




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (3): 174-187.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0743
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
周旭东1,2( ), 韩天华3, 申云鑫1, 施竹凤1, 贺彪3, 杨明英1, 裴卫华1, 何永宏1, 杨佩文1(
), 韩天华3, 申云鑫1, 施竹凤1, 贺彪3, 杨明英1, 裴卫华1, 何永宏1, 杨佩文1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-09-04
接受日期:2022-10-31
出版日期:2024-03-15
发布日期:2024-03-07
通讯作者:
杨佩文
作者简介:周旭东E-mail:1018595481@qq.com;
基金资助:
Xudong ZHOU1,2( ), Tianhua HAN3, Yunxin SHEN1, Zhufeng SHI1, Biao HE3, Mingying YANG1, Weihua PEI1, Yonghong HE1, Peiwen YANG1(
), Tianhua HAN3, Yunxin SHEN1, Zhufeng SHI1, Biao HE3, Mingying YANG1, Weihua PEI1, Yonghong HE1, Peiwen YANG1( )
)
Received:2022-09-04
Accepted:2022-10-31
Online:2024-03-15
Published:2024-03-07
Contact:
Peiwen YANG
摘要:
为探究烤烟与不同作物轮作对长期连作植烟土壤质量调控的效果,以连作10年以上的植烟田块为对照(CK),设置大麦-烤烟(YCDM)、大蒜-烤烟(YCDS)、油菜-烤烟(YCYC)和蚕豆-烤烟(YCCD)共4种不同作物与烤烟轮作,分析不同轮作处理下土壤的理化性质、酶活性及微生物群落结构。基于相关性分析和冗余分析,解析土壤理化性质和酶活性与微生物群落结构间的关系。结果表明,轮作处理的土壤容重较CK降低26.58%~30.29%,总孔隙度增加21.13%~48.26%;其中烤烟-蚕豆(YCCD)轮作模式下土壤的pH、水解氮(available nitrogen,AN)、有效磷(available phosphorus,AP)和速效钾( available potassium,AK)含量较CK显著提高11.84%、30.57%、6.42%和41.5 1%。轮作处理的土壤过氧化氢酶(catalase,CAT)、蔗糖酶(invertase,INV)、脲酶(urease,URE)和酸性磷酸酶(acid phosphatase,ACP)的活性较CK分别提高16.81%~42.35%、38.09%~51.48%、7.69%~64.29%和5.82%~76.33%,蚕豆-烤烟(YCCD)轮作模式的提升效果最为显著。高通量测序结果表明,轮作处理下细菌的OTUs数量显著高于CK。α多样性显示,不同轮作处理间的细菌群落丰富度和多样性差异显著;真菌群落的丰富度差异显著,而多样性差异不显著。β多样性分析显示,不同轮作处理之间土壤真菌群落差异较小,细菌群落差异较大。其中,蚕豆-烤烟(YCCD)轮作处理的细菌、真菌群落与CK差异较大。在门水平,烤烟-蚕豆(YCCD)轮作使酸杆菌门(Acidobacteria)和放线菌门(Actinobacteria)的相对丰度增加,子囊菌门(Ascomycota)的相对丰度减少。相关性分析和冗余分析表明,URE、AN、AK和pH是影响土壤微生物群落结构的关键因子。综上所述,烤烟与其他作物合理轮作可提高土壤速效养分含量和土壤酶活性,调节土壤微生物群落结构,消减烤烟连作障碍,最终达到烤烟稳产、增产的目的。
中图分类号:
周旭东, 韩天华, 申云鑫, 施竹凤, 贺彪, 杨明英, 裴卫华, 何永宏, 杨佩文. 4种轮作模式下长期连作烟田土壤微生态的响应特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 174-187.
Xudong ZHOU, Tianhua HAN, Yunxin SHEN, Zhufeng SHI, Biao HE, Mingying YANG, Weihua PEI, Yonghong HE, Peiwen YANG. Response Characteristics of Soil Microecology in Long-term Continuous Cropping Tobacco Field Under 4 Rotation Patterns[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(3): 174-187.
