




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (5): 34-45.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0761
白道宽( ), 郭宝健, 洪益, 张萌娜, 朱娟, 吕超, 王菲菲, 许如根(
), 郭宝健, 洪益, 张萌娜, 朱娟, 吕超, 王菲菲, 许如根( )
)
收稿日期:2022-09-09
接受日期:2022-12-15
出版日期:2023-05-20
发布日期:2023-07-13
通讯作者:
许如根
作者简介:白道宽 E-mail: b19711208b@163.com;
基金资助:
Daokuan BAI( ), Baojian GUO, Yi HONG, Mengna ZHANG, Juan ZHU, Chao LYU, Feifei WANG, Rugen XU(
), Baojian GUO, Yi HONG, Mengna ZHANG, Juan ZHU, Chao LYU, Feifei WANG, Rugen XU( )
)
Received:2022-09-09
Accepted:2022-12-15
Online:2023-05-20
Published:2023-07-13
Contact:
Rugen XU
摘要:
为探究温度对大麦黄化突变体表型及光合特性的影响,以二棱啤用大麦品种‘扬农啤5号’及其经甲磺酸乙酯(ethyl methanesulfonate,EMS)诱变筛选到的黄化突变体G039为材料,测定分析田间自然条件和室内不同温度条件下突变体和野生型的叶色、植株主要性状、光合特性、组织结构及光合相关基因的表达;同时利用突变体与野生型及‘扬农啤7号’的杂种F1和F2群体,对突变基因进行遗传分析。结果表明,在自然低温条件下,G039苗期叶色呈现黄色,叶绿素a与叶绿素b含量较‘扬农啤5号’极显著降低;随着气温回升,叶色逐渐转绿,G039灌浆期叶绿素a与‘扬农啤5号’无差异,叶绿素b存在显著差异。G039的株高、穗长、穗下节间长、分蘖数与每穗粒数极显著低于‘扬农啤5号’,粒长、粒宽与千粒重极显著高于‘扬农啤5号’。不同温度处理下,突变体G039叶色受生长温度影响显著,低温造成G039叶绿体数目减少,基粒片层疏松;在10~20 ℃之间,温度越低,黄化越严重,SPAD值与叶绿素含量越低,净光合速率、胞间CO2浓度及水分利用率与‘扬农啤5号’的差异越大,大麦光合作用的最适温度在20 ℃左右。G039表型受1对隐性核基因控制。qRT-PCR结果显示,在不同温度下叶绿素合成、叶绿体发育及光系统建成等相关基因的表达在野生型与突变体G039间均存在极显著差异。以上结果为解析G039叶色突变机理和分子调控机制奠定基础。
中图分类号:
白道宽, 郭宝健, 洪益, 张萌娜, 朱娟, 吕超, 王菲菲, 许如根. 一个大麦黄化突变体的突变机理及其遗传机制研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 34-45.
