




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (3): 124-133.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0799
• 动植物健康 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2022-09-20
接受日期:2023-01-16
出版日期:2024-03-15
发布日期:2024-03-07
通讯作者:
杨莉
作者简介:张桐毓 E-mail: 953445964@qq.com;
基金资助:
Tongyu ZHANG( ), Ying GOU, Qi LI, Li YANG(
), Ying GOU, Qi LI, Li YANG( )
)
Received:2022-09-20
Accepted:2023-01-16
Online:2024-03-15
Published:2024-03-07
Contact:
Li YANG
摘要:
为研究锈腐病对人参品质和土壤相关因子的影响,以罹患锈腐病人参、健康人参及其根际土壤为试验材料,检测土壤理化性质、土壤酶活性,利用高效液相色谱法检测人参根及根际土壤内酚酸、皂苷含量,并利用分子手段检测土壤中病原菌数量。结果表明,人参根内大部分皂苷含量随锈腐病的加剧而减少,降幅为50.1%~72.5%;土壤中参根分泌的化感物质的种类、含量与人参病害程度密切相关,部分皂苷类物质含量升高,最高增长了7.5倍,且频率有所增加;丁二酸、肉桂酸含量显著高于健康株,较健康株分别增加3.69、2.39倍。对土壤因子的测定发现,除过氧化氢酶的活性随病害的加剧而升高,其余土壤质量指标均随病害的加剧而下降,其中速效磷降幅高达55.0%,且在病害初发时含量即开始下降,可以表征人参锈腐病的发生。相关性分析表明,病原菌数量与土壤因子的灰色关联度为0.362 5~0.497 5,与化感物质的灰色关联度为0.182 5~0.619 9。以上结果表明,人参患锈腐病后会影响人参品质,因此,改善土壤环境、调节土壤生态平衡、降低人参患病几率、是提高人参质量的有效途径。
中图分类号:
张桐毓, 勾颖, 李琪, 杨莉. 人参锈腐病对人参品质和土壤相关因子的影响研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 124-133.
Tongyu ZHANG, Ying GOU, Qi LI, Li YANG. Effects of Ginseng Rust Rot on Ginseng Quality and Soil Related Factors[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(3): 124-133.
取样点 Sample point | 种植时间 Planting time/a | 病级 Disease degree | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||
敦化市 Dunhua city | 2 | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 3 | √ | √ | √ | |||
| 4 | √ | √ | ||||
珲春市 Hunchun city | 4 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
龙井市 Longjing city | 4 | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 5 | √ | √ | ||||
汪清县 Wangqing county | 5 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
表1 取样点信息
Table 1 Sample point information
取样点 Sample point | 种植时间 Planting time/a | 病级 Disease degree | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||
敦化市 Dunhua city | 2 | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 3 | √ | √ | √ | |||
| 4 | √ | √ | ||||
珲春市 Hunchun city | 4 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
龙井市 Longjing city | 4 | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 5 | √ | √ | ||||
汪清县 Wangqing county | 5 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
时间 Time/min | 水 Water/% | 乙腈 Acetonitrile/% |
|---|---|---|
| 40 | 79 | 21 |
| 42 | 74 | 26 |
| 46 | 68 | 32 |
| 72 | 60 | 40 |
| 74 | 51 | 49 |
| 78 | 15 | 85 |
| 80 | 0 | 100 |
| 82 | 81 | 19 |
表2 皂苷洗脱程序
Table 2 Saponins elution procedures