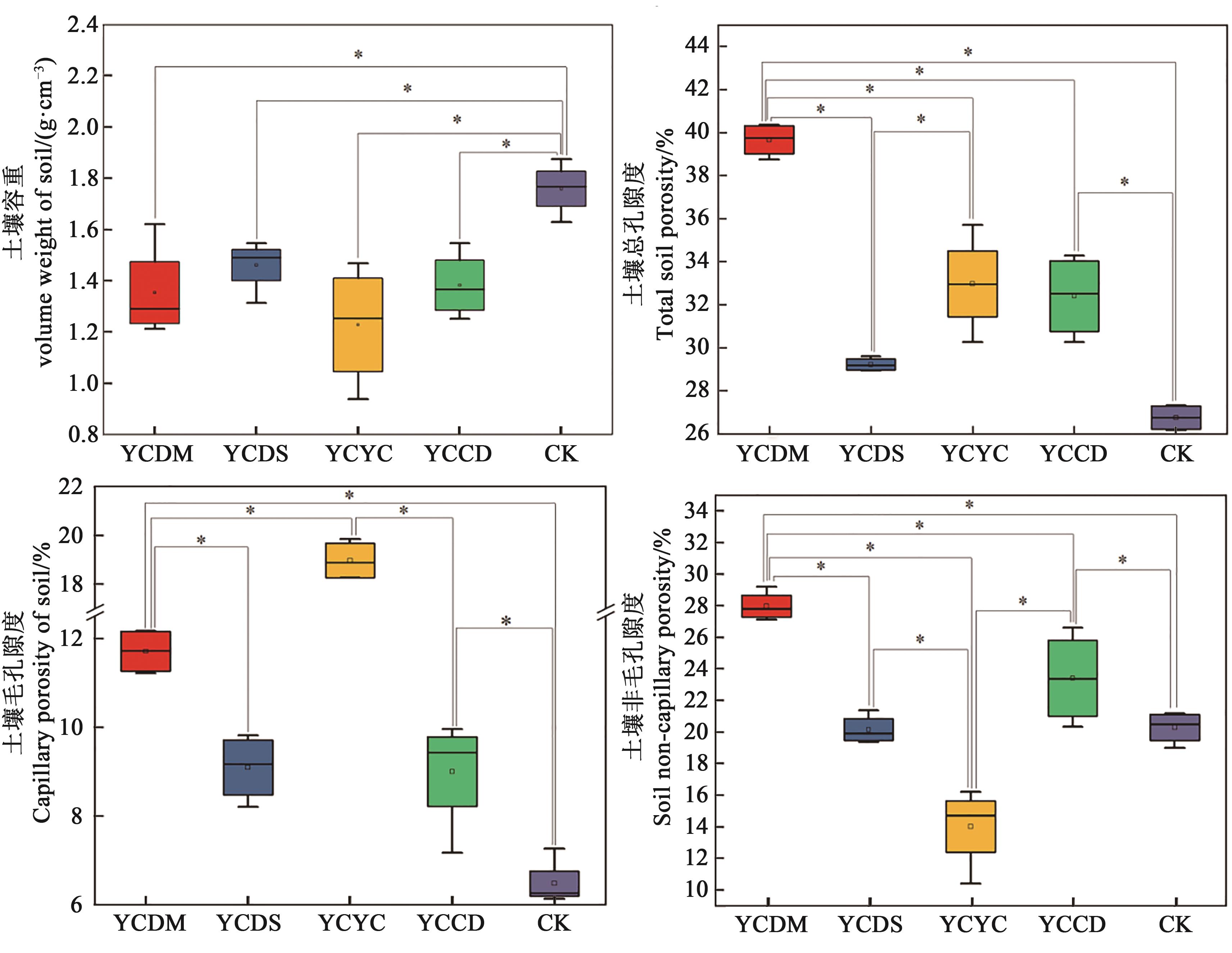
图1 不同轮作模式下土壤的物理性状注:*表示不同轮作模式间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 Soil physical properties of different rotation patternsNote: * indicates significant difference between different rotation patterns at P<0.05 level.
土壤化学指标 Soil chemical indicater | YCDM | YCDS | YCYC | YCCD | CK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 5.29±0.74 bc | 6.02±0.13 ab | 5.69±0.59 ab | 6.25±0.26 a | 4.73±0.36 c |
电导率 Electric conductivity/(μS·cm-1) | 107.72±13.58 b | 156.93±11.09 a | 75.39±12.65 c | 120.59±8.31 b | 118.56±16.01 b |
有机质 Organic matter/(g·kg-1) | 49.91±5.86 a | 35.44±5.64 b | 33.11±7.67 b | 40.50±21.41 b | 38.34±1.41 b |
全氮 Total nitrogen/(g·kg-1) | 1.89±0.14 a | 1.87±0.26 b | 1.87±0.43 b | 1.87±0.14 b | 1.84±0.11 c |
碱解氮 Available nitrogen/(mg·kg-1) | 194.03±6.29 c | 185.26±7.83 c | 193.95±4.55 c | 231.30±6.49 a | 205.71±8.26 b |
全磷 Total phosphorus/(g·kg-1) | 1.55±0.24 a | 1.22±0.16 ab | 1.11±0.18 b | 1.31±0.30 ab | 1.22±0.15 ab |
有效磷 Available phosphorus/(mg·kg-1) | 115.73±7.25 a | 84.02±4.79 d | 105.75±4.34 b | 121.50±1.74 a | 91.49±5.64 c |
全钾 Total potassium/(g·kg-1) | 15.94±2.33 a | 15.68±1.08 a | 15.32±0.71 a | 16.29±1.19 a | 15.66±1.03 a |
速效钾 Available potassium/(mg·kg-1) | 313.04±5.21 a | 316.59±10.65 a | 128.11±7.14 d | 244.76±5.26 b | 158.12±10.28 c |
表1 轮作模式下土壤的化学性质
