




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (8): 63-73.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.1069
收稿日期:2022-12-07
接受日期:2023-02-13
出版日期:2024-08-15
发布日期:2024-08-12
作者简介:白世践E-mail:594748964@qq.com
基金资助:
Shijian BAI( ), Jinge HU, Chao LI, Junshe CAI
), Jinge HU, Chao LI, Junshe CAI
Received:2022-12-07
Accepted:2023-02-13
Online:2024-08-15
Published:2024-08-12
摘要:
为筛选及优化西北干旱区鲜食葡萄优质高效栽培架式,以‘新郁’葡萄为试验材料,设置独龙干+水平叶幕(SDTS-H)、顺行龙干+水平叶幕(ISDTS-H)和顺行龙干+V+水平叶幕(ISDTS-VH)3种栽培架式,分析其对‘新郁’葡萄叶片光合特性、果穗微域环境、果实品质及经济效益的影响。结果表明,相比SDTS-H,ISDTS-VH叶片净光合速率提高7.73%,ISDTS-H水分利用效率提高14.13%;ISDTS-H、ISDTS-VH比SDTS-H果穗微域环境平均温度分别升高2.29 和2.24 ℃,平均湿度分别减小4.96和3.85个百分点,日均总辐射分别为SDTS-H的2.66和1.31倍;ISDTS-H、ISDTS-VH葡萄较SDTS-H早熟,成熟期果实可溶性固形物、花色苷、类黄酮、维生素C含量及葡萄果实色泽指数均显著高于SDTS-H,SDTS-VH果实成熟后期果粒质量最大,为13.99 g,类黄酮和维生素C含量最高,分别为7.36和44.18 mg·kg-1,且具有适度的花色苷含量(1.22 mg·g-1),综合品质最好;SDTS-VH实际果穗数、实际产量与目标值相似指数最高,分别为0.73和1.06;ISDTS-VH相比传统SDTS-H,累计工时投入减少48.00%,经济效益提高189.58%。综上所述,ISDTS-VH栽培的‘新郁’葡萄叶片光合速率最高,果穗微域环境最优,利于品质形成和产量控制,栽培经济效益最高。
中图分类号:
白世践, 户金鸽, 李超, 蔡军社. 3种架式对‘新郁’葡萄栽培性状及果实品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 63-73.
Shijian BAI, Jinge HU, Chao LI, Junshe CAI. Effects of 3 Trellis Systems on Cultivation Characters and Berry Quality of ‘Xinyu’ Grape[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(8): 63-73.
栽培架式 Cultivation trellis system | 净光合速率 Pn/(µmol·m-2·s-1) | 蒸腾速率 Tr/(mmol·m-2·s-1) | 气孔导度 Gs/(mmol·m-2·s-1) | 胞间CO2浓度 Ci/(µmol·mol-1) | 水分利用效率 WUE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDTS-H | 14.23±0.07 b | 4.96±0.07 a | 133.18±3.50 b | 167.45±3.30 b | 2.83±0.09 b |
| ISDTS-H | 14.13±0.08 b | 4.41±0.09 b | 131.23±1.27 b | 167.66±1.69 b | 3.23±0.07 a |
| ISDTS-VH | 15.33±0.41 a | 5.15±0.14 a | 160.81±2.47 a | 187.23±4.84 a | 2.99±0.04 b |
表1 3种架式下‘新郁’葡萄叶片光合参数
Table 1 Photosynthetic parameters of ‘Xinyu’ grape leaves under 3 trellis systems
栽培架式 Cultivation trellis system | 净光合速率 Pn/(µmol·m-2·s-1) | 蒸腾速率 Tr/(mmol·m-2·s-1) | 气孔导度 Gs/(mmol·m-2·s-1) | 胞间CO2浓度 Ci/(µmol·mol-1) | 水分利用效率 WUE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDTS-H | 14.23±0.07 b | 4.96±0.07 a | 133.18±3.50 b | 167.45±3.30 b | 2.83±0.09 b |
| ISDTS-H | 14.13±0.08 b | 4.41±0.09 b | 131.23±1.27 b | 167.66±1.69 b | 3.23±0.07 a |
| ISDTS-VH | 15.33±0.41 a | 5.15±0.14 a | 160.81±2.47 a | 187.23±4.84 a | 2.99±0.04 b |
| 参数 Parameter | 栽培架式 Cultivation trellis system | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| SDTS-H | ISDTS-H | ISDTS-VH | |
