




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (9): 186-196.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0111
高静1,2( ), 徐明岗1,2, 李然3, 蔡泽江3, 孙楠3(
), 徐明岗1,2, 李然3, 蔡泽江3, 孙楠3( ), 张强4(
), 张强4( ), 郑磊4
), 郑磊4
收稿日期:2022-02-17
接受日期:2022-08-18
出版日期:2023-09-15
发布日期:2023-09-28
通讯作者:
孙楠,张强
作者简介:高静E-mail:1131320695@qq.com
基金资助:
Jing GAO1,2( ), Minggang XU1,2, Ran LI3, Zejiang CAI3, Nan SUN3(
), Minggang XU1,2, Ran LI3, Zejiang CAI3, Nan SUN3( ), Qiang ZHANG4(
), Qiang ZHANG4( ), Lei ZHENG4
), Lei ZHENG4
Received:2022-02-17
Accepted:2022-08-18
Online:2023-09-15
Published:2023-09-28
Contact:
Nan SUN,Qiang ZHANG
摘要:
为量化生物炭施用对土壤pH的影响,为生物炭在改良土壤、培肥地力中提供理论依据,采用数据整合分析(Meta-analysis)的方法,基于中国知网、万方数据和Web of Science数据库,用关键词“生物炭”“Biochar”“土壤pH”和“土壤酸碱度”进行检索,收集到国内外关于生物炭对土壤酸碱度影响研究已公开发表的59篇文献中413组试验数据,分析土壤条件、生物炭特性、生物炭施用量等对土壤pH的定量影响。结果表明,与不施生物炭相比,生物炭施用能显著提高土壤pH,平均增幅为8.70%。其中,以强酸性(4.5<pH≤5.5)和极强酸性土壤(pH≤4.5)增幅最大,分别为15.17%和9.68%;不同原料生物炭对土壤pH的提升效果表现为秸秆类生物炭(10.04%)>壳渣类生物炭(7.02%)>木材类生物炭(6.61%)。不同热解温度下,以≤400 ℃制得的生物炭提升效果最佳,为15.26%;而在热解温度400~700 ℃时,随着热解温度升高,提升效果降低。施用生物炭3个月内土壤pH的增幅最大,之后增幅逐渐减缓。以上结果表明在强酸性(4.5<pH≤5.5)土壤中,优先选用秸秆低温(≤400 ℃)热解生物炭施用能更好地改善土壤pH,结果为生物炭的推广应用提供科学依据。
中图分类号:
高静, 徐明岗, 李然, 蔡泽江, 孙楠, 张强, 郑磊. 整合分析生物炭施用对土壤pH的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 186-196.
Jing GAO, Minggang XU, Ran LI, Zejiang CAI, Nan SUN, Qiang ZHANG, Lei ZHENG. Effects of Biochar Application on Soil pH: A Meta-Analysis[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 186-196.
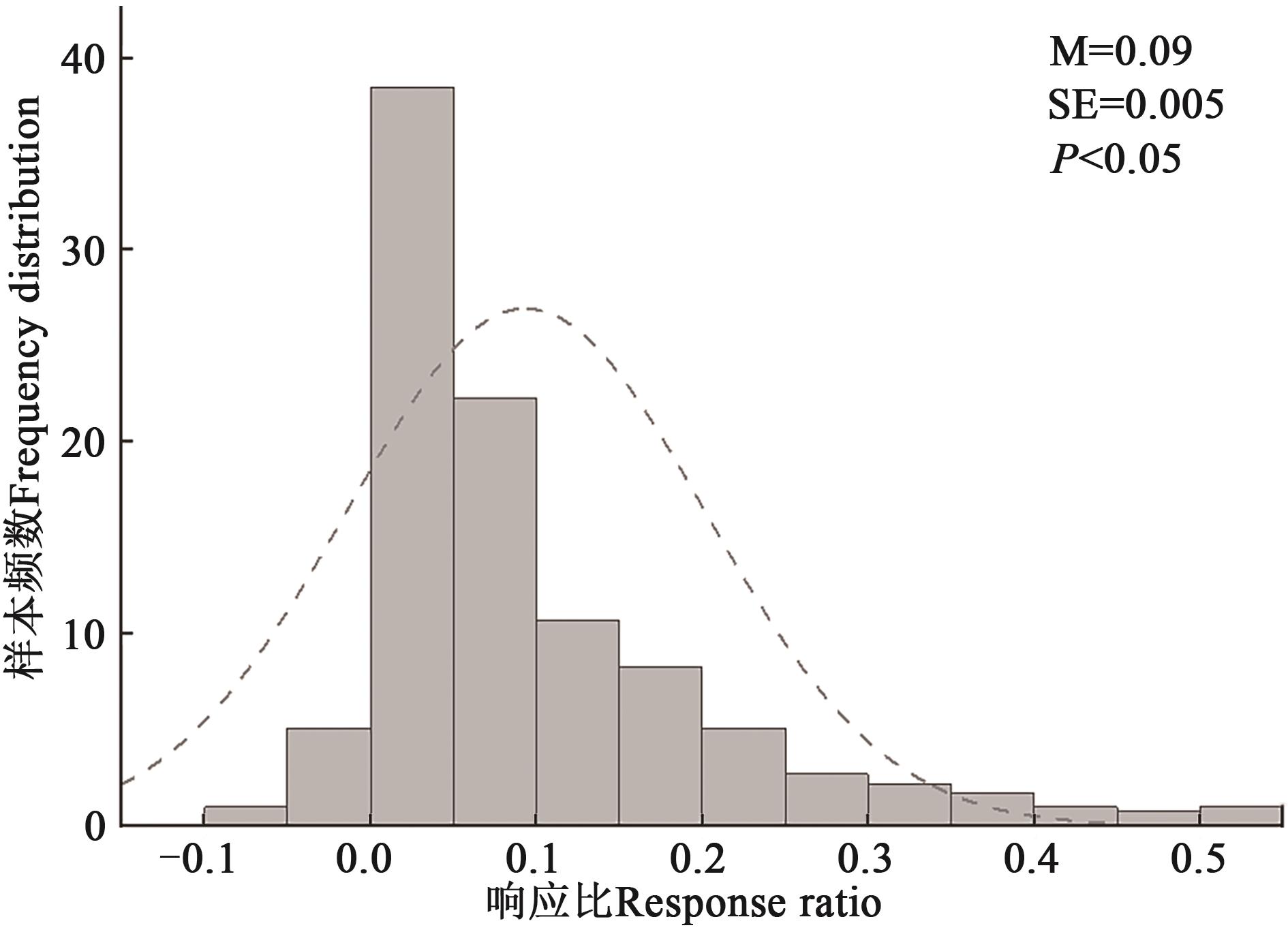
图1 生物炭施用后土壤pH变化的响应比注: M和SE分别表示土壤pH变化响应比的平均值和均值的标准误。
Fig. 1 Response ratio of soil pH change with biochar applicationNote: M and SE represent the mean and standard error of soil pH change response ratio, respectively.
