




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (5): 49-60.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0847
收稿日期:2023-11-18
接受日期:2024-01-18
出版日期:2025-05-15
发布日期:2025-05-20
通讯作者:
赵小强,余斌
作者简介:毛桃桃 E-mail: m15294392789@163.com
基金资助:
Taotao MAO1( ), Xiaoqiang ZHAO2(
), Xiaoqiang ZHAO2( ), Xiaodong BAI1, Bin YU2(
), Xiaodong BAI1, Bin YU2( )
)
Received:2023-11-18
Accepted:2024-01-18
Online:2025-05-15
Published:2025-05-20
Contact:
Xiaoqiang ZHAO,Bin YU
摘要:
为探究玉米幼苗对低温胁迫的响应机制,以低温敏感型GS2264和耐低温型LY2030玉米幼苗为试材,在10(低温)和22 ℃(对照)处理7 d后测定其幼苗生长、叶片活性氧、渗透调节、抗氧化酶活性、光合性能的变化及抗氧化酶相关基因的表达特征。结果表明,低温胁迫显著抑制玉米幼苗的生长发育。与常温对照相比,低温胁迫下玉米幼苗的苗长、根长、苗鲜重、根鲜重及根冠比分别下降22.98%、31.70%、32.27%、37.40%和7.83%;净光合速率、气孔导度、蒸腾速率、Rubisco活性、水分利用效率、光系统Ⅱ的最大光能转化效率及光系统Ⅱ的潜在光化学活性分别下降42.88%、27.09%、15.23%、59.38%、29.78%、31.90%和32.88%;胞间CO2浓度升高50.84%;玉米幼苗体内O
中图分类号:
毛桃桃, 赵小强, 柏小栋, 余斌. 低温胁迫对玉米幼苗光合性能、抗氧化酶系统及相关基因表达的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(5): 49-60.
Taotao MAO, Xiaoqiang ZHAO, Xiaodong BAI, Bin YU. Effect of Low Temperature Stress on Photosynthetic Performance, Antioxidant Enzyme System and Related Gene Expression in Maize Seedlings[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(5): 49-60.
基因名称 (编码蛋白) Gene ID (encoded protein) | 基因位置 Gene position | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5’-3’) | 基因功能 Gene function |
|---|---|---|---|
GRMZM2G106928 (超氧化物歧化酶 1a Superoxide dismutase 1a, SOD1a) | 染色体1 Chromosome 1 (206405747_206408926 bp) | F: TTCGCCGCTCCCTATTCC R:GTCCTGTCGATATGCACCCA | 超氧化物歧化酶活性(GO:0004784);超氧化物代谢过程(GO:0006801);氧化还原过程(O:0055114);氧化还原过程(GO:0055114) Superoxide dismutase activity (GO:0004784); superoxide metabolic process (GO:0006801); oxidation-reduction process (GO:0055114); oxidation-reduction process (GO:0055114) |
GRMZM2G059991 (超氧化物歧化酶 3 Superoxide dismutase 3, SOD3) | 染色体 6 Chromosome 6 (146855550_146859685 bp) | F: TCACCCAAGAGGGAGATG R: TTGCTCGCAGGATTGTAG | 清除超氧化物自由基(GO:0019430);超氧化物歧化酶活性(GO:0004784);氧化还原酶活性(GO:0016491) Removal of superoxide radicals (GO:0019430); superoxide dismutase activity (GO:0004784); oxidoreductase activity (GO:0016491) |
表1 8个候选基因RT-qPCR分析的引物序列及其功能注释
Table 1 Sequences of primers used in RT-qPCR and functional annotation of 8 candidate genes
基因名称 (编码蛋白) Gene ID (encoded protein) | 基因位置 Gene position | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5’-3’) | 基因功能 Gene function |
|---|---|---|---|
GRMZM2G106928 (超氧化物歧化酶 1a Superoxide dismutase 1a, SOD1a) | 染色体1 Chromosome 1 (206405747_206408926 bp) | F: TTCGCCGCTCCCTATTCC R:GTCCTGTCGATATGCACCCA | 超氧化物歧化酶活性(GO:0004784);超氧化物代谢过程(GO:0006801);氧化还原过程(O:0055114);氧化还原过程(GO:0055114) Superoxide dismutase activity (GO:0004784); superoxide metabolic process (GO:0006801); oxidation-reduction process (GO:0055114); oxidation-reduction process (GO:0055114) |
GRMZM2G059991 (超氧化物歧化酶 3 Superoxide dismutase 3, SOD3) | 染色体 6 Chromosome 6 (146855550_146859685 bp) | F: TCACCCAAGAGGGAGATG R: TTGCTCGCAGGATTGTAG | 清除超氧化物自由基(GO:0019430);超氧化物歧化酶活性(GO:0004784);氧化还原酶活性(GO:0016491) Removal of superoxide radicals (GO:0019430); superoxide dismutase activity (GO:0004784); oxidoreductase activity (GO:0016491) |
基因名称(编码蛋白) Gene ID (encoded protein) | 基因位置 Gene position | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5’-3’) | 基因功能 Gene function |
|---|---|---|---|
GRMZM2G089982 (过氧化物酶72 Peroxidase 72, POD72) | 染色体3 Chromosome 3 (40547079_ 40549178 bp) | F: GGATGTATCCTACGCCGCAA R: TTGTCAAACTTGGCAGGGGT | 过氧化物酶活性(GO:0004601);氧化还原酶活性(GO:0016491);对氧化应激的反应(GO:0006979) Peroxidase activity (GO:0004601); oxidoreductase activity (GO:0016491); response to oxidative stress (GO:0006979) |
