




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (6): 72-82.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0903
喻好好1,2( ), 董相书1, 赵颢1, 李忠贤2, 胡发广2, 李亚男2, 娄予强2, 何飞飞1(
), 董相书1, 赵颢1, 李忠贤2, 胡发广2, 李亚男2, 娄予强2, 何飞飞1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-12-08
接受日期:2024-03-28
出版日期:2025-06-15
发布日期:2025-06-23
通讯作者:
何飞飞
作者简介:喻好好 E-mail:y550570@163.com;
基金资助:
Haohao YU1,2( ), Xiangshu DONG1, Hao ZHAO1, Zhongxian LI2, Faguang HU2, Yanan LI2, Yuqiang LOU2, Feifei HE1(
), Xiangshu DONG1, Hao ZHAO1, Zhongxian LI2, Faguang HU2, Yanan LI2, Yuqiang LOU2, Feifei HE1( )
)
Received:2023-12-08
Accepted:2024-03-28
Online:2025-06-15
Published:2025-06-23
Contact:
Feifei HE
摘要:
为丰富小粒咖啡的SNP(single nucleotide polymorphism)位点,并阐明可变剪接(alternative splicing,AS)事件在小粒咖啡响应干旱胁迫中的作用,以小粒咖啡‘Catimor’为供试材料,分别进行7和14 d的干旱胁迫处理,利用RNA-seq技术结合生物信息学方法对小粒咖啡抗旱相关SNP位点和AS事件进行统计分析。结果表明,在所有样品中共鉴定到265 047个SNP位点,转换率和颠换率分别为60.72%和39.28%,分布于11条染色体,其中2号染色体上的SNP最多。位于基因外显子和内含子的SNP位点分别为110 582和100 936个。对SNP位点序列注释发现,SNP位点主要富集于氨基酸合成、运输及碳代谢等方面。AS事件分析表明,在干旱0 d与干旱7 d、干旱7 d与干旱14 d的比较中,分别鉴定到3 809、4 142个差异AS,其中外显子跳跃(skipped exon,SE)是最主要的剪接方式,这些发生AS事件的基因主要与剪接体、mRNA监控等途径显著关联。经差异表达基因与AS基因的比较分析,筛选出LOC113699257、LOC113712703、LOC113741326、LOC113730764共4个在干旱胁迫下持续显著上调的剪接因子,这些因子可能在调控咖啡响应干旱胁迫或根系发育中发挥重要作用。以上研究结果为进一步揭示小粒咖啡响应干旱胁迫的分子机制奠定了基础。
中图分类号:
喻好好, 董相书, 赵颢, 李忠贤, 胡发广, 李亚男, 娄予强, 何飞飞. 干旱胁迫下小粒咖啡SNP位点与可变剪接分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(6): 72-82.
Haohao YU, Xiangshu DONG, Hao ZHAO, Zhongxian LI, Faguang HU, Yanan LI, Yuqiang LOU, Feifei HE. Analysis of SNP Loci and Alternative Splicing Events in Coffea arabica L. Under Drought Stress[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(6): 72-82.