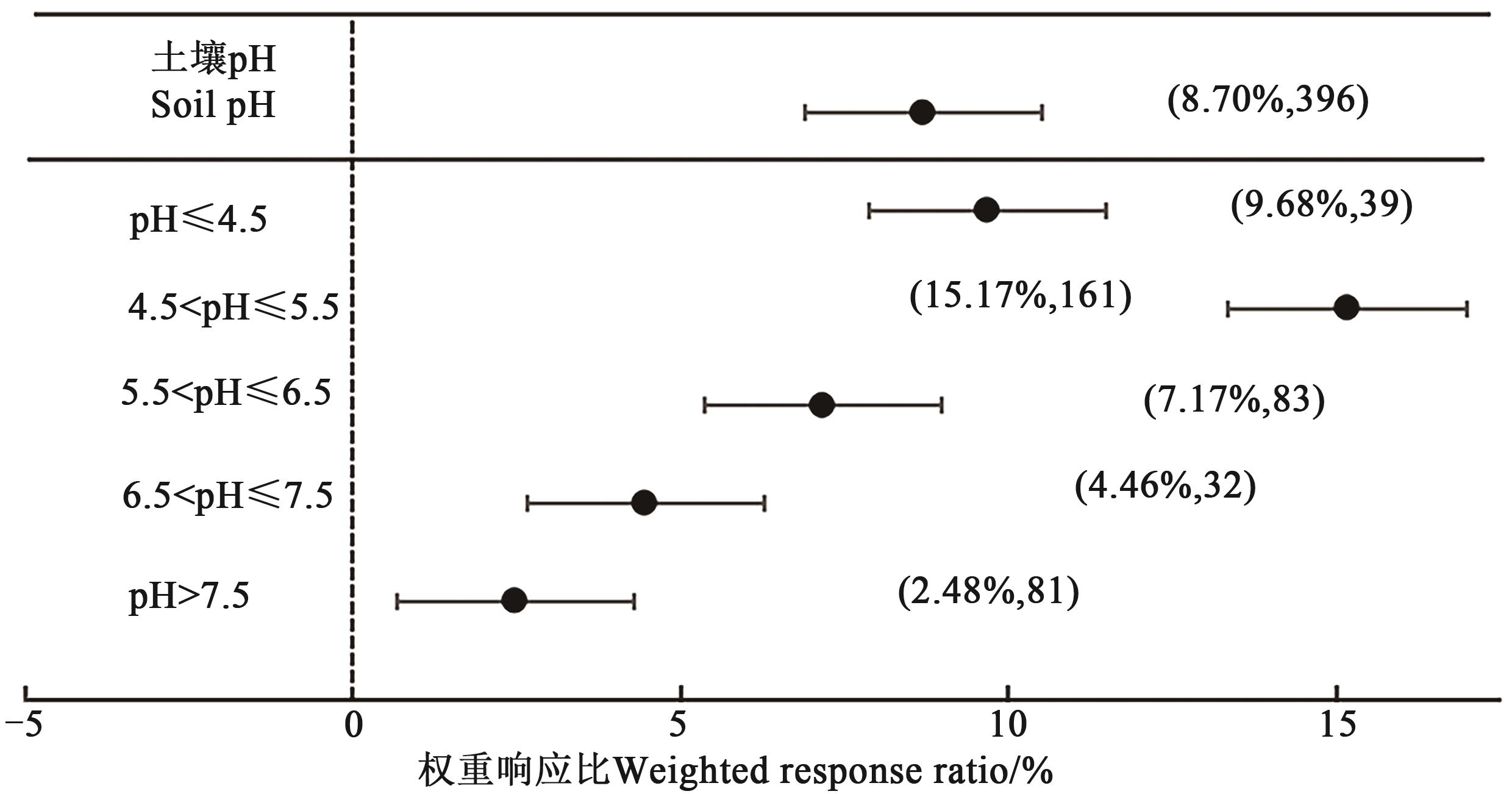
图2 不同酸碱度土壤施用生物炭对土壤pH的权重响应比注: 括号内数值分别为土壤pH的增幅百分数和样本量。
Fig. 2 Weighted response ratio of biochar application to soil pH under different pHNote: Values in brackets show the percentage increased in soil pH and sample size, respectively.
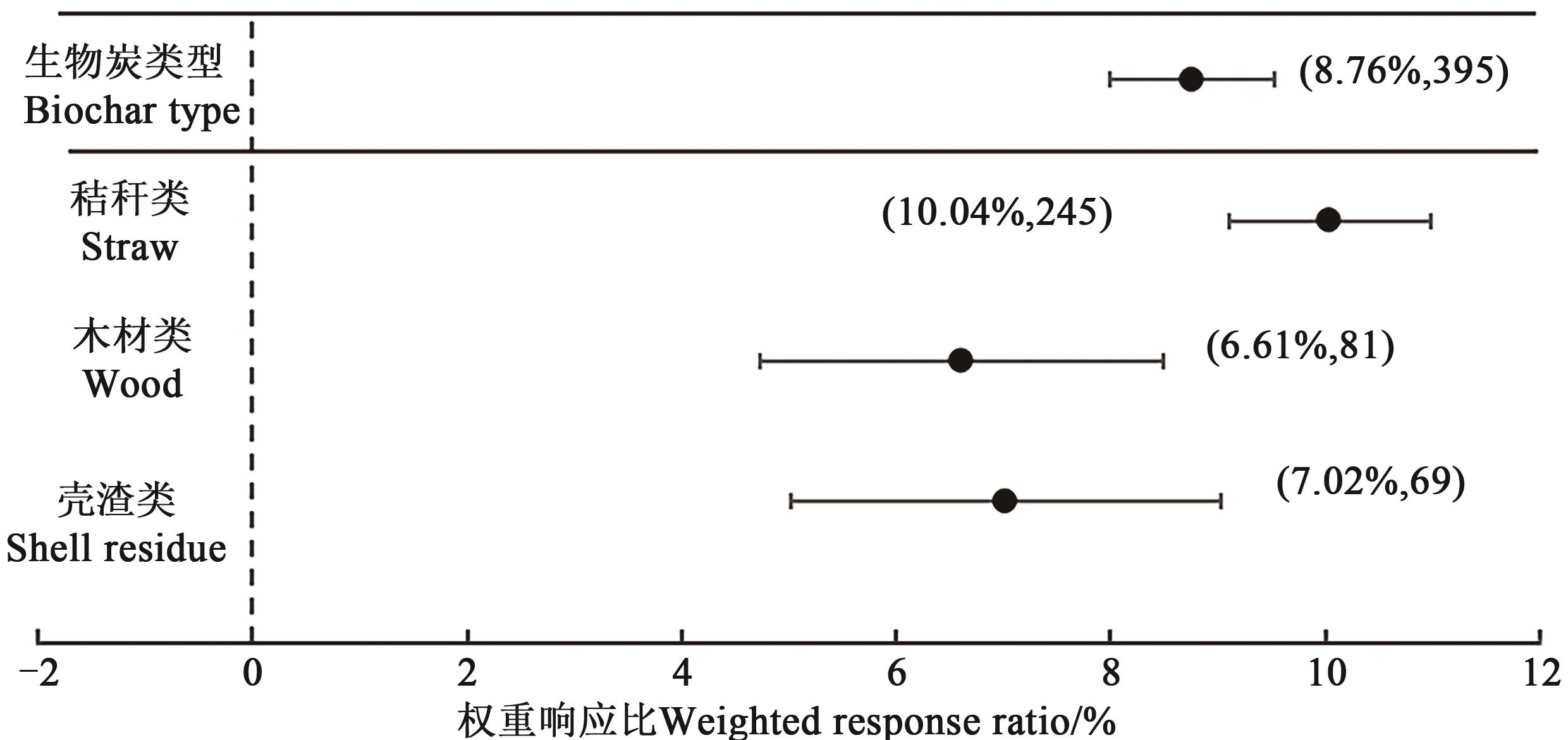
图3 施用不同原料制备的生物炭对土壤pH的权重响应比注: 括号内数值分别为土壤pH的增幅百分数和样本量。
Fig. 3 Weighted response ratio of biochar prepared with different raw materials to soil pHNote: Values in brackets show the percentage increased in soil pH and sample size, respectively.
