




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (4): 57-67.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0810
• BIOTECHNOLOGY & LIFE SCIENCE • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhiduo DONG1( ), Qiuping FU1(
), Qiuping FU1( ), Jian HUANG2(
), Jian HUANG2( ), Tong QI2, Yanbo FU2,3, Kuerban Kaisaier3
), Tong QI2, Yanbo FU2,3, Kuerban Kaisaier3
Received:2023-11-05
Accepted:2024-01-08
Online:2025-04-15
Published:2025-04-15
Contact:
Qiuping FU,Jian HUANG
董志多1( ), 付秋萍1(
), 付秋萍1( ), 黄建2(
), 黄建2( ), 祁通2, 付彦博2,3, 开赛尔·库尔班3
), 祁通2, 付彦博2,3, 开赛尔·库尔班3
通讯作者:
付秋萍,黄建
作者简介:董志多E-mail:1281228561@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Zhiduo DONG, Qiuping FU, Jian HUANG, Tong QI, Yanbo FU, Kuerban Kaisaier. Analysis of Salt Tolerance Capacity of Xinjiang Cotton Guring Germination[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(4): 57-67.
董志多, 付秋萍, 黄建, 祁通, 付彦博, 开赛尔·库尔班. 新疆棉花萌发期的耐盐能力分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(4): 57-67.
处理 Treatment | 盐碱组分 Salt composition | ||||
| NaCl | Na2SO4 | NaHCO3 | Na2CO3 | ||
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| S1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| S2 | 9 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| S3 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 1 | |
| S4 | 9 | 1 | 9 | 1 | |
Table 1 Saline-alkali components and their molar ratio in each treatment
处理 Treatment | 盐碱组分 Salt composition | ||||
| NaCl | Na2SO4 | NaHCO3 | Na2CO3 | ||
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| S1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| S2 | 9 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| S3 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 1 | |
| S4 | 9 | 1 | 9 | 1 | |
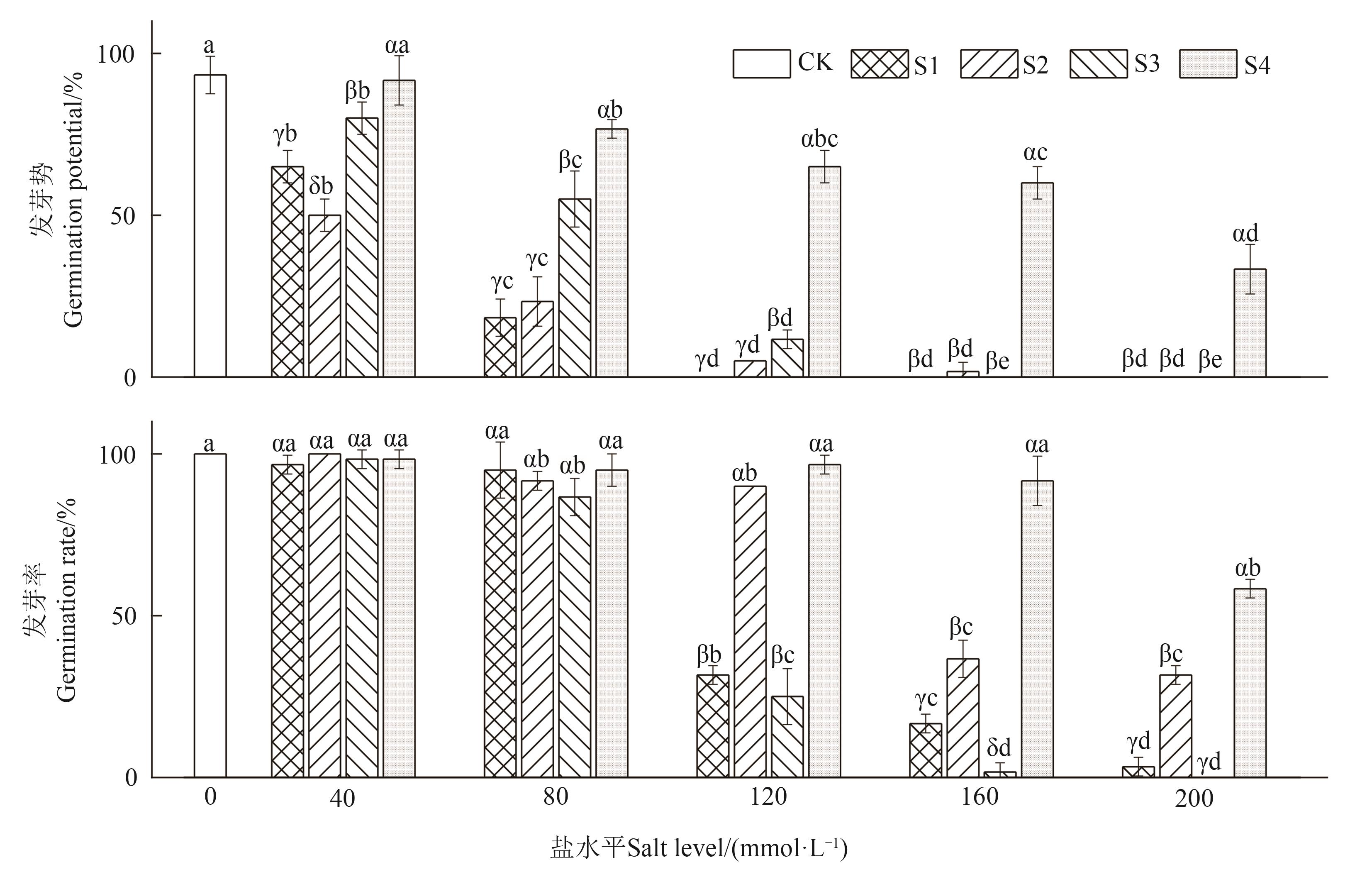
Fig. 1 Germination potential and germination rate of cotton seeds of Tahe 2 under 4 salt stressesNote:Different Greece letters indicate the significant differences between different saline stresses of the same salt level at P<0.05 level, and different English letters indicate significant differences between different salt level under same salinity stress at P<0.05 level.

