




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (12): 77-87.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0151
• BIOTECHNOLOGY & LIFE SCIENCE • Previous Articles Next Articles
Meixin CHEN1,2( ), Shuying GU2, Jia LIU2, Hao LIU1, Jingen LI2, Chaoguang TIAN2(
), Shuying GU2, Jia LIU2, Hao LIU1, Jingen LI2, Chaoguang TIAN2( )
)
Received:2023-03-04
Accepted:2023-04-06
Online:2024-12-15
Published:2024-12-17
Contact:
Chaoguang TIAN
陈美欣1,2( ), 顾淑莹2, 刘佳2, 刘浩1, 李金根2, 田朝光2(
), 顾淑莹2, 刘佳2, 刘浩1, 李金根2, 田朝光2( )
)
通讯作者:
田朝光
作者简介:陈美欣 E-mail:2813841338@qq.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Meixin CHEN, Shuying GU, Jia LIU, Hao LIU, Jingen LI, Chaoguang TIAN. Research on Regulation Mechanism of Xylose Metabolism in Myceliophthora thermophila[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(12): 77-87.
陈美欣, 顾淑莹, 刘佳, 刘浩, 李金根, 田朝光. 嗜热毁丝霉木糖代谢调控机制研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(12): 77-87.
| 引物名称 Prime name | 引物序列 Prime sequence(5’-3’) | 备注 Note |
|---|---|---|
| cre-1-up-F/R | GAGGACTTGACGCTGC/GTCGTTAGACTCTTTCA | cre-1 5’ |
| cre-1-down-F/R | GTGCCCCTGATAATAGC/CGACGGAATTGAGGATG | cre-1 3’ |
| xlnR-up-F/R | CACAGTACACGAGGACTTG/CAATATCAGTTAACGTCG | xlnR 5’ |
| xlnR-down-F/R | GAGTTCTTCTGATAATGAC/GAGGATCAGGACTGG | xlnR 3’ |
| neo-F/R | CTACGACGTTAACTG/CAGAAGAACTCGTC | neo |
| bar-F/R | CAAAGATATTGAAG/GATCACTAGTACAGG | bar |
| OE xlnR-F/R | GTTCTTCAGAATGTTGT/GATCCCTACAGCGCCAGAC | xlnR |
| U6p-cre-1-R | GAGTTGCTCCAACACGAGGAAAGAAAGAAAAGAAG | U6p-cre-1-sgRNA |
| cre-1-gRNA-F | TGTTGGAGCAACTCCGCTTGTTTTAGAGCTAGAAATAG | |
| U6p-xlnR-R | TAGCTGGTTGCACTGATCGCGAGGAAAGAAAG | U6p-xlnR-sgRNA |
| xlnR-gRNA-F | AGTGCAACCAGCTAGTTTTAGAGCTAGAAATAGC | |
| U6-F/gRNA-R | GTGGAGTGAAGTTCGGAA/AAAAAGCACCGACTC | sgRNA |
| cas-F/R | TCCGAGGTTCGACATCAG/GCTCCCTCTAAACAAGTG | cas9 |
| cre-1-emsa-F/R | CCAAAATCGGATCTGGTTCCGCGTGGATCCCAGCAGAAGCAGCAAGAACAACA/GATGCGGCCCTAGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGCATGGCGGCGTGCTGATGATG | cre-1-EMSA |
| xlnR-emsa-F/R | CCAAAATCGGATCTGGTTCCGCGTGGATCCGCTCGGACTGGCCCTCAACCGA/CTAGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGTGAATTCTCGGTCTTCTGGC | xlnR-EMSA |
Table 1 Primers used to amplify the target fragments
| 引物名称 Prime name | 引物序列 Prime sequence(5’-3’) | 备注 Note |
|---|---|---|
| cre-1-up-F/R | GAGGACTTGACGCTGC/GTCGTTAGACTCTTTCA | cre-1 5’ |