图1 SNP基本特征A:SNP突变类型统计; B:SNP在染色体上的分布情况; C:SNP在参考基因组功能元件上的分布
Fig. 1 Basic characteristics of SNPA: Statistics of SNP mutation types; B: Distribution of all SNP on chromosomes; C: Distribution of SNP on functional elements of the reference genome
| 样品Sample | 移码替换Frameshift substitution | 非移码替换Nonframeshift substitution | 同义单核苷酸突变 Synonymous SNV | 非同义单核苷酸突变 Nonsynonymous SNV | 终止密码子增加 Stopgain | 终止密码子减少 Stoploss | 未知类型Unknown |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK1 | 1 620 | 374 | 36 596 | 34 741 | 111 | 42 | 630 |
| CK2 | 1 634 | 379 | 37 284 | 35 619 | 114 | 39 | 632 |
| CK3 | 1 612 | 347 | 35 002 | 32 972 | 103 | 39 | 605 |
| CK4 | 1 609 | 382 | 36 612 | 34 849 | 109 | 35 | 646 |
| D1 | 1 461 | 298 | 30 708 | 28 819 | 98 | 29 | 587 |
| D2 | 1 440 | 306 | 30 213 | 28 156 | 97 | 29 | 541 |
| D3 | 1 550 | 295 | 30 583 | 28 769 | 103 | 33 | 600 |
| D4 | 1 404 | 282 | 27 954 | 26 104 | 85 | 27 | 533 |
| HD1 | 1 251 | 255 | 25 352 | 23 035 | 70 | 26 | 473 |
| HD2 | 1 281 | 221 | 23 966 | 21 613 | 64 | 25 | 475 |
| HD3 | 1 208 | 239 | 22 441 | 20 450 | 61 | 29 | 390 |
| HD4 | 1 294 | 248 | 24 817 | 22 921 | 70 | 25 | 475 |
表1 编码区SNP变异位点类型分布
Table 1 Distribution of SNP variant loci types in coding region
| 样品Sample | 移码替换Frameshift substitution | 非移码替换Nonframeshift substitution | 同义单核苷酸突变 Synonymous SNV | 非同义单核苷酸突变 Nonsynonymous SNV | 终止密码子增加 Stopgain | 终止密码子减少 Stoploss | 未知类型Unknown |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK1 | 1 620 | 374 | 36 596 | 34 741 | 111 | 42 | 630 |
| CK2 | 1 634 | 379 | 37 284 | 35 619 | 114 | 39 | 632 |
| CK3 | 1 612 | 347 | 35 002 | 32 972 | 103 | 39 | 605 |
| CK4 | 1 609 | 382 | 36 612 | 34 849 | 109 | 35 | 646 |
| D1 | 1 461 | 298 | 30 708 | 28 819 | 98 | 29 | 587 |
| D2 | 1 440 | 306 | 30 213 | 28 156 | 97 | 29 | 541 |
| D3 | 1 550 | 295 | 30 583 | 28 769 | 103 | 33 | 600 |
| D4 | 1 404 | 282 | 27 954 | 26 104 | 85 | 27 | 533 |
| HD1 | 1 251 | 255 | 25 352 | 23 035 | 70 | 26 | 473 |
| HD2 | 1 281 | 221 | 23 966 | 21 613 | 64 | 25 | 475 |