GRMZM2G088212 (过氧化氢酶1 Catalase 1, CAT1) | 染色体5 Chromosome 5 (65470836_65475331 bp) | F:CCGAATCCAAAGACCAATR: ATGCCAACATCGTCAAAGAG | 过氧化氢酶活性(GO:0004096);过氧化物酶活性(GO:0004601);氧化应激反应(GO:0006979);对热的响应(GO:0009408) Catalase activity (GO:0004096); peroxidase activity (GO:0004601); response to oxidative stress (GO:0006979); response to heat (GO:0009408) |
GRMZM2G090568 (过氧化氢酶2 Catalase 2, CAT2) | 染色体1 Chromosome 1 (7144389_7146665 bp) | F:CCCCAACTACCTGCTGCTACR: TGGTTATGAACCGCTCTTGC | |
GRMZM2G054300 (L -抗坏血酸过氧化物酶 L-ascorbate peroxidase 1, APX1) | 染色体9 Chromosome 9 (141020666_141024519 bp) | F: TTCAGCTCCCAAGTGACAAAR: TCTAGGCAAACGGAAAATGG | 过氧化物酶活性(GO:0004601);氧化应激反应(GO:0006979);氧化还原过程(GO:0055114) Peroxidase activity (GO:0004601); response to oxidative stress (GO:0006979); oxidation-reduction process (GO:0055114) |
GRMZM2G004211 (抗坏血酸过氧化物酶3 Peroxisomal ascorbate peroxidase 3, APX3) | 染色体 10 Chromosome 10 (101526024_101527964 bp) | F:CCAGATCTGCGAATAAACACAAR: AAATACATGTGCACAGAACTGAAA | 过氧化物酶活性(GO:0004601);氧化应激反应(GO:0006979);氧化还原过程(GO:0055114);氧化还原过程(GO:0055114) Peroxidase activity (GO:0004601); response to oxidative stress (GO:0006979); oxidation-reduction process (GO:0055114); oxidation-reduction process (GO:0055114) |
GRMZM2G172322 (谷胱甘肽还原酶1 Glutathione reductase 1, GR1) | 染色体1 Chromosome 1 (13177263_13183612 bp) | F: CGGTGCAATAGTGGTTGATGR: CCTATTGGTGGTTGGGAGAA | 谷胱甘肽-二硫还原酶活性(GO:0004362);谷胱甘肽代谢过程(GO:0006749);氧化还原过程(GO:0055114) Glutathione-disulfide reductase activity (GO:0004362); glutathione metabolic process (GO:0006749); oxidation-reduction process (GO:0055114) |
GRMZM2G126010 (肌动蛋白1 Actin 1) | 染色体8 Chromosome 8 (102332780_102336553 bp) | F: CGATTGAGCATGGCATTGTCAR: CCCACTAGCGTACAACGAA | ATP结合(GO:0005524);核苷酸结合(GO:0000166) ATP binding (GO:0005524); nucleotide binding (GO:0000166) |
续表1 8个候选基因RT-qPCR分析的引物序列及其功能注释
Continued Table 1 Sequences of primers used in RT-qPCR and functional annotation of 8 candidate genes
基因名称(编码蛋白) Gene ID (encoded protein) | 基因位置 Gene position | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5’-3’) | 基因功能 Gene function |
|---|---|---|---|
GRMZM2G089982 (过氧化物酶72 Peroxidase 72, POD72) | 染色体3 Chromosome 3 (40547079_ 40549178 bp) | F: GGATGTATCCTACGCCGCAA R: TTGTCAAACTTGGCAGGGGT | 过氧化物酶活性(GO:0004601);氧化还原酶活性(GO:0016491);对氧化应激的反应(GO:0006979) Peroxidase activity (GO:0004601); oxidoreductase activity (GO:0016491); response to oxidative stress (GO:0006979) |
GRMZM2G088212 (过氧化氢酶1 Catalase 1, CAT1) | 染色体5 Chromosome 5 (65470836_65475331 bp) | F:CCGAATCCAAAGACCAATR: ATGCCAACATCGTCAAAGAG | 过氧化氢酶活性(GO:0004096);过氧化物酶活性(GO:0004601);氧化应激反应(GO:0006979);对热的响应(GO:0009408) Catalase activity (GO:0004096); peroxidase activity (GO:0004601); response to oxidative stress (GO:0006979); response to heat (GO:0009408) |
GRMZM2G090568 (过氧化氢酶2 Catalase 2, CAT2) | 染色体1 Chromosome 1 (7144389_7146665 bp) | F:CCCCAACTACCTGCTGCTACR: TGGTTATGAACCGCTCTTGC | |
GRMZM2G054300 (L -抗坏血酸过氧化物酶 L-ascorbate peroxidase 1, APX1) | 染色体9 Chromosome 9 (141020666_141024519 bp) | F: TTCAGCTCCCAAGTGACAAAR: TCTAGGCAAACGGAAAATGG | 过氧化物酶活性(GO:0004601);氧化应激反应(GO:0006979);氧化还原过程(GO:0055114) Peroxidase activity (GO:0004601); response to oxidative stress (GO:0006979); oxidation-reduction process (GO:0055114) |
GRMZM2G004211 (抗坏血酸过氧化物酶3 Peroxisomal ascorbate peroxidase 3, APX3) | 染色体 10 Chromosome 10 (101526024_101527964 bp) | F:CCAGATCTGCGAATAAACACAAR: AAATACATGTGCACAGAACTGAAA | 过氧化物酶活性(GO:0004601);氧化应激反应(GO:0006979);氧化还原过程(GO:0055114);氧化还原过程(GO:0055114) Peroxidase activity (GO:0004601); response to oxidative stress (GO:0006979); oxidation-reduction process (GO:0055114); oxidation-reduction process (GO:0055114) |
