




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (2): 125-135.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0647
• ANIMAL AND PLANT HEALTH • Previous Articles
Jincheng LUO( ), Xiaolin ZHU, Xiaohong WEI(
), Xiaolin ZHU, Xiaohong WEI( ), Xian WANG, Baoqiang WANG, Xuefen DU
), Xian WANG, Baoqiang WANG, Xuefen DU
Received:2023-08-29
Accepted:2023-11-25
Online:2025-02-15
Published:2025-02-14
Contact:
Xiaohong WEI
罗金城( ), 朱晓林, 魏小红(
), 朱晓林, 魏小红( ), 王贤, 王宝强, 杜雪芬
), 王贤, 王宝强, 杜雪芬
通讯作者:
魏小红
作者简介:罗金城 E-mail:778415115@qq.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Jincheng LUO, Xiaolin ZHU, Xiaohong WEI, Xian WANG, Baoqiang WANG, Xuefen DU. Effect of Exogenous NO on Expression of Tomato Antioxidant Enzyme Gene Under Tomato Yellowing Leaf Curl Virus Stress[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(2): 125-135.
罗金城, 朱晓林, 魏小红, 王贤, 王宝强, 杜雪芬. 番茄黄化曲叶病毒胁迫下外源NO对番茄抗氧化物酶基因表达的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(2): 125-135.
| 基因Gene | 引物序列Primer sequence(5’-3’) |
|---|---|
| Chl Cu-Zn SOD | F: TATGCTGTCACTACCCCTAA,R: TATTGGAGTCAAACCAACCA |
| Chl GR | F: CGGCATTACGATTTCGATTT,R: ACAATGGCAATTTTGTCAGG |
| Pla CAT7 | F: GTTCCGTTATACTCGTGACA,R: ATTGCCATAACAGGGTGAAT |
| Pla CAT8 | F: ACGTTCATCAGATACCAGTG,R: CCCAGTTATAGCAACCACAT |
| Cyt APX2 L-5 | F: CTGATTTCCTTCGTTTAGCG,R: GAAATTCCGGATCATCAAGC |
| Min Mn SOD | F: CCAAATTGCACAGTGCCCTC,R: CCCAGCCAAGAGAACCCTTT |
| Per CAT2 | F: TACGGTTGGTGCAAGAGGTC,R: CAGCACAGGTAAGGTGAGCA |
| UBI | F: TCGTAAGGAGTGCCCTAATGCTGA,R: CAATCGCCTCCAGCCTTGTTGTAA |
Table 1 qRT-PCR primer sequence
| 基因Gene | 引物序列Primer sequence(5’-3’) |
|---|---|
| Chl Cu-Zn SOD | F: TATGCTGTCACTACCCCTAA,R: TATTGGAGTCAAACCAACCA |
| Chl GR | F: CGGCATTACGATTTCGATTT,R: ACAATGGCAATTTTGTCAGG |
| Pla CAT7 | F: GTTCCGTTATACTCGTGACA,R: ATTGCCATAACAGGGTGAAT |
| Pla CAT8 | F: ACGTTCATCAGATACCAGTG,R: CCCAGTTATAGCAACCACAT |
| Cyt APX2 L-5 | F: CTGATTTCCTTCGTTTAGCG,R: GAAATTCCGGATCATCAAGC |
| Min Mn SOD | F: CCAAATTGCACAGTGCCCTC,R: CCCAGCCAAGAGAACCCTTT |
| Per CAT2 | F: TACGGTTGGTGCAAGAGGTC,R: CAGCACAGGTAAGGTGAGCA |
| UBI | F: TCGTAAGGAGTGCCCTAATGCTGA,R: CAATCGCCTCCAGCCTTGTTGTAA |
抗氧化酶 Antioxidant enzyme | 基因数量 Number of genes | 亚细胞区室 Subcellular compartment |
|---|---|---|
| 超氧化物歧化酶SOD | 9 | 细胞质、叶绿体、线粒体、核膜 Cytoplasm, chloroplast, mitochondrion, nucleus membrane |
| 过氧化氢酶CAT | 18 | 细胞质、内质网、过氧化物酶体、细胞膜、液泡 Cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, peroxisome, plasma membrane, vacuole |
| 谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶GPX | 6 | 叶绿体、细胞核、细胞质 Chloroplast, nucleus, cytoplasm |
| 抗坏血酸过氧化物酶APX | 9 | 细胞质、线粒体、叶绿体 Cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast |
| 单脱氢抗坏血酸还原酶MR | 4 | 叶绿体、细胞质、过氧化物酶体 Chloroplast, cytoplasm, peroxisome |
| 谷胱甘肽还原酶GR | 2 | 叶绿体、细胞膜Chloroplast, plasma membrane |
| 脱氢抗坏血酸还原酶DR | 7 | 细胞质、细胞核、叶绿体、线粒体 Cytoplasm, nucleus, chloroplast, mitochondrion |
Table 2 Basic information of tomato antioxidant enzymes
抗氧化酶 Antioxidant enzyme | 基因数量 Number of genes | 亚细胞区室 Subcellular compartment |
|---|---|---|
| 超氧化物歧化酶SOD | 9 | 细胞质、叶绿体、线粒体、核膜 Cytoplasm, chloroplast, mitochondrion, nucleus membrane |
| 过氧化氢酶CAT | 18 | 细胞质、内质网、过氧化物酶体、细胞膜、液泡 Cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, peroxisome, plasma membrane, vacuole |
| 谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶GPX | 6 | 叶绿体、细胞核、细胞质 Chloroplast, nucleus, cytoplasm |
