




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (10): 98-109.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0022
徐皖菁1,2( ), 彭芳1, 赵豆豆1,2, 罗姣姣1, 陶珊1, 廖海浪1, 毛常清1, 吴宇1, 朱秀3, 徐正君2(
), 彭芳1, 赵豆豆1,2, 罗姣姣1, 陶珊1, 廖海浪1, 毛常清1, 吴宇1, 朱秀3, 徐正君2( ), 张超1(
), 张超1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-09
接受日期:2024-03-11
出版日期:2024-10-15
发布日期:2024-10-18
通讯作者:
徐正君,张超
作者简介:徐皖菁 E-mail:1315024678@qq.com
基金资助:
Wanjing XU1,2( ), Fang PENG1, Doudou ZHAO1,2, Jiaojiao LUO1, Shan TAO1, Hailang LIAO1, Changqing MAO1, Yu WU1, Xiu ZHU3, Zhengjun XU2(
), Fang PENG1, Doudou ZHAO1,2, Jiaojiao LUO1, Shan TAO1, Hailang LIAO1, Changqing MAO1, Yu WU1, Xiu ZHU3, Zhengjun XU2( ), Chao ZHANG1(
), Chao ZHANG1( )
)
Received:2024-01-09
Accepted:2024-03-11
Online:2024-10-15
Published:2024-10-18
Contact:
Zhengjun XU,Chao ZHANG
摘要:
为了解不同水平镉(Cd)胁迫下川芎基因表达和代谢产物的变化规律,探究川芎对Cd胁迫的响应机制,利用盆栽试验,以不添加Cd溶液的清洁土壤为对照,设置1、3、6、10 mg·kg-1共4个Cd胁迫处理水平,采用转录组学测序(RNA sequencing,RNA-seq)和超高效液相色谱质谱联用(ultra performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry,UPLC-MS/MS)技术,筛选川芎抗Cd胁迫的关键基因与代谢通路。结果表明,共筛选到8 569个差异表达基因,包括上调基因6 859个,下调基因1 710个。与对照相比,4个Cd处理组的共有差异基因仅1个,为CML19,可能是川芎抗Cd胁迫的关键基因。代谢组共标注和定量了1 238种差异代谢物,在KEGG数据库中注释得到76条代谢通路,其中包括氨基酸代谢、氨酰基-tRNA的生物合成和脂肪酸的生物合成等。联合分析表明,当受到不同水平Cd胁迫时,川芎通过调节不同种类氨基酸来维持自身代谢平衡,在川芎抗Cd胁迫中发挥重要作用。研究结果为川芎抗Cd胁迫提供科学支撑与理论依据,为针对川芎资源的栽培育种及缓解Cd胁迫等相关研究提供基础。
中图分类号:
徐皖菁, 彭芳, 赵豆豆, 罗姣姣, 陶珊, 廖海浪, 毛常清, 吴宇, 朱秀, 徐正君, 张超. 基于转录组和代谢组解析川芎对镉胁迫的响应机制[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(10): 98-109.
Wanjing XU, Fang PENG, Doudou ZHAO, Jiaojiao LUO, Shan TAO, Hailang LIAO, Changqing MAO, Yu WU, Xiu ZHU, Zhengjun XU, Chao ZHANG. Analysis of Response Mechanism of Ligusticum chuanxiong to Cadmium Stress Based on Transcriptome and Metabolome[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(10): 98-109.