GRMZM2G172322 (谷胱甘肽还原酶1 Glutathione reductase 1, GR1) | 染色体1 Chromosome 1 (13177263_13183612 bp) | F: CGGTGCAATAGTGGTTGATGR: CCTATTGGTGGTTGGGAGAA | 谷胱甘肽-二硫还原酶活性(GO:0004362);谷胱甘肽代谢过程(GO:0006749);氧化还原过程(GO:0055114) Glutathione-disulfide reductase activity (GO:0004362); glutathione metabolic process (GO:0006749); oxidation-reduction process (GO:0055114) |
GRMZM2G126010 (肌动蛋白1 Actin 1) | 染色体8 Chromosome 8 (102332780_102336553 bp) | F: CGATTGAGCATGGCATTGTCAR: CCCACTAGCGTACAACGAA | ATP结合(GO:0005524);核苷酸结合(GO:0000166) ATP binding (GO:0005524); nucleotide binding (GO:0000166) |
| 自交系 Inbred line | 处理 Treatment | 苗长SL/cm | 根长RL/cm | 苗鲜重SFW/g | 根鲜重RFW/g | 根冠比 RSR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LY2030 | CK | 38.66±2.00 a | 41.63±4.54 a | 0.96±0.05 a | 1.48±0.15 a | 1.54±0.15 a |
| LT | 35.93±2.74 b | 33.47±1.81 b | 0.78±0.09 b | 1.12±0.05 b | 1.42±0.12 b | |
| GS2264 | CK | 30.16±1.76 a | 41.23±4.79 a | 0.83±0.02 a | 1.05±0.10 a | 1.27±0.15 a |
| LT | 18.43±0.49 b | 23.17±3.76 b | 0.45±0.02 b | 0.52±0.03 b | 1.17±0.02 b |
表2 不同温度处理下2份玉米自交系的生长参数
Table 2 Growth parameters of 2 maize inbred lines under different temperature treatments
| 自交系 Inbred line | 处理 Treatment | 苗长SL/cm | 根长RL/cm | 苗鲜重SFW/g | 根鲜重RFW/g | 根冠比 RSR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LY2030 | CK | 38.66±2.00 a | 41.63±4.54 a | 0.96±0.05 a | 1.48±0.15 a | 1.54±0.15 a |
| LT | 35.93±2.74 b | 33.47±1.81 b | 0.78±0.09 b | 1.12±0.05 b | 1.42±0.12 b | |
| GS2264 | CK | 30.16±1.76 a | 41.23±4.79 a | 0.83±0.02 a | 1.05±0.10 a | 1.27±0.15 a |
| LT | 18.43±0.49 b | 23.17±3.76 b | 0.45±0.02 b | 0.52±0.03 b | 1.17±0.02 b |
自交系 Inbred line | 处理 Treatment | 净光合速率 Pn/(μmol·m-2·s-1) | 胞间CO2浓度Ci/(μmol·m-2·s-1) | 气孔导度 Gs/(μmol·m-2·s-1) | 蒸腾速率 Tr/(mmol·m-2·s-1) | Rubisco活性 Rubisco activity/(mmol·m-2·s-1) | 水分利用效率 WUE | 最大光能转化效率 Fv/Fm | PSII的潜在光化学活性 Fv/Fo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LY2030 | CK | 16.70±1.57 a | 52.04±2.41 b | 11.35±0.79 a | 0.49±0.02 a | 0.32±0.006 a | 34.08±1.11 a | 0.73±0.03 a | 2.61±0.11 a |
| LT | 11.23±0.93 b | 62.24±1.25 a | 9.44±0.70 b | 0.36±0.03 b | 0.18±0.001 b | 31.19±1.98 b | 0.55±0.02 b | 1.94±0.13 b | |
| GS2264 | CK | 14.51±1.07 a | 51.15±1.85 a | 10.39±0.74 a | 0.51±0.01 a | 0.28±0.002 a | 28.45±0.78 a | 0.69±0.04 a | 2.57±0.18 a |
| LT | 6.82±1.92 b | 93.41±2.75 b | 6.51±0.51 b | 0.49±0.01 b | 0.07±0.001 b | 13.92±1.91 b | 0.42±0.01 b | 1.54±0.15 b |
表3 不同温度处理下2份玉米自交系的光合参数和叶绿素荧光参数
Table 3 Photosynthetic parameters and chlorophyll fluorescence of 2 maize in inbred lines under different temperature treatments
自交系 Inbred line | 处理 Treatment | 净光合速率 Pn/(μmol·m-2·s-1) | 胞间CO2浓度Ci/(μmol·m-2·s-1) | 气孔导度 Gs/(μmol·m-2·s-1) | 蒸腾速率 Tr/(mmol·m-2·s-1) | Rubisco活性 Rubisco activity/(mmol·m-2·s-1) | 水分利用效率 WUE | 最大光能转化效率 Fv/Fm | PSII的潜在光化学活性 Fv/Fo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LY2030 | CK | 16.70±1.57 a | 52.04±2.41 b | 11.35±0.79 a | 0.49±0.02 a | 0.32±0.006 a | 34.08±1.11 a | 0.73±0.03 a | 2.61±0.11 a |
| LT | 11.23±0.93 b | 62.24±1.25 a | 9.44±0.70 b | 0.36±0.03 b | 0.18±0.001 b | 31.19±1.98 b | 0.55±0.02 b | 1.94±0.13 b | |
| GS2264 | CK | 14.51±1.07 a | 51.15±1.85 a | 10.39±0.74 a | 0.51±0.01 a | 0.28±0.002 a | 28.45±0.78 a | 0.69±0.04 a | 2.57±0.18 a |
| LT | 6.82±1.92 b | 93.41±2.75 b | 6.51±0.51 b | 0.49±0.01 b | 0.07±0.001 b | 13.92±1.91 b | 0.42±0.01 b | 1.54±0.15 b |
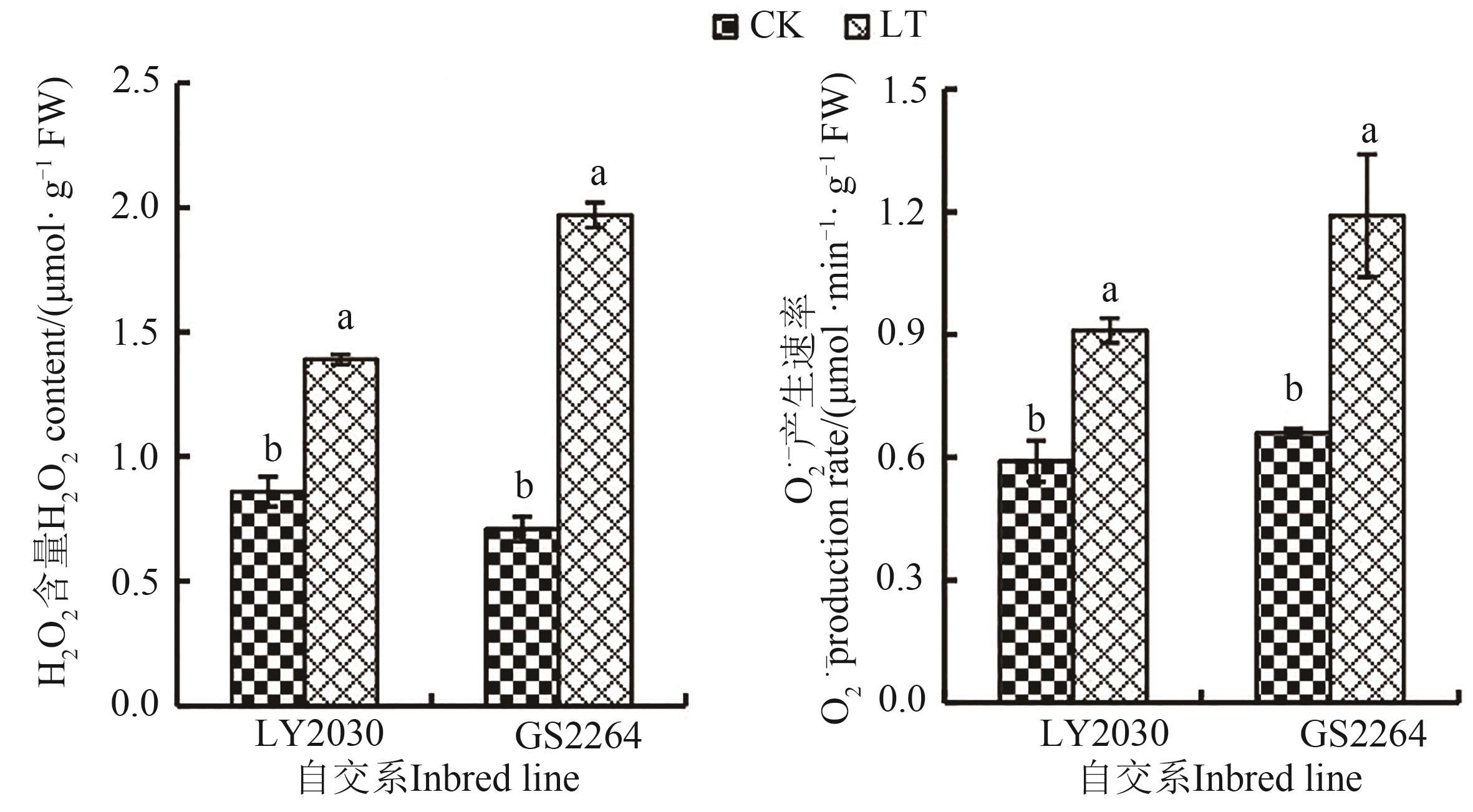
图1 不同温度处理下2份玉米自交系的ROS注:不同小写字母表示同一自交系不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 ROS of 2 maize inbred lines under different temperature treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of same inbred line at P<0.05 level.