| HD3 | 1 208 | 239 | 22 441 | 20 450 | 61 | 29 | 390 |
| HD4 | 1 294 | 248 | 24 817 | 22 921 | 70 | 25 | 475 |

图2 SNP变异位点功能注释A:GO生物过程富集; B:GO细胞组分过程富集; C:GO分子功能富集; D:KEGG注释
Fig. 2 Functional annotation of SNP variant lociA: Biological process of GO enrichment; B: Cell component of GO enrichment; C: Molecular function of GO enrichment; D: KEGG annotation
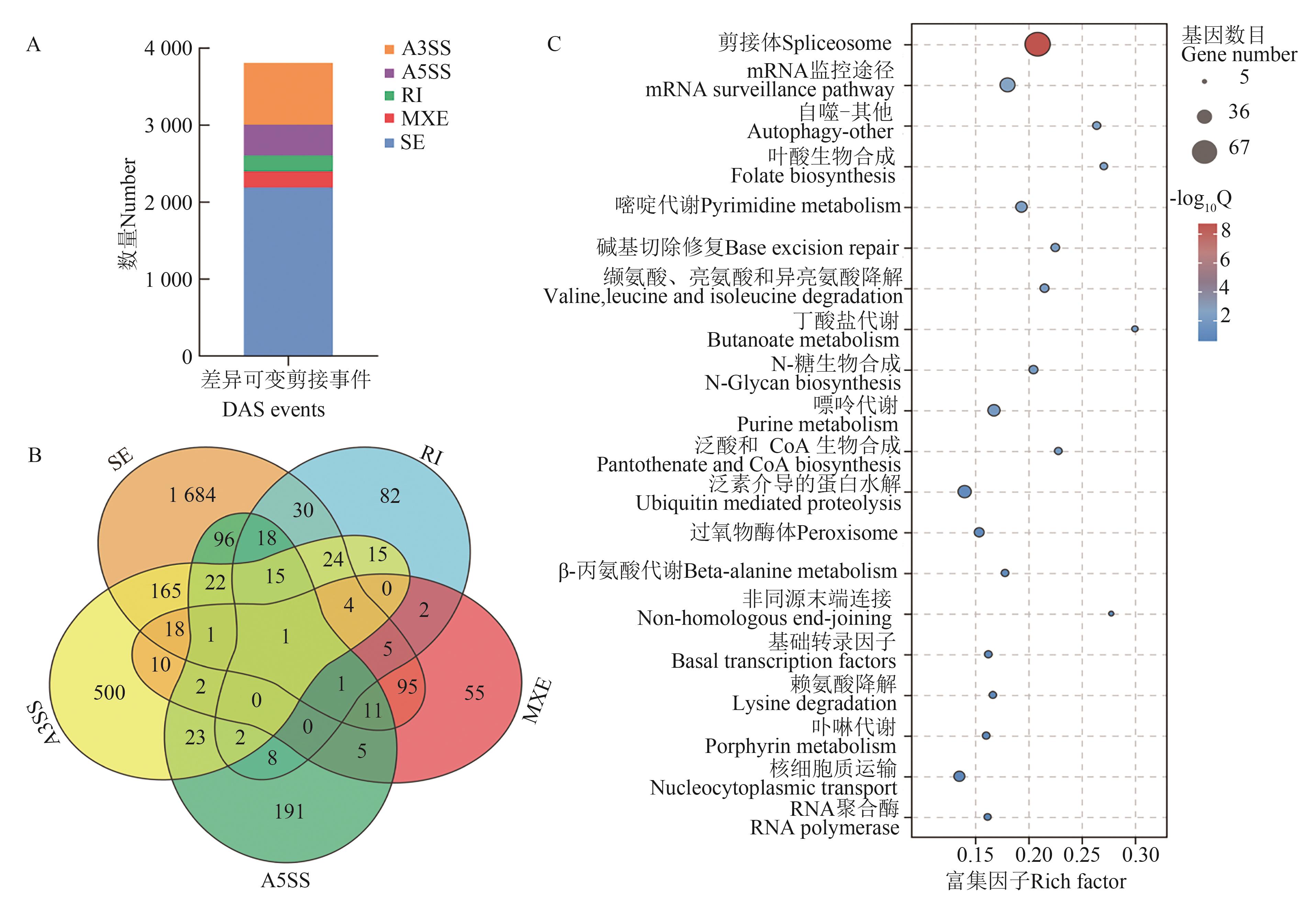
图3 干旱胁迫7 d后差异可变剪接事件统计与功能分析A:显著差异可变剪接事件分类统计; B:显著差异可变剪接事件韦恩分析; C:发生显著差异可变剪接事件的基因功能注释。A3SS—3’端可变剪接;A5SS—5’端可变剪接;RI—内含子保留;MXE—外显子互斥;SE—外显子跳跃
Fig. 3 Statistics and functional analysis of differential AS events after 7 d of drought stress.A: Categorical statistics of significant differential AS events; B: Venn analysis of significant differential AS events; C: Functional annotation of genes with significant differential AS events. A3SS—Alternative 3’ splice site; A5SS—Alternative 5’ splice site; RI—Retained intron; MXE—Mutually exclusive exon; SE—Skipped exon
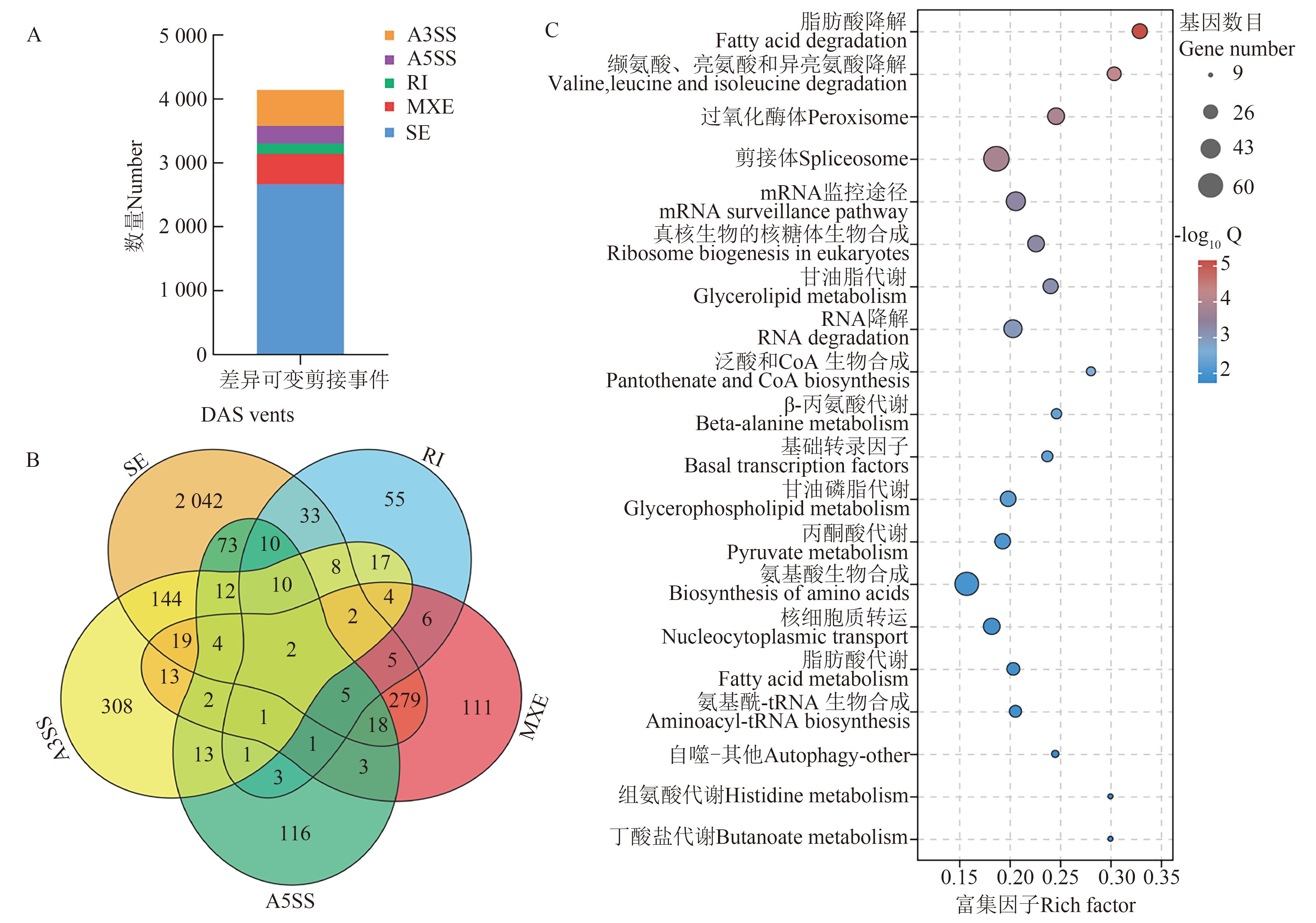
图4 干旱胁迫14 d后差异可变剪接事件统计与功能分析A:显著差异可变剪接事件分类统计; B:显著差异可变剪接事件韦恩分析; C:发生显著差异可变剪接事件的基因功能注释。A3SS—3’端可变剪接;A5SS—5’端可变剪接;RI—内含子保留;MXE—外显子互斥;SE—外显子跳跃
Fig. 4 Statistics and functional analysis of differential AS events after 14 d of drought stress.A: Categorical statistics of significant differential AS events; B: Venn analysis of significant differential AS events; C: Functional annotation of genes with significant differential AS events. A3SS—Alternative 3’ splice site; A5SS—Alternative 5’ splice site; RI—Retained intron; MXE—Mutually exclusive exon; SE—Skipped exon
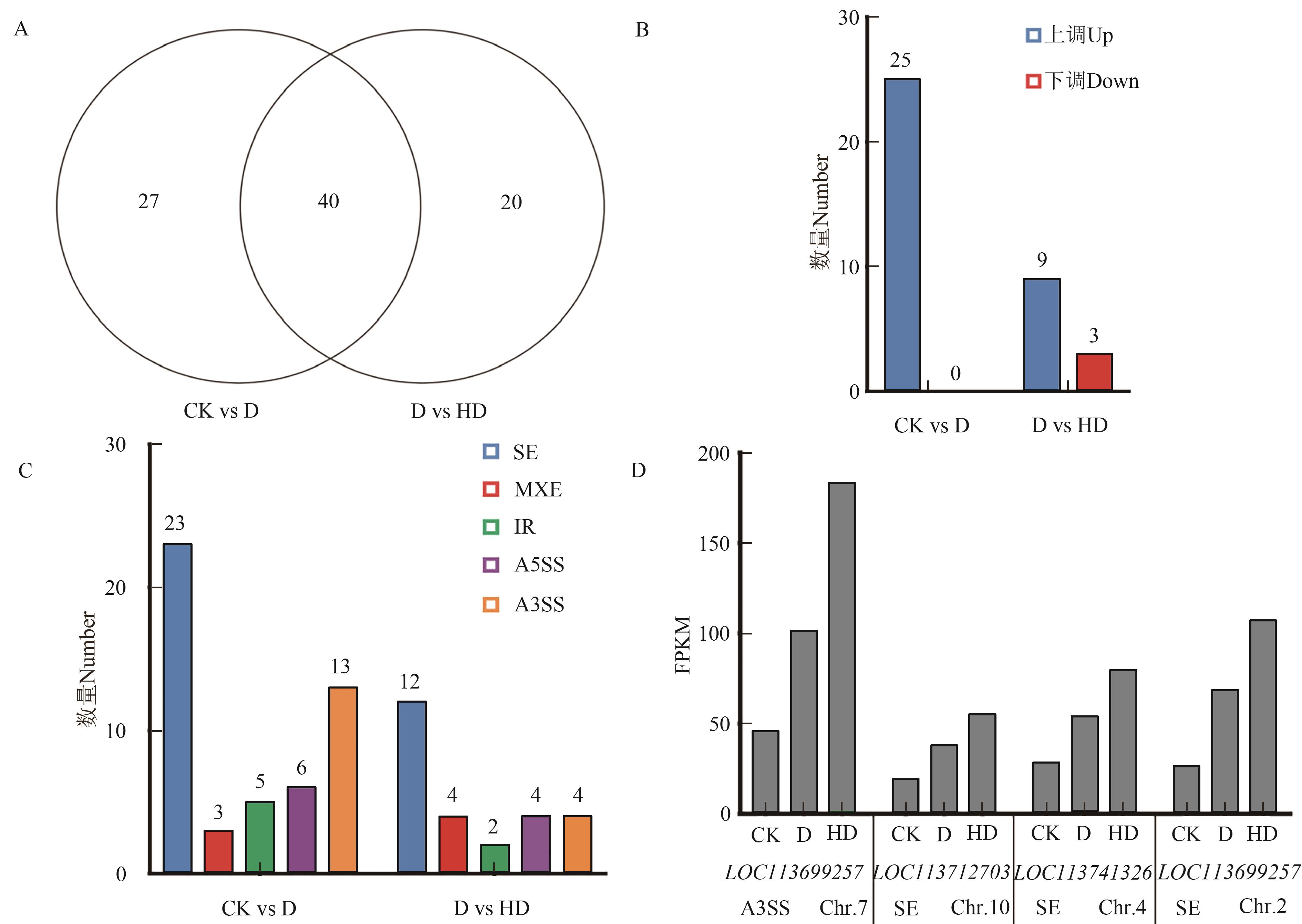
图5 剪接体相关基因在不同条件下的差异表达和可变剪接分析A:剪接体相关基因的韦恩图; B:剪接体相关基因差异表达分析; C:剪接体相关差异基因的可变剪接模式; D:4个剪接体基因在不同条件下的表达模式。A3SS—3’端可变剪接;A5SS—5’端可变剪接;RI—内含子保留;MXE—外显子互斥;SE—外显子跳跃
Fig. 5 Differential expression and AS analysis of spliceosome related genes under different conditionsA: Venn analysis of spliceosome related genes; B: Differential expression analysis of spliceosome related genes; C: AS patterns of spliceosome related differential genes; D: Expression patterns of four spliceosome genes under different conditions. A3SS—Alternative 3’ splice site; A5SS—Alternative 5’ splice site; RI—Retained intron; MXE—Mutually exclusive exon; SE—Skipped exon