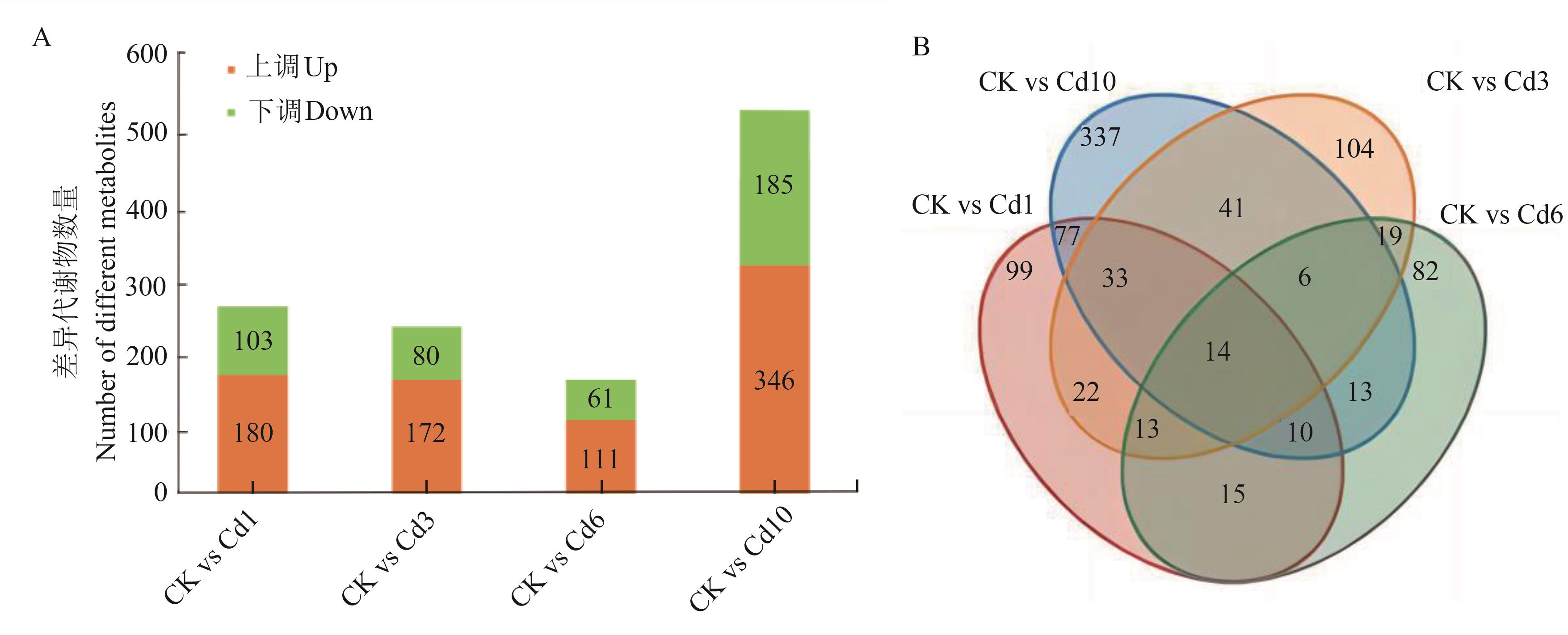
图1 两两比较中上调和下调差异累积代谢物数量A:各组差异累积代谢物数量;B:差异累积代谢物韦恩图
Fig. 1 Numbers of the up-regulated and down-regulated DAMs in pairwise comparisonsA:Number of differential accumulated metabolites in each group; B:Differential accumulated metabolite Venn diagram

图2 不同水平Cd处理下川芎根茎代谢产物偏最小二乘判别分析正交投影评分图注: TP—预测成分得分值;TO—正交成分得分值。
Fig. 2 Partial least squares discriminant analysis orthogonal projection score of metabolites of Ligusticum chuanxiong treated with different levels of CdNote: TP—Score value of the predicted component;TO—Score value of the orthogonal component.