时间 Time/min | 水 Water/% | 乙腈 Acetonitrile/% |
|---|---|---|
| 40 | 79 | 21 |
| 42 | 74 | 26 |
| 46 | 68 | 32 |
| 72 | 60 | 40 |
| 74 | 51 | 49 |
| 78 | 15 | 85 |
| 80 | 0 | 100 |
| 82 | 81 | 19 |
时间 Time/min | 甲醇 Methanol/% | 磷酸二氢钠 Sodium dihydrogen phosphate/% |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 45.0 | 55.0 |
| 10 | 55.0 | 45.0 |
| 13 | 71.0 | 29.0 |
| 15 | 45.0 | 55.0 |
表3 酚酸洗脱程序
Table 3 Phenol pickling process
时间 Time/min | 甲醇 Methanol/% | 磷酸二氢钠 Sodium dihydrogen phosphate/% |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 45.0 | 55.0 |
| 10 | 55.0 | 45.0 |
| 13 | 71.0 | 29.0 |
| 15 | 45.0 | 55.0 |
成分 Ingredient | 回归方程 Regression equation | 决定系数 R2 | 线性范围 Linearity range/(µg·mL-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rg1 | Y=471.10X+7.325 | 1.000 0 | 0.125~2.000 |
| Re | Y=385.02X+5.727 | 0.999 9 | 0.125~2.000 |
| Rf | Y=357.20X+0.938 | 1.000 0 | 0.125~2.000 |
| Rb1 | Y=276.14X+5.638 | 1.000 0 | 0.125~2.000 |
| Rg2 | Y=450.48X+2.952 | 0.999 9 | 0.125~2.000 |
| Rc | Y=239.24X+5.564 | 0.999 9 | 0.125~2.000 |
| Rb2 | Y=269.98X+3.067 | 0.999 9 | 0.125~2.000 |
| Rb3 | Y=269.55X+0.705 | 0.999 9 | 0.125~2.000 |
| Rg3 | Y=302.66X+3.355 | 0.999 7 | 0.125~2.000 |
| Rd | Y=286.91X+0.928 | 0.999 9 | 0.125~2.000 |
| 苯甲酸Benzoic acid | Y=2.546 8X+1.176 | 0.999 3 | 1.000~8.000 |
| 邻苯二甲酸Phthalic acid | Y=4.120 9X+3.160 | 0.999 1 | 1.000~8.000 |
| 肉桂酸Cinnamic acid | Y=4.195 2X+1.279 | 0.999 0 | 1.000~8.000 |
| 丁二酸Succinic acid | Y=3.703 1X+2.326 | 0.999 2 | 1.000~8.000 |
表4 14种有效成分回归方程
Table 4 Regression equations of 14 effective components
成分 Ingredient | 回归方程 Regression equation | 决定系数 R2 | 线性范围 Linearity range/(µg·mL-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rg1 | Y=471.10X+7.325 | 1.000 0 | 0.125~2.000 |
| Re | Y=385.02X+5.727 | 0.999 9 | 0.125~2.000 |
| Rf | Y=357.20X+0.938 | 1.000 0 | 0.125~2.000 |
| Rb1 | Y=276.14X+5.638 | 1.000 0 | 0.125~2.000 |
| Rg2 | Y=450.48X+2.952 | 0.999 9 | 0.125~2.000 |
| Rc | Y=239.24X+5.564 | 0.999 9 | 0.125~2.000 |
| Rb2 | Y=269.98X+3.067 | 0.999 9 | 0.125~2.000 |
| Rb3 | Y=269.55X+0.705 | 0.999 9 | 0.125~2.000 |
| Rg3 | Y=302.66X+3.355 | 0.999 7 | 0.125~2.000 |
| Rd | Y=286.91X+0.928 | 0.999 9 | 0.125~2.000 |
| 苯甲酸Benzoic acid | Y=2.546 8X+1.176 | 0.999 3 | 1.000~8.000 |
| 邻苯二甲酸Phthalic acid | Y=4.120 9X+3.160 | 0.999 1 | 1.000~8.000 |
| 肉桂酸Cinnamic acid | Y=4.195 2X+1.279 | 0.999 0 | 1.000~8.000 |
| 丁二酸Succinic acid | Y=3.703 1X+2.326 | 0.999 2 | 1.000~8.000 |