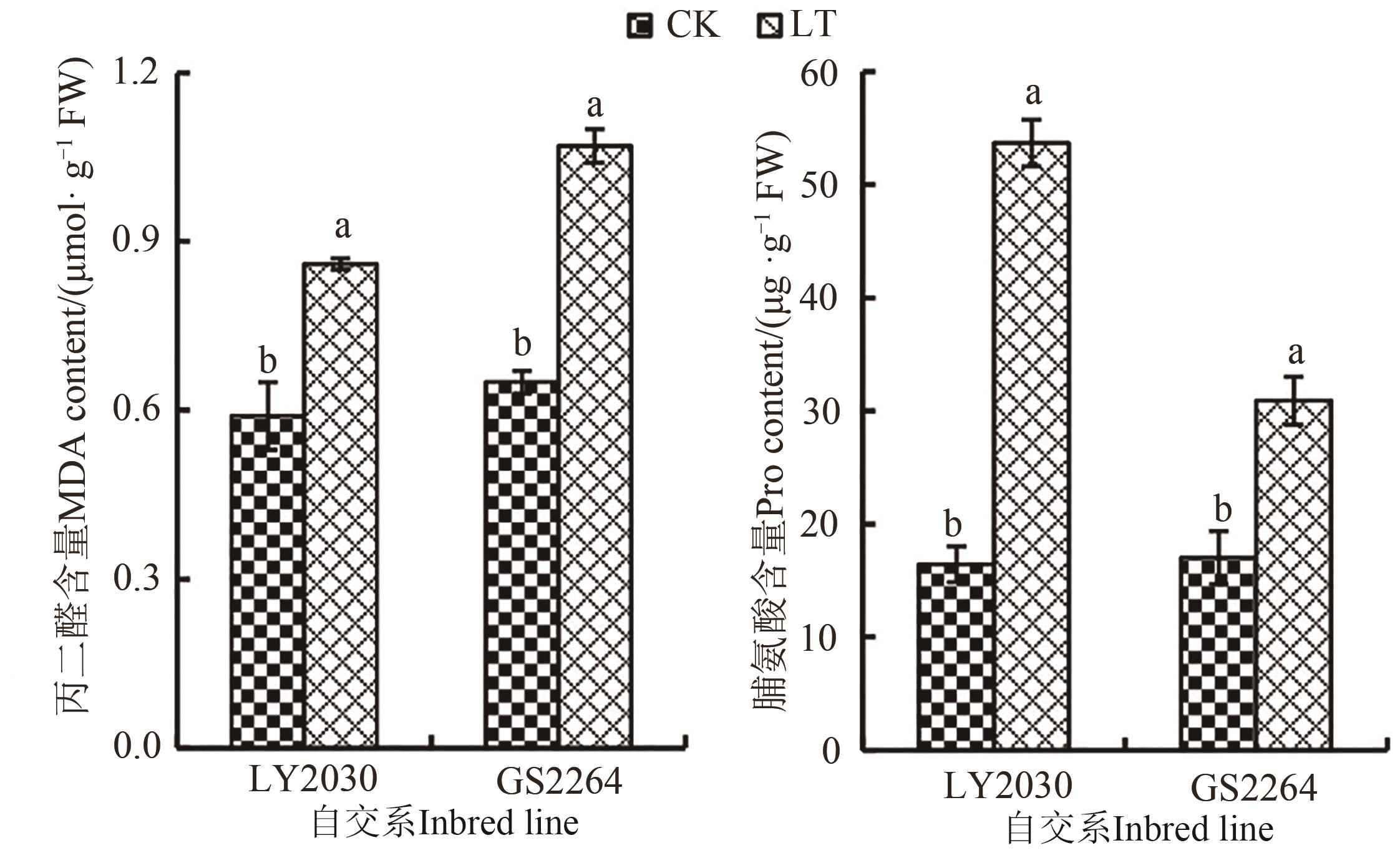
图2 不同温度处理下2份玉米自交系的丙二醛和脯氨酸含量注:不同小写字母表示同一自交系不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 MDA content and proline content of 2 maize inbred lines under different temperature treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of same inbred line at P<0.05 level.