Daokuan BAI, Baojian GUO, Yi HONG, Mengna ZHANG, Juan ZHU, Chao LYU, Feifei WANG, Rugen XU. Research on Mutagenic Mechanism and Genetic Mechanism of a Yellowing Mutant in Barley[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(5): 34-45.
基因名称 Gene name | 基因ID Gene ID | 正向引物 Forward primer(5’-3’) | 反向引物 Reverse primer(5’-3’) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HvCAO | HORVU.MOREX.r3.3HG0324440 | TGGTGCCCATAGATTGTTTC | GCCCTCATTCACTGAACCAAG |
| COR | HORVU.MOREX.r3.2HG0191600 | TCTGCCTGCAAACCCCTCCTAG | TGTCCGTGGCATCCTGGACCTT |
| PORB | HORVU.MOREX.r3.1HG0047060 | AGGCGTACAAGGACAGCAAGG | GTAGAGCGACGCGAAGGTGA |
| PORA | HORVU.MOREX.r3.2HG0209470 | CCGTTCCAGAAGTTCGTCACC | CCTTGTTCCAGCTCCAGTACAC |
| YCF3 | HORVU.MOREX.r3.5HG0423760 | GGTCTTTATCCTCGTCGTAT | TGTTCAATTTCTCGTGGAGT |
| HvPTOX | HORVU.MOREX.r3.2HG0213170 | CTCTTAATCATGGAAGCGTTGG | TGGCGACAGTGACGAAGTAG |
| MSH1 | HORVU.MOREX.r3.2HG0180240 | CCGAAGAAGAGTTCAGCAAT | TTCCATGCGAGGACATCACG |
| HvCMF3 | HORVU.MOREX.r3.6HG0559110 | AATGCGAAATGCGAGGAGG | GGTCTTCGGTGCCTTTGTC |
| GAPDH | HORVU.MOREX.r3.7HG0703580 | GTGAGGCTGGTGCTGATTACG | TGGTGCAGCTAGCATTTGAGA |
| α-tublin | HORVU.MOREX.r3.1HG0082050 | AGTGTCCTGTCCACCCACTC | AGCATGAAGTGGATCCTTGG |
表1 叶绿素合成、光合作用相关基因的定量引物
Table 1 Primer of chlorophyll synthesis, photosynthesis related genes used fou quantitative real-time PCR