图1 罹病人参皂苷单体含量注:*表示与0级健康株相比差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 1 Monomer content of infected ginsenosidesNote: * indicates significant difference compared with 0 degree healthy strains at P<0.05 level.
| 病级Disease degree | 参数 Parameter | 皂苷含量Saponin content/(μg·g-1) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rg1 | Re | Rf | Rb1 | Rg2 | Rc | Rb2 | Rb3 | Rg3 | Rd | ||
0级 0 degree | 最小值Minimum | 0.11 | 0.31 | 2.25 | 0.49 | 2.65 | 0.43 | 2.05 | 2.06 | 1.07 | 1.66 |
| 最大值Maximum | 4.43 | 6.42 | 48.17 | 11.82 | 2.65 | 0.43 | 6.25 | 7.64 | 5.47 | 14.72 | |
| 均值Mean | 1.49 | 2.82 | 15.97 | 4.45 | 2.65 | 0.43 | 3.86 | 3.69 | 2.99 | 4.22 | |
| 频率Frequency/% | 35.71 | 28.57 | 71.43 | 57.14 | 3.57 | 3.57 | 10.71 | 28.57 | 25.00 | 60.71 | |
1级 1 degree | 最小值Minimum | 0.22 | 0.21 | 1.29 | 0.81 | 2.58 | 0.54 | 1.69 | 2.43 | 1.52 | 1.69 |
| 最大值Maximum | 6.27 | 3.43 | 31.21 | 15.34 | 38.49 | 0.88 | 7.88 | 10.80 | 8.67 | 25.43 | |
| 均值Mean | 2.37 | 1.82 | 9.02 | 7.17 | 20.53 | 0.71 | 4.47 | 5.12 | 4.96 | 6.56 | |
| 频率Frequency/% | 23.81 | 9.52 | 71.43 | 38.10 | 9.52 | 9.52 | 23.81 | 47.62 | 33.33 | 66.67 | |
2级 2 degree | 最小值Minimum | 0.60 | 0.28 | 6.26 | 0.88 | 12.55 | — | 7.49 | 4.60 | 4.89 | 3.41 |
| 最大值Maximum | 8.36 | 1.31 | 50.68 | 17.33 | 33.74 | — | 7.49 | 96.44 | 5.06 | 15.23 | |
| 均值Mean | 2.97 | 0.79 | 27.92 | 8.24 | 23.14 | — | 7.49 | 27.44 | 4.97 | 7.28 | |
| 频率Frequency/% | 53.85 | 15.38 | 53.85 | 46.15 | 15.38 | 0.00 | 7.69 | 38.46 | 15.38 | 30.77 | |
3级 3 degree | 最小值Minimum | 0.85 | 0.45 | 24.83 | 3.46 | 26.47 | 2.96 | — | 39.78 | 1.35 | 1.50 |
| 最大值Maximum | 14.17 | 1.80 | 36.25 | 7.59 | 26.47 | 2.96 | — | 39.78 | 17.26 | 6.93 | |
| 均值Mean | 7.51 | 1.13 | 30.54 | 5.53 | 26.47 | 2.96 | — | 39.78 | 9.31 | 4.22 | |
| 频率Frequency/% | 50.00 | 50.00 | 50.00 | 50.00 | 25.00 | 25.00 | 0.00 | 25.00 | 50.00 | 50.00 | |
4级 4 degree | 最小值Minimum | 0.31 | 0.31 | 1.52 | 0.40 | 2.02 | — | — | 5.61 | 6.36 | 4.94 |
| 最大值Maximum | 19.92 | 0.31 | 40.55 | 11.28 | 34.75 | — | — | 38.67 | 6.36 | 4.94 | |
| 均值Mean | 10.99 | 0.31 | 21.03 | 6.86 | 15.52 | — | — | 22.14 | 6.36 | 4.94 | |
| 频率Frequency/% | 100.00 | 33.33 | 66.67 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 66.67 | 33.33 | 33.33 | |
表5 罹病人参根际土壤中皂苷含量
Table 5 Saponins content in rhizosphere soil of infected ginseng
| 病级Disease degree | 参数 Parameter | 皂苷含量Saponin content/(μg·g-1) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rg1 | Re | Rf | Rb1 | Rg2 | Rc | Rb2 | Rb3 | Rg3 | Rd | ||