自交系 Inbred line | 处理 Treatment | SOD活性 SOD activity | POD活性 POD activity | CAT活性 CAT activity | APX活性 APX activity | GR活性 GR activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LY2030 | CK | 1.99±0.09 b | 1.01±0.07 b | 0.28±0.03 b | 6.61±0.54 b | 4.06±0.08 b |
| LT | 3.12±0.14 a | 2.07±0.12 a | 0.81±0.02 a | 8.30±0.39 a | 5.05±0.08 a | |
| GS2264 | CK | 2.08±0.08 b | 0.84±0.05 b | 0.29±0.02 b | 6.04±0.25 a | 3.67±0.30 a |
| LT | 2.84±0.14 a | 1.58±0.06 a | 0.66±0.05 a | 5.02±0.14 b | 2.53±0.35 b |
表4 不同温度处理下2份玉米自交系的抗氧化酶活性
Table 4 Antioxidant enzyme activities of 2 maize inbred lines under different temperature treatments (μmol·min-1·g-1)
自交系 Inbred line | 处理 Treatment | SOD活性 SOD activity | POD活性 POD activity | CAT活性 CAT activity | APX活性 APX activity | GR活性 GR activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LY2030 | CK | 1.99±0.09 b | 1.01±0.07 b | 0.28±0.03 b | 6.61±0.54 b | 4.06±0.08 b |
| LT | 3.12±0.14 a | 2.07±0.12 a | 0.81±0.02 a | 8.30±0.39 a | 5.05±0.08 a | |
| GS2264 | CK | 2.08±0.08 b | 0.84±0.05 b | 0.29±0.02 b | 6.04±0.25 a | 3.67±0.30 a |
| LT | 2.84±0.14 a | 1.58±0.06 a | 0.66±0.05 a | 5.02±0.14 b | 2.53±0.35 b |

图3 22个性状间的相关性分析注:Ci—胞间CO2浓度;O2·-—O2·-产生率;MDA—丙二醛;H2O2—H2O2含量;SOD—超氧化物歧化酶;CAT—过氧化氢酶;POD—过氧化物酶;Pro—脯氨酸;APX—抗坏血酸过氧化物酶;GR—谷胱甘肽还原酶;RSR—根冠比;SL—苗长;WUE—水分利用效率;RFW—根鲜重;SFW—苗鲜重;Gs—气孔导度;RL—根长;Pn—净光合速率;Rubisco—二磷酸核酮糖羧化酶;Fv/Fm—最大光能转化效率;Fv/Fo—潜在光化学活性;Tr—蒸腾速率;*和**分别表示P<0.05和P<0.01水平相关显著。
Fig. 3 Correlation analysis among 22 traitsNote:Ci—Intercellular CO2 concentration; O2·-—O2·- production rate; MDA—Malondialdehyde; H2O2—H2O2 content; SOD—Superoxide dismutase activity; CAT—Catalase activity; POD—Peroxidase activity; Pro—Proline; APX—Ascorbate peroxidase activity; GR—Glutathione reductase activity; RSR—Root-shoot ratio; SL—Seedling length; WUE—Water use efficiency; RFW—Root fresh weight; SFW—Seedling fresh weight; Gs—Stomatal conductance; RL—Root length; Pn—Net photosynthetic rate; Rubisco—Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase; Fv/Fm—Maximal light conversion efficiency; Fv/Fo—Potential photochemical activity; Tr—Transpiration rate; * and ** indicate significant correlations at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectoively.
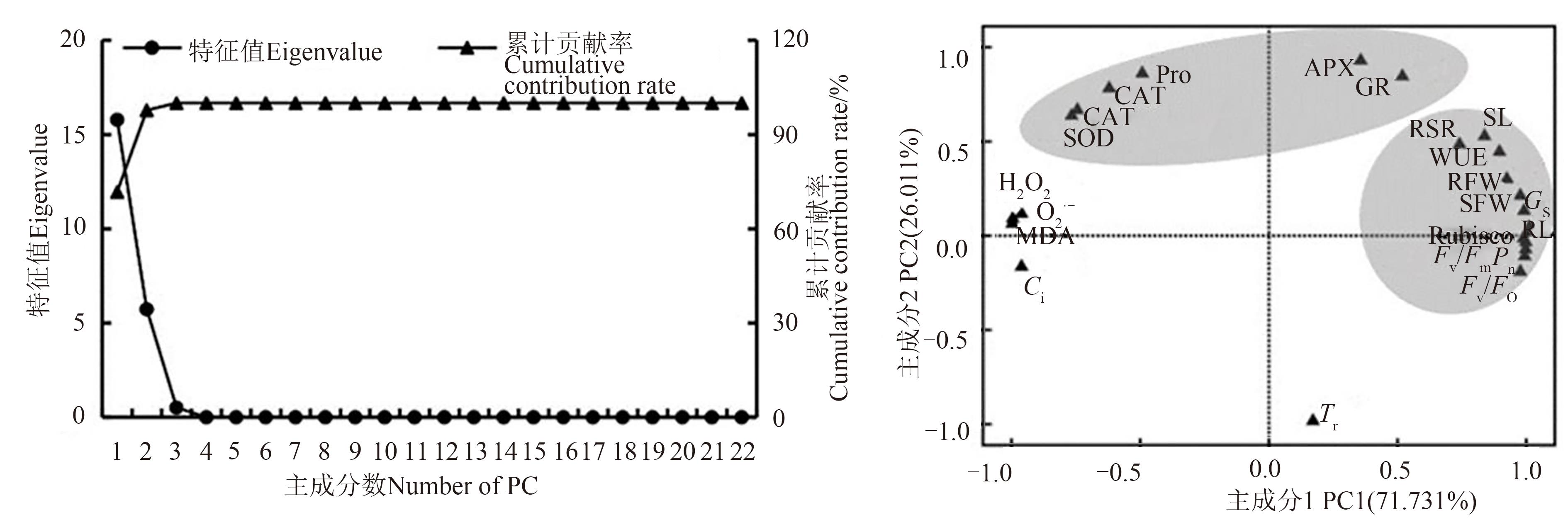
图4 22个性状的主成分分析注:SL—苗长;RL—根长;SFW—苗鲜重;RFW—根鲜重;RSR—根冠比;MDA—丙二醛;Pro—脯氨酸;Pn—净光合速率;Tr—蒸腾速率;Ci—胞间CO2浓度;Gs—气孔导度;WUE—水分利用效率;Fv/Fm—最大光能转化效率;Fv/Fo—潜在光化学活性;O2·-—O2·-产生率;H2O2—H2O2含量;Rubisco—二磷酸核酮糖羧化酶;SOD—超氧化物歧化酶;POD—过氧化物酶;CAT—过氧化氢酶;APX—抗坏血酸过氧化物酶;GR—谷胱甘肽还原酶。
Fig. 4 Principal component analysis among 22 traitsNote:SL—Seedling length; RL—Root length; SFW—Seedling fresh weight; RFW—Root fresh weight; RSR—Root-shoot ratio; MDA—Malondialdehyde; Pro—Proline; Pn—Net photosynthetic rate; Tr—Transpiration rate; Ci—Intercellular CO2 concentration; Gs—Stomatal conductance; WUE—Water use efficiency; Fv/Fm—Maximal light conversion efficiency; Fv/Fo—Potential photochemical activity;O2·-—O2·- production rate; H2O2—H2O2 content; Rubisco—Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase; SOD—Superoxide dismutase; POD—Peroxidase; CAT—Catalase; APX—Ascorbate peroxidase; GR—Glutathione reductase.