| 平均最高温 Average maximum temperature/℃ | 37.05 | 37.01 | 36.90 |
| 平均最低温 Average minimum temperature/℃ | 16.02 | 18.79 | 18.74 |
| 平均温度 Average temperature/℃ | 25.40 | 27.69 | 27.64 |
| 平均温差 Average temperature difference/℃ | 20.65 | 18.23 | 18.16 |
| 超过35 ℃温差总和 Sum of temperature difference above 35 ℃/℃ | 234.50 | 215.00 | 209.00 |
| ≥35 ℃高温时长 Time of temperature above 35 ℃/h | 254.00 | 349.50 | 343.00 |
| 平均最大湿度 Average maximum humidity/% | 78.18 | 65.65 | 66.78 |
| 平均最小湿度 Average minimum humidity/% | 21.25 | 26.52 | 27.47 |
| 平均湿度 Average humidity/% | 48.56 | 43.60 | 44.71 |
| ≤45%低湿时长 Sum of humidity difference below 45%/h | 919.50 | 1 046.00 | 980.00 |
| 日均叶幕透射辐射 Daily average PARtran/(µmol·m-2·s-1) | 2.37 | 9.29 | 4.17 |
| 日均土壤反射辐射 Daily average PARsoil/(µmol·m-2·s-1) | 4.29 | 8.48 | 5.61 |
| 日均总辐射 Daily average total radiation/(µmol·m-2·s-1) | 6.67 | 17.77 | 9.78 |
表2 3种架式下‘新郁’葡萄果穗微域环境参数
Table 2 Cluster micro-environment parameters of ‘Xinyu’ grape under 3 trellis systems
| 参数 Parameter | 栽培架式 Cultivation trellis system | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| SDTS-H | ISDTS-H | ISDTS-VH | |
| 平均最高温 Average maximum temperature/℃ | 37.05 | 37.01 | 36.90 |
| 平均最低温 Average minimum temperature/℃ | 16.02 | 18.79 | 18.74 |
| 平均温度 Average temperature/℃ | 25.40 | 27.69 | 27.64 |
| 平均温差 Average temperature difference/℃ | 20.65 | 18.23 | 18.16 |
| 超过35 ℃温差总和 Sum of temperature difference above 35 ℃/℃ | 234.50 | 215.00 | 209.00 |
| ≥35 ℃高温时长 Time of temperature above 35 ℃/h | 254.00 | 349.50 | 343.00 |
| 平均最大湿度 Average maximum humidity/% | 78.18 | 65.65 | 66.78 |
| 平均最小湿度 Average minimum humidity/% | 21.25 | 26.52 | 27.47 |
| 平均湿度 Average humidity/% | 48.56 | 43.60 | 44.71 |
| ≤45%低湿时长 Sum of humidity difference below 45%/h | 919.50 | 1 046.00 | 980.00 |
| 日均叶幕透射辐射 Daily average PARtran/(µmol·m-2·s-1) | 2.37 | 9.29 | 4.17 |
| 日均土壤反射辐射 Daily average PARsoil/(µmol·m-2·s-1) | 4.29 | 8.48 | 5.61 |
| 日均总辐射 Daily average total radiation/(µmol·m-2·s-1) | 6.67 | 17.77 | 9.78 |
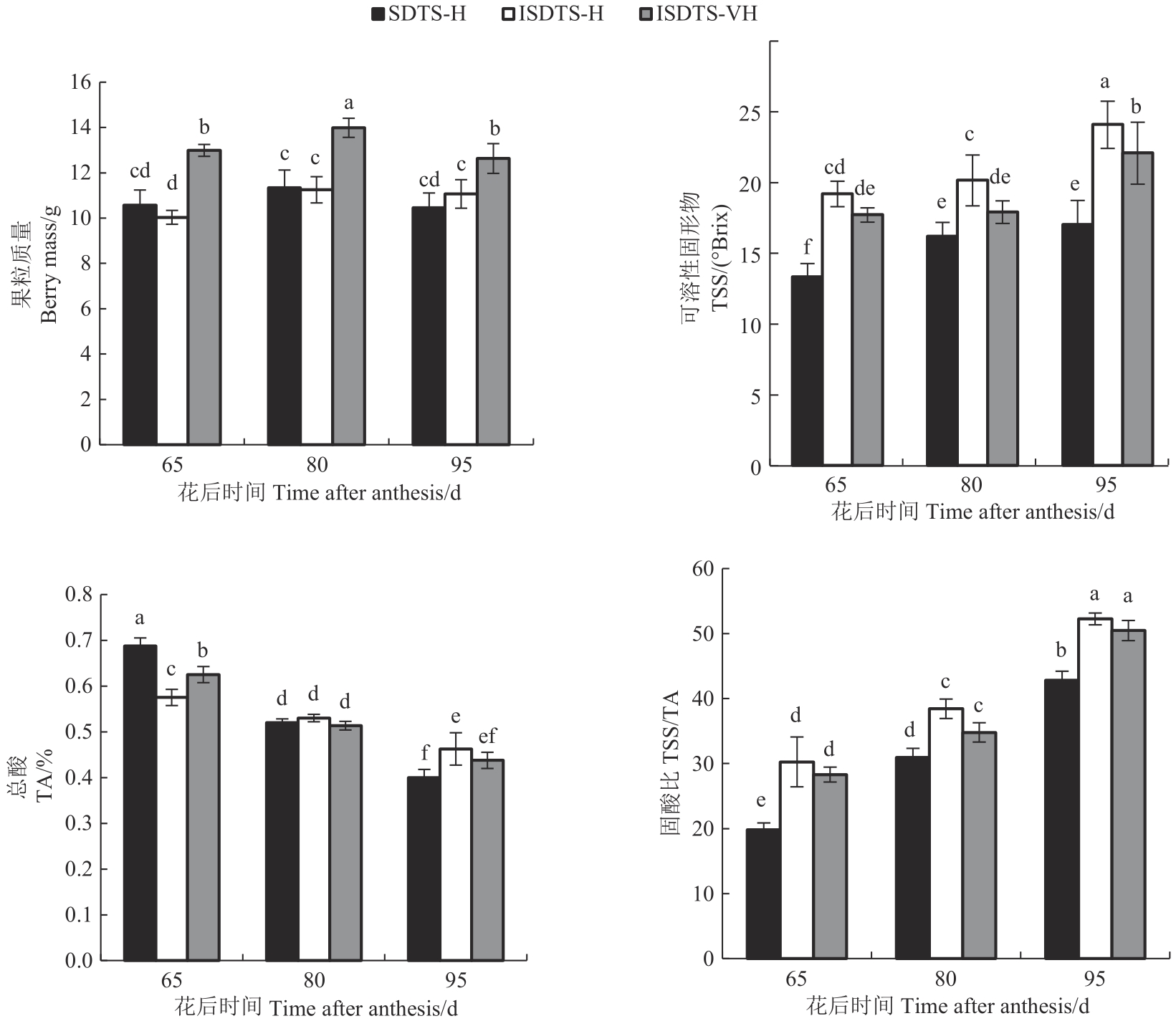
图2 3种架式不同时期‘新郁’葡萄果粒质量及可溶性固形物、总酸含量注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 Berry mass, total soluble solids and total acid content of ‘Xinyu’ grape in different periods under 3 trellis systemsNote:Difference lowercase letters indicate significant difference among different treatment at P<0.05 level.
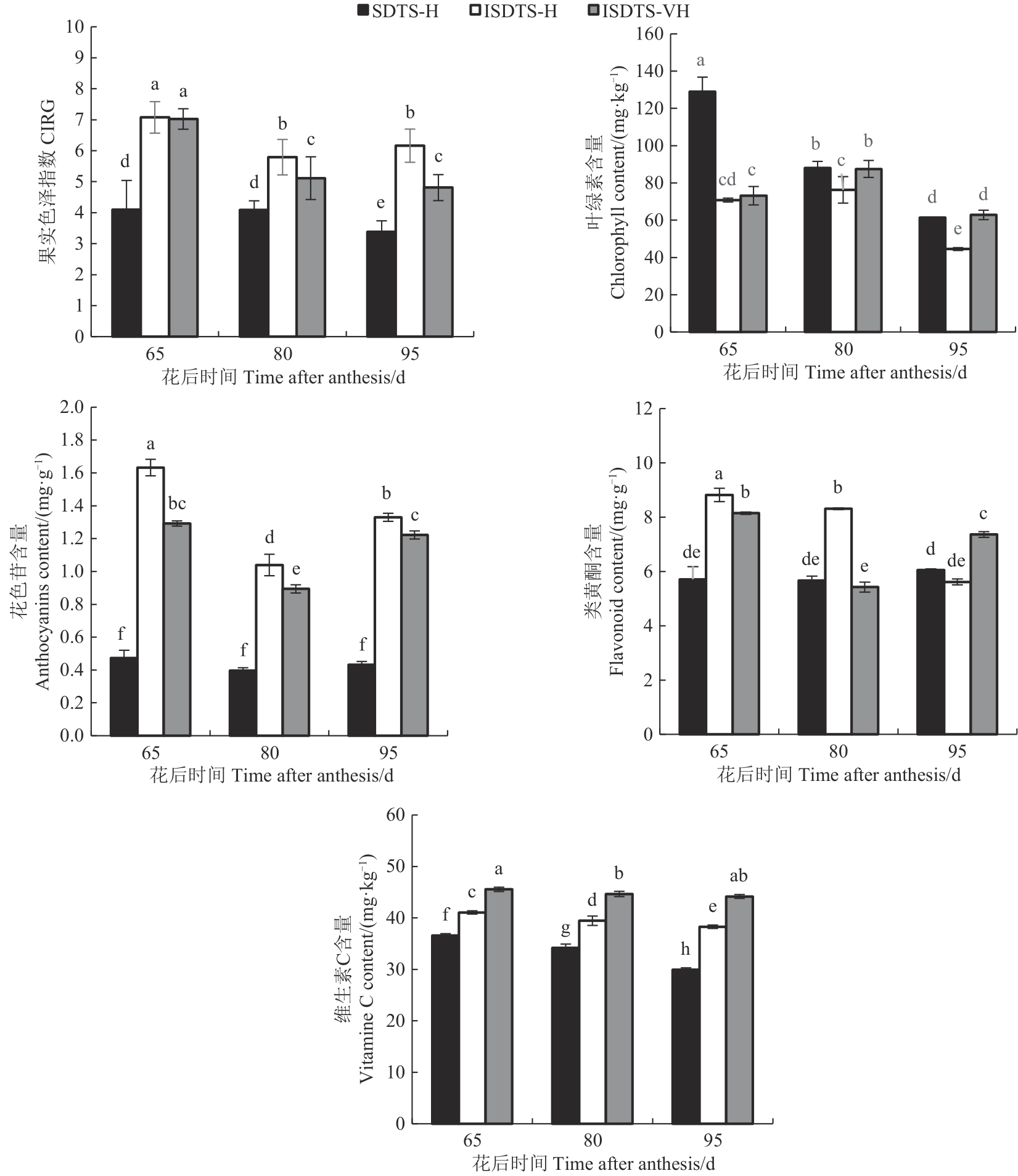