| cre-1-down-F/R | GTGCCCCTGATAATAGC/CGACGGAATTGAGGATG | cre-1 3’ |
| xlnR-up-F/R | CACAGTACACGAGGACTTG/CAATATCAGTTAACGTCG | xlnR 5’ |
| xlnR-down-F/R | GAGTTCTTCTGATAATGAC/GAGGATCAGGACTGG | xlnR 3’ |
| neo-F/R | CTACGACGTTAACTG/CAGAAGAACTCGTC | neo |
| bar-F/R | CAAAGATATTGAAG/GATCACTAGTACAGG | bar |
| OE xlnR-F/R | GTTCTTCAGAATGTTGT/GATCCCTACAGCGCCAGAC | xlnR |
| U6p-cre-1-R | GAGTTGCTCCAACACGAGGAAAGAAAGAAAAGAAG | U6p-cre-1-sgRNA |
| cre-1-gRNA-F | TGTTGGAGCAACTCCGCTTGTTTTAGAGCTAGAAATAG | |
| U6p-xlnR-R | TAGCTGGTTGCACTGATCGCGAGGAAAGAAAG | U6p-xlnR-sgRNA |
| xlnR-gRNA-F | AGTGCAACCAGCTAGTTTTAGAGCTAGAAATAGC | |
| U6-F/gRNA-R | GTGGAGTGAAGTTCGGAA/AAAAAGCACCGACTC | sgRNA |
| cas-F/R | TCCGAGGTTCGACATCAG/GCTCCCTCTAAACAAGTG | cas9 |
| cre-1-emsa-F/R | CCAAAATCGGATCTGGTTCCGCGTGGATCCCAGCAGAAGCAGCAAGAACAACA/GATGCGGCCCTAGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGCATGGCGGCGTGCTGATGATG | cre-1-EMSA |
| xlnR-emsa-F/R | CCAAAATCGGATCTGGTTCCGCGTGGATCCGCTCGGACTGGCCCTCAACCGA/CTAGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGTGAATTCTCGGTCTTCTGGC | xlnR-EMSA |
引物名称 Prime name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5’-3’) | 备注 Note |
|---|---|---|
| Orf-cre-1-F/R | CGATACTCGACCAAGAA/GAACCACTCTGGCTGCT | ∆cre-1 |
| Orf-xlnR-F/R | GCTCCCCATCGCCG/GGCCAGAAGACCGAG | ∆xlnR |
| Orf-OExlnR-F/R | GCGTAACCCCACCAAC/GCTGATCTGACCAGT | OexlnR |
Table 2 Verification primer of mutation
引物名称 Prime name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5’-3’) | 备注 Note |
|---|---|---|
| Orf-cre-1-F/R | CGATACTCGACCAAGAA/GAACCACTCTGGCTGCT | ∆cre-1 |
| Orf-xlnR-F/R | GCTCCCCATCGCCG/GGCCAGAAGACCGAG | ∆xlnR |
| Orf-OExlnR-F/R | GCGTAACCCCACCAAC/GCTGATCTGACCAGT | OexlnR |
引物名称 Prime name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5’-3’) | 备注 Note |
|---|---|---|
| cre-1-P-F/R | CCGTAGGTACCTGG/ GTTTTAAATGACGC | cre-1探针cre-1 probe |
| xlnR-P-F/R | GGCATCCCTTGGTC/ GCTCCGCCGGTGCTAA | xlnR探针xlnR probe |
Table 3 Probe amplification primer
引物名称 Prime name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5’-3’) | 备注 Note |
|---|---|---|
| cre-1-P-F/R | CCGTAGGTACCTGG/ GTTTTAAATGACGC | cre-1探针cre-1 probe |
| xlnR-P-F/R | GGCATCCCTTGGTC/ GCTCCGCCGGTGCTAA | xlnR探针xlnR probe |
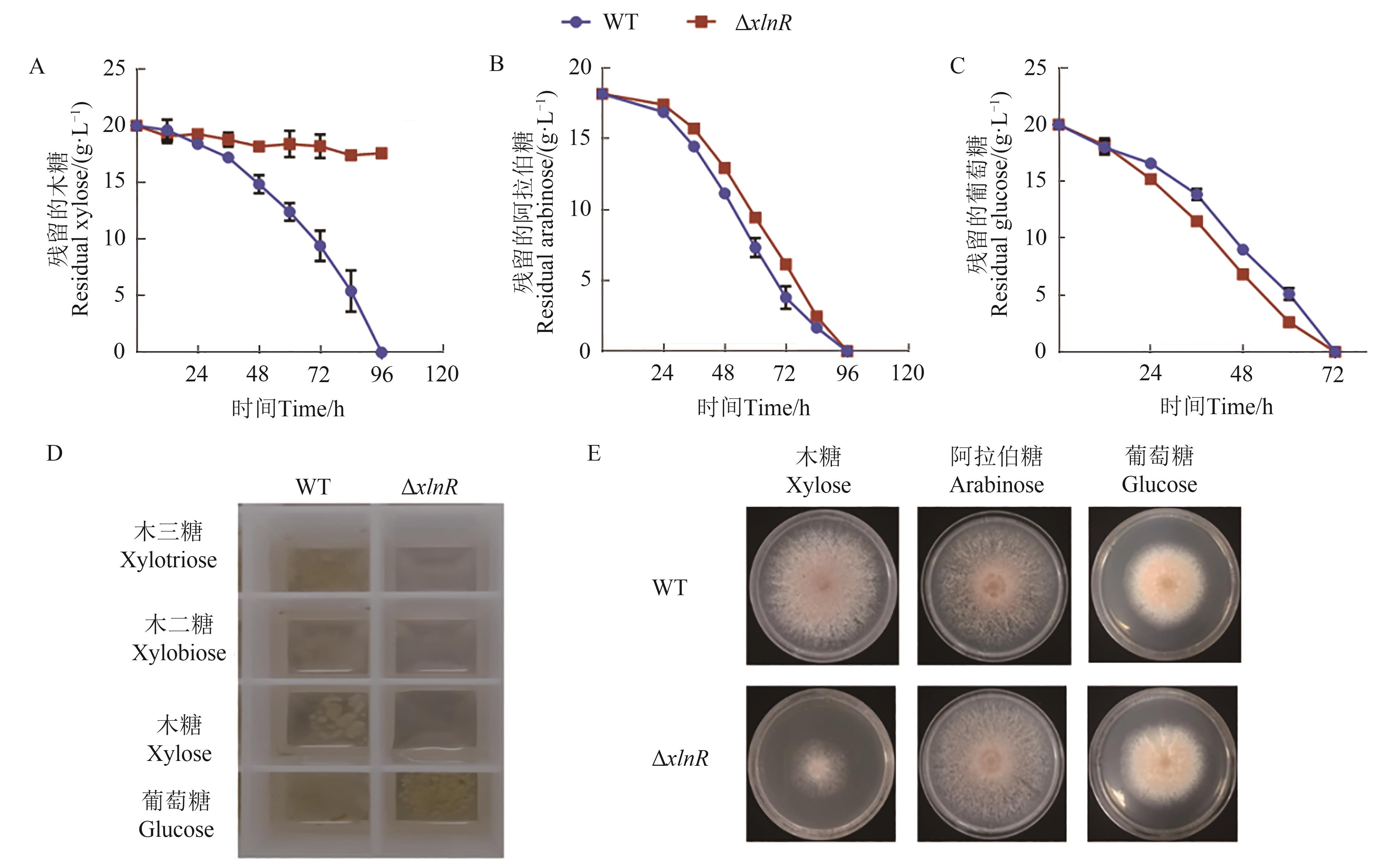