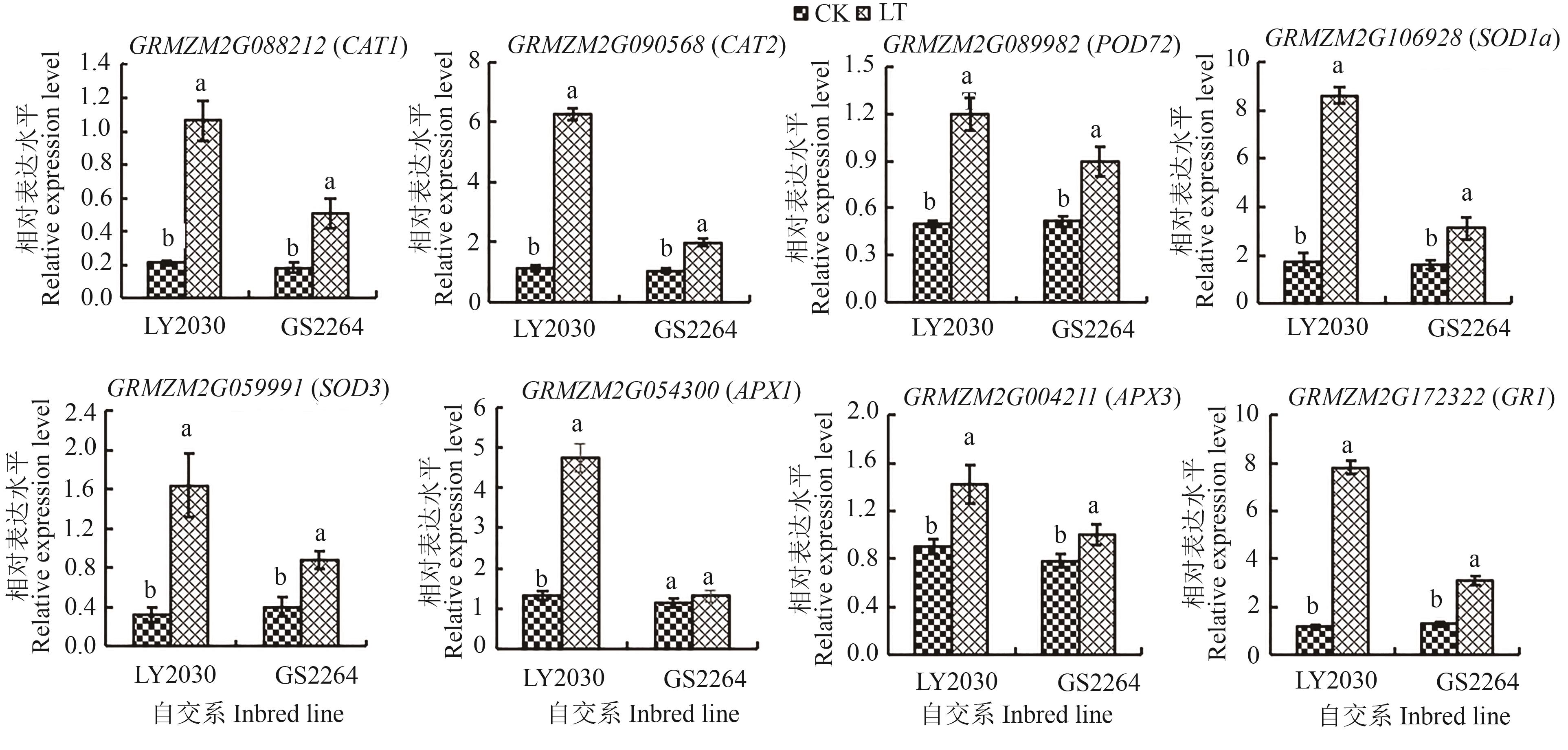
图5 不同温度处理下2份玉米自交系8个候选基因的相对表达水平注:不同小写字母表示同一自交系不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 5 Relative expression level of 8 candidate genes of 2 maize genotypes under different temperature treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of same inbred line at P<0.05 level.
| 1 | ZHAO X, ZHAO C, NIU Y,et al..Understanding and comprehensive evaluation of cold resistance in the seedlings of multiple maize genotypes [J].Plants (Basel),2022,11(14):1881-1901. |
| 2 | 赵小强,方鹏,彭云玲,等.低温胁迫下不同玉米自交系对 外源甜菜碱的生理响应[J].干旱地区农业研究,2020,38(3):81-88. |
| ZHAO X Q, FANG P, PENG Y L, et al.. Physiological response of different maize inbred lines to exogenous GB under low-temperature stress [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2020,38(3):81-88. | |
| 3 | 王丽, 路运才.玉米抗低温灾害调控技术研究进展[J].农学学报,2021,11(5):1-4. |
| WANG L, LU Y C.Regulation technology in maize low temperature stress:research advances [J]. J.Agric.,2021,11(5):1-4. | |
| 4 | SOBKOWIAK A, JOŃCZYK M, JAROCHOWSKA E,et al..Genome-wide transcriptomic analysis of response to low temperature reveals candidate genes determining divergent cold-sensitivity of maize inbred lines [J].Plant Mol.Biol.,2014,85(3):317-331. |
| 5 | 赵小强,彭云玲,方鹏,等.不同外源调节物质对低温胁迫下玉米的缓解效应分析[J].干旱地区农业研究,2018,36(3):184-193, 229. |
| ZHAO X Q, PENG Y L, FANG P, et al.. Mitigation effect analysis of different exogenous regulatory substances on maize under low-temperature stress [J].Agric.Res.Arid Areas,2018,36(3):184-193, 229. | |
| 6 | OBEIDAT W, AVILA L, EARL H, et al.. Leaf spectral reflectance of maize seedlings and Its relationship to cold tolerance [J]. Crop Sci., 2018, 58: 2569-2580. |
| 7 | LI X, HU H, HU X,et al..Transcriptome analysis of near-isogenic lines provides novel insights into genes associated with seed low-temperature germination ability in maize (Zea mays L.) [J]. Plants (Basel),2022,11(7):887-902. |
| 8 | LI Z, HU G, LIU X, et al.. Transcriptome sequencing identified genes and gene ontologies associated with early freezing tolerance in maize [J/OL]. Plant Sci.,2016,7:1477 [2023-10-20]. . |
| 9 | 向婷颖,田茂燕,钟川,等.砧用茄子种质耐冷性鉴定及耐性生理响应[J].南方农业学报,2021,52(1):163-171. |
| XIANG T Y, TIAN M Y, ZHONG C, et al.. Identification of cold resistance and resistance physiological response of eggplant germplasms for rootstock [J].J.South.Agric.,2021,52(1):163-171. | |
| 10 | YAO C, TANG J W, REN H Z, et al..Exogenous activation of the ethylene signaling pathway enhances the freezing tolerance of young tea shoots by regulating the plant’s antioxidant system [J/OL]. Horticulturae, 2023, 9(8):875 [2023-10-20]. . |
| 11 | 赵小强,钟源,周文期,等.外源脯氨酸诱导提高玉米对低温胁迫的生理响应[J].分子植物育种,2023,21(5):1675-1684. |
| ZHAO X Q, ZHONG Y, ZHOU W Q, et al.. Exogenous proline induced improvement of physiological response in Maize (Zea mays) under low-temperature stress [J].Mol. Plant Breed.,2023,21(5):1675-1684. | |
| 12 | 于乔乔.低温胁迫下玉米幼苗光合及呼吸代谢特性的研究[D].哈尔滨:东北农业大学,2021. |
| YU Q Q. Study on the characteristics of photosynthesis and respiratory metabolism of maize seedlings under low temperature stress [D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2021. | |
| 13 | FRACHEBOUD Y, JOMPUK C, RIBAUT J M, et al.. Genetic analysis of cold-tolerance of photosynthesis in maize [J].Plant Mol. Biol., 2004,56(2):241-253. |
| 14 | 宋静爽,吕俊恒,王静,等.植物耐低温机制研究进展[J].湖南农业科学,2019(9):107-113. |
| SONG J S, LYU J H, WANG J, et al.. Advances in research on low temperature tolerance mechanism of plants [J].Hunan Agric. Sci., 2019(9):107-113. | |
| 15 | 王海玲,张雅芳,段维兴,等.甘蔗光合低温耐受性及其与抗旱性的关联[J].生态学杂志,2021,40(11):3577-3584. |
| WANG H L, ZHANG Y F, DUAN W X, et al.. Correlation between photosynthetic chilling resistance and drought tolerance in sugarcane [J]. Chin. J. Ecol., 2021,40(11):3577-3584. | |