图3 3种架式下不同时期‘新郁’葡萄色泽及维生素C、类黄酮含量注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 3 Fruit color, vitamin C and flavonoid content of ‘Xinyu’ grape in different periods under 3 trellis systemsNote:Difference lowercase letters indicate significant difference among different treatment at P<0.05 level.
栽培架式 Cultivation trellis system | 果穗质量 Cluster mass/g | 实际果穗数 Actual number of clusters/(104·hm-2) | 目标果穗数Objective number of clusters/(104·hm-2) | 实际产量 Actual yield/ (t·hm-2) | 目标产量 Objective yield/(t·hm-2) | 相似指数 Similarity index | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 果穗数Number of clusters | 产量Yield | ||||||
| SDTS-H | 1 175.32±173.11 a | 2.48±0.16 a | 3.75 | 29.10±3.37 a | 30.02 | 0.66 | 0.97 |
| ISDTS-H | 861.25±34.56 b | 1.82±0.13 c | 2.86 | 15.63±1.14 c | 22.87 | 0.64 | 0.68 |
| ISDTS-VH | 1 172.38±58.27 a | 2.07±0.14 b | 2.86 | 24.30±1.84 b | 22.87 | 0.73 | 1.06 |
表3 3种架式下‘新郁’葡萄的产量
Table 3 Yield of ‘Xinyu’ grape under 3 trellis systems
栽培架式 Cultivation trellis system | 果穗质量 Cluster mass/g | 实际果穗数 Actual number of clusters/(104·hm-2) | 目标果穗数Objective number of clusters/(104·hm-2) | 实际产量 Actual yield/ (t·hm-2) | 目标产量 Objective yield/(t·hm-2) | 相似指数 Similarity index | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 果穗数Number of clusters | 产量Yield | ||||||
| SDTS-H | 1 175.32±173.11 a | 2.48±0.16 a | 3.75 | 29.10±3.37 a | 30.02 | 0.66 | 0.97 |
| ISDTS-H | 861.25±34.56 b | 1.82±0.13 c | 2.86 | 15.63±1.14 c | 22.87 | 0.64 | 0.68 |
| ISDTS-VH | 1 172.38±58.27 a | 2.07±0.14 b | 2.86 | 24.30±1.84 b | 22.87 | 0.73 | 1.06 |
| 参数 Parameter | 栽培架式 Cultivation trellis system | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| SDTS-H | ISDTS-H | ISDTS-VH | |
| 顶端优势 Apical dominance | 较明显 Obvious | 不明显 Not obvious | 不明显 Not obvious |
| 主蔓高度 Main vine setting height/cm | 190 | 190 | 150 |
| 结果带高度 Fruit setting height/cm | 180 | 180 | 160 |
| 疏果工时 Fruit thinning hours/(h·hm-2) | 480 | 360 | 240 |
| 新梢绑缚工时 Fruit branch binding hours/(h·hm-2) | 480 | 480 | 360 |
| 夏季修剪工时 Summer pruning hours/(h·hm-2) | 300 | 60 | 60 |
| 上、下架工时 Tying and untying hours/(h·hm-2) | 240 | 120 | 120 |
| 累计工时 Cumulative hours/(h·hm-2) | 1 500 | 1 020 | 780 |
| 商品率 Commodity rate/% | 60~70 | 90 | 90 |
| 经济效益/(104元·hm-2) Economic performance/(104 yuan·hm-2) | 5.47 | 8.04 | 15.84 |
表4 3种架式用工成本及效益
Table 4 Labor costs and benefits under 3 trellis systems
| 参数 Parameter | 栽培架式 Cultivation trellis system | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| SDTS-H | ISDTS-H | ISDTS-VH | |