基因名称 Gene name | 基因ID Gene ID | 正向引物 Forward primer(5’-3’) | 反向引物 Reverse primer(5’-3’) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HvCAO | HORVU.MOREX.r3.3HG0324440 | TGGTGCCCATAGATTGTTTC | GCCCTCATTCACTGAACCAAG |
| COR | HORVU.MOREX.r3.2HG0191600 | TCTGCCTGCAAACCCCTCCTAG | TGTCCGTGGCATCCTGGACCTT |
| PORB | HORVU.MOREX.r3.1HG0047060 | AGGCGTACAAGGACAGCAAGG | GTAGAGCGACGCGAAGGTGA |
| PORA | HORVU.MOREX.r3.2HG0209470 | CCGTTCCAGAAGTTCGTCACC | CCTTGTTCCAGCTCCAGTACAC |
| YCF3 | HORVU.MOREX.r3.5HG0423760 | GGTCTTTATCCTCGTCGTAT | TGTTCAATTTCTCGTGGAGT |
| HvPTOX | HORVU.MOREX.r3.2HG0213170 | CTCTTAATCATGGAAGCGTTGG | TGGCGACAGTGACGAAGTAG |
| MSH1 | HORVU.MOREX.r3.2HG0180240 | CCGAAGAAGAGTTCAGCAAT | TTCCATGCGAGGACATCACG |
| HvCMF3 | HORVU.MOREX.r3.6HG0559110 | AATGCGAAATGCGAGGAGG | GGTCTTCGGTGCCTTTGTC |
| GAPDH | HORVU.MOREX.r3.7HG0703580 | GTGAGGCTGGTGCTGATTACG | TGGTGCAGCTAGCATTTGAGA |
| α-tublin | HORVU.MOREX.r3.1HG0082050 | AGTGTCCTGTCCACCCACTC | AGCATGAAGTGGATCCTTGG |
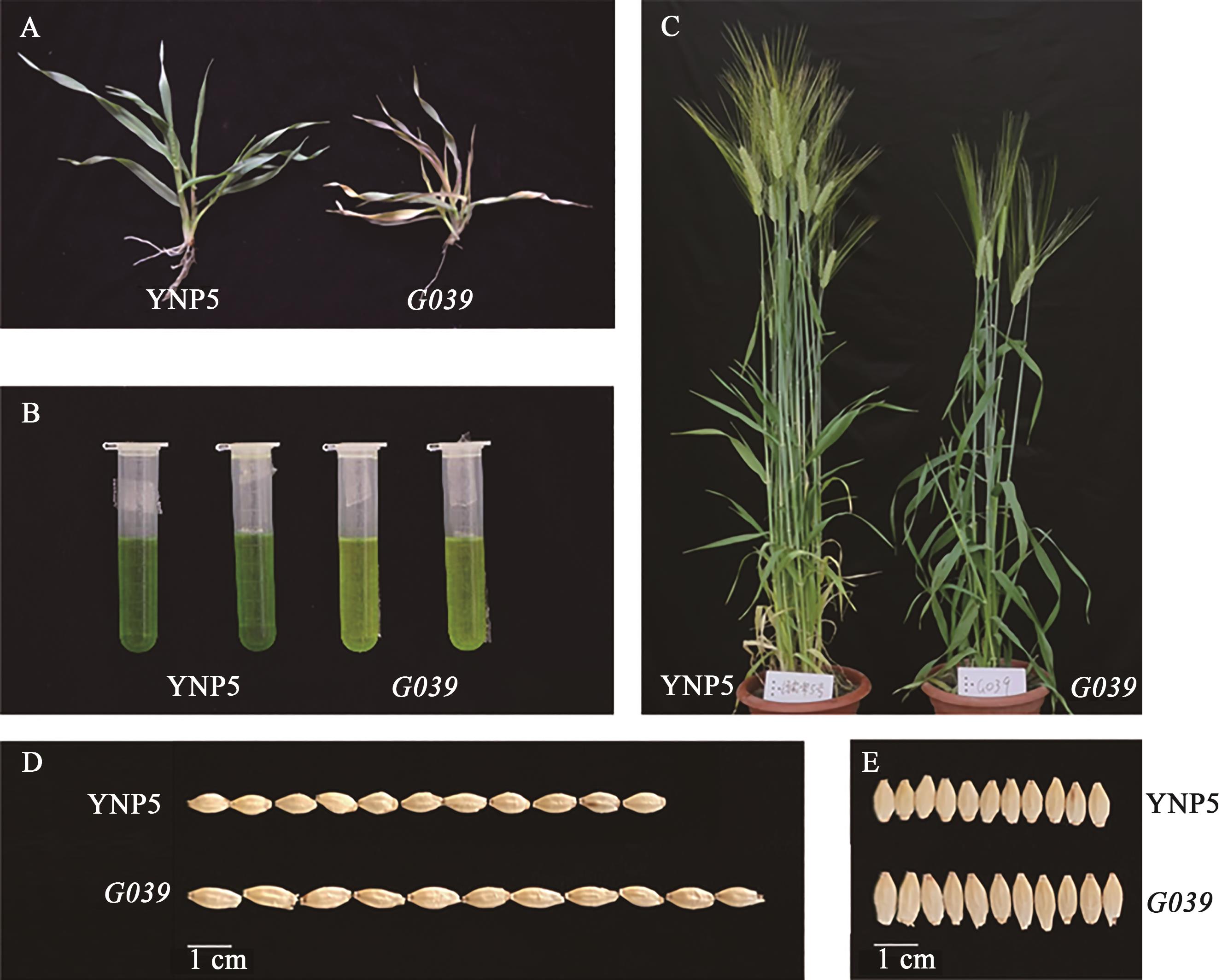

图1 自然条件下野生型‘扬农啤5号’和突变体G039的表型A:苗期植株;B:苗期叶绿素浸提液;C:灌浆期植株;D:粒长;E:粒宽
Fig. 1 Phenotypes of ‘YNP5’ and G039 under natural conditionA: Plant at seedling period; B: Extracts of photosynthetic pigments in the seedling period; C: Plant at filling period; D: Grain length; E: Grain width
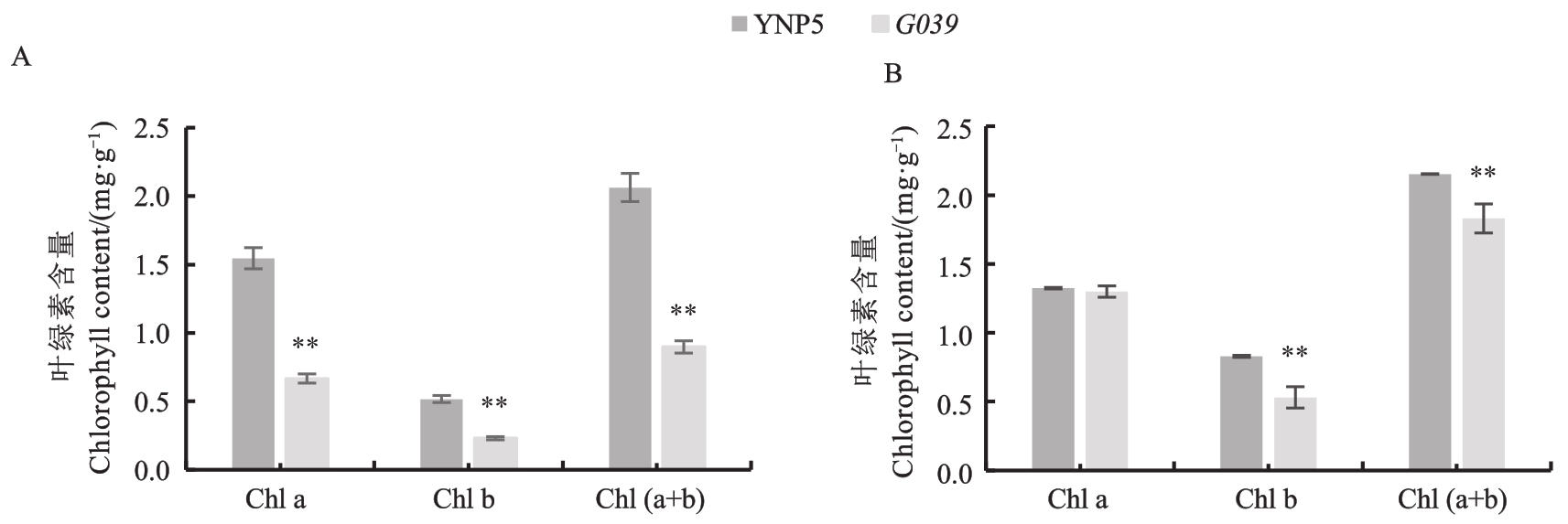
图2 野生型‘扬农啤5号’和突变体G039叶绿素含量A:苗期;B:灌浆期。**表示材料间在P<0.01水平差异显著
