




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (2): 80-88.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0332
• BIOTECHNOLOGY & LIFE SCIENCE • Previous Articles Next Articles
Shixu QU1( ), Yu SUN2, Yizhen SUO1, Haipeng YUAN1, Yuhong ZHANG1(
), Yu SUN2, Yizhen SUO1, Haipeng YUAN1, Yuhong ZHANG1( )
)
Received:2023-04-24
Accepted:2023-06-29
Online:2025-02-15
Published:2025-02-14
Contact:
Yuhong ZHANG
屈施旭1( ), 孙宇2, 所怡祯1, 苑海鹏1, 张玉红1(
), 孙宇2, 所怡祯1, 苑海鹏1, 张玉红1( )
)
通讯作者:
张玉红
作者简介:屈施旭 E-mail:996717353@qq.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Shixu QU, Yu SUN, Yizhen SUO, Haipeng YUAN, Yuhong ZHANG. Effects of Exogenous Calcium on Physiological Characteristics and Secondary Metabolites of Cannabis sativa L. Under Salt Stress[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(2): 80-88.
屈施旭, 孙宇, 所怡祯, 苑海鹏, 张玉红. 外源钙对盐胁迫下火麻生理特性及次生代谢产物的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(2): 80-88.
处理 Treatment | 盐胁迫 Salt stress | CaCl2含量 CaCl2 content/(mmol∙L-1) |
|---|---|---|
| CK | - | 0 |
| C0 | + | 0 |
| C1 | + | 5 |
| C2 | + | 10 |
| C3 | + | 20 |
Table 1 Different experimental treatments of C. sativa
处理 Treatment | 盐胁迫 Salt stress | CaCl2含量 CaCl2 content/(mmol∙L-1) |
|---|---|---|
| CK | - | 0 |
| C0 | + | 0 |
| C1 | + | 5 |
| C2 | + | 10 |
| C3 | + | 20 |
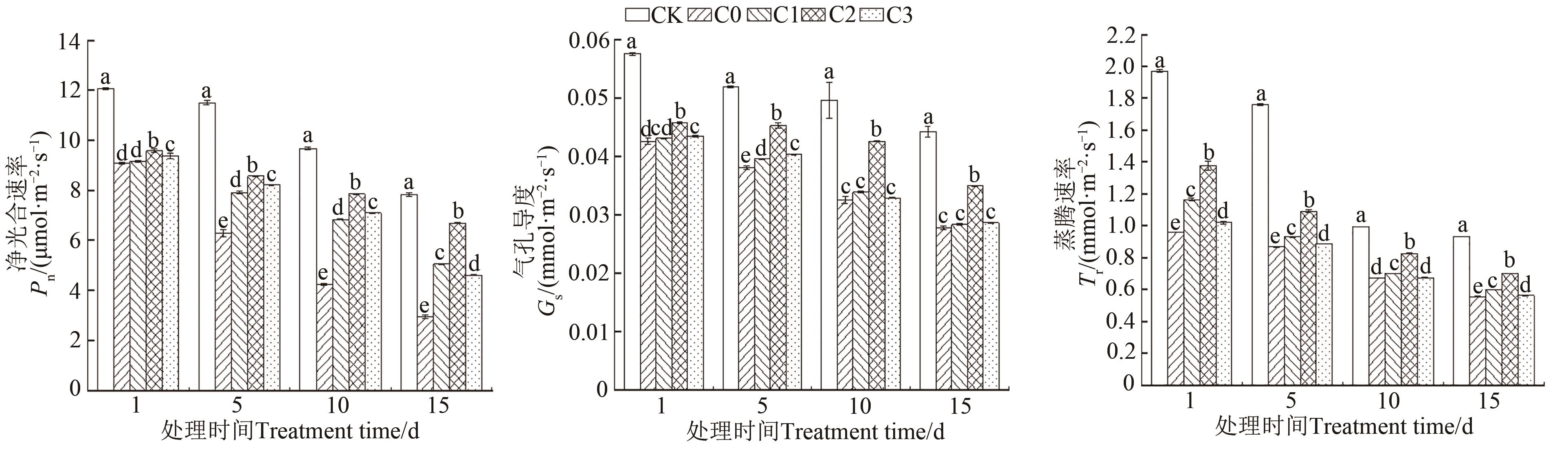
Fig. 1 Photosynthesis characteristics of C. sativa leaves under different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of same time at P<0.05 level.