0级 0 degree | 最小值Minimum | 0.11 | 0.31 | 2.25 | 0.49 | 2.65 | 0.43 | 2.05 | 2.06 | 1.07 | 1.66 |
| 最大值Maximum | 4.43 | 6.42 | 48.17 | 11.82 | 2.65 | 0.43 | 6.25 | 7.64 | 5.47 | 14.72 | |
| 均值Mean | 1.49 | 2.82 | 15.97 | 4.45 | 2.65 | 0.43 | 3.86 | 3.69 | 2.99 | 4.22 | |
| 频率Frequency/% | 35.71 | 28.57 | 71.43 | 57.14 | 3.57 | 3.57 | 10.71 | 28.57 | 25.00 | 60.71 | |
1级 1 degree | 最小值Minimum | 0.22 | 0.21 | 1.29 | 0.81 | 2.58 | 0.54 | 1.69 | 2.43 | 1.52 | 1.69 |
| 最大值Maximum | 6.27 | 3.43 | 31.21 | 15.34 | 38.49 | 0.88 | 7.88 | 10.80 | 8.67 | 25.43 | |
| 均值Mean | 2.37 | 1.82 | 9.02 | 7.17 | 20.53 | 0.71 | 4.47 | 5.12 | 4.96 | 6.56 | |
| 频率Frequency/% | 23.81 | 9.52 | 71.43 | 38.10 | 9.52 | 9.52 | 23.81 | 47.62 | 33.33 | 66.67 | |
2级 2 degree | 最小值Minimum | 0.60 | 0.28 | 6.26 | 0.88 | 12.55 | — | 7.49 | 4.60 | 4.89 | 3.41 |
| 最大值Maximum | 8.36 | 1.31 | 50.68 | 17.33 | 33.74 | — | 7.49 | 96.44 | 5.06 | 15.23 | |
| 均值Mean | 2.97 | 0.79 | 27.92 | 8.24 | 23.14 | — | 7.49 | 27.44 | 4.97 | 7.28 | |
| 频率Frequency/% | 53.85 | 15.38 | 53.85 | 46.15 | 15.38 | 0.00 | 7.69 | 38.46 | 15.38 | 30.77 | |
3级 3 degree | 最小值Minimum | 0.85 | 0.45 | 24.83 | 3.46 | 26.47 | 2.96 | — | 39.78 | 1.35 | 1.50 |
| 最大值Maximum | 14.17 | 1.80 | 36.25 | 7.59 | 26.47 | 2.96 | — | 39.78 | 17.26 | 6.93 | |
| 均值Mean | 7.51 | 1.13 | 30.54 | 5.53 | 26.47 | 2.96 | — | 39.78 | 9.31 | 4.22 | |
| 频率Frequency/% | 50.00 | 50.00 | 50.00 | 50.00 | 25.00 | 25.00 | 0.00 | 25.00 | 50.00 | 50.00 | |
4级 4 degree | 最小值Minimum | 0.31 | 0.31 | 1.52 | 0.40 | 2.02 | — | — | 5.61 | 6.36 | 4.94 |
| 最大值Maximum | 19.92 | 0.31 | 40.55 | 11.28 | 34.75 | — | — | 38.67 | 6.36 | 4.94 | |
| 均值Mean | 10.99 | 0.31 | 21.03 | 6.86 | 15.52 | — | — | 22.14 | 6.36 | 4.94 | |
| 频率Frequency/% | 100.00 | 33.33 | 66.67 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 66.67 | 33.33 | 33.33 | |
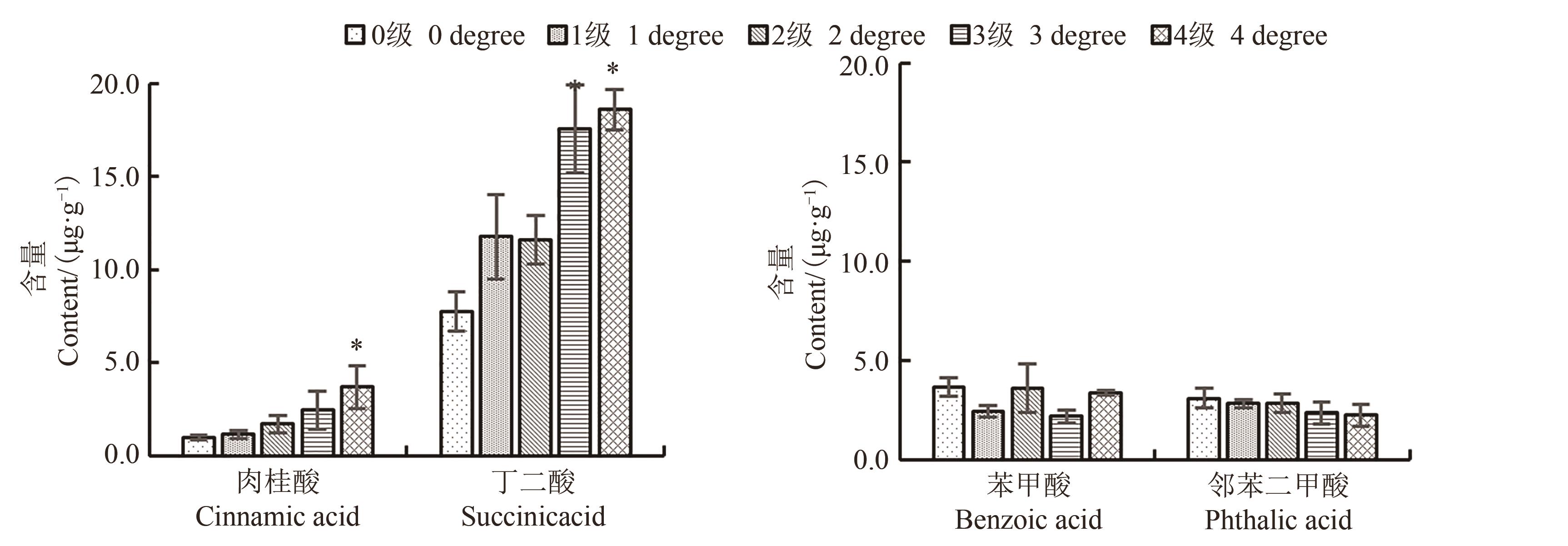
图2 罹病人参根际土壤中酚酸含量注:*表示与0级健康株相比差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 2 Content of phenolic acid in rhizosphere soil of infected ginsengNote: * indicates significant difference compared with 0 degree healthy strains at P<0.05 level.
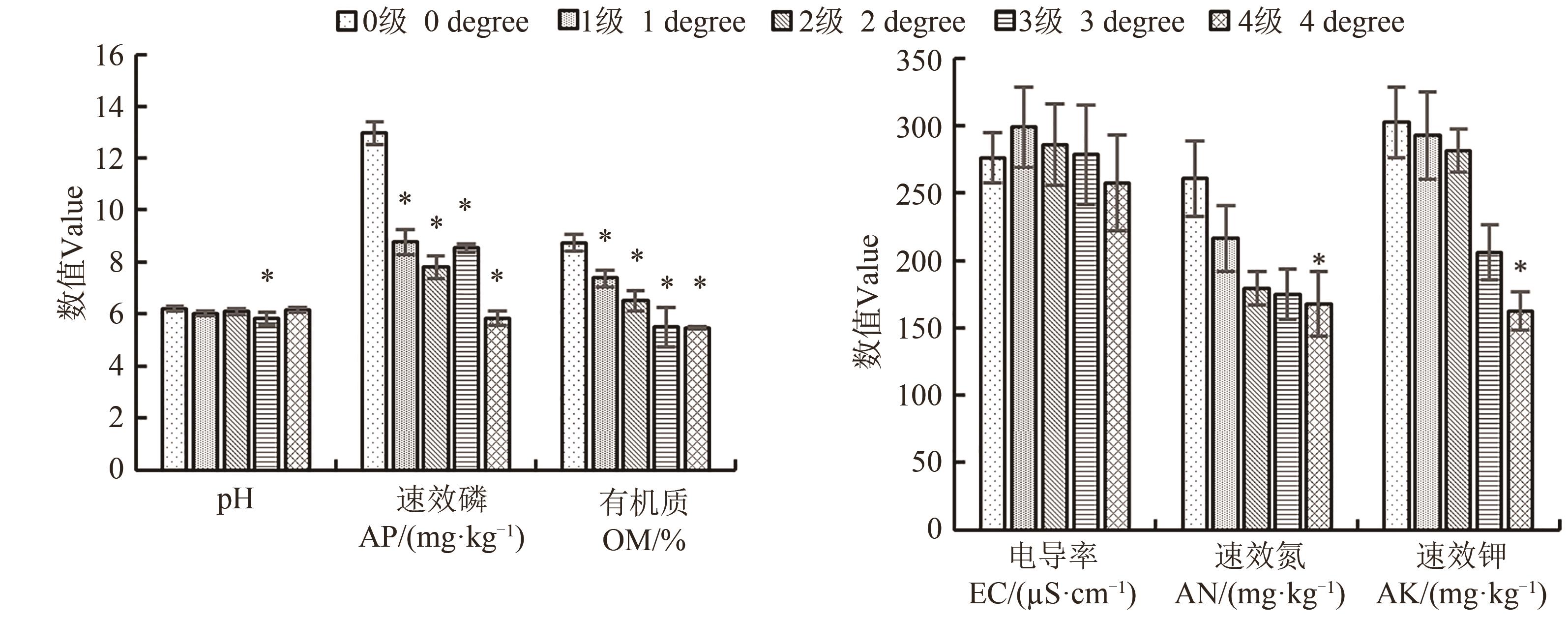
图3 罹病人参根际土壤理化性质注:*表示与0级健康株相比差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 3 Physicochemical properties of soil of diseased ginseng rhizosphereNote: * indicates significant difference compared with grade 0 healthy strains at P<0.05 level.