| 1 | 黄家雄,李贵平.中国咖啡遗传育种研究进展[J].西南农业学报,2008,21(4):1178-1181. |
| HUANG J X, LI G P.Research progress of coffee breeding in China [J]. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci., 2008,21(4):1178-1181. | |
| 2 | DAMATTA F M, AVILA R T, CARDOSO A A,et al..Physiological and agronomic performance of the coffee crop in the context of climate change and global warming: a review [J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2018,66(21):5264-5274. |
| 3 | 唐国勇,李昆,孙永玉,等.干热河谷不同利用方式下土壤活性有机碳含量及其分配特征[J].环境科学,2010,31(5):1365-1371. |
| TANG G Y, LI K, SUN Y Y,et al..Soil labile organic carbon contents and their allocation characteristics under difierent land uses at dry-hot valley [J]. Environ. Sci., 2010,31(5):1365-1371. | |
| 4 | 于璐.云南地区季节性干旱特征分析[J].农业与技术,2018,38(7):149-150. |
| 5 | 唐立群,肖层林,王伟平.SNP分子标记的研究及其应用进展[J].中国农学通报,2012,28(12):154-158. |
| TANG L Q, XIAO C L, WANG W P. Research and application progress of SNP markers [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2012,28(12):154-158. | |
| 6 | WANG S, WONG D, FORREST K,et al..Characterization of polyploid wheat genomic diversity using a high-density 90,000 single nucleotide polymorphism array [J]. Plant Biotechnol. J., 2014,12(6):787-796. |
| 7 | ZHANG D P, VEGA F E, INFANTE F,et al.. Accurate differentiation of green beans of Arabica and robusta coffee using nanofluidic array of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers [J]. J. AOAC Int., 2020,103(2):315-324. |
| 8 | MEROT-L’ANTHOENE V, TOURNEBIZE R, DARRACQ O,et al.. Development and evaluation of a genome-wide Coffee 8.5K SNP array and its application for high-density genetic mapping and for investigating the origin of Coffea arabica L. [J]. Plant Biotechnol. J., 2019,17(7):1418-1430. |
