




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (3): 178-187.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0474
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles
Tingting NIE1( ), Yiqiang DONG1,2,3(
), Yiqiang DONG1,2,3( ), Helong YANG1,2,3, Asitaiken Julihaiti1, Shijie ZHOU1, Shazhou AN1,2,3
), Helong YANG1,2,3, Asitaiken Julihaiti1, Shijie ZHOU1, Shazhou AN1,2,3
Received:2022-06-05
Accepted:2022-06-30
Online:2023-03-15
Published:2023-05-22
Contact:
Yiqiang DONG
聂婷婷1( ), 董乙强1,2,3(
), 董乙强1,2,3( ), 杨合龙1,2,3, 阿斯太肯·居力海提1, 周时杰1, 安沙舟1,2,3
), 杨合龙1,2,3, 阿斯太肯·居力海提1, 周时杰1, 安沙舟1,2,3
通讯作者:
董乙强
作者简介:聂婷婷 E-mail:1783239058@qq.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Tingting NIE, Yiqiang DONG, Helong YANG, Asitaiken Julihaiti, Shijie ZHOU, Shazhou AN. Effects of Enclosure on Plant and Soil Stoichiometric Characteristics in an Artemisia Desert[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(3): 178-187.
聂婷婷, 董乙强, 杨合龙, 阿斯太肯·居力海提, 周时杰, 安沙舟. 围栏封育对蒿类荒漠植物-土壤碳氮磷化学计量特征的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 178-187.
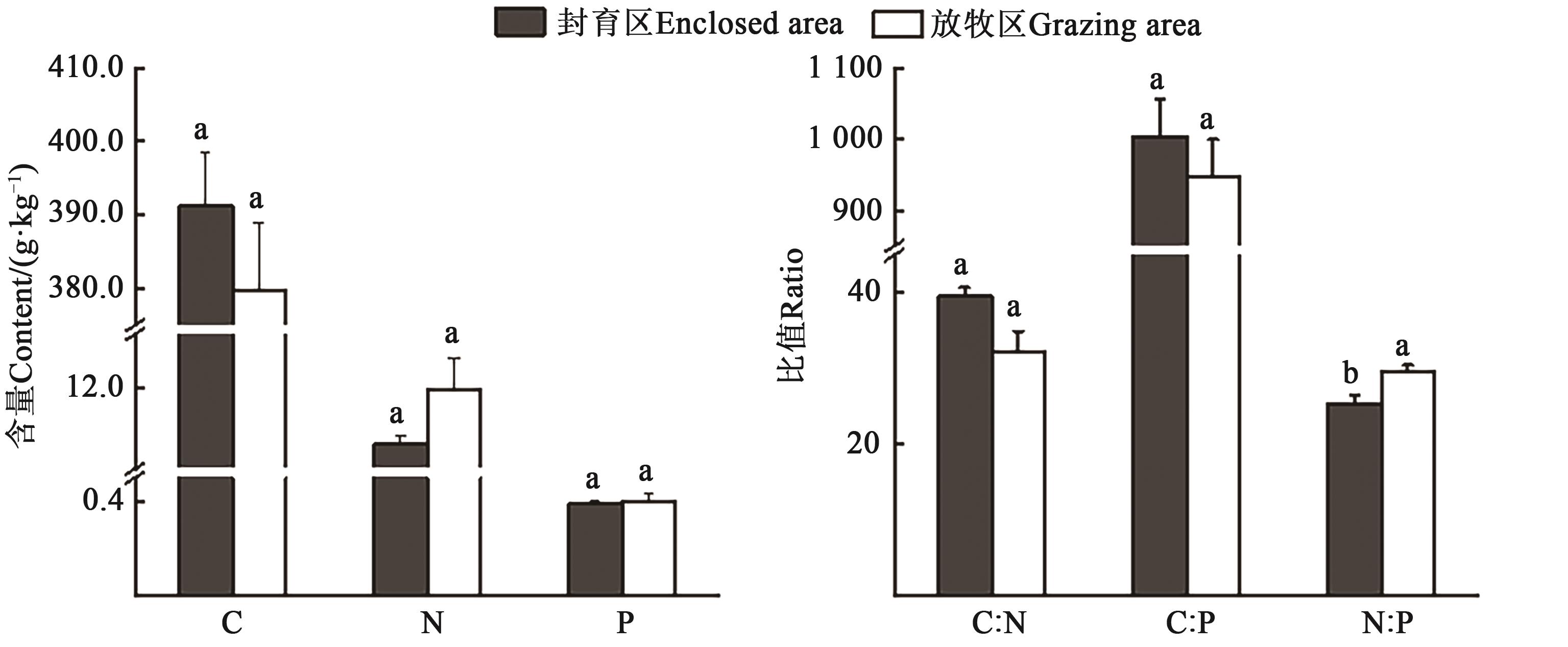
Fig. 1 C, N and P contents of plant stems and stoichiometric characteristics in Artemisia desert plant communities under fencing and sealingNote: Different lowercase letters in same index indicate significant differences at P < 0.05 level.
