




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (5): 65-76.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0622
石玉涛1( ), 谢惠珍1, 郑淑琳1, 羽观华1, 王飞权1, 李力1, 张渤1, 李远华1, 罗盛财2
), 谢惠珍1, 郑淑琳1, 羽观华1, 王飞权1, 李力1, 张渤1, 李远华1, 罗盛财2
收稿日期:2023-08-18
接受日期:2023-09-12
出版日期:2024-05-15
发布日期:2024-05-14
作者简介:石玉涛 E-mail:ytshi@wuyiu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Yutao SHI1( ), Huizhen XIE1, Shulin ZHENG1, Guanhua YU1, Feiquan WANG1, Li LI1, Bo ZHANG1, Yuanhua LI1, Shengcai LUO2
), Huizhen XIE1, Shulin ZHENG1, Guanhua YU1, Feiquan WANG1, Li LI1, Bo ZHANG1, Yuanhua LI1, Shengcai LUO2
Received:2023-08-18
Accepted:2023-09-12
Online:2024-05-15
Published:2024-05-14
摘要:
为探明武夷山地方茶树种质主要生化成分特性和茶多糖清除超氧阴离子自由基活性差异,测定了31份武夷山地方茶树种质主要生化成分含量,采用水提醇沉淀法提取茶多糖,并采用黄嘌呤氧化酶法比较了茶多糖SOD活力。结果表明,武夷山地方茶树种质主要生化成分存在较强的变异和遗传多样性,具有较大的遗传改良潜力。平均变异系数为21.84%,平均遗传多样性指数为2.08,平均改良潜力为50.92%;茶多酚、游离氨基酸、黄酮类化合物、可溶性糖含量和酚氨比均呈正态分布;茶多酚含量与黄酮类化合物含量呈极显著正相关,与可溶性糖含量呈极显著负相关,游离氨基酸含量与可溶性糖含量呈极显著负相关;提取的前2个主成分包含了5个生化指标81.08%的信息,游离氨基酸和茶多酚含量是5个生化性状的特征指标,主成分综合得分排名前5位的茶树种质为‘白牡丹’‘红海棠’‘向天梅’‘半天妖’和‘香石角’,可作为武夷山茶区优质乌龙茶品种选育和推广栽培的良好材料;基于生化成分的聚类分析将31份茶树种质分为3类,第Ⅰ类群13份种质茶多酚和黄酮类化合物含量高,可溶性糖含量低,第Ⅱ类群8份种质游离氨基酸含量较低,可溶性糖含量较高,第Ⅲ类群10份种质酚氨比较高,可溶性糖含量中等;基于茶多糖SOD活力的聚类分析,可将31份茶树种质分为3类,第Ⅰ类群8份种质茶多糖SOD活力低,第Ⅱ类群19份种质茶多糖SOD活力居中,第Ⅲ类群4份种质茶多糖SOD活力高;茶多糖SOD活力存在丰富的变异,变异系数达40.62%,遗传多样性指数为2.07;‘白鸡冠’‘大红袍’‘大红梅’和‘灵芽’4份种质茶多糖SOD活力高,清除超氧阴离子自由基能力强。研究结果可为武夷山地方茶树种质的改良和开发利用提供科学依据。
中图分类号:
石玉涛, 谢惠珍, 郑淑琳, 羽观华, 王飞权, 李力, 张渤, 李远华, 罗盛财. 武夷山地方茶树种质生化特性和茶多糖清除超氧阴离子自由基活性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 65-76.
