




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2022, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (9): 166-176.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0385
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles
Qian YANG1( ), Na WU1, Cong ZHAO1, Yu HAN1, Zhonghua MA1, Yongsen YANG1, Jili LIU2(
), Na WU1, Cong ZHAO1, Yu HAN1, Zhonghua MA1, Yongsen YANG1, Jili LIU2( )
)
Received:2021-05-08
Accepted:2021-12-09
Online:2022-09-15
Published:2022-10-11
Contact:
Jili LIU
杨茜1( ), 吴娜1, 赵匆1, 韩羽1, 麻仲花1, 杨永森1, 刘吉利2(
), 吴娜1, 赵匆1, 韩羽1, 麻仲花1, 杨永森1, 刘吉利2( )
)
通讯作者:
刘吉利
作者简介:杨茜 E-mail:13619575969@163.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Qian YANG, Na WU, Cong ZHAO, Yu HAN, Zhonghua MA, Yongsen YANG, Jili LIU. Effects of Zinc Fertilizer Application on Physiological Characteristics and Grain Zn Content of Maize in Saline-alkali Soil[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(9): 166-176.
杨茜, 吴娜, 赵匆, 韩羽, 麻仲花, 杨永森, 刘吉利. 施锌对盐碱地玉米生理特性及籽粒锌含量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(9): 166-176.

Fig.1 Pro content in maize leaves under different treatmentNote: Different small letters indicate significant difference among different treatments at the same growth stage at P<0.05 level.
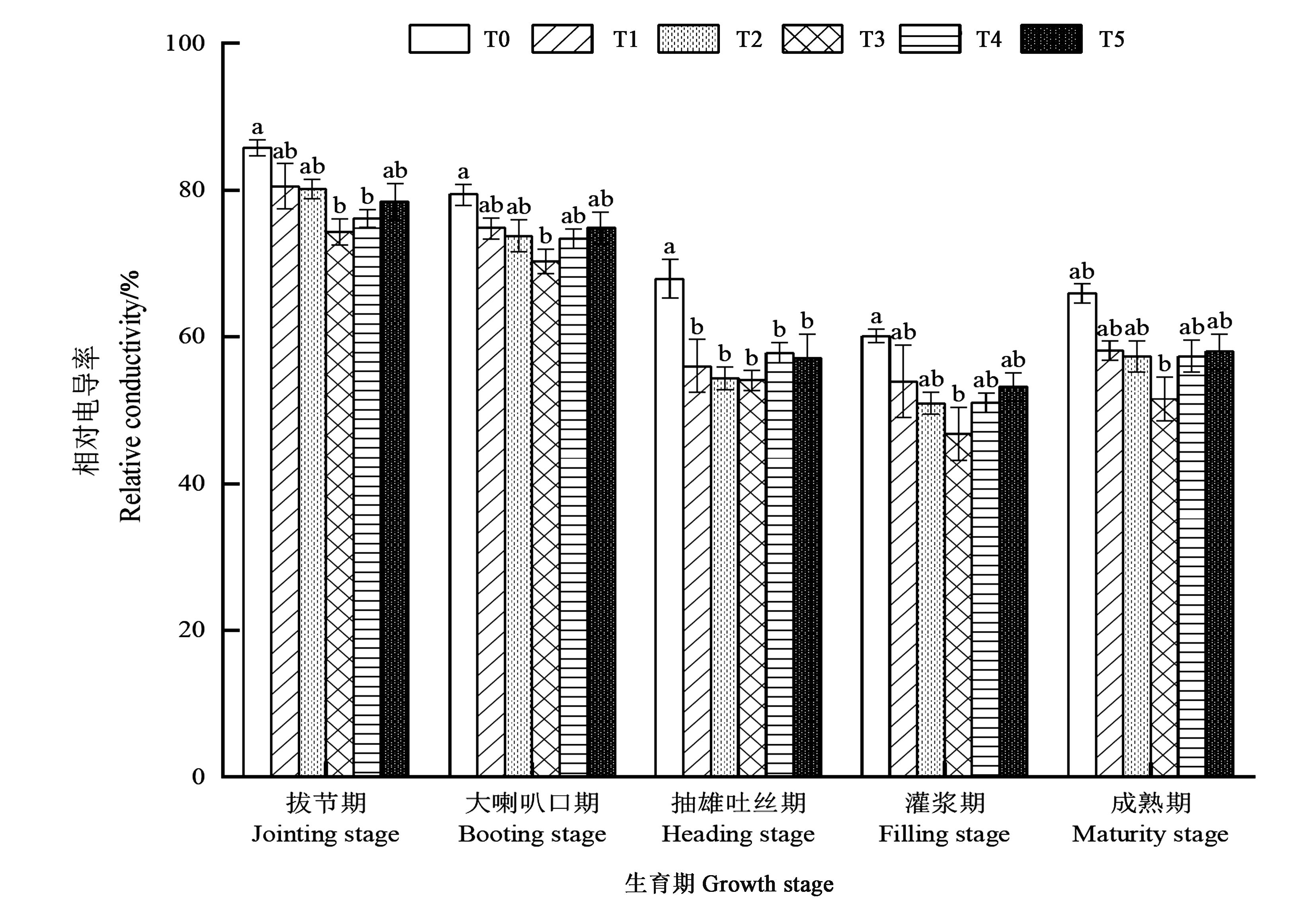
Fig. 2 Relative conductivity in maize leaves under different treatmentsNote: Different small letters indicate significant difference among different treatments at the same growth stage at P<0.05 level.