样品编号 Sample number | Clean reads数目 Number of clean reads | 总碱基数 Total base number/nt | GC含量 GC content/% | Q30/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK-1 | 29 678 610 | 8 835 337 288 | 43.62 | 93.76 |
| CK-2 | 24 429 573 | 7 276 365 402 | 43.79 | 93.26 |
| CK-3 | 19 868 507 | 5 905 914 150 | 44.19 | 93.33 |
| Cd1-1 | 20 935 573 | 6 215 766 952 | 44.79 | 93.93 |
| Cd1-2 | 25 071 449 | 7 465 487 210 | 43.97 | 93.66 |
| Cd1-3 | 21 681 836 | 6 460 887 440 | 43.92 | 93.61 |
| Cd3-1 | 19 483 124 | 5 787 607 824 | 43.61 | 93.79 |
| Cd3-2 | 20 832 819 | 6 215 838 452 | 43.87 | 93.05 |
| Cd3-3 | 21 394 788 | 6 382 109 148 | 43.90 | 93.59 |
| Cd6-1 | 20 610 107 | 6 120 785 704 | 43.97 | 93.70 |
| Cd6-2 | 20 640 197 | 6 157 201 056 | 43.79 | 93.78 |
| Cd6-3 | 22 624 009 | 6 720 661 646 | 43.88 | 93.87 |
| Cd10-1 | 19 376 308 | 5 766 904 348 | 43.94 | 93.65 |
| Cd10-2 | 19 731 742 | 5 880 325 626 | 43.67 | 93.46 |
| Cd10-3 | 21 006 650 | 6 270 393 312 | 43.95 | 93.36 |
| 合计 Total | 327 365 292 | 97 461 585 558 | — | — |
表1 转录组测序产物分析
Table 1 Transcriptome sequencing product analysis
样品编号 Sample number | Clean reads数目 Number of clean reads | 总碱基数 Total base number/nt | GC含量 GC content/% | Q30/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK-1 | 29 678 610 | 8 835 337 288 | 43.62 | 93.76 |
| CK-2 | 24 429 573 | 7 276 365 402 | 43.79 | 93.26 |
| CK-3 | 19 868 507 | 5 905 914 150 | 44.19 | 93.33 |
| Cd1-1 | 20 935 573 | 6 215 766 952 | 44.79 | 93.93 |
| Cd1-2 | 25 071 449 | 7 465 487 210 | 43.97 | 93.66 |
| Cd1-3 | 21 681 836 | 6 460 887 440 | 43.92 | 93.61 |
| Cd3-1 | 19 483 124 | 5 787 607 824 | 43.61 | 93.79 |
| Cd3-2 | 20 832 819 | 6 215 838 452 | 43.87 | 93.05 |
| Cd3-3 | 21 394 788 | 6 382 109 148 | 43.90 | 93.59 |
| Cd6-1 | 20 610 107 | 6 120 785 704 | 43.97 | 93.70 |
| Cd6-2 | 20 640 197 | 6 157 201 056 | 43.79 | 93.78 |
| Cd6-3 | 22 624 009 | 6 720 661 646 | 43.88 | 93.87 |
| Cd10-1 | 19 376 308 | 5 766 904 348 | 43.94 | 93.65 |
| Cd10-2 | 19 731 742 | 5 880 325 626 | 43.67 | 93.46 |
| Cd10-3 | 21 006 650 | 6 270 393 312 | 43.95 | 93.36 |
| 合计 Total | 327 365 292 | 97 461 585 558 | — | — |
数据库 Database | Unigenes数量 Number of unigenes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
总量 Total | 300≤长度<1 000 bp 300≤Length<1 000 bp | 长度≥1 000 bp Length≥1 000 bp | 占比 Proportion/% | |
| COG | 11 717 | 4 635 | 7 082 | 32.25 |
| GO | 28 277 | 11 510 | 16 747 | 77.82 |
| KEGG | 23 357 | 9 252 | 14 105 | 64.28 |
| KOG | 21 487 | 8 946 | 12 541 | 59.13 |
| Pfam | 28 001 | 10 941 | 17 060 | 77.06 |
| Swiss-Prot | 22 042 | 8 924 | 13 118 | 60.66 |
| TrEMBL | 31 952 | 13 037 | 18 915 | 87.93 |
| EggNOG4.5 | 26 245 | 10 422 | 15 823 | 72.23 |
| NR | 34 643 | 14 628 | 20 015 | 95.34 |
总注释转录本 Total annotated transcript | 36 336 | 15 887 | 20 429 | 100.00 |
表2 Unigene注释统计
Table 2 Statistics of unigene annotation
数据库 Database | Unigenes数量 Number of unigenes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