Fig. 2 Maximum photochemical efficiency and chlorophyll content in leaves of C. sativa under different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of same time at P<0.05 level.
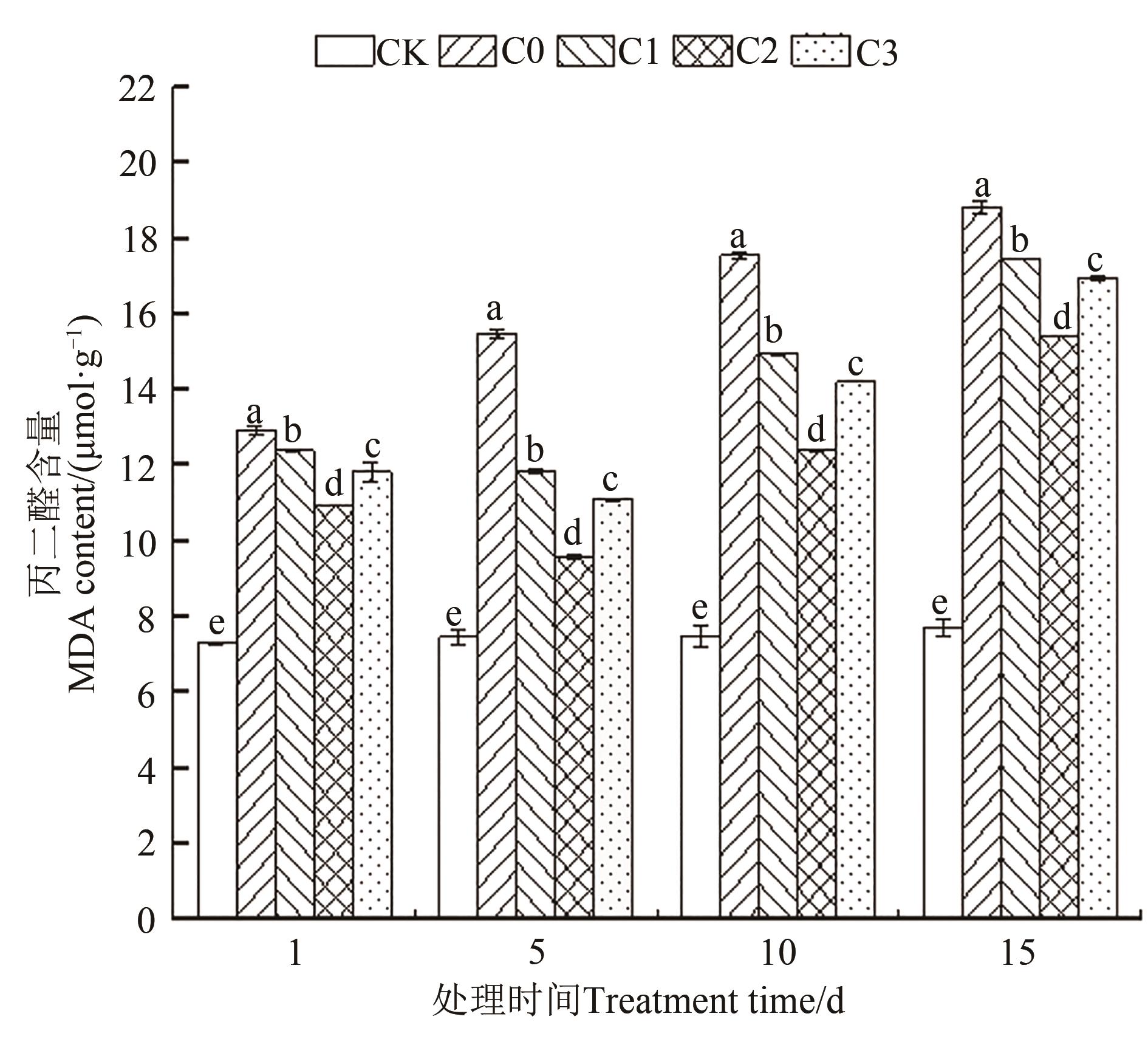
Fig. 3 MDA content in leaves of C. sativa under different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of same time at P<0.05 level.