Fig.3 MDA content in maize leaves under different treatmentsNote: Different small letters indicate significant difference among different treatments at the same growth stage at P<0.05 level.

Fig. 4 SOD activity in maize leaves under different treatmentsNote: Different small letters indicate significant difference among different treatments at the same growth stage at P<0.05 level.
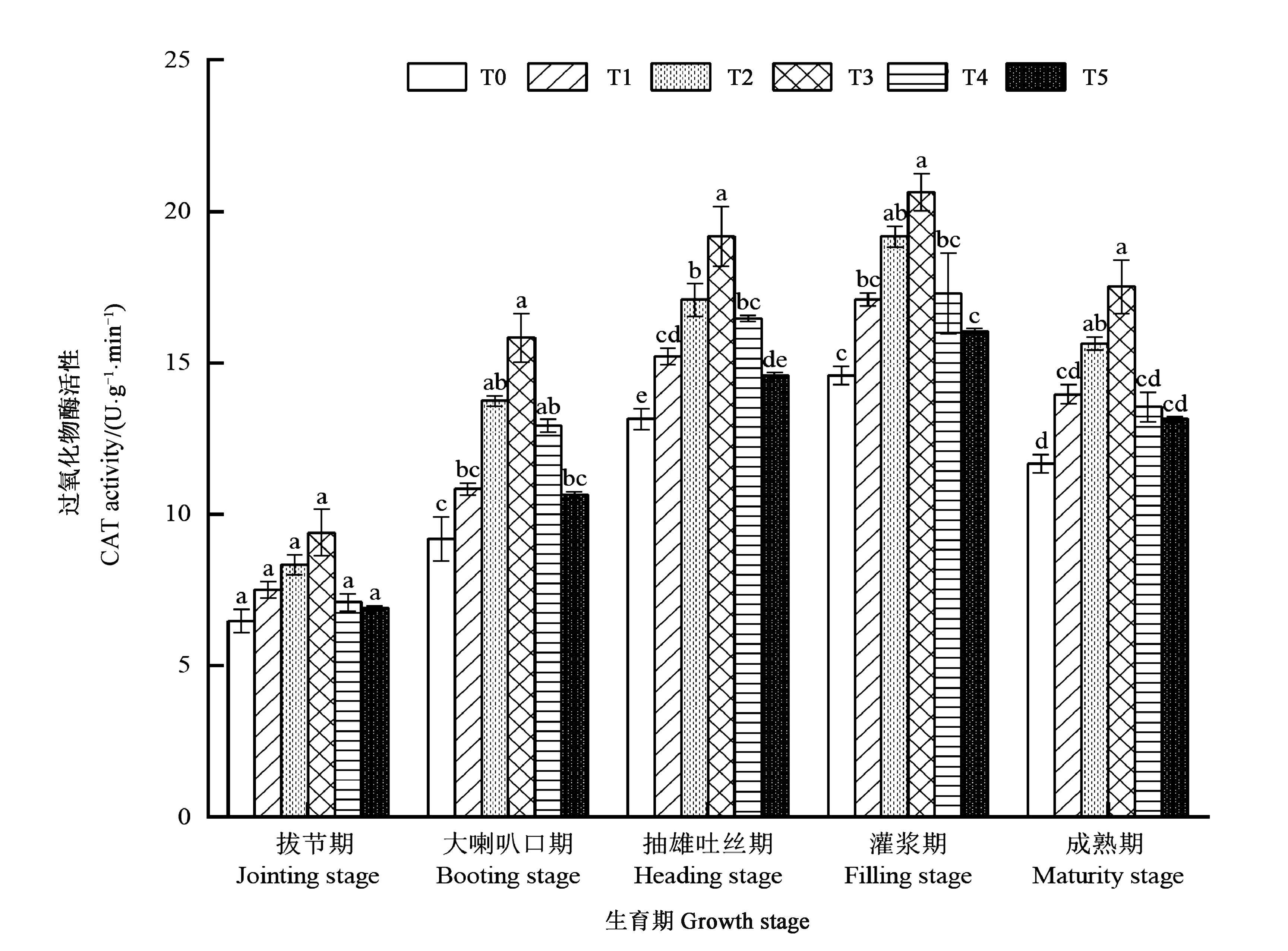
Fig.5 CAT activity in maize leaves under different treatmentsNote: Different small letters indicate significant difference among different treatments at the same growth stage at P<0.05 level.