Fig. 1 Phenotypic analysis of M. thermophila strains WT and ΔxlnRA: Xylose utilization after the inoculation of the conidia from strains WT and ΔxlnR; B: Arabinose utilization after the inoculation of the conidia from strains WT and ΔxlnR; C: Glucose utilization after the inoculation of the conidia from strains WT and ΔxlnR; D: Growth phenotypes of ΔxlnR mutant on xylotriose, xylobiose, xylose and glucose; E: Growth phenotypes of ΔxlnR mutant on the agar plate with xylose, arabinose or glucose as the carbon source
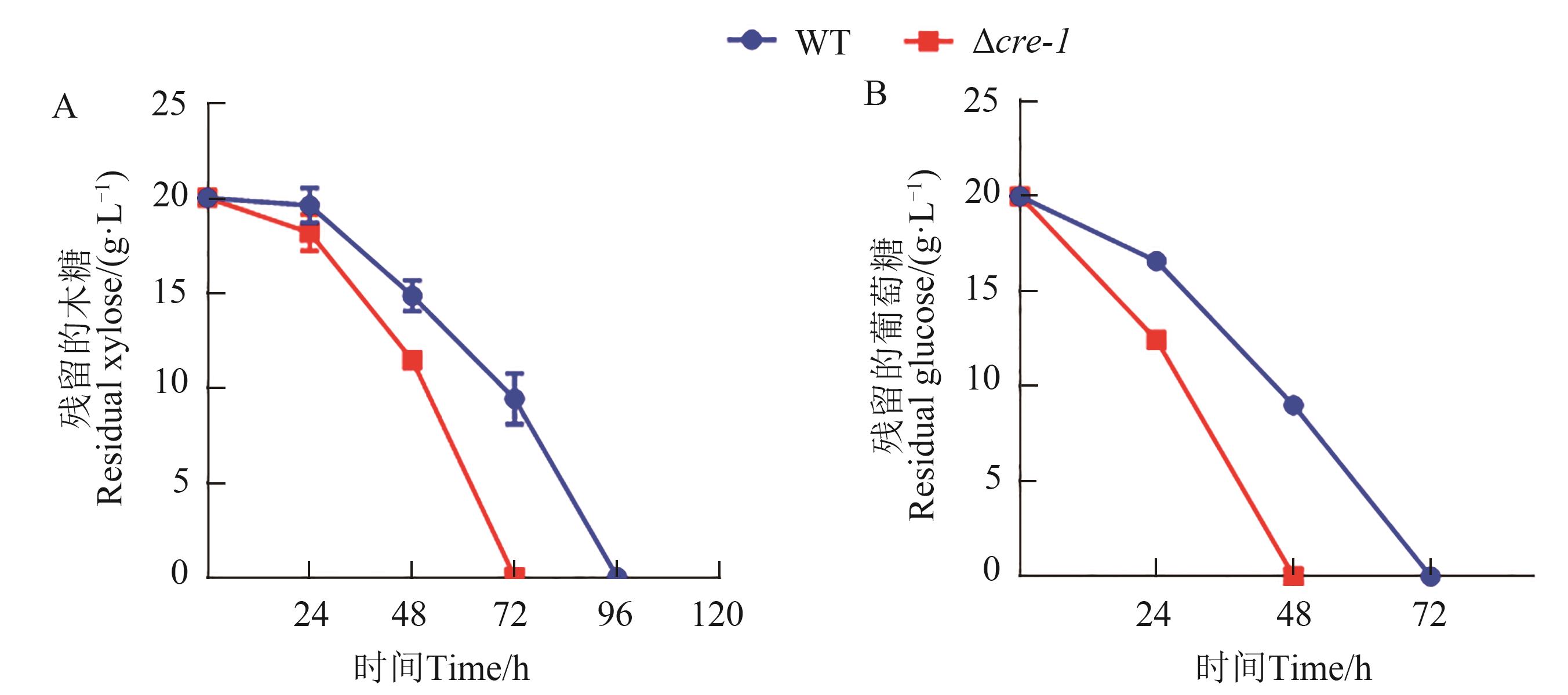
Fig. 3 Phenotypic analysis of M. thermophila strain Δcre-1A: Xylose utilization of M. thermophila strains WT and Δcre-1; B: Glucose utilization of M. thermophila strains WT and Δcre-1
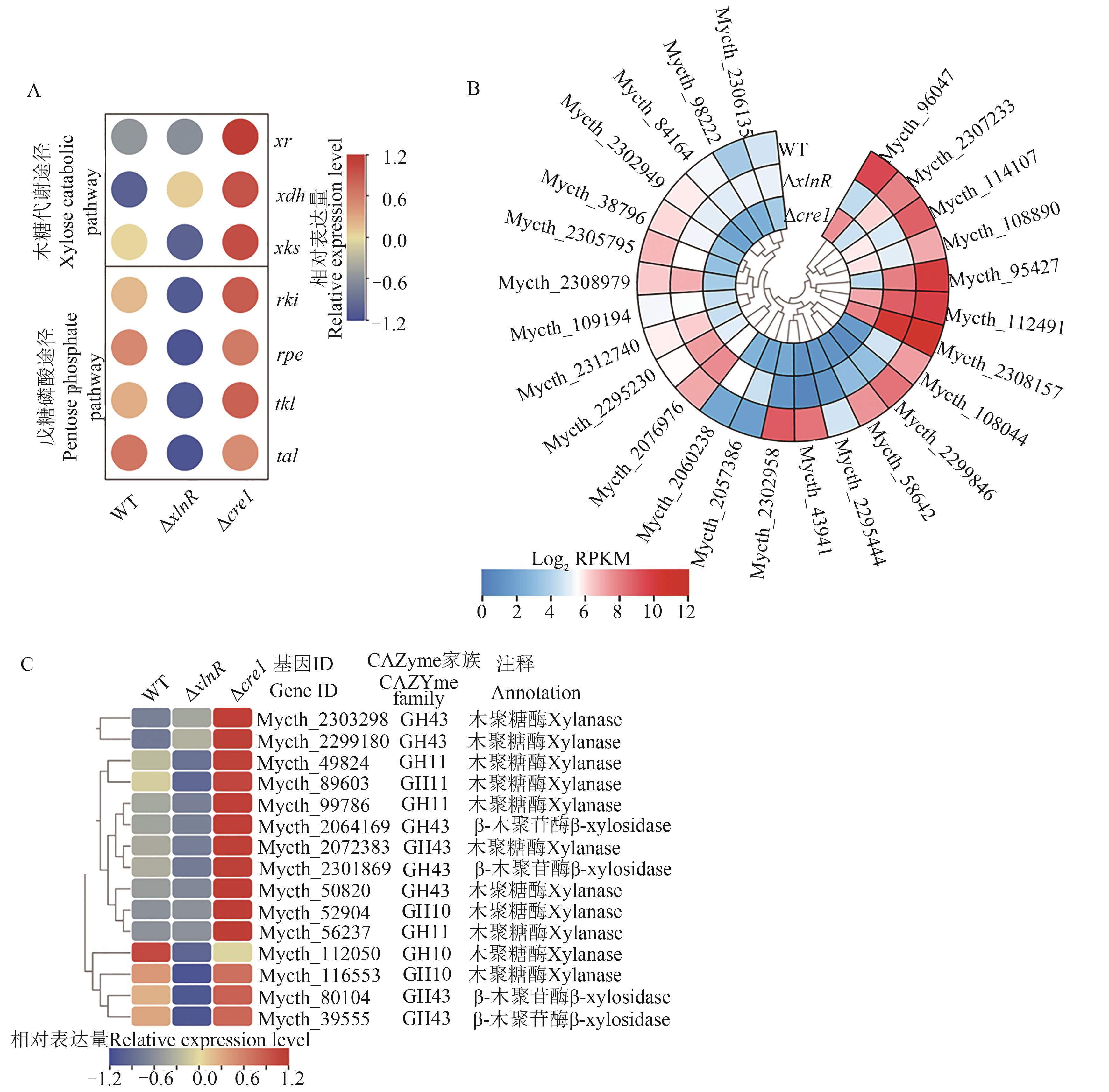
Fig. 4 Transcriptome analysis of M. thermophila strains WT, Δcre-1, and ΔxlnR mutation induced by xyloseA: Heatmap analysis of expression levels of genes involved in xylose catabolism and pentose phosphate pathway in strains WT, ΔxlnR, and Δcre-1 under xylose condition; B; Heatmap analysis of expression levels of putative sugar transporter genes; C: Heatmap analysis of expression levels of genes. xr—Xylose reductase gene; xdh—Xylitol dehydrogenase gene; xks—Xylulose kinase gene; rki—Ribose 5-phosphate isomerase gene; rpe—Ribulose phosphate 3-epimerase gene; tkl—Transketolase gene; tal—Transaldolase gene

Fig. 5 Analysis of regulatory function of Cre-1 on transcriptional activator XlnR in M. thermophilaA: Analysis of EMSA; B: Expression level of xlnR in the wild-type strain and mutant Δcre-1 under xylose condition; C: Relationship between transcription factor Cre-1 and XlnR, and their regulation in xylose metabolism
| 1 | TAKKELLAPATI S, LI T, GONZALEZ M A. An overview of biorefinery derived platform chemicals from a cellulose and hemicellulose biorefinery [J]. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy, 2018, 20(7):1615-1630. |
| 2 | ALI S S, NUGENT B, MULLINS E, et al.. Fungal-mediated consolidated bioprocessing: the potential of Fusarium oxysporum for the lignocellulosic ethanol industry [J/OL]. AMB Express, 2016, 6(1):13 [2023-02-10]. . |
| 3 | ZNAMEROSKI E A, CORADETTI S T, ROCHE C M, et al.. Induction of lignocellulose-degrading enzymes in Neurospora crassa by cellodextrins [J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2012, 109(16):6012-6017. |