Fig. 2 Contents of chlorophyll pigments in ‘YNP5’ and G039A: Seedling stage; B: Grain filling stage. ** means significantly differences between materials at P<0.01 level
| 性状 Trait | 扬农啤5号 YNP5 | G039 |
|---|---|---|
株高 Plant height/cm | 86.46±5.94 | 72.86±5.42** |
穗下节间长 Internode length below the spike/cm | 30.88±3.36 | 22.38±2.40** |
分蘖数 Number of tillers | 17.82±8.36 | 8.85±3.40** |
穗长 Panicle length/cm | 6.71±0.48 | 5.95±0.66** |
每穗粒数 Grains per panicle | 28.35±2.42 | 25.86±2.23** |
千粒重 1 000-grain weight/g | 41.93±0.34 | 48.04±0.36** |
粒长 Grain length/mm | 6.86±0.03 | 7.62±0.03** |
粒宽 Grain width/mm | 3.05±0.02 | 3.15±0.02** |
表2 野生型‘扬农啤5号’与突变体G039的主要农艺性状
Table 2 Agronomic traits of the wild type ‘YNP5’ and mutant G039
| 性状 Trait | 扬农啤5号 YNP5 | G039 |
|---|---|---|
株高 Plant height/cm | 86.46±5.94 | 72.86±5.42** |
穗下节间长 Internode length below the spike/cm | 30.88±3.36 | 22.38±2.40** |
分蘖数 Number of tillers | 17.82±8.36 | 8.85±3.40** |
穗长 Panicle length/cm | 6.71±0.48 | 5.95±0.66** |
每穗粒数 Grains per panicle | 28.35±2.42 | 25.86±2.23** |
千粒重 1 000-grain weight/g | 41.93±0.34 | 48.04±0.36** |
粒长 Grain length/mm | 6.86±0.03 | 7.62±0.03** |
粒宽 Grain width/mm | 3.05±0.02 | 3.15±0.02** |
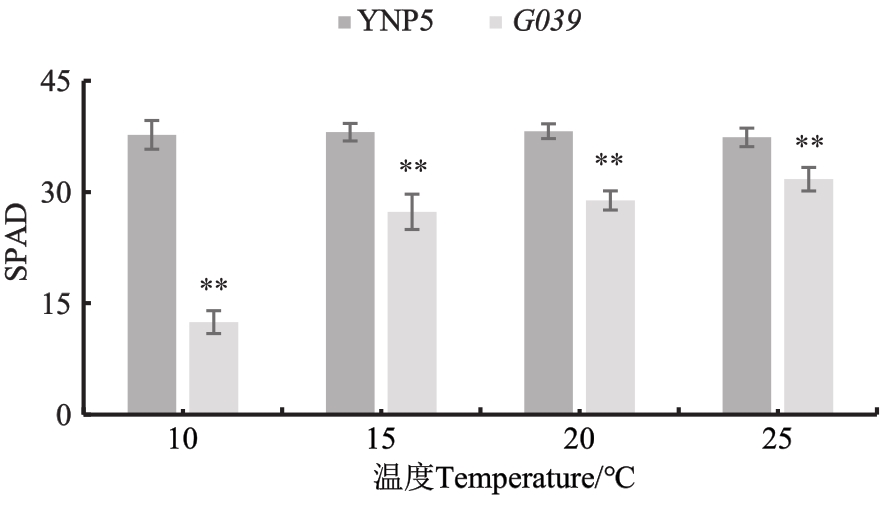
图3 不同温度下野生型‘扬农啤5号’与突变体G039的SPAD值注:**表示材料间在P<0.01水平差异显著。
Fig. 3 SPAD values of the ‘YNP5’ and G039 under different temperature conditionsNote:** means significantly difference between materials at P<0.01 level.