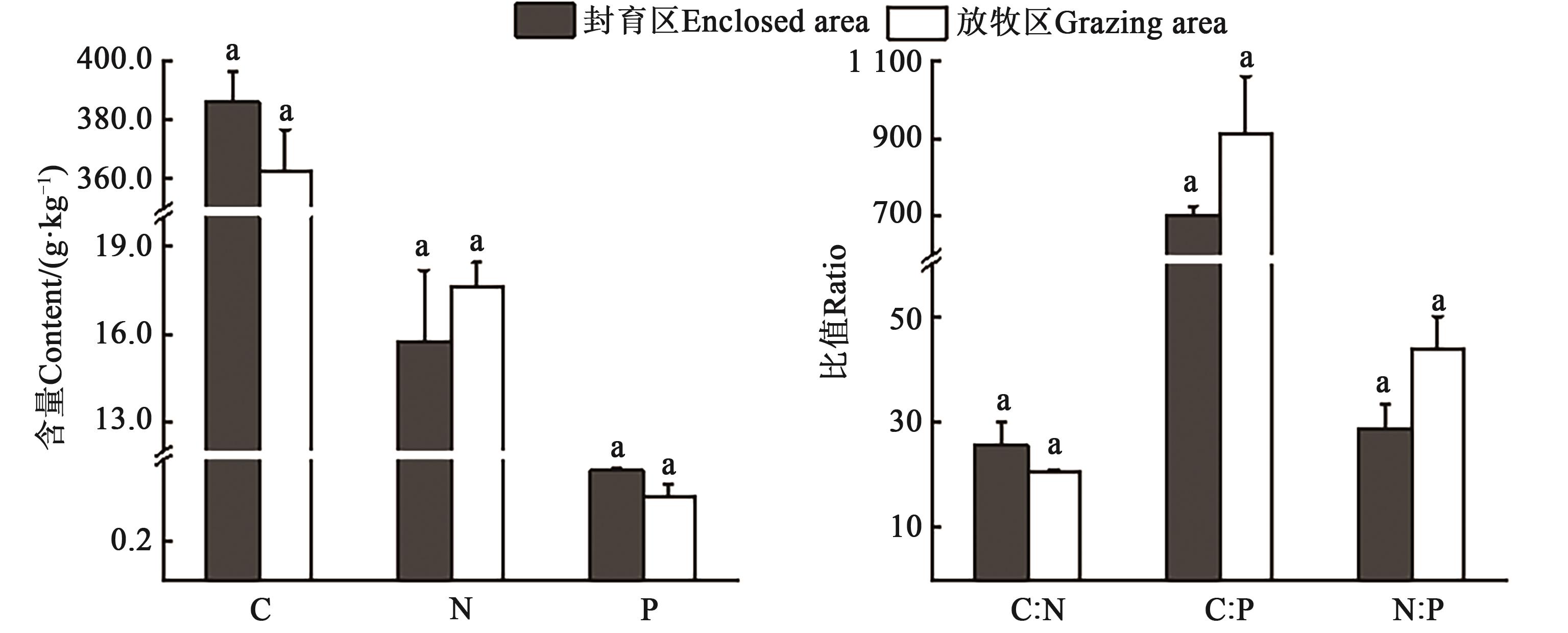
Fig. 2 C, N and P contents of plant leafs and stoichiometric characteristics in Artemisia desert plant communities under fencing and sealingNote: Different lowercase letters in same index indicate significant differences at P<0.05 level.
土层 Layer/cm | 处理 Treatment | C含量 C content/(g·kg-1) | N含量 N content/(g·kg-1) | P含量 P content/(g·kg-1) | C∶N | C∶P | N∶P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—5 | U G | 192.43±64.08 a 242.37±26.18 a | 18.69±1.13 a 18.85±0.96 a | 0.67±0.02 a 0.86±0.11 a | 10.52±3.61 a 13.06±2.00 a | 282.63±84.01 a 301.75±73.74 a | 28.10±2.16 a 22.72±2.67 a |
| 5—10 | U G | 280.64±30.22 a 243.17±10.51 a | 17.91±0.39 a 22.34±4.03 a | 0.68±0.10 a 0.82±0.15 a | 15.67±1.64 a 11.70±2.26 a | 423.86±53.02 a 314.67±47.68 a | 27.57±3.83 a 30.51±9.40 a |
| 10—20 | U G | 275.76±21.35 a 260.67±13.74 a | 17.64±0.56 a 21.74±1.42 a | 0.58±0.03 a 0.75±0.13 a | 15.71±1.53 a 12.03±0.51 b | 477.29±25.48 a 370.67±73.39 a | 30.73±1.98 a 31.01±6.69 a |
| 20—30 | U G | 303.39±20.09 a 209.23±26.74 b | 15.76±1.26 a 19.23±1.12 a | 0.69±0.03 a 0.68±0.07 a | 19.50±1.97 a 10.79±0.82 b | 442.08±11.76 a 312.25±42.76 b | 23.03±1.79 a 28.86±2.82 a |
| 30—50 | U G | 283.93±33.95 a 255.36±33.14 a | 14.34±1.23 b 18.34±1.03 a | 0.66±0.01 a 0.54±0.04 b | 20.46±3.88 a 13.82±1.05 a | 427.78±51.99 a 485.27±91.78 a | 21.56±1.73 b 34.53±3.75 a |
| 50—70 | U G | 297.89±27.30 a 239.16±41.46 a | 13.30±1.01 a 17.55±1.97 a | 0.68±0.09 a 0.59±0.03 a | 22.36±0.86 a 13.59±1.86 b | 459.42±91.23 a 409.47±86.03 a | 20.30±3.20 a 29.75±3.91 a |