Tab 1 Soil chemical properties under different rotation patterns
土壤化学指标 Soil chemical indicater | YCDM | YCDS | YCYC | YCCD | CK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 5.29±0.74 bc | 6.02±0.13 ab | 5.69±0.59 ab | 6.25±0.26 a | 4.73±0.36 c |
电导率 Electric conductivity/(μS·cm-1) | 107.72±13.58 b | 156.93±11.09 a | 75.39±12.65 c | 120.59±8.31 b | 118.56±16.01 b |
有机质 Organic matter/(g·kg-1) | 49.91±5.86 a | 35.44±5.64 b | 33.11±7.67 b | 40.50±21.41 b | 38.34±1.41 b |
全氮 Total nitrogen/(g·kg-1) | 1.89±0.14 a | 1.87±0.26 b | 1.87±0.43 b | 1.87±0.14 b | 1.84±0.11 c |
碱解氮 Available nitrogen/(mg·kg-1) | 194.03±6.29 c | 185.26±7.83 c | 193.95±4.55 c | 231.30±6.49 a | 205.71±8.26 b |
全磷 Total phosphorus/(g·kg-1) | 1.55±0.24 a | 1.22±0.16 ab | 1.11±0.18 b | 1.31±0.30 ab | 1.22±0.15 ab |
有效磷 Available phosphorus/(mg·kg-1) | 115.73±7.25 a | 84.02±4.79 d | 105.75±4.34 b | 121.50±1.74 a | 91.49±5.64 c |
全钾 Total potassium/(g·kg-1) | 15.94±2.33 a | 15.68±1.08 a | 15.32±0.71 a | 16.29±1.19 a | 15.66±1.03 a |
速效钾 Available potassium/(mg·kg-1) | 313.04±5.21 a | 316.59±10.65 a | 128.11±7.14 d | 244.76±5.26 b | 158.12±10.28 c |
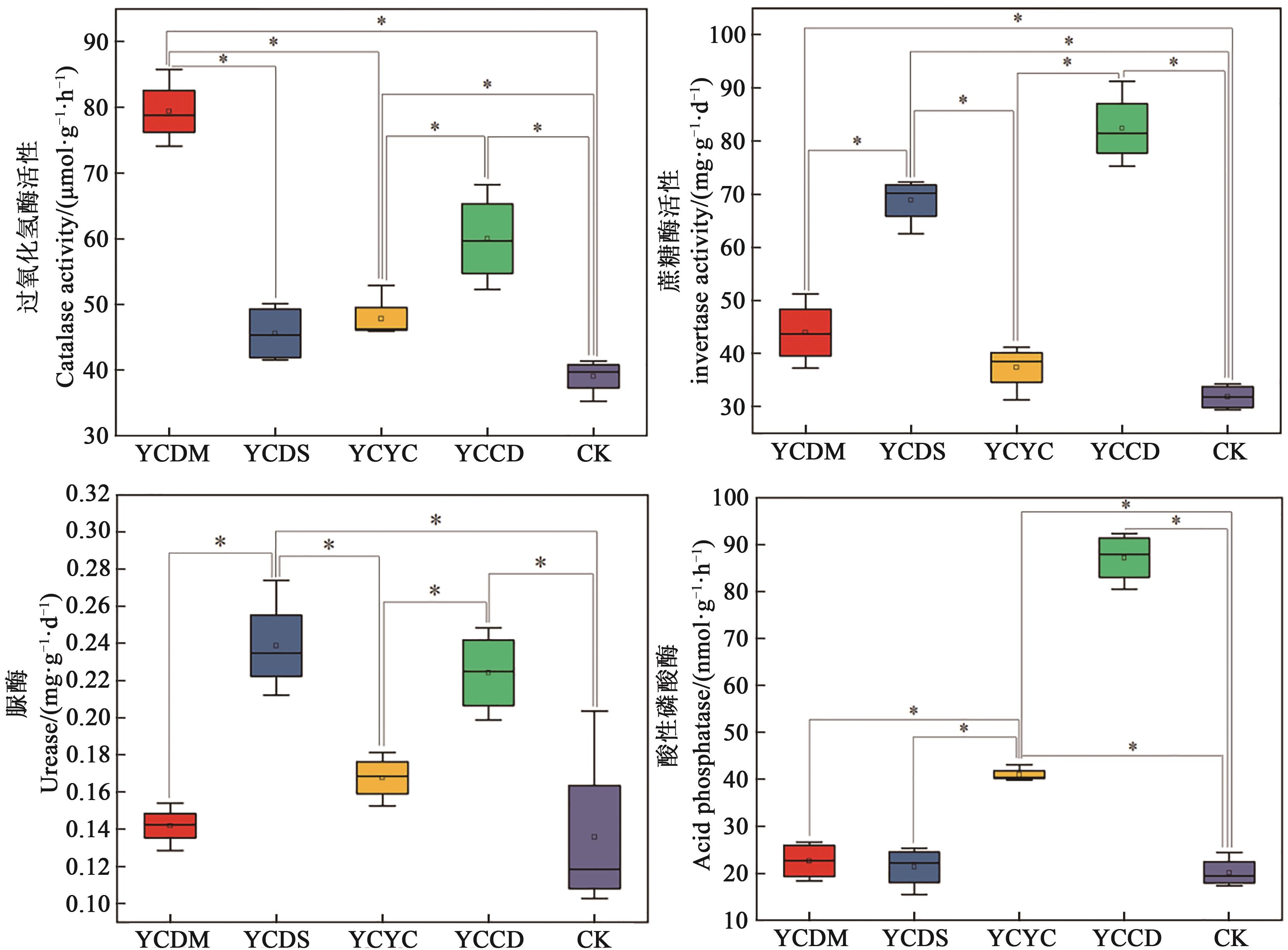
图2 不同轮作模式下土壤酶活性注:*表示不同轮作模式间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 Soil enzyme activities of different rotation patternsNote: * indicates significant difference between different rotation patterns at P<0.05 level.