Fig. 6 POD activity in maize leaves under different treatmentsNote: Different small letters indicate significant difference among different treatments at the same growth stage at P<0.05 level.
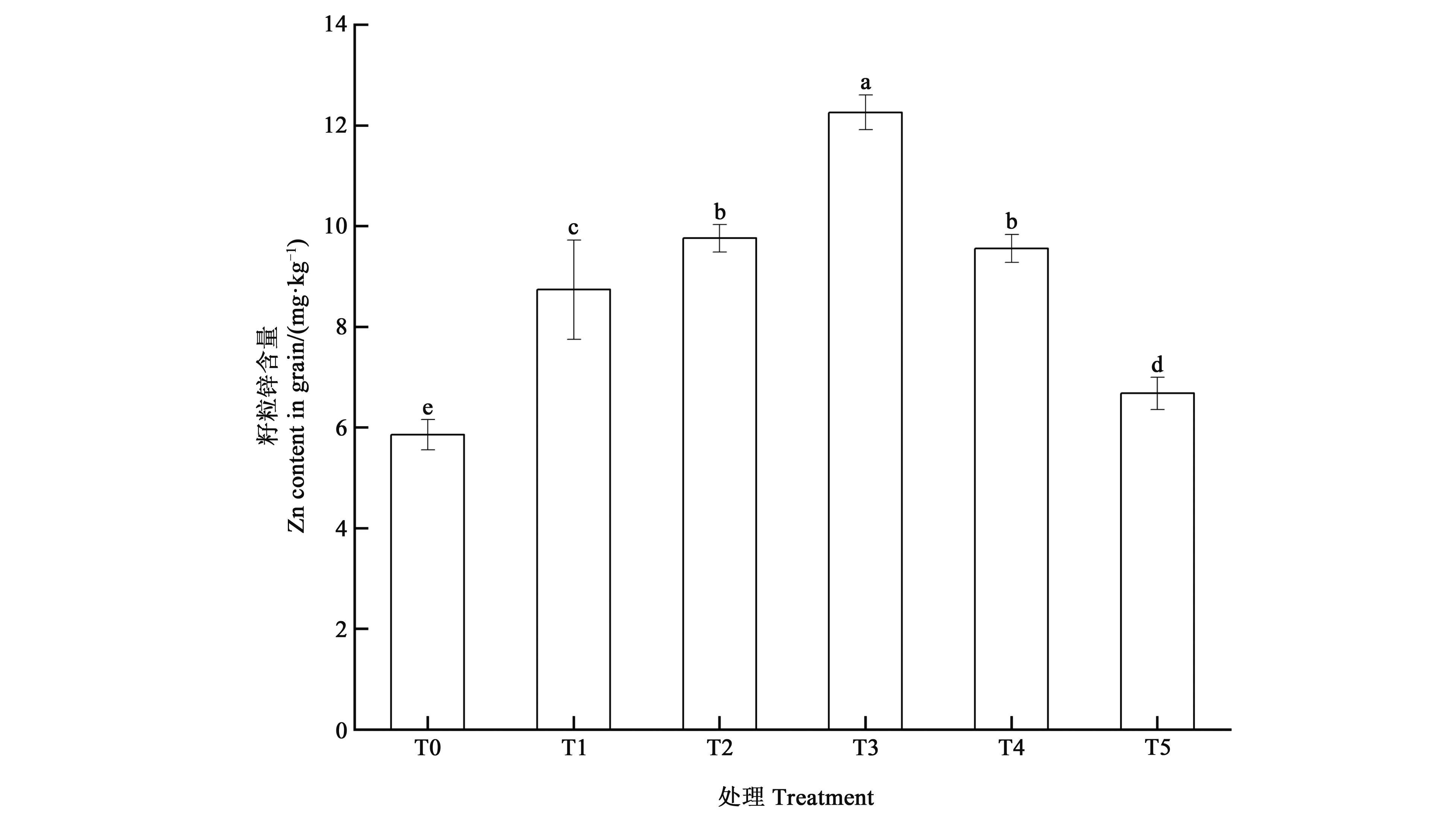
Fig. 7 Grain Zn content of maize under different treatmentsNote: Different small letters indicate significant difference among different treatments at P<0.05 level.