总量 Total | 300≤长度<1 000 bp 300≤Length<1 000 bp | 长度≥1 000 bp Length≥1 000 bp | 占比 Proportion/% | |
| COG | 11 717 | 4 635 | 7 082 | 32.25 |
| GO | 28 277 | 11 510 | 16 747 | 77.82 |
| KEGG | 23 357 | 9 252 | 14 105 | 64.28 |
| KOG | 21 487 | 8 946 | 12 541 | 59.13 |
| Pfam | 28 001 | 10 941 | 17 060 | 77.06 |
| Swiss-Prot | 22 042 | 8 924 | 13 118 | 60.66 |
| TrEMBL | 31 952 | 13 037 | 18 915 | 87.93 |
| EggNOG4.5 | 26 245 | 10 422 | 15 823 | 72.23 |
| NR | 34 643 | 14 628 | 20 015 | 95.34 |
总注释转录本 Total annotated transcript | 36 336 | 15 887 | 20 429 | 100.00 |
分组 Group | 差异表达基因总数 Total number of differentially expressed genes | 上调 Up | 下调 Down |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK vs Cd1 | 2 385 | 2 247 | 138 |
| CK vs Cd3 | 5 703 | 4 205 | 1 498 |
| CK vs Cd6 | 286 | 257 | 29 |
| CK vs Cd10 | 195 | 150 | 45 |
| 合计 Total | 8 569 | 6 859 | 1 710 |
表3 差异表达基因统计结果
Table 3 Statistical results of differentially expressed genes
分组 Group | 差异表达基因总数 Total number of differentially expressed genes | 上调 Up | 下调 Down |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK vs Cd1 | 2 385 | 2 247 | 138 |
| CK vs Cd3 | 5 703 | 4 205 | 1 498 |
| CK vs Cd6 | 286 | 257 | 29 |
| CK vs Cd10 | 195 | 150 | 45 |
| 合计 Total | 8 569 | 6 859 | 1 710 |
| 1 | 王艺涵,赵佳琛,金艳,等.经典名方中川芎的本草考证[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2022,28(10):262-274. |
| WANG Y H, ZHAO J C, JIN Y, et al.. Herbal textual research on Chuanxiong rhizoma in famous classical formulas [J]. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae, 2022,28(10):262-274. | |
| 2 | 廖雪梅,陈媛媛,陶珊,等.川芎重金属镉污染现状及降镉策略研究进展[J].河南农业科学,2020,49(10):1-11. |
| LIAO X M, CHEN Y Y, TAO S,et al..Research progress on present situation of heavy metal cadmium pollution and strategies to reduce cadmium in Ligusticum chuanxiong [J]. J.Henan Agric. Sci., 2020,49(10):1-11. | |
| 3 | 王晓亚,鲁建丽.川芎和抚芎的多糖和重金属含量分析[J].广东微量元素科学,2006,13(1):49-52. |
| WANG X Y, LU J L.Determination of polysaccharides and heavy mentals in Ligusticum chuanxiong hort and Ligusticum chuanxiong hort cv.Fuxiong [J].Guangdong Trace Elem.Sci.,2006,13(1):49-52. | |
| 4 | 何平,李佳颖,刘宇哲,等.土壤镉污染背景下川芎生态适宜区规划研究[J].中国中药杂志,2022,47(5):1196-1204. |
| HE P, LI J Y, LIU Y Z,et al..Planning of ecologically suitable areas for Ligusticum chuanxiong under background of soil cadmium pollution [J].China J.Chin.Mater.Med.,2022,47(5):1196-1204. | |
| 5 | 陈云子,刘薇,黎智,等.川芎镉污染现状调查及原因分析[J].中药与临床,2022,13(6):1-4, 13. |
| CHEN Y Z, LIU W, LI Z,et al..Investigation and analysis of cadmium pollution in Chuanxiong [J].Pharm.Clin.Chin.Mater.Med.,2022,13(6):1-4, 13. | |
| 6 | 李笑媛,陈润芍,许安妮,等.川芎对镉、铅及其复合处理的生理响应[J].应用与环境生物学报,2019,25(2):321-327. |
| LI X Y, CHEN R S, XU A N,et al..Physiological response to cadmium,lead,and their combination stress in Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort [J].Chin.J.Appl.Environ.Biol.,2019,25(2):321-327. | |