Yutao SHI, Huizhen XIE, Shulin ZHENG, Guanhua YU, Feiquan WANG, Li LI, Bo ZHANG, Yuanhua LI, Shengcai LUO. Analysis of Biochemical Characteristics and Superoxide Anion Radical Scavenging Activity of Tea Polysaccharides of Local Tea Germplasms in Wuyishan[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(5): 65-76.
| 编号Code | 名称Name | 来源地Origin | 编号Code | 名称Name | 来源地Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LM001 | 正白毫 Zhengbaihao | 岚谷乡岭阳村 Languxianglingyangcun | JM044 | 红鸡冠 Hongjiguan | 内鬼洞 Neiguidong |
| JM063 | 玉井流香 Yujingliuxiang | 内鬼洞 Neiguidong | JM035 | 金鸡母 Jinjimu | 九龙窠 Jiulongke |
| JM003 | 白牡丹 Baimudan | 马头岩水洞口 Matouyanshuidongkou | JM053 | 铁罗汉 Tieluohan | 内鬼洞 Neiguidong |
| JM073 | 正柳条 Zhengliutiao | 九龙窠 Jiulongke | JM018 | 灵芽 Lingya | 刘官寨 Liuguanzhai |
| JM031 | 金丁香 Jindingxiang | 野猪槽 Yezhucao | JM081 | 醉墨 Zuimo | 九龙窠 Jiulongke |
| JM012 | 岭上梅 Lingshangmei | 状元岭 Zhuangyuanling | JM029 | 向天梅 Xiangtianmei | 北斗峰 Beidoufeng |
| JM068 | 岭下兰 Lingxialan | 慧苑狗洞 Huiyuangoudong | JM026 | 月桂 Yuegui | 霞宾岩下溪仔边 Xiabinyanxiaxizaibian |
| JM008 | 玉笪 Yuda | 北斗峰 Beidoufeng | JM062 | 大红袍 Dahongpao | 九龙窠 Jiulongke |
| JM022 | 九龙兰 Jiulonglan | 外九龙窠 Waijiulongke | JM061 | 正太阴 Zhengtaiyin | 外鬼洞 Waiguidong |
| JM078 | 九龙珠 Jiulongzhu | 九龙窠 Jiulongke | JM067 | 九龙奇 Jiulongqi | 十八寨 Shibazhai |
| JM064 | 水金龟 Shuijingui | 牛栏坑杜葛寨 Niulankengdugezhai | JM079 | 正太阳 Zhengtaiyang | 外鬼洞 Waiguidong |
| JM055 | 小红梅 Xiaohongmei | 九龙窠 Jiulongke | JM007 | 半天妖 Bantianyao | 三花峰 Sanhuafeng |
| JM051 | 肉桂 Rougui | 马枕峰 Mazhenfeng | JM039 | 香石角 Xiangshijiao | 水濂洞 Shuiliandong |
| JM034 | 醉贵姬 Zuiguiji | 内鬼洞 Neiguidong | JM002 | 白鸡冠 Baijiguan | 外鬼洞 Waiguidong |