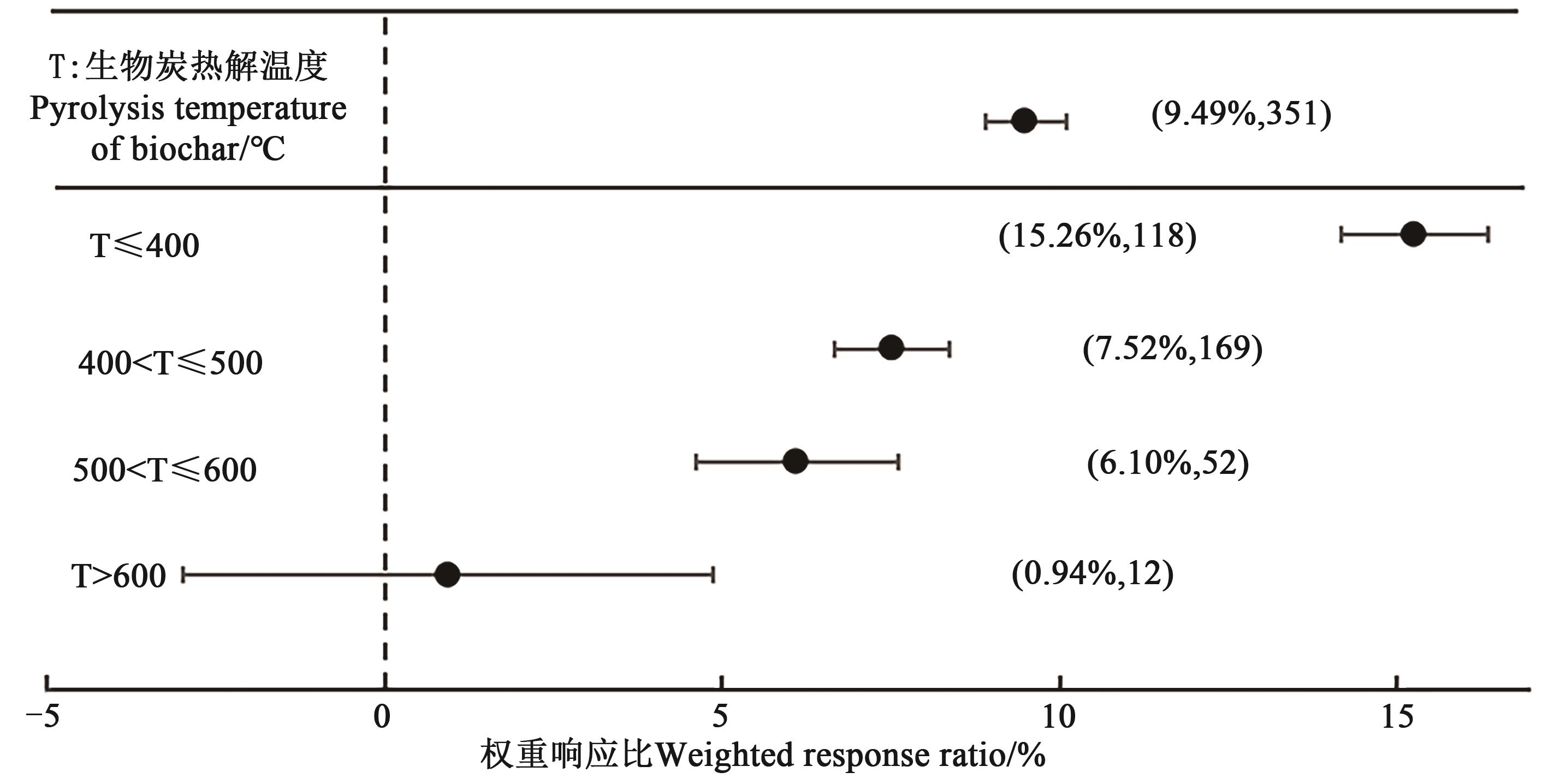
图4 施用不同热解温度范围下的生物炭对土壤pH的权重响应比注: 括号内数值分别为土壤pH的增幅百分数和样本量。
Fig. 4 Weighted response ratio of biochar to soil pH under different pyrolysis temperature rangesNote: Values in brackets show the percentage increased in soil pH and sample size, respectively.
