




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (3): 201-213.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0741
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
张二豪( ), 刘盼盼, 何萍, 简阅, 徐雨婷, 陈诚欣, 禄亚洲, 兰小中(
), 刘盼盼, 何萍, 简阅, 徐雨婷, 陈诚欣, 禄亚洲, 兰小中( ), 索朗桑姆
), 索朗桑姆
收稿日期:2022-09-02
接受日期:2022-10-24
出版日期:2024-03-15
发布日期:2024-03-07
通讯作者:
兰小中,索朗桑姆
作者简介:张二豪E-mail:zhangerhao@xza.edu.cn
基金资助:
Erhao ZHANG( ), Panpan LIU, Ping HE, Yue JIAN, Yuting XU, Chengxin CHEN, Yazhou LU, Xiaozhong LAN(
), Panpan LIU, Ping HE, Yue JIAN, Yuting XU, Chengxin CHEN, Yazhou LU, Xiaozhong LAN( ), Sangmu SUOLANG
), Sangmu SUOLANG
Received:2022-09-02
Accepted:2022-10-24
Online:2024-03-15
Published:2024-03-07
Contact:
Xiaozhong LAN,Sangmu SUOLANG
摘要:
为研究甘青青兰根际土壤理化性质与根际土壤细菌和真菌群落结构组成特征,以西藏自治区工布江达县(GB)、卡诺区(KR)和洛隆县(LL)的甘青青兰根际土壤微生物为研究对象,采用Illumina MiSeq高通量测序技术对根际土壤细菌和真菌群落结构组成进行分析,同时测定根际土壤的理化性质,并与根际土壤核心微生物菌群进行相关性分析。结果表明,不同地区甘青青兰根际土壤理化性质差异显著。甘青青兰根际土壤共获得3 900个细菌OTUs和1 990个真菌OTUs,不同地区间土壤微生物多样性存在明显差异。在门水平,GB、KR和LL样品的优势细菌门均为放线菌门(Actinobacteria),GB样品的优势真菌门是担子菌门(Basidiomycota),KR和LL样品的优势真菌门是子囊菌门(Ascomycota);在属水平,不同地区甘青青兰根际土壤优势微生物菌群存在明显差异。主成分分析显示,不同地区甘青青兰根际土壤细菌和真菌群落结构组成差异较大。核心微生物菌群分析表明,甘青青兰根际土壤核心细菌菌群有257个属;核心真菌菌群有102个属。相关性分析表明,核心微生物菌群的改变与根际土壤理化因子间存在不同程度的相关性,且土壤全钾、全磷、全氮、速效钾和速效氮含量是影响甘青青兰根际土壤微生物群落结构组成的重要因子。综上所述,不同地区甘青青兰根际土壤微生物群落结构组成存在显著差异,且根际土壤微生物群落结构的变化与土壤理化因子密切相关,为甘青青兰人工种植及筛选有益微生物菌群提供了理论依据。
中图分类号:
张二豪, 刘盼盼, 何萍, 简阅, 徐雨婷, 陈诚欣, 禄亚洲, 兰小中, 索朗桑姆. 甘青青兰根际土壤理化性质及微生物群落结构特征分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 201-213.
Erhao ZHANG, Panpan LIU, Ping HE, Yue JIAN, Yuting XU, Chengxin CHEN, Yazhou LU, Xiaozhong LAN, Sangmu SUOLANG. Physiochemical Properties and Microbial Community Structure in Rhizosphere Soil of Dracocephalum tanguticum[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(3): 201-213.