Fig. 2 Germination potential and germination rate of cotton seeds of Xinluzhong 62 under 4 salt stressesNote:Different Greece letters indicate the significant differences between different saline stresses of the same salt level at P<0.05 level, and different English letters indicate significant differences between different salt level under same salinity stress at P<0.05 level.
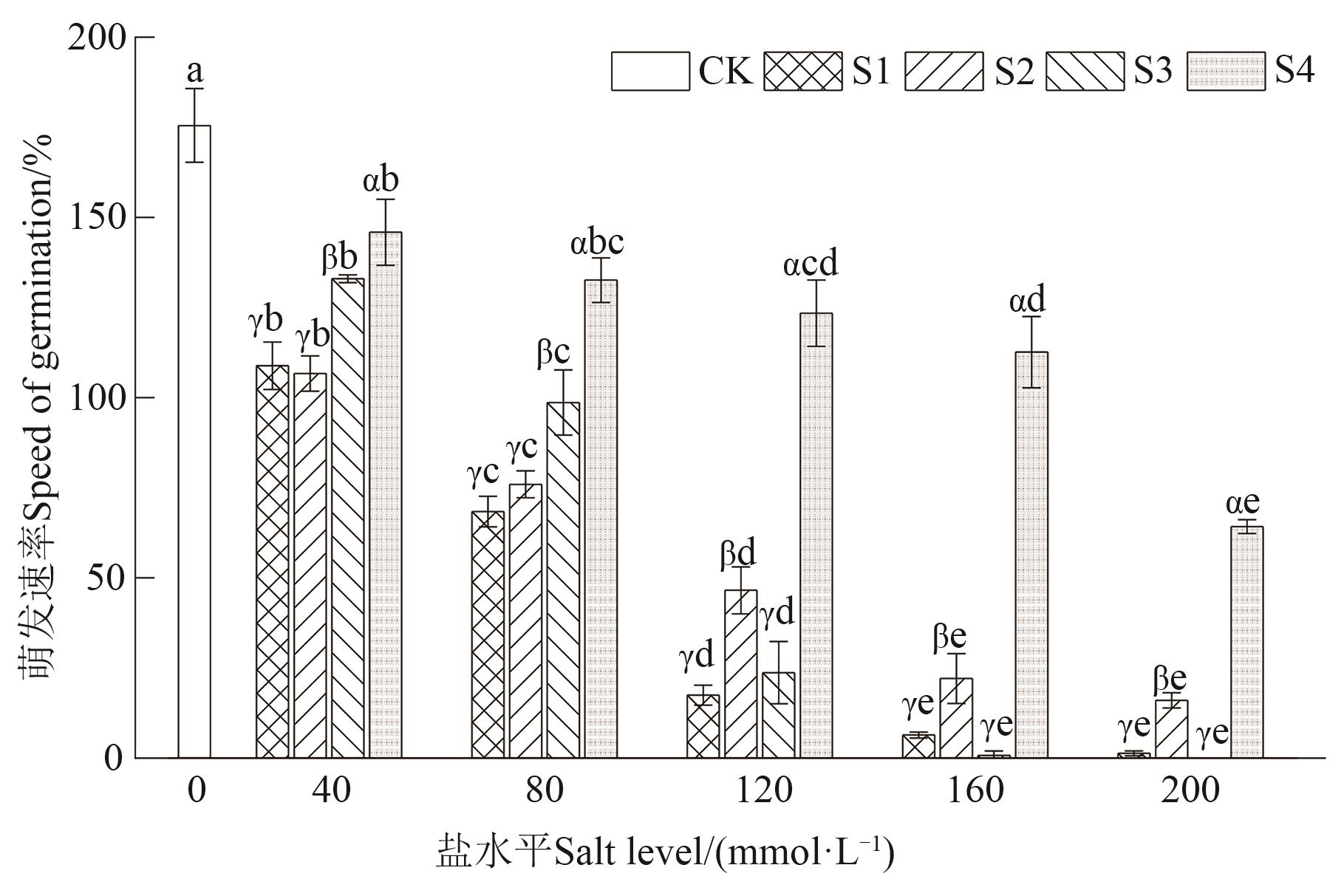
Fig. 4 Speed of germination of Tahe 2 cotton seeds under 4 salt stressesNote:Different Greece letters indicate the significant differences between different saline stresses of the same salt level at P<0.05 level, and different English letters indicate significant differences between different salt level under same salinity stress at P<0.05 level.
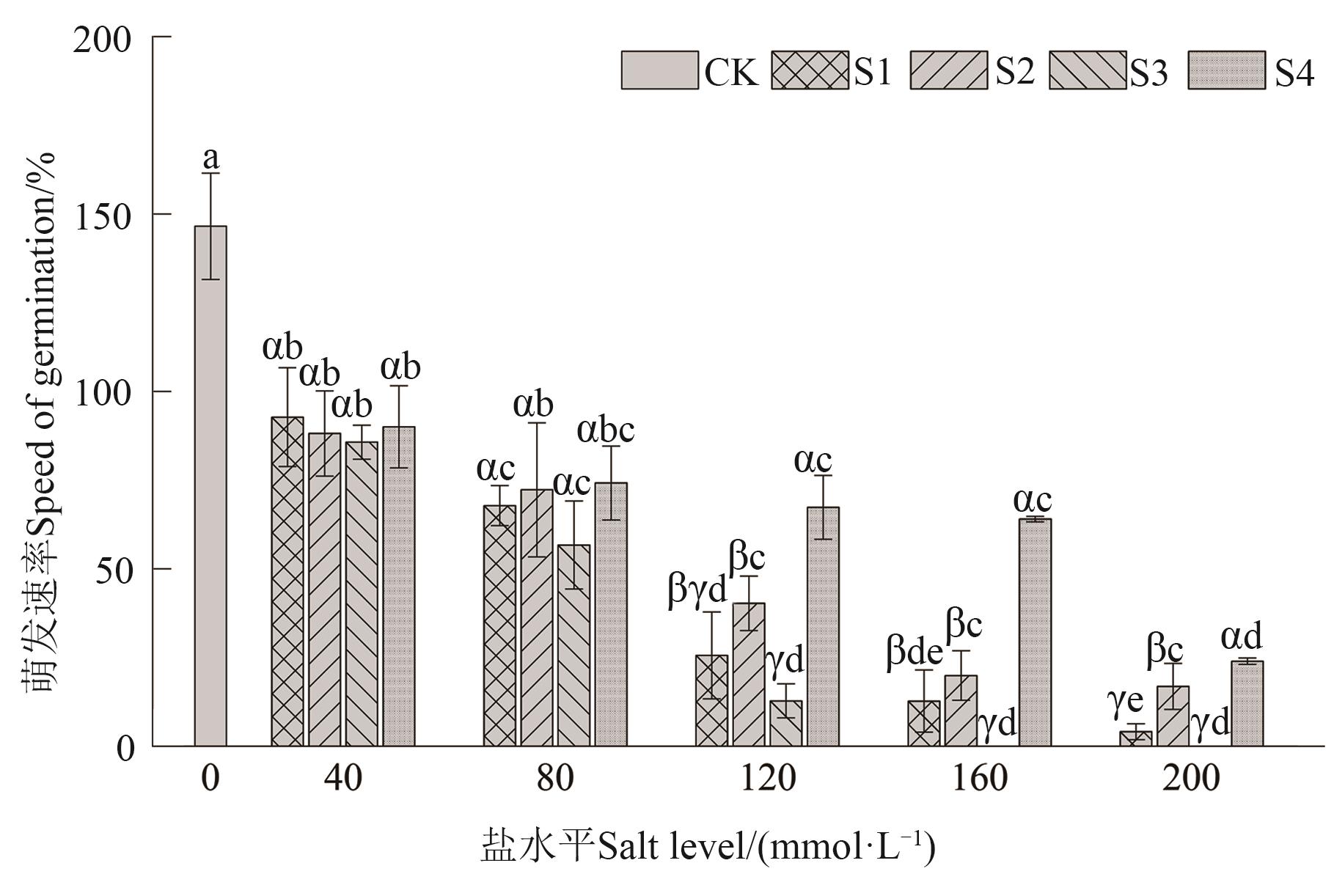
Fig. 5 Speed of germination of Xinluzhong 62 cotton seeds under 4 salt stressesNote:Different Greece letters indicate the significant differences between different saline stresses of the same salt level at P<0.05 level, and different English letters indicate significant differences between different salt level under same salinity stress at P<0.05 level.

Fig. 7 Comprehensive effects of 4 types of salt stress on various parameters of cotton seedsA:Heat map of correlation analysis of each index of Tahe 2; B: Heat map of correlation analysis of each index of Xinluzhong 62; C: Biplot of principal component analysis individual and vector of Tahe 2; D: Biplot of principal component analysis individual and vector of Xinluzhong 62. *, ** and *** indicate significance at P<0.05, P<0.01 and P<0.001 levels, respectively. X1—Germination potential; X2—Germination rate; X3—Germination speed; X4—Fresh weight; X5—Dry weight
处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | 拟合方程 Fitting equation | R2 | 半致死浓度 Critical salinity concentration/(mmol·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 塔河2号Tahe 2 | y=8.26+90.71/[1+(x/107.74)9.22] | 0.992 6 | 109.62 |
| 新陆中62号Xinluzhong 62 | y=5.23+89.65/[1+(x/115.11)5.22] | 0.993 3 | 115.99 | |
| S2 | 塔河2号Tahe 2 | y=31.48+65.75/[1+(x/136.96)15.78] | 0.991 0 | 145.34 |
| 新陆中62号Xinluzhong 62 | y=30.62+62.6/[1+(x/124.21)8.75] | 0.988 1 | 137.12 | |