处理 Treatment | 茎中锌素/ (mg·株-1) Zn in leaf/ (mg·plant-1) | 叶中锌素/ (mg·株-1) Zn in stem/ (mg·plant-1) | 锌素转移量/(mg·株-1) Zn transfer quantity/ (mg·plant-1) | 转移率 Transport rate/% | 贡献率 Contribution rate/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 抽雄期Tasseling period | 成熟期Maturation period | 抽雄期Tasseling period | 成熟期Maturation period | 茎 Stem | 叶 Leaf | 茎 Stem | 叶 Leaf | 茎 Stem | 叶 Leaf | |
| T0 | 1.16 f | 0.8 e | 2.24 f | 1.38 e | 0.36 e | 0.86 e | 30.73 b | 38.22 b | 44.38 b | 61.86 b |
| T1 | 1.39 e | 0.97 d | 3.04 e | 1.81 d | 0.42 d | 1.23 d | 30.10 a | 40.46 ab | 43.06 b | 67.97 ab |
| T2 | 1.71 b | 1.15 b | 4.06 d | 2.41 c | 0.56 b | 1.65 c | 32.57 a | 40.73 ab | 48.31 a | 68.98 ab |
| T3 | 1.76 a | 1.18 a | 5.00 a | 2.90 a | 0.58 a | 2.11 a | 32.78 a | 42.06 a | 48.77 a | 72.67 a |
| T4 | 1.69 c | 1.14 b | 4.60 b | 2.74 b | 0.54 b | 1.86 b | 32.09 a | 40.47 ab | 47.26 a | 67.99 ab |
| T5 | 1.53 d | 1.04 c | 4.16 c | 2.54 c | 0.49 c | 1.62 c | 31.88 a | 38.92 ab | 46.81 a | 63.73 ab |
Table 1 Zinc translocation and contribution rate in maize stems and leaves under different treatments
处理 Treatment | 茎中锌素/ (mg·株-1) Zn in leaf/ (mg·plant-1) | 叶中锌素/ (mg·株-1) Zn in stem/ (mg·plant-1) | 锌素转移量/(mg·株-1) Zn transfer quantity/ (mg·plant-1) | 转移率 Transport rate/% | 贡献率 Contribution rate/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 抽雄期Tasseling period | 成熟期Maturation period | 抽雄期Tasseling period | 成熟期Maturation period | 茎 Stem | 叶 Leaf | 茎 Stem | 叶 Leaf | 茎 Stem | 叶 Leaf | |
| T0 | 1.16 f | 0.8 e | 2.24 f | 1.38 e | 0.36 e | 0.86 e | 30.73 b | 38.22 b | 44.38 b | 61.86 b |
| T1 | 1.39 e | 0.97 d | 3.04 e | 1.81 d | 0.42 d | 1.23 d | 30.10 a | 40.46 ab | 43.06 b | 67.97 ab |
| T2 | 1.71 b | 1.15 b | 4.06 d | 2.41 c | 0.56 b | 1.65 c | 32.57 a | 40.73 ab | 48.31 a | 68.98 ab |
| T3 | 1.76 a | 1.18 a | 5.00 a | 2.90 a | 0.58 a | 2.11 a | 32.78 a | 42.06 a | 48.77 a | 72.67 a |
| T4 | 1.69 c | 1.14 b | 4.60 b | 2.74 b | 0.54 b | 1.86 b | 32.09 a | 40.47 ab | 47.26 a | 67.99 ab |
| T5 | 1.53 d | 1.04 c | 4.16 c | 2.54 c | 0.49 c | 1.62 c | 31.88 a | 38.92 ab | 46.81 a | 63.73 ab |
处理 Treatment | 穗长 Ear length/cm | 穗粗 Ear coarse/cm | 秃尖 Bald tip/cm | 行粒数 kernel number | 穗行数 Row number | 穗数 Ear number | 穗粒数 Grain number | 百粒重 100-grain weight/g | 产量 Yield/ (kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | 17.83 b | 47.82 b | 1.71 a | 36.40 b | 14.40 b | 6.81 a | 509.33 b | 33.98 b | 10 025.54 b |
| T1 | 18.58 ab | 48.54 ab | 1.37 ab | 38.10 ab | 15.00 ab | 6.89 a | 549.56 ab | 34.82 ab | 11 162.63 b |
| T2 | 19.23 ab | 49.15 a | 1.13 b | 39.08 ab | 15.40 ab | 6.92 a | 577.33 a | 35.00 ab | 11 874.61 b |
| T3 | 19.47 a | 49.46 a | 0.96 b | 41.00 a | 16.00 a | 6.90 a | 592.89 a | 35.37 a | 12 433.86 a |
| T4 | 18.67 ab | 48.71 ab | 1.16 b | 39.80 ab | 15.20 ab | 6.86 a | 552.22 ab | 34.78 ab | 11 222.41 ab |
| T5 | 18.53 ab | 48.69 ab | 1.67 a | 38.60 ab | 15.00 ab | 6.80 a | 516.22 b | 34.64 ab | 10 349.42 b |
Table 2 Maize yield and compose factor of maize yield under different treatment
处理 Treatment | 穗长 Ear length/cm | 穗粗 Ear coarse/cm | 秃尖 Bald tip/cm | 行粒数 kernel number | 穗行数 Row number | 穗数 Ear number | 穗粒数 Grain number | 百粒重 100-grain weight/g | 产量 Yield/ (kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | 17.83 b | 47.82 b | 1.71 a | 36.40 b | 14.40 b | 6.81 a | 509.33 b | 33.98 b | 10 025.54 b |