| 样品采集点 Sampling site | 经度 Longitude | 纬度 Latitude | 海拔Altitude/m |
|---|---|---|---|
| 工布江达县GB | 92°47′38″ E | 29°55′46″ N | 3 854 |
| 卡诺区KR | 97°35′48″ E | 31°17′29″ N | 4 107 |
| 洛隆县LL | 95°53′36″ E | 30°45′18″ N | 3 922 |
表1 样品采集点信息
Table 1 Information of sampling site
| 样品采集点 Sampling site | 经度 Longitude | 纬度 Latitude | 海拔Altitude/m |
|---|---|---|---|
| 工布江达县GB | 92°47′38″ E | 29°55′46″ N | 3 854 |
| 卡诺区KR | 97°35′48″ E | 31°17′29″ N | 4 107 |
| 洛隆县LL | 95°53′36″ E | 30°45′18″ N | 3 922 |
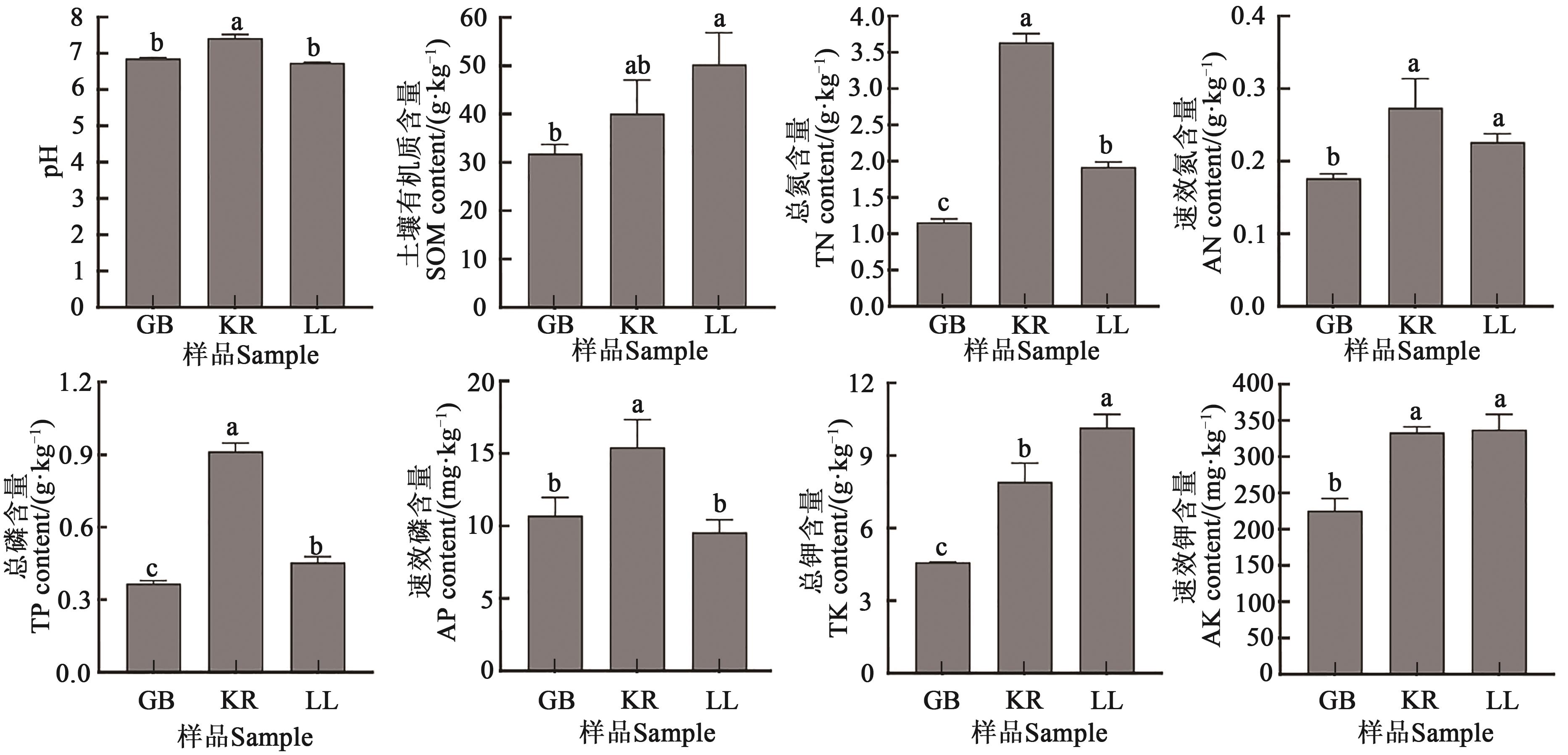
图1 根际土壤的理化性质注:不同小写字母表示不同样品间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 Physical and chemical properties of rhizosphere soilNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different samples at P<0.05 level.