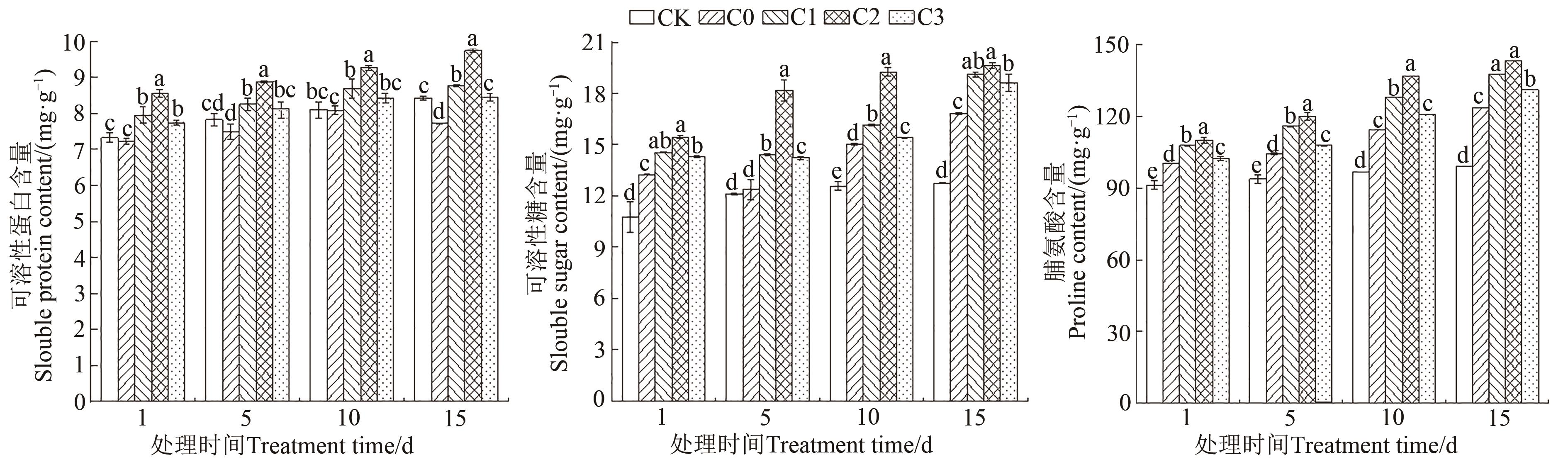
Fig. 4 Content of osmoregulatory substances in C. sativa leaves under different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of same time at P<0.05 level.

Fig. 5 Antioxidant enzyme activity in leaves of C. sativa under different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of same time at P<0.05 level.