| JM048 | 红孩儿 Honghaier | 内鬼洞 Neiguidong | JM001 | 不见天 Bujiantian | 九龙窠 Jiulongke |
| JM046 | 红海棠 Honghaitang | 内鬼洞 Neiguidong | JM019 | 玉蟾 Yuchan | 刘官寨 Liuguanzhai |
| JM077 | 大红梅 Dahongmei | 十八寨 Shibazhai |
表1 供试茶树种质基本信息
Table 1 Basic information of tea germplasms for testing
| 编号Code | 名称Name | 来源地Origin | 编号Code | 名称Name | 来源地Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LM001 | 正白毫 Zhengbaihao | 岚谷乡岭阳村 Languxianglingyangcun | JM044 | 红鸡冠 Hongjiguan | 内鬼洞 Neiguidong |
| JM063 | 玉井流香 Yujingliuxiang | 内鬼洞 Neiguidong | JM035 | 金鸡母 Jinjimu | 九龙窠 Jiulongke |
| JM003 | 白牡丹 Baimudan | 马头岩水洞口 Matouyanshuidongkou | JM053 | 铁罗汉 Tieluohan | 内鬼洞 Neiguidong |
| JM073 | 正柳条 Zhengliutiao | 九龙窠 Jiulongke | JM018 | 灵芽 Lingya | 刘官寨 Liuguanzhai |
| JM031 | 金丁香 Jindingxiang | 野猪槽 Yezhucao | JM081 | 醉墨 Zuimo | 九龙窠 Jiulongke |
| JM012 | 岭上梅 Lingshangmei | 状元岭 Zhuangyuanling | JM029 | 向天梅 Xiangtianmei | 北斗峰 Beidoufeng |
| JM068 | 岭下兰 Lingxialan | 慧苑狗洞 Huiyuangoudong | JM026 | 月桂 Yuegui | 霞宾岩下溪仔边 Xiabinyanxiaxizaibian |
| JM008 | 玉笪 Yuda | 北斗峰 Beidoufeng | JM062 | 大红袍 Dahongpao | 九龙窠 Jiulongke |
| JM022 | 九龙兰 Jiulonglan | 外九龙窠 Waijiulongke | JM061 | 正太阴 Zhengtaiyin | 外鬼洞 Waiguidong |
| JM078 | 九龙珠 Jiulongzhu | 九龙窠 Jiulongke | JM067 | 九龙奇 Jiulongqi | 十八寨 Shibazhai |
| JM064 | 水金龟 Shuijingui | 牛栏坑杜葛寨 Niulankengdugezhai | JM079 | 正太阳 Zhengtaiyang | 外鬼洞 Waiguidong |
| JM055 | 小红梅 Xiaohongmei | 九龙窠 Jiulongke | JM007 | 半天妖 Bantianyao | 三花峰 Sanhuafeng |
| JM051 | 肉桂 Rougui | 马枕峰 Mazhenfeng | JM039 | 香石角 Xiangshijiao | 水濂洞 Shuiliandong |
| JM034 | 醉贵姬 Zuiguiji | 内鬼洞 Neiguidong | JM002 | 白鸡冠 Baijiguan | 外鬼洞 Waiguidong |