| 抗坏血酸过氧化物酶APX | 9 | 细胞质、线粒体、叶绿体 Cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast |
| 单脱氢抗坏血酸还原酶MR | 4 | 叶绿体、细胞质、过氧化物酶体 Chloroplast, cytoplasm, peroxisome |
| 谷胱甘肽还原酶GR | 2 | 叶绿体、细胞膜Chloroplast, plasma membrane |
| 脱氢抗坏血酸还原酶DR | 7 | 细胞质、细胞核、叶绿体、线粒体 Cytoplasm, nucleus, chloroplast, mitochondrion |
登记号 Gene accession No. | 名称 Name | 氨基酸数量 Number of amino acids | 分子质量 Molecular weight/Da | 等电点 Isoelectric point | 亲水性 GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solyc01g067740.3 | Cyt Cu-Zn SOD2 | 152 | 15 284.95 | 5.47 | -0.199 |
| Solyc02g021140.3 | Chl Fe SOD3 | 252 | 29 126.27 | 6.65 | -0.348 |
| Solyc03g062890.3 | Cyt Cu-Zn SOD1 | 156 | 15 870.86 | 6.53 | -0.022 |
| Solyc03g095180.3 | Chl Fe SOD1 | 303 | 34 575.69 | 5.38 | -0.627 |
| Solyc06g048410.3 | Chl Fe SOD2 | 278 | 31 144.47 | 6.60 | -0.270 |
| Solyc06g048420.2 | Nucp Fe SOD | 109 | 12 193.83 | 5.38 | -0.322 |
| Solyc06g049080.3 | Mit Mn SOD | 228 | 25 314.79 | 7.13 | -0.318 |
| Solyc08g079830.3 | Chl SOD copper chaperone 1 | 311 | 32 987.61 | 6.45 | -0.027 |
| Solyc11g066390.2 | Chl Cu-Zn SOD | 217 | 22 281.92 | 6.01 | -0.018 |
| Solyc01g099420.2 | Cyt CAT isozyme 2 | 106 | 12 121.88 | 5.26 | 0.004 |
| Solyc01g100630.2 | ER CAT | 427 | 47 770.03 | 6.20 | -0.008 |
| Solyc01g100640.3 | Pla CAT isozyme 1 | 220 | 25 603.58 | 8.37 | -0.140 |
| Solyc12g096380.1 | Pla CAT1a | 599 | 65 926.19 | 8.64 | 0.497 |
| Solyc12g094620.2 | Per CAT1 | 497 | 57 078.50 | 6.56 | -0.538 |
| Solyc12g011370.2 | Pla CAT8 | 586 | 64 090.11 | 8.76 | 0.539 |
| Solyc11g006710.2 | Pla CAT7 | 584 | 63 360.16 | 7.02 | 0.651 |
| Solyc10g081460.2 | Vac CAT | 650 | 67 933.20 | 6.58 | 0.628 |
| Solyc10g018600.2 | Pla CAT9 | 569 | 60 434.61 | 6.34 | 0.820 |
| Solyc08g077823.1 | Pla CAT6a | 305 | 33 185.14 | 8.88 | 0.573 |
| Solyc08g077820.3 | Pla CAT6b | 229 | 26 277.39 | 9.03 | 0.808 |
Table 3 Basic physicochemical properties of tomato antioxidase-encoded proteins
登记号 Gene accession No. | 名称 Name | 氨基酸数量 Number of amino acids | 分子质量 Molecular weight/Da | 等电点 Isoelectric point | 亲水性 GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solyc01g067740.3 | Cyt Cu-Zn SOD2 | 152 | 15 284.95 | 5.47 | -0.199 |
| Solyc02g021140.3 | Chl Fe SOD3 | 252 | 29 126.27 | 6.65 | -0.348 |
| Solyc03g062890.3 | Cyt Cu-Zn SOD1 | 156 | 15 870.86 | 6.53 | -0.022 |
| Solyc03g095180.3 | Chl Fe SOD1 | 303 | 34 575.69 | 5.38 | -0.627 |
| Solyc06g048410.3 | Chl Fe SOD2 | 278 | 31 144.47 | 6.60 | -0.270 |
| Solyc06g048420.2 | Nucp Fe SOD | 109 | 12 193.83 | 5.38 | -0.322 |
| Solyc06g049080.3 | Mit Mn SOD | 228 | 25 314.79 | 7.13 | -0.318 |
| Solyc08g079830.3 | Chl SOD copper chaperone 1 | 311 | 32 987.61 | 6.45 | -0.027 |
| Solyc11g066390.2 | Chl Cu-Zn SOD | 217 | 22 281.92 | 6.01 | -0.018 |
| Solyc01g099420.2 | Cyt CAT isozyme 2 | 106 | 12 121.88 | 5.26 | 0.004 |
| Solyc01g100630.2 | ER CAT | 427 | 47 770.03 | 6.20 | -0.008 |
| Solyc01g100640.3 | Pla CAT isozyme 1 | 220 | 25 603.58 | 8.37 | -0.140 |
| Solyc12g096380.1 | Pla CAT1a | 599 | 65 926.19 | 8.64 | 0.497 |
| Solyc12g094620.2 | Per CAT1 | 497 | 57 078.50 | 6.56 | -0.538 |
| Solyc12g011370.2 | Pla CAT8 | 586 | 64 090.11 | 8.76 | 0.539 |
| Solyc11g006710.2 | Pla CAT7 | 584 | 63 360.16 | 7.02 | 0.651 |
| Solyc10g081460.2 | Vac CAT | 650 | 67 933.20 | 6.58 | 0.628 |
| Solyc10g018600.2 | Pla CAT9 | 569 | 60 434.61 | 6.34 | 0.820 |
