




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (3): 194-205.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0534
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
赵玉鹏1,2( ), 冯耀祖3(
), 冯耀祖3( ), 王治国1, 付彦博1,4, 陈波浪2, 扁青永4, 饶晓娟5
), 王治国1, 付彦博1,4, 陈波浪2, 扁青永4, 饶晓娟5
收稿日期:2023-07-10
接受日期:2024-03-01
出版日期:2025-03-15
发布日期:2025-03-14
通讯作者:
冯耀祖
作者简介:赵玉鹏 E-mail:1422289169@qq.com;
基金资助:
Yupeng ZHAO1,2( ), Yaozu FENG3(
), Yaozu FENG3( ), Zhiguo WANG1, Yanbo FU1,4, Bolang CHEN2, Qingyong BIAN4, Xiaojuan RAO5
), Zhiguo WANG1, Yanbo FU1,4, Bolang CHEN2, Qingyong BIAN4, Xiaojuan RAO5
Received:2023-07-10
Accepted:2024-03-01
Online:2025-03-15
Published:2025-03-14
Contact:
Yaozu FENG
摘要:
为分析增氧水输入对沙土土壤氮素转化的影响,采用室内土壤培养试验方法研究常规水(SCK)、自然空气供氧曝气增氧(SD1)、33%增氧供氧曝气增氧(SD2)和90%增氧供氧曝气增氧(SD3)4种不同增氧水输入对沙土土壤硝化作用和矿化作用的影响,利用硝化动力学方程评价硝态氮(NO
中图分类号:
赵玉鹏, 冯耀祖, 王治国, 付彦博, 陈波浪, 扁青永, 饶晓娟. 增氧水输入对沙土土壤氮素硝化与矿化的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(3): 194-205.
Yupeng ZHAO, Yaozu FENG, Zhiguo WANG, Yanbo FU, Bolang CHEN, Qingyong BIAN, Xiaojuan RAO. Effect of Oxygenated Water Input on Nitrogen Nitrification and Mineralization in Sandy Soil[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(3): 194-205.
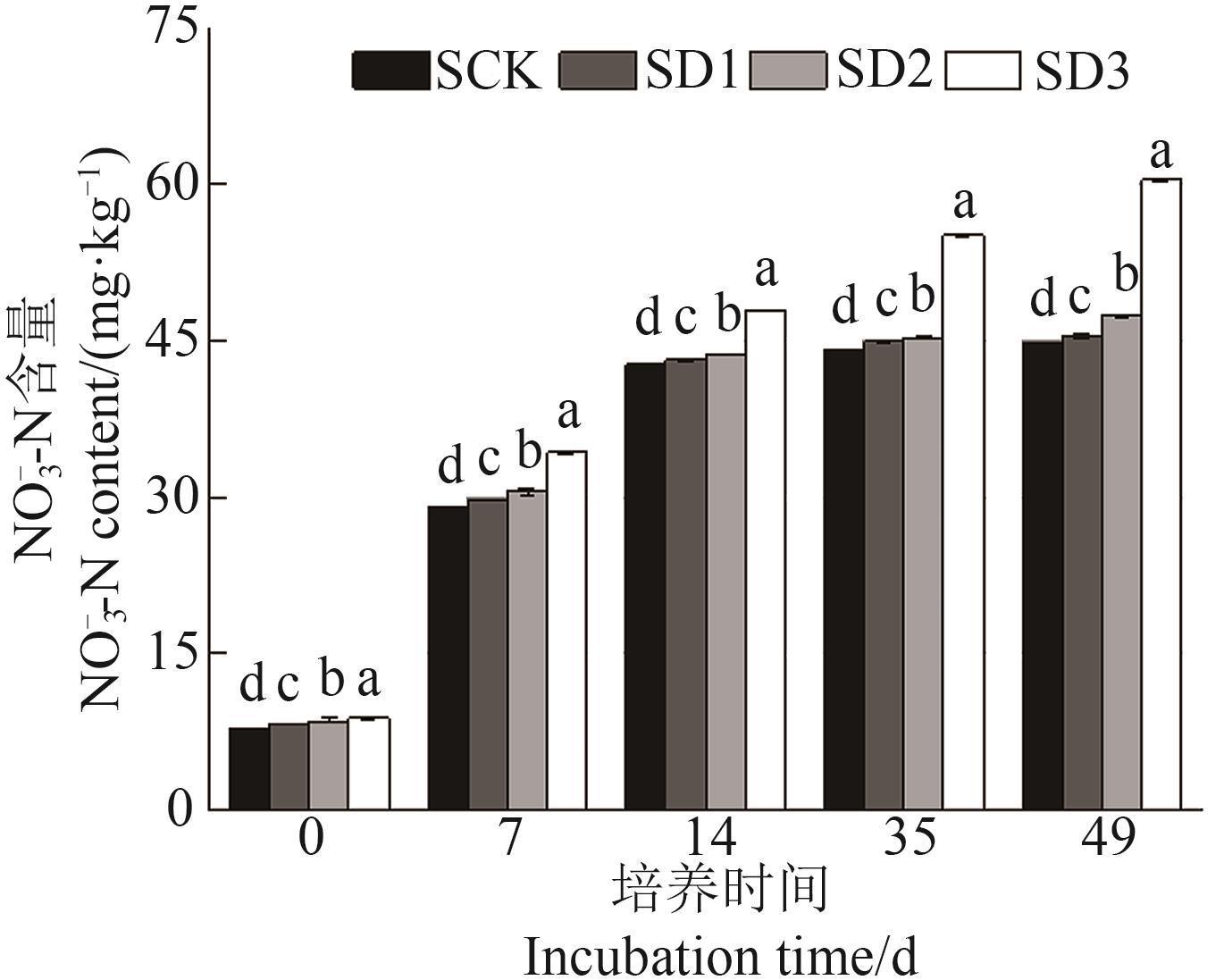
图1 矿化培养过程中不同处理的NO3--N含量注:不同小写字母表示相同培养时间不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 NO3--N content during mineralization culture in different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in same culture time at P <0.05 level.