| T1 | 18.58 ab | 48.54 ab | 1.37 ab | 38.10 ab | 15.00 ab | 6.89 a | 549.56 ab | 34.82 ab | 11 162.63 b |
| T2 | 19.23 ab | 49.15 a | 1.13 b | 39.08 ab | 15.40 ab | 6.92 a | 577.33 a | 35.00 ab | 11 874.61 b |
| T3 | 19.47 a | 49.46 a | 0.96 b | 41.00 a | 16.00 a | 6.90 a | 592.89 a | 35.37 a | 12 433.86 a |
| T4 | 18.67 ab | 48.71 ab | 1.16 b | 39.80 ab | 15.20 ab | 6.86 a | 552.22 ab | 34.78 ab | 11 222.41 ab |
| T5 | 18.53 ab | 48.69 ab | 1.67 a | 38.60 ab | 15.00 ab | 6.80 a | 516.22 b | 34.64 ab | 10 349.42 b |
指标 Index | 秃尖 Bald tip | 穗长 Ear length | 穗粗 Ear coarse | 穗行数 Row number | 行粒数 Kernel number | 穗数 Ear number | 穗粒数 Grain number per ear | 百粒重 100-kernel weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 穗长Ear length | -0.209 | |||||||
| 穗粗Ear coarse | -0.448 | 0.711** | ||||||
| 穗行数Ear rows | -0.249 | 0.339 | 0.107 | . | ||||
| 行粒数Line grain | -0.513* | 0.205 | 0.515* | -0.070 | ||||
| 穗数Ear number | -0.411 | -0.034 | 0.243 | 0.245 | 0.413 | |||
| 穗粒数Kernel number per ear | -0.612** | 0.447 | 0.607** | 0.472* | 0.795** | 0.463 | ||
| 百粒重100-kernel weight | -0.493* | 0.549* | 0.667** | 0.321 | 0.337 | 0.198 | 0.521* | |
| 产量Yield | -0.658** | 0.464 | 0.664** | 0.471* | 0.768** | 0.578* | 0.972** | 0.655** |
Table 3 Correlation between maize yields and compose factors
指标 Index | 秃尖 Bald tip | 穗长 Ear length | 穗粗 Ear coarse | 穗行数 Row number | 行粒数 Kernel number | 穗数 Ear number | 穗粒数 Grain number per ear | 百粒重 100-kernel weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 穗长Ear length | -0.209 | |||||||
| 穗粗Ear coarse | -0.448 | 0.711** | ||||||
| 穗行数Ear rows | -0.249 | 0.339 | 0.107 | . | ||||
| 行粒数Line grain | -0.513* | 0.205 | 0.515* | -0.070 | ||||
| 穗数Ear number | -0.411 | -0.034 | 0.243 | 0.245 | 0.413 | |||
| 穗粒数Kernel number per ear | -0.612** | 0.447 | 0.607** | 0.472* | 0.795** | 0.463 | ||
| 百粒重100-kernel weight | -0.493* | 0.549* | 0.667** | 0.321 | 0.337 | 0.198 | 0.521* | |
| 产量Yield | -0.658** | 0.464 | 0.664** | 0.471* | 0.768** | 0.578* | 0.972** | 0.655** |
| 1 | 沈汀兰.我国玉米产业发展与粮食安全[J].农经,2021(5): 44-49. |
| 2 | 李新,许志斌,佘奎军,等.宁夏玉米产业的现状和发展[J].种子,2009,28(9):104-106. |
| LI X, XU Z B, SHE K J, et al.. Status and development of maize industry in Ningxia province [J]. Seed, 2009, 28(9): 104-106. | |
| 3 | 李成军,吴宏亮,康建宏,等.宁夏中部干旱区玉米种植保护性耕作及覆盖措施研究[J].农业科学研究,2009,30(4):6-10. |
| LI C J, WU H L, KANG J H, et al.. Study on protective tilling and plastic mulching technique to maize planting in the drought zone of middle Ningxia [J]. J.Agric. Sci., 2009,30(4): 6-10. | |
| 4 | 黄建成,陈国栋,李鹏.宁夏引黄灌区土壤盐渍化现状与改良[J].水土保持研究,2008,15(6):256-258. |
| HANG J C, CHEN G D, LI P. Present situation and improvement of soil Salinity in directly yellow-irrigated areas of Ningxia [J]. Res. Soil Water Convers., 2008, 15(6): 256-258. | |
| 5 | 刘学军,刘平,蒋正文.宁夏扬黄灌区土壤盐渍化防治对策[J].宁夏农林科技,2018,59(9): 54-58. |
| LIU X J, LIU P, JIANG Z W. Control of soil salinization in irrigation area of yellow river in Ningxia [J]. J. Ningxia For. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2018, 59(9):54-58. | |
| 6 | 孙文涛,汪仁,安景文,等.平衡施肥技术对玉米产量影响的研究[J].玉米科学,2008(3):109-111. |
| SUN W T, WANG R, AN J W, et al.. Study on effect of balanced fertilization technology on the yield of corn [J].J. Maize Sci., 2008, 16(3):109-111. | |