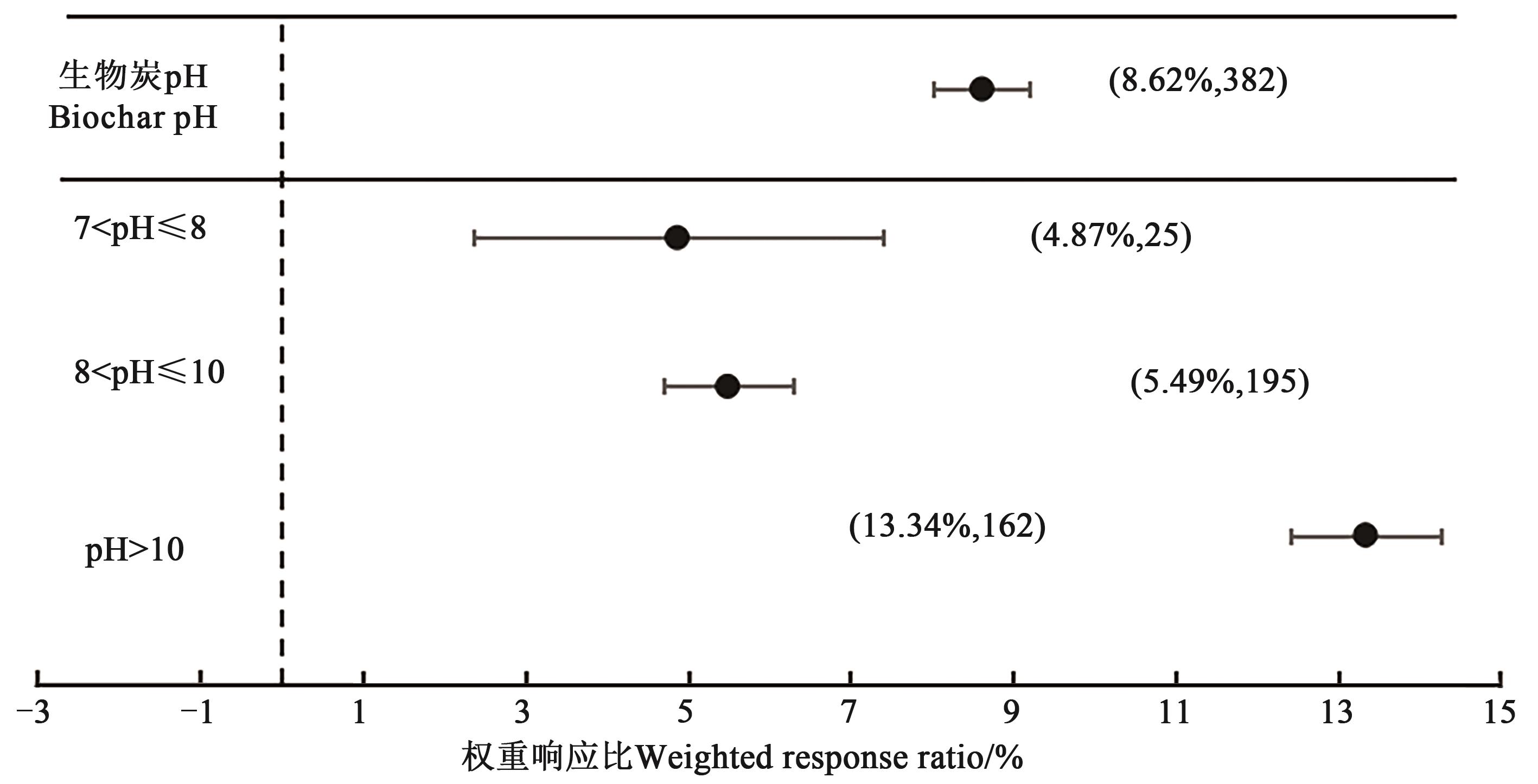
图5 施用不同pH的生物炭对土壤pH的权重响应比注: 括号内数值分别为土壤pH的增幅百分数和样本量。
Fig. 5 Weighted response ratio of biochar with different pH values to soil pHNote: Values in brackets show the percentage increased in soil pH and sample size, respectively.
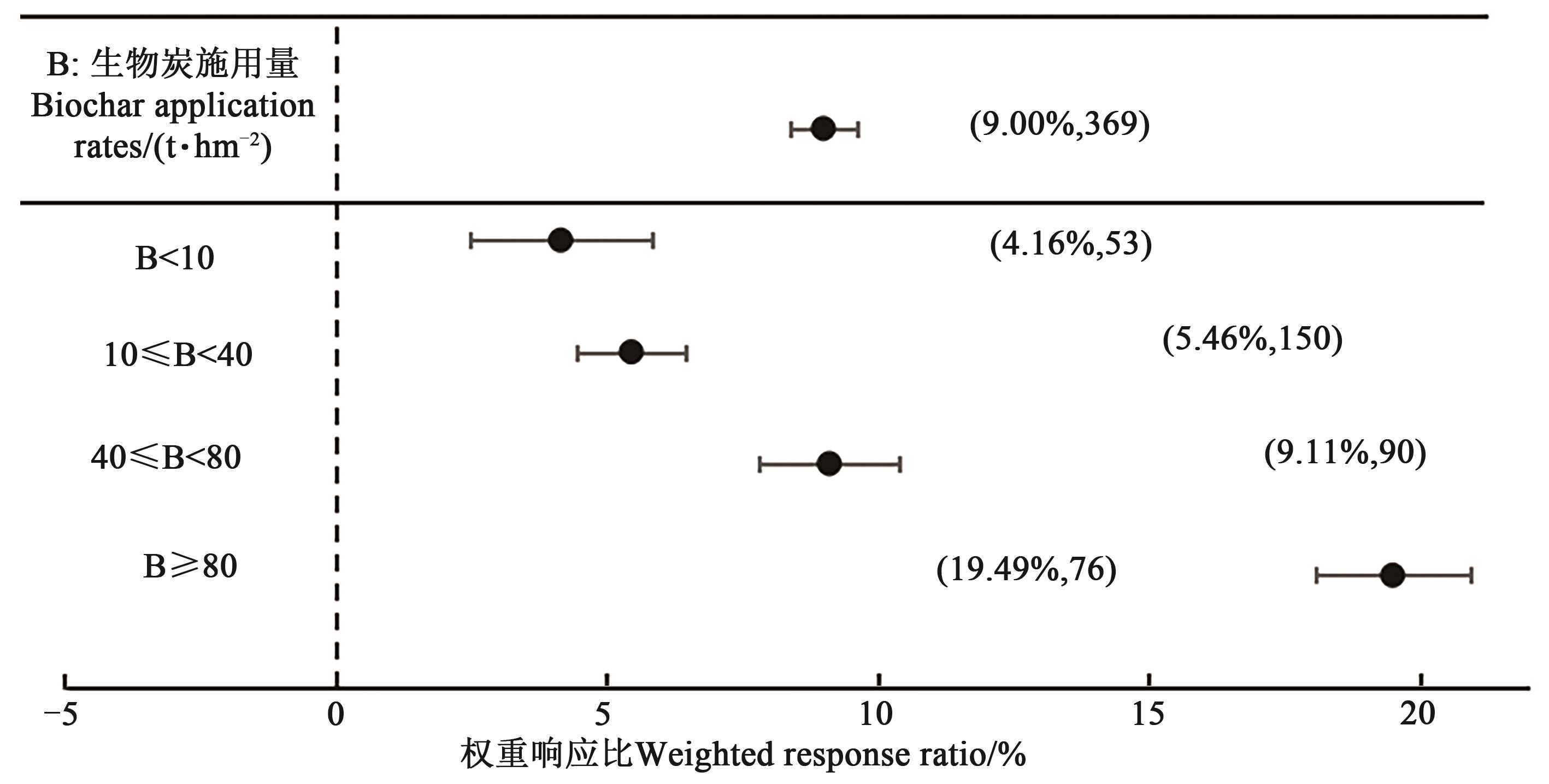
图6 生物炭施用量对土壤pH的权重响应比注: 括号内数值分别为土壤pH的增幅百分数和样本量。
Fig. 6 Weight response ratio of biochar application rate to soil pHNote: Values in brackets show the percentage increased in soil pH and sample size, respectively.