| 指标 Index | 变异来源 Source of variation | 平方和 Sum of squares | 自由度 Degree of freedom | 均方 Mean square | F值 F value | 显著性 Significance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO | SCK | 组间Inter group | 2 769.67 | 4 | 692.42 | 42 636.59 | P<0.01 |
| 组内Intra group | 0.16 | 10 | 0.02 | ||||
| 总计Total | 2 769.84 | 14 | |||||
| SD1 | 组间Inter group | 2 703.34 | 4 | 675.84 | 24 469.07 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.28 | 10 | 0.03 | ||||
| 总计Total | 2 703.62 | 14 | |||||
| SD2 | 组间Inter group | 2 523.38 | 4 | 630.85 | 17 049.89 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.37 | 10 | 0.04 | ||||
| 总计Total | 2 523.75 | 14 | |||||
| SD3 | 组间Inter group | 2 422.83 | 4 | 605.71 | 24 358.25 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.25 | 10 | 0.03 | ||||
| 总计Total | 2 423.08 | 14 | |||||
| NH | SCK | 组间Inter group | 2 769.67 | 4 | 692.42 | 42 636.59 | P<0.01 |
| 组内Intra group | 0.16 | 10 | 0.02 | ||||
| 总计Total | 2 769.84 | 14 | |||||
| SD1 | 组间Inter group | 2 703.34 | 4 | 675.84 | 24 469.07 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.28 | 10 | 0.03 | ||||
| 总计Total | 2 703.62 | 14 | |||||
| SD2 | 组间Inter group | 2 523.38 | 4 | 630.85 | 17 049.89 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.37 | 10 | 0.04 | ||||
| 总计Total | 2 523.75 | 14 | |||||
| SD3 | 组间Inter group | 2 422.83 | 4 | 605.71 | 24 358.25 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.25 | 10 | 0.03 | ||||
| 总计Total | 2 423.08 | 14 | |||||
表1 矿化培养NO3--N和NH4+-N含量结果方差分析
Table 1 Analysis of variance of results of NO3--N and NH4+-N content in mineralized culture
| 指标 Index | 变异来源 Source of variation | 平方和 Sum of squares | 自由度 Degree of freedom | 均方 Mean square | F值 F value | 显著性 Significance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO | SCK | 组间Inter group | 2 769.67 | 4 | 692.42 | 42 636.59 | P<0.01 |
| 组内Intra group | 0.16 | 10 | 0.02 | ||||
| 总计Total | 2 769.84 | 14 | |||||
| SD1 | 组间Inter group | 2 703.34 | 4 | 675.84 | 24 469.07 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.28 | 10 | 0.03 | ||||
| 总计Total | 2 703.62 | 14 | |||||
| SD2 | 组间Inter group | 2 523.38 | 4 | 630.85 | 17 049.89 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.37 | 10 | 0.04 | ||||
| 总计Total | 2 523.75 | 14 | |||||
| SD3 | 组间Inter group | 2 422.83 | 4 | 605.71 | 24 358.25 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.25 | 10 | 0.03 | ||||
| 总计Total | 2 423.08 | 14 | |||||
| NH | SCK | 组间Inter group | 2 769.67 | 4 | 692.42 | 42 636.59 | P<0.01 |
| 组内Intra group | 0.16 | 10 | 0.02 | ||||
| 总计Total | 2 769.84 | 14 | |||||
| SD1 | 组间Inter group | 2 703.34 | 4 | 675.84 | 24 469.07 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.28 | 10 | 0.03 | ||||
| 总计Total | 2 703.62 | 14 | |||||
| SD2 | 组间Inter group | 2 523.38 | 4 | 630.85 | 17 049.89 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.37 | 10 | 0.04 | ||||
| 总计Total | 2 523.75 | 14 | |||||
| SD3 | 组间Inter group | 2 422.83 | 4 | 605.71 | 24 358.25 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.25 | 10 | 0.03 | ||||
| 总计Total | 2 423.08 | 14 | |||||

图2 矿化培养过程中不同处理的NH4+-N含量注:不同小写字母表示相同培养时间不同处理间在P <0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 NH4+-N content during mineralization cultur in different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in same culture time at P<0.05 level.
| 指标 Index | 变异来源 Source of variation | 平方和 Sum of squares | 自由度 Degree of freedom | 均方 Mean square | F值 F value | 显著性 Significance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO | SCK | 组间Inter group | 10 866.46 | 4 | 2 716.62 | 44 486.06 | P<0.01 |
| 组内Intra group | 0.61 | 10 | 0.06 | ||||
| 总计Total | 10 867.07 | 14 | |||||
| SD1 | 组间Inter group | 19 945.85 | 4 | 4 986.46 | 41 244.51 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 1.21 | 10 | 0.12 | ||||
| 总计Total | 19 947.06 | 14 | |||||
| SD2 | 组间Inter group | 25 952.30 | 4 | 6 488.08 | 110 755.81 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.59 | 10 | 0.06 | ||||
| 总计Total | 25 952.89 | 14 | |||||
| SD3 | 组间Inter group | 50 386.63 | 4 | 12 596.66 | 121 730.36 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 1.04 | 10 | 0.10 | ||||
| 总计Total | 50 387.67 | 14 | |||||
| NH | SCK | 组间Inter group | 7 321.01 | 4 | 1 830.25 | 58 238.83 | P<0.01 |
| 组内Intra group | 0.31 | 10 | 0.03 | ||||
| 总计Total | 7 321.32 | 14 | |||||
| SD1 | 组间Inter group | 6 846.92 | 4 | 1 711.73 | 43 548.10 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.39 | 10 | 0.04 | ||||
| 总计Total | 6 847.32 | 14 | |||||
| SD2 | 组间Inter group | 6 876.68 | 4 | 1 719.17 | 64 646.67 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.27 | 10 | 0.03 | ||||
| 总计Total | 6 876.95 | 14 | |||||
| SD3 | 组间Inter group | 7 439.66 | 4 | 1 859.92 | 87 814.67 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.21 | 10 | 0.02 | ||||
| 总计Total | 7 439.87 | 14 | |||||
表2 硝化培养NO3--N和NH4+-N含量试验结果方差分析
Table 2 Analysis of variance of test results of NO3--N and NH4+-N content in nitrification culture
| 指标 Index | 变异来源 Source of variation | 平方和 Sum of squares | 自由度 Degree of freedom | 均方 Mean square | F值 F value | 显著性 Significance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO | SCK | 组间Inter group | 10 866.46 | 4 | 2 716.62 | 44 486.06 | P<0.01 |
| 组内Intra group | 0.61 | 10 | 0.06 | ||||
| 总计Total | 10 867.07 | 14 | |||||
| SD1 | 组间Inter group | 19 945.85 | 4 | 4 986.46 | 41 244.51 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 1.21 | 10 | 0.12 | ||||
| 总计Total | 19 947.06 | 14 | |||||
| SD2 | 组间Inter group | 25 952.30 | 4 | 6 488.08 | 110 755.81 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.59 | 10 | 0.06 | ||||
| 总计Total | 25 952.89 | 14 | |||||
| SD3 | 组间Inter group | 50 386.63 | 4 | 12 596.66 | 121 730.36 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 1.04 | 10 | 0.10 | ||||
| 总计Total | 50 387.67 | 14 | |||||
| NH | SCK | 组间Inter group | 7 321.01 | 4 | 1 830.25 | 58 238.83 | P<0.01 |
| 组内Intra group | 0.31 | 10 | 0.03 | ||||
| 总计Total | 7 321.32 | 14 | |||||
| SD1 | 组间Inter group | 6 846.92 | 4 | 1 711.73 | 43 548.10 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.39 | 10 | 0.04 | ||||
| 总计Total | 6 847.32 | 14 | |||||
| SD2 | 组间Inter group | 6 876.68 | 4 | 1 719.17 | 64 646.67 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.27 | 10 | 0.03 | ||||
| 总计Total | 6 876.95 | 14 | |||||
| SD3 | 组间Inter group | 7 439.66 | 4 | 1 859.92 | 87 814.67 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.21 | 10 | 0.02 | ||||
| 总计Total | 7 439.87 | 14 | |||||

图3 硝化培养过程中不同处理NO3--N含量注:不同小写字母表示相同培养时间不同处理间在P <0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 3 NO3--N content during nitrification culture in different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in same culture time at P<0.05 level.