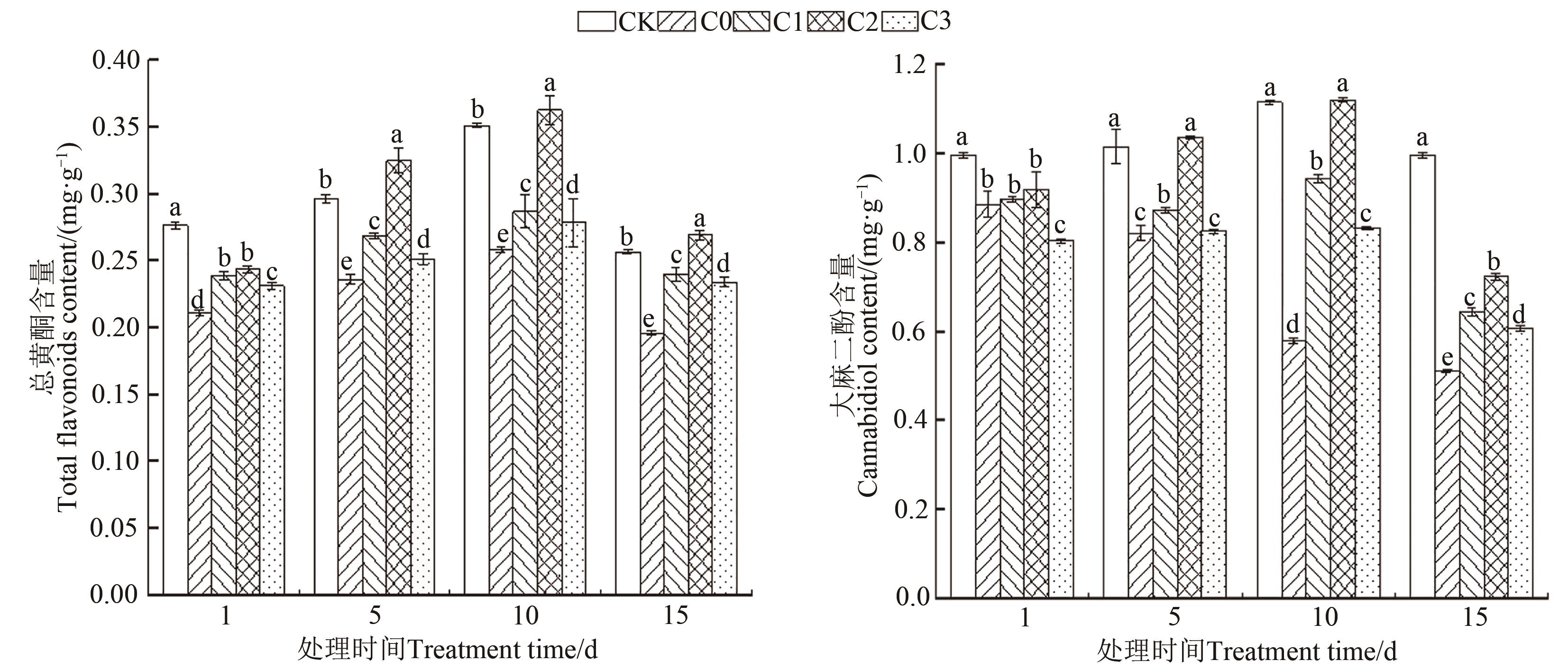
Fig. 6 Total flavonoids and cannabidiol contents of C. sativa leaves under different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of same time at P<0.05 level.
| 1 | 杨真,王宝山.中国盐渍土资源现状及改良利用对策[J].山东农业科学,2015,47(4):125-130. |
| YANG Z, WANG B S. Present status of saline soil resources and countermeasures for improvement and utilization in China [J]. Shandong Agric. Sci., 2015, 47(4):125-130. | |
| 2 | RAHNAMA A, JAMES RA, POUSTINI K, et al.. Stomatal conductance as a screen for osmotic stress tolerance in durum wheat growing in saline soil [J]. Funct. Plant Biol., 2010, 37(3):255-263. |
| 3 | 杨怡帆,吕新民,鲁晓燕,等.CaCl2对NaCl胁迫下酸枣幼苗抗逆生理指标的影响[J].石河子大学学报(自然科学版),2016,34(4):415-423. |
| YANG Y F, LYU X M, LU X Y, et al.. Effects of CaCl2 on physiological indexes of sour jujube seedlings under NaCl stress [J]. J. Shihezi Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2016, 34(4):415-423. | |
| 4 | CHEN Y Y, WANG J C, YAO L R, et al.. Combined proteomic and metabolomic analysis of the molecular mechanism underlying the response to salt stress during seed germination in barley [J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2022, 23(18):10515 [2023-03-14]. . |
| 5 | 苏文欣,许凌欣,姜宛彤,等.不同外源物质对盐碱胁迫下紫苏种子萌发、幼苗生长及生理的影响[J].草地学报,2022,30(9):2415-2422. |
| SU W X, XU L X, JIANG W T, et al.. Effects of different exogenous substances on seed germination and seedling growth and physiology of Perilla frutescens under saline-alkali stress [J]. Acta. Agrestia Sin., 2022, 30(9):2415-2422. | |
| 6 | HU W J, LIU J Y, LIU T W, et al.. Exogenous calcium regulates the growth and development of Pinus massoniana detecting by physiological, proteomic and calcium-related genes expression analysis [J]. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 2023, 196:1122-1136. |
| 7 | VERMA S, NEGI N P, NARWAL P, et al.. Calcium signaling in coordinating plant development, circadian oscillations and environmental stress responses in plants [J/OL]. Environ. Exp. Bot., 2022, 201:104935 [2023-03-14]. . |
| 8 | ZHANG Z H, SUN H, SHAO C, et al.. Calcium affects growth and physiological indices of Panax quinquefolium L. [J]. Hortscience, 2022, 57(1):112-117. |
| 9 | 尹大川,祁金玉,邓勋,等.施用外源钙对干旱胁迫下樟子松苗木生理特性的影响[J].沈阳农业大学学报,2018,49(5):559-565. |
| YIN D C, QI J Y, DENG X, et al.. Effects of exogenous calcium on the metabolic system of Pinus sylvestris var. Mongolica under drought stress [J]. J. Shenyang Agric. Univ., 2018, 49(5):559-565. | |
| 10 | 中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会.中国植物志[M].北京:科学出版社,1998:223-225. |
| 11 | HU H, LIU H, LIU F. Seed germination of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) cultivars responds differently to the stress of salt type and concentration [J]. Ind. Crop. Prod., 2018, 123:254-261. |
| 12 | 国家药典委员会.中华人民共和国药典:一部[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社,2020:81-82. |
| 13 | BRITCH S C, BABALONIS S, WALSH S L. Cannabidiol: pharmacology and therapeutic targets [J]. Psychopharmacology, 2020, 238(1):9-28. |