| 9 | MEKBIB Y, TESFAYE K, DONG X,et al..Whole-genome resequencing of Coffea Arabica L.(Rubiaceae) genotypes identify SNP and unravels distinct groups showing a strong geographical pattern [J].BMC Plant Biol.,2022,22(1):69 [2023-11-15]. . |
| 10 | JOSÉ-LUIS S C, PAULINO P R, BELLO-BELLO J J, et al.. SNP markers identification by genome wide association study for chemical quality traits of coffee (Coffea spp.) germplasm [J]. Mol. Biol. Rep., 2022,49(6):4849-4859. |
| 11 | 何芳练,刘莉莉,蒋慧萍,等.芋全长转录组测序分析及淀粉生物合成相关基因挖掘[J].西南农业学报,2022,35(6):1252-1260. |
| HE F L, LIU L L, JIANG H P, et al.. Full-length transcriptome sequences and the identification of putative genes for starch biosynthesis in Colocasia esculenta [J]. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci., 2022,35(6):1252-1260. | |
| 12 | 杨新森,李来一,刘彩月,等.山栏稻SNP位点与抗旱相关可变剪接鉴定及分析[J].分子植物育种,2023,21(20):6752-6759. |
| YANG X S, LI L Y, LIU C Y, et al.. Identification and analysis of SNP loci and drought resistance related alternative splicing in Shanlan upland rice [J]. Mol. Plant Breed., 2023, 21(20):6752-6759. | |
| 13 | 胡悦,安硕,张小砣,等.盐胁迫和ABA处理下水稻基因组的可变剪接事件分析[J].复旦学报(自然科学版),2023,63(1):47-58. |
| HU Y, AN S, ZHANG X T, et al.. Analysis of alternative splicing events in rice genome under salt stress and ABA treatment [J]. J. Fudan Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2023, 63(1):47-58. | |
| 14 | BARCISZEWSKA-PACAK M, KNOP K, JARMOŁOWSKI A, et al.. Arabidopsis thaliana microRNA162 level is posttranscriptionally regulated via splicing and polyadenylation site selection [J]. Acta Biochim. Pol., 2016,63(4):811-816. |
| 15 | SEOK H Y, LEE S Y, SARKER S, et al.. Genome-wide analysis of stress-responsive genes and alternative splice variants in Arabidopsis roots under osmotic stresses [J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2023,24(19):14580 [2023-11-15]. . |
| 16 | SANYAL S K, KANWAR P, SAMTANI H, et al.. Alternative splicing of CIPK3 results in distinct target selection to propagate ABA signaling in Arabidopsis [J/OL].Front. Plant Sci., 2017, 8:11 [2023-11-15]. . |
| 17 | 周琳.EST:SNP分子标记技术在茶和咖啡中的开发与应用[D].南京:南京农业大学,2017. |