样品 Sample | 有效序列数Effective sequence number | 平均长度Average length/bp | 测序覆盖度Sequencing coverage/% | OTUs数量Number of OTUs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
细菌 Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | 细菌 Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | 细菌 Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | 细菌 Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | |
| GB | 15 316 | 42 048 | 376 | 284 | 97.78 | 99.83 | 1 149 | 489 |
| KR | 16 714 | 51 312 | 376 | 243 | 97.11 | 99.67 | 1 473 | 883 |
| LL | 16 733 | 50 384 | 376 | 252 | 97.46 | 99.85 | 1 278 | 618 |
表2 甘青青兰根际土壤微生物OTUs及相关序列指数
Table 2 OTUs and related sequence indexes in rhizosphere soil of D. tanguticum
样品 Sample | 有效序列数Effective sequence number | 平均长度Average length/bp | 测序覆盖度Sequencing coverage/% | OTUs数量Number of OTUs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
细菌 Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | 细菌 Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | 细菌 Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | 细菌 Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | |
| GB | 15 316 | 42 048 | 376 | 284 | 97.78 | 99.83 | 1 149 | 489 |
| KR | 16 714 | 51 312 | 376 | 243 | 97.11 | 99.67 | 1 473 | 883 |
| LL | 16 733 | 50 384 | 376 | 252 | 97.46 | 99.85 | 1 278 | 618 |
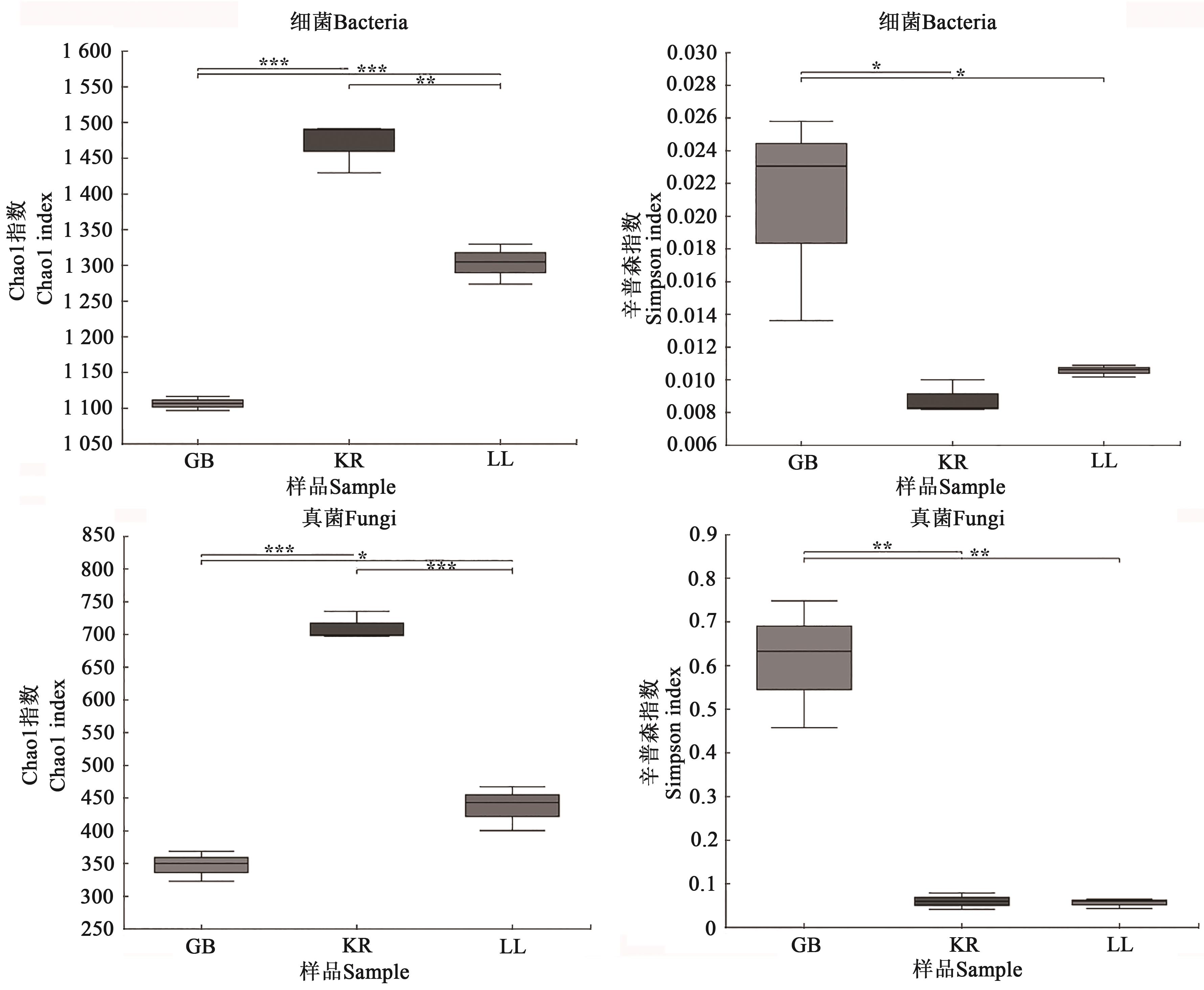
图3 甘青青兰根际土壤微生物α多样性指数注:*、**和***分别表示不同样本间在P<0.05、P<0.01和P<0.001水平差异显著。
Fig. 3 α diversity indexes of microbial community in rhizosphere soil of D. tanguticum.Note: *, ** and *** represent significant differences between different samples at P<0.05, P<0.01 and P<0.001 levels, respectively.
