38.4%,紫纹羽病发病率由大到小依次为CK(13.4%)>施用新特锐菌(3.4%)>施用重茬灵(0%)。2种微生物菌肥均可有效防控川党参紫纹羽病,且重茬灵的防控效果更佳。与CK相比,重茬灵处理的单株鲜重提高了20.3%,产量提高了71.4%;新特锐菌处理的单株鲜重提高了34.6%,产量提高了85.7%。此外,重茬灵和新特锐菌处理均显著提升了川党参叶片叶绿素a含量,增幅分别为4.9%和2.6%;并显著提升了总叶绿素含量,增幅分别为5.3%和3.0%。与CK相比,重茬灵处理下川党参叶片的过氧化氢酶、过氧化物酶、超氧化物歧化酶活性及丙二醛和超氧阴离子自由基含量显著下降,而可溶性糖和可溶性蛋白含量则显著升高;新特锐菌处理下仅可溶性蛋白含量显著升高。重茬灵处理显著提高了川党参根茎总蛋白含量,增幅为15.6%~16.5%,新特锐菌处理则显著提高了其炔苷含量,增幅为10.1%~15.3%。土壤酶活性对施用2种微生物菌肥的响应规律一致,与CK相比,重茬灵和新特锐菌处理均显著提高了连作土壤的脲酶、碱性磷酸酶及蔗糖酶活性,显著降低了过氧化氢酶活性。综上所述,微生物菌肥能够通过影响川党参植株的光合代谢、抗氧化能力以及土壤酶活性来改善其生长,从而有效防控川党参连作障碍和紫纹羽病害。
中图分类号:
李小玲, 周武先, 蒋小刚, 李大荣, 黄大野, 张美德. 微生物菌肥对川党参连作障碍及紫纹羽病的防控效果[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 119-131.
Xiaoling LI, Wuxian ZHOU, Xiaogang JIANG, Darong LI, Daye HUANG, Meide ZHANG. Control Effect of Microbial Fertilizers on the Replanting Disease and Helicobasidium mompa Tanaka of Codonopsis tangshen Oliv.[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(3): 119-131.
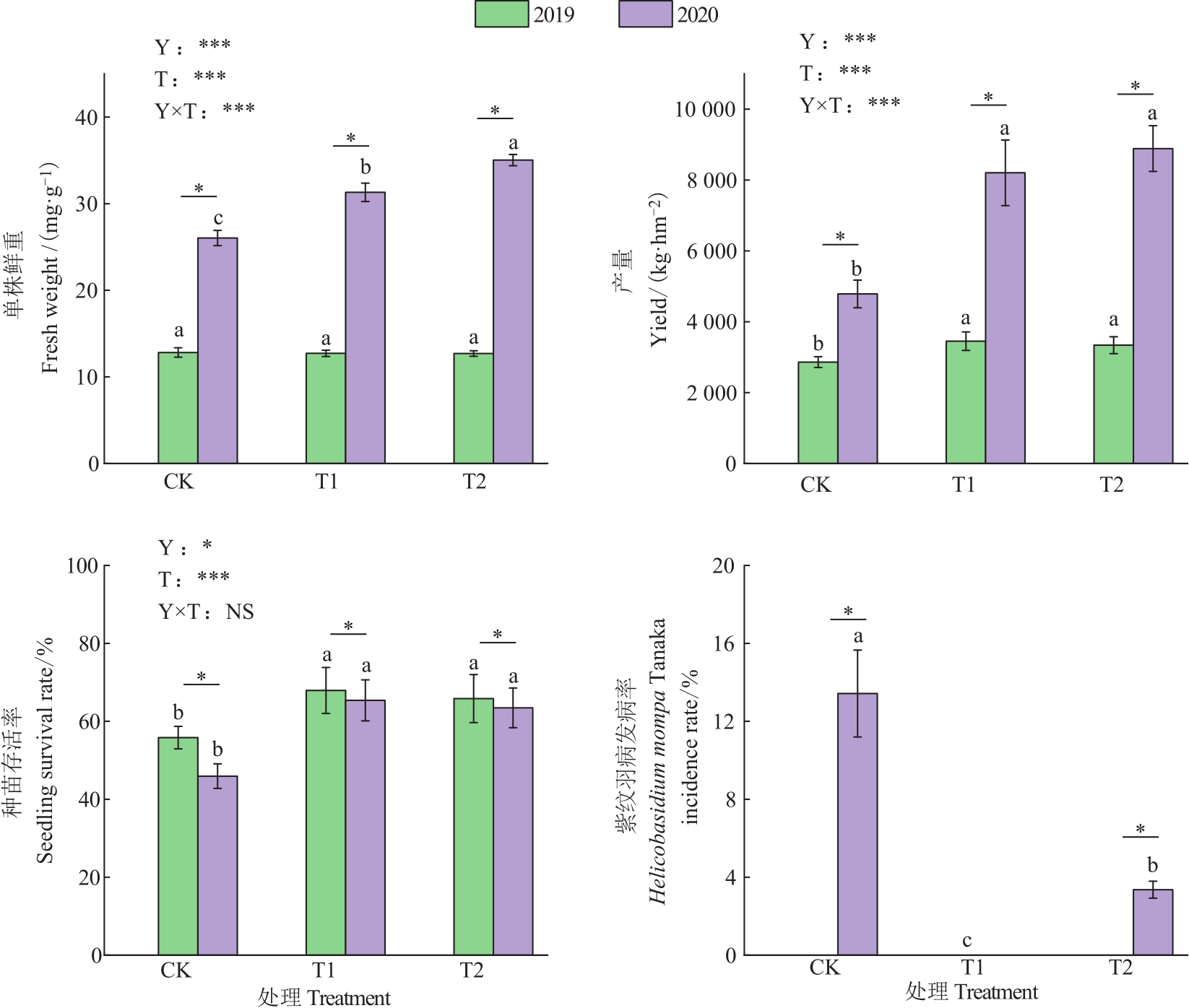
图1 施用微生物菌肥下连作川党参生长及紫纹羽病害发生情况注:同一年份不同的小写字母表示处理之间差异在P<0.05水平显著。Y—栽培年限;T—生物菌肥类型;Y×T—栽培年限与生物菌肥类型的交互效应;NS—无显著影响; *和***分别表示在P<0.05和P<0.001水平显著。
Fig. 1 Situations of the growth and Helicobasidium mompa Tanaka incidence in continuous cropping C. tangshen Oliv.under using microbial fertilizersNote: Different lowercase letters of same year indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05 level. Y—Cultivated years;T—Types of microbial fertilizer;Y×T—Interaction effect of the cultivated years and types of microbial fertilizer;NS—No significant effect; * and *** indicate significant at P<0.05 and P<0.001 levels, respectively.
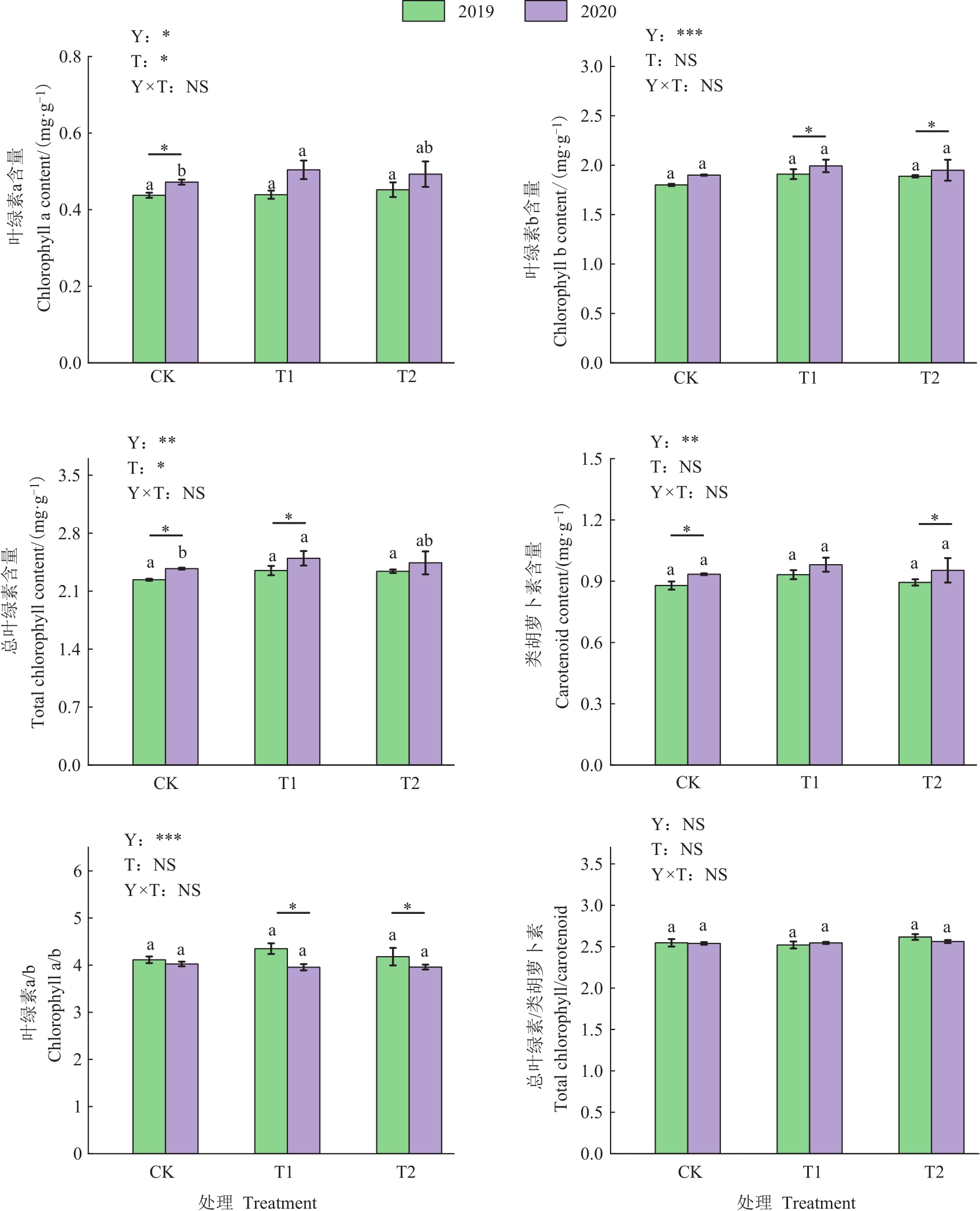
图2 施用微生物菌肥下连作川党参的光合色素情况注:同一年份不同的小写字母表示处理之间差异在P<0.05水平显著。Y—栽培年限;T—生物菌肥类型;Y×T—栽培年限与生物菌肥类型的交互效应;NS—无显著影响; *、** 和***分别表示在 P<0.05、P<0.01和P<0.001水平显著。
Fig. 2 Situations of the photosynthetic pigment content in continuous cropping C. tangshen Oliv. under using microbial fertilizersNote: Different lowercase letters of same year indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05 level. Y—Cultivated years;T—Types of microbial fertilizer;Y×T—Interaction effect of the cultivated years and types of microbial fertilizer;NS—No significant effect; *,** and *** indicate significant at P<0.05,P<0.01 and P<0.001 levels, respectively.

图3 施用微生物菌肥下连作川党参抗氧化系统、可溶性糖及可溶性蛋白的情况注:同一年份不同的小写字母表示处理之间差异在P<0.05水平显著。Y—栽培年限;T—生物菌肥类型;Y×T—栽培年限与生物菌肥类型的交互效应;NS—无显著影响; *、** 和***分别表示在 P<0.05、P<0.01和P<0.001水平显著。
Fig. 3 Situations of the antioxidant system, soluble sugar, and soluble protein in continuous cropping C. tangshen Oliv. under using microbial fertilizersNote: Different lowercase letters of same year indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05 level. Y—Cultivated years;T—Types of microbial fertilizer;Y×T—Interaction effect of the cultivated years and types of microbial fertilizer;NS—No significant effect; *,** and *** indicate significant at P<0.05,P<0.01 and P<0.001 levels, respectively.

图4 施用微生物菌肥下连作川党参的品质状况注:同一年份不同的小写字母表示处理之间差异在P<0.05水平显著。Y—栽培年限;T—生物菌肥类型;Y×T—栽培年限与生物菌肥类型的交互效应;NS—无显著影响; *、**和***分别表示在P<0.05、P<0.01和P<0.001水平显著。
Fig. 4 Quality situations of continuous cropping C. tangshen Oliv.under using microbial fertilizersNote:Different lowercase letters of same year indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05 level. Y—Cultivated years;T—Types of microbial fertilizer;Y×T—Interaction effect of the cultivated years and types of microbial fertilizer;NS—No significant effect; *,** and *** indicate significant at P<0.05,P<0.01 and P<0.001 levels, respectively.
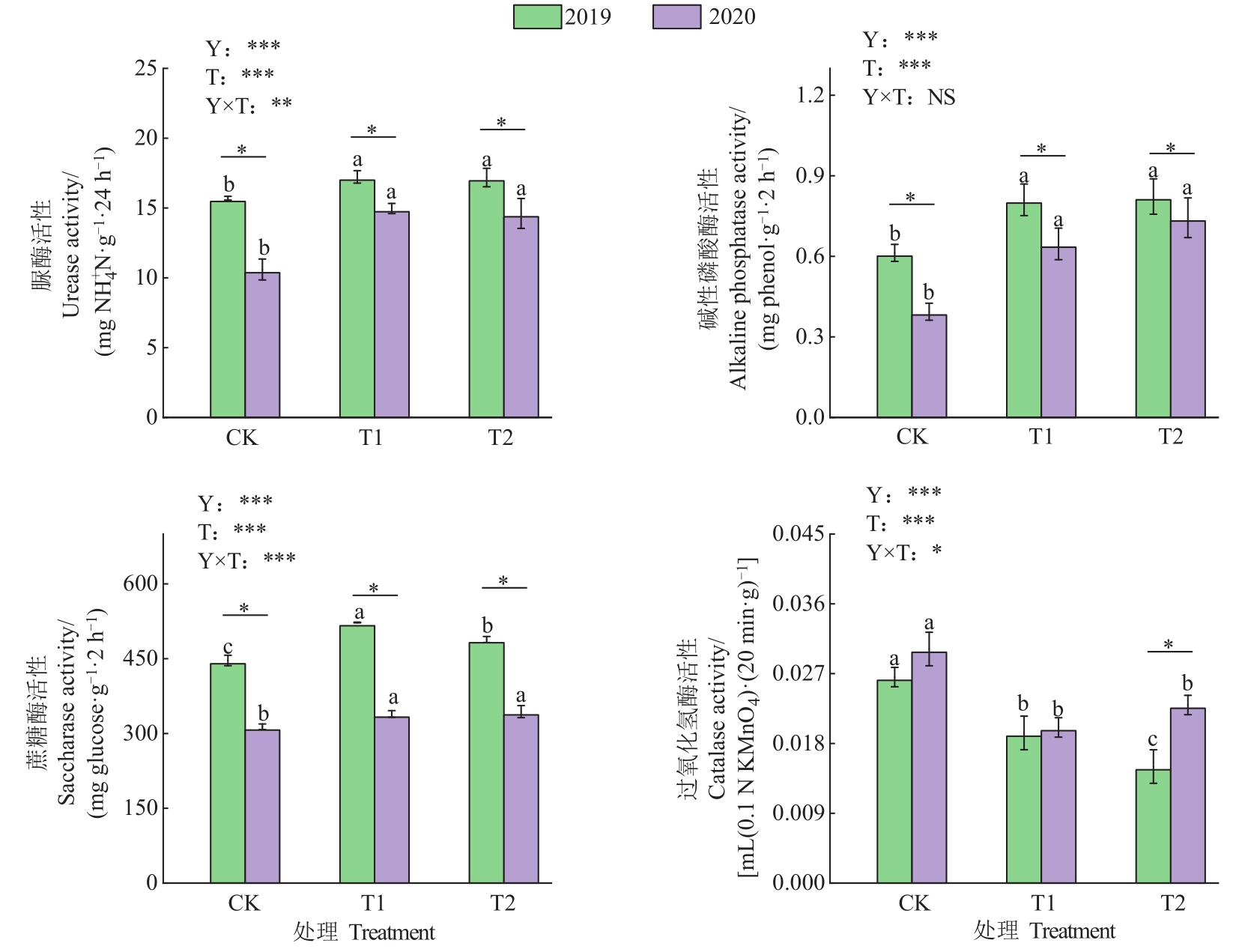
图5 施用微生物菌肥下的土壤酶活情况注:同一年份不同的小写字母表示处理之间差异在P<0.05水平显著。Y—栽培年限;T—生物菌肥类型;Y×T—栽培年限与生物菌肥类型的交互效应;NS—无显著影响; *、** 和***分别表示在 P<0.05、P<0.01和P<0.001水平显著。
Fig. 5 Soil enzyme activities situations of continuous cropping C. tangshen Oliv. under using microbial fertilizersNote: Different lowercase letters of same year indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05 