| S3 | 塔河2号Tahe 2 | y=-1.49+100.65/[1+(x/104.29)7.42] | 0.999 8 | 103.64 |
| 新陆中62号Xinluzhong 62 | y=-1.79+97.02/[1+(x/94)6.45] | 0.997 9 | 92.54 | |
| S4 | 塔河2号Tahe 2 | y=-10 219.61+10 317.28/[1+(x/389.75)8.34] | 0.989 5 | — |
| 新陆中62号Xinluzhong 62 | y=-465 228.22+465 318.48/[1+(x/1163.57)5.09] | 0.930 5 | 186.13 |
Table 2 Fitting equations and critical salinity concentrations of cotton seed germination rate under 4 salt stresses
处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | 拟合方程 Fitting equation | R2 | 半致死浓度 Critical salinity concentration/(mmol·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 塔河2号Tahe 2 | y=8.26+90.71/[1+(x/107.74)9.22] | 0.992 6 | 109.62 |
| 新陆中62号Xinluzhong 62 | y=5.23+89.65/[1+(x/115.11)5.22] | 0.993 3 | 115.99 | |
| S2 | 塔河2号Tahe 2 | y=31.48+65.75/[1+(x/136.96)15.78] | 0.991 0 | 145.34 |
| 新陆中62号Xinluzhong 62 | y=30.62+62.6/[1+(x/124.21)8.75] | 0.988 1 | 137.12 | |
| S3 | 塔河2号Tahe 2 | y=-1.49+100.65/[1+(x/104.29)7.42] | 0.999 8 | 103.64 |
| 新陆中62号Xinluzhong 62 | y=-1.79+97.02/[1+(x/94)6.45] | 0.997 9 | 92.54 | |
| S4 | 塔河2号Tahe 2 | y=-10 219.61+10 317.28/[1+(x/389.75)8.34] | 0.989 5 | — |
| 新陆中62号Xinluzhong 62 | y=-465 228.22+465 318.48/[1+(x/1163.57)5.09] | 0.930 5 | 186.13 |
| 1 | 刘毅.全区棉花播种面积超140万亩[N].新疆日报(汉),2023-04-10(001). |
| 2 | 刘传迹,金晓斌,徐伟义,等.2000—2020 年南疆地区棉花种植空间格局及其变化特征分析[J].农业工程学报,2021,37(16):223-232. |
| LIU C J, JIN X B, XU W Y, et al.. Analysis of the spatial distribution and variation characteristics of cotton planting in southern Xinjiang from 2000 to 2020 [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2021,37(16):223-232. | |
| 3 | 刘群,彭斌,田长彦,等.8种盐生植物种子萌发特征与NaCl盐度的关系探究[J].生态学报 2023,43(17):7284-7293. |
| LIU Q, PENG B, TIAN C Y, et al.. Study on the relationship between germination characteristics of 8 halophytes and NaCl salinity [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2023,43(17): 7284-7293. | |
| 4 | 苏莹,郭安慧,华金平.棉花耐盐性鉴定方法探讨[J].中国农业大学学报,2021,26(12):11-19. |
| SU Y, GUO A H, HUA J P. Strategies for evaluation the salt tolerance in cotton [J]. J. China Agric. Univ., 2021,26(12):11-19. | |
| 5 | 石婧,刘东洋,张凤华.棉花幼苗对盐胁迫的生理响应与耐盐机理[J].浙江农业学报,2020,32(7):1141-1148. |