| Solyc08g077823.1 | Pla CAT6a | 305 | 33 185.14 | 8.88 | 0.573 |
| Solyc08g077820.3 | Pla CAT6b | 229 | 26 277.39 | 9.03 | 0.808 |
登记号 Gene accession No. | 名称 Name | 氨基酸数量 Number of amino acids | 分子质量 Molecular weight/Da | 等电点 Isoelectric point | 亲水性 GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solyc08g077810.2 | Pla CAT2 | 228 | 26 105.16 | 9.03 | 0.791 |
| Solyc04g082460.3 | Pla CAT3 | 956 | 109 204.40 | 8.35 | -0.450 |
| Solyc02g082760.3 | Per CAT2 | 492 | 56 896.20 | 6.73 | -0.540 |
| Solyc02g081850.3 | Pla CAT5 | 592 | 64 871.75 | 8.44 | 0.493 |
| Solyc02g070280.3 | Pla CAT1 | 604 | 65 810.94 | 8.60 | 0.501 |
| Solyc02g070270.2 | Pla CAT1b | 596 | 64 632.50 | 8.15 | 0.554 |
| Solyc02g037510.3 | Pla CAT4 | 599 | 63 406.56 | 6.45 | 0.788 |
| Solyc06g073460.3 | Chl GPX | 192 | 21 862.33 | 8.30 | -0.081 |
| Solyc08g006720.3 | Chl GPX2 | 238 | 26 203.87 | 9.18 | -0.239 |
| Solyc08g068800.3 | Nuc GPX | 250 | 27 955.88 | 9.40 | -0.336 |
| Solyc08g080940.3 | Chl GPX3 | 239 | 26 749.72 | 9.16 | -0.249 |
| Solyc09g064850.3 | Chl GPX1 | 170 | 19 094.83 | 9.33 | -0.449 |
| Solyc12g056240.2 | Cyt GPX | 170 | 19 362.01 | 4.97 | -0.436 |
| Solyc09g007270.3 | Cyt APX1 | 250 | 27 635.37 | 5.63 | -0.421 |
| Solyc01g111510.3 | Cyt APX L-3 | 287 | 31 615.03 | 7.10 | -0.349 |
| Solyc02g083620.3 | Cyt APX1 L-5 | 289 | 32 010.40 | 6.10 | -0.388 |
| Solyc02g083630.3 | Cyt APX2 L-5 | 292 | 32 406.84 | 7.15 | -0.349 |
| Solyc06g005150.3 | Mit APX | 250 | 27 322.09 | 5.86 | -0.300 |
| Solyc06g005160.3 | Cyt APX2 | 250 | 27 408.20 | 5.61 | -0.319 |
| Solyc06g060260.3 | Chl APX1 | 345 | 37 836.83 | 8.48 | -0.414 |
| Solyc08g059760.3 | Chl APX L-6 | 326 | 35 424.51 | 5.65 | -0.094 |
| Solyc11g018550.3 | Chl APX2 | 425 | 46 457.42 | 8.15 | -0.443 |
| Solyc06g075050.2 | Chl MR1 | 270 | 30 996.41 | 7.79 | -0.429 |
| Solyc06g075070.3 | Cyt MR | 324 | 36 420.12 | 5.80 | -0.454 |
| Solyc08g081530.3 | Chl MR2 | 491 | 53 665.29 | 8.09 | -0.126 |
| Solyc09g009390.3 | Per MR | 433 | 47 021.62 | 5.77 | -0.110 |
| Solyc09g065900.3 | Chl GR | 557 | 60 088.30 | 7.62 | -0.161 |
| Solyc09g091840.3 | Pla GR | 508 | 55 036.30 | 5.96 | -0.071 |
| Solyc05g054760.3 | Cyt DR | 210 | 23 554.29 | 6.32 | -0.158 |
| Solyc04g064470.2 | Nuc DR1 | 167 | 19 060.07 | 9.17 | -0.318 |
| Solyc05g013950.1 | Chl DR1 | 141 | 15 856.59 | 8.55 | 0.311 |
| Solyc06g075513.1 | Mit DR | 183 | 20 598.15 | 8.65 | 0.132 |
| Solyc09g056180.3 | Chl DR2 | 103 | 11 732.43 | 6.35 | -0.283 |
| Solyc11g011250.2 | Chl DR3 | 288 | 32 305.36 | 8.71 | -0.206 |
| Solyc11g039930.2 | Chl DR4 | 95 | 10 801.51 | 6.16 | -0.085 |
Table 3 Basic physicochemical properties of tomato antioxidase-encoded proteins
登记号 Gene accession No. | 名称 Name | 氨基酸数量 Number of amino acids | 分子质量 Molecular weight/Da | 等电点 Isoelectric point | 亲水性 GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solyc08g077810.2 | Pla CAT2 | 228 | 26 105.16 | 9.03 | 0.791 |
| Solyc04g082460.3 | Pla CAT3 | 956 | 109 204.40 | 8.35 | -0.450 |
| Solyc02g082760.3 | Per CAT2 | 492 | 56 896.20 | 6.73 | -0.540 |
| Solyc02g081850.3 | Pla CAT5 | 592 | 64 871.75 | 8.44 | 0.493 |
| Solyc02g070280.3 | Pla CAT1 | 604 | 65 810.94 | 8.60 | 0.501 |
| Solyc02g070270.2 | Pla CAT1b | 596 | 64 632.50 | 8.15 | 0.554 |
| Solyc02g037510.3 | Pla CAT4 | 599 | 63 406.56 | 6.45 | 0.788 |
| Solyc06g073460.3 | Chl GPX | 192 | 21 862.33 | 8.30 | -0.081 |