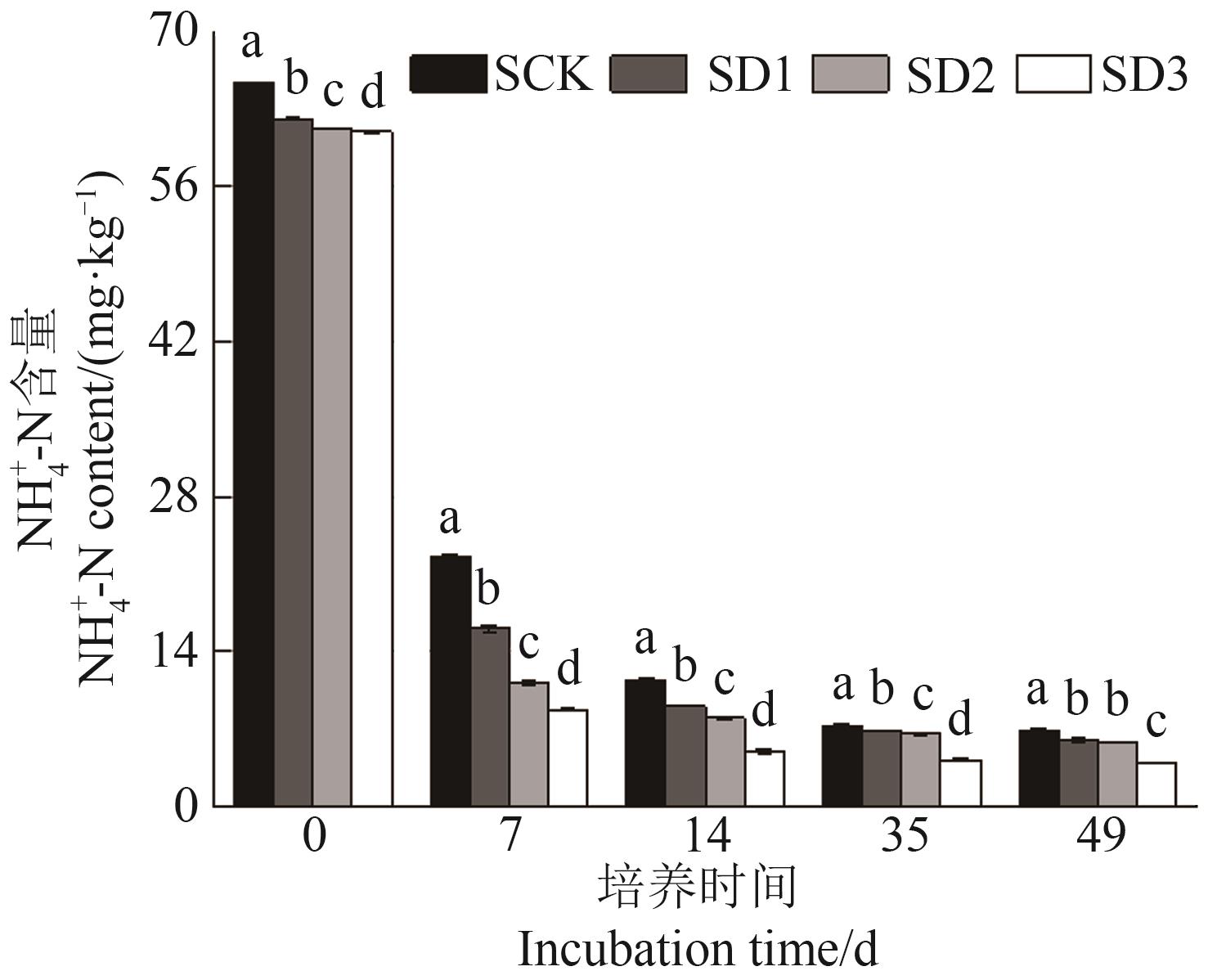
图4 硝化培养过程中不同处理NH4+-N含量注:不同小写字母表示相同培养时间不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 4 NH4+-N content during nitrification cultureNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in same culture time at P<0.05 level.in different treatments
指标 Index | 处理Treatment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCK | SD1 | SD2 | SD3 | |
矿化 NO Mineralization NO | 0.087 | 0.079 | 0.014* | 0.044* |
矿化 NH Mineralization NH | 0.077 | 0.059 | 0.040* | 0.021* |
硝化 NO Nitrification NO | 0.091 | 0.012* | 0.046* | 0.047* |
硝化 NH Nitrification NH | 0.089 | 0.071 | 0.055 | 0.073 |
表3 不同增氧量下沙土土壤的无机氮素含量的变化值 (mg·kg-1)
Table 3 Change value of inorganic nitrogen content in sandy soil under different oxygen content
指标 Index | 处理Treatment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCK | SD1 | SD2 | SD3 | |
矿化 NO Mineralization NO | 0.087 | 0.079 | 0.014* | 0.044* |
矿化 NH Mineralization NH | 0.077 | 0.059 | 0.040* | 0.021* |
硝化 NO Nitrification NO | 0.091 | 0.012* | 0.046* | 0.047* |
硝化 NH Nitrification NH | 0.089 | 0.071 | 0.055 | 0.073 |
处理 Treatment | R2 | 标准差 Standard deviation | 拟合方程 Fitting equation | 初始消耗速率 V0/(mg·kg-1·d-1) | 最大消耗速率 Vmax/(mg·kg-1·d-1) | 达到最大消耗速率 所用时间 TVmax/d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCK | 0.99 | 2.55 | Nt=65-56.43/[1+exp(21.92-3.29t)] | 0.00 | 46.41 | 6.66 |
| SD1 | 1.00 | 1.53 | Nt=65-57.75/[1+exp(2.94-0.66t)] | 1.82 | 9.58 | 4.43 |
| SD2 | 1.00 | 1.11 | Nt=65-58.22/[1+exp(2.67-0.74t)] | 2.62 | 10.75 | 3.61 |
| SD3 | 1.00 | 0.51 | Nt=65-60.63/[1+exp(2.64-0.74t)] | 2.79 | 11.26 | 3.56 |
表4 不同处理沙土NH4+-N转化模型拟合结果及其诊断值
Table 4 Fitting results and diagnostic values of NH4+-N transformation model of sandy soil under different treatments
处理 Treatment | R2 | 标准差 Standard deviation | 拟合方程 Fitting equation | 初始消耗速率 V0/(mg·kg-1·d-1) | 最大消耗速率 Vmax/(mg·kg-1·d-1) | 达到最大消耗速率 所用时间 TVmax/d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCK | 0.99 | 2.55 | Nt=65-56.43/[1+exp(21.92-3.29t)] | 0.00 | 46.41 | 6.66 |
| SD1 | 1.00 | 1.53 | Nt=65-57.75/[1+exp(2.94-0.66t)] | 1.82 | 9.58 | 4.43 |
| SD2 | 1.00 | 1.11 | Nt=65-58.22/[1+exp(2.67-0.74t)] | 2.62 | 10.75 | 3.61 |
| SD3 | 1.00 | 0.51 | Nt=65-60.63/[1+exp(2.64-0.74t)] | 2.79 | 11.26 | 3.56 |
| 指标Index | 变异来源 Source of variation | 平方和 Sum of squares | 自由度 Degree of freedom | 均方 Mean square | F值 F value | 显著性 Significance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
净氮矿化量 Net nitrogen mineralization | SCK | 组间Inter group | 1.77 | 3 | 0.59 | 18.35 | P<0.01 |
| 组内Intra group | 0.26 | 8 | 0.03 | ||||
| 总计Total | 2.03 | 11 | |||||
| SD1 | 组间Inter group | 4.75 | 3 | 1.58 | 36.20 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.35 | 8 | 0.04 | ||||
| 总计Total | 5.10 | 11 | |||||
| SD2 | 组间Inter group | 19.96 | 3 | 6.65 | 43.32 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 1.23 | 8 | 0.15 | ||||
| 总计Total | 21.18 | 11 | |||||