| JM048 | 红孩儿 Honghaier | 内鬼洞 Neiguidong | JM001 | 不见天 Bujiantian | 九龙窠 Jiulongke |
| JM046 | 红海棠 Honghaitang | 内鬼洞 Neiguidong | JM019 | 玉蟾 Yuchan | 刘官寨 Liuguanzhai |
| JM077 | 大红梅 Dahongmei | 十八寨 Shibazhai |
指标 Index | 平均 Mean | 最大值 Maximum | 最小值 Minimum | 标准差 SD | 变异系数 CV/% | 多样性 指数H' | 改良潜力 Improving potential/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 茶多酚TP/% | 22.87 | 31.75 | 15.23 | 3.61 | 15.77 | 1.91 | 38.83 |
| 游离氨基酸AA/% | 2.48 | 4.03 | 1.38 | 0.60 | 24.14 | 2.00 | 62.72 |
| 黄酮类化合物FLA/(mg·g-1) | 9.11 | 12.73 | 5.37 | 1.46 | 15.98 | 1.90 | 39.80 |
| 可溶性糖SS/% | 1.26 | 1.87 | 0.69 | 0.31 | 24.31 | 2.17 | 48.92 |
| 酚氨比TP/AA | 9.71 | 15.95 | 4.73 | 2.81 | 28.99 | 2.42 | 64.33 |
表2 31份武夷山茶树种质主要生化成分的基本统计参数
Table 2 Characteristic statistic parameters of main biochemical components in 31 tea germplasms from Wuyishan
指标 Index | 平均 Mean | 最大值 Maximum | 最小值 Minimum | 标准差 SD | 变异系数 CV/% | 多样性 指数H' | 改良潜力 Improving potential/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 茶多酚TP/% | 22.87 | 31.75 | 15.23 | 3.61 | 15.77 | 1.91 | 38.83 |
| 游离氨基酸AA/% | 2.48 | 4.03 | 1.38 | 0.60 | 24.14 | 2.00 | 62.72 |
| 黄酮类化合物FLA/(mg·g-1) | 9.11 | 12.73 | 5.37 | 1.46 | 15.98 | 1.90 | 39.80 |
| 可溶性糖SS/% | 1.26 | 1.87 | 0.69 | 0.31 | 24.31 | 2.17 | 48.92 |
| 酚氨比TP/AA | 9.71 | 15.95 | 4.73 | 2.81 | 28.99 | 2.42 | 64.33 |
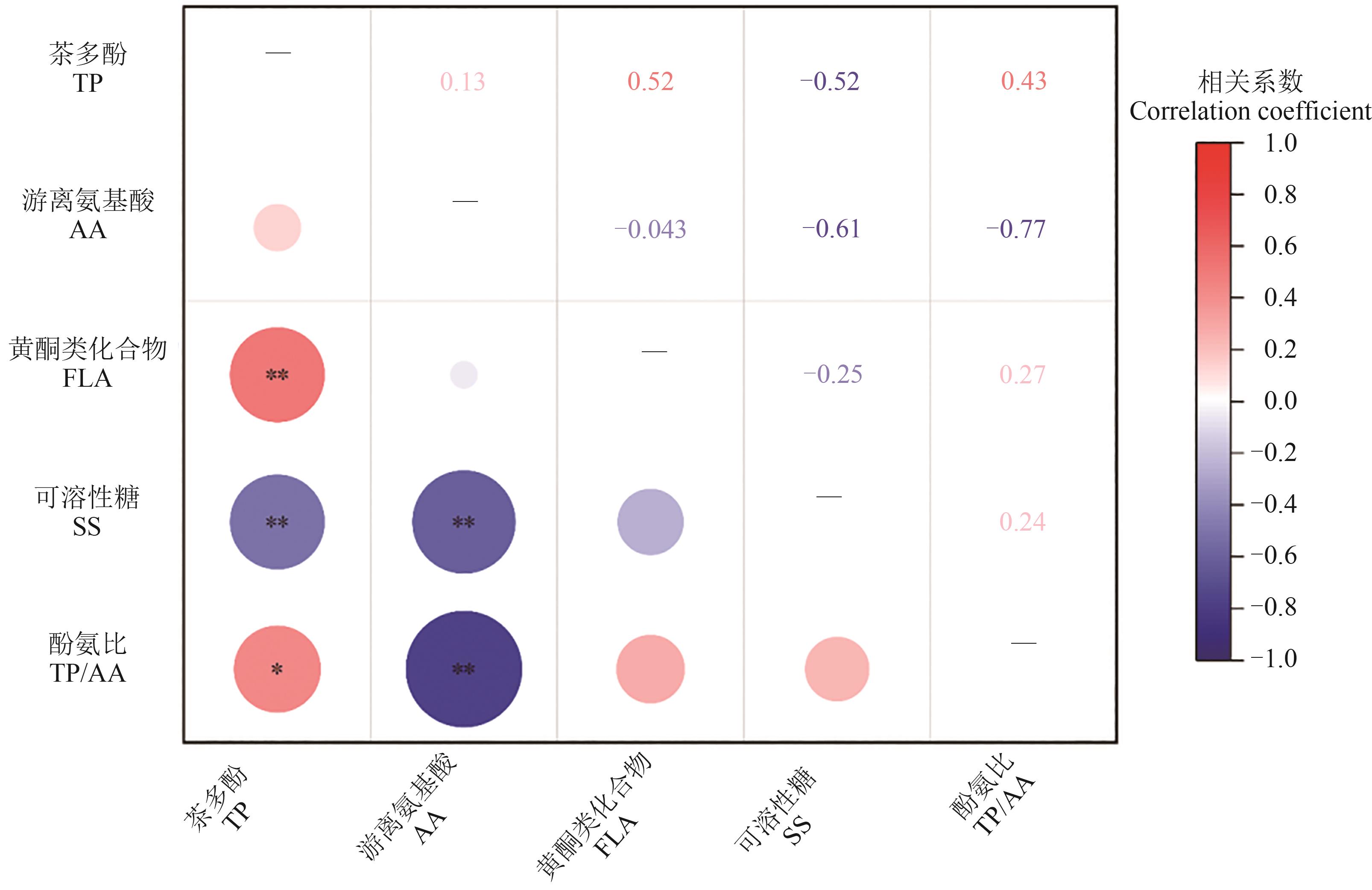
图2 不同茶树种质生化成分间的相关性注:*和**分别表示在P<0.05和P<0.01水平显著相关。
Fig. 2 Correlation among 5 biochemical components in tea germplasmsNote: * and ** indicate significant correlation at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively.