| 顶端优势 Apical dominance | 较明显 Obvious | 不明显 Not obvious | 不明显 Not obvious |
| 主蔓高度 Main vine setting height/cm | 190 | 190 | 150 |
| 结果带高度 Fruit setting height/cm | 180 | 180 | 160 |
| 疏果工时 Fruit thinning hours/(h·hm-2) | 480 | 360 | 240 |
| 新梢绑缚工时 Fruit branch binding hours/(h·hm-2) | 480 | 480 | 360 |
| 夏季修剪工时 Summer pruning hours/(h·hm-2) | 300 | 60 | 60 |
| 上、下架工时 Tying and untying hours/(h·hm-2) | 240 | 120 | 120 |
| 累计工时 Cumulative hours/(h·hm-2) | 1 500 | 1 020 | 780 |
| 商品率 Commodity rate/% | 60~70 | 90 | 90 |
| 经济效益/(104元·hm-2) Economic performance/(104 yuan·hm-2) | 5.47 | 8.04 | 15.84 |
| 1 | 刘凤之.中国葡萄栽培现状与发展趋势[J].落叶果树,2017,49(1):1-4. |
| 2 | 张大鹏,姜红英,陈星黎,等. 叶幕PAR光能截留和分配对葡萄群体光合同化物库源关系的调控[J].植物生态学报,1995,19(4): 302-310. |
| ZHANG D P, JIANG H Y, CHEN X L . et al .. Regulating effects of canopy light (PAR) interception and distribution on photosynthate ‘sink-source’ relation in grapevine population with different canopy structures [J]. Chin. J. Plant Ecol., 1995, 19(4): 302-310. | |
| 3 | 刘笑宏,孙永江,孙红,等.不同叶幕类型对‘摩尔多瓦’葡萄果穗微域环境及果实品质的影响[J].中国农业科学, 2016, 49(21): 4246-4254. |
| LIU X H, SUN Y J, SUN H, et al.. Effect of canopy types on the cluster micro-environment and fruit quality of the ‘Moldova’ grapes [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2016, 49(21): 4246-4254. | |
| 4 | TROUGHT M C T, NAYLOR A P, FRAMPTON C. Effect of row orientation, trellis type, shoot and bunch position on the variability of Sauvignon Blanc (Vitis vinifera L.) juice composition [J]. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res., 2017, 23: 240-250. |
| 5 | 王晓玥,张国军,孙磊,等. 2种架式对3个鲜食葡萄品种栽培性状及果实品质的影响[J].中国农业科学, 2019,52(7):1150-1163. |
| WANG X Y, ZHANG G J, SUN L, et al.. Effects of two trellis systems on viticultural characteristics and fruit quality of three table grape cultivars [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2019,52(7):1150-1163. | |
| 6 | WOLF T K, DRY P R, ILAND P G, et al.. Response of Shiraz grapevines to five different training systems in the Barossa Valley, Australia [J]. Aus. J. Grape Wine Res., 2003, 9: 82-95. |
| 7 | TROUGHT M C T, NAYLOR A P, FRAMPTON C. Effect of row orientation, trellis type, shoot and bunch position on the variability of Sauvignon Blanc (Vitis vinifera L.) juice composition [J]. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res., 2017, 23: 240-250. |