| SHI J, LIU D Y, ZHANG F H. Physiological response and salt tolerance mechanism of cotton seedlings to salt stress [J]. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis, 2020,32(7):1141-1148. | |
| 6 | 杨淑萍,危常州,梁永超.盐胁迫对不同基因型海岛棉种子萌发特性的影响[J].中国棉花,2012,39(12):6-10. |
| YANG S P, WEI C Z, LIANG Y C. Effects of NaCl stress on characteristics of seed germination of sea island cotton with different genotypes [J]. China Cott., 2012,39(12):6-10. | |
| 7 | 江晓慧,高阳,王广帅,等.基于FvCB模型分析盐分胁迫对棉花叶片光合作用的影响[J].应用生态学报,2020,31(5):1653-1659. |
| JIANG X H, GAO Y, WANG G S, et al.. Examining effects of salt stress on leaf photosynthesis of cotton based on the FvCB model [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2020,31(5):1653-1659. | |
| 8 | 郭家鑫,鲁晓宇,陶一凡,等.硫酸盐胁迫对棉花生理和代谢的影响[J].棉花学报,2022,34(6):479-493. |
| GUO J X, LU X Y, TAO Y F, et al.. Effects of sulfate stress on physiology and metabolism of cotton [J]. Cott. Sci., 2022,34(6):479-493. | |
| 9 | 李双男,郭慧娟,王晶,等.不同盐碱胁迫对棉花种子萌发的影响[J].种子,2018,37(1):38-45. |
| LI S N, GUO H J, WANG J, et al.. Effects of different saline and alkaline stress on seed [J]. Seed, 2018,37(1):38-45. | |
| 10 | 徐曼,王茜,王奕骁,等.不同盐胁迫对长穗偃麦草种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J].中国草地学报,2020,42(1):15-20. |
| XU M, WANG Q, WANG Y X, et al.. Effects of different salt stress on seed germination and seedling growth of Elytrigia elongate [J]. Chin. J. Grassland, 2020,42(1):15-20. | |
| 11 | 井源.陆地棉苗期耐盐性响应性状的鉴定与评价[D].保定:河北农业大学,2019. |
| JING Y. Identification and evaluation of salt tolerance correlated traits in seedling stage of gossypium hirsutum [D]. Baoding:Hebei Agricultural University, 2019. | |
| 12 | 李媛媛,陈博,姚立蓉,等.283份小麦品种(系)萌发期耐盐碱性评价及种质筛选[J].中国农业科技导报,2021,23(3):25-33. |
| LI Y Y, CHEN B, YAO L R, et al.. Evaluation of salt and alkali tolerance and germplasm screening of 283 wheat varieties (lines)during germination [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2021,23(3):25-33. | |
| 13 | 杨发荣,刘文瑜,黄杰,等.不同藜麦品种对盐胁迫的生理响应及耐盐性评价[J].草业学报,2017,26(12):77-88. |
| YANG F R, LIU W Y, HUANG J, et al.. Physiological responses of different quinoa varieties to salt stress and evaluation of salt tolerance [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2017,26(12):77-88. | |