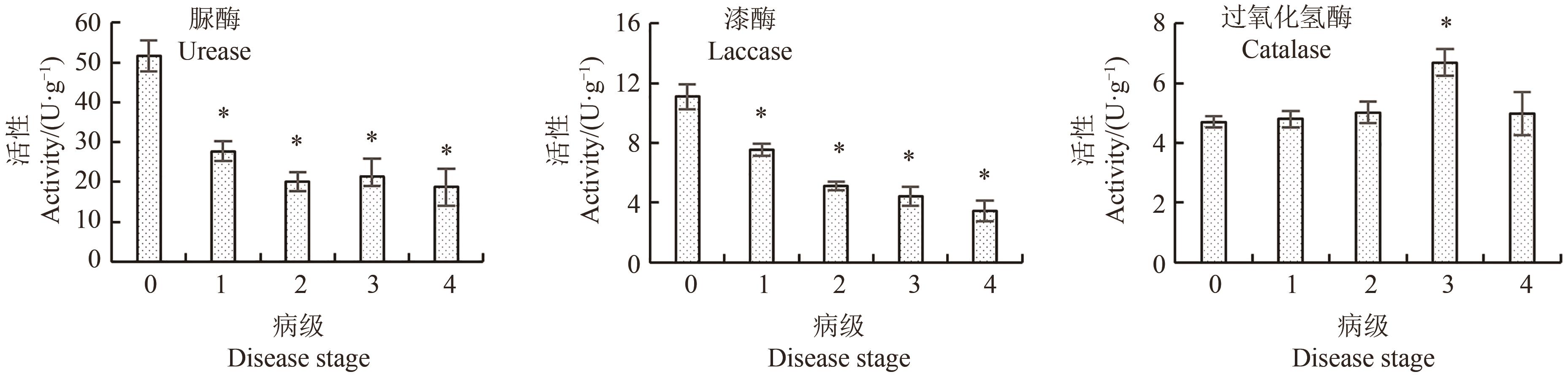
图4 罹病人参根际土壤酶活性注:*表示与0级健康株相比差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 4 Enzyme activity of rhizosphere soil of infected ginsengNote: * indicates significant difference compared with 0 degree healthy strains at P<0.05 level.
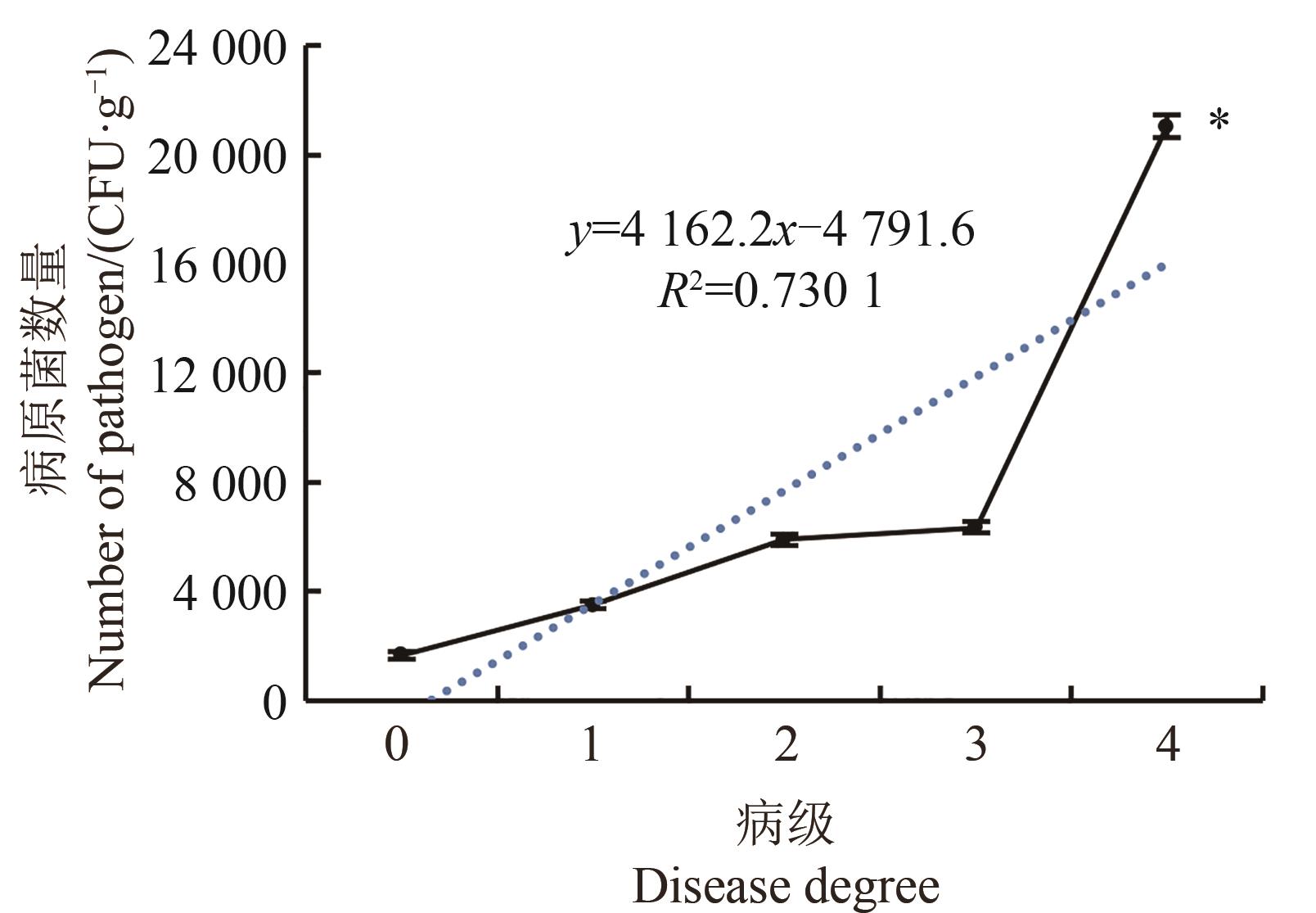
图5 罹病人参根际土壤中强壮土赤壳菌数量注:*表示与0级健康株相比差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 5 Number of arachnoides in rhizosphere soil of infected ginsengNote:* indicates significant difference compared with 0 degree healthy strains at P<0.05 level.
种类 Kind | 因子 Factor | 灰色关联度 Grey relational degree |
|---|---|---|
皂苷类物质 Saponin | Rg3 | 0.467 1 |
| Rd | 0.343 9 | |
| Rb1 | 0.393 4 | |
| Rb3 | 0.402 0 | |
| Rf | 0.372 2 | |
| Rg2 | 0.376 9 | |
| Rg1 | 0.611 1* | |
| Rb2 | 0.182 5 | |
| Rc | 0.271 8 | |
| Re | 0.318 1 | |
酚酸类物质 Phenolic acid | 肉桂酸 Cinnamic acid | 0.619 9* |
| 己二酸 Adipic acid | 0.381 0 | |
| 丁二酸 Succinic acid | 0.457 8 | |
| 苯甲酸 Benzoic acid | 0.374 9 | |
| 邻苯二甲酸 Phthalic acid | 0.413 2 | |
酶活性 Enzyme activity | 脲酶 Urease | 0.365 1 |
| 过氧化氢酶 Catalase | 0.421 6 | |
| 漆酶 Laccase | 0.367 4 | |
理化性质 Physicochemical property | pH | 0.488 0 |
| 电导率Electrical conductivity | 0.456 6 | |
| 碱解氮Available nitrogen | 0.496 7 | |
| 有效磷Available phosphate | 0.497 5 | |
| 速效钾Rapidly available potassium | 0.362 5 | |
| 有机质 Organic matter | 0.414 0 |
表6 各因子与病原菌数量的灰色关联度
Table 6 Grey correlation degree between each factor and the number of pathogenic bacteria
种类 Kind | 因子 Factor | 灰色关联度 Grey relational degree |
|---|---|---|
皂苷类物质 Saponin | Rg3 | 0.467 1 |
| Rd | 0.343 9 | |
| Rb1 | 0.393 4 | |
| Rb3 | 0.402 0 | |
| Rf | 0.372 2 | |
| Rg2 | 0.376 9 | |
| Rg1 | 0.611 1* | |
| Rb2 | 0.182 5 | |
| Rc | 0.271 8 | |
| Re | 0.318 1 | |
酚酸类物质 Phenolic acid | 肉桂酸 Cinnamic acid | 0.619 9* |
| 己二酸 Adipic acid | 0.381 0 | |
| 丁二酸 Succinic acid | 0.457 8 | |
| 苯甲酸 Benzoic acid | 0.374 9 | |
| 邻苯二甲酸 Phthalic acid | 0.413 2 | |
酶活性 Enzyme activity | 脲酶 Urease | 0.365 1 |
| 过氧化氢酶 Catalase | 0.421 6 | |
| 漆酶 Laccase | 0.367 4 | |
理化性质 Physicochemical property | pH | 0.488 0 |
| 电导率Electrical conductivity | 0.456 6 | |
| 碱解氮Available nitrogen | 0.496 7 | |
| 有效磷Available phosphate | 0.497 5 | |
| 速效钾Rapidly available potassium | 0.362 5 | |
| 有机质 Organic matter | 0.414 0 |
| 1 | 张道明. 人参皂苷Rg5对人食管癌细胞促凋亡及联合顺铂抗肿瘤作用的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2018. |
| ZHANG D M. Researches on anti-apoptosis effect of ginsenoside Rg5 and anti-tumor effect combined with cisplatin on human esophageal cancer cells [D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2018. | |