| SD3 | 组间Inter group | 390.13 | 3 | 130.04 | 1 411.47 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.74 | 8 | 0.09 | ||||
| 总计Total | 390.87 | 11 | |||||
净氮矿化速率 Net nitrogen mineralization rate | SCK | 组间Inter group | 0.02 | 3 | 0.01 | 32.30 | P<0.01 |
| 组内Intra group | 0.00 | 8 | 0.00 | ||||
| 总计Total | 0.02 | 11 | |||||
| SD1 | 组间Inter group | 0.02 | 3 | 0.01 | 72.10 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.00 | 8 | 0.00 | ||||
| 总计Total | 0.02 | 11 | |||||
| SD2 | 组间Inter group | 0.02 | 3 | 0.01 | 6.07 | P<0.05 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.01 | 8 | 0.00 | ||||
| 总计Total | 0.03 | 11 | |||||
| SD3 | 组间Inter group | 0.12 | 3 | 0.04 | 36.37 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.01 | 8 | 0.00 | ||||
| 总计Total | 0.13 | 11 | |||||
表5 土壤净氮矿化量结果方差分析
Table 5 Variance analysis of results of soil net nitrogen mineralization
| 指标Index | 变异来源 Source of variation | 平方和 Sum of squares | 自由度 Degree of freedom | 均方 Mean square | F值 F value | 显著性 Significance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
净氮矿化量 Net nitrogen mineralization | SCK | 组间Inter group | 1.77 | 3 | 0.59 | 18.35 | P<0.01 |
| 组内Intra group | 0.26 | 8 | 0.03 | ||||
| 总计Total | 2.03 | 11 | |||||
| SD1 | 组间Inter group | 4.75 | 3 | 1.58 | 36.20 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.35 | 8 | 0.04 | ||||
| 总计Total | 5.10 | 11 | |||||
| SD2 | 组间Inter group | 19.96 | 3 | 6.65 | 43.32 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 1.23 | 8 | 0.15 | ||||
| 总计Total | 21.18 | 11 | |||||
| SD3 | 组间Inter group | 390.13 | 3 | 130.04 | 1 411.47 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.74 | 8 | 0.09 | ||||
| 总计Total | 390.87 | 11 | |||||
净氮矿化速率 Net nitrogen mineralization rate | SCK | 组间Inter group | 0.02 | 3 | 0.01 | 32.30 | P<0.01 |
| 组内Intra group | 0.00 | 8 | 0.00 | ||||
| 总计Total | 0.02 | 11 | |||||
| SD1 | 组间Inter group | 0.02 | 3 | 0.01 | 72.10 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.00 | 8 | 0.00 | ||||
| 总计Total | 0.02 | 11 | |||||
| SD2 | 组间Inter group | 0.02 | 3 | 0.01 | 6.07 | P<0.05 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.01 | 8 | 0.00 | ||||
| 总计Total | 0.03 | 11 | |||||
| SD3 | 组间Inter group | 0.12 | 3 | 0.04 | 36.37 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.01 | 8 | 0.00 | ||||
| 总计Total | 0.13 | 11 | |||||

图5 矿化培养过程中不同处理土壤净氮矿化量注:不同小写字母表示相同培养时间不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 5 Soil net nitrogen mineralization during mineralization culture in different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in same culture time at P <0.05 level.
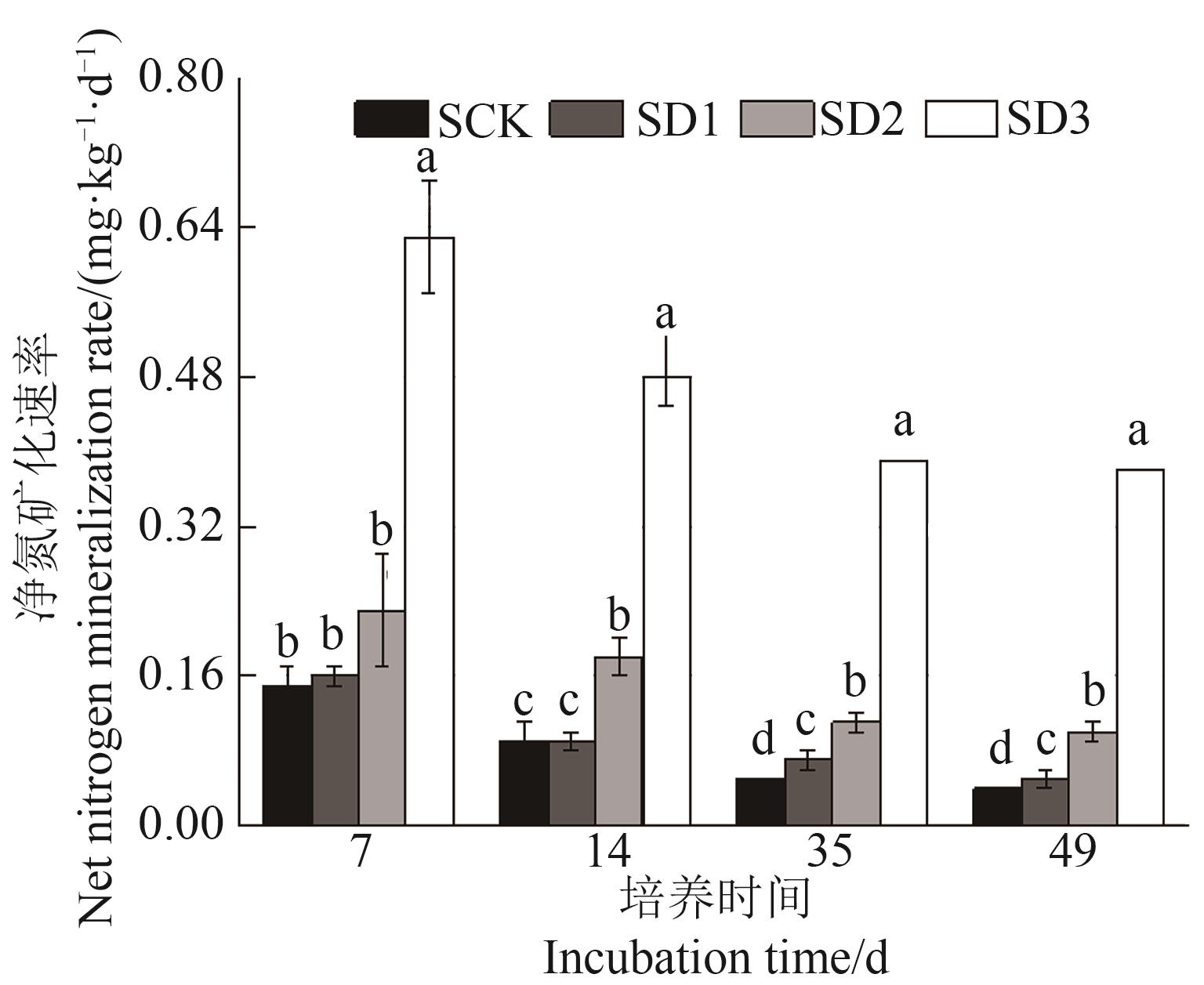
图6 矿化培养过程中不同处理土壤净氮矿化速率注:不同小写字母表示相同培养时间不同处理间在P <0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 6 Soil net nitrogen mineralization rate during mineralization culture in different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in same culture time at P<0.05 level.