Table 1 C, N and P contents and stoichiometric characteristics of below-ground root systems of Artemisia deserts under fencing and sealing
土层 Layer/cm | 处理 Treatment | C含量 C content/(g·kg-1) | N含量 N content/(g·kg-1) | P含量 P content/(g·kg-1) | C∶N | C∶P | N∶P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—5 | U G | 192.43±64.08 a 242.37±26.18 a | 18.69±1.13 a 18.85±0.96 a | 0.67±0.02 a 0.86±0.11 a | 10.52±3.61 a 13.06±2.00 a | 282.63±84.01 a 301.75±73.74 a | 28.10±2.16 a 22.72±2.67 a |
| 5—10 | U G | 280.64±30.22 a 243.17±10.51 a | 17.91±0.39 a 22.34±4.03 a | 0.68±0.10 a 0.82±0.15 a | 15.67±1.64 a 11.70±2.26 a | 423.86±53.02 a 314.67±47.68 a | 27.57±3.83 a 30.51±9.40 a |
| 10—20 | U G | 275.76±21.35 a 260.67±13.74 a | 17.64±0.56 a 21.74±1.42 a | 0.58±0.03 a 0.75±0.13 a | 15.71±1.53 a 12.03±0.51 b | 477.29±25.48 a 370.67±73.39 a | 30.73±1.98 a 31.01±6.69 a |
| 20—30 | U G | 303.39±20.09 a 209.23±26.74 b | 15.76±1.26 a 19.23±1.12 a | 0.69±0.03 a 0.68±0.07 a | 19.50±1.97 a 10.79±0.82 b | 442.08±11.76 a 312.25±42.76 b | 23.03±1.79 a 28.86±2.82 a |
| 30—50 | U G | 283.93±33.95 a 255.36±33.14 a | 14.34±1.23 b 18.34±1.03 a | 0.66±0.01 a 0.54±0.04 b | 20.46±3.88 a 13.82±1.05 a | 427.78±51.99 a 485.27±91.78 a | 21.56±1.73 b 34.53±3.75 a |
| 50—70 | U G | 297.89±27.30 a 239.16±41.46 a | 13.30±1.01 a 17.55±1.97 a | 0.68±0.09 a 0.59±0.03 a | 22.36±0.86 a 13.59±1.86 b | 459.42±91.23 a 409.47±86.03 a | 20.30±3.20 a 29.75±3.91 a |
| 土层Layer/cm | 处理Treatment | C∶N | C∶P | N∶P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—5 | U G | 12.88±1.58 a 8.63±1.85 a | 25.35±1.90 a 26.86±0.63 a | 2.00±0.13 a 3.38±0.62 a |
| 5—10 | U G | 10.82±2.50 a 6.66±1.09 a | 18.76±1.26 a 14.76±1.51 a | 1.90±0.40 a 2.33±0.39 a |