类别 Category | 处理Treatment | 物种数目 Number of species | 丰富度指数Richness index | 多样性指数Diversity index | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Ace指数 Ace index | Chao指数 Chao index | Shannon指数Shannon index | Simpson指数Simpson index | |||
细菌 Bacteria | YCDM | 2 617±29.61 bc | 2 630.09±25.21 b | 2 637.78±23.85 bc | 5.36±0.08 ab | 0.011 2±0.000 0 a |
| YCDS | 2 689.33±91.50 b | 2 703.30±13.66 a | 2 692.47±94.15 b | 5.36±0.16 ab | 0.011 0±0.020 1 a | |
| YCYC | 2 576±33.72 c | 2 587.98±18.32 bc | 2 581.78±41.67 bc | 5.29±0.06 ab | 0.015 0±0.010 1 a | |
| YCCD | 2 760.33±44.28 a | 2 757.22±49.40 a | 2 791.57±76.03 a | 5.47±0.12 a | 0.008 9±0.000.0 b | |
| CK | 2 545.67±64.05 c | 2 547.97±59.53 c | 2 555.88±60.62 c | 5.26±0.09 b | 0.014 7±0.011 1 a | |
真菌 Fungi | YCDM | 357.33±15.57 c | 365.73±14.86 c | 366.13±10.87 c | 3.14±1.03 a | 0.115 8±0.071 2 a |
| YCDS | 379.00±26.15 c | 389.52±26.52 c | 391.63±26.11 bc | 3.32±0.19 a | 0.079 9±0.051 1 a | |
| YCYC | 439.00±23.07 a | 450.15±20.14 a | 452.71±20.36 a | 4.06±0.30 a | 0.038 4±0.010 3 a | |
| YCCD | 389.67±18.01 bc | 398.71±17.10 bc | 404.67±16.30 ab | 3.82±0.54 a | 0.059 0±0.041 5 a | |
| CK | 421.33±14.29 ab | 428.48±16.15 ab | 429.39±16.18 ab | 3.92±0.31 a | 0.039 1±0.011 2 a | |
表2 不同轮作模式土壤微生物群落α多样性分析
Tab 2 Analysis of soil microbial community α diversity under different rotation patterns
类别 Category | 处理Treatment | 物种数目 Number of species | 丰富度指数Richness index | 多样性指数Diversity index | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Ace指数 Ace index | Chao指数 Chao index | Shannon指数Shannon index | Simpson指数Simpson index | |||
细菌 Bacteria | YCDM | 2 617±29.61 bc | 2 630.09±25.21 b | 2 637.78±23.85 bc | 5.36±0.08 ab | 0.011 2±0.000 0 a |
| YCDS | 2 689.33±91.50 b | 2 703.30±13.66 a | 2 692.47±94.15 b | 5.36±0.16 ab | 0.011 0±0.020 1 a | |
| YCYC | 2 576±33.72 c | 2 587.98±18.32 bc | 2 581.78±41.67 bc | 5.29±0.06 ab | 0.015 0±0.010 1 a | |
| YCCD | 2 760.33±44.28 a | 2 757.22±49.40 a | 2 791.57±76.03 a | 5.47±0.12 a | 0.008 9±0.000.0 b | |
| CK | 2 545.67±64.05 c | 2 547.97±59.53 c | 2 555.88±60.62 c | 5.26±0.09 b | 0.014 7±0.011 1 a | |
真菌 Fungi | YCDM | 357.33±15.57 c | 365.73±14.86 c | 366.13±10.87 c | 3.14±1.03 a | 0.115 8±0.071 2 a |
| YCDS | 379.00±26.15 c | 389.52±26.52 c | 391.63±26.11 bc | 3.32±0.19 a | 0.079 9±0.051 1 a | |
| YCYC | 439.00±23.07 a | 450.15±20.14 a | 452.71±20.36 a | 4.06±0.30 a | 0.038 4±0.010 3 a | |
| YCCD | 389.67±18.01 bc | 398.71±17.10 bc | 404.67±16.30 ab | 3.82±0.54 a | 0.059 0±0.041 5 a | |
| CK | 421.33±14.29 ab | 428.48±16.15 ab | 429.39±16.18 ab | 3.92±0.31 a | 0.039 1±0.011 2 a | |

图7 理化性质与土壤微生物优势菌门间的相关性分析A:细菌;B:真菌。EC—电导率;SOM—有机质;TN—全氮;AN—碱解氮;TP—全磷;AP—有效磷;TK—全钾;AK—速效钾;CAT—过氧化氢酶;INV—蔗糖酶;URE—脲酶;ACP—酸性磷酸酶。*表示在P<0.05水平相关显著