| Solyc08g006720.3 | Chl GPX2 | 238 | 26 203.87 | 9.18 | -0.239 |
| Solyc08g068800.3 | Nuc GPX | 250 | 27 955.88 | 9.40 | -0.336 |
| Solyc08g080940.3 | Chl GPX3 | 239 | 26 749.72 | 9.16 | -0.249 |
| Solyc09g064850.3 | Chl GPX1 | 170 | 19 094.83 | 9.33 | -0.449 |
| Solyc12g056240.2 | Cyt GPX | 170 | 19 362.01 | 4.97 | -0.436 |
| Solyc09g007270.3 | Cyt APX1 | 250 | 27 635.37 | 5.63 | -0.421 |
| Solyc01g111510.3 | Cyt APX L-3 | 287 | 31 615.03 | 7.10 | -0.349 |
| Solyc02g083620.3 | Cyt APX1 L-5 | 289 | 32 010.40 | 6.10 | -0.388 |
| Solyc02g083630.3 | Cyt APX2 L-5 | 292 | 32 406.84 | 7.15 | -0.349 |
| Solyc06g005150.3 | Mit APX | 250 | 27 322.09 | 5.86 | -0.300 |
| Solyc06g005160.3 | Cyt APX2 | 250 | 27 408.20 | 5.61 | -0.319 |
| Solyc06g060260.3 | Chl APX1 | 345 | 37 836.83 | 8.48 | -0.414 |
| Solyc08g059760.3 | Chl APX L-6 | 326 | 35 424.51 | 5.65 | -0.094 |
| Solyc11g018550.3 | Chl APX2 | 425 | 46 457.42 | 8.15 | -0.443 |
| Solyc06g075050.2 | Chl MR1 | 270 | 30 996.41 | 7.79 | -0.429 |
| Solyc06g075070.3 | Cyt MR | 324 | 36 420.12 | 5.80 | -0.454 |
| Solyc08g081530.3 | Chl MR2 | 491 | 53 665.29 | 8.09 | -0.126 |
| Solyc09g009390.3 | Per MR | 433 | 47 021.62 | 5.77 | -0.110 |
| Solyc09g065900.3 | Chl GR | 557 | 60 088.30 | 7.62 | -0.161 |
| Solyc09g091840.3 | Pla GR | 508 | 55 036.30 | 5.96 | -0.071 |
| Solyc05g054760.3 | Cyt DR | 210 | 23 554.29 | 6.32 | -0.158 |
| Solyc04g064470.2 | Nuc DR1 | 167 | 19 060.07 | 9.17 | -0.318 |
| Solyc05g013950.1 | Chl DR1 | 141 | 15 856.59 | 8.55 | 0.311 |
| Solyc06g075513.1 | Mit DR | 183 | 20 598.15 | 8.65 | 0.132 |
| Solyc09g056180.3 | Chl DR2 | 103 | 11 732.43 | 6.35 | -0.283 |
| Solyc11g011250.2 | Chl DR3 | 288 | 32 305.36 | 8.71 | -0.206 |
| Solyc11g039930.2 | Chl DR4 | 95 | 10 801.51 | 6.16 | -0.085 |
| 抗氧化酶Antioxidant enzyme | 外显子数量Number of exons(基因名称Gene name) |
|---|---|
| 超氧化物歧化酶SOD | 4(Nucp Fe SOD)~9(Chl Fe SOD1) |
| 过氧化氢酶CAT | 1(Pla CAT5)~15(Pla CAT4) |
| 谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶GPX | 6 |
| 抗坏血酸过氧化物酶APX | 8(Cyt APX2 L-5)~12(Chl APX2) |
| 单脱氢抗坏血酸还原酶MR | 7(Chl MR1)~17(Chl MR2) |
| 谷胱甘肽还原酶GR | 10(Chl GR)~16(Pla GR) |
| 脱氢抗坏血酸还原酶DR | 3(Chl DR2)~6(Chl DR3) |
Table 4 Number of exons of coding genes each antioxidant enzyme
| 抗氧化酶Antioxidant enzyme | 外显子数量Number of exons(基因名称Gene name) |
|---|---|
| 超氧化物歧化酶SOD | 4(Nucp Fe SOD)~9(Chl Fe SOD1) |
| 过氧化氢酶CAT | 1(Pla CAT5)~15(Pla CAT4) |
| 谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶GPX | 6 |
| 抗坏血酸过氧化物酶APX | 8(Cyt APX2 L-5)~12(Chl APX2) |
| 单脱氢抗坏血酸还原酶MR | 7(Chl MR1)~17(Chl MR2) |
| 谷胱甘肽还原酶GR | 10(Chl GR)~16(Pla GR) |
| 脱氢抗坏血酸还原酶DR | 3(Chl DR2)~6(Chl DR3) |
亚细胞区室 Subcellular compartment | 基因数量Number of genes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
总计 Total | 不响应TYLCV Not respond to TYLCV | 响应TYLCV Respond to TYLCV | 响应TYLCV和NO Respond to TYLCV and NO | |
| 细胞质Cytoplasm | 11 | 3 | 7 | 3 |
| 细胞膜Plasma membrane | 14 | 7 | 6 | 4 |
| 叶绿体Chloroplast | 19 | 8 | 10 | 5 |
| 线粒体Mitochondrial | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| 过氧化物酶体Peroxysome | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
细胞核Nucleus 核膜Nuclear membrane | 2 1 | 1 1 | 1 0 | 0 0 |
| 液泡Vacuole | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 内质网Endoplasmic reticulum | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Table 5 Number of antioxidase-coding genes responsed to TYLCV and NO regulation in different subcellular compartment of tomato