| 7 | GHATAK A, CHATURVEDI P, WECKWERTH W.Metabolomics in plant stress physiology [J].Adv Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol.,2018,164:187-236. |
| 8 | 罗庆.镉、铅胁迫下东南景天根系分泌物的代谢组学研究[D].沈阳:东北大学,2015. |
| LUO Q. Metabolomics study on root exudates of Sedum alfredii under Cd and Pb stress [D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2015. | |
| 9 | 盛莎莎,刘荣鹏,王晓云,等.车前响应镉胁迫的生理学和代谢组学分析[J].植物科学学报,2023,41(2):234-244. |
| SHENG S S, LIU R P, WANG X Y,et al..Physiological and metabolomic analysis of Plantago asiatica L.in response to cadmium stress [J]. Plant Sci. J., 2023,41(2):234-244. | |
| 10 | 汪京超.基于转录组学的油菜镉胁迫响应机制研究[D].重庆:西南大学,2016. |
| WANG J C. Mechanism research on cadmium stress response of brassica based on transcriptomic [D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2016. | |
| 11 | 王书凤.高低镉积累油菜品种响应镉胁迫的分子机制研究[D].重庆:西南大学,2019. |
| WANG S F. Study on the molecular mechanisms of high/low cadmium accumulation rapeseed cultivars response to Cd stress [D]. Chongqing: Southwest University,2019. | |
| 12 | 吴迪,张燕燕,林楠,等.基于代谢组学和转录组学探究草珊瑚叶和根中黄酮类成分差异积累的转录调控机制[J].中国中药杂志,2023,48(21):5767-5778. |
| WU D, ZHANG Y Y, LIN N,et al..Transcriptional regulation mechanism of differential accumulation of flavonoids in leaves and roots of Sarcandra glabra based on metabonomics and transcriptomics [J].China J. Chin. Mater. Med.,2023,48(21):5767-5778. | |
| 13 | 刁瑞宁,杨莎,张佳蕾,等.基于转录组学和代谢组学解析氮调控花生结瘤固氮的机理[J].山东农业科学,2023,55(4):1-10. |
| DIAO R N, YANG S, ZHANG J L,et al.. Mechanism analysis of nitrogen regulation on peanut nodulating based on transcriptomes and metabonomics [J].Shandong Agric.Sci.,2023,55(4):1-10. | |
| 14 | 王婷婷,陈鸽,包悦琳,等.大豆根系响应早期缺铁胁迫的转录组分析[J].南京农业大学学报,2022,45(2):224-234. |
| WANG T T, CHEN G, BAO Y L, et al.. Transcriptome analysis of soybean roots in response to early iron deficiency stress [J].J.Nanjing Agric.Univ., 2022,45(2):224-234. | |
| 15 | 武丽娟,刘海学,张亚东,等.不同镉胁迫水平对水稻幼苗差异代谢物的影响[J/OL].分子植物育种,2022:1-21[2023-12-08]. . |
| WU L J, LIU H X, ZHANG Y D, et al.. Effects of different cadmium stress levels on differential metabolites in rice seedlings [J/OL]. Mol. Plant Breeding,2022:1-21 [2023-12-08]. . | |
| 16 | 宋佳阳,胡瑜,徐倩,等.不同秋眠级紫花苜蓿叶片响应渍水胁迫的代谢组学分析[J].草地学报,2023,31(11):3355-3363. |
| SONG J Y, HU Y, XU Q,et al..Metabolomic analysis on the response of leaves of alfalfa with different fall dormancy levels to waterlogging stress [J].Acta Agrestia Sin.,2023,31(11):3355-3363. | |
| 17 | 袁俊,盛莎莎,刘荣鹏,等.镉胁迫对丹参生理特性和代谢特征的影响[J].植物科学学报,2022,40(3):408-417. |
| YUAN J, SHENG S S, LIU R P,et al..Effects of cadmium on physiological characteristics and metabolic profiles of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge [J]. Plant Sci. J., 2022,40(3):408-417. | |
| 18 | STEPANSKY A, LEUSTEK T.Histidine biosynthesis in plants [J].Amino Acids,2006,30(2):127-142. |
| 19 | 马洪娜,吴依琳,马珊珊,等.朱砂根叶响应Ca2+胁迫的差异代谢物分析[J].植物生理学报,2023,59(9):1771-1782. |
| MA H N, WU Y L, MA S S, et al.. Analysis of differential metabolites in Ardisia crenata leaves in response to Ca2+ stress [J]. Plant Physiol. J., 2023, 59(9):1771-1782. | |