| 样品Sample | 门Phylum | 纲Class | 目Order | 科Family | 属Genus | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
细菌 Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | 细菌Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | 细菌Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | 细菌Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | 细菌Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | |
| GB | 26 | 10 | 62 | 28 | 133 | 66 | 197 | 132 | 360 | 190 |
| KR | 26 | 9 | 68 | 31 | 159 | 83 | 237 | 163 | 415 | 276 |
| LL | 23 | 8 | 55 | 29 | 125 | 62 | 193 | 137 | 332 | 225 |
表3 甘青青兰根际土壤细菌学和真菌学分类阶层总数
Table 3 Total numbers of bacterial and fungal taxa detected in the rhizosphere soil of D. tanguticum.
| 样品Sample | 门Phylum | 纲Class | 目Order | 科Family | 属Genus | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
细菌 Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | 细菌Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | 细菌Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | 细菌Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | 细菌Bacteria | 真菌Fungi | |
| GB | 26 | 10 | 62 | 28 | 133 | 66 | 197 | 132 | 360 | 190 |
| KR | 26 | 9 | 68 | 31 | 159 | 83 | 237 | 163 | 415 | 276 |
| LL | 23 | 8 | 55 | 29 | 125 | 62 | 193 | 137 | 332 | 225 |

图9 根际土壤核心微生物菌群与土壤理化因子间的相关性注:*、**和***分别表示在P<0.05、P<0.01和P<0.001水平显著相关。
Fig. 9 Correlation between physical and chemical properties and core microbiota in the rhizosphere soil.Note: *, ** and *** represent significant correlations at P<0.05, P<0.01 and P<0.001 levels, respectively.
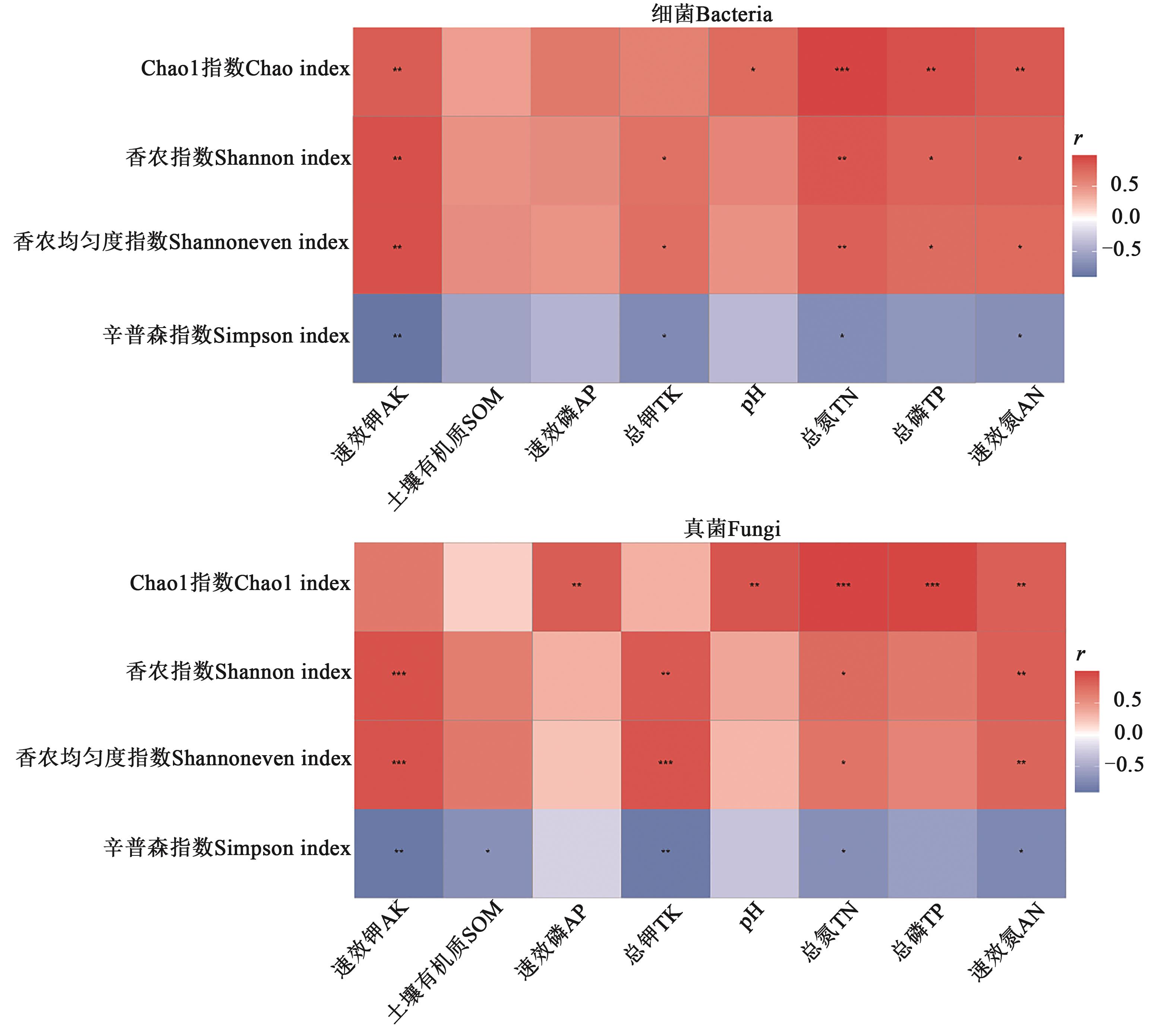
图10 根际土壤微生物多样性与土壤理化因子间的相关性注:*、**和***分别表示在P<0.05、P<0.01和P<0.001水平相关显著。
Fig. 10 Correlation between physical, chemical properties and microbial diversity index in rhizosphere soilNote: *, ** and *** represent significant correlations at P<0.05, P<0.01 and P<0.001 levels, respectively.
| 1 | 中华人民共和国卫生部药典委员会.卫生部药品标准·藏药分册[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,1995. |
| 2 | LI Q, LIU Y Q, HAN L F, et al.. Chemical constituents and quality control of two Dracocephalum species based on high-performance liquid chromatographic fingerprints coupled with tandem mass spectrometry and chemometrics [J]. J. Separaton Sci., 2016, 39(21):4075-4081. |
| 3 | 左马怡,杨超,田倩,等.青兰属植物甘青青兰化学成分研究[J].云南民族大学学报(自然科学版),2015,24(2):101-103. |
| ZUO M Y, YANG C, TIAN Q, et al.. Chemical constituents of Dracocephalum tanguticum Maxim. of genus Dracocephalum [J]. J. Yunnan Minzu Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2015, 24(2):101-103. | |
| 4 | 刘建英,刘玉梅.青兰属植物的化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J].食品科学,2012,33(13):314-319. |