| 14 | 侯文静,马祥,张志莹,等.混合盐碱胁迫对鹰嘴紫云英种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响[J].草原与草坪,2020,40(3):90-98. |
| HOU W J, MA X, ZHANG Z Y, et al.. Effects of mixed saline-alkali stress on seed germination and physiological characteristics of Astragalus cicer [J]. Grassland Turf, 2020,40(3):90-98. | |
| 15 | 兰艳,朱林,王甜甜,等.混合盐碱胁迫对3种稗属牧草种子萌发的影响[J].种子,2022,41(3):37-44. |
| LAN Y, ZHU L, WANG T T, et al.. Effects of mixed saline-alkali stress on seed germination of three kinds of Echinochloa grass [J]. Seed, 2022,41(3):37-44. | |
| 16 | 付鸾鸿.不同基因型燕麦耐盐碱性鉴定及生理生化响应机制研究[D].大庆:黑龙江八一农垦大学,2019. |
| FU L H. Identification of saline-alkaline tolerance and physiological and biochemical response mechanisms of different oat genotypes [D]. Daqing: Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 2019. | |
| 17 | 徐婷,柳延涛,王海江,等.盐碱胁迫对花生种子发芽特性影响及盐害综合鉴定评价[J].中国油料作物学报,2022,44(5):1037-1047. |
| XU T, LIU Y T, WANG H J, et al.. Effects of saline-alkali stress on germination characteristics of peanut seeds and comprehensive identification and evaluation of salt damage [J]. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci., 2022,44(5):1037-1047. | |
| 18 | 徐安阳,李琴,李代阔,等.花铃期干旱胁迫对南疆4个主推棉花品种产量及品质的影响[J].中国棉花,2023, 50(7):29-32. |
| XU A Y, LI Q, LI D K, et al.. Effects of drought stress at the flowering and boll period on yield and quality of four main cotton varieties in southern Xinjiang [J]. China Cott., 2023, 50(7):29-32. | |
| 19 | 孙文君.低温和盐碱胁迫下棉花幼苗对外源褪黑素的生理响应[D].阿拉尔:塔里木大学,2021. |
| SUN W J. Physiological response of cotton seedlings to exogenous melatonin under low temperature and salt-alkaline stress [D]. Alar: Tarim University, 2021. | |
| 20 | 陈雅琦.醉马草内生真菌共生体种子耐盐碱性与施氮对种子产量的影响[D].兰州:兰州大学,2022. |
| CHENG Y Q. The saline-alkali tolerance of seed of Epichloë endophytic fungi-Achnatherum inebrians symbiont and effects of nitrogen application on seed yield [D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2022. | |
| 21 | HU H, HAO L, LIU F. Seed germination of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) cultivars responds differently to the stress of salt type and concentration [J]. Ind. Crops Products, 2018, 123: 254-261. |