| 14 | 于宛彤,侯康鑫,苏新堯,等.药用大麻活性成分、产品开发及育种研究进展[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2023,29(3):213-222. |
| YU W T, HOU K X, SU X Y, et al.. Active ingredients, product development and breeding of medicinal cannabis: a review [J]. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Form., 2023, 29(3):213-222. | |
| 15 | 曹焜,孙宇峰,张晓艳,等.盐碱胁迫对工业大麻生长发育的影响[J].种子,2022,41(11):37-46. |
| CAO K, SUN Y F, ZHANG X Y, et al.. Effects of salt-alkali stress on growth and development of industrial hemp [J]. Seed, 2022, 41(11):37-46. | |
| 16 | 高彦龙,张德,张瑞,等.外源CaCl2对盐胁迫下苹果砧木T337生理特性的影响[J].华北农学报,2021,36(5):118-126. |
| GAO Y L, ZHANG D, ZHANG R, et al.. Effect of exogenous CaCl2 on physiological characteristics of apple rootstock T337 under salt stress [J]. Acta. Agric. Boreali-Sin., 2021, 36(5):118-126. | |
| 17 | 王学奎,黄见良.植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M].第3版.北京:高等教育出版社,2015:1-324. |
| 18 | 付立忠,赵利梅,刘骞,等.氮素形态对三叶青块根主要化学成分含量及抗氧化活性的影响[J].中国药学杂志,2021,56(8):633-639. |
| FU L Z, ZHAO L M, LIU Q, et al.. Effects of nitrogen forms on main phytochemical content and antioxidant activity in root tubers of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum [J]. Chin. Pharm. J., 2021, 56(8):633-639. | |
| 19 | 刘胜贵,马海悦,李智高,等.HPLC法测定工业大麻花叶中的CBD和THC的含量[J].云南化工,2020,47(5):62-64. |
| LIU S G, MA H Y, LI Z G, et al.. Determination of CBD and THC in industrial hemp flowers and leaves by HPLC [J]. Yunnan Chem. Technol., 2020, 47(5):62-64. | |
| 20 | REHMAN S, ABBAS G, SHAHID M, et al.. Effect of salinity on cadmium tolerance, ionic homeostasis and oxidative stress responses in conocarpus exposed to cadmium stress: implications for phytoremediation [J]. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety, 2019, 171:146-153. |
| 21 | 秦楚. SOS基因在紫花苜蓿中的表达及其抗逆性研究[D].银川:宁夏大学,2017. |
| QIN C. Research on the expression and stress resistance of SOS gene in alfalfa [D]. Yinchuan: Ningxia University., 2017. | |
| 22 | YANG Z, LI J L, LIU L N, et al.. Photosynthetic regulation under salt stress and salt-tolerance mechanism of sweet sorghum [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2020, 10:1722 [2023-03-14]. . |
| 23 | KESAWAT M S, SATHEESH N, KHERAWAT B S, et al.. Regulation of reactive oxygen species during salt stress in plants and their crosstalk with other signaling molecules-current perspectives and future directions [J/OL]. Plants Basel, 2023, 12(4):864 [2023-03-14]. . |
| 24 | ZHAO S S, ZHANG Q K, LIU M Y, et al.. Regulation of plant responses to salt stress [J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, 22(9):4609 [2023-03-14]. . |
| 25 | 杨舒贻,陈晓阳,惠文凯,等.逆境胁迫下植物抗氧化酶系统响应研究进展[J].福建农林大学学报(自然科学版),2016,45(5):481-489. |
| YANG S Y, CHEN X Y, HUI W K, et al.. Progress in responses of antioxidant enzyme systems in plant to environmental stresses [J]. J. Fujian Agric. For. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2016, 45(5):481-489. | |
| 26 | ZAHRA N, HINAIMSA L, HAFEEZ M B, et al.. Regulation of photosynthesis under salt stress and associated tolerance mechanisms [J]. Plant Physiol. Bioch., 2022, 178:55-69. |