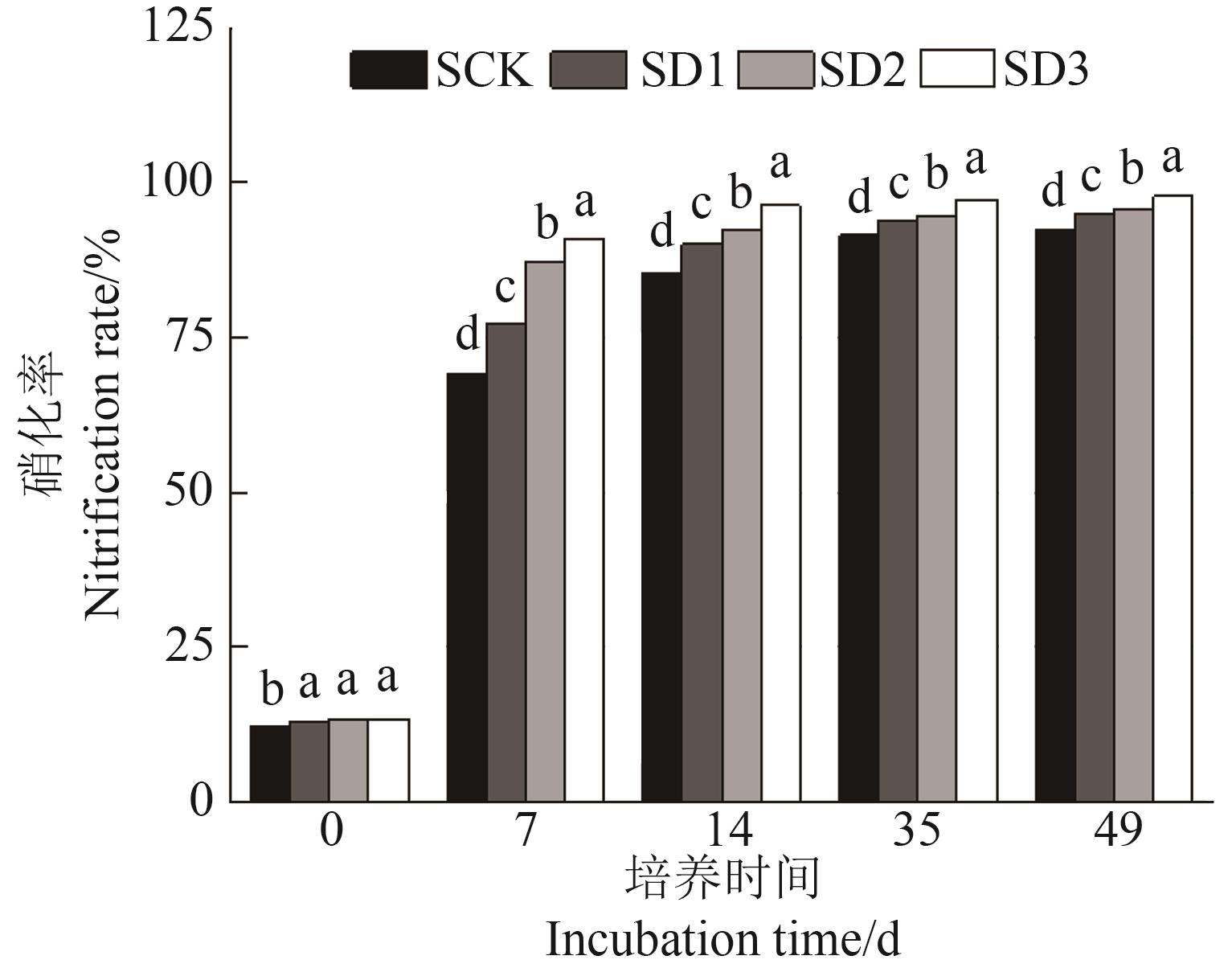
图7 硝化培养过程中不同处理土壤硝化率注:不同小写字母表示相同培养时间不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 7 Soil nitrification rate during nitrification culture in differen treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in same culture time at P<0.05 level.