| 22 | 王桂峰,魏学文,贾爱琴.5个棉花品种的耐盐鉴定与筛选试验[J].山东农业科学,2013,45(10):51-55. |
| WANG G F, WEI X W, JIA A Q. Identification and screening test on salt tolerance of five cotton varieties [J]. Shandong Agric. Sci., 2013,45(10):51-55. | |
| 23 | 赵广兴,李王成,贾振江,等.盐碱复合胁迫对白茎盐生草种子萌发的影响[J].草业科学,2021,38(8):1469-1476. |
| ZHAO G X, LI W C, JIA Z J, et al.. Effects of salt-alkali mixed stresses on the seed germination of Halogeton arachnoideus [J]. Pratac. Sci., 2021,38(8):1469-1476. |
| [1] | Chang CHEN, Dan GUO, Qinghong BAI, Yang ZHANG, Maolin YAN. Research on International Comparison and Development Strategy of Competitiveness of China’s Oilseed Industry [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(4): 1-11. |
| [2] | Zhongzhong DOU, Yiqi LIU. Simulation Analysis of Arc-jaw Type Potato Precision Seed Discharger [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(4): 110-119. |
| [3] | Xiaoqing HOU, Zihao JIANG, Yang FU, Zhongzhen SONG, Zhimin YU. Composition and Structure of Extracellular Polysaccharides from Sphingomonas sp. and Their Promoting Effects on Barley Seedlings [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(4): 201-208. |
| [4] | Zihao WANG, Xue ZHOU, Donghan ZHANG, Hongyi LIANG, Yan WANG, Ziang ZHAO, Qing CHEN. Effect of Water-soluble Fertilizers Containing Humic-acids on Maize Seedlings Growth and Soil Properties [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(4): 209-220. |
| [5] | Yixin CHEN, Xiubo YANG, Shijun TIAN, Cong WANG, Zhiying BAI, Cundong LI, Ke ZHANG. Response of GhCOMT28 to Drought Stress in Gossypium hirsutum [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(4): 45-56. |
| [6] | Lintao CHEN, Zhaoxiang LIU, Ying LAN, Xiangwei MOU, Xu MA, Rijun WANG. Research on Rice Variety Identification Based on Hyperspectral Technology and Principal Component Analysis [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(3): 104-111. |
| [7] | Jing XU, Han LI, Pinglu CHEN, Jiangni LUO, Chenglu TANG, Muhua LIU. Calibration and Validation of Discrete Element Model for Camelliaoleifera Seed Meal [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(3): 112-121. |