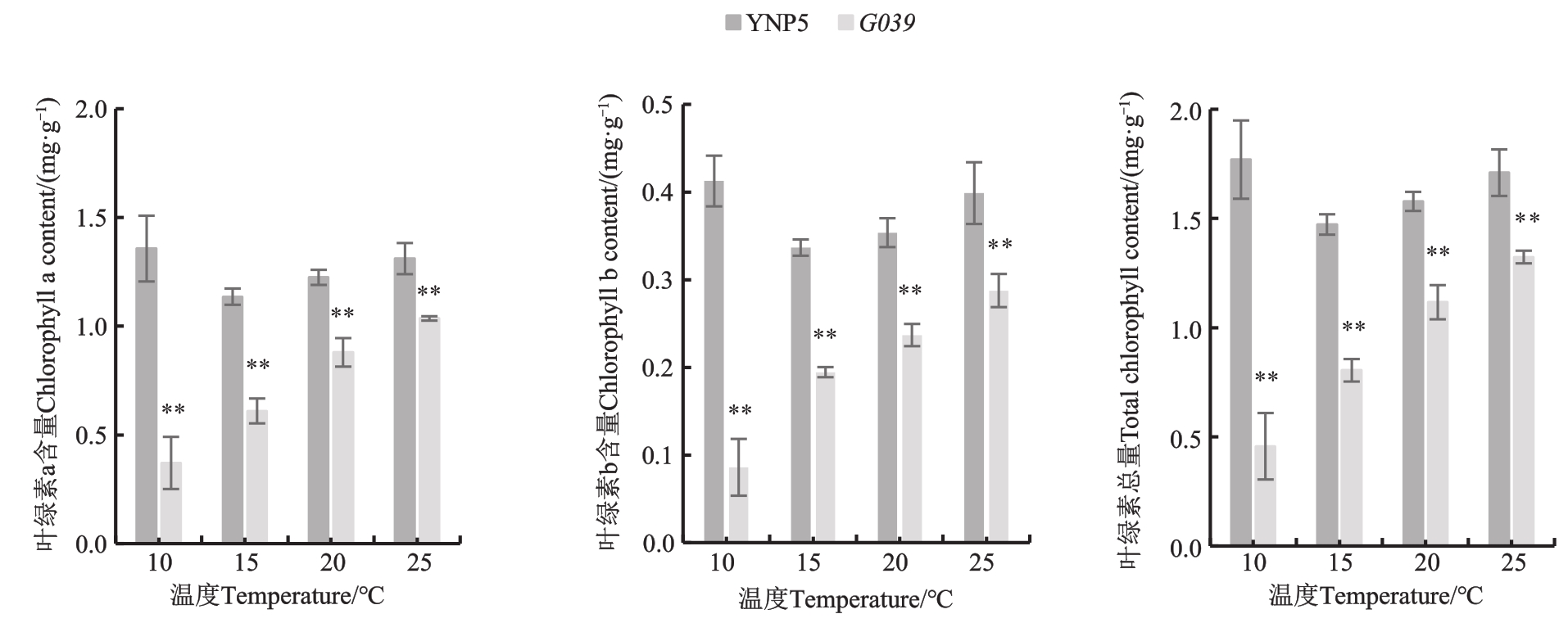
图5 不同温度下野生型‘扬农啤5号’与突变体G039的叶绿素含量注:**表示材料间在P<0.01水平差异显著
Fig. 5 Chlorophyll content of the ‘YNP5’ and G039 under different temperature conditionsNote: ** means significantly difference between materials at P<0.01 level

图6 不同温度下‘扬农啤5号’与G039的光合指标A~E:依次为净光合速率、蒸腾速率、气孔导度、水分利用率与胞间CO2浓度的大小。*和**分别表示材料间差异在P<0.05和P<0.01水平显著
Fig. 6 Photosynthetic indices of ‘YNP 5’ and G039 under different temperature conditionsA~E: Net photosynthetic rate, transpiration rate, stomatal conductance, water use efficiency and intercellular CO2 concentration are sequentially shown. * and ** mean significantly differences between materials at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels,respectively
杂交组合 Cross combination | 植株数量 Number of plants | χ2 | P值(0.05) P value(0.05) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
F2群体 F2 population | 野生表型 Wild type phenotype | 突变表型 Mutant phenotype | |||
| G039/扬农啤5号 | 388 | 297 | 91 | 0.49 | 3.84 |
| G039/扬农啤7号 | 332 | 252 | 80 | 0.14 | 3.84 |
表3 突变性状的遗传分析
Table 3 Genetic analysis of the mutant trait
杂交组合 Cross combination | 植株数量 Number of plants | χ2 | P值(0.05) P value(0.05) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
F2群体 F2 population | 野生表型 Wild type phenotype | 突变表型 Mutant phenotype | |||
| G039/扬农啤5号 | 388 | 297 | 91 | 0.49 | 3.84 |
| G039/扬农啤7号 | 332 | 252 | 80 | 0.14 | 3.84 |

图8 不同温度下叶绿素合成相关基因的相对表达量注:**表示在P<0.01水平显著。
Fig. 8 Expression levels in genes involved in chlorophyll synthesis of YNP 5 and G039 under different temperature conditionsNote: ** means significant at P<0.01 level.