| 20 | HO C L, SAITO K. Molecular biology of the plastidic phosphorylated serine biosynthetic pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Amino Acids, 2001,20(3):243-259. |
| 21 | WADITEE R, BHUIYAN N H, HIRATA E,et al..Metabolic engineering for betaine accumulation in microbes and plants [J]. J.Biol. Chem.,2007,282(47):34185-34193. |
| 22 | ROS R, CASCALES-MIÑANA B, SEGURA J, et al.. Serine biosynthesis by photorespiratory and nonphotorespiratory pathways: an interesting interplay with unknown regulatory networks [J]. Plant Biol., 2013,15:707-712. |
| 23 | PENG H, HE X, GAO J,et al..Transcriptomic changes during maize roots development responsive to Cadmium (Cd) pollution using comparative RNAseq-based approach [J].Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2015,464(4):1040-1047. |
| 24 | 张尉欣,刘阳,刘帅,等.镉胁迫下菜心的转录组分析[J].深圳大学学报(理工版),2018,35(5):543-550. |
| ZHANG Y X, LIU Y, LIU S,et al..Transcriptome analysis of Brassica rapa ssp.chinensis var. parachinensis under cadmium stress [J]. J. Shenzhen Univ. (Sci.Eng.), 2018,35(5):543-550. | |
| 25 | ARBONA V, MANZI M, OLLAS C D,et al..Metabolomics as a tool to investigate abiotic stress tolerance in plants [J].Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2013,14(3):4885-4911. |
| 26 | BHEEMAREDDY B R, PULIPETA M, IYER P, et al.. Effect of the total galactose content on complement-dependent cytotoxicity of the therapeutic anti-CD20 IgG1 antibodies under temperature stress conditions [J/OL]. J. Carbohydr. Chem., 2019,38(1):1541995 [2023-12-08]. . |
| 27 | NÄGELE T, STUTZ S, HÖRMILLER I I,et al..Identification of a metabolic bottleneck for cold acclimation in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Plant J., 2012,72(1):102-114. |
| 28 | 王丽华,李改玲,李晶,等.外源糖对盐胁迫下小黑麦幼苗糖代谢的影响[J].麦类作物学报,2017,37(4):548-553. |
| WANG L H, LI G L, LI J, et al.. Effect of exogenous sugar on the sugar metabolism in Triticale seedling under salt stress [J]. J.Triticeae Crops,2017,37(4):548-553. | |
| 29 | LI C, LIU Y, TIAN J,et al.. Changes in sucrose metabolism in maize varieties with different cadmium sensitivities under cadmium stress [J/OL].PLoS One,2020,15(12):e0243835 [2023-12-08]. . |
| 30 | 陈文玲,张晴晴,唐韶华,等.甘油-3-磷酸酰基转移酶在植物脂质代谢、生长及逆境反应中的作用[J].植物生理学报,2018,54(5):725-735. |
| CHEN W L, ZHANG Q Q, TANG S H,et al..Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase in lipid metabolism,growth and response to stresses in plants [J].Plant Physiol.J.,2018,54(5):725-735. | |
| 31 | 汪怡文.转录组和代谢组整合分析冬小麦镉胁迫响应的关键代谢通路[D].武汉:华中农业大学, 2022. |
| WANG Y W. Integrated transcriptome and metabonomic analysis of key metabolic pathways in response to cadmium stress in winter wheat [D].Wuhan:Huazhong Agricultural University, 2022. | |
| 32 | 钱禛锋,谷书杰,赵雪婷,等.基于转录组的蔗茅CML基因家族鉴定及冷胁迫表达分析[J].农业生物技术学报,2022,30(5):885-895. |