指标 Index | 变异来源 Source of variation | 平方和 Sum of squares | 自由度 Degree of freedom | 均方 Mean square | F值 F value | 显著性 Significance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
硝化率 Nitrification rate | SCK | 组间Inter group | 1.36 | 4 | 0.34 | 136 204.15 | P<0.01 |
| 组内Intra group | 0.00 | 10 | 0.00 | ||||
| 总计Total | 1.36 | 14 | |||||
| SD1 | 组间Inter group | 1.44 | 4 | 0.36 | 123 817.34 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.00 | 10 | 0.00 | ||||
| 总计Total | 1.44 | 14 | |||||
| SD2 | 组间Inter group | 1.52 | 4 | 0.38 | 59 246.65 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.00 | 10 | 0.00 | ||||
| 总计Total | 1.52 | 14 | |||||
| SD3 | 组间Inter group | 1.63 | 4 | 0.41 | 198 119.38 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.00 | 10 | 0.00 | ||||
| 总计Total | 1.63 | 14 | |||||
净硝化速率 Net nitrification rate | SCK | 组间Inter group | 65.03 | 4 | 16.26 | 12 255.21 | P<0.01 |
| 组内Intra group | 0.01 | 10 | 0.00 | ||||
| 总计Total | 65.05 | 14 | |||||
| SD1 | 组间Inter group | 78.29 | 4 | 19.57 | 12 875.90 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.02 | 10 | 0.00 | ||||
| 总计Total | 78.30 | 14 | |||||
| SD2 | 组间Inter group | 159.40 | 4 | 39.85 | 46 336.19 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.01 | 10 | 0.00 | ||||
| 总计Total | 159.41 | 14 | |||||
| SD3 | 组间Inter group | 227.95 | 4 | 56.99 | 502 835.38 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.00 | 10 | 0.00 | ||||
| 总计Total | 227.95 | 14 | |||||
表6 土壤硝化率结果方差分析
Table 6 Variance analysis of soil nitrification rate results
指标 Index | 变异来源 Source of variation | 平方和 Sum of squares | 自由度 Degree of freedom | 均方 Mean square | F值 F value | 显著性 Significance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
硝化率 Nitrification rate | SCK | 组间Inter group | 1.36 | 4 | 0.34 | 136 204.15 | P<0.01 |
| 组内Intra group | 0.00 | 10 | 0.00 | ||||
| 总计Total | 1.36 | 14 | |||||
| SD1 | 组间Inter group | 1.44 | 4 | 0.36 | 123 817.34 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.00 | 10 | 0.00 | ||||
| 总计Total | 1.44 | 14 | |||||
| SD2 | 组间Inter group | 1.52 | 4 | 0.38 | 59 246.65 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.00 | 10 | 0.00 | ||||
| 总计Total | 1.52 | 14 | |||||
| SD3 | 组间Inter group | 1.63 | 4 | 0.41 | 198 119.38 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.00 | 10 | 0.00 | ||||
| 总计Total | 1.63 | 14 | |||||
净硝化速率 Net nitrification rate | SCK | 组间Inter group | 65.03 | 4 | 16.26 | 12 255.21 | P<0.01 |
| 组内Intra group | 0.01 | 10 | 0.00 | ||||
| 总计Total | 65.05 | 14 | |||||
| SD1 | 组间Inter group | 78.29 | 4 | 19.57 | 12 875.90 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.02 | 10 | 0.00 | ||||
| 总计Total | 78.30 | 14 | |||||
| SD2 | 组间Inter group | 159.40 | 4 | 39.85 | 46 336.19 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.01 | 10 | 0.00 | ||||
| 总计Total | 159.41 | 14 | |||||
| SD3 | 组间Inter group | 227.95 | 4 | 56.99 | 502 835.38 | P<0.01 | |
| 组内Intra group | 0.00 | 10 | 0.00 | ||||
| 总计Total | 227.95 | 14 | |||||
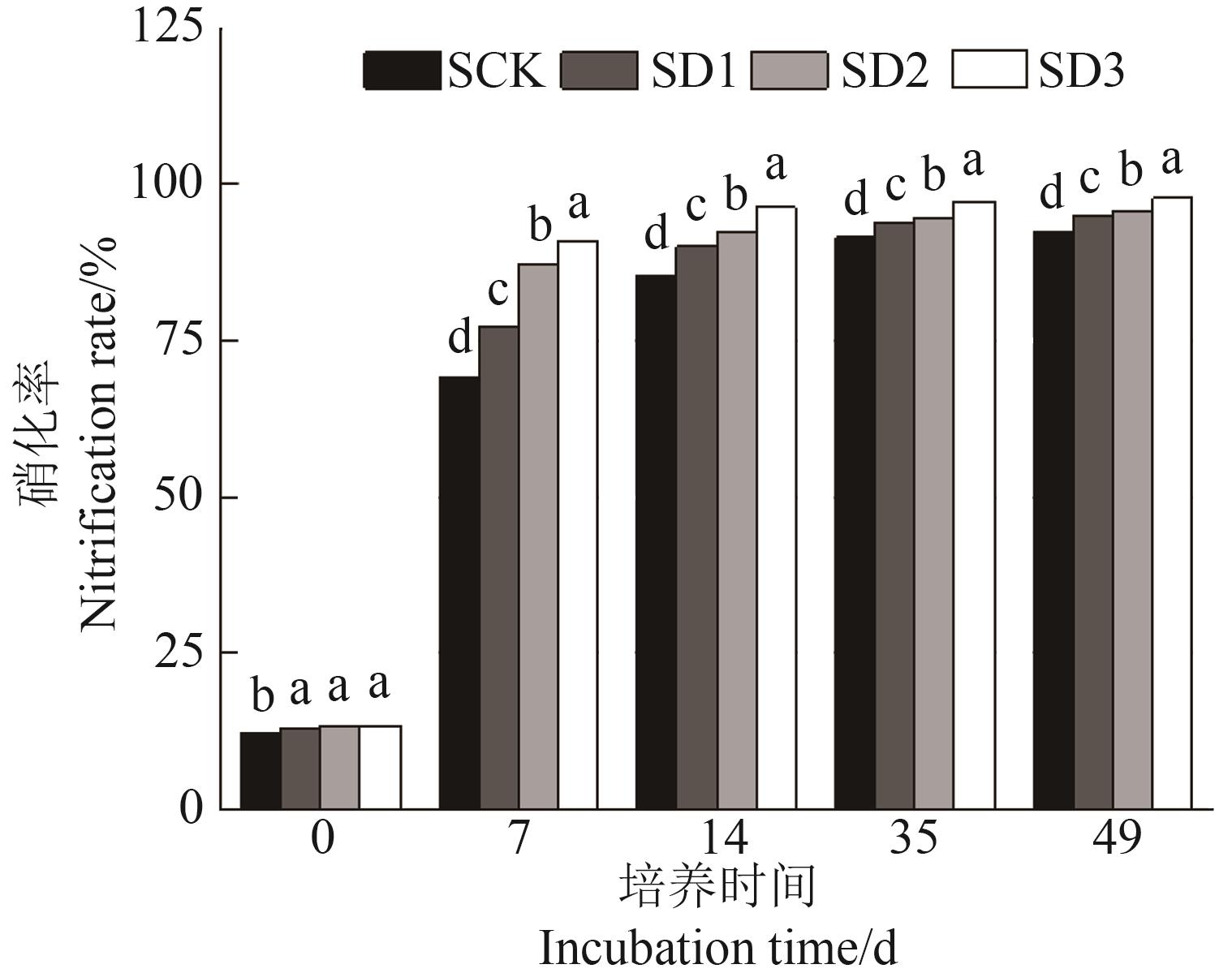
图8 硝化培养过程中不同处理土壤净硝化速率注:不同小写字母表示相同培养时间不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 8 Soil nitrification rate during nitrification culture in differen treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in same culture time at P<0.05 level.