| 16 | ASLAM M, FAKHER B, ASHRAF M A, et al.. Plant low-temperature stress: signaling and response [J]. Agronomy, 2022,12 (3):702-702. |
| 17 | 王志军,田又升,赵曾强,等.干旱胁迫下陆地棉光合叶绿素荧光参数与产量品质间的关联性分析[J].分子植物育种,2021,19(21):7202-7212. |
| WANG Z J, TIAN Y S, ZHAO Z Q,et al..Correlation of photosynthetic chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and yield quality in upland cotton under drought stress [J].Mol.Plant Breed., 2021,19(21):7202-7212. | |
| 18 | 程艳,陈璐,米艳华,等.水稻抗氧化酶活性测定方法的比较研究[J].江西农业学报,2018,30(2):108-111. |
| CHENG Y, CHEN L, MI Y H,et al..Comparative study on various methods for determination of activity of antioxidant enzymes in rice [J]. Acta Agric. Jiangxi, 2018,30(2):108-111. | |
| 19 | 曾秀存,孙万仓,方彦,等.白菜型冬油菜抗坏血酸过氧化物酶(APX)基因的克隆、表达及其活性分析[J].作物学报,2013,39(8):1400-1408. |
| ZENG X C, SUN W C, FANG Y, et al.. Cloning,expression,and activity analysis of ascorbate peroxidase (APX) gene from winter turnip rape (Brassica campestris L.) [J].Acta Agron. Sin.,2013,39(8):1400-1408. | |
| 20 | 张腾国,聂亭亭,孙万仓,等.逆境胁迫对油菜谷胱甘肽还原酶基因表达及其酶活性的影响[J].应用生态学报,2018,29(1):213-222. |
| ZHANG T G, NIE T T, SUN W C, et al.. Effects of diverse stresses on gene expression and enzyme activity of glutathione reductase in Brassica campestris [J]. Chin. J.Appl. Ecol., 2018,29(1):213-222. | |
| 21 | WEI S S, WANG X Y, JIANG D,et al..Physiological and proteome studies of maize (Zea mays L.) in response to leaf removal under high plant density [J/OL]. BMC Plant Biol., 2018,18(1):8 [2023-10-20]. . |
| 22 | 杜锦,向春阳,丁建文,等.外源SA和CaCl2对低温胁迫下糯玉米幼苗生理特性的影响[J].干旱地区农业研究,2023,41(6):64-71. |
| DU J, XIANG C Y, DING J W, et al.. Effects of exogenous salicylic acid and calcium chloride on physiology of waxy maize seedlings under low temperature stress [J].Agric.Res.Arid Areas, 2023,41(6):64-71. | |
| 23 | 李海燕,毕文双,王燚,等.外源ALA对低温胁迫下玉米幼苗根系生长及生理特性的影响[J].东北农业大学学报,2019,50(2):9-17. |
| LI H Y, BI W S, WANG Y, et al.. Effect of exogenous ALA on root growth and physiological characteristics of maize seedlings under low temperature stress [J]. J. Northeast Agric. Univ., 2019,50(2):9-17. | |
| 24 | 丁焓赟,何序晨,方芳,等.玉米自交系苗期对低温胁迫的响应机制研究[J].种子,2022,41(10):1-10. |
| DING H B, HE X C, FANG F, et al.. Response mechanism of maize inbred lines to cold stress at seedling stage [J].Seed,2022,41(10):1-10. | |
| 25 | 郑春芳,陈威,刘伟成,等.低温胁迫后红树植物秋茄幼苗光合特性及蔗糖代谢的恢复机制[J].生态学杂志,2020,39(12):4048-4056. |
| ZHENG C F, CHEN W, LIU W C, et al.. Recovery mechanisms of photosynthesis and sucrose metabolism in Kandelia obovata seedlings from low temperature stress [J].Chin.J.Ecol., 2020,39(12):4048-4056. | |
| 26 | 米文博,刘自刚,徐春梅,等.低温胁迫下甘蓝型冬油菜蛋白质组学及光合特性分析[J].分子植物育种,2021,19(21):7222-7231. |
| MI W B, LIU Z G, XU C M, et al.. Proteomics and photosynthetic characteristics analysis of winter rape (Brassica napus L.) under low temperature stress [J]. Mol. Plant Breed., 2021,19(21):7222-7231. | |
| 27 | 路佳明,任红茹,赵灿,等.低温冷害对水稻孕穗期叶片光合特性及抗氧化酶系统的影响[J].扬州大学学报(农业与生命科学版),2023,44(4):15-23, 36. |
| LU J M, REN H R, ZHAO C, et al.. Effects of chilling injury on leaf photosynthetic characteristics and antioxidant enzyme system of rice at booting stage [J]. J. Yangzhou Univ. (Agric. Life Sci.,) 2023, 44(4):15-23, 36. | |
| 28 | 钟信念,梁其干,李有忠,等.蕾期低温胁迫对棉花光合特性的影响[J].新疆农业科学,2022,59(7):1573-1581. |
| ZHONG X N, LIANG Q G, LI Y Z, et al.. Effects of low temperature stress in bud stage on photosynthetic characteristics of cotton [J].Xinjiang Agric. Sci., 2022,59(7):1573-1581. | |
| 29 | NAHAR K, HASANUZZAMAN M, ALAM M M,et al..Exogenous spermidine alleviates low temperature injury in mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) seedlings by modulating ascorbate-glutathione and glyoxalase pathway [J].Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2015,16(12):30117-30132. |