| ZHOU L. Development and application of EST-SNP molecular markers in tea and coffee [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2017. | |
| 18 | 温玉洁,赵雅杰,朱孔艳,等.向日葵抗旱自交系叶片转录组SNP位点信息挖掘[J].中国农学通报,2023,39(9):106-114. |
| WEN Y J, ZHAO Y J, ZHU K Y, et al.. Information mining of SNP sites in the leaf transcriptome of sunflower drought-resistant inbred lines [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2023,39(9):106-114. | |
| 19 | SOUSA T V, CAIXETA E T, ALKIMIM E R,et al..Early selection enabled by the implementation of genomic selection in Coffea Arabica breeding [J/OL].Front. Plant Sci.,2018,9:1934 [2023-11-15]. . |
| 20 | 武瑞瑞,黄家雄,杨阳,等.干旱和复水对4种咖啡叶片叶绿素荧光特性和SPAD的影响[J].热带农业科学,2019,39(10):66-74. |
| WU R R, HUANG J X, YANG Y, et al.. Effect of drought stress and rehydration on chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and SPAD of leaves of four Catimor cultivars of Coffea arabica [J]. Chin. J. Trop. Agric., 2019, 39(10):66-74. | |
| 21 | DE AQUINO S O, DE ARAÚJO CARNEIRO F, RÊGO E C S, et al.. Functional analysis of different promoter haplotypes of the coffee (Coffea canephora) CcDREB1D gene through genetic transformation of Nicotiana tabacum [J]. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult., 2018,132(2):279-294. |
| 22 | CHENG C Y, KRISHNAKUMAR V, CHAN A P,et al..Araport11: a complete reannotation of the Arabidopsis thaliana reference genome [J]. Plant J., 2017,89(4):789-804. |
| 23 | ZHANG Z F, XIAO B Z. Comparative alternative splicing analysis of two contrasting rice cultivars under drought stress and association of differential splicing genes with drought response QTLs [J/OL]. Euphytica, 2018,214(4):73 [2023-11-15]. . |
| 24 | LI S X, YU X, CHENG Z H, et al.. Large-scale analysis of the cassava transcriptome reveals the impact of cold stress on alternative splicing [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2020,71(1):422-434. |
| 25 | XU Y Y, ZENG A S, SONG L X,et al..Comparative transcriptomics analysis uncovers alternative splicing events and molecular markers in cabbage (Brassica oleracea L.) [J].Planta, 2019,249(5):1599-1615. |