亚细胞区室 Subcellular compartment | 基因数量Number of genes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
总计 Total | 不响应TYLCV Not respond to TYLCV | 响应TYLCV Respond to TYLCV | 响应TYLCV和NO Respond to TYLCV and NO | |
| 细胞质Cytoplasm | 11 | 3 | 7 | 3 |
| 细胞膜Plasma membrane | 14 | 7 | 6 | 4 |
| 叶绿体Chloroplast | 19 | 8 | 10 | 5 |
| 线粒体Mitochondrial | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| 过氧化物酶体Peroxysome | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
细胞核Nucleus 核膜Nuclear membrane | 2 1 | 1 1 | 1 0 | 0 0 |
| 液泡Vacuole | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 内质网Endoplasmic reticulum | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
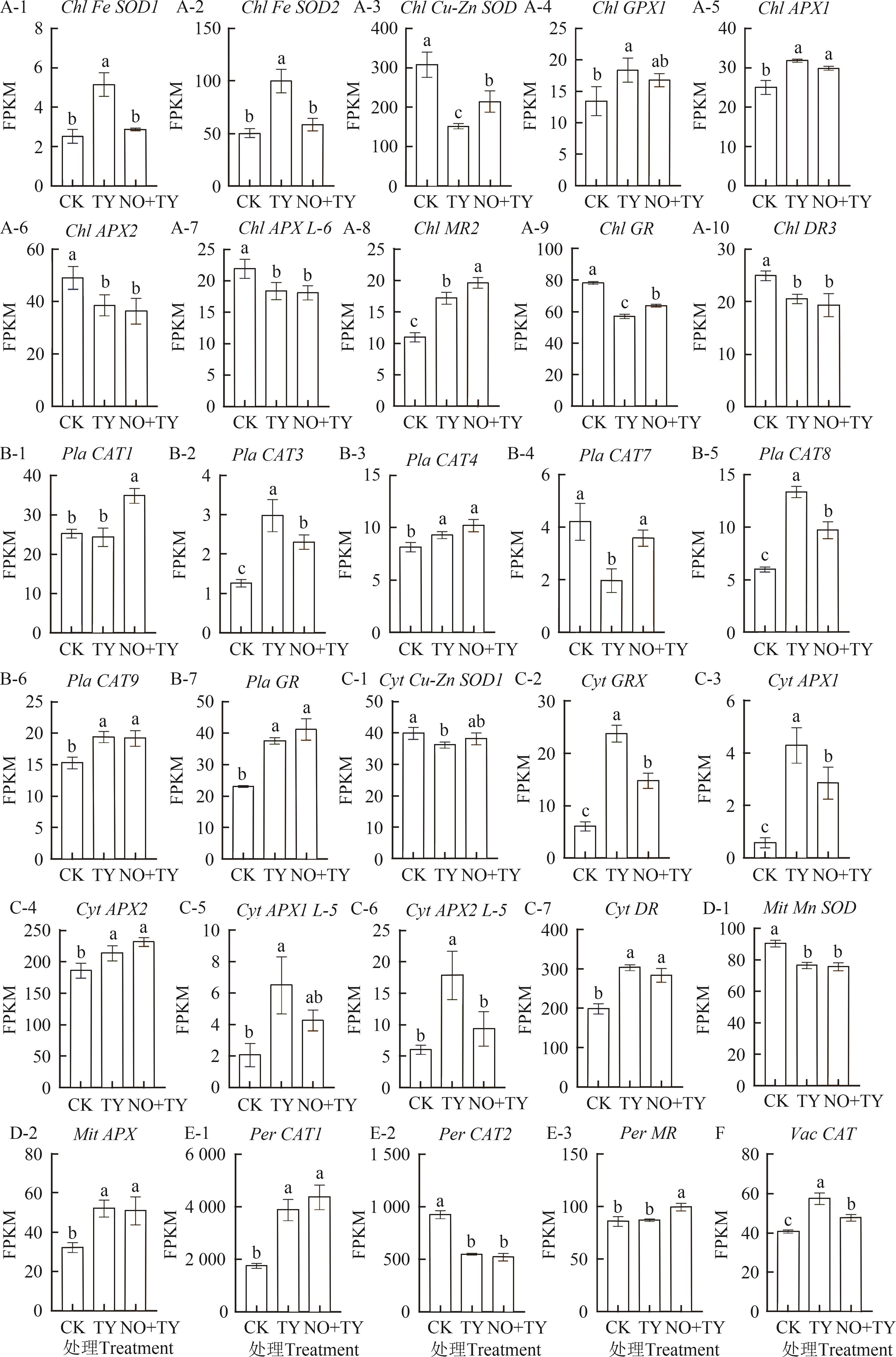
Fig. 2 Expression levels of antioxidase coding genes under different treatmentA-1~A-10: Response genes located in chloroplasts; B-1~B-7: Response genes located in cell membrane; C-1~C-7: Response genes located in cytoplasm; D-1~D-2: Response genes located in mitochondria;E-1~E-3: Response genes located in peroxisome; F: Response genes located in vacuole. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level
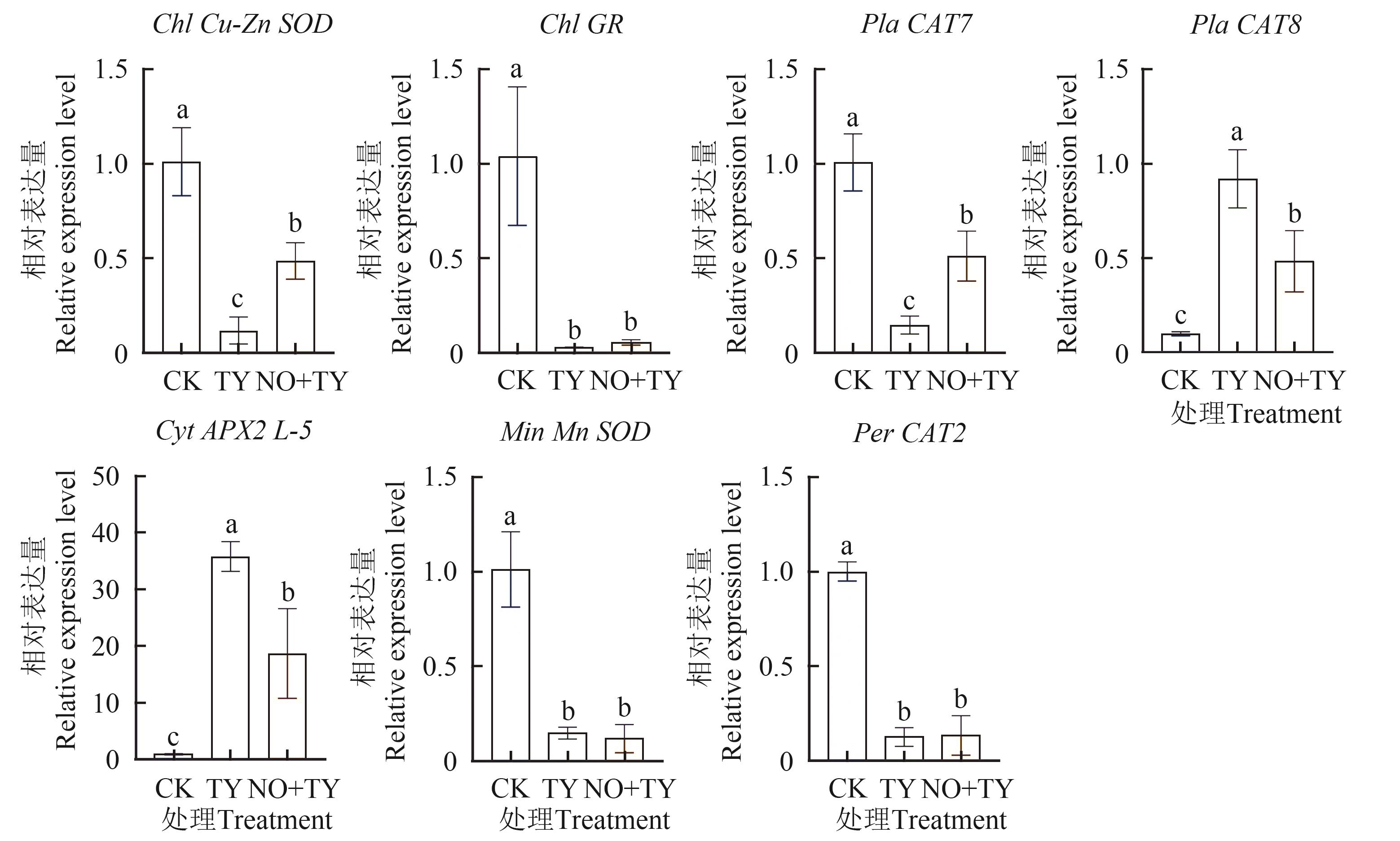
Fig. 3 Relative expression level of differential gene based on qRT-PCRNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 1 | VAN ECK J, KIRK D D, WALMSLEY A M. Tomato (Lycopersicum esculentum) [J]. Methods Mol. Biol., 2006, 343(1):459-473. |
| 2 | 国艳梅,杜永臣,王孝宣,等.番茄黄化卷叶病毒病(TYLCV)的研究进展[J].中国农业科技导报,2009,11(5):30-35. |
| GUO Y M, DU Y C, WANG X X, et al.. Research progress in tomato yellow leaf curl viruses [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2009, 11(5):30-35. | |
| 3 | LI T, WANG Y H, HUANG Y, et al.. A novel plant protein-disulfide isomerase participates in resistance response against the TYLCV in tomato [J/OL]. Planta, 2020, 252(2):1 [2023-07-20]. . |
| 4 | PRASAD A, SHARMA N, HARI-GOWTHEM G, et al.. Tomato yellow leaf curl virus: impact, challenges, and management [J]. Trends Plant Sci., 2020, 25(9):897-911. |
| 5 | SUN W J, LYU W J, LI L N, et al.. Eugenol confers resistance to tomato yellow leaf curl virus (TYLCV) by regulating the expression of SlPer1 in tomato plants [J]. New Biotechnol., 2016, 33(3):345-389. |
| 6 | PITERKOVÁ J, LUHOVÁ L, MIESLEROVÁ B, et al.. Nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species regulate the accumulation of heat shock proteins in tomato leaves in response to heat shock and pathogen infection [J]. Plant Sci., 2013, 207(1):57-65. |
| 7 | ZHENG Y, HONG H, CHEN L, et al.. LeMAPK1, LeMAPK2, and LeMAPK3 are associated with nitric oxide-induced defense response against Botrytis cinerea in the Lycopersicon esculentum fruit [J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2014, 62(6):1390-1396. |
| 8 | NOORBAKHSH Z, TAHERI P. Nitric oxide: a signaling molecule which activates cell wall-associated defense of tomato against Rhizoctonia solani [J]. Eur. J. Plant Pathol., 2016, 144(3):551-568. |
| 9 | SIVAKUMARAN A, AKINYEMI A, MANDON J, et al.. ABA suppresses botrytis cinerea elicited NO production in tomato to influence H2O2 generation and increase host susceptibility [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2016,7:709 [2023-07-20]. . |