| QIAN Z F, GU S J, ZHAO X T,et al.. Identification and cold stress expression analysis of CML gene family in Erianthus fulvus based on transcriptome [J].J.Agric.Biotechnol.,2022,30(5):885-895. | |
| 33 | MAGNAN F, RANTY B, CHARPENTEAU M,et al.. Mutations in AtCML9,a calmodulin-like protein from Arabidopsis thaliana,alter plant responses to abiotic stress and abscisic acid [J]. Plant J., 2008,56(4):575-589. |
| 34 | HIRAI M Y, SAWADA Y, KANAYA S,et al.. Toward genome-wide metabolotyping and elucidation of metabolic system:metabolic profiling of large-scale bioresources [J]. J. Plant Res., 2010,123(3):291-298. |
| 35 | 赵云霞,魏艳玲,黄先忠.新疆无苞芥类钙调素蛋白基因OpCML13的克隆与分析[J].西北植物学报,2014,34(3):431-437. |
| ZHAO Y X, WEI Y L, HUANG X Z. Clone and expression analysis of calmodulin-like protein gene OpCML13 from Olimarabidopsis pumila of Xinjiang [J]. Acta Bot.Bor-Occid. Sin., 2014,34(3):431-437. | |
| 36 | VANDERBELD B, SNEDDEN W A. Developmental and stimulus-induced expression patterns of Arabidopsis calmodulin-like genes CML37,CML38 and CML39 [J].Plant Mol. Biol., 2007,64(6):683-697. |
| [1] | 张倩, 门丽娜, 李一然, 刘巧, 胡晓雯, 张宇宏, 张志伟, 张伟. 桃蛀果蛾雌雄虫不同发育时期嗅觉基因的表达水平差异[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 151-162. |
| [2] | 张永芳, 董世妍, 王佳轩, 郭绪虎, 张畅, 王艳星, 王钰烨, 吴静凤, 鲍甜芳, 张宏发, 于萍, 李富恒. 老山芹层积前后种子差异代谢物分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(7): 37-49. |
| [3] | 鲁一薇, 夏雪岩, 赵宇, 崔纪菡, 刘猛, 黄玫红, 褚程, 刘建军, 李顺国. 缺钾胁迫下谷子转录组分析及相关基因挖掘[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 30-44. |
| [4] | 徐佳睿, 王逸茹, 赵绍赓, 李坤, 郑军. 玉米木质素合成途径基因ZmCCoAOMT1功能研究及转录组分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 30-43. |
| [5] | 李双, 王爱英, 焦浈, 池青, 孙昊, 焦涛. 盐胁迫下不同抗性小麦幼苗生理生化特性及转录组分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 20-32. |
| [6] | 郑宏斌, 王聪, 席奇亮, 张仲文, 王卫民, 王昕, 郭进, 何欢欢, 芦伟龙, 许自成, 王文超, 贾玮. 施氮量对云烟121上部烟叶代谢及品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(10): 215-225. |
| [7] | 夏雪岩, 崔纪菡, 黄玫红, 郭帅, 刘猛, 赵宇, 鲁一薇, 赵文庆, 王京新, 李顺国. 谷子苗期氮高效转录组分析与基因挖掘[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(10): 41-57. |
| [8] | 张彩虹, 张力, 王卫民, 赵炯平, 韩丹, 许自成, 张仲文, 邵惠芳. 基于非靶向代谢组学的上部烟叶不同成熟度差异分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(10): 58-70. |
| [9] | 冀薇, 樊莹, 黄家兴, 杨慧鹏, 徐进, 李小英, 郭岳琴, 吴跃国, 李继莲, 姚军. 不同授粉强度对蓝莓柱头响应机制的转录组分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(10): 71-82. |
| [10] | 李相吴, 刘自扬, 徐玉俊, 祝建波, 吴燕民. 真菌诱导子调控紫草素合成的分子机制探究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 78-88. |
| [11] | 姜雪敏, 陈向前, 李红燕, 姜奇彦. 小麦盐胁迫响应的代谢组学分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 43-56. |
| [12] | 肖锐, 谭璐, 吴亮, 张皓, 郭佳源, 杨海君. 镉胁迫下地肤根际与非根际土壤微生物群落结构及多样性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 203-215. |
| [13] | 王潇然, 李笑语, 孙慧, 于海东, 石永春. 硼胁迫下烟草叶片转录组分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 53-64. |
| [14] | 吴香, 李娟, 曹艳, 程艳荣, 闫旭宇, 李玲. 植物根系分泌物响应镉胁迫的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 12-20. |
| [15] | 王云胜, 陈银翠, 程在, 张锦, 张传博. 过表达veA基因对冠突散囊菌次级代谢的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 77-86. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号