| 2 | 方斯文. 人参化感物质对土壤酶、微生物多样性的影响及其在土壤中的迁移研究[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2012. |
| FANG S W. Ginseng allelochemicals’ impact on soil enzyme activities and microbial diversity, as well as ginseng allelochemicals’ mobility in soil [D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2012. | |
| 3 | 王梓, 李勇, 丁万隆. 人参化感自毒作用与连作障碍机制研究进展[J]. 中国现代中药, 2017, 19(7): 1040-1044. |
| WANG Z, LI Y, DING W L. Advances in allelopathic autotoxicity and continuous cropping obstacle of Panax ginseng [J]. Mod. Chin. Med., 2017, 19(7): 1040-1044. | |
| 4 | 黄玉茜, 韩晓日, 杨劲峰, 等.花生连作土壤微生物区系变化研究[J]. 土壤通报, 2011, 42(3): 552-556. |
| HUANG Y Q, HAN X R, YANG J F, et al.. Studies on the changes of soil microbial communities under peanuts continuous cropping [J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2011, 42(3): 552-556 | |
| 5 | 李振方, 杨燕秋, 谢冬凤, 等. 连作条件下地黄药用品质及土壤微生态特性分析[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2012, 20(2): 217-224. |
| LI Z F, YANG Y Q, XIE D F, et al.. Effects of continuous cropping on the quality of Rehmannia glutinosa L. and soil micro-ecology [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2012, 20(2): 217-224. | |
| 6 | ABBOROVA D, SAYYED R Z, AZIMOV A, et al.. Impact of mineral fertilizers on mineral nutrients in the ginger rhizome and on soil enzymes activities and soil properties [J]. Saudi J. Biol. Sci., 2021, 28(9): 5268-5274. |
| 7 | 丛微, 喻海茫, 于晶晶, 等. 人参种植对林地土壤细菌群落结构和代谢功能的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(1): 162-171. |
| CONG W, YU H M, YU J J, et al.. Effects of ginseng cultivation on soil microbial community structure and metabolic functions in forest land [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2021, 41(1): 162-171. | |
| 8 | 李昕月, 付俊范, 魏晓兵, 等. 长白山区人参锈腐病发生危害调查及杀菌剂田间药效试验[J]. 农学学报, 2015, 5(9): 69-72. |
| LI X Y, FU J F, WEI X B, et al.. Toxicity test and field control effects of 11 new fungicides against cylindrocarpon destructans [J]. J. Agric., 2015, 5(9): 69-72. | |
| 9 | 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000: 1-495. |
| 10 | 关松荫. 土壤酶及其研究法[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1986:1-346. |
| 11 | RAHMAN M, PUNJA Z K. Biochemistry of ginseng root tissues affected by rusty root symptoms [J]. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 2005, 43(12): 1103-1114. |
| 12 | 刘延硕. 农田人参锈腐病影响因素的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2011. |
| LIU Y S. The study on influencing factors of the rust and rot of farmland ginseng [D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2011. | |