| 7 | 孙建华.玉米施锌吸收积累及有效化调控机理的研究[D].长春:吉林农业大学,2013. |
| SUN J H. Studies on influence of zinc fertilizer on the absorption and accumulation of zinc content and the regulatory mechanism of zinc availability [D].Changchun: Jilin Agricultual University, 2013. | |
| 8 | 张金尧,汪洪.锌肥施用与人体锌素营养健康[J].肥料与健康,2020,47(1):11-16, 36. |
| ZHANG J Y, WANG H. Zinc fertilizer application and human Zinc nutrition health [J]. Fert. Health, 2020, 47(1): 11-16, 36. | |
| 9 | 李淑云,董小坤.论锌对人体健康的重要性[J].胜利油田师范专科学校学报,2000(4):52-53. |
| 10 | ISMAIL C. Tansley review No. 111: possible roles of zinc in protecting plant cells from damage by reactive oxygen species [J]. New Phytol., 2000, 146(2): 185-205. |
| 11 | LAMBERS H, BRUNDRETT M C, RAVEN J A, et al.. Plant mineral nutrition in ancient landscapes: high plant species diversity on infertile soils is linked to functional diversity for nutritional strategies [J]. Plant Soil, 2011, 348(1-2):7-27. |
| 12 | 李文宗,张兰,徐妙云,等.富锌玉米的筛选及叶面喷施锌肥对玉米籽粒中矿物元素的影响分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018,20(1):47-54. |
| LI W Z, ZHANG L, XU M Y, et al.. Screening of zinc rich corn and the investigation of mineral element in corn grain sprayed with zinc fertilizer [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Tech., 2018, 20(1):47-54. | |
| 13 | ALLOWAY B J. Soil factors associated with zinc deficiency in crops and humans[J]. Environ. Geochem. Health, 2009, 31(5):537-548. |
| 14 | 王子腾,耿元波.国内外主要粮食作物对施用锌肥响应的研究进展[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2018,24(3):805-816. |
| WANG Z T, GENG Y B. Research advances on the response of main food crops to zinc fertilization at China and abroad [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2018, 24(3): 805-816. | |
| 15 | SHIVAY Y S, KUMAR D, PRASAD R, et al.. Relative yield and zinc uptake by rice from zinc sulphate and zinc oxide coatings onto urea [J]. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst.,2008,80(2): 181-188. |
| 16 | 尚清芳,董莉丽,张建明,等.宁夏银北平原灌淤土耕层土壤微量元素的空间变异性研究[J].安徽农业科学,2010,38(32): 18173-18176. |
| SHANG Q F, DONG L F, ZHANG J M, et al.. Spatial variability of trace elements in irrigation-silted soil in north of yinchuan plain of Ningxia [J]. J. Anhui Agric. Sci., 2010, 38(32): 18173-18176. | |
| 17 | 曹婷,代惠萍.锌胁迫对4种紫花苜蓿叶片生理特性的影响[J].湖北农业科学,2014(10):2365-2367. |
| CAO T, DAI H P. Biochemical characteristics of different alfalfa leaves under zinc stress [J]. Hubei Agric. Sci., 2014(10): 2365-2367. | |
| 18 | 王兴义.锌、铁肥种子处理对玉米生长发育及光合特性的影响[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2016. |
| WANG X Y. Effect of seed treatment of zinc and iron fertilizer on the growth and photosynthetic characteristics of maize [D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2016. | |
| 19 | 杨建肖,杨国航,孙世贤,等.硫酸锌处理对玉米种子萌发的生理效应[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2009(2): 410-415. |
| YANG J X, YANG G H, SUN S X, et al.. Physiological effects of zinc sulphate on maize seed germination [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2009(2): 410-415. | |
| 20 | 孙建华,李志洪,李辛,等.高量施锌肥对玉米Zn吸收和积累及产量的影响[J].水土保持学报,2012,26(4):212-215. |
| SUN J H, LI Z H, LI X, et al.. Influence of high-application of Zinc fertilizers on absorption and accumulation of Zn content and maize yield [J]. J. Soil Water Conser., 2012, 26(4): 212-215. | |
| 21 | 鲁如坤.土壤农业化学分析方法[M].北京:中国农业科技出版社,2000:335-336. |