level. Y—Cultivated years;T—Types of microbial fertilizer;Y×T—Interaction effect of the cultivated years and types of microbial fertilizer;NS—No significant effect; *,** and *** indicate significant at P<0.05,P<0.01 and P<0.001 levels, respectively.
处理 Treatment | 生长响应指数PGRI | 综合效应 CE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
产量 Yield | 多糖 Polysaccharide | 炔苷 Lobetyolin | 生物碱 Alkaloid | 可溶性蛋白 Soluble protein | ||
| CK | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| T1 | 0.290 | 0.001 | 0.092 | 0.119 | 0.137 | 0.128 |
| T2 | 0.300 | 0.028 | 0.112 | 0.124 | 0.040 | 0.121 |
表1 微生物菌肥对川党参生长的综合效应
Table 1 The comprehensive effects of microbial fertilizers on the growth of continuous cropping C. tangshen Oliv.
处理 Treatment | 生长响应指数PGRI | 综合效应 CE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
产量 Yield | 多糖 Polysaccharide | 炔苷 Lobetyolin | 生物碱 Alkaloid | 可溶性蛋白 Soluble protein | ||
| CK | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| T1 | 0.290 | 0.001 | 0.092 | 0.119 | 0.137 | 0.128 |
| T2 | 0.300 | 0.028 | 0.112 | 0.124 | 0.040 | 0.121 |

图6 生长指标与土壤酶活性的相关性分析注:*、** 和***分别表示相关在P<0.05、P<0.01和P<0.001水平显著。
Fig. 6 Analysis of the correlation between growth index and soil enzyme activitiesNote: *,** and *** indicate significant correlation at P<0.05,P<0.01 and P<0.001 levels, respectively.