| 8 | 单守明,杨恕玲,王振平,等.不同架式对设施葡萄生长发育和主芽坏死的影响[J].北方园艺,2011(2): 51-53. |
| SHAN S M, YANG S L, WANG Z P, et al.. Effects of different training structures on the grape development and bud abortion in greenhouse [J]. Northern Hortic., 2011(2): 51-53. | |
| 9 | 冀晓昊,刘凤之,史祥宾,等.架式和新梢间距对‘巨峰’葡萄果实品质的影响[J].中国农业科学,2019,52(7):1164-1172. |
| JI X H, LIU F Z, SHI X B, et al.. The effects of different training systems and shoot spacing on the fruit quality of ‘Kyoho’ grape [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2019,52(7):1164-1172. | |
| 10 | 史祥宾,刘凤之,程存刚,等.不同叶幕形对设施葡萄叶幕微环境、叶片质量及果实品质的影响[J].应用生态学报,2015,26(12):3730-3736. |
| SHI X B, LIU F Z, CHENG C G, et al.. Effects of canopy shapes of grape on canopy microenvironment, leaf and fruit quality in greenhouse [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2015, 26(12): 3730-3736. | |
| 11 | ZHANG F C, ZHONG H X, ZHOU X M, et al.. Photosynthesis of grape leaves with ‘OSC’ trellis and cordon based on data model fitting [J]. Photosynthetica, 2021,59:160-170. |
| 12 | 骆强伟,孙峰,蔡军社,等.葡萄新品种“新郁”[J].园艺学报,2007,34(3):797. |
| LUO Q W, SUN F, CAI J S, et al.. A new grape cultivar ‘Xinyu’ [J]. Acta Hortic. Sin., 2007, 34(3): 797. | |
| 13 | 贾杨,廖康,骆强伟,等.无核白葡萄不同栽培架式叶幕微气候及产量品质差异分析[J].新疆农业科学,2016,53(7):1210-1216. |
| JIA Y, LIAO K, LUO Q W, et al.. Analysis on the canopy microclimate and yield and quality of the different grape cultivation trellis in Turpan [J]. Xinjiang Agric. Sci., 2016, 53(7): 1210-1216. | |
| 14 | AMIRI M E, FALLAHI E, PARSEH S. Application of ethephon and ABA at 40% veraison advanced maturity and quality of ‘Beidaneh Ghermez’ grape [J]. Acta Hortic., 2010, 884: 371-377. |
| 15 | 中华人民共和国国家健康委员会,国家市场监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准食品中总酸的测定: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2021. |
| 16 | 高俊凤.植物生理学指导[M].北京:高等教育出版,2006:203-204. |
| 17 | MEYERS K J, WATKINS C B, PRITTS M P, et al.. Antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of strawberries [J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2003, 51(23):6887-6892. |
| 18 | WELLBURM A R. The spectral determination of chlorophylls a and b, as well as total carotenoids using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolutions [J]. J. Plant Physiol., 1994, 144: 307-313. |
| 19 | ORAK H H. Total antioxidant activities, phenolics, anthocyanins, polyphenoloxidase activities of selected red grape cultivars and their correlations [J]. Sci. Hortic., 2007, 111(3): 235-241. |