| 10 | MAŁOLEPSZA U, RÓZALSKA S. Nitric oxide and hydrogen peroxide in tomato resistance. nitric oxide modulates hydrogen peroxide level in o-hydroxyethylorutin-induced resistance to Botrytis cinerea in tomato [J]. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 2005, 43(6):623-635. |
| 11 | DELLEDONNE M, ZEIER J, MAROCCO A, et al.. Signal interactions between nitric oxide and reactive oxygen intermediates in the plant hypersensitive disease resistance response [J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2001, 98(23):13454-13459. |
| 12 | ROMERO-PUERTAS M C, LAXA M, MATTÈ A, et al.. S-nitrosylation of peroxiredoxin II E promotes peroxynitrite-mediated tyrosine nitration [J]. Plant Cell, 2007, 19(12):4120-4130. |
| 13 | DELLEDONNE M. NO news is good news for plants [J]. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol., 2005, 8(4):390-396. |
| 14 | 胡炎.东南景天对镉胁迫的响应和镉再转运的生理与分子机制[D].杭州:浙江大学,2019. |
| HU Y. Physiological and molecular responses and cadmium retranslocation in sedum alfredii under cadmium stress [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Uniiversity, 2019. | |
| 15 | KENNETH J L, THOMAS D S. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and thg 2-∆∆CT method [J]. Method, 2001, 25(4): 402-408. |
| 16 | CHOE S, CHOI B, KANG J H, et al.. Tolerance to tomato yellow leaf curl virus in transgenic tomato overexpressing a cellulose synthase-like gene [J]. Plant Biotechnol. J., 2021, 19(4):657-659. |
| 17 | ALI S, HUANG Z, LI H, et al.. Antioxidant enzyme influences germination, stress tolerance, and virulence of Isaria fumosorosea [J]. J. Basic Microbiol., 2013, 53(6):489-497. |
| 18 | HAO Q, ZHANG L, YANG Y, et al.. Genome-wide analysis of the WOX gene family and function exploration of GmWOX18 in soybean [J/OL]. Plants (Basel), 2019, 8(7): 8070215 [2023-07-20]. . |
| 19 | YU W, KONG G, CHAO J, et al.. Genome-wide identification of the rubber tree superoxide dismutase (SOD) gene family and analysis of its expression under abiotic stress [J/OL]. PeerJ, 2022, 10: 14251 [2023-07-20]. . |
| 20 | ZHANG Y, ZHENG L, YUN L, et al.. Catalase (CAT) gene family in wheat (Triticum aestivum L .): evolution, expression pattern and function analysis [J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2022, 23(1):542 [2023-07-20]. . |
| 21 | 刘放.不同番茄材料黄化曲叶病毒病抗性研究[D].兰州:甘肃农业大学,2020. |
| LIU F. Study on resistance to yellow leaf curl virus disease in different tomato materials [D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2020. | |
| 22 | 韦弟,韦莉萍,周维,等.香蕉枯萎病菌对不同抗性香蕉品种根系抗氧化能力的影响[J].南方农业学报,2021,52(7):1851-1859. |
| WEI D, WEI L P, ZHOU W, et al.. Effects of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense on antioxidant capacity in roots of different resistant banana varieties [J]. J. Southern Agric., 2021, 52(7):1851-1859. | |
| 23 | 丁玉梅,张杰,谢俊俊,等.枯萎病菌胁迫下3种黑籽南瓜HQRGA2表达及抗氧化酶活性差异分析[J].植物生理学报,2019,55(3):349-358. |
| DING Y M, ZHANG J, XIE J J, et al.. Expression analysis of HQRGA2 and differences of anti-oxidant enzymes in three varieties of Cucurbita ficifolia under stress of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Cucumerinum [J]. Plant Physiol. J., 2019, 55(3):349-358. | |
| 24 | SHANG S, TANG Y, DAI J, et al.. Genomic analysis of the principal members of antioxidant enzymes in simulated stresses response and postharvest physiological deterioration in Cassava [J]. Trop. Plant Biol., 2021,14(1):419-428. |