| 27 | BACHANI J, MAHANTY A, AFTAB T, et al.. Insight into calcium signalling in salt stress response [J]. South African J. Bot., 2022, 151:1-8. |
| 28 | 苏江硕,陈素梅,管志勇,等.外源钙离子对NaCl胁迫下菊花幼苗生理特性的影响[J].江苏农业科学,2016,44(9):199-203. |
| SU J S, CHEN S M, GUAN Z Y, et al.. Effects of exogenous calcium ions on physiological characteristics of Chrysanthemum morifolium seedlings under NaCl stress [J]. Jiangsu Agric. Sci., 2016, 44(9):199-203. | |
| 29 | MOMENI M M, KALANTAR M, DEHGHANI-ZAHEDANI M. Physiological, biochemical and molecular responses of durum wheat under salt stress [J]. Plant Genet. Resour., 2021, 19(2):93-103. |
| 30 | MIJITI M, ZHANG YM, ZHANG CR, et al.. Physiological and molecular responses of Betula platyphylla Suk to salt stress [J]. Trees Struct Funct., 2017, 31(5):1653-1665. |
| 31 | 朱营营,张倩,董元杰.外源NO缓解花生盐胁迫的效果及机理[J].中国农业大学学报,2020,25(12):30-39. |
| ZHU Y Y, ZHANG Q, DONG Y J. Effects of exogenous nitric oxide on the physiological characteristics of peanut seedlings under salt stress [J]. J. Chin. Agric. Univ., 2020, 25(12):30-39. | |
| 32 | WANG X D, LAN Z Q, TIAN L, et al.. Change of physiological properties and ion distribution by synergistic effect of Ca2+ and grafting under salt stress on cucumber seedlings [J/OL]. Agronomy, 2021, 11(5):848 [2023-03-14]. . |
| 33 | KETEHOULI T, QUOC V H N, DONG J Y, et al.. Overview of the roles of calcium sensors in plants’ response to osmotic stress signaling [J]. Funct. Plant Biol., 2022, 49(7):589-599. |
| 34 | 吴华鑫,赵野,王浩宇,等.外源Ca2+对西伯利亚白刺盐胁迫伤害的缓解效应[J].山东农业科学,2022,54(8):73-78. |
| WU H X, ZHAO Y, WANG H Y, et al.. Relieving effect of exogenous Ca2+ on salt stress injury to Nitraria sibirica [J]. Shandong Agric. Sci., 2022, 54(8):73-78. | |
| 35 | CERINO P, BUONERBA C, CANNAZZA G, et al.. A review of hemp as food and nutritional supplement [J]. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res., 2021, 6(1):19-27. |
| [1] | Tingting MA, Yanrong ZHAO, Yuqing WEI, Yuejuan WANG, Xuefei WANG, Erdong ZHANG. Dynamic Characteristics of Stem Growth and Sugar Accumulation of Sweet Sorghum at Late Growth Stage Under Soil Salt Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(2): 42-50. |
| [2] | Zhichao REN, Yaohui MU, Xuyang YAO, Shue LI, Yongfeng ZHANG, Tianbao REN, Guoshun LIU, Quanyu YIN. Physiological Response of Tobacco Infected by Phytophthora to Trichoderma harzianum Inoculation Sequence [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(1): 155-164. |
| [3] | Xuewen XU, Xingpeng WANG, Hongbo WANG, Zhenxi CAO. Physiological Regulation of Growth of Cotton Seedlings Under Salt Stress by Rhamnolipids [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(1): 72-79. |
| [4] | Fulin ZHANG, Rui XI, Yuxiang LIU, Zhaolong CHEN, Qinghui YU, Ning LI. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Tomato BURP Structural Domain Gene Family [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(8): 51-62. |