| 20 | 张付春,潘明启,伍新宇,等.葡萄埋土防寒区水平棚架“顺沟倾斜龙干”树形研究初报[J].干旱地区农业研究, 2015, 33(5): 69-74. |
| ZHANG F C, PAN M Q, WU X Y, et al.. Preliminary research on single cordon obliquely along the ditch of grape in cold areas [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2015, 33(5): 69-74. | |
| 21 | CORTÁZAR V G, CÓRDOVA C, PINTO M. Canopy structure and photosynthesis modelling of grapevines (Vitis vinifera L. cv. Sultana) grown on an overhead (parronal) trellis system in Chile [J]. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res., 2005, 11(3): 328-338. |
| 22 | 张洁,杨伟伟,容新民,等.构建不同树形葡萄树体结构的三维虚拟模型[J].新疆农业科学,2021,58(2): 265-275. |
| ZHANG J, YANG W W, RONG X M, et al.. Digital study on the canopy structure of grape with different tree shapes [J]. Xinjiang Agric. Sci., 2021, 58(2): 265-275. | |
| 23 | FARQUHAR G D, EHLERINGER J R, HUBICKKT. Carbon isotope discrimination and photosynthesis [J]. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol., 2003, 40(1):503-537. |
| 24 | 许大全.光合作用气孔限制分析中的一些问题[J].植物生理学通讯,1997,33(4):241-244. |
| XU D Q. Some problems in stomatal limitation analysis of photosynthesis [J]. Plant Physiol. Commun., 1997, 33(4):241-244. | |
| 25 | GARDEA A A, NORIEGA J R, OROZCO J A, et al.. Advanced maturity of ‘Perlette’ table grapes by training systems which increase foliage exposure to sunlight [J]. Rev. Fitotec. Mex., 2008, 31(1): 27-33. |
| 26 | 潘明启,张付春,钟海霞,等.北方葡萄水平棚架“顺沟高厂”树形的高光效、省力化评价[J].果树学报,2017,34(9):1134-1143. |
| PAN M Q, ZHANG F C, ZHONG H X, et al.. Evaluation of photosynthetic efficiency and labor cost in cultivation of grape with an “oblique single cordon along ditch” trellis type in northern China [J]. J. Fruit Sci., 2017,34(9): 1134-1143. | |
| 27 | 张大鹏,姜红英.叶幕微气候与葡萄生理、产量和品质形成之间的基本关系研究[J].园艺学报,1995,22 (2):110-116. |
| ZHANG D P, JIANG H Y. Studies on the essential relationship between canopy microclimate,vine growth,grape yield and berry quality [J]. Acta Hortic. Sin., 1995, 22(2):110-116. | |
| 28 | 问亚琴,张艳芳,潘秋红.葡萄果实有机酸的研究进展[J].海南大学学报(自然科学版),2009,27(3):302-307. |
| WEN Y Q, ZHANG Y F, PAN Q H. The research progress of grapefruit organic acids [J]. J. Hainan Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2009, 27(3): 302-307. | |
| 29 | BERGQVIST J, DOKOOZLIAN N K, EBISUDA N. Sunlight exposure and temperature effects on berry growth and composition of Cabernet Sauvignon and Grenache in the Central San Joaquin Valley in California [J/OL]. Am. J. Enol. Vitic., 2001, 52(1):1 [2022-11-06]. . |