| 1 | 刘晔, 姜瑛, 王国文, 等. 不同连作年限对植烟土壤理化性状及微生物区系的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2016, 32(13): 136-140. |
| LIU H, JIANG Y, WANG G W, et al.. Effect of different continuous cropping years on tobacco-growing soil’s physical and chemical properties and microflora [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2016, 32(13): 136-140. | |
| 2 | 李世金, 朱启法, 裴洲洋, 等. 烟草种植连作障碍产生的原因及防治对策[J]. 现代农业科技, 2018(4): 54-56, 58. |
| LI S J, ZHU Q F, PEI Z Y, et al.. Reasons and countermeasures of tobacco successive cropping obstacle [J]. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2018(4): 54-56, 58. | |
| 3 | 张重义, 林文雄. 药用植物的化感自毒作用与连作障碍[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2009, 17(1): 189-196. |
| ZHANG C Y, LIN W X. Continuous cropping obstacle and allelopathic autotoxicity of medicinal plants [J]. Chin. J. Ecol. Agric., 2009, 17(1): 189-196. | |
| 4 | 刘来. 连作土壤酸化及改良对土壤性状和辣椒生理代谢的影响[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2013. |
| LIU L. Effect of continuous cropping on properties of soil and growth, physiological metabolism of pepper [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2013. | |
| 5 | 石程仁, 禹山林, 杜秉海, 等. 连作花生土壤理化性质的变化特征及其与土壤微生物相关性分析[J]. 花生学报, 2018, 47(4): 1-6, 18. |
| SHI C R, YU S L, DU B H, et al.. The characteristics variation of soil physical and chemical properties and its correlation with soil microorganisms under continuous peanut cropping [J]. J. Peanut Sci., 2018, 47(4): 1-6, 18. | |
| 6 | 李奉国, 马龙传, 孔勇, 等. 连作对大蒜土壤养分、微生物结构和酶活的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(1): 141-147. |
| LI F G, MA L C, KONG Y, et al.. Effect of continuous garlic cropping on soil nutrients, microbial structure and enzyme activity [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2019, 21(1): 141-147. | |
| 7 | ZHANG X H, LANG D Y, ZHANG E H, et al.. Effect of autotoxicity and soil microbes in continuous cropping soil on Angelica sinensis seedling growth and rhizosphere soil microbial population [J]. Chin. Herbal Med., 2015, 7(1): 88-93. |
| 8 | 苏世鸣, 任丽轩, 霍振华, 等. 西瓜与旱作水稻间作改善西瓜连作障碍及对土壤微生物区系的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2008, 41(3): 704-712. |
| SU S M, REN L X, HUO Z H, et al.. Effects of intercropping watermelon with rain fed rice on fusarium wilt and the microflora in the rhizosphere soil [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2008, 41(3): 704-712. | |
| 9 | 余中莲, 雷美艳, 蒲盛才, 等. 重庆党参真菌病害种类调查及病原鉴定[J]. 中药材, 2015,38(6): 1119-1122. |
| YU Z L, LEI M Y, PU S C, et al.. Fungal disease survey and pathogen identification on Codonopsis tangshen in Chongqing [J]. J. Chin. Med. Mater., 2015,38(6): 1119-1122. | |
| 10 | 刘兴元. 党参紫纹羽病的发生与防治[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2006, 34(14): 3392. |
| LIU X Y. Occurrence and prevention of Helicobasidium mompa Tanaka of Codonopsis tangshen Oliv. [J]. J. Anhui Agric. Sci., 2006, 34(14): 3392. | |
| 11 | WU H M. Rhizosphere responses to environmental conditions in Radix pseudostellariae under continuous monoculture regimes [J]. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ., 2019,270-271: 19-31. |
| 12 | 韩凤梅, 程伶俐, 陈勇. 板桥党参多糖的分离纯化及组成研究[J]. 中国药学杂志, 2005, 39(18): 1381-1383. |
| HAN F M, CHENG L L, CHEN Y. Study on isolation and composition of Codonopsis tangshen polysaccharides [J]. Chin. Pharm. J., 2005, 39(18): 1381-1383. | |
| 13 | 傅盼盼. 党参多糖降血糖作用及其机制的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2008. |
| FU P P. Studies on hypoglycemic effects and the mechanism of polysaccharides from radix Codonopsis [D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2008. | |
| 14 | 晏永新, 张丽, 贾海芳, 等. 党参多糖口服液对小鼠免疫功能的影响[J]. 中国兽药杂志, 2013, 47(3): 18-20. |
| YAN Y X, ZHANG L, JIA H F, et al.. Effects of Codonopsis pilosula polysaccharide oral liquids on the immunity function of mice [J]. Chin. J. Veterinary Drug, 2013, 47(3): 18-20. | |
| 15 | 闫彦芳, 张壮, 韦颖, 等. 党参总皂苷抗缺氧缺糖再给氧诱导大鼠星形胶质细胞损伤的作用[J]. 北京中医药大学学报, 2006, 29(12): 826-829, 871. |