Fig. 7 Correlation analysis between physical and chemical properties and dominant phyla of soil microorganismsA:Bacteria; B:Fungi. EC—Electrical conductivity; SOM—Organic matter; TN—Total nitrogen; AN—Available nitrogen; TP—Total phosphorus; AP—Available phosphorus; TK—Total potassium; AK—Available potassium; CAT—Catalase; INV—Invertin; URE—Urease; ACP—Acid phosphatase; * indicates significant correlation at P<0.05 level
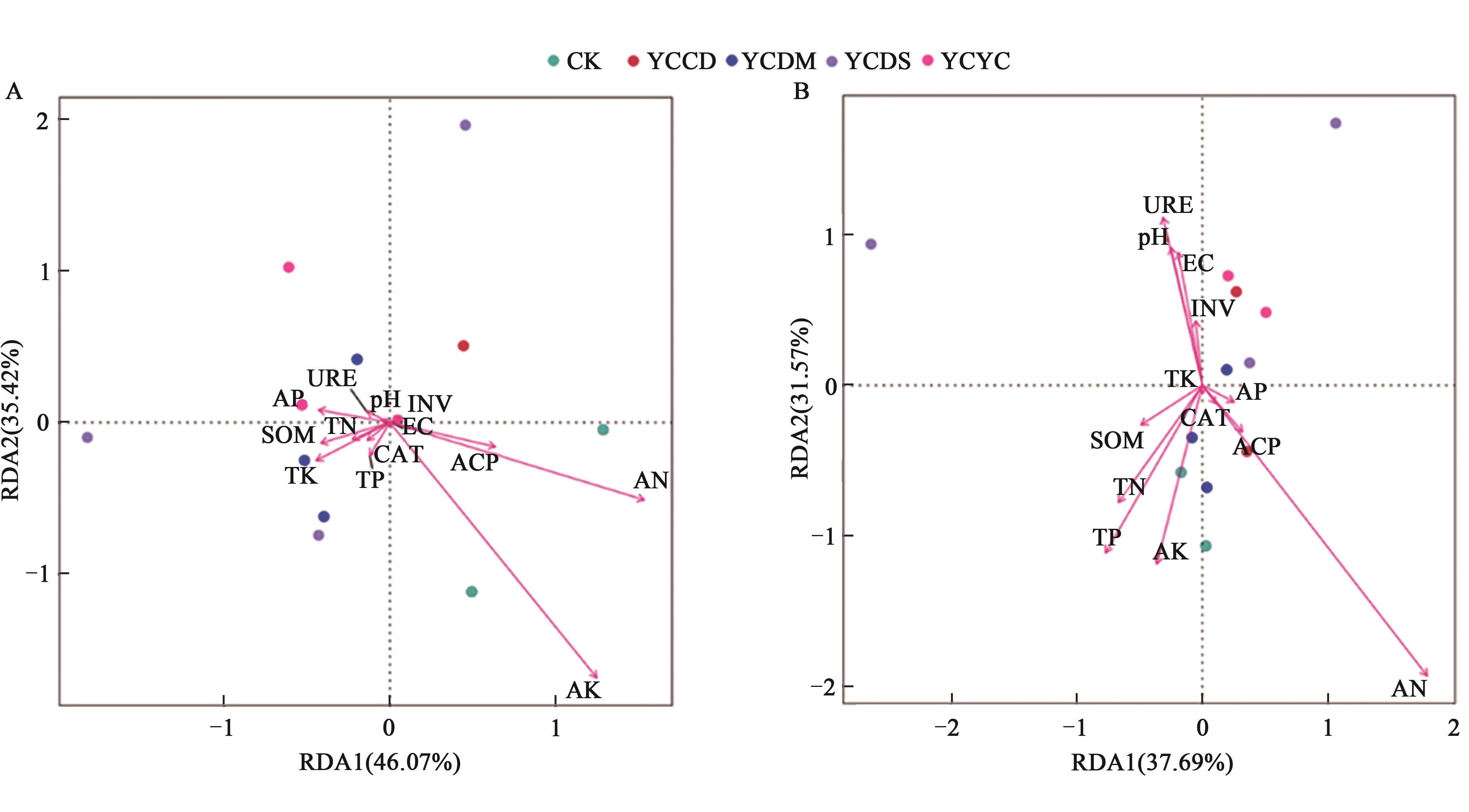
图8 土壤微生物优势菌门与理化性质的冗余分析A:细菌;B:真菌。EC—电导率;SOM—土壤有机质;TN—全氮;AN—碱解氮;TP—全磷;AP—有效磷;TK—全钾;AK—速效钾;CAT—过氧化氢酶;INV—蔗糖酶;URE—脲酶;ACP—酸性磷酸酶
Fig. 8 Redundancy analysis of dominant phyla and physicochemical properties of soil microorganismsA: Bacteria; B: Fungi. EC—Electrical conductivity; SOM—Soil organic matter; TN—Total nitrogen; AN—Available nitrogen; TP—Total phosphorus; AP—Available phosphorus; TK—Total potassium; AK—Available potassium; CAT—Catalase; INV—Invertin; URE—Urease; ACP—Acid phosphatase
| 1 | 芶久兰,顾小凤,张萌,等.不同烤烟种植模式对贵州土壤养分、酶活性及细菌群落结构的影响[J].核农学报,2022,36(7):475-484. |
| GOU J L, GU X F, ZHANG M, et al.. Effects of different flue-cured tobacco planting patterns on nutrients, enzyme activities and bacterial community structure in soil of Guizhou province [J]. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci., 2022, 36(7):475-484. | |
| 2 | 鲁韦坤,逄涛,余凌翔,等.市场经济对云南规划烟区耕地资源的影响分析[J].中国农学通报,2021,37(5):137-142. |
| LU W K, PANG T, YU L X, et al.. The influence of market economy on cultivated land resources in planned tobacco area of Yunnan [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2021, 37(5):137-142. | |
| 3 | 陈华,赵文军,王正旭,等.不同轮作模式下氮素调控对烤烟产质量及氮肥利用的影响[J].河南农业科学,2021,50(9):87-95. |
| CHEN H, ZHAO W J, WANG Z X, et al.. Effects of nitrogen management on yield,quality and nitrogen utilization of flue-cured tobacco under different rotation patterns [J]. J. Henan Agric. Sci., 2021, 50(9):87-95. | |
| 4 | CHEN S, QI G, LUO T, et al.. Continuous‐cropping tobacco caused variance of chemical properties and structure of bacterial network in soils [J]. Land Degrad. Dev., 2018, 29(11):4106-4120. |
| 5 | 陈浩,魏立本,王亚麒,等.烤烟不同种植施肥模式对土壤养分、酶活性及细菌多样性的影响[J].南方农业学报,2019,50(5):982-989. |
| CHEN H, WEI L B, WANG Y Q, et al.. Effects of different planting and fertilizing modes on soil nutrient,enzyme activity and bacterial diversity of tobacco [J]. J. Southern Agric., 2019, 50(5):982-989. | |
| 6 | 朱维伟.不同轮作模式对黄瓜幼苗生长及土壤环境的影响[D].哈尔滨:东北农业大学,2020. |
| ZHU W W. Effects of Different rotation sysetems on growth and soil environment of cucumber seedling [D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2020. | |
| 7 | 赵庆雷,信彩云,王瑜,等.不同轮作模式对花生病虫害及产量的影响[J].植物保护学报,2018,45(6):1321-1327. |