| 30 | CONDE C, SILVA P, FONTES N, et al.. Biochemical changes throughout grape berry development and fruit and wine quality [J]. Structure, 2007, l: l-22. |
| 31 | ALJIBURY F, BREWER R, CHRISTENSEN P. Grape response to cooling with sprinklers [J]. Am. J. Enol. Vitic., 1975, 26: 214-217. |
| 32 | 刘洪波,白云岗,张江辉,等.不同微喷弥雾调控方式下微气候因子对极端干旱区葡萄果实生长及糖度的影响[J].干旱地区农业研究,2020,38(4):159-167. |
| LIU H B, BAI Y G, ZHANG J H, et al.. Effects of microclimate factors on grape fruit growth and sugar content in extreme arid regions under different micro spray mist control [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2020, 38(4): 159-167. | |
| 33 | CARAVIA L, PAGAY V, COLLINS C, et al.. Application of sprinkler cooling within the bunch zone during ripening of Cabernet Sauvignon berries to reduce the impact of high temperature [J]. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res., 2017, 23: 48-57. |
| 34 | 蔡军社,白世践.吐鲁番地区‘火焰无核’葡萄顺架龙干式栽培示范及效益分析[J].中外葡萄与葡萄酒,2018(5):45-48. |
| CAI J S, BAI S J. Inclined trunk with same row direction cultivation demonstration and benefit analysis of ‘Flame Seedless’ grapevine in Turpan region [J]. Sino-Overseas Grapevine Wine, 2018(5): 45-48. | |
| 35 | CASTELLARIN S D, GASPERO G D, MARCONI R, et al.. Colour variation in red grapevines (Vitis Vinifera L .): organisationgenomic, expression of flavonoid 3'-hydroxylase, flavonoid 3',5'-hydroxylase genes and related metabolite profiling of red cyanidin-/blue delphinidin-based anthocyanins in berry skin [J/OL]. BMC Genomics, 2006, 7:12[2022-11-06]. . |
| 36 | AZUMAA, YAKUSHIJI H, KOSHITA Y, et al.. Flavonoid biosynthesis-related genes in grape skin are differentially regulated by temperature and light conditions [J].Planta,2012, 236(4):1067-1080. |
| 37 | MARTINEZ-LUSCHER J, CHEN C C L, BRILLANTE L, et al.. Partial solar radiation exclusion with color shade nets reduces the degradation of organic acids and flavonoids of grape berry (Vitis vinifera L.) [J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2017, 15: 10693-10702. |
| 38 | TORRES N, MARTINEZ-LUSCHER J, PORTE E, et al.. Impacts of leaf removal and shoot thinning on cumulative daily light intensity and thermal time and their cascading effects of grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) berry and wine chemistry in warm climates [J/OL]. Food Chem., 2020, 343:128447 [2022-11-06]. . |