| 10—20 | U G | 9.37±2.79 a 7.41±1.17 a | 14.96±2.30 a 16.76±2.74 a | 1.73±0.22 b 2.26±0.06 a |
| 20—30 | U G | 6.29±1.35 a 8.13±0.96 a | 10.40±0.51 b 16.49±1.77 a | 1.79±0.31 a 2.05±0.15 a |
| 30—50 | U G | 5.91±1.46 a 5.61±0.60 a | 8.93±1.24 a 10.34±0.83 a | 1.62±0.27 a 1.86±0.09 a |
| 50—70 | U G | 5.13±2.43 a 4.65±0.82 a | 4.39±1.78 a 7.98±2.59 a | 0.91±0.06 a 1.65±0.29 a |
Table 2 Chemometric characteristics of C, N and P in Artemisia desert soils under fencing and sealing
| 土层Layer/cm | 处理Treatment | C∶N | C∶P | N∶P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—5 | U G | 12.88±1.58 a 8.63±1.85 a | 25.35±1.90 a 26.86±0.63 a | 2.00±0.13 a 3.38±0.62 a |
| 5—10 | U G | 10.82±2.50 a 6.66±1.09 a | 18.76±1.26 a 14.76±1.51 a | 1.90±0.40 a 2.33±0.39 a |
| 10—20 | U G | 9.37±2.79 a 7.41±1.17 a | 14.96±2.30 a 16.76±2.74 a | 1.73±0.22 b 2.26±0.06 a |
| 20—30 | U G | 6.29±1.35 a 8.13±0.96 a | 10.40±0.51 b 16.49±1.77 a | 1.79±0.31 a 2.05±0.15 a |
| 30—50 | U G | 5.91±1.46 a 5.61±0.60 a | 8.93±1.24 a 10.34±0.83 a | 1.62±0.27 a 1.86±0.09 a |
| 50—70 | U G | 5.13±2.43 a 4.65±0.82 a | 4.39±1.78 a 7.98±2.59 a | 0.91±0.06 a 1.65±0.29 a |
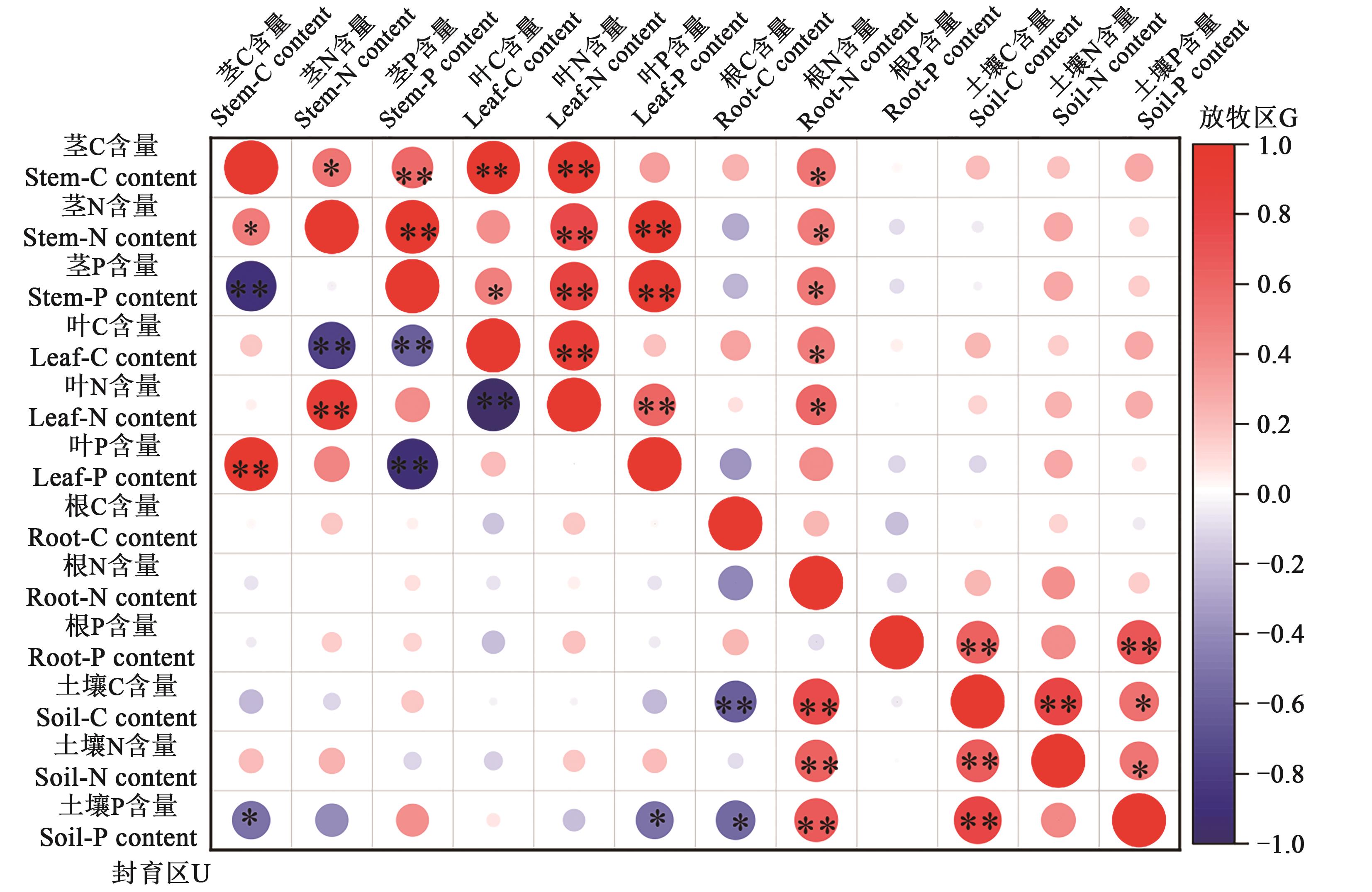
Fig. 4 Correlation analysis of plant and soil nutrientsNote: Lower left corner is the enclosed area (U) and the upper right corner is the grazing area (G); red represents positive correlation and blue represents negative correlation, the darker the color is, the greater the correlation coefficient is; * and ** indicate significant correlations at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels,respectively.