| 4 | BALAT M. Production of bioethanol from lignocellulosic materials via the biochemical pathway: a review [J]. Energy Convers. Manage., 2011, 52(2):858-875. |
| 5 | VITIKAINEN M, ARVAS M, PAKULA T, et al.. Array comparative genomic hybridization analysis of Trichoderma reesei strains with enhanced cellulase production properties [J/OL]. BMC Genomics, 2010, 11(1):441 [2023-02-10]. . |
| 6 | ALI S S, NUGENT B, MULLINS E, et al.. Insights from the fungus Fusarium oxysporum point to high affinity glucose transporters as targets for enhancing ethanol production from lignocellulose [J/OL]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(1):e54701 [2023-02-10]. . |
| 7 | LIU G, QU Y. Engineering of filamentous fungi for efficient conversion of lignocellulose: tools, recent advances and prospects [J]. Biotechnol. Adv., 2019, 37(4):519-529. |
| 8 | VISSER H, JOOSTEN V, PUNTPETER J, et al.. Development of a mature fungal technology and production platform for industrial enzymes based on a Myceliophthora thermophila isolate, previously known as Chrysosporium lucknowense C1 [J]. Ind. Biotechnol., 2011, 7:214-223. |
| 9 | DRUZHININA I S, KUBICEK C P. Genetic engineering of Trichoderma reesei cellulases and their production [J]. Microb. Biotechnol., 2017, 10(6):1485-1499. |
| 10 | LI N, LIU Y, LIU D, et al.. MtTRC-1, a novel transcription factor, regulates cellulase production via directly modulating the genes expression of the Mthac-1 and Mtcbh-1 in Myceliophthora thermophila [J/OL]. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2022, 88(19):e0126322 [2023-02-10]. . |
| 11 | HECTOR R E, QURESHI N, RHUGHES S, et al.. Expression of a heterologous xylose transporter in a Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain engineered to utilize xylose improves aerobic xylose consumption [J]. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2008, 80(4):675-684. |
| 12 | WU V W, THIEME N, HUBERMAN L B, et al.. The regulatory and transcriptional landscape associated with carbon utilization in a filamentous fungus [J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2020, 117(11):6003-6013. |
| 13 | DENG H, BAI Y, FAN T P, et al.. Advanced strategy for metabolite exploration in filamentous fungi [J]. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol., 2020, 40(2):180-198. |
| 14 | ADNAN M, ZHENG W, ISLAM W, et al.. Carbon catabolite repression in filamentous fungi [J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2017, 19(1):48 [2023-02-10]. . |