| LIU J Y, LIU Y M. Research advance in chemical compositions and pharmacological effects of Dracocephalum [J]. Food Sci., 2012, 33(13):314-319. | |
| 5 | 谢建锋,朱林燕,孔子铭,等.唐古特青兰总黄酮的提取及其体外抗氧化活性的研究[J].华西药学杂志,2015,30(4):422-424. |
| XIE J F, ZHU L Y, KONG Z M, et al.. Study on the extraction of total flavonoids from Dracocephalumn tanguticum and its activity in vitro [J]. West China J. Pharm. Sci., 2015, 30(4):422-424. | |
| 6 | 李永芳,李延斌,杨梅,等.唐古特青兰对低氧性肺动脉高压大鼠ET-1和NO的影响[J].中成药,2016,38(10):2260-2262. |
| 7 | YAO H, ZHOU L C, TANG L L, et al.. Protective effects of luteolin-7-O-glucoside against starvation-induced injury through upregulation of autophagy in H9c2 Cells [J]. Biosci. Trends., 2017, 11(5):557-564. |
| 8 | 胡君茹,姜华,李喜香.对藏药甘青青兰4种提取物抑菌作用的研究[J].西部中医药,2014,27(6):10-12. |
| HU J R, JIANG H, LI X X. Study on antibacterial activity of four kinds of extracts from Tibetan medicine Ganqing Qinglan [J]. Western. J. Tradition Chin. Med., 2014, 27(6):10-12. | |
| 9 | 杨毅,田侃,倪新兴,等.中药材品质影响因素实证研究[J].中药材,2016,39(6):1251-1256. |
| 10 | 罗守杨,田春杰,张加凡,等.根际微生物对药材道地性的影响及应用前景展望[J].时珍国医国药,2022,33(4):948-950. |
| 11 | CARDONE L, CASTRONUOVO D, PERNIOLA M, et al.. Evaluation of corm origin and climatic conditions on saffron (Crocus sativus L.) yield and quality [J]. J. Sci. Food Agric., 2019, 99(13):5858-5869. |
| 12 | 徐锦堂,郭顺星,范黎,等.天麻种子与小菇属真菌共生萌发的研究[J].菌物学报,2001(01):137-141. |
| XU J T, GUO S X, FAN L, et al.. Symbiotic germination between Gasterodia elata and fungal species of Mycena [J]. Mycosystema, 2001(01):137-141. | |
| 13 | KIM Y S, BALARAJU K, JEON Y. Biological characteristics of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens AK‐0 and suppression of ginseng root rot caused by Cylindrocarpon destructans [J]. J. Appl. Microbiol., 2017, 122(1):166-179. |
| 14 | EGAMBERDIEVA D, LI L, LINDSTROM K, et al.. A synergistic interaction between salt-tolerant Pseudomonas and Mesorhizobium strains improves growth and symbiotic performance of liquorice (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fish.) under salt stress [J]. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2016, 100(6):2829-2841. |
| 15 | KHALEDIYAN N, WEISANY W, SCHENK P M. Arbuscular mycorrhizae and rhizobacteria improve growth, nutritional status and essential oil production in Ocimum basilicum and Satureja hortensis [J/OL]. Ind. Crops Prod., 2020, 160:113163 [2022-08-10]. . |
| 16 | RUI H R, CHEN Y L, PARE P W, et al.. Beneficial soil microbe promotes seed germination, plant growth and photosynthesis in herbal crop Codonopsis pilosula [J]. Crop Pasture Sci., 2016, 67(1):91-98. |