| 1 | 李强强,赵玥,李璠,等.作物源库关系及其生理调控途径的研究进展[J].江苏农业科学,2020,48(9):50-56. |
| LI Q Q, ZHAO Y, LI F, et al.. Research progress of source-sink relationship and its underlying regulation mechanisms [J]. Jiangsu Agric. Sci., 2020, 48(9): 50-56. | |
| 2 | GAO F, ZHANG H J, ZHANG W J, et al.. Engineering of the cytosolic form of phosphoglucose isomerase into chloroplasts improves plant photosynthesis and biomass [J]. New Phytol., 2021, 231(1) : 315-325. |
| 3 | 李佳佳,于旭东,蔡泽坪,等.高等植物叶绿素生物合成研究进展[J].分子植物育种,2019,17(18):6013-6019. |
| LI J J, YU X D, CAI Z P, et al.. An overview of chlorophyll biosynthesis in higher plants [J]. Mol. Plant Breed., 2019, 17(18): 6013-6019. | |
| 4 | 李素贞,杨文竹,陈茹梅.水稻黄绿叶突变体研究进展[J].生物技术通报,2018,34(11):15-21. |
| LI S Z, YANG W Z, CHEN R M. An overview on yellow green leaf mutants in rice [J]. Biotechnol. Bull., 2018, 34(11): 15-21. | |
| 5 | 李军,朱梦珂,田激旋,等.水稻高温白化复绿突变体tcd52的遗传分析和分子定位[J].上海师范大学学报(自然科学版),2022,51(2):243-250. |
| LI J, ZHU M K, TIAN J X, et al.. Genetic analysis and molecular mapping of high-temperature albino regreen mutant tcd52 in rice [J]. J. Shanghai Normal Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2022, 51(2): 243-250. | |
| 6 | 莫祎,孙志忠,丁佳,等.水稻白条纹叶突变体wsl1的遗传分析及基因精细定位[J].作物学报,2019,45(7):1050-1058. |
| MO Y, SUN Z Z, DING J, et al.. Genetic analysis and fine mapping of white stripe leaf mutant wsl1 in rice [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2019, 45(7): 1050-1058. | |
| 7 | 鄢小青,陈能刚,李欢,等.水稻白条纹转绿突变体wsl887的鉴定和基因定位[J].核农学报, 2021, 35(11) : 2451-2462. |
| YAN X Q, CHEN N G, LI H, et al.. Phenotypic identification and gene mapping of green revertible white-stripes mutant wsl887 in rice (Oryza sativa L.) [J]. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci., 2021, 35(11): 2451-2462. | |
| 8 | 郭均瑶,刘斌美,杨惠杰,等.水稻叶脉黄化突变体yml的遗传分析及基因定位[J].作物学报, 2022, 48(12): 3120-3129. |
| GUO J Y, LIU B M, YANG H J, et al.. Genetic analysis and gene mapping of the yellow midrib leaf mutant (yml) in rice(Oryza sativa L.) [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2022, 48(12): 3120-3129. | |
| 9 | 李秦,杜何为.玉米叶色突变体研究进展[J].南方农业,2019,13(28):14-21, 7. |
| LI Q, DU H W. Advances in research on maize leaf color mutants [J]. South Chin. Agric., 2019, 13(28): 14-21, 7. | |
| 10 | REINBOTHE S, REINBOTHE C, HOLTORF H, et al.. Two NADPH: protochlorophyllide oxidoreductases in barley: evidence for the selective disappearance of PORA during the light-induced greening of etiolated seedlings [J]. Plant Cell, 1995,7(11):1933-1940. |
| 11 | BUHR F, LAHROUSSI A, SPRINGER A, et al.. NADPH: protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase B (PORB) action in Arabidopsis thaliana revisited through transgenic expression of engineered barley PORB mutant proteins [J]. Plant Mol. Biol., 2017, 94(1-2):45-59. |
| 12 | XU D D, SUN D, DIAO Y L, et al.. Fast mapping of a chlorophyll b synthesis-deficiency gene in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) via bulked-segregant analysis with reduced-representation sequencing [J]. Crop J., 2019, 7(1): 58-64. |
| 13 | MAHDI R, STUART D, HANSSON M, et al.. Heterologous expression of the barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Xantha-f, -g and -h genes that encode magnesium chelatase subunits [J]. Protein J., 2020, 39(5):554-562. |