| 22 | 李合生.植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2000:164-178. |
| 23 | 李超, 唐海明, 汪柯,等. 栽培模式对南方丘陵红壤旱地春玉米生理生化特性及产量的影响[J].华南农业大学学报,2016,37(4): 13-17. |
| LI C H, TANG H M, WANG K, et al.. Effects of cultivation models on physiological and biochemical characteristics and yield of spring maize in hilly red soil upland of southern China [J]. J. South China Agric. Univ., 2016, 37(4): 13-17. | |
| 24 | 黄骥,王建飞,张红生.植物C2H2型锌指蛋白的结构与功能[J].遗传,2004(3): 414-418. |
| HUANG J, WANG J F, ZHANG H S.Structure and function of plant C2H2 type zinc finger protein [J]. Hereditas, 2004(3): 414-418. | |
| 25 | 蔡鑫鑫,杨克军,王玉凤,等.锌肥对寒地春玉米生理生化指标的影响[J].耕作与栽培,2013(5):13-15. |
| CAI X X, YANG K J, WANG Y F, et al.. Effects of zinc on physiological and biochemical indexes of spring maize in cold areas [J]. Tillage Cultiv., 2013(5): 13-15. | |
| 26 | 黄伟东.锌-硼喷施对寒地玉米生理特性及产量品质的影响[D].大庆:黑龙江八一农垦大学,2020. |
| HUANG W D. Effects of zinc-boron spraying on physiological characteristics, yield and quality of maize in cold region [D]. Daqing: Heilongjiang Bayi Agriculture University, 2020. | |
| 27 | 李萌.不同栽培模式和锌肥对干旱半干旱地区夏玉米抗旱性的影响[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2008. |
| LI M. Effect of different cultivation patterns and zinc fertilization on the drought resistance of summer maize in arid and semiarid region [D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2008. | |
| 28 | 李靖,张玉喜,姜雯.不同基因型旱稻早期锌吸收与利用差异研究[J].中国农学通报,2014,30(27): 229-233. |
| LI J, ZHANG Y X, JIANG W. Study on difference of zinc uptake and utilization in early stage of upland rice with different genotypes [J].Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2014, 30(27): 229-233. | |
| 29 | ERENOGLU B, NIKOLIC M, ROMHELD V, et al... Uptake and transport of foliar applied zinc (65Zn) in bread and durum wheat cultivar differing in zinc efficiency [J]. Plant Soil, 2002, 241: 251-257. |
| 30 | CAKMANK I, PFEIFFER W H, MCCLAFFERTY B. Bio-fortification of durum wheat with zinc and iron [J]. Cereal Chem., 2010, 87: 10-20. |
| 31 | 毛晖.锌肥与水分对旱地缺锌区玉米生长及品质的影响[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2013. |
| KANG H. Effect of zinc fertilizer and water on maize growth and quality in zinc different area of dryland [D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2013. | |
| 32 | 康蓉,牛建彪,陈政仁,等.不同锌肥组合处理对玉米农艺性状和产量的影响[J].大麦与谷类科学,2019,36(4): 35-38. |
| KANG R, NIU J B, CHEN Z R, et al.. Effects of different zinc-fertilizer combinations on the agronomic characters and yield of maize [J]. Barley Cereal Sci., 2019, 36(4): 35-38. | |
| 33 | 曹殿云.硫、锌肥对玉米生长发育、元素吸收及产量的影响[D].沈阳:沈阳农业大学,2017. |
| CAO D Y. Effect of sulfur and zinc fertilizer on growth, element absorption and yield of maize [D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2017. |
| [1] | Shuai WANG, Wei SONG, Ronghuan WANG, Jiuran ZHAO. Progress of Maize Biology Research in China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(7): 23-31. |
| [2] | Ming CHENG, Ying ZHU, Xiaonan WANG, Ping LUO, Yong CHEN, Zhuanfang HAO, Zhangying XI. Drought Resistance Regulated by Allelic Variations of ZmSNAC13 in Maize [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(5): 24-31. |