| 26 | LEE H J, EOM S H, LEE J H, et al.. Genome-wide analysis of alternative splicing events during response to drought stress in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) [J]. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol., 2020, 95(3):286-293. |
| 27 | MARQUEZ Y, BROWN J W, SIMPSON C,et al..Transcriptome survey reveals increased complexity of the alternative splicing landscape in Arabidopsis [J]. Genome Res., 2012,22(6):1184-1195. |
| 28 | THATCHER S R, DANILEVSKAYA O N, MENG X,et al.. Genome-wide analysis of alternative splicing during development and drought stress in maize [J]. Plant Physiol., 2015,170(1):586-599. |
| 29 | YANG H, LI P, JIN G H, et al.. Temporal regulation of alternative splicing events in rice memory under drought stress [J]. Plant Divers., 2022,44(1):116-125. |
| 30 | PANG H B, WU Y M, LIU Z R,et al..Genome-wide differences of alternative splicing between Oryza sativa ssp.indica and Oryza sativa ssp.Japonica [J/OL].Acta Physiol.Plantarum,2023,45(2):37 [2023-11-15]. . |
| 31 | SONG L, PAN Z, CHEN L,et al.. Analysis of whole transcriptome RNA-seq data reveals many alternative splicing events in soybean roots under drought stress conditions [J/OL].Genes (Basel),2020,11(12):E1520 [2023-11-15]. . |
| 32 | FENG J L, LI J J, GAO Z X,et al.. SKIP confers osmotic tolerance during salt stress by controlling alternative gene splicing in Arabidopsis [J]. Mol. Plant, 2015,8(7):1038-1052. |
| 33 | LAN Y G, ZHANG K M, HE T,et al.. Systematic analysis of the serine/arginine-rich protein splicing factors (SRs) and focus on salt tolerance of PtSC27 in Populus trichocarpa [J]. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 2022,173:97-109. |
| 34 | WENG X, ZHOU X X, XIE S Q,et al..Identification of cassava alternative splicing-related genes and functional characterization of MeSCL30 involvement in drought stress [J]. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 2021,160:130-142. |