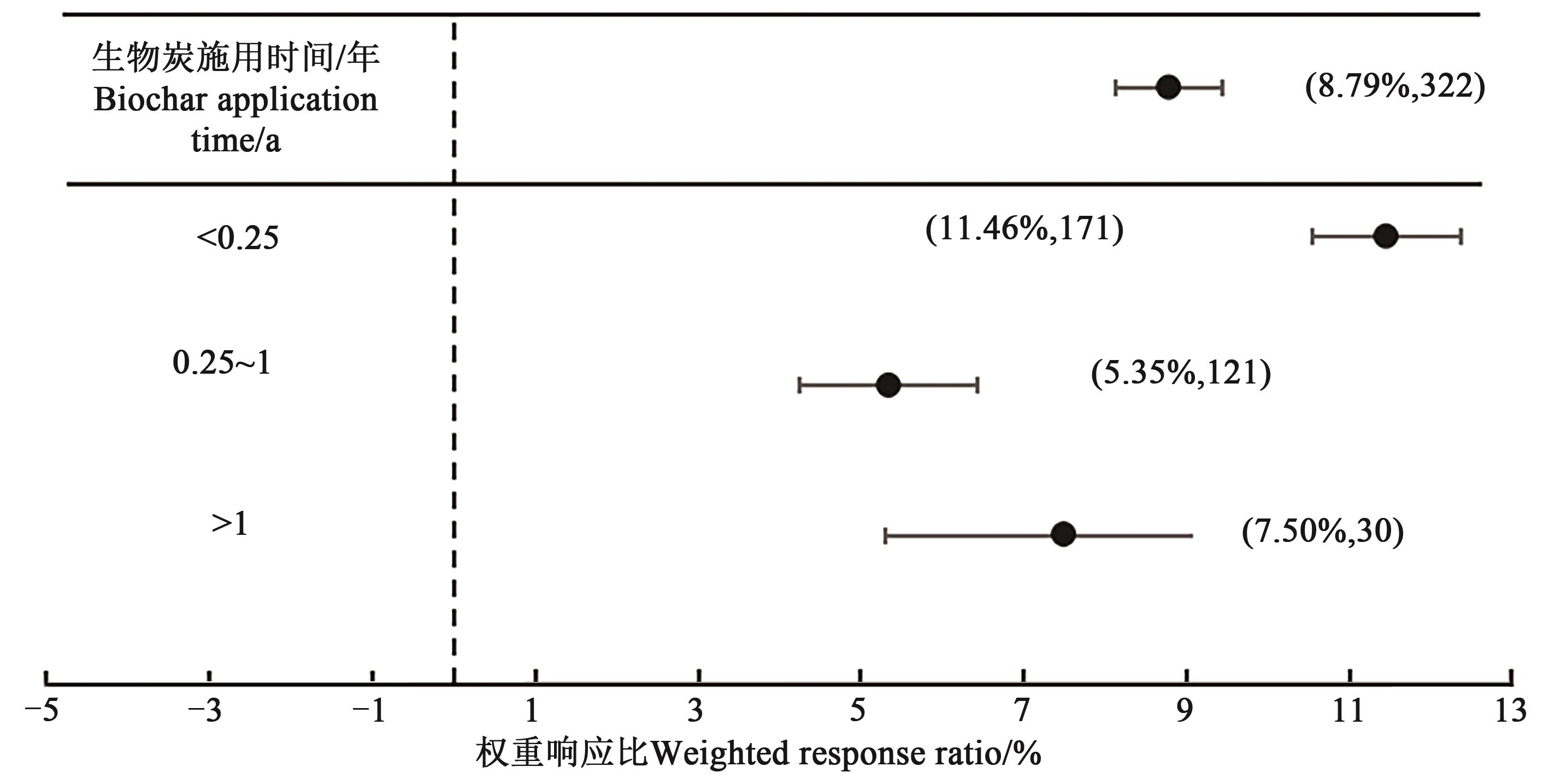
图7 生物炭施用时间对土壤pH的权重响应比注: 括号内数值分别为土壤pH的增幅百分数和样本量。
Fig. 7 Weighted response ratio of biochar application time to soil pHNote: Values in brackets show the percentage increased in soil pH and sample size, respectively.