| 1 | SOGBEDJI J M, VAN ES H M, YANG C L,et al.. Nitrate leaching and nitrogen budget as affected by maize nitrogen rate and soil type [J]. J. Environ. Quality, 2000, 29(6):1813-1820. |
| 2 | 房祥吉,姜远茂,彭福田,等.不同沙土配比对盆栽平邑甜茶的生长及15N吸收、利用和损失的影响[J].水土保持学报,2011,25(4):131-134. |
| FANG X J, JIANG Y M, PENG F T, et al..Effects of different sand/soil ratio on growth and 15N absorption,utilization and loss of potted Malus hupenhensis [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2011,25(4):131-134. | |
| 3 | 李薇. 溶解氧水平对富营养化水体底泥氮磷转化影响的研究[D].南京:南京理工大学,2014. |
| LI W. study on the impact of DO on the release of nitrogen and phosphorus from sediment in eutrophic water [D]. Nanjing:Nanjing University of Technology, 2014. | |
| 4 | SHEN Q R, RAN W, CAO Z H.Mechanisms of nitrite accumulation occurring in soil nitrification [J]. Chemosphere, 2003,50(6):747-753. |
| 5 | 范晓晖,朱兆良.旱地土壤中的硝化-反硝化作用[J].土壤通报,2002,33(5):385-391. |
| FAN X H, ZHU Z L. Nitrification and denitrification in upland soils [J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2002,33(5):385-391. | |
| 6 | 刘若萱,张丽梅,白刃,等.模拟条件下土壤硝化作用及硝化微生物对不同水分梯度的响应[J].土壤学报,2015,52(2):415-422. |
| LIU R X, ZHANG L M, BAI R, et al.. Response of nitrification and nitrifier to change in soil moisture content under simulated conditions [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2015,52(2):415-422. | |
| 7 | LEI H J, BHATTARAI S, BALSYS R, et al.. Temporal and spatial dimension of dissolved oxygen saturation with fluidic oscillator and Mazzei air injector in soil-less irrigation systems [J]. Irrig. Sci., 2016,34(6):421-430. |
| 8 | 臧明,雷宏军, SURYA B,等.不同增氧滴灌方式对蔬菜生长生理指标的影响[J].排灌机械工程学报,2020,38(3):310-317. |
| ZANG M, LEI H J, SURYA B, et al.. Effects of different oxygen-enriched drip irrigation methods on physiological indexes of vegetable growth [J]. J. Drain. Irrig. Mach. Eng., 2020,38 ( 3 ):310-317. | |
| 9 | BENJAMIN L R, GREENWAY H. Effects of a range of O2 concentrations on porosity of barley roots and on their sugar and protein concentrations [J]. Ann. Bot., 1979, 43(3):383-391. |
| 10 | THOMSON C, ARMSTRONG W, WATERS I, et al.. Aerenchyma formation and associated oxygen movement in seminal and nodal roots of wheat [J]. Plant Cell Environ., 1990,13:395-403. |
| 11 | 饶晓娟.增氧对新疆膜下滴灌棉田土壤肥力及棉花生长的影响[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆农业大学,2017. |
| RAO X J. Effects of oxygen addition on soil fertility and cotton growth in cotton field under mulched drip irrigation in Xinjiang [D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2017. | |
| 12 | 饶晓娟,付彦博,黄建,等.增氧灌溉对棉花营养特征及土壤肥力的影响[J].土壤学报,2018,55(4):797-803. |
| RAO X J, FU Y B, HUANG J,et al..Effects of oxygenated irrigation on nutritional characteristics of cotton and soil fertility [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2018,55(4):797-803. | |
| 13 | 吴越,马红亮,彭园珍.新鲜土壤样品储存温度和时间对不同形态氮素的影响[J].应用生态学报,2018,29(6):1999-2006. |
| WU Y, MA H L, PENG Y Z. Effects of storage temperature and time on the contents of different nitrogen forms in fresh soil samples [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2018,29(6):1999-2006. | |
| 14 | 辛亮,王文章,范锐锋.增氧微咸水灌溉对土壤氮素转化的影响[J].乡村科技,2022,13(13):143-145. |
| 15 | 陶宝先,张保华,董杰,等.设施耕作促进农田土壤有机碳矿化[J].农业环境科学学报,2017,36(12):2486-2492. |
| TAO B X, ZHANG B H, DONG J, et al.. Soil organic carbon mineralization promoted by facility tillage [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2017,36(12):2486-2492. | |
| 16 | 胡容.若尔盖高寒湿地退化过程中土壤有机氮矿化演变特征[D]. 成都:四川农业大学,2019. |
| HU R. Evolution characteristics of soil organic nitrogen mineralization during the degradation process of Ruoergai alpine wetland [D]. Chengdu: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2019. | |
| 17 | 焦如珍,董玉红,孙启武. 森林土壤氮的测定: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2015. |
| 18 | 朱兆良.中国土壤氮素研究[J].土壤学报,2008,45(5):778-783. |
| ZHU Z L.Research on soil nitrogen in China [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2008,45(5):778-783. | |
| 19 | 李平,郎漫,李煜姗,等.不同施肥处理对黑土硝化作用和矿化作用的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2015,34(7):1326-1332. |
| LI P, LANG M, LI Y S,et al..Effects of different fertilization on nitrification and mineralization in black soil [J]. J. Agro- Environ. Sci., 2015,34(7):1326-1332. | |
| 20 | 李光敏,陈伏生,徐志文,等.间伐和林下植被剔除对毛竹林土壤氮矿化速率及其温度敏感性的影响[J].生态学报,2019,39(11):4106-4115. |
| LI G M, CHEN F S, XU Z W,et al.. Effects of thinning and understory removal on soil nitrogen mineralization rate and temperature-sensitivity in a moso-bamboo plantation [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2019,39(11):4106-4115. | |
| 21 | SABEY B R, FREDERICK L R, BARTHOLOMEW W V. The formation of nitrate from ammonium nitrogen in soils:IV.use of the delay and maximum rate phases for making quantitative predictions [J]. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J., 1969,33(2):276-278. |
| 22 | 张树兰,杨学云,吕殿青,等.几种土壤剖面的硝化作用及其动力学特征[J].土壤学报,2000,37(3):372-379. |
| ZHANG S L, YANG X Y, LYU D Q, et al.. Nitrification and dynamics in profiles of differently managed soil types [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2000,37(3):372-379. | |
| 23 | 张树兰,杨学云,吕殿青,等.温度、水分及不同氮源对土壤硝化作用的影响[J].生态学报,2002,22(12):2147-2153. |
| ZHANG S L, YANG X Y, LYU D Q,et al.. Effect of soil moisture, temperature and different nitrogen fertilizers on nitrification [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2002,22(12):2147-2153. | |