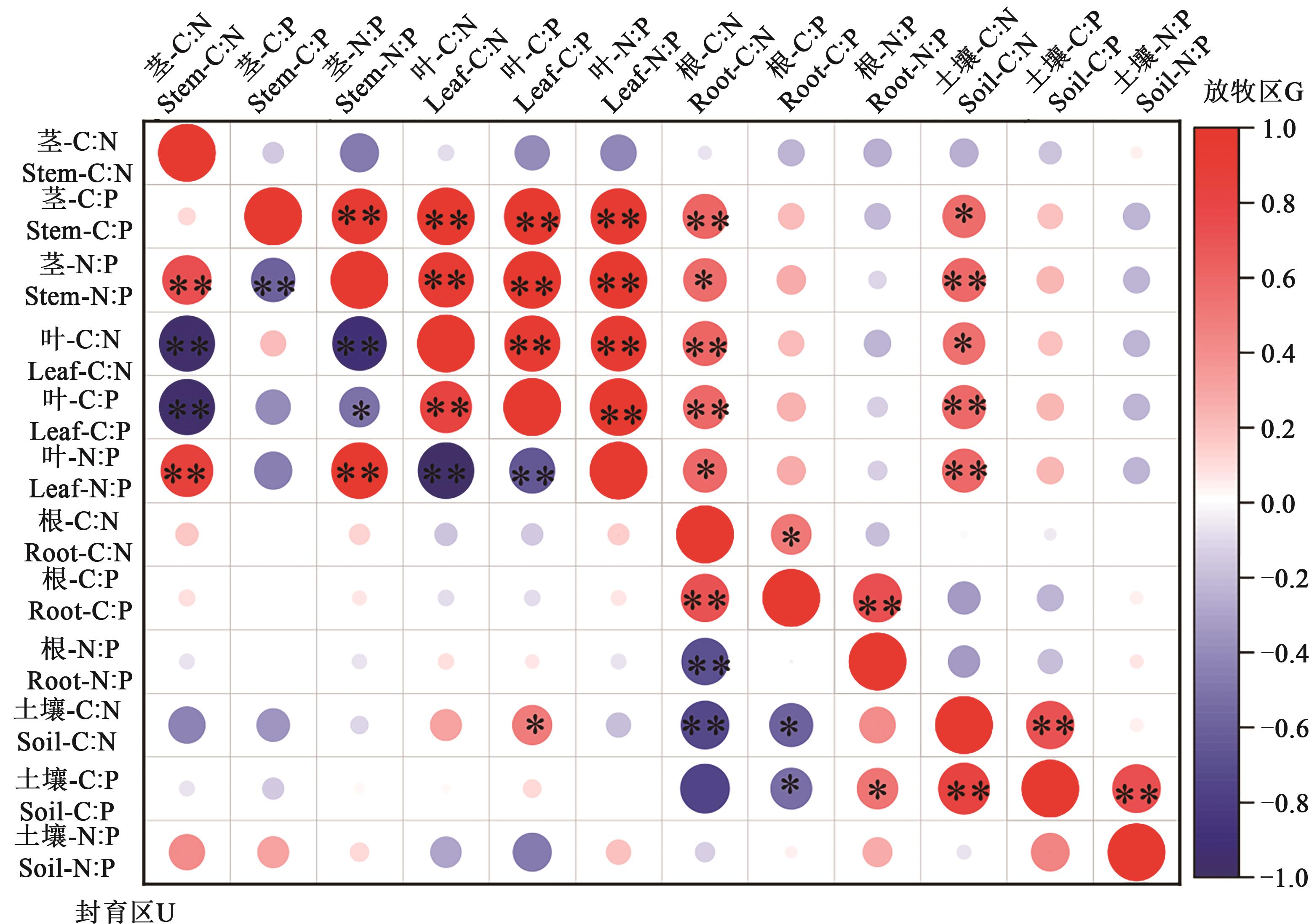
Fig. 5 Correlation analysis of stoichiometric characteristics of plant and soil nutrientsNote: Lower left corner is the enclosed area (U) and the upper right corner is the grazing area (G); red represents positive correlation and blue represents negative correlation, the darker the color is, the greater the correlation coefficient is; * and ** indicate significant correlations at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels,respectively.
| 1 | 何龙, 安沙舟, 靳瑰丽, 等.退化伊犁绢蒿荒漠草地高光谱特征分析[J]. 草地学报, 2014, 22(2): 271- 276. |
| HE L, AN S Z, JIN G L, et al.. Analysis on high spectral characteristics of degraded Seriphidium transiliense desert grassland [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2014, 22(2): 271-276. | |
| 2 | 田新春.新疆草地生态问题思考和对策建议[J]. 草食家畜, 2022(2):48-53. |
| TIAN X C. Causes of grassland degradation in Xinjiang and its impact on soil ecology and biodiversity [J]. Grass-feed. Lives., 2022(2): 48-53. | |
| 3 | 王宏生, 宋梅玲, 王玉琴, 等. 不同恢复措施对黄帚橐吾及毒害草型退化草地群落的影响[J].中国草地学报, 2022, 44(4): 32-39. |
| WANG H S, SONG M L, WANG Y Q, et al.. Effects of different restoration methods on Ligularia virgaurea and toxic weed dominated degraded grassland community [J]. Chin. J. Grassland, 2022, 44(4): 32-39. | |
| 4 | 周华坤, 周立, 刘伟, 等. 封育措施对退化与未退化矮嵩草草甸的影响[J]. 中国草地, 2003,25(5):16-23. |
| ZHOU H K, ZHOU L, LIU W, et al.. The influence of fencing on degraded Kobresia Humilis meadows an nondegraded [J]. Grassland China, 2003, 25(5): 16-23. | |
| 5 | 杨静, 孙宗玖, 柴艳. 封育对沙质荒漠草地植被特征及稳定性影响[J]. 中国草地学报, 2017, 39(3): 65-71, 108. |
| YANG J, SUN Z J, CHAI Y. Effects of enclosure on vegetation characteristics and stability of sandy desert grassland [J]. Chin. J. Grassland, 2017, 39(3): 65-71, 108. | |
| 6 | 吕世海, 冯长松, 高吉喜, 等. 呼伦贝尔沙化草地围封效应及生物多样性变化研究[J]. 草地学报, 2008, 16(5): 442-447. |
| LYU S H, FENG C S, GAO J X, et al.. Study on enclosing effects and biodiversity variation of desertification grassland in Hulunbeir steppe [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2008, 16(5): 442-447. | |
| 7 | 沙文生, 王蕾, 张娜, 等. 围封对荒漠草原植物群落特征的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2021, 49(3): 81-83. |
| SHA W S, WANG L, ZHANG N, et al.. Effects of enclosure on plant community characteristics in desert steppe [J]. Anhui Agric. Sci., 2021, 49(3): 81-83. | |
| 8 | 赵勇钢, 赵世伟, 华娟, 等. 半干旱典型草原区封育草地土壤结构特征研究[J]. 草地学报, 2009, 17(1): 106-112. |
| ZHAO Y G, ZHAO S W, HUA J, et al.. Soil structural properties of enclosed steppe in the semiarid area [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2009, 17(1): 106-112. | |
| 9 | 程杰, 高亚军. 云雾山封育草地土壤养分变化特征[J]. 草地学报, 2007, 15(3): 273-277. |
| CHENG J, GAO Y J. Variability of soil nutrient in enclosed grassland of Yunwu mountain [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2007, 15(3): 273-277. | |
| 10 | 孙宗玖,安沙舟,马金昌.围栏封育对草原植被及多样性的影响[J]. 干旱区研究, 2007, 24(5): 669-674. |
| SUN Z J, AN S Z, MA J C. Effect of fencing on vegetation and diversity of steppe in the middle section of the Tianshan mountains, China [J]. Arid Zone Res., 2007, 24(5): 669-674. | |
| 11 | SUN J, LIU M, FU B, et al.. Reconsidering the efficiency of grazing exclusion using fences on the Tibetan plateau [J]. Sci. Bull., 2020, 65(16): 1405-1414. |
| 12 | CHENG J M, JING G H, WEI L, et al.. Long-term grazing exclusion effects on vegetation characteristics, soil properties and bacterial communities in the semi-arid grasslands of China [J]. Ecol. Eng., 2016, 97(12): 170-178. |
| 13 | 刘凤婵, 李红丽, 董智, 等. 封育对退化草原植被恢复及土壤理化性质影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 2012, 10(5): 116-122. |