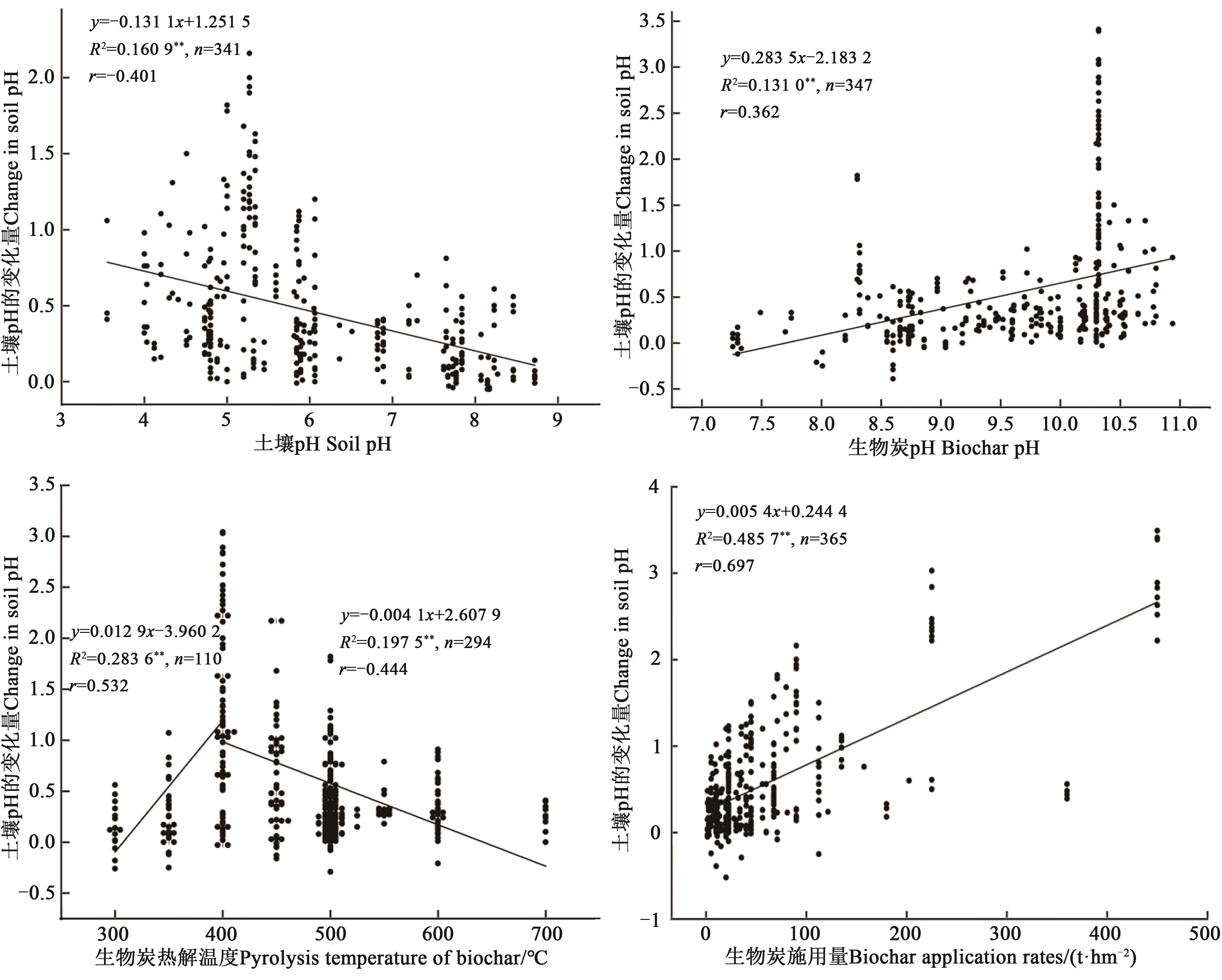
图8 土壤pH的变化量与土壤pH、生物炭pH、生物炭热解温度和生物炭施用量的关系注: **表示相关程度在P<0.01水平显著。
Fig. 8 Relationship between soil pH change and soil pH, biochar pH, biochar pyrolysis temperature and biochar pplication amountNote: **indicates significant correlation at P<0.01 level.
| 1 | 张强, 魏钦平, 齐鸿雁, 等. 北京果园土壤养分和pH与微生物数量的相关分析及优化方案[J]. 果树学报, 2011, 28(1): 15-19. |
| ZHANG Q, WEI Q P, QI H Y, et al.. Optimal schemes and correlation analysis between soil nutrient, pH and microorganism population in orchard of Beijing suburb [J]. J. Fruit Sci., 2011, 28(1): 15-19. | |
| 2 | 唐琨, 朱伟文, 周文新, 等. 土壤pH对植物生长发育影响的研究进展[J]. 作物研究, 2013, 27(2): 207-212. |
| TANG K, ZHU W W, ZHOU W X, et al.. Research progress on effects of soil pH on plant growth and development [J]. Crop Res., 2013, 27(2): 207-212. | |
| 3 | 徐仁扣. 土壤酸化及其调控研究进展[J]. 土壤, 2015, 47(2): 238-244. |
| XU R K. Research progresses in soil acidification and its control [J]. Soils, 2015, 47(2): 238-244. | |
| 4 | PETE S. Soil carbon sequestration and biochar as negative emission technologies [J]. Global Change Biol., 2016, 22(3): 1315-1324. |
| 5 | El-NAGGAR A, LEE S S, RINKLEBE J, et al.. Biochar application to low fertility soils: a review of current status, and future prospects [J]. Geoderma, 2019, 337: 536-554. |
| 6 | PURAKAYASTHA T J, BERA T, BHADURI D, et al.. A review on biochar modulated soil condition improvements and nutrient dynamics concerning crop yields: pathways to climate change mitigation and global food security [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 227: 345-365. |
| 7 | YOUNIS U, MALIK S A, RIZWAN M, et al.. Biochar enhances the cadmium tolerance in spinach (Spinacia oleracea) through modification of Cd uptake and physiological and biochemical attributes [J]. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res., 2016, 23(21): 1-10. |
| 8 | 袁帅, 赵立欣, 孟海波, 等. 生物炭主要类型、理化性质及其研究展望[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2016, 22(5): 1402-1417. |
| YUAN S, ZHAO L X, MENG H B, et al.. The main types of biochar and their properties and expectative researches [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2016, 22(5): 1402-1417. | |
| 9 | 阎海涛, 殷全玉, 丁松爽, 等. 生物炭对褐土理化特性及真菌群落结构的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(5): 2412-2419. |
| YAN H T, YIN Q Y, DING S S, et al.. Effect of biochar amendment on physicochemical properties and fungal community structures of cinnamon soil [J]. Environ. Sci., 2018, 39(5): 2412-2419. | |
| 10 | 花莉. 城市污泥堆肥资源化过程与污染物控制机理研究[D].杭州:浙江大学, 2008. |
| HUA L. Research on mechanism of sludge reclamation and pollution control [D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University, 2008. | |
| 11 | 徐秋桐, 邱志腾, 章明奎. 生物质炭对不同pH土壤中碳氮磷的转化与形态的影响[J]. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2014, 40(3): 303-313. |
| XU Q T, QIU Z T, ZHANG M K. Effects of biochar application on transformation and chemical forms of C,N and P in soils with different pH [J]. J. Zhejiang Univ. (Agric. Life Sci.), 2014, 40(3): 303-313. | |
| 12 | 黄超, 刘丽君, 章明奎. 生物质炭对红壤性质和黑麦草生长的影响[J]. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2011, 37(4): 439-445. |
| HUANG C, LIU L J, ZHANG M K. Effects of biochar on properties of red soil and ryegrass growth [J]. J. Zhejiang Univ. (Agric. Life Sci.), 2011, 37(4): 439-445. | |
| 13 | 张祥, 王典, 姜存仓, 等. 生物炭对我国南方红壤和黄棕壤理化性质的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2013, 21(8): 979-984. |
| ZHANG X, WANG D, JIANG C C, et al.. Effect of biochar on physicochemical properties of red and yellow brown soils in the South China region [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2013, 21(8): 979-984. | |
| 14 | 陈心想,何绪生,耿增超,等.生物炭对不同土壤化学性质、小麦和糜子产量的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(20): 6534-6542. |
| CHEN X X, HE X S, GENG Z C, et al.. Effects of biochar on selected soil chemical properties and on wheat and millet yield [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2013, 33(20): 6534-6542. | |
| 15 | 杨彩迪, 宗玉统, 卢升高. 不同生物炭对酸性农田土壤性质和作物产量的动态影响[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(4): 1914-1920. |
| YANG C D, ZONG Y T, LU S G. Dynamic effects of different biochars on soil properties and crop yield of acid farmland [J]. Environ. Sci., 2020, 41(4): 1914-1920. | |
| 16 | 董颖. 不同地区油菜秸秆生物质炭改良红壤酸度的差异性研究[D]. 洛阳:河南科技大学, 2018. |
| DONG Y. Amelioration of an ultisol acidity by biochars derived from canola straw varied with their cultivating soils [D]. Luoyang:Henan University of Science and Technology, 2018. | |
| 17 | 武春成, 王彩云, 曹霞, 等. 不同用量生物炭对连作土壤改良及黄瓜生长的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2017 (19): 150-154. |