| [8] | Na LI, Hua ZHANG, Xinzhu XING, Zhenqi SHAO, Zhanwu YANG, Xihuan LI, Caiying ZHANG. Function Analysis of Soybean Expansin Gene GmEXLA1 inPlantPod and Seed Development [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(3): 49-59. |
| [9] | Gang LEI, Rong FANG, Kunhua ZHOU, Xuejun CHEN, Xinjie YUAN, Yueqin HUANG, Gege LI, Yuanyuan XIE, Xiaomin SONG. Establishment of Comprehensive Evaluation System of Pepper Germplasm Resources on Heat Tolerance at Seedling Stage [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(3): 60-70. |
| [10] | Zicheng PENG, Hongli DU, Ming WANG, Fenghua ZHANG, Haichang YANG. Research on AMF Regulation of Cotton Growth and Ion Balance Under Salt Alkali Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(2): 33-41. |
| [11] | Tingting MA, Yanrong ZHAO, Yuqing WEI, Yuejuan WANG, Xuefei WANG, Erdong ZHANG. Dynamic Characteristics of Stem Growth and Sugar Accumulation of Sweet Sorghum at Late Growth Stage Under Soil Salt Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(2): 42-50. |
| [12] | Ningning WANG, Xuemei LUO, Mingyuan CHEN, Rui GUO, Jianguo LIU. Effects of Exogenous Melatonin on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Cyperusesculentus L. Under Salt and Drought Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(2): 51-61. |
| [13] | Shixu QU, Yu SUN, Yizhen SUO, Haipeng YUAN, Yuhong ZHANG. Effects of Exogenous Calcium on Physiological Characteristics and Secondary Metabolites of Cannabis sativa L. Under Salt Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(2): 80-88. |
| [14] | Yumang ZHANG, Guijuan CHEN, Hongyan CHANG, Yongheng WANG, Shuxia LIU, Yunxiu YING. Effect of New Degradable Soil Water-retaining Agent on Growth and Development of Maize Seedlings Under Water Stress at Seedling Stage [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(1): 201-210. |
| [15] | Songjiang DUAN, Haoran HU, Chengjie ZHANG, Wei SUN, Yifan WU, Rensong GUO, Jusong ZHANG. Differences in Nitrogen Efficiency of Different Genotypes of Island Cotton and Their Effects on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Yield [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(1): 61-71. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号