| 15 | TAMAYO E N, VILLANUEVA A, HASPER A A, et al.. CreA mediates repression of the regulatory gene xlnR which controls the production of xylanolytic enzymes in Aspergillus nidulans [J]. Fungal Genet. Biol., 2008, 45(6):984-993. |
| 16 | ANTONIETO A C, DOS SANTOS CASTRO L, SILVA-ROCHA R, et al.. Defining the genome-wide role of CRE1 during carbon catabolite repression in Trichoderma reesei using RNA-Seq analysis [J]. Fungal Genet. Biol., 2014, 73:93-103. |
| 17 | PORTNOY T, MARGEOT A, LINKE R, et al.. The CRE1 carbon catabolite repressor of the fungus Trichoderma reesei:a master regulator of carbon assimilation [J/OL]. BMC Genomics, 2011, 12:269 [2023-02-10]. . |
| 18 | FURUKAWA T, SHIDA Y, KITAGAMI N, et al.. Identification of specific binding sites for XYR1, a transcriptional activator of cellulolytic and xylanolytic genes in Trichoderma reesei [J]. Fungal Genet. Biol., 2009, 46(8):564-574. |
| 19 | PORTNOY T, MARGEOT A, SEIDL-SEIBOTH V, et al.. Differential regulation of the cellulase transcription factors XYR1, ACE2, and ACE1 in Trichoderma reesei strains producing high and low levels of cellulase [J]. Eukaryot. Cell, 2011, 10(2):262-271. |
| 20 | DOS SANTOS GOMES A C, FALKOSKI D, BATTAGLIA E, et al.. Myceliophthora thermophila Xyr1 is predominantly involved in xylan degradation and xylose catabolism [J/OL]. Biotechnol. Biofuels, 2019, 12:220 [2023-02-10]. . |
| 21 | CRAIG J P, CORADETTI S T, STARR T L, et al.. Direct target network of the Neurospora crassa plant cell wall deconstruction regulators CLR-1, CLR-2, and XLR-1 [J/OL]. Mbio, 2015, 6(5):e01452-15 [2023-02-10]. . |
| 22 | HASPER A A, TRINDADE L M, VAN DER VEEN D, et al.. Functional analysis of the transcriptional activator XlnR from Aspergillus niger [J]. Microbiology, 2004, 150(Pt5):1367-1375. |
| 23 | HASPER A A, VISSER J, DE GRAAFF L H. The Aspergillus niger transcriptional activator XlnR, which is involved in the degradation of the polysaccharides xylan and cellulose, also regulates d-xylose reductase gene expression [J]. Mol. Microbiol., 2000, 36(1):193-200. |
| 24 | MACH-AIGNER R, PUCHER E, STEIGER G, et al.. Transcriptional regulation of xyr1, encoding the main regulator of the xylanolytic and cellulolytic enzyme system in Hypocrea jecorina [J]. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2008,74(21):6554-6562. |