| [1] | 秦岭, 王艳珂, 陈二影, 杨延兵, 黎飞飞, 张梦媛, 管延安. ABA缓解谷子幼苗干旱胁迫生理特性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(4): 36-44. |
| [2] | 陈宜新, 杨秀波, 田士军, 王聪, 白志英, 李存东, 张科. 陆地棉GhCOMT28对干旱胁迫的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(4): 45-56. |
| [3] | 薛振宇, 张康康, 张元元, 闫强强, 姚立蓉, 张宏, 孟亚雄, 司二静, 李葆春, 马小乐, 王化俊, 汪军成. 优质抗旱小麦种质的筛选及功能基因检测[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 35-49. |
| [4] | 桂意云, 李海碧, 梁强, 杨荣仲, 韦金菊, 韦德斌, 李文教, 刘昔辉, 周会. 基于人为控水和自然水分胁迫下的甘蔗茎节生长变化[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(7): 25-36. |
| [5] | 魏茜雅, 林欣琪, 梁腊梅, 秦中维, 李映志. 褪黑素引发对干旱胁迫下辣椒种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(4): 46-57. |
| [6] | 张振伟, 董相书, 杨婧, 李学俊, 杞美军, 蒋快乐, 杨永林, 王步天, 施学东, 邱俊超, 陈治华, 葛宇. 小粒咖啡叶绿素合成基因CaPOR的全基因组鉴定及表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(10): 83-97. |
| [7] | 田蕊, 张华, 黄玫红, 邵振启, 李喜焕, 张彩英. 大豆抗旱遗传位点及候选基因发掘[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 69-82. |
| [8] | 王艳成, 张纪月, 冯帅奇, 梁雪, 张振, 董微巍, 姬文秀. 外源促生菌联合有机肥对干旱胁迫下参地土壤性状及人参抗逆性影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 196-202. |
| [9] | 王爽, 侯毅兴, 冯琳骄, 卢倩倩, 周龙. 干旱胁迫对鲜食葡萄叶片解剖结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 40-49. |
| [10] | 张一龙, 孙晓梵, 李硕, 李培英, 孙宗玖. 不同抗旱性狗牙根种质的抗旱生理响应差异分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 59-70. |
| [11] | 唐靓婷, 黄世会, 牛熙, 李升, 王嘉福, 冉雪琴. 发情周期对香猪卵巢生物钟相关基因表达的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(12): 67-84. |
| [12] | 陆青, 梁婷, 王伟伟, 汪德州, 吴娴, 王小燕, 唐益苗. 小麦热激蛋白基因TaHSP90-1的克隆与表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(8): 44-54. |
| [13] | 王莉莉, 殷丛培, 李峰, 杨志敏, 刘芳明, 林柏松, 刘晓静, 刘海军, 孙靖, 单东东, 崔江慧, 张振清. 马铃薯根际土壤细菌群落结构及其对干旱胁迫的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(6): 58-69. |
| [14] | 王方玲, 张明月, 周亚茹, 管庆林, 李欣燕, 钟秋, 赵铭钦. 干旱胁迫下TS-PAA保水剂对雪茄烟生长发育和光合特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(4): 162-172. |
| [15] | 董云萍, 龙宇宙, 林兴军, 莫丽珍, 朱华康, 赵青云, 孙燕. 不同施肥量对小粒咖啡产量、品质及经济效益的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(3): 197-203. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号