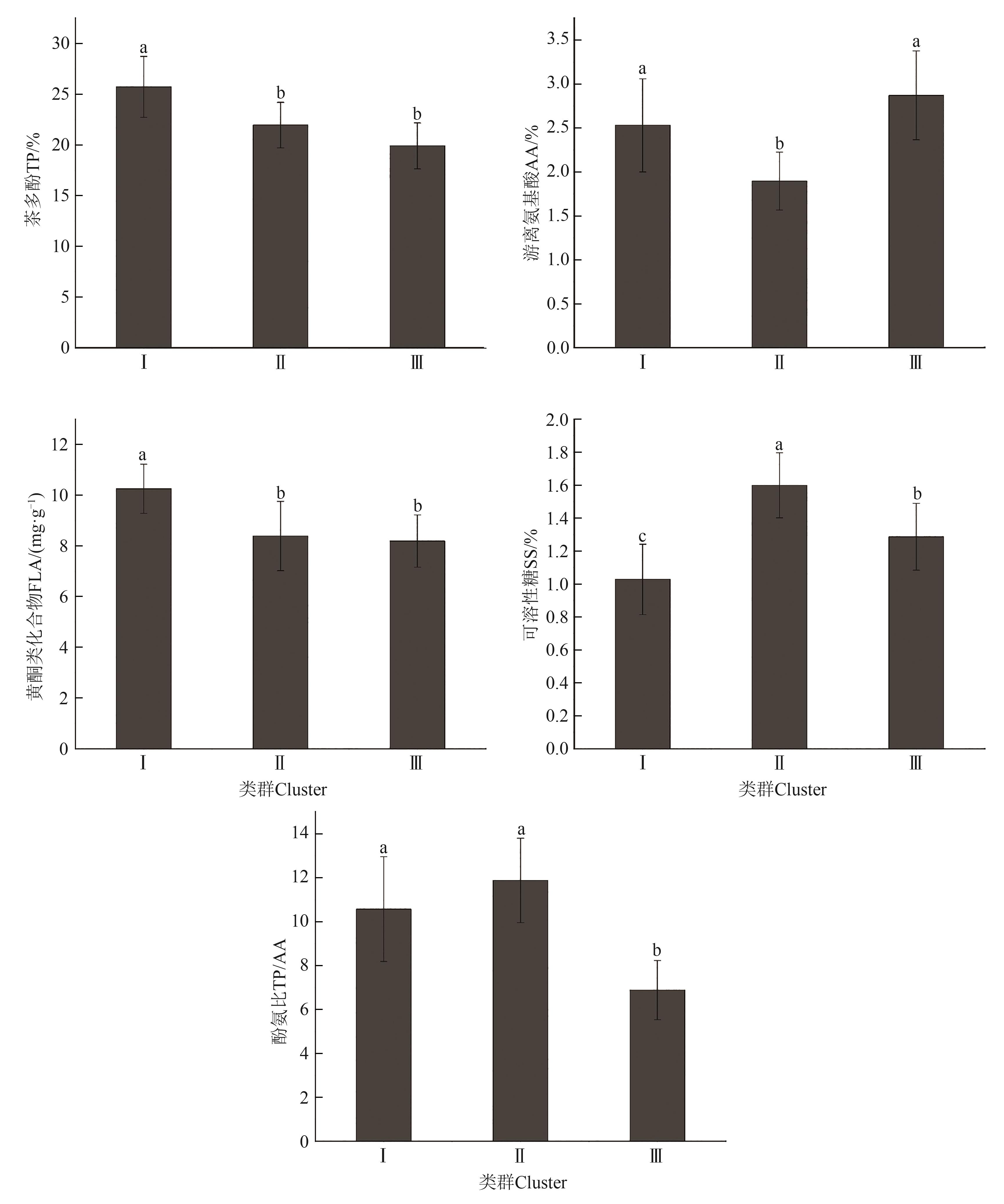
图6 不同类群茶树种质的主要生化成分含量注:图中不同小写字母表示P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 6 Biochemical components of different tea germplasms clustersNote: Different small letters indicate significant difference at P<0.05 level.