| LIU F C, LI H L, DONG Z, et al.. Advances in research on enclosure effects on vegetation restoration and soil physicochemical property of degraded grassland [J]. Sci. Soil Water Conserv., 2012, 10(5): 116-122. | |
| 14 | SHI X M, LI X G, LI C T, et al.. Grazing exclusion decreases soil organic C storage at an alpine grassland of the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau [J]. Ecol. Eng., 2013, 57(3): 183-187. |
| 15 | 李润富, 牛海山, 孔倩, 等. 围栏封育对高寒草原植被-土壤养分含量的影响[J]. 草业科学, 2021, 38(3): 399-409. |
| LI R F, NIU H S, KONG Q, et al.. Effects of exclosure on plant and soil nutrients in an alpine grassland [J]. Pratac. Sci., 2021, 38(3): 399-409. | |
| 16 | 李国旗, 赵盼盼, 邵文山, 等.围封条件下荒漠草原两种植物群落土壤理化性状与酶活性的研究[J].草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 49-59. |
| LI G Q, ZHAO P P, SHAO W S, et al.. Studies on the soil physical and chemical properties and enzyme activities of two fenced plant communities in desert steppe grassland [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2019, 28(7): 49-59. | |
| 17 | 刘兴华, 公彦庆, 陈为峰, 等. 黄河三角洲自然保护区植被与土壤C、N、P化学计量特征[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2018, 26(11): 1720-1729. |
| LIU X H, GONG Y Q, CHEN W F, et al.. C, N and P stoichiometry of typical plants and soils in the Yellow River delta natural reserve [J]. Chin. J. Ecol-Agric., 2018, 26(11): 1720-1729. | |
| 18 | AGREN G I. The C∶N∶P stoichiometry of autotrophs-theory and observations [J]. Ecol. Lett., 2004, 7(3): 185-191. |
| 19 | 刘万德, 苏建荣, 李帅锋, 等.云南普洱季风常绿阔叶林演替系列植物和土壤C、N、P化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(23): 6581-6590. |
| LIU W D, SU J R, LI S F, et al.. Stoichiometry study of C, N and P in plant and soil at different successional stages of monsoon everareen broad-leaved forest in Pu'er, Yunnan province [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2010, 30(23): 6581-6590. | |
| 20 | PANG Y, TIAN J, ZHAO X, et al.. The linkages of plant, litter and soil C:N:P stoichiometry and nutrient stock in different secondary mixed forest types in the Qinling mountains, China [J/OL]. Peer J., 2020, 8(4): e9274 [2022-05-02]. . |
| 21 | 崔雨萱, 孙宗玖, 刘慧霞, 等. 短期封育对蒿类荒漠草地现存生物量及植物群落多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 17-26. |
| CUI Y X, SUN Z J, LIU H X, et al.. Effects of short-term grazing exclusion on standing biomass and plant community diversity in Sagebrush desert [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2020, 29(12): 17-26. | |
| 22 | 李坤, 董乙强, 安沙舟, 等. 短期封育对伊犁绢蒿荒漠群落特征的影响[J]. 草业科学, 2018, 35(5): 978-983. |
| LI K, DONG Y Q, AN S Z, et al.. Effect of short-term fencing on Seriphidium transiliense desert community characteristics [J]. Pratac. Sci., 2018, 35(5): 978-983. | |
| 23 | 董乙强, 孙宗玖, 安沙舟, 等. 放牧强度对伊犁绢蒿种群特征及其群落多样性的影响[J].草地学报, 2016, 24(1): 22-27, 46. |
| DONG Y Q, SUN Z J, AN S Z, et al.. Effect of grazing intensity on population characteristics and community diversity of Seriphidium transiliense [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2016, 24(1): 22-27, 46. | |
| 24 | 阿斯太肯·居力海提, 董乙强, 李靖, 等. 禁牧对不同气候区蒿类荒漠植被和土壤养分及化学计量特征的影响[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2021, 35(11): 157-164. |
| Julihaiti Astaiken, DONG Y Q, LI J, et al.. Effects of grazing exclusion on nutrition and stoichiometry characteristics of Artemisia desert vegetation and soil [J]. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ., 2021, 35(11): 157-164. | |
| 25 | 王森, 张山清, 刘纪疆, 等. 基于GIS的呼图壁县制种玉米精细化气候区划[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2021, 15(4): 130-137. |