| [3] | Guanglei CHENG, Jun QIU, Xiaoguang WANG, Tianjun XU, Chuanyong CHEN, Chunyuan ZHANG, Qianqian XIA, Yuanqi WU, Jiuran ZHAO, Ronghuan WANG. Changes of Agronomic Traits, Biomass Yield and Quality of National Silage Maize Combinations (Varieties) [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(4): 30-37. |
| [4] | Hua SUN, Ning GUO, Xiaojuan ZHENG, Jie SHI, Lirong ZHANG, Hongfei YAN. Identification and Biological Characteristics Analysis of Fusarium andiyazi Causing Maize Ear Rot [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(2): 145-151. |
| [5] | Junjie ZOU, Miaoyun XU, Lan ZHANG, Yanzhong LUO, Yuan LIU, Hongyan ZHENG, Lei WANG. Molecular Characterizations of Stacked Transgenic Maize BBHTL8-1 with Insect Resistance, Glyphosate Tolerance and Improved Quality [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(2): 77-85. |
| [6] | Zhidan WANG, Jili LIU, Na WU. Effects of Fenlong Tillage on Photosynthetic Physiological Characteristics and Yield of Sweet Sorghum [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(1): 148-156. |
| [7] | Junjie ZOU, Miaoyun XU, Lan ZHANG, Hongyan ZHENG, Lei WANG. Molecular Characteristics and Functional Evaluation of Transgenic Maize BFL4-1 With Stacked Insect and Herbicide Resistance Traits [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(1): 31-37. |
| [8] | FAN Hongye, LI Yaoyao, LU Xiaju, GU Shenghao, GUO Xinyu, , LIU Yuhua. [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(9): 112-120. |
| [9] | ZHU Lixia, CHEN Jutian, XU Siwei, CHEN Rubing, LI Lili. Dynamics of Soil Microbial Biomass Carbon and Nitrogen After Biochar Application [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(8): 193-200. |
| [10] | LIU Zhongxiang, YANG Yanzhong, WANG Xiaojuan, LIAN Xiaorong, ZHOU Wenqi, HE Haijun, ZHOU Yuqian, KOU Sirong. Phenotypic Identification and Combining Ability Effect Analysis of Mutants by Fast Neutron Irradiation [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(6): 184-194. |
| [11] | SHI Lihong, TANG Haiming, XIAO Xiaoping, LI Chao, Liu Qu, CHENG Aiwu, CHENG Kaikai, LI Weiyan, WEN Li. Effects of Crop Residue and Mineral Fertilizer on Physiological Characteristics of Barley Leaves and Yield under Double-cropping Rice Field [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(5): 143-152. |
| [12] | YANG Hua1, LI Jiang2, ZHANG Wei1, ZHOU Zhengfu1, YAN Yongliang1, GUO Jia3, LIU Xiangguo3, HAO Dongyun3, LIN Min1, KE Xiubin1*. Maize Growth Promotion and Nitrogen-fixing Rates by Inoculation with Wild-type and Ammonium-excreting Mutant of Pseudomonas stutzeri [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(4): 76-84. |
| [13] | WANG Xiujuan, XIE Zhanjun, HAN Yingzuo, LOU Chunrong, DONG Huan, HE Zhigang. Effects of Organic Fertilization on Soil Fertility, Nitrogen Utilization Efficiency and Yield of Maize [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(3): 132-138. |
| [14] | GU Huimin1, CHEN Bolang1*, SUN Jin2. Influences of Mycorrhizal Seedling on Growth and Physiological Characteristics of Processing Tomato Under Salt Stress#br# [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(3): 166-177. |
| [15] | WANG Zhiheng, YANG Xiuliu, ZOU Fang, HUANG Siqi, ZHOU Wuyan, XU Zhongwei, WEI Yuqing*. Effects of Salt and Drought Cross Stress on Germination and Physiological Characteristics of Sweet Sorghum Seeds [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(2): 37-49. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号