| WU C C, WANG C Y, CAO X, et al.. Effects of different biochar application rate on improvement of continuous cropping soil and cucumber growth [J]. Northern Hortic., 2017(19): 150-154. | |
| 18 | 孙向阳. 土壤学[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2005: 1-360. |
| 19 | 吴伟祥, 孙雪, 董达, 等. 生物质炭土壤环境效应[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015: 1-468. |
| WU W X, SUN X, DONG D, et al.. Environmental Effects of Biochar in Soil [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2015: 1-468. | |
| 20 | 全国土壤普查办公室. 中国土壤[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1998: 1-1253. |
| 21 | 郭明, 李新. Meta分析及其在生态环境领域研究中的应用[J]. 中国沙漠, 2009, 29(5): 911-919. |
| GUO M, LI X. Meta-analysis: a new quantitative research approach in eco-environmental sciences [J]. J. Desert Res., 2009, 29(5): 911-919. | |
| 22 | 肖婧, 徐虎, 蔡岸冬, 等. 生物质炭特性及施用管理措施对作物产量影响的整合分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 2017, 50(10): 1830-1840. |
| XIAO J, XU H, CAI A D, et al.. A meta-analysis of effects of biochar properties and management practices on crop yield [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2017, 50(10): 1830-1840. | |
| 23 | HEDGES L V, GUREVITCH J, CURTIS P S, et al.. The meta-analysis of response ratios in experimental ecology [J]. Ecology, 1999, 80(4): 1150-1156. |
| 24 | LUO Y, HUI D, ZHANG D. Elevated CO2 stimulates net accumulations of carbon and nitrogen in land ecosystems: a meta-analysis [J]. Ecology, 2006, 87(1): 53-63. |
| 25 | NIU L A, HAO J M, ZHANG B Z, et al.. Influences of long-term fertilizer and tillage management on soil fertility of the north China plain [J]. Pedosphere, 2011, 21(6): 813-820. |
| 26 | 鲁艳红, 廖育林, 聂军, 等. 长期施用氮磷钾肥和石灰对红壤性水稻土酸性特征的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2016, 53(1): 202-212. |
| LU Y H, LIAO Y L, NIE J, et al.. Effects of long-term application of N, P, K fertilizer and lime on acid properties of red paddy soil [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2016, 53(1): 202-212. | |
| 27 | UCHIMIYA M, WARTELLE L H, KLASSON K T, et al.. Influence of pyrolysis temperature on biochar property and function as a heavy metal sorbent in soil [J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2011, 59(6): 2501-2510. |
| 28 | 袁金华,徐仁扣. 稻壳制备的生物质炭对红壤和黄棕壤酸度的改良效果[J].生态与农村环境学报, 2010, 26(5): 472-476. |
| YUAN J H, XU R K. Effect of rice-hull-based biochar regulating acidity of red soil and yellow brown soil [J]. J. Ecol. Rural Environ., 2010, 26(5): 472-476. | |
| 29 | YUAN J H, XU R K, WANG N, et al.. Amendment of acid soils with crop residues and biochars [J]. Pedosphere, 2011, 21(3): 302-308. |
| 30 | 王义祥, 辛思洁, 叶菁, 等. 生物炭对强酸性茶园土壤酸度的改良效果研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2018, 34(12): 108-111. |
| WANG Y X, XIN S J, YE J, et al.. Improvement effect of biochar on soil acidity in strong acidity tea garden [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2018, 34(12): 108-111. | |
| 31 | MOKOLOBATE M S, HAYNES R J. Increases in pH and soluble salts influence the effect that additions of organic residues have on concentrations of exchangeable and soil solution aluminium [J]. Eur. J. Soil Sci.,2010,53(3):481-489. |
| 32 | 赵旋彤, 王鸿斌, 赵兰坡, 等. 吉林省三种典型农耕土壤酸碱缓冲性能及影响因素[J/OL]. 吉林农业大学学报,2020:55752[2022-01-06].. |
| ZHAO X T, WANG H B, ZHAO L P, et al.. Acid-base buffering properties and influencing factors of three typical agricultural soils in Jilin province [J/OL]. J. Jilin Agric. Univ.,2020:55752 [2022-01-06].. | |
| 33 | 李艳梅, 孙焱鑫, 廖上强, 等. 不同原料与温度制备生物炭的性质及其农用潜力分析[C]//《环境工程》2019年全国学术年会论文集(下册). 北京:《环境工程》编辑部,2019: 731-736. |
| LI Y M, SUN Y X, LIAO S Q, et al.. Effects of feedstock sources and pyrolysis temperature on biochar’s property and their resulting agronomic effects [C] // Proceedings of the 2019 National Conference on Environmental Engineering (Volume 2).Beijing: Editorial Department of Environmental Engineering,2019: 731-736. | |
| 34 | 吴愉萍, 李雅颖, 周萍, 等. 不同原料及热解条件下农业废弃物生物炭的特性[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2019, 47(8): 230-233. |
| WU Y P, LI Y Y, ZHOU P, et al.. Characteristics of agricultural waste biochar under different raw materials and pyrolysis conditions [J]. Jiangsu Agric. Sci., 2019, 47(8): 230-233. | |
| 35 | 陈义轩, 宋婷婷, 方明, 等. 四种生物炭对潮土土壤微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(2): 394-404. |
| CHEN Y X, SONG T T, FANG M, et al.. The effect of four biochar on the structure of microbial communities in alluvial soil [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2019, 38(2): 394-404. | |
| 36 | GASKIN J W, STEINER C, HARRIS K, et al.. Effect of low-temperature pyrolysis conditions on biochar for agricultural use [J]. Trans. Asabe, 2008, 51( 6) : 2061-2069. |