| 25 | MACH-AIGNER A R, OMONY J, JOVANOVIC B, et al.. D-Xylose concentration-dependent hydrolase expression profiles and the function of CreA and XlnR in Aspergillus niger [J]. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2012, 78(9):3145-3155. |
| 26 | BERKA R M, GRIGORIEV I V, OTILLAR R, et al.. Comparative genomic analysis of the thermophilic biomass-degrading fungi Myceliophthora thermophila and Thielavia terrestris [J]. Nat. Biotechnol., 2011, 29(10):922-927. |
| 27 | XU J, LI J, LIN L, et al.. Development of genetic tools for Myceliophthora thermophila [J/OL]. BMC Biotechnol., 2015, 15:35 [2023-02-10]. . |
| 28 | SONG R, ZHAI Q, SUN L, et al.. CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing technology in filamentous fungi:progress and perspective [J]. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2019, 103(17):6919-6932. |
| 29 | SWIAT M A, DASHKO S, DEN RIDDER M, et al.. FnCpf1:a novel and efficient genome editing tool for Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Nucleic Acids Res., 2017, 45(21):12585-12598. |
| 30 | PATEL H, RAWAT S. Thermophilic fungi: diversity, physiology, genetics, and applications [J]. New Future Dev. Microb. Biotechnol. Bioeng., 2021, 13(6):69-93. |
| 31 | LIU Q, GAO R, LI J, et al.. Development of a genome-editing CRISPR/Cas9 system in thermophilic fungal Myceliophthora species and its application to hyper-cellulase production strain engineering [J/OL]. Biotechnol. Biofuels, 2017, 10:1 [2023-02-10]. . |
| 32 | LI J, GU S, ZHAO Z, et al.. Dissecting cellobiose metabolic pathway and its application in biorefinery through consolidated bioprocessing in Myceliophthora thermophila [J/OL].Fungal Biol. Biotechnol., 2019, 6:21 [2023-02-10]. . |
| 33 | XU Q, SINGH A, HIMMEL M E. Perspectives and new directions for the production of bioethanol using consolidated bioprocessing of lignocellulose [J]. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 2009, 20(3):364-371. |
| 34 | WANG B, LI J, GAO J, et al.. Identification and characterization of the glucose dual-affinity transport system in Neurospora crassa:pleiotropic roles in nutrient transport, signaling, and carbon catabolite repression [J/OL]. Biotechnol. Biofuels, 2017, 10:17 [2023-02-10]. . |