| 24 | SCHIMEL J P, BILBROUGH C, WELKER J M. Increased snow depth affects microbial activity and nitrogen mineralization in two Arctic tundra communities [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2004,36(2):217-227. |
| 25 | 陈祥伟,陈立新,刘伟琦.不同森林类型土壤氮矿化的研究[J].东北林业大学学报,1999,27(1):5-9. |
| CHEN X W, CHEN L X, LIU W Q. Nitrogen mineralization in different forest soil [J]. J. Northeast. For. Univ., 1999,27(1):5-9. | |
| 26 | NAKANO Y. Response of tomato root systems to environmental stress under soilless culture [J]. Japan. Agric. Res. Q., 2007,41(1):7-15. |
| 27 | 赵进,张越,赵丽清,等.水肥一体化智能管理系统设计[J].中国农机化学报,2019,40(6):184-190. |
| ZHAO J, ZHANG Y, ZHAO L Q, et al.. Design of integral management system of water and fertilization [J]. J. Chin. Agric. Mech., 2019,40(6):184-190. | |
| 28 | 李晓爽. 掺沙及施用生物有机肥对盐碱地水盐运移和冬小麦生长发育影响的研究[D].北京:中国农业科学院,2020. |
| LI X S. Effects of sand mixing and bio organic fertilizer application on water and salt transport in saline alkali land and growth and development of winter wheat [D]. Beijing:Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2020. | |
| 29 | 雷宏军,刘欢,刘鑫,等.水肥气一体化灌溉对温室辣椒地土壤N2O排放的影响[J].农业机械学报,2019,50(3):262-270. |
| LEI H J, LIU H, LIU X,et al..Effects of oxyfertigation on soil N2O emission under greenhouse pepper cropping system [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach., 2019,50(3):262-270. | |
| 30 | 张立成,胡德勇,杨敬林,等.增氧条件下施用有机肥对水稻土壤微生物的影响[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2018,46(11):55-62. |
| ZHANG L C, HU D Y, YANG J L, et al.. Effects of organic fertilizer application on rice soil microorganisms under aerobic conditions [J]. J. Northwest A&F Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2018, 46(11):55-62. | |
| 31 | 胡继杰,朱练峰,胡志华,等.土壤增氧方式对其氮素转化和水稻氮素利用及产量的影响[J].农业工程学报,2017,33(1):167-174. |
| HU J J, ZHU L F, HU Z H,et al.. Effects of soil aeration methods on soil nitrogen transformation,rice nitrogen utilization and yield [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2017,33(1):167-174. | |
| 32 | 臧明,雷宏军,潘红卫,等.增氧地下滴灌改善土壤通气性促进番茄生长[J].农业工程学报,2018,34(23):109-118. |
| ZANG M, LEI H J, PAN H W, et al.. Aerated subsurface drip irrigation improving soil aeration and tomato growth [J]. Trans.Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2018,34(23):109-118. | |
| 33 | 胡志华,朱练峰,林育炯,等.根部增氧模式对水稻产量与氮素利用的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2016,22(6):1503-1512. |
| HU Z H, ZHU L F, LIN Y J, et al.. Effect of root aeration methods on rice yield and nitrogen utilization [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2016,22(6):1503-1512. | |
| 34 | 周晚来,易永健,屠乃美,等.根际增氧对水稻根系形态和生理影响的研究进展[J].中国生态农业学报,2018,26(3):367-376. |
| ZHOU W L, YI Y J, TU N M, et al.. Research progress on the effects of rhizosphere oxygenation on rice root morphology and physiology [J]. Chin. J. Ecol. Agric., 2018,26(3):367-376 | |
| 35 | 黄容.有机替代对菜园土壤温室气体排放和氮转化的影响[D].重庆:西南大学,2019. |
| HUANG R. Effects of organic substitution on greenhouse gas emissions and nitrogen transformation in vegetable soils [D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2019. | |
| 36 | 张金波,宋长春.土壤氮素转化研究进展[J].吉林农业科学,2004,29(1):38-43, 46. |
| ZHANG J B, SONG C C.A review of soil nitrogen transformation [J]. J. Agric. Sci., 2004,29(1):38-43, 46. | |
| 37 | ZHANG Q C, WANG G H, XIE W X, et al.. Soil organic N forms and N supply as affected by fertilization under intensive rice cropping system [J]. Pedosphere, 2006,16(3):345-353. |
| 38 | 张国桢.石灰性土壤硝化作用模型的研究[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2007. |
| ZHANG G Z. Study on nitrification model of calcareous soil [D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2007. | |
| 39 | 曲植,李铭江,王全九,等.培养条件下微纳米增氧水添加对新疆砂壤土硝化作用的影响[J].农业工程学报,2020,36(22):189-196. |
| QU Z, LI M J, WANG Q J,et al.. Effects of micro-nano oxygenated water addition on nitrification of Xinjiang sandy loam soil under controlled conditions [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2020,36(22):189-196. | |
| 40 | 张国桢,李世清.三种氨态氮肥在石灰性土壤中硝化作用的模拟研究[J].干旱地区农业研究,2007,25(6):177-182, 211. |
| ZHANG G Z, LI S Q.Three kinds of ammonium nitrogen fertilizer on nitrification and model analysis [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2007,25(6):177-182, 211. |
| [1] | 李明, 董帅, 庞永强, 燕洁华, 叶汪忠. 风沙土混拌刀具的改良设计与试验[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(4): 87-96. |
| [2] | 丛文成, 袁立敏, 蒙仲举, 杨宇. 玉米芯颗粒对风沙土毛管水运移和蒸发特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 198-207. |
| [3] | 高海燕, 袁立敏, 张胜男, 闫德仁. 水溶性固沙剂对沙地土壤蒸发的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(12): 138-144. |
| [4] | 刘威, 赵园园, 陈小龙, 史宏志. 土壤含水率对豫中植烟土壤微生物群落多样性及氮循环功能基因丰度的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 214-225. |
| [5] | 张盼盼, 李川, 张美微, 赵霞, 牛军, 乔江方. 氮肥减施下添加硝化抑制剂对夏玉米氮素累积转运和产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 181-189. |
| [6] | 何丽娟, 蒙仲举, 党晓宏, 吕涛. 种植甘草对风沙土机械组成与养分的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 169-176. |
| [7] | 李宝石, 刘文科, 王奇, 查凌雁, 张玉彬, 周成波, 邵明杰. 根区施用硝化抑制剂DMPP对不同栽培方式下黄瓜产量及根区温室气体排放的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(9): 184-192. |
| [8] | 刘志梅1,吴胜军1*,梁震2*,黄平1,王小晓1. 三峡库区消落带土壤氮矿化及影响因素研究进展 [J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(11): 81-91. |
| [9] | 白优爱[1] 巨晓棠[2] 等. 商品有机肥及蔬菜残体在菜地土壤中的氮素矿化研究[J]. , 2003, 5(2): 45-49. |
| [10] | 邹国元[1] 张福锁[2] 等. 秸秆还田对旱地土壤反硝化的影响[J]. , 2001, 3(6): 47-50. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号