| 17 | ARORA M, SAXENA P, CHOUDHARY D K, et al..Dual symbiosis between Piriformospora indica and Azotobacter chroococcum enhances the artemisinin content in Artemisia annua L . [J]. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2016, 32(2):1-10. |
| 18 | 魏艳晨,陈吉祥,王永刚,等.荒漠植物珍珠猪毛菜根际土壤细菌多样性与土壤理化性质相关性分析[J].中国农业科技导报,2022,24(5):209-217. |
| WEI Y C, CHEN J X, WANG Y G, et al.. Analysis of bacterial diversity in the rhizosphere soil of Salsola passerina and its correlation with the soil physical and chemical properties [J]. J. Agric Sci Technol., 2022, 24(5):209-217. | |
| 19 | 张二豪,赵润东,禄亚洲,等.不同种源地喜马拉雅紫茉莉根际土壤理化性质及细菌群落结构组成分析[J].山东农业科学,2022,54(4): 82-89. |
| ZHANG E H, ZHAO R D, LU Y Z, et al.. Soil physiochemical properties and microbial community structure of mirabilis himalaica rhizosphere from different provenances [J]. Shandong Agric Sci., 2022, 54(4): 82-89. | |
| 20 | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析 [M].第2版.北京:中国农业出版社,1999:34-108. |
| 21 | 李茜,徐瑞蔓,陈迪,等.不同栽培年限人参根际土壤细菌群落与土壤理化性质和酶活性的相关性[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2022,28(2):313-324. |
| L X, XU R M, CHEN D, et al.. Correlation of bacterial community with soil physicochemical properties and enzyme activities in rhizosphere soil under different cultivation years of Ginseng (Panax ginseng C. A. Mey.) [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2022, 28(2):313-324. | |
| 22 | 李毳,刘怡,刘晋仙.药用植物根际细菌群落多样性驱动因素分析[J].生态环境学报,2020,29(10):1988-1993. |
| LI C, LIU Y, LIU J X. Analysis of driving factors of rhizosphere bacterial community diversityin three genuine medicine plants [J]. Ecol. Environ. Sci., 2020, 29(10):1988-1993. | |
| 23 | 李毳,刘怡.晋东南3种道地药材植物根际真菌群落特性[J].生态环境学报,2019,28(7):1388-1393. |
| LI C, LIU Y. Characteristics of rhizosphere fungal community of three genuine medicinal plants in southeast Shanxi province [J]. Ecol. Environ. Sci., 2019, 28(7):1388-1393. | |
| 24 | BURNS J H, ANACKER B L, STRAUSS S Y, et al.. Soil microbial community variation correlates most strongly with plant species identity, followed by soil chemistry, spatial location and plant genus [J]. AoB Plants, 2015, 7(3):207-240. |
| 25 | PHILIPPOT L, ANDERSSON S G E, BATTIN T J, et al.. The ecological coherence of high bacterial taxonomic ranks [J]. Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2010, 8(7):523-529. |
| 26 | MENENDEZ E, CARRO L. Actinobacteria and their role as plant probiotics//giri b, prasad r, wu qs, varma a. biofertilizers for sustainable agriculture and environment [J]. Biofert. Sust. Agric. Environ., 2019, 55:333-351. |
| 27 | 宋兆齐,王莉,刘秀花,等.云南4处酸性热泉中的变形菌门细菌多样性[J].河南农业大学学报,2016,50(3):376-382. |
| SONG Z Q, WANG L, LIU X Y, et al.. The diversities of proteobacteria in four acidic hot springs in Yunnan [J]. J. Henan Agric. Univ., 2016, 50(3):376-382. | |