| ZHAO Q L, XIN C Y, WANG Y, et al.. Effects of different rotation patterns on peanut diseases, pests and yield [J]. J. Plant Prot., 2018, 45(6):1321-1327. | |
| 8 | 徐新雯,林正全,拓阳阳,等.烟蒜轮作对烟株根际土壤细菌群落结构的影响[J].西南农业学报,2020,33(9):1917-1924, 2137. |
| XU X W, LIN Z Q, TUO Y Y, et al.. Effects of tobacco garlic crop rotation on bacterial community structure of tobacco rhizosphere soil [J]. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci., 2020, 33(9):1917-1924, 2137. | |
| 9 | 阳显斌,李廷轩,张锡洲,等.烟蒜轮作与套作对土壤微生物类群数量的影响[J].土壤,2016,48(4):698-704. |
| YANG X B, LI T X, ZHANG X Z, et al.. Effects of tobacco garlic crop rotation and tobacco garlic crop intercropping on soil microbial groups in tobacco fields [J]. Soils, 2016, 48(4):698-704. | |
| 10 | 苏燕,李婕,曹雪颖,等.水旱轮作模式下马铃薯根际土壤细菌群落多样性分析[J].南方农业学报,2020,51(10):2374-2382. |
| SU Y, LI J, CAO X Y, et al.. Diversity analysis of bacterial community in potato rhizosphere soil under the mode of paddy-upland rotation [J]. J. Southern Agric., 2020, 51(10):2374-2382. | |
| 11 | 姚小东,李孝刚,丁昌峰,等.连作和轮作模式下花生土壤微生物群落不同微域分布特征[J].土壤学报,2019,56(4):975-985. |
| YAO X D, LI X G, DING C F, et al.. Microzone distribution characteristics of soil microbial community with peanut cropping system, monocropping or rotation [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2019, 56(4):975-985. | |
| 12 | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2005:1-495. |
| 13 | 李润根,曾慧兰,李兴杰,等.连作龙牙百合与铁炮百合根际土壤真菌群落结构的差异分析[J].生态科学,2022,41(4):189-195. |
| LI R G, ZENG H L, LI X J, et al.. Differences of rhizosphere soil fungi between Lilium brownii var and Lilium longifllorum in continuous cropping [J]. Acta Ecol. Sci., 2022, 41(4):189-195. | |
| 14 | 李林蓉,冯建路,刘苗苗,等.作物种植模式对土壤微生物和农田有害生物的影响[J].中国农学通报,2021,37(29):99-106. |
| LI L R, FENG J L, LIU M M, et al.. Effect of crop planting Patterns on soil microorganisms and crop pests in farm [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2021, 37(29):99-106. | |
| 15 | 于春雷,高嵩,孙文松,等.连作对辽细辛土壤理化性质和根际微生物群落特征的影响[J].江苏农业科学,2022,50(14):250-258. |
| 16 | 刘会芳,韩宏伟,王强,等.不同蔬菜与番茄轮作对设施土壤微生物多样性、酶活性及土壤理化性质的影响[J].微生物学报,2021,61(1):167-182. |
| LIU H F, HAN H W, WANG Q, et al.. Effect of vegetables-tomato rotation on soil microbial diversity, enzyme activity and physicochemical properties of vegetables in greenhouse [J]. Acta Microbiol. Sin., 2021, 61(1):167-182. | |
| 17 | SHI G, FANG J, WEI S, et al.. Characteristics of rhizosphere fungal community in spring wheat under different rotation fallow modes [J/OL]. E3S Web Conf, 2021, 292:03093. [2023-07-12]. . |
| 18 | SU Y, ZI H, WEI X, et al.. Application of manure rather than plant-origin organic fertilizers alters the fungal community in continuous cropping tobacco soil [J/OL]. Front Microbiol., 2022:1158 [2022-08-23]. . |
| 19 | 谢涛.不同栽培模式下稻麦轮作土壤速效养分供应特征[D].扬州:扬州大学,2022. |