| WANG S, ZHANG S Q, LIU J J, et al.. Fine climate division of maize seed production in Hutubi county based on GIS [J]. Desert Oasis Meteo., 2021, 15(4): 130-137. | |
| 26 | 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2013: 72-75. |
| 27 | 郭晨睿, 杨敬坡, 李少伟, 等.围封对藏北高寒草原土壤矿质元素和群落特征的影响[J].草业科学, 2022, 39(4): 645-659. |
| GUO C R, YANG J P, LI S W, et al.. Effects of grazing exclusion by fencing on soil mineral elements and plant community in alpine steppes of the northern Tibetan plateau [J]. Pratac. Sci., 2022, 39(4):645-659. | |
| 28 | 刘岩, 李宝林, 袁烨城, 等. 基于三江源高寒草甸群落结构变化评估围栏封育对草地恢复的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(18): 7125-7137. |
| LIU Y, LI B L, YUAN Y C, et al.. Assessment of grazing exclusion on grassland restoration through the changes of plant community structure of alpine meadow in the Three River headwater region [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2021, 41(18): 7125-7137. | |
| 29 | FRANK D A. Ungulate and topographic control of nitrogenz: phosphorus stoichiometry in a temperate grassland; soils, plants and mineralization rates [J]. Oikos, 2008, 117(4): 591-601. |
| 30 | 范燕敏, 武红旗, 靳瑰丽, 等. 封育对荒漠草地生态系统C、N、P化学计量特征的影响[J].中国草地学报, 2018, 40(3): 76-81. |
| FAN Y M, WU H Q, JIN G L, et al.. Effects of enclosure on stoichiometric characteristics of C, N, P in desert grassland ecosystem [J]. Chin. J. Grassland, 2018, 40(3): 76-81. | |
| 31 | 李永强, 赵萌莉, 韩国栋, 等.不同年限草原撂荒地土壤理化特性研究[J].中国草地学报, 2012, 34(3): 61-64, 69. |
| LI Y Q, ZHAO M L, HAN G D, et al.. Studies on soil physical and chemical properties of abandoned land [J]. Chin. J. Grassland, 2012, 34(3): 61-64, 69. | |
| 32 | 杨合龙. 封育对轻度退化下伊犁绢蒿荒漠植被及土壤养分的影响[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2015. |
| YANG H L. Effects of enclosure on plants and soil nutrients of Seriphidium transiliense desert grassland under light degeneration [D]. Urumqi : Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2015. | |
| 33 | KOERSELMAN W, MEULEMAN, ARTHUR F M. The vegetation N:P ratio: a new tool to detect the nature of nutrient limitation [J]. J. Appl. Ecol., 1996, 33(6): 1441-1450. |
| 34 | 李娜娜, 杨九艳, 贾喆亭, 等. 不同放牧方式对阿拉善左旗主要草场类型群落特征和土壤养分的影响[J]. 草地学报, 2021, 29(5): 991-1003. |
| LI N N, YANG J Y, JIA Z T, et al.. Effects of different grazing patterns on community characteristics and soil nutrients in the main pasture types of Alxa Zuoqi [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2021, 29(5): 991-1003. | |
| 35 | 王悦骅, 靳宇曦, 王忠武, 等. 8年围封对内蒙古荒漠草原植物和土壤的影响[J]. 草地学报, 2021, 29(10): 2339-2345. |
| WANG Y H, JIN Y X, WANG Z W, et al.. Effects of eight years enclosure on plants and soil of desert steppe in Inner Mongolia [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2021, 29(10): 2339-2345. | |
| 36 | 孙海燕, 万书波, 李林, 等. 放牧对荒漠草原土壤养分及微生物量的影响[J]. 水土保持通报, 2015, 35(2): 82-88, 93. |
| SUN H Y, WAN S B, LI L, et al.. Effects of grazing on soil nutrients and microbial biomass in desert steppe [J]. Bull. Soil Water Conserv., 2015, 35(2): 82-88, 93. | |
| 37 | 崔雨萱. 封育对蒿类荒漠草地土壤有机碳及土壤细菌多样性的影响[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2021. |
| CUI Y X. Effect of grazing exclusion on soil organic carbon and soil bacterial diversity in sagebrush desert [D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2021. | |
| 38 | 陈文, 王桔红, 彭玉姣, 等.不同生境中鬼针草(Bidens pilosa)碳氮磷化学计量特征及其营养利用策略[J]. 广西植物, 2018, 38(3): 281-288. |
| CHEN W, WANG J H, PENG Y J, et al.. Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometric characteristics of alien species Bidens pilosa from different habitats and strategy on their nutrient utilization [J]. Guangxi Plants, 2018, 38(3): 281-288. | |