| 13 | TAN G, LIU Y J, PENG S G, et al.. Soil potentials to resist continuous cropping obstacle: three field cases [J/OL]. Environ. Res., 2021, 200: 111319 [2022-08-20]. . |
| 14 | 张爱华, 雷锋杰, 许永华, 等. 外源人参皂苷对人参种子萌发和幼根抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2009, 29(9): 4934-4941. |
| ZHANG A H, LEI F J, XU Y H, et al.. Effects of ginsenosides on the germinating of ginseng seeds and on the activity of antioxidant enzymes of the radicles of ginseng seedlings in vitro [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2009,29(9): 4934-4941. | |
| 15 | CHU L L, BAE H. Bacterial endophytes from ginseng and their biotechnological application [J]. J. Ginseng Res., 2022, 46(1): 1-10. |
| 16 | VIVIANE R, JANA B W, SUSANNE K, et al.. Correction to: reduced microbial potential for the degradation of phenolic compounds in the rhizosphere of apple plantlets grown in soils affected by replant disease [J/OL]. Environ. Microbiome, 2019, 14(1): 9 [2022-08-20]. . |
| 17 | 班洁静, 侯明生, 蔡丽. 土壤pH对芸薹根肿菌侵染及病害发生的影响[J]. 植物保护, 2015, 41(6): 55-59. |
| BAN J J, HOU M S, CAI L. Effects of pH on Plasmodiophora brassica infection and disease development [J]. Plant Prot., 2015, 41(6): 55-59. | |
| 18 | XIE Z W, MA Q, PENG W Y, et al.. Research progress on continuous cropping obstacle and green control of strawberry [J/OL]. E3S Web of Conferences, 2021, 251: 02044 [2022-08-20]. . |
| 19 | DANIEL C S, KENDALL K, BRYAN C, et al.. Soil acidification modifies soil depth-microbiome relationships in a no-till wheat cropping system [J/OL]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2020, 149: 107939 [2022-08-20]. . |
| 20 | 洪艳华. 长期耕作对黑土理化性质及微生物群落结构的影响[D]. 大庆:黑龙江八一农垦大学, 2021. |
| HONG Y H. Effects of long-term tillage on physicochemical properties and microbial community structure of black soil [D]. Daqing: Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 2021. | |
| 21 | 韩海蓉, 李屹, 陈来生, 等. 设施辣椒连作对土壤理化性状、酶活性及微生物区系的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2021(3): 237-242. |
| HAN H R, LI Y, CHEN L S, et al.. Effects of continuous pepper cultivation on soil physical and chemical properties, enzyme activity and microbial flora [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2021(3): 237-242. | |
| 22 | 舒健虹, 蔡一鸣, 丁磊磊, 等. 不同放牧强度对贵州人工草地土壤养分及活性有机碳的影响[J]. 生态科学, 2018, 37(1): 42-48. |
| SHU J H, CAI Y M, DING L L, et al.. Effects of different grazing intensities on soil nutrient and active organic carbon in Guizhou artificial grassland [J]. Ecol. Sci., 2018, 37(1): 42-48. | |