| 14 | LI M J, HENSEL G, MASCHER M, et al.. Leaf variegation and impaired chloroplast development caused by a truncated CCT domain gene in albostrians barley [J]. Plant Cell, 2019, 31(7) : 1430-1445. |
| 15 | LI M J, HENSEL G, MELZER M, et al.. Mutation of the ALBOSTRIANS ohnologous gene HvCMF3 impairs chloroplast development and thylakoid architecture in barley [J]. Front. Plant Sci., 2021, 12: 732608-732630. |
| 16 | LI M J, GUO G G, PIDON H, et al.. ATP-dependent Clp protease subunit C1, HvClpC1, is a strong candidate gene for barley variegation mutant luteostrians as revealed by genetic mapping and genomic re-sequencing [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2021,12:664085 [2022-11-16]. . |
| 17 | LANDAU A M, LOKSTEIN H, SCHELLER H V, et al.. A cytoplasmically inherited barley mutant is defective in photosystem Ⅰ assembly due to a temperature-sensitive defect in ycf3 splicing [J]. Plant Physiol., 2009, 151(4): 1802-1811. |
| 18 | LENCINA F, LANDAU A, PRINA A R. The barley chloroplast mutator (cpm) mutant: all roads lead to the Msh1 gene [J]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2022, 23(3):1814-1828. |
| 19 | BOSCO C D, BUSCONI M, GOVONI C, et al.. cor gene expression in barley mutants affected in chloroplast development and photosynthetic electron transport [J]. Plant Physiol., 2003,131(2):793-802. |
| 20 | QIN D D, DONG J, XU F C, et al.. Characterization and fine mapping of a novel barley stage green-revertible albino gene (HvSGRA) by bulked segregant analysis based on SSR assay and specific length amplified fragment sequencing [J]. BMC Genomics, 2015, 16: 838-851. |
| 21 | ROTASPERTI L, SANSONI F, MIZZOTTI C, et al.. Barley’s second spring as a model organism for chloroplast research [J]. Plants (Basel), 2020, 9(7): 803-826. |
| 22 | WANG R, YANG F, ZHANG X Q, et al.. Characterization of a thermo-inducible chlorophyll-deficient mutant in barley [J]. Front. Plant Sci., 2017, 8: 1936-1944. |
| 23 | 闫伟平,赵洪祥,张丽华,等.半干旱区温度变化对不同密度玉米植株光合作用的影响[J].吉林农业科学,2015,40(5):14-20. |
| YAN W P, ZHAO H X, ZHANG L H, et al.. Effect of temperature changes rates of maize under different density in semiarid area [J]. Jilin Agric. Sci., 2015, 40(5): 14-20. | |
| 24 | 江华,师生波,许大全.冬季小麦叶片光合作用对温度响应方式的变化[J].植物生理学报,2000,26(1):70-75. |
| JIANG H, SHI S B, XU D Q. Change in the pattern of photosynthetic response to temperature in wheat leaves in winter [J]. Plant Physiol. J., 2000, 26(1): 70-75. | |
| 25 | 杨淑巧,许琦,刘跃鹏,等.冬小麦光合作用和叶绿素荧光特性的研究[J].农学学报,2015,5(3):5-10. |
| YANG S Q, XU Q, LIU Y P, et al.. Research on the photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorspar characteristic of winter wheat [J]. J. Agric., 2015, 5(3): 5-10. | |
| 26 | 闫蓉,李凤霞,赵维忠,等.气象条件对水稻蒸腾速率的影响[J].宁夏农林科技,2005(2):7-8, 10. |
| YAN R, LI F X, ZHAO W Z, et al.. Effect of meteorological conditions on transpiration rate of rice (Oryza sativa L.) [J]. Ningxia J. Agric. For., 2005 (2): 7-8, 10. | |
| 27 | 董树亭,胡昌浩,周关印.玉米叶片气孔导度、蒸腾和光合特性研究[J].玉米科学,1993,1(2):41-44. |
| DONG S T, HU C H, ZHOU G Y. Stomatal conductance, transpiration and photosynthetic characteristics of maize leaves [J]. J. Maize Sci., 1993, 1(2): 41-44. | |
| 28 | 刘亮,郝立华,李菲,等. CO2浓度和温度对玉米光合性能及水分利用效率的影响[J].农业工程学报,2020,36(5):122-129. |