| 25 | JIANG M, MIAO L X, HE C. Overexpression of an oil radish superoxide dismutase gene in broccoli confers resistance to downy mildew [J]. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep., 2012,30(1):966-972. |
| 26 | MHAMDI A, NOCTOR G, BAKER A. Plant catalases: peroxisomal redox guardians [J]. Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 2012,525(2):181-194. |
| 27 | 张志刚.大白菜抗芜菁花叶病毒(TuMV)遗传规律及过氧化氢等保护酶与抗病性关系的研究[D].泰安:山东农业大学,2011. |
| ZHANG Z G. Studies on Inheritance of TuMV resistance of Chinese cabbage and the relationship between protective enzymes and TuMV resistance [D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2011. | |
| 28 | 赵晓菊,张丽霞,满秀玲.NO对盐胁迫下长春花种子萌发和幼苗生理代谢的影响[J].植物研究,2018,38(5):669-674, 681. |
| ZHAO X J, ZHANG L X, MAN X L. Effects of exogenous NO on seed germination and physiological metabolism in Catharanthus roseus seedling under NaCl stress [J]. Bull. Bot. Res., 2018, 38(5):669-674, 681. | |
| 29 | SHI H T, LI R J, CAI W, et al.. In vivo role of nitric oxide in plant response to abiotic and biotic stress [J]. Plant Signaling Behav., 2012, 7(3):437-439. |
| 30 | WANG X, WANG B, ZHU X, et al.. Exogenous nitric oxide alleviates the damage caused by tomato yellow leaf curl virus in tomato through regulation of peptidase inhibitor genes [J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2022, 23(20):12542 [2023-07-20]. . |
| 31 | CHOE S, CHOI B, KANG J H, et al.. Tolerance to tomato yellow leaf curl virus in transgenic tomato overexpressing a cellulose synthase-like gene [J]. Plant Biotechnol. J., 2021, 19(4):657-659. |
| 32 | LI Y, CAO X L, ZHU Y, et al.. Osa-miR398b boosts H2O2 production and rice blast disease-resistance via multiple superoxide dismutases [J]. New Phytol., 2019, 222(3):1507-1522. |
| 33 | 于力,郭世荣,朱为民,等.番茄黄化曲叶病毒对番茄叶片光合特性和叶绿体超微结构的影响[J].西北植物学报,2011,31(7):1355-1359. |
| YU L, GUO S R, ZHU W M, et al.. Effects of tomato yellow leaf curl virus on photosynthetic characteristics and chloroplast ultra-structure of the tomato leaves [J]. Acta Bot. Bor-Occid. Sin., 2011, 31(7):1355-1359. | |
| 34 | 张永平,朱为民.TYLCV侵染对番茄叶片解剖结构和保护酶系统的影响[J].安徽农业科学,2009,37(29):14188-14190. |
| ZHANG Y P, ZHU W M. The effects of TYLCV infection on leaf anatomical structure and protective enzyme system of tomato [J]. J. Anhui Agric. Sci., 2009, 37(29):14188-14190. | |
| 35 | 许培磊,杨义明,秦红艳,等.不同品种山葡萄接种霜霉病菌后叶片的超微结构与抗氧化酶活性变化[J].北方园艺,2018(17):45-54. |
| XU P L, YANG Y M, QIN H Y, et al.. Changes of ultrastructure and antioxidant enzyme in leaves of two cultivars of Vitis amurensis in response to downy mildew [J]. Northern Hortic., 2018 (17):45-54. |
| [1] | Chunjiao MI, Hongren SUN, Jiping ZHANG, Yucai LYU, Yandi ZHANG. Abundance-deficiency Index of Soil Available Phosphorus and Recommended Phosphorus Fertilizer Application Rates for Tomato in China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(1): 222-232. |
| [2] | Xianguo LI, Qi DAI, Zepeng WANG, Zhaolong CHEN, Huizhuan YAN, Ning LI. Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of Tomato CCCH-like Zinc Finger Protein Family [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(1): 80-95. |
| [3] | Junlei ZHANG, Xiaotong GE, Zhengting ZHAO, Di LIU, Jinfeng WANG, Ning JIANG, Yating LIU. Establishment and Optimization of RT-LAMP Assay System for Tobacco Tomato Spotted Wilt Virus [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(8): 140-150. |