| 1 | 黎裕,李英慧,杨庆文,等.基于基因组学的作物种质资源研究:现状与展望[J].中国农业科学,2015,48(17):3333-3353. |
| LI Y, LI Y H, YANG Q W, et al.. Genomics-based crop germplasm research: advances and perspectives [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2015, 48(17):3333-3353. | |
| 2 | 金基强,张晨禹,马建强,等.茶树种质资源研究“十三五”进展及“十四五”发展方向[J].中国茶叶,2021,43(9):42-49, 76. |
| JIN J Q, ZHANG C Y, MA J Q, et al.. Research progress on tea germplasms during the “13th five-year” plan period and development direction in the “14th five-year” plan period [J]. China Tea J., 2021, 43(9):42-49, 76. | |
| 3 | 李力,罗盛财,王飞权,等.基于GBS-SNP的武夷茶树(Camellia sinensis, Synonym: Thea bohea L.)遗传分析及标记开发[J].茶叶科学,2023,43(3):310-324. |
| LI L, LUO S C, WANG F Q, et al.. Genetic analysis and marker development for Wuyi tea (Camellia sinensis, synonym: Thea bohea L.) based on GBS-SNP [J]. J. Tea Sci., 2023, 43(3):310-324. | |
| 4 | 董方,李小飞,沈思言,等.江西茶树资源的遗传多样性分析及优异种质筛选[J].江西农业大学学报,2022,44(6):1466-1477. |
| DONG F, LI X F, SHEN S Y, et al.. Genetic diversity analysis and screening of excellent germplasm of tea plant resources in Jiangxi [J]. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis, 2022, 44(6):1466-1477. | |
| 5 | 王飞权,冯花,罗盛财,等.武夷名丛茶树种质资源农艺性状多样性分析[J].中国农业科技导报,2019,21(6):43-54. |
| WANG F Q, FENG H, LUO S C, et al.. Diversity analysis of agronomic traits of Wuyi Mingcong tea plant germplasm resources [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2019, 21(6):43-54. | |
| 6 | 王飞权,李纪艳,冯花,等.武夷名丛茶树种质资源叶片解剖结构分析[J].热带作物学报,2019,40(12):2375-2389. |
| WANG F Q, LI J Y, FENG H, et al.. Analysis of leaf anatomical structure of Wuyi Mingcong tea germplasm resources [J]. Chin. J. Trop. Crops, 2019, 40(12):2375-2389. | |
| 7 | 石玉涛,郑淑琳,王飞权,等.武夷名丛茶树种质资源矿质元素含量特征分析[J].中国农业科技导报,2020,22(7):37-50. |
| SHI Y T, ZHENG S L, WANG F Q, et al.. Characteristics analysis of mineral element contents in Wuyi Mingcong tea plant germplasm resources [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2020, 22(7):37-50. | |
| 8 | DU L L, FU Q Y, XIANG L P, et al.. Tea polysaccharides and their bioactivities [J]. Molecules, 2016, 25(2):144-149. |
| 9 | YAO J, WENG Y, DICKEY A, et al.. Plants as factories for human pharmaceuticals: applications and challenges [J]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2015, 16(12):28549-28565. |
| 10 | 陈薛,左欣欣,徐安安,等.不同茶树品种鲜叶多糖的理化性质和抗氧化活性比较研究[J].茶叶科学,2022,42(6):806-818. |
| CHEN X, ZUO X X, XU A A, et al.. Comparative study on the physicochemical characteristics and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides in different tea cultivars [J]. J. Tea Sci., 2022, 42(6):806-818. | |
| 11 | 陈玉琼,余志,张芸,等.茶树品种、部位和嫩度对茶多糖含量和活性的影响[J].华中农业大学学报, 2005, 24(4):406-409. |
| CHEN Y Q, YU Z, ZHANG Y, et al.. Effect of tea cultivars and tenderness on tea polysaccharide [J]. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ., 2005, 24(4):406-409. | |