| YAN Y F, ZHANG Z, WEI Y, et al.. Preventive effect of total saponin of radix Codonopsis on ast lesion induced by hypoxia and hypoglycemia reoxygenation in rats [J]. J. Beijing Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med., 2006, 29(12): 826-829, 871. | |
| 16 | 黄圆圆, 张元, 康利平, 等. 党参属植物化学成分及药理活性研究进展[J]. 中草药, 2018, 49(1): 239-250. |
| HUANG Y Y, ZHANG Y, KANG L P, et al.. Research progress on chemical constituents and their pharmacological activities of plant from Codonopsis [J]. China Tradit. Herb Drugs, 2018, 49(1): 239-250. | |
| 17 | 杜毛笑, 邱黛玉, 任凤英, 等. 间作植物和茬口对连作党参生长和品质产量的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2021, 41(11): 1884-1892. |
| DU M X, QIU D Y, REN F Y, et al.. Effects of intercropping crops and stubbles on growth, yield and quality of Codonopsis pilosula [J]. Acta Bot. Bor-Occid. Sin., 2021, 41(11): 1884-1892. | |
| 18 | HE Y S, ZHANG M D, ZHOU W X, et al.. Transcriptome analysis reveals novel insights into the continuous cropping induced response in Codonopsis tangshen, a medicinal herb [J]. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 2019, 141: 279-290. |
| 19 | 吴红淼, 林文雄. 药用植物连作障碍研究评述和发展透视[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2020, 28(6): 775-793. |
| WU H M, LIN W X. A commentary and development perspective on the consecutive monoculture problems of medicinal plants [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2020, 28(6): 775-793. | |
| 20 | 邓妍, 王娟玲, 王创云, 等. 生物菌肥与无机肥配施对藜麦农艺性状、产量性状及品质的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2021, 47(7): 1383-1390. |
| DENG Y, WANG J L, WANG C Y, et al.. Effects of combined application of bio-bacterial fertilizer and inorganic fertilizer on agronomic characters, yield, and quality in quinoa [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2021, 47(7): 1383-1390. | |
| 21 | 王文丽, 李娟, 赵旭. 生物有机肥对连作当归根际土壤细菌群落结构和根腐病的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(8): 2813-2821. |
| WANG W L, LI J, ZHAO X. Effects of biological organic fertilizer on rhisosphere soil bacteria community and root rot diseases of continuous cropping Angelica sinensis [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2019, 30(8): 2813-2821. | |
| 22 | 陈慧. 连作白术根际土壤变化及PGPR菌肥缓解白术连作障碍研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2014. |
| CHEN H. Variation of rhizosphere soil on continues cropping Atractylodes macrocephala and alleviation for A .macrocephala cropping obstacles through different kinds of PGPR fertilizer [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry, 2014. | |
| 23 | 吴莉雅. 微生物菌肥对连作太子参的生长状况及品质提高的探究[J]. 海峡药学, 2019, 31(11): 56-59. |
| WU L Y. Study of microbial fertilizer on soil remediation and quality of improvement of continuous cropping of Pseudostellaria heterophylla [J]. Strait Pharmaceutical J., 2019, 31(11): 56-59. | |
| 24 | 周武先, 刘翠君, 何银生, 等. 3种改良剂对连作川党参生长及土壤生化性质的影响[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2021, 38(1): 43-52. |
| ZHOU W X, LIU C J, HE Y S, et al.. Effects of three amendments on the growth of Codonopsis tangshen and soil biochemical properties in a continuous cropping system [J]. J. Agric. Resour. Environ., 2021, 38(1): 43-52. | |
| 25 | 张志良, 瞿伟菁. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2002: 57-60. |
| 26 | 高俊凤. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006:1-287. |
| 27 | 王学奎. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2010:1-324. |
| 28 | 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000:1-289. |
| 29 | 周武先, 李梦歌, 谭旭辉, 等. 播种密度对不同季节半夏生长、品质及土壤酶活性的影响[J/OL]. 作物杂志,2022:1-12[2022-03-30]. . |
| ZHOU W X, LI M G, TAN X H, et al.. Effects of sowing density on growth, nutritional quality and soil enzyme activity of Pinellia ternata under different seasons [J/OL]. Crops,2022:1-12 [2022-03-30]. . | |
| 30 | 关松荫. 土壤酶及其研究方法[M]. 北京: 农业出版社, 1986:1-376. |
| 31 | 周武先, 何银生, 朱盈徽, 等. 生石灰和钙镁磷肥对酸化川党参土壤的改良效果[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(9): 3224-3232. |