| 23 | 战宇, 张连学, 孟祥茹, 等. 不同盆栽人参土壤酚酸含量及酶活性变化研究[J/OL]. 吉林农业大学学报, 2022 [2022-08-20]. . |
| ZHAN Y, ZHANG L X, MENG X R, et al.. Changes of phenolic acid content and enzyme activity in soil of different pot ginseng [J/OL]. J. Jilin Agric.Univ., 2022 [2022-08-20]. . | |
| 24 | 李雪萍, 李建宏, 漆永红, 等. 青稞根腐病对根际土壤微生物及酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(17): 5640-5649. |
| LI X P, LI J H, QI Y H, et al.. Effects of naked barley root rot on rhizosphere soil microorganisms and enzyme activity [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2017, 37(17): 5640-5649. |
| [1] | 郭靖捷, 任晓萌, 蒙仲举, 王涛, 祁帅, 宋佳佳, 宝孟克那顺, 韩胜利. 半干旱风沙草原区盐湖植物防护体系土壤理化性状特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 182-192. |
| [2] | 肖锐, 谭璐, 吴亮, 张皓, 郭佳源, 杨海君. 镉胁迫下地肤根际与非根际土壤微生物群落结构及多样性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 203-215. |
| [3] | 尹兴盛, 包玲凤, 濮永瑜, 孙加利, 张庆, 李海平, 杨明英, 林跃平, 王怀鑫, 何永宏, 杨佩文. 减氮配施生物有机肥对植烟土壤特性及烟草青枯病的防效研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 122-131. |
| [4] | 刘宏元, 周志花, 赵光昕, 沈钦瑞. 黄淮海平原农田土壤温室气体排放对长期施加生物炭的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 178-186. |
| [5] | 庞喆, 王启龙, 李娟. 不同土壤改良剂对陕北低洼盐碱地土壤理化性质及水稻产量和经济效益的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 174-180. |
| [6] | 孟璐, 范敬文, 赛欣娱, 曾路生, 宋祥云, 崔德杰. 石灰对苹果园土壤改良和植株生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 197-204. |
| [7] | 郭巨先, 欧阳碧珊, 李桂花, 符梅, 罗文龙, 骆善伟, 陆美莲. 微生物有机肥对连作菜薹生长及土壤性质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 182-191. |
| [8] | 闫宁, 战宇, 苗馨月, 王二刚, 陈长宝, 李琼. 强还原土壤灭菌处理对人参连作土壤细菌群落结构及土壤酶活的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(6): 133-144. |
| [9] | 魏艳晨, 陈吉祥, 王永刚, 孟彤彤, 韩亚龙, 李美. 荒漠植物珍珠猪毛菜根际土壤细菌多样性与土壤理化性质相关性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 209-217. |
| [10] | 李敏, 李钢铁, 张宏武, 陈家欢. 平茬对3种苗木来源蛋白桑林地土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 172-182. |
| [11] | 范娜,彭之东,白文斌*,赵建武. 微生物菌剂对土壤酶活性及高粱生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(2): 185-192. |
| [12] | 王思霁, 国艳春, 曾路生, 孙显旻, 初庆刚, 王胜. 碱蓬播种量对滨海盐碱地土壤酶活性和团聚性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(12): 179-185. |
| [13] | 黄艳飞, 陈君梅, 辛亚宁, 吴庆丽. 石膏对苏打盐碱土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(11): 139-146. |
| [14] | 高日平, §, 刘小月, §, 杜二小, 韩云飞, 任永峰, 高宇, 赵沛义, 李焕春, 张鹏, . 垄膜沟播与秸秆还田对内蒙古黄土高原玉米农田土壤水分、酶活性及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(11): 181-190. |
| [15] | 杨晶晶,张青青*,吐尔逊娜依·热依木,阿马努拉·依明尼亚孜,雪热提江·麦提努日. 游牧和定居对伊犁绢蒿荒漠草地土壤真菌群落多样性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(7): 166-173. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号