| [4] | Fulin ZHANG, Rui XI, Yuxiang LIU, Zhaolong CHEN, Qinghui YU, Ning LI. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Tomato BURP Structural Domain Gene Family [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(8): 51-62. |
| [5] | Zifan WANG, Yan LI, Qingyin ZHANG, Dandan WANG, Jianhua SHI, Xiaobin GENG, Dongliang TIAN, Zengming ZHONG, Xiaoming ZHAO, Lianfen QI. Effect of Microbicides on Main Diseases and Soil Microbial Communities of Tomatoes in Facilities [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(6): 102-112. |
| [6] | Mingbo LI, Yule LIU, Zhimin MU, Junwang GUO, Yong WEI, Dongyue REN, Jishen JIA, Zezhong WEI, Yuhong LI. Tomato Fruit Recognition Based on YOLOX-L-TN Model [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(4): 97-105. |
| [7] | Daye HUANG, Zhibin YU, Zhongyi WAN, Dan YANG, Jinping LI, Chunxia CAO. Study on Control Effect of Streptomyces phaeoluteichromatogenes HEBRC45958 Strain on Corynespora Leaf Spot of Tomato [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(11): 136-142. |
| [8] | Xiubo XIA, Tao LI, Shoujun CAO, Jiangang YAO, Hongyun WANG, Lili ZHANG. Effect of Liquid Organic Fertilizer Partial Replacing Chemical Fertilizer on Bacterial Community in Greenhouse Tomato Root Zone [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(7): 187-196. |
| [9] | LIU Qianjie, CHENG Yunxia, JIA Kai, SHI Zhenyu, ZHANG Jing, WEI Shaowei, WU Hui*. Influences of Nitrogen Application on Nitrogen Metabolism Enzymes Activities, Yield and Quality of Tomato in Composite Sand Culture [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(4): 183-191. |
| [10] | GU Huimin1, CHEN Bolang1*, SUN Jin2. Influences of Mycorrhizal Seedling on Growth and Physiological Characteristics of Processing Tomato Under Salt Stress#br# [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(3): 166-177. |
| [11] | CHEN Xiaojie, LYU Desheng, WANG Zhenhua, LI Wenhao, ZONG Rui, WEN Yue, ZOU Jie. Effects of Water and Nitrogen Coupling on the Yield and Quality of Processing Tomato Under Aerated Irrigation [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(11): 191-200. |
| [12] | LI Yanmei1, ZHOU Yawen2, ZHANG Lin1, LIAO Shangqiang1*, SUN Yanxin1*. Coupling Effects of Stress-resistant Substances and Osmotic Regulators on Tomato Yield and Water Use Efficiency and Its Possible Mechanism [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(1): 43-50. |
| [13] | CUI Huaxing1§, WANG Ning2,3§, HOU Min2,3, XU Junfeng1, GUO Wenchao2,3, AN Kang4, CHEN Yanghui4, CUI Weidong2,3*. Application of Bacillus subtilis DNKAS to Control Orobanche aegyptiaca of Processing Tomato [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(12): 105-114. |
| [14] | YANG Jiajia1, LIU Yifei1*, LIU Wenke1,2*. Effects of Straw Fermentation in Furrow Soil on Root Zone Temperature, CO2 Release and Tomato Growth Cultivated by Soil-ridged and Substrate-embedded Cultivation Method [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(12): 137-145. |
| [15] | LI Chuanyou1, DOU Shuo2, XIONG Bo1, ZHANG Li1, LI Zhen1, TENG Fei1, LIU Jingrui1, YANG Ye1, CHEN Yumei1. Study on the Operation Ways and Parameters of Cold Aerosol Sprayer at Different Growth Stages of Tomato in Greenhouse [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(11): 87-94. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号