| ZHOU W X, HE Y S, ZHU Y H, et al.. Improvement effects of quicklime and calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer on acidified soil cultivating Codonopsis tangshen [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2019, 30(9): 3224-3232. | |
| 32 | 赵江涛, 李晓峰, 李航, 等. 可溶性糖在高等植物代谢调节中的生理作用[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2006, 34(24): 6423-6425, 6427. |
| ZHAO J T, LI X F, LI H, et al.. Research on the role of the soluble sugar in the regulation of physiological metabolism in higher plant [J]. J. Anhui Agric. Sci., 2006, 34(24): 6423-6425, 6427. | |
| 33 | 闫帅, 崔明, 周金星, 等. 外生菌根菌肥对白皮松光响应的影响[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2015, 43(7): 42-46. |
| YAN S, CUI M, ZHOU J X, et al.. Effects of ectomycorrhizal fungi on Pinus bungeana of light response of photosynthesis [J]. J. Northeast For. Univ., 2015, 43(7): 42-46. | |
| 34 | BARTO E K, CIPOLLINI D. Testing the optimal defense theory and the growth-differentiation balance hypothesis in arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Oecologia, 2005, 146(2): 169-178. |
| 35 | 张树衡, 丁德东, 何静, 等. 两种生物肥料配施对再植花椒生长及光合特性的影响[J]. 西北农业学报, 2021, 30(9): 1355-1364. |
| ZHANG S H, DING D D, HE J, et al.. Effect of two biofertilizer mixtures on growth and photosynthetic characteristics of replanted Zanthoxylum bungeanum [J]. Acta Agric. Bor-Occid. Sin., 2021, 30(9): 1355-1364. | |
| 36 | 何嘉, 马婷慧, 白小军, 等. 微生物菌剂对枸杞生长发育、产量品质及土壤养分的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2021, 49(14): 149-154. |
| HE J, MA T H, BAI X J, et al.. Effects of microbial agents on growth,yield and quality of Lycium barbarum L. and soil nutrients [J]. Jiangsu Agric. Sci., 2021, 49(14): 149-154. | |
| 37 | 罗静静, 刘小龙, 李克梅, 等. 几种微生物菌剂对连作棉田枯黄萎病的防病效应[J]. 西北农业学报, 2015, 24(7): 136-143. |
| LUO J J, LIU X L, LI K M, et al.. Effects of microbial agent inoculations on controlling Fusarium oxysporum and Verticillium dahliae in cotton fields of continuous cropping [J]. Acta Agric. Bor-Occid. Sin., 2015, 24(7): 136-143. | |
| 38 | 谢达平, 彭道林, 黄祖民, 等. 微生物菌肥的作用机理研究[J]. 常德师范学院学报(自然科学版), 2002, 14(1): 48-50. |
| XIE D P, PEN D L, HUANG Z M, et al.. The study of the bacteria manure’s role to the crop [J]. J. Changde Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2002, 14(1): 48-50. | |
| 39 | 郭润芳, 刘晓光, 高克祥,等. 拮抗木霉菌在生物防治中的应用与研究进展[J]. 中国生物防治, 2002, 18(4): 5. |
| GUO R F, LIU X G, GAO K X, et al.. Progress in biocontrol research with Trichoderma [J]. Chin. J. Biol. Con., 2002, 18(4): 5. | |
| 40 | 王雪, 陈美兰, 杨光, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌与哈茨木霉菌合用对连作丹参生长及质量的影响[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2014, 39(9): 1574-1578. |
| WANG X, CHEN M L, YANG G, et al.. Effect of Glomus versiforme and Trichodema harzianum on growth and quality of Salvia miltiorrhiza [J]. Chin. J. Chin. Mater. Med., 2014, 39(9): 1574-1578. | |
| 41 | 李红磊. 玉米青枯病生防菌筛选及其应用技术研究[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2010. |
| LI H L. Screeining of biocontrol against corn stalk bot and studies on the application technology [D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agriculture University, 2010. | |
| 42 | 宋以玲, 于建, 陈士更, 等. 复合微生物菌剂对棉花生理特性及根际土壤微生物和化学性质的影响[J]. 土壤, 2019, 51(3): 477-487. |
| SONG Y L, YU J, CHEN S G, et al.. Effects of complex microbial agent on cotton physiological characteristics, microorganism and physicochemical properties in rhizosphere soil [J]. Soils, 2019, 51(3): 477-487. | |
| 43 | 谢奎忠, 胡新元, 张彤彤, 等. 不同杀菌剂对旱地连作马铃薯土壤水分效应、微生物和产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 103-111. |
| XIE K Z, HU X Y, ZHANG T T, et al.. Effects of different soil amendment measures on soil water relations, microbial community structure and yield in potato continuous cropping in dry land [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2019, 28(7): 103-111. | |
| 44 | 阎世江, 李照全, 张治家. 生物菌肥的研究现状与应用[J]. 北方园艺, 2017(5): 189-192. |