| XIE T. Characteristics of soil available nutrient supply in rice-wheat rotation under different cultivation modes [D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2022. | |
| 20 | 张成君,师尚礼,康文娟,等.不同轮作模式土壤酶活性特征及与化学性质的关系[J].中国草地学报,2020,42(5):92-102. |
| ZHANG C J, SHI S L, KANG W J, et al.. Characteristics of soil enzyme activities and its relationship with chemical properties under different rotation patterns [J]. Chin. J. Grass., 2020, 42(5):92-102. | |
| 21 | 魏全全,芶久兰,赵欢,等.黄壤区烤烟轮作与连作根系形态、产量及养分吸收的变化[J].西南农业学报,2018,31(11):2294-2299. |
| WEI Q Q, GOU J L, ZHAO H, et al.. Changes in root morphology, yield and nutrient uptake of flue-cured tobacco under rotation and continuous cropping in yellow soil [J]. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci., 2018, 31(11):2294-2299. | |
| 22 | 樊俊,谭军,王瑞,等.秸秆还田和腐熟有机肥对植烟土壤养分、酶活性及微生物多样性的影响[J].烟草科技,2019,52(2):12-18, 61. |
| FAN J, TAN J, WANG R, et al.. Effects of straw Returning and decomposed organic manure on soil nutrients, enzyme activities and microbial diversity for tobacco-planting [J]. Tob. Sci. Tech., 2019, 52(2):12-18, 61. | |
| 23 | 罗影,王立光,陈军,等.不同种植模式对甘肃中部高寒区胡麻田土壤酶活性及土壤养分的影响[J].核农学报,2017,31(6):1185-1191. |
| LUO Y, WANG L G, CHEN J, et al.. Effects of different flex cropping modes on soil enzyme activities and soil nutrients in the cold area of middle part of Gansu [J]. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci., 2017, 31(6):1185-1191. | |
| 24 | RAMONEDA J, LE ROUX J, STADELMANN S, et al.. Soil microbial community coalescence and fertilization interact to drive the functioning of the legume-rhizobium symbiosis [J]. J. Appl. Ecol., 2021, 58(11):2590-2602. |
| 25 | 索炎炎,张翔,司贤宗,等.AM真菌和根瘤菌对连作花生养分吸收及土壤微生物特性的影响[J/OL].中国土壤与肥料,2023(2):106-112. |
| SUO Y Y, ZHANG X, SI X Z, et al.. Effects of Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and rhizobia on nutrient uptake and soil microbial characteristics of continuous cropping peanut [J/OL]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2023(2):106-112. | |
| 26 | 饶德安,刘潘洋,邹路易,等.长期连作及强还原土壤灭菌处理对烤烟根际土壤真菌群落的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料,2022(4):47-56. |
| RAO D A, LIU P Y, ZOU L Y, et al.. Effects of long-term continuous cropping and reductive soil disinfestation on fungal community in flue-cured tobacco rhizosphere [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2022(4):47-56. | |
| 27 | 段玉琪,晋艳,陈泽斌,等.烤烟轮作与连作土壤细菌群落多样性比较[J].中国烟草学报,2012,18(6):53-59. |
| DUAN Y Q, JIN Y, CHEN Z B, et al. Comparison of bacteria diversity between tobacco plantation soils of rotational cropping and continuous cropping [J]. Acta Tab. Sin., 2012, 18(6):53-59. | |
| 28 | 苏贝贝,张英,道日娜.4种豆科植物根际土壤真菌群落特征与土壤理化因子间相关性分析[J].草地学报,2021,29(12):2670-2677. |