| 30 | WANG W J, SHI S L, KANG W J, et al.. Enriched endogenous free Spd and Spm in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) under drought stress enhance drought tolerance by inhibiting H2O2 production to increase antioxidant enzyme activity [J]. J. Plant Physiol., 2023, 291:154139-154151. |
| 31 | QI Z X, LING F L, JIA D S,et al..Effects of low nitrogen on seedling growth,photosynthetic characteristics and antioxidant system of rice varieties with different nitrogen efficiencies [J].Sci. Rep., 2023,13:19780-19792. |
| 32 | 孙海燕,孔德庸,周娈,等.外源白藜芦醇对渗透胁迫下玉米幼苗抗氧化系统及生长的影响[J].黑龙江八一农垦大学学报,2022,34(4):9-15. |
| SUN H Y, KONG D Y, ZHOU L, et al.. Effects of exogenous resveratrol on antioxidant system and growth of maize seedlings under osmotic stress [J]. J. Heilongjiang Bayi Agric. Univ., 2022,34(4):9-15. | |
| 33 | CAO Q J, LI G, CUI Z G, et al.. Seed priming with melatonin improves the seed germination of waxy maize under chilling stress via promoting the antioxidant system and starch metabolism [J/OL]. Sci. Rep.,2019,9:15044 [2023-10-20]. . |
| 34 | MENG A, WEN D, ZHANG C.Maize seed germination under low-temperature stress impacts seedling growth under normal temperature by modulating photosynthesis and antioxidant metabolism [J/OL].Plant Sci.,2022,13:843033 [2023-10-20]. . |
| 35 | JIANG Z Z, ZHU H G, ZHU H Y, et al.. Exogenous ABA enhances the antioxidant defense system of maize by regulating the AsA-GSH cycle under drought stress [J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14(5): 3071-3085. |
| 36 | 邵文静,张今杰,盖胜男,等.低温胁迫下高粱幼苗叶片生理变化及相关基因表达分析[J].农业生物技术学报,2021,29(5):857-870. |
| SHAO W J, ZHANG J J, GAI S N, et al.. Physiological changes and related genes expression analysis of Sorghum(Sorghum bicolor)seedlings under low temperature stress [J].J.Agric.Biotechnol., 2021,29(5):857-870. | |
| 37 | 赵训超,盖胜男,魏玉磊,等.低温胁迫下玉米根系生理变化及相关基因表达分析[J].农业生物技术学报,2020,28(1):32-41. |
| ZHAO X C, GAI S N, WEI Y L, et al.. Analysis of root physiology and related gene expression in maize (Zea mays) under low temperature stress [J]. J. Agric. Biotechnol., 2020,28(1):32-41. |
| [1] | 罗金城, 朱晓林, 魏小红, 王贤, 王宝强, 杜雪芬. 番茄黄化曲叶病毒胁迫下外源NO对番茄抗氧化物酶基因表达的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(2): 125-135. |
| [2] | 刘萌, 林辰壹, 吴瑞, 曹爽, 梁志豪, 张若楠. 香菇菌丝热胁迫响应及耐热综合评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 90-100. |
| [3] | 张绥林, 李洋, 李琰, 张赟齐, 齐建勋, 侯智霞. 核桃晚霜危害特性及影响机制研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(4): 18-26. |
| [4] | 苗宇, 王婕, 赵尧尧, 张丽佳, 刘美君. 低温胁迫后紫花苜蓿叶片光合作用的恢复特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 80-89. |
| [5] | 贾滢暄, 张树林, 张达娟, 戴伟, 毕相东. 磷恢复对磷饥饿铜绿微囊藻光合色素和部分抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 70-77. |
| [6] | 钟鹏, 苗丽丽, 王建丽, 刘杰, 王晓龙. 油莎豆种质资源低温胁迫生理响应与耐寒性评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 83-96. |
| [7] | 王艳成, 张纪月, 冯帅奇, 梁雪, 张振, 董微巍, 姬文秀. 外源促生菌联合有机肥对干旱胁迫下参地土壤性状及人参抗逆性影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 196-202. |
| [8] | 闫艺薇, 田洁. 大蒜NAC基因家族的鉴定与低温表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 67-76. |
| [9] | 滕泽, 张玉霞, 陈卫东, 丛百明, 田永雷, 张庆昕, 张永亮, 王东儒. 壳聚糖对苜蓿抗寒性及抗寒保护物质含量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 192-198. |
| [10] | 郭胜微, 边思文, 丁建文, 张晓辰, 杨兴, 杜锦, 向春阳. 糯玉米萌发期耐低温品种资源的综合评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 38-47. |
| [11] | 黄丽芳, 龙宇宙, 李金芹, 董云萍, 王晓阳, 陈鹏, 王宪文, 闫林. 低温胁迫对小粒种咖啡幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 60-67. |
| [12] | 燕辉. 基于叶绿素荧光分析的油菜响应低温胁迫机制研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(1): 58-64. |
| [13] | 刘洋, 张启昌, 张璐, 李玉灵. 水肥耦合对蓝靛果忍冬幼苗细根生长及根抗氧化酶的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(9): 197-207. |
| [14] | 肖雨沁, 雷晓, 张明金, 张远盖, 唐珊, 姬鸿飞, 王川, 马翠玲, 景延秋. 三种芽孢杆菌菌剂对烤烟育苗效果的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 85-92. |
| [15] | 孙晓春, 黄文静, 李铂. 水杨酸对干旱胁迫下桔梗幼苗生理生化指标及相关基因表达的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 63-70. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号