| 35 | SUN J, TIAN C, DIAMOND S, et al.. Deciphering transcriptional regulatory mechanisms associated with hemicellulose degradation in Neurospora crassa [J]. Eukaryot. Cell, 2012, 11(4):482-493. |
| 36 | SUN J, GLASS N L. Identification of the CRE-1 cellulolytic regulon in Neurospora crassa [J/OL]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(9):e25654 [2023-02-10]. . |
| 37 | FURUKAWA T, SHIDA Y, KITAGAMI N, et al.. Identification of specific binding sites for XYR1, a transcriptional activator of cellulolytic and xylanolytic genes in Trichoderma reesei [J]. Fungal Genet. Biol., 2009, 46(8):564-574. |
| 38 | LI J, LIN L, SUN T, et al.. Direct production of commodity chemicals from lignocellulose using Myceliophthora thermophila [J]. Metab. Eng., 2020, 61:416-426. |
| 39 | WEINHANDL K, WINKLER M, GLIEDER A, et al.. Carbon source dependent promoters in yeasts [J/OL]. Microb. Cell Fact., 2014, 13:5[2023-02-10].. |
| [1] | Zitian PU, Fei WANG, Chang LI, Xinxin WANG. Research Progress of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Affecting Plant Nitrogen Absorption and Transport [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(11): 171-179. |
| [2] | Yaping FAN, Baiquan SONG, Changxian WANG. Progress of Research on Alleviating Obstacles of Continuous Cropping by Soil Sterilization and Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(10): 158-167. |
| [3] | Zihui CAI, Wenxin CHEN, Juanjuan LI, Hong LI, Xue CHI, Yanqiong TANG, Zhu LIU, Xiang MA. Impact of ExsA on the Pathogenicity of Aeromonas veronii [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(9): 129-136. |
| [4] | Jiping WANG, Tiedong LU, Zhiheng LIANG, Ye ZHANG, Tianming SU, Tieguang HE. Effects of Microorganisms from Different Sources on the Composting Process of Grape Branches and Pig Manure [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(9): 224-233. |
| [5] | Zifan WANG, Yan LI, Qingyin ZHANG, Dandan WANG, Jianhua SHI, Xiaobin GENG, Dongliang TIAN, Zengming ZHONG, Xiaoming ZHAO, Lianfen QI. Effect of Microbicides on Main Diseases and Soil Microbial Communities of Tomatoes in Facilities [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(6): 102-112. |