| 39 | MORI K, SUGAYA S, GEMMA H. Decreased anthocyanin biosynthesis in grape berries grown under elevated night temperature condition [J]. Sci. Hortic., 2015, 105 (3):319-330. |
| 40 | MOVAHED N, PASTORE C, CELLINI A, et al.. The grapevine VviPrx31 peroxidase as a candidate gene involved in anthocyanin degradation in ripening berries under high temperature [J]. J. Plant Res., 2016, 129: 513-526. |
| 41 | SPAYD S E, TARARA J M, MEE D L, et al.. Separation of sunlight and temperature effects on the composition of Vitis vinifera cv. Merlot berries [J]. Am. J. Enol. Vitic.,2002, 53(3):171-182. |
| [1] | 卢登洋, 童盼盼, 闫敏, 鲍荆凯, 刘鸣哲, 夏怡蕾, 吴翠云. 库尔勒香梨大果芽变的鉴定与评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 52-64. |
| [2] | 张海军, 张娟, 贾毅男, 王江龙, 冯丽. 不同架式对‘南太湖特早’葡萄果实香气成分及品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 201-213. |
| [3] | 杜彩艳, 鲁海燕, 熊艳竹, 孙曦, 孙秀梅, 普继雄, 张乃明. 连续两年沼液与化肥配施对桃生长及土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 165-175. |
| [4] | 白世践, 户金鸽, 吴久赟, 张雯, 谢辉, 赵荣华, 陈光, 蔡军社. 不同砧木对吐鲁番地区‘克瑞森无核’葡萄生长特性及果实品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 76-87. |
| [5] | 朱士江, 李虎, 徐文, 冯雅婷. 三峡库区土壤含水量对柑橘园果实品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 201-207. |
| [6] | 贾毅男, 万仲武, 许昌, 张光弟, 王江龙, 张昆明, 侯小健, 包文毅, 王玉, 陈卫军. 露地栽培‘大青葡萄’架面不同位置果实品质指标分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(12): 44-57. |
| [7] | 郭娟娟, 王珊, 栾好安, 李寒, 郭素萍, 齐国辉, 张雪梅. 微生物菌剂对红树莓生长、果实品质及土壤磷钾的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(10): 198-209. |
| [8] | 刘迁杰,程云霞,贾凯,时振宇,张婧,魏少伟,吴慧*. 施氮量对复合沙培番茄氮代谢酶活性及品质和产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(4): 183-191. |
| [9] | 杨梦宇1,张琦1*,袁振杨1,陈俊1,闫利2. 温室生草对南疆桃叶片、果实质量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(3): 178-185. |
| [10] | 李泰, 卢士军, 黄家章, 陈磊, 范协裕. 苹果品质评价标准研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(11): 121-130. |
| [11] | 程大伟,陈锦永*,顾红,鲁会冉,张洋,郭西智,祁帅,李正阳. 红地球葡萄花穗整形方式研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(9): 44-50. |
| [12] | 师建华1§,齐连芬1§,王丹丹1,李燕1,张庆银1,葛喜珍2,田东良1*. 不同防控措施对温室番茄品质、产量及发病率的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(4): 88-95. |
| [13] | 马文瑶1,2,程大伟2,黄海娜2,陈锦永2*,杨英军1*. PDJ对‘巨玫瑰’葡萄果实着色及品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(3): 118-125. |
| [14] | 张任,张鹏程,邬欢欢,张学东*. 气象因子对南疆地区骏枣果实品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(7): 113-122. |
| [15] | 王成1,2,吴东峰2,何伟忠2,吴文良1*. 新疆骏枣营养品质特点及其表征指标初探[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(12): 91-98. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号