| 28 | 郭凤仙,刘越,唐丽,等.药用植物根际微生物研究现状与展望[J].中国农业科技导报,2017,19(5):12-21. |
| GUO F X, LIU Y, TANG L, et al.. Research status and prospect on rhizosphere microbiome of medicinal plants [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2017, 19(5):12-21. | |
| 29 | 李洁,林莹,徐美玉,等.泰山白首乌根际土壤真菌多样性分析[J].中国农业科技导报,2022,24(6):70-81. |
| LI J, LIN Y, XU M Y, et al.. Sequencing analysis of fungal diversity in rhizosphere soil of Cynanchum bungei Decne [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2022, 24(6):70-81. | |
| 30 | YELLE D J, RALPH J, LU F, et al.. Evidence for cleavage of lignin by a brown rot basidiomycete [J]. Environ. Microbiol., 2010, 10(7):1844-1849. |
| 31 | 许国琪,刘怡萱,曹鹏熙,等.青藏高原冰川棘豆(Oxytropis glacialis)内生菌核心微生物组的界定及其互作网络分析[J].微生物学通报,2020,47(9):2746-2758. |
| XU G Q, LIU Y X, CAO P X, et al.. Core microflora and endophytic interaction network of Oxytropis glacialis in Qinghai-Tibet plateau [J]. Microbiol. China, 2020, 47(9):2746-2758. | |
| 32 | LIU Y H, WEI Y Y, MOHAMAD O, et al.. Diversity, community distribution and growth promotion activities of endophytes associated with halophyte Lycium ruthenicum Murr [J/OL]. 3 Biotech., 2019, 9(4):144 [2022-08-10]. . |
| 33 | SONG X, WU H, YIN Z, et al.. Endophytic bacteria isolated from panax ginseng improves ginsenoside accumulation in adventitious ginseng root culture [J/OL]. Molecules, 2017, 22(6):837 [2022-08-10]. . |
| 34 | 吕志堂,刘志恒.假诺卡氏菌科的分类学研究进展[J].微生物学通报,1999(3):210-215. |
| 35 | ASAF S, KHAN A L, KHAN M A, et al.. Osmoprotective functions conferred to soybean plants via inoculation with Sphingomonas sp. LK11 and exogenous trehalose [J/OL]. Microbiol. Res., 2017:135 [2022-08-10]. . |
| 36 | NIU X G, SONG L C, XIAO Y N, et al.. Drought-tolerant plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria associated with foxtail millet in a semi-arid agroecosystem and their potential in alleviating drought stress [J/OL]. Front. Microbiol., 2018, 8:2580 [2022-08-10]. . |
| 37 | DIAS M P, BASTOS M S, XAVIER V B, et al.. Plant growth and resistance promoted by Streptomyces spp. in tomato [J]. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 2017, 118(9):479-493. |
| 38 | 金航. 丝状真菌被孢霉生长群体感应的初步研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2016. |
| JIN H. A preliminary research on the quorum-sensing of filamentous Mortierella [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2016. | |
| 39 | 于帮红,徐慧,张传博.一株冬虫夏草来源真菌的鉴定及抑菌活性检测[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2016,22(8):36-40 |
| YU B H, XU H, ZHANG C B. Identification of fungi from Cordyceps sinensis and its antibacterial activity [J]. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Form., 2016, 22(8):36-40. | |