| 37 | HOSSAIN M K, STREZOV V, CHAN K, et al.. Agronomic properties of wastewater sludge biochar and bioavailability of metals in production of cherry tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) [J]. Chemosphere, 2010, 78(9): 1167-1171. |
| 38 | CANTRELL K B, HUNT P G, UCHIMIYA M, et al.. Impact of pyrolysis temperature and manure source on physicochemical [J]. Bioresour. Technol., 2012, 107: 419-428. |
| 39 | HAO Z, WANG Z, XIA D, et al.. Characteristics and nutrient values of biochars produced from giant reed at different temperatures [J]. Bioresour. Technol., 2013, 130(2):463-471. |
| 40 | CAO X, HARRIS W. Properties of dairy-manure-derived biochar pertinent to its potential use in remediation [J]. Bioresour. Technol., 2010, 101(14):5222-5228. |
| 41 | 周强, 黄代宽, 余浪, 等. 热解温度和时间对生物炭pH值的影响[J]. 地球环境学报,2015,6(3):195-200. |
| ZHOU Q, HUANG D K, YU L, et al.. Effects of pyrolysis temperature, time and biochar mass ratio on pH value determination for four biochar solutions [J]. J. Earth Environ., 2015,6(3):195-200. | |
| 42 | XU X, CAO X, ZHAO L, et al.. Removal of Cu, Zn, and Cd from aqueous solutions by the dairy manure-derived biochar [J]. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. Int., 2013, 20(1):358-368. |
| 43 | KEILUWEIT M, NICO P S, JOHNSON M G, et al.. Dynamic molecular structure of plant biomass-derived black carbon (biochar) [J]. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2010, 44(4):1247-1253. |
| 44 | 韦思业. 不同生物质原料和制备温度对生物炭物理化学特征的影响[D]. 广州:中国科学院大学(中国科学院广州地球化学研究所), 2017. |
| WEI S Y. Influence of biomass feedstocks and pyrolysis temperatures on physical and chemical properties of biochar [D]. Guangzhou:University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, CAS), 2017. | |
| 45 | LEHMANN J. Bio-energy in the black [J]. Front. Ecol. Environ., 2007, 5: 381–387. |
| 46 | 郑慧芬, 吴红慧, 翁伯琦, 等. 施用生物炭提高酸性红壤茶园土壤的微生物特征及酶活性[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2019(2): 68-74. |
| ZHENG H F, WU H H, WEN B Q, et al.. Improved soil microbial characteristics and enzyme activities with wheat straw biochar addition to an acid tea plantation in red soil [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2019(2): 68-74. | |
| 47 | DAI Z, ZHANG X, TANG C, et al.. Potential role of biochars in decreasing soil acidification: a critical review [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2017, 581/582: 601-611. |
| 48 | RYSA D, NI N, JNNA D, et al.. Beneficial dual role of biochars in inhibiting soil acidification resulting from nitrification [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 234: 43-51. |
| 49 | 张文锋, 周际海, 袁颖红, 等. 低剂量生物质炭对旱地红壤增肥增产效果[J]. 生态学杂志, 2016(3): 647-654. |
| ZHANG W F, ZHOU J H, YUAN Y H, et al.. Effects of low-dose biochar on the enhancement of fertility and yield in upland red soils [J]. Chin. J. Ecol., 2016(3): 647-654. |
| [1] | 张晨阳, 徐明岗, 王斐, 李然, 孙楠. 施用有机肥对我国大豆产量及土壤养分的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 148-156. |
| [2] | 刘宏元, 周志花, 赵光昕, 沈钦瑞. 黄淮海平原农田土壤温室气体排放对长期施加生物炭的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 178-186. |
| [3] | 王旭东, 任雪冰, 汤舒, 郭琴, 薛梦瑶, 金鹏, 张云华. 污泥生物炭在土壤改良中的应用研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 165-173. |
| [4] | 刘云飞, 韦凤杰, 夏茂林, 于兆锦, 夏昊, 衣春宇, 常剑波, 姬小明. 新型复合水凝胶对镉胁迫烟草幼苗的缓解效应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 188-197. |
| [5] | 杨玲, 张富仓, 孙鑫, 张少辉, 王海东, ABDELGHANY Ahmed Elsayed, 陈占飞, 方玉川. 生物炭和滴灌量对陕北榆林沙土性质和马铃薯生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 221-233. |
| [6] | 郑云珠, 孙树臣. 秸秆生物炭和秸秆对麦玉轮作系统土壤养分及作物产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 152-162. |
| [7] | 刘著文, 杨龙飞, 刘茂林, 贾国涛, 姚倩, 马一琼, 崔廷, 杨欣玲, 陈洋, 程良琨. 不同土壤改良剂对土壤养分及烤烟内在品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(11): 190-198. |
| [8] | 周蕾, 陈兆兰, 严玉波, 李桥. 鸡粪生物炭吸附固定铅的研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(11): 199-207. |
| [9] | 魏俞涌, 张庆法, 盛奎川. 生物炭对玉米醇溶蛋白/聚丙烯复合材料力学性能的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(10): 161-168. |
| [10] | 朱利霞, 陈居田, 徐思薇, 陈如冰, 李俐俐. 生物炭施用下土壤微生物量碳氮的动态变化[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(8): 193-200. |
| [11] | 胡朝华, 刘曰明, 庞孜钦, 袁照年. 农田土壤活性氮损失现状和生物炭调控途径研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(6): 120-129. |
| [12] | 黄清扬, 江超, 俞元春, 谢祖彬. 不同秸秆生物炭复配基质对波斯菊生理性质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(6): 147-153. |
| [13] | 何甜甜, 刘天, 云菲, 马彩娟, 符云鹏. 生物炭对农田N2O排放的影响机制研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(5): 124-131. |
| [14] | 王鑫宇1,2,张曦2,孟海波2,沈玉君2,解恒燕1*,周海宾2,程红胜2,宋立秋2. 温度对生物炭吸附重金属特性的影响研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(2): 150-158. |
| [15] | 肖生苓1,荆勇1,2,冯晶2,申瑞霞2*,赵立欣2,王全亮1,张迎2. 木质生物炭对厌氧发酵产甲烷性能的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(1): 128-135. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号