| 12 | 石玉涛,郑淑琳,吴伟伟,等.武夷名丛茶树种质资源茶多糖抗氧化活性分析[J].福建农业学报,2020,35(7):801-810. |
| SHI Y T, ZHENG S L, WU W W, et al.. Antioxidant activity of polysaccharides in Wuyi Mingcong tea germplasms [J]. Fujian J. Agric. Sci., 2020, 35(7):801-810. | |
| 13 | 李远华.茶学综合实验[M]. 北京:中国轻工业出版社, 2018:193-194. |
| 14 | 张正竹.茶叶生物化学实验教程(第二版)[M].北京:中国农业出版社, 2021:44-45. |
| 15 | 魏广伟,阳慧怡,王敏,等.芝麻种质资源表型性状遗传多样性分析及综合评价[J].江苏农业科学,2022,50(18):122-130. |
| 16 | 代涛,万嘉欣,黎洁华,等.基于主成分与聚类分析综合评价杧果种质资源果实糖酸品质[J].果树学报,2022,39(12):2253-2263. |
| DAI T, WAN J X, LI J H, et al.. Comprehensive evaluation of fruit sugar and acid quality of mango germplasm based on principal component and cluster analysis [J]. J. Fruit Sci., 2022, 39(12):2253-2263. | |
| 17 | CHEN C J, CHEN H, ZHANG Y, et al.. TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data [J]. Mol. Plant, 2020, 13(8): 1194-1202. |
| 18 | 杨春,郭灿,乔大河,等.三都野生茶树表型性状和生化组分多样性分析[J].江苏农业科学,2023,51(8):111-119. |
| 19 | 杨丽英,陈进,葛再伟.云南花生种质丰产性和品质性状的改良潜力[J].花生学报,2002,31(1):33-36. |
| YANG L Y, CHEN J, GE Z W, et al.. Improving potential of productivity and quality in groundnut in Yunnan province [J]. J. Peanut Sci., 2002, 31(1):33-36. | |
| 20 | 严碧蓉,黄飞毅,蓝华中.地方特色茶树种质资源江华苦茶研究与产业化开发[J].湖南农业,2022(8):30-31. |
| 21 | 罗盛财,陈德华,黄贤格,等.武夷名丛单丛茶树种质资源收集、整理鉴定与保护利用研究[J].中国茶叶,2017,39(12):18-20. |
| 22 | 闫满朝,肖长顺,陈志龙,等.西乡县地方茶树种质资源的生物学性状观察及生化成分分析[J].西北农业学报,2020,29(8):1224-1231. |
| YAN M C, XIAO C S, CHEN Z L, et al.. Analysis of biological characteristics and biochemical components of tea germplasm resources in Xixiang county [J]. Acta Agric. Bor-Occid. Sin., 2020, 29(8):1224-1231. | |
| 23 | XIA E H, TONG W, WU Q, et al.. Tea plant genomics: achievements, challenges and perspectives [J/OL]. Hortic. Res., 2020, 7:7 [2023-07-08]. . |
| 24 | 疏再发,刘瑜,邵静娜,等.浙南早生茶树种质资源主要品质成分分析及优异资源鉴选[J].浙江农业学报,2022,34(11):2438-2450. |
| SHU Z F, LIU Y, SHAO J N, et al.. Analysis of main quality components and selection of excellent resources of early-sprouting tea germplasm resources in southern Zhejiang, China [J]. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis, 2022, 34(11):2438-2450. | |
| 25 | 江新凤,李琛,曹挥华,等.‘黄金菊’和‘宁州2号’茶树生化成分季节变化特征分析[J].食品安全质量检测学报,2023, 14(10):261-269. |
| JIANG X F, LI C, CAO H H, et al.. Seasonal variation characteristics of biochemical components of Camellia sinensis var. ‘Huangjinju’ and Camellia sinensis var. ‘Ningzhou 2’ [J]. J. Food Saf. Qual., 2023, 14(10):261-269. | |
| 26 | SARKER U, OBA S. Polyphenol and flavonoid profiles and radical scavenging activity in leafy vegetable Amaranthus gangeticus [J/OL]. BMC Plant Biol., 2020, 20(1):2700-0 [2023-07-08]. . |
| 27 | FAN Y, ZHOU X, HUANG G. Preparation, structure, and properties of tea polysaccharide [J]. Chem. Biol. Drug Des., 2022, 99(1):75-82. |