| SU B B, ZHAN Y, DAO R N. Correlation analysis between fungal community characteristics and soil physicochemical factors in the rhizosphere of four legumes [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2021, 29(12):2670-2677. | |
| 29 | 温美娟,杨思存,王成宝,等.深松和秸秆还田对灌耕灰钙土土壤细菌多样性和群落结构的影响[J].农业资源与环境学报,2023,40(2):423-433. |
| WEN M J, YANG S C, WANG C B, et al.. Effects of subsoiling and the return of straw on soil bacterial diversity and community structure in an irrigated sierozem farmland [J]. J. Agric. Resour. Environ., 2023, 40(2):423-433. | |
| 30 | 叶嘉,张浩,郭海燕,等.蚓粪对大蒜中蒜氨酸和大蒜素含量及大蒜精油抗菌活性的影响[J].中国瓜菜,2021,34(10):98-103. |
| YE J, ZHANG H, GUO H Y, et al.. Effects of vermicompost on alliin and allicin contents and antibacterial activity of garlic oil in garlic [J]. China Cucurbits Veget., 2021, 34(10):98-103. |
| [1] | 张桐毓, 勾颖, 李琪, 杨莉. 人参锈腐病对人参品质和土壤相关因子的影响研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 124-133. |
| [2] | 郭靖捷, 任晓萌, 蒙仲举, 王涛, 祁帅, 宋佳佳, 宝孟克那顺, 韩胜利. 半干旱风沙草原区盐湖植物防护体系土壤理化性状特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 182-192. |
| [3] | 刘威, 赵园园, 陈小龙, 史宏志. 土壤含水率对豫中植烟土壤微生物群落多样性及氮循环功能基因丰度的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 214-225. |
| [4] | 李慧君, 张伟健, 吴伟健, 李高洋, 陈艺杰, 黄枫城, 黄永相, 蔺中, 甄珍. 种植海水稻对滨海盐土化学性质和微生物群落影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 147-156. |
| [5] | 高静娟, 朱晨宇, 柯玉琴, 郑朝元, 李春英, 李文卿. 烟稻轮作条件下有机肥施用时期对烤烟碳氮代谢的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 157-165. |
| [6] | 肖锐, 谭璐, 吴亮, 张皓, 郭佳源, 杨海君. 镉胁迫下地肤根际与非根际土壤微生物群落结构及多样性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 203-215. |
| [7] | 尹兴盛, 包玲凤, 濮永瑜, 孙加利, 张庆, 李海平, 杨明英, 林跃平, 王怀鑫, 何永宏, 杨佩文. 减氮配施生物有机肥对植烟土壤特性及烟草青枯病的防效研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 122-131. |
| [8] | 刘宏元, 周志花, 赵光昕, 沈钦瑞. 黄淮海平原农田土壤温室气体排放对长期施加生物炭的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 178-186. |
| [9] | 庞喆, 王启龙, 李娟. 不同土壤改良剂对陕北低洼盐碱地土壤理化性质及水稻产量和经济效益的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 174-180. |
| [10] | 可艳军, 张雨萌, 郭艳杰, 张丽娟, 张子涛, 吉艳芝. 生物有机肥配合深松对农田土壤肥力和作物产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 157-166. |
| [11] | 孟璐, 范敬文, 赛欣娱, 曾路生, 宋祥云, 崔德杰. 石灰对苹果园土壤改良和植株生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 197-204. |
| [12] | 郑云珠, 孙树臣. 秸秆生物炭和秸秆对麦玉轮作系统土壤养分及作物产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 152-162. |
| [13] | 郭巨先, 欧阳碧珊, 李桂花, 符梅, 罗文龙, 骆善伟, 陆美莲. 微生物有机肥对连作菜薹生长及土壤性质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 182-191. |
| [14] | 蒯雁, 苏欣悦, 王晋峰, 范志勇, 李建华, 孙楠, 张久权, 徐明岗. 大理典型烟区土壤有机质与全氮时空演变特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(12): 177-185. |
| [15] | 李峰, 殷丛培, 殷冉, 王凡, 韩永亮, 杨志敏, 刘建成. 燕麦根际土壤细菌多样性对盐胁迫的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(1): 153-165. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号