| LIU L, HAO L H, LI F, et al.. Effects of CO2 concentration and temperature on leaf photosynthesis and water use efficiency in maize [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2020, 36(5): 122-129. | |
| 29 | KUSUMI K, HIROTSUKA S, SHIMADA H, et al.. Contribution of chloroplast biogenesis to carbon-nitrogen balance during early leaf development in rice [J]. Plant Res., 2010, 123 (4): 617-622. |
| 30 | SUGIMOTO H, KUSUMI K, NOGUCHI K, et al.. The rice nuclear gene, VIRESCENT 2, is essential for chloroplast development and encodes a novel type of guanylate kinase targeted to plastids and mitochondria [J]. Plant J., 2007, 52 (3): 512-527. |
| 31 | HUANG W F, ZHANG Y, SHEN L Q, et al.. Accumulation of the RNA polymerase subunit RpoB depends on RNA editing by OsPPR16 and affects chloroplast development during early leaf development in rice [J]. New Phytol., 2020, 228(4): 1401-1416. |
| 32 | HEIN P, STÖCKEL J, BENNEWITZ S, et al.. A protein related to prokaryotic UMP kinases is involved in psaA/B transcript accumulation in Arabidopsis [J]. Plant Mol. Biol., 2009, 69 (5) : 517-528. |
| 33 | YANG S M, OVERLANDER M, FIEDLER J. Genetic analysis of the barley variegation mutant, grandpa1.a [J]. BMC Plant Biol., 2021, 21(1) : 134-144. |
| [1] | 周宇, 李佳玉, 王乐, 贾晓爽, 高思琦, 王潇, 焦健. 金黄色葡萄球菌小菌落突变体诱导筛选及特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 147-157. |
| [2] | 陈琛, 石柯, 朱长伟, 姜桂英, 罗澜, 孟威威, 刘芳, 申凤敏, 刘世亮. 种植密度和施氮量对豫北潮土区小麦光合特性和产量及土壤氮素的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 24-33. |
| [3] | 陈军, 李静雯, 王立光, 朱天地, 陈琛, 包奇军, 欧巧明. 低醇溶蛋白转基因大麦氮素转移特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 47-56. |
| [4] | 高日平, 刘小月, 潘遵天, 张东旭, 沈祥军, 栗艳芳, 黄洁, 景宇鹏. 生物菌剂对玉米秸秆堆沤过程水热状况及酶活性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 174-181. |
| [5] | 张傲, 白皓, 毕瑜林, 黄应权, 王志秀, 江勇, 陈国宏, 常国斌. 鸡体核温度影响因素研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(1): 26-34. |
| [6] | 褚志云, 祁惠, 李颖, 万一兵, 任志雨, 刘春, 袁素霞. 八仙花‘Bailmer’花萼和叶片内铝离子的动态变化[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(1): 65-71. |
| [7] | 高桐梅, 李丰, 苏小雨, 王东勇, 田媛, 张鹏钰, 李同科, 杨自豪, 卫双玲. 减施氮肥对芝麻农艺性状、光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(6): 176-188. |
| [8] | 王鑫, 张玉霞, 陈卫东, 林聪颖, 候文慧, 斯日古楞, 丛百明. 追施氮肥对不同饲用燕麦品种产量及光合荧光特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 170-179. |
| [9] | 王方玲, 张明月, 周亚茹, 管庆林, 李欣燕, 钟秋, 赵铭钦. 干旱胁迫下TS-PAA保水剂对雪茄烟生长发育和光合特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(4): 162-172. |
| [10] | 钟鹏, 苗丽丽, 刘杰, 王建丽, 陆海燕, 于洪久, 张楠. 种植密度和方式对油莎豆群体结构和产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(3): 186-196. |
| [11] | 包奇军, 潘永东, 张华瑜, 柳小宁, 张东佳, 赵锋, 牛小霞, 陈军. 甘肃与欧洲、北美啤酒大麦品种农艺及品质性状比较分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(3): 57-66. |
| [12] | 李宝石, 刘文科, 王奇, 邵明杰. 起垄内嵌基质栽培对日光温室夏季黄瓜根区温度、生长和产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 177-183. |
| [13] | 周元成, 曹永立, 王镇, 贾志荣, 姚勇, 陈爱萍. 不同大麦品种抗旱性鉴定指标的筛选与评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 86-92. |
| [14] | 孙逸凡, 黄志磊, 李葆春, 姚立蓉, 汪军成, 司二静, 杨轲, 孟亚雄, 马小乐, 王化俊. 大麦种质资源抗叶斑病评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(11): 43-54. |
| [15] | 甘子鹏, 徐海燕, 薛守业, 梁冰妍, 种碧莹, 李莉莎, 张博, 李小明, 刘桂民, 吴晓东. 青藏高原不同气候区青稞品质差异[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(11): 55-67. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号