| 39 | 胡艳宇, 乌云娜, 霍光伟, 等. 不同放牧强度下羊草草原群落斑块植被-土壤特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(1): 9-16. |
| HU Y Y, WU Y N, HUO G W, et al..Vegetation and soil characteristics of plant community micro-patches under different grazing intensities [J]. Chin. J. Ecol., 2018, 37(1): 9-16. | |
| 40 | 黄菊莹, 余海龙, 王丽丽, 等.不同氮磷比处理对甘草生长与生态化学计量特征的影响[J].植物生态学报, 2017, 41(3): 325-336. |
| HUANG J Y, YU H L, WANG L L, et al.. Effects of different nitrogen:phosphorus levels on the growth and ecological stoichiometry of Glycyrrhiza uralensis [J]. Chin. J. Plant Ecol., 2017, 41(3): 325-336. | |
| 41 | 赵如梦. 围栏封育对内蒙古草原生态系统化学计量特征的影响[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2019. |
| ZHAO R M. Efffects of fence enclosure on the stoichiometric characteristics of grassland ecosystem in Inner Mongolia [D]. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University, 2019. |
| [1] | Jia YAO, Jiaxin LIU, Yan SU, Xiaojuan SU. Effects of Combined Application of Tobacco Stem Biochar and Nitrogen Fertilizers on Corn Growth and Soil Properties in Seeding Stage [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(3): 140-151. |
| [2] | Yunzhu ZHENG, Shuchen SUN. Effects of Straw Biochar and Straw on Soil Nutrients and Crop Yield in Wheat-Maize Rotation System [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(2): 152-162. |
| [3] | Xiaolan LI, Ruihui LI, Xuehua LI, Ying GUO, Yifeng TIAN, Shujing JIA. Effects of Enclosure on Soil Extracellular Enzyme Activities and Nematode Communities in Ulmus pumila Scatered Woodland of Horqin Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(1): 166-174. |
| [4] | Chuang LU, Haitang HU, Yuan QIN, Heju HUAI, Cunjun LI. Delineating Management Zones in Spring Maize Field Based on UAV Multispectral Image [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(9): 106-115. |
| [5] | Kuiyuan CHEN, Hui LIU, Wei DING. Effect of Glyphosate on Soil Nutrient and the Functional Enzyme Activities in Soybean Fields [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(5): 180-188. |
| [6] | Zhenjia HE, Wangtao FAN, Yichun DU, Qilong WANG. Effects of Water and Fertilizer Coupling on the Physical and Chemical Properties of Rice Soil and Yield Based on Soil Organic Reconstruction [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(3): 176-185. |
| [7] | Lijuan HE, Zhongju MENG, Xiaohong DANG, Tao LYU. Effects of Planting Glycyrrhizauralensis on Mechanical Composition and Nutrients of Aeolian Sandy Soil [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(2): 169-176. |
| [8] | Zhuwen LIU, Longfei YANG, Maolin LIU, Guotao JIA, Qian YAO, Yiqiong MA, Ting CUI, Xinling YANG, Yang CHEN, Liangkun CHENG. Effects of Different Soil Amendments on Soil Nutrients and Inherent Quality of Flue-cured Tobacco [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(11): 190-198. |
| [9] | PU Quanming1, YANG Peng1*, DENG Yuchuan2, XIANG Chengyong1, LIN Bangmin1, LIU Lisha1, SHI Songmei3, HE Zemin1, YONG Lei1. Effects of Different Fertilization Methods on Soil Enzyme Activity, Soil Nutrients and Quality of Spring Cabbage [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(7): 130-139. |
| [10] | WU Xin-jia, WANG Hong, ZHANG Ai-jun, ZHANG Rui-fang, ZHOU Da-mai. Effect of Different Fertilizer Treatments on Nutrient and Enzymatic Activity of Soil in River Ancient Channel [J]. , 2009, 11(6): 118-122. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号