| 28 | JIE Z, LIU J, SHU M, et al.. Detection strategies for superoxide anion: a review [J/OL]. Talanta, 2022, 236: 122892 [2023-07-08]. . |
| 29 | VO Q V, HOA N T, THONG N M, et al.. The hydroperoxyl and superoxide anion radical scavenging activity of anthocyanidins in physiological environments: theoretical insights into mechanisms and kinetics [J/OL]. Phytochemistry, 2021, 192: 112968 [2023-09-08]. . |
| 30 | LIU Y, SUN Y, HANG G. Preparation and antioxidant activities of important traditional plant polysaccharides [J]. Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2018, 111:780-786. |
| 31 | CHEN L, HUANG G. Antioxidant activities of phosphorylated pumpkin polysaccharide [J]. Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2019, 125:256-261. |
| 32 | CHEN F, HUANG G, YANG Z, et al.. Antioxidant activity of Momordica charantia polysaccharide and its derivatives [J]. Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2019, 138:673-680. |
| [1] | 潘越, 王宝庆, 王季姣, 马勇, 李亚兰. 不同山葡萄品种CO2响应模型拟合及评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(4): 58-66. |
| [2] | 曹婷婷, 刘春, 范又维, 马力, 任志雨, 袁素霞, 张军云, 钱遵姚, 杨光炤. 不同氮素供应水平对微型盆栽月季生长发育的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 67-79. |
| [3] | 孟盼盼, 何海燕, 曹钰昕, 张丽欣, 吕清豪, 祁瑞林, 张红瑞. 5个栽培类型药菊分枝期抗旱性综合评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 90-99. |
| [4] | 李生梅, 庞博, 耿世伟, 宋武, 李红梅, 马茂森, 张茹, 王新燕, 高文伟. 棉花海陆回交群体盛铃期的光合特性及其生理基础[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 40-51. |
| [5] | 卢倩倩, 阿布都外力·阿不力米提, 侯毅兴, 李志慧, 王爽, 周龙. 复合盐碱胁迫下7个鲜食葡萄品种光合特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 63-76. |
| [6] | 王爽, 侯毅兴, 冯琳骄, 卢倩倩, 周龙. 干旱胁迫对鲜食葡萄叶片解剖结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 40-49. |
| [7] | 郑淑琳, 石玉涛, 王飞权, 吴邦强, 李远华, 张渤, 叶乃兴. 不同茶树种质资源花器矿质元素含量分析与综合评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 178-188. |
| [8] | 郭胜微, 边思文, 丁建文, 张晓辰, 杨兴, 杜锦, 向春阳. 糯玉米萌发期耐低温品种资源的综合评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 38-47. |
| [9] | 张月欣, 麻云霞, 马秀枝, 张金旺, 王月林, 俞海生. 大青山不同林龄榆树林的土壤酶和养分特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(12): 168-176. |
| [10] | 刘宇鹏, 陈芳, 古书鸿, 王芳. 贵州不同产地冬荪营养成分及品质评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(11): 143-153. |
| [11] | 张会芳, 张建红, 刘海礁, 孙岩, 齐红志, 王楠, 段俊枝, 郭燕, 尹海燕. 近20年黄淮冬麦区南片小麦种质性状演变及其育种价值评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(11): 28-41. |
| [12] | 丁丁, 郑伶杰, 王红宝, 郑丽锦, 郭艳超. 滨海地区不同茶菊品种农艺性状及有效成分综合评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(10): 45-53. |
| [13] | 柴冠群, 刘桂华, 周玮, 张秀锦, 李龙品, 范成五. 贵州乌蒙山区设施土壤重金属污染风险评估与来源解析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(8): 144-153. |
| [14] | 李夏夏, 张思语, 程智慧. 中国优质大蒜品种区域试验评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 58-68. |
| [15] | 刘阳阳, 潘越, 王世伟, 虎海防. 不同山葡萄品种光响应模型拟合及综合评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 104-114. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号