| 40 | 黄晓丽.毛壳菌(Chaetomium spp.)生防菌株的筛选及其生物防治机制研究[D].雅安:四川农业大学,2009. |
| HUANG X L. Screens biocontrol strains from Chaetomium spp. and studies on biocontrol mechanisms of Chaetomium spp. [D]. Ya’an: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2009. | |
| 41 | LIU X, CUI X, JI D, et al.. Luteolin-induced activation of the phenylpropanoid metabolic pathway contributes to quality maintenance and disease resistance of sweet cherry [J/OL]. Food Chem., 2020, 342(1):128309 [2022-08-10]. . |
| 42 | WANG X Y, ZHANG X H, YANG M X, et al.. Multi-Site evaluation of accumulated temperature and rainfall for maize yield and disease in Loess plateau [J/OL]. Agriculture, 2021, 11(4):373 [2022-08-10]. . |
| [1] | 张桐毓, 勾颖, 李琪, 杨莉. 人参锈腐病对人参品质和土壤相关因子的影响研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 124-133. |
| [2] | 周旭东, 韩天华, 申云鑫, 施竹凤, 贺彪, 杨明英, 裴卫华, 何永宏, 杨佩文. 4种轮作模式下长期连作烟田土壤微生态的响应特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 174-187. |
| [3] | 方泰军, 侯璐, 白露超. 柴达木地区患根腐病枸杞根际土壤微生物多样性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 133-139. |
| [4] | 郭靖捷, 任晓萌, 蒙仲举, 王涛, 祁帅, 宋佳佳, 宝孟克那顺, 韩胜利. 半干旱风沙草原区盐湖植物防护体系土壤理化性状特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 182-192. |
| [5] | 刘威, 赵园园, 陈小龙, 史宏志. 土壤含水率对豫中植烟土壤微生物群落多样性及氮循环功能基因丰度的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 214-225. |
| [6] | 李慧君, 张伟健, 吴伟健, 李高洋, 陈艺杰, 黄枫城, 黄永相, 蔺中, 甄珍. 种植海水稻对滨海盐土化学性质和微生物群落影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 147-156. |
| [7] | 邵社刚, 李婷, 柳勇, 林兰稳, 张东, 倪栋, 李俊杰, 朱立安. 外源菌剂对稻秆腐解及微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 166-177. |
| [8] | 肖锐, 谭璐, 吴亮, 张皓, 郭佳源, 杨海君. 镉胁迫下地肤根际与非根际土壤微生物群落结构及多样性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 203-215. |
| [9] | 尹兴盛, 包玲凤, 濮永瑜, 孙加利, 张庆, 李海平, 杨明英, 林跃平, 王怀鑫, 何永宏, 杨佩文. 减氮配施生物有机肥对植烟土壤特性及烟草青枯病的防效研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 122-131. |
| [10] | 刘宏元, 周志花, 赵光昕, 沈钦瑞. 黄淮海平原农田土壤温室气体排放对长期施加生物炭的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 178-186. |
| [11] | 贾晶莹, 李雅辉, 伏兵哲, 马云, 蔡小艳. 苜蓿miRs表达谱分析及跨界潜力miRs初步筛选[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 43-53. |
| [12] | 庞喆, 王启龙, 李娟. 不同土壤改良剂对陕北低洼盐碱地土壤理化性质及水稻产量和经济效益的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 174-180. |
| [13] | 麻仲花, 陈娟, 吴娜, 满本菊, 王晓港, 者永清, 刘吉利. 盐胁迫与供磷水平对柳枝稷苗期光合特性与总生物量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 190-200. |
| [14] | 孟璐, 范敬文, 赛欣娱, 曾路生, 宋祥云, 崔德杰. 石灰对苹果园土壤改良和植株生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 197-204. |
| [15] | 赵柏霞, 闫建芳. 高通量技术分析‘砂蜜豆’甜樱桃不同组织内生细菌多样性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 66-77. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号