| YAN S J, LI Z Q, ZHANG Z J. Research status and application of bacterial manure [J]. Northern Hortic., 2017(5): 189-192. | |
| 45 | 柳玲玲, 王文华, 杨再刚, 等. 不同生物有机肥对钩藤产量、品质及土壤生物性状的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2018(3): 116-121. |
| LIU L L, WANG W H, YANG Z G, et al.. Effects of different biological organic fertilizer on yield and quality of Uncaria rhynchophylla and the soil biological properties [J]. China Soils Fert., 2018(3): 116-121. | |
| 46 | 许馨露, 李丹丹, 马元丹, 等. 四季桂抗氧化防御系统对干旱、高温及协同胁迫的响应[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(1): 72-81. |
| XU X L, LI D D, MA Y D, et al.. Responses of the antioxidant defense system of Osmanthus fragrans cv. ‘Tian Xiang Tai Ge’ to drought, heat and the synergistic stress [J]. Chin. Bull. Bot., 2018, 53(1): 72-81. | |
| 47 | PARIDA A K, DAS A B, MOHANTY P. Defense potentials to NaCl in a mangrove, bruguiera parviflora: differential changes of isoforms of some antioxidative enzymes [J]. J. Plant Physiol., 2004, 161(5): 531-542. |
| 48 | 查倩, 奚晓军, 蒋爱丽, 等. 高温胁迫对葡萄幼树叶绿素荧光特性和抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 植物生理学报, 2016, 52(4): 525-532. |
| CHA Q, XI X J, JIANG A L, et al.. Effects of heat stress on chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics and antioxidant activity in grapevines (Vitis vinifera L. cv. Xiahei) [J]. Acta Phytophysiol. Sin., 2016, 52(4): 525-532. | |
| 49 | ASADUZZAMAN M, KOBAYASHI Y, ISOGAMI K, et al.. Growth and yield recovery in strawberry plants under autotoxicity through electrodegradation [J]. Eur. J. Hortic. Sci., 2012, 77(2): 58-67. |
| 50 | 田方, 陈锡, 王普昶, 等. 微生物菌剂对白刺花苗期抗旱酶系及生理生化指标的影响[J]. 植物生理学报, 2022, 58(2): 435-446. |
| TIAN F, CHEN X, WANG P X, et al.. Effect of microbial agents on resistant enzyme system and biochemical indexes of drought resistance in Sophora davidii [J]. Acta Phytophysiol. Sin., 2022, 58(2): 435-446. | |
| 51 | 刘彬, 曹尚杰, 王营, 等. 过表达细叶百合LpNAC6基因增强烟草的耐盐性[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2020,42(4): 69-79. |
| LIU B, CAO S J, WANG Y, et al.. Overexpression of LpNAC6 gene in Lilium pumilum enhancing salt tolerance in transgenic tobacco [J]. J. Beijing For. Univ., 2020,42(4): 69-79. | |
| 52 | 王亚文, 史慧芳, 张鹏, 等. 微生物菌肥在设施蔬菜生产中的研究进展[J]. 农学学报, 2021, 11(11): 27-32. |
| WANG Y W, SHI H F, ZHANG P, et al.. Research progress of microbial fertilizer in facility vegetable production [J]. J. Agric., 2021, 11(11): 27-32. | |
| 53 | 王涛, 乔卫花, 李玉奇, 等. 轮作和微生物菌肥对黄瓜连作土壤理化性状及生物活性的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2011, 42(3): 578-583. |
| WANG T, QIAO W H, LI Y Q, et al.. Effects of rotation and microbial fertilizers on the properties of continuous cucumber cropping soil [J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2011, 42(3): 578-583. |
| [1] | 杨莉, 于俐, 孙卓, 张桐毓, 张阳, 杨利民. 人参根系分泌物中有机酸及皂苷对人参病原菌与生防菌的化感差异研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(6): 145-155. |
| [2] | 陈福慧, 申乃坤, 姜明国, 王一兵. 作物重茬连作障碍中自毒物质的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(10): 125-132. |
| [3] | 李浩成1,2,左应梅2,杨绍兵2,杨天梅2,李纪潮2,杨维泽2,张金渝2*. 三七根系分泌物在连作障碍中的生态效应及缓解方法[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(8): 159-167. |
| [4] | 李庆凯1,2,3,刘苹2,3*,赵海军3,宋效宗2,林海涛2,沈玉文2,李林1,万书波1,3*. 玉米根系分泌物对连作花生土壤酚酸类物质化感作用的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(3): 119-130. |
| [5] | 珊丹,荣浩*,刘艳萍,邢恩德. 草原露天矿排土场微生物菌肥施用效果研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(6): 129-135. |
| [6] | 王佩雯1,朱金峰2,任志广1,陈征1,许自成1*. 不同土壤改良剂处理下连作植烟土壤化学性质及土壤酶活性的耦合分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(4): 82-91. |
| [7] | 张翠绵1,李洪涛1,李晓芝2,贾楠1,胡栋1,王占武1. 链霉菌S506对设施黄瓜根际生态和生产性状的影响[J]. , 2010, 12(5): 98-102. |
| [8] | 张子龙,王文全. 药用植物连作障碍的形成机理及其防治[J]. , 2009, 11(6): 19-23. |
| [9] | 薛泉宏,同延安. 土壤生物退化及其修复技术研究进展[J]. , 2008, 10(4): 28-35. |
| [10] | 阮维斌,王敬国,张福锁,申建波. 根际微生态系统理论在连作障碍中的应用[J]. , 1999, 1(4): 53-58. |
| [11] | 段玉琪1,陈冬梅2,晋艳1,王海斌2,杨宇虹1,尤垂淮2,田卫霞2,林文雄2. 不同肥料对连作烟草根际土壤微生物及酶活性的影响[J]. , 1, 1(1): 122-126. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号