| [5] | Hongshuo ZHAO, Hongyu CAO, Guanglei GAO, Zhe SUN, Ying ZHANG, Guodong DING. Effects of Sand Fixation Using Microbially Induced Carbonate Precipitation on Leaf Traits and Physiological Characteristics of Typical Psammophytes [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(6): 170-182. |
| [6] | Shuang LI, Aiying WANG, Zhen JIAO, Qing CHI, Hao SUN, Tao JIAO. Physiological and Chemical Characteristics and Transcriptome Analysis of Different Type of Wheat Seedlings Under Salt Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(2): 20-32. |
| [7] | Shengmei LI, Bo PANG, Shiwei GENG, Wu SONG, Hongmei LI, Maosen MA, Ru ZHANG, Xinyan WANG, Wenwei GAO. Photosynthetic and Physiological Characteristics of Gossypium hirsutum L. × Gossypium barbadense L. Backross Populations in Full Boll Stage [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(1): 40-51. |
| [8] | Xuemin JIANG, Xiangqian CHEN, Hongyan LI, Qiyan JIANG. Metabolomic Analysis of Wheat Response to Salt Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 43-56. |
| [9] | Yulu WU, Jiaxin HU, Yuxi CHEN, Bingsong ZHENG, DaoLiang YAN. Effects of External Application of α-Ketoglutarate on Growth, Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus Accumulation and Their Stoichiometric Relationships in Kosteletzkya virginica Under Salt Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 170-177. |
| [10] | Zhonghua MA, Juan CHEN, Na WU, Benju MAN, Xiaogang WANG, Yongqing ZHE, Jili LIU. Effects of Salt Stress and Phosphorus Supply on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Total Biomass of Switchgrass at Seedling Stage [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(6): 190-200. |
| [11] | Yongyan LIU, Zhengxiong SONG, Jiawei JIN, Jing WANG, Min XU, Junxue ZHOU, Zhanmin LI, Shimin ZHAO, Yunpeng FU, Xiaoyan DAI. Effects of Molybdenum and Zinc Nutrition on Physiological Characteristics and Quality of Flue-cured Tobacco [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(6): 216-224. |
| [12] | Fan ZHANG, Hong WANG, Xuebing ZHANG, Jianjun CHEN. Physiological and Biochemical Responses of Peach Self-rooted Rootstock to NaCl and Analysis of Salt Tolerance Threshold [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(11): 70-79. |
| [13] | Feng LI, Congpei YIN, Ran YIN, Fan WANG, Yongliang HAN, Zhimin YANG, Jiancheng LIU. Response of Rhizosphere Soil Bacterial Community Diversity to Salt Stress in Oat (Avena sativa L.) [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(1): 153-165. |
| [14] | Qian YANG, Na WU, Cong ZHAO, Yu HAN, Zhonghua MA, Yongsen YANG, Jili LIU. Effects of Zinc Fertilizer Application on Physiological Characteristics and Grain Zn Content of Maize in Saline-alkali Soil [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(9): 166-176. |
| [15] | Yanling HAO, Wei YAN. Effects of Mixed Salt Stress on Morphological and Physiological Indexes of Ulmus pumila Seedlings [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(7): 69-76. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号