| [6] | Zhimin YANG, Huihao ZHANG, Yuanyuan ZHANG, Hongyan DU, Xiaodong LIU, Yaguang HOU, Yi WANG, Daolong XU, Jingui HUANG, Xiaoning CHENG, Yang SUI, Ruili WANG, Chao YU, Lingling ZHAO, Chunmei CHEN, Ru YA, Li JIA, Mingyue ZHANG, Hongwei WANG, Songyao YAO, Ying ZHAO, Ke SHAO. Identification of Streptomyces rochei HM85 and Its Biocontrol and Growth-promoting Effects on Sugar Beet [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(5): 148-155. |
| [7] | Siqi GAO, Xinjian YANG, Deqi ZHU, Mingwei GUAN, Yunting KOU, Cheng MAN, Jian JIAO. Bactericidal Mechanism of Antimicrobial Peptide PAJE Against Staphylococcus aureus and SCVs [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(5): 156-166. |
| [8] | Yi CAO, Wenjing CUI, Ruiqiang MA. Research and Application of Directed Micro-Ecology in Soybean-Nodulating Rhizobia [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(4): 215-224. |
| [9] | Zequn LU, Ning LIU, Honglian ZHANG, Yuan WANG, Huoqing HUANG. Improvement of Heterologous Protein Secretion and Folding Pathways of Pichia pastoris [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(1): 18-27. |
| [10] | Jingli GUO, Dlxat Nilufar, Daqing WANG. Development Strategy on Agricultural Microbial Industry in China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(11): 1-7. |
| [11] | Aihua LI, Tao WANG, Miaomiao WANG, Junyu DENG, Jia LIU, Jidong YA, Yu ZHANG. Diversity of Endophytic Fungi in Holcoglossum rupestre and Effects of Symbiotic Fungi on Seed Germination of Dendrobium denneanum [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(10): 91-98. |
| [12] | Shuai LUO, Yaqin WEN, Hua ZHU, Rong ZHANG, Xiaowen WANG, Lili LIU, Jianya ZHU. Effect of ECF-Sig16 on Avermectin Production in Streptomyces avermitilis [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 113-121. |
| [13] | Yu MENG, Gang TAO, Deqi HUANG, Xiajun YAO. Diversity of Phosphate⁃solubilizing Fungi and Their Applications in Agriculture and Ecology [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(11): 208-217. |
| [14] | Xin PENG, Can FENG, Xiang MA, Hong LI, Yanqiong TANG, Juanjuan LI, Zhu LIU. Screening of Acidic Protease Producing Strains and Its Application in Seed Germination [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(9): 88-95. |
| [15] | Congcong MA, Zehua LUO, Bin CAI, Haobao LIU, Yunshan WANG, Rui MA, Jingang GU. Screening of Carbon Sources for Growth and Spore Formation of Bacillus altitudinis YC-9 [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(7): 77-85. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号