




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (11): 180-190.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0126
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
张伟健( ), 冯景翊, 李悦, 何婉莹, 车延静, 王紫颖, 白雪燕, 谷思玉(
), 冯景翊, 李悦, 何婉莹, 车延静, 王紫颖, 白雪燕, 谷思玉( )
)
收稿日期:2023-02-24
接受日期:2024-07-12
出版日期:2024-11-15
发布日期:2024-11-19
通讯作者:
谷思玉
作者简介:张伟健 E-mail:zwj18371121113@163.com;
基金资助:
Weijian ZHANG( ), Jingyi FENG, Yue LI, Wanying HE, Yanjing CHE, Ziying WANG, Xueyan BAI, Siyu GU(
), Jingyi FENG, Yue LI, Wanying HE, Yanjing CHE, Ziying WANG, Xueyan BAI, Siyu GU( )
)
Received:2023-02-24
Accepted:2024-07-12
Online:2024-11-15
Published:2024-11-19
Contact:
Siyu GU
摘要:
为探究有机质对东北黑土磷(P)吸附及有效性的影响, 选用高有机质黑土(T1)、中有机质黑土(T2)、低有机质黑土(T3)3种不同有机质水平黑土,通过去除有机质操作探讨磷吸附-解吸是否受内源有机质影响。并选用高有机质黑土为材料,设置有机肥添加量分别为0%(CK)、1%(C1)、2%(C2)、3%(C3)共4个处理,分析不同有机肥添加量对土壤理化性质及磷有效性的影响。结果表明,随着有机质含量的提高,黑土吸附亲和力常数(K)、最大吸附量(qm)、土壤最大缓冲量上升,土壤磷饱和度(soil phosphorus saturation,DPS)降低,表明磷在有机质高的土壤中不易流失。有机质含量越高,土壤对磷吸附能力越强,当平衡含量为100 mg·L-1时,T1、T2、T3处理土壤磷吸附量分别为754.83、722.58、660.65 mg·kg-1。有机质含量越低,土壤对磷解吸能力越强,磷有效性越强。去除有机质操作使不同水平有机质含量黑土磷吸附量下降5.90%~17.33%,增强了土壤磷有效性。对于磷等温吸附方程决定系数(R2),Langmuir方程大于Freundlich方程,拟合程度较好;土壤磷吸附主要由化学吸附主导。不同剂量有机肥施加均可以降低黑土对磷的吸附速率,且随有机肥添加量增加,吸附速率显著降低。当达到最大磷平衡含量时,C3处理土壤磷吸附量降低程度最大,土壤磷有效性最强,准二级动力学方程能较好地表达有机肥对土壤磷吸附动力学特征。添加有机肥使土壤pH、速效磷、有效磷和酸性磷酸酶活性分别显著增加1.05%~3.97%、121.43%~251.35%、8.38%~12.65%和42.96%~57.77%。研究结果为科学管理不同区域黑土、合理施用有机肥、提高磷素的有效性提供科学支撑。
中图分类号:
张伟健, 冯景翊, 李悦, 何婉莹, 车延静, 王紫颖, 白雪燕, 谷思玉. 内-外源有机质对黑土磷素吸附及有效性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(11): 180-190.
Weijian ZHANG, Jingyi FENG, Yue LI, Wanying HE, Yanjing CHE, Ziying WANG, Xueyan BAI, Siyu GU. Effect of Endogenous and Exogenous Organic Matter on Phosphorus Adsorption and Availability in Black Soil[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(11): 180-190.
| 处理 Treatment | 有机质 SOM/(g·kg-1) | 全氮 TN/ (g·kg-1) | P / (g·kg-1) 全磷 T | N / (mg·kg-1) 碱解氮 A | 速效磷 AP/ (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 AK/ (mg·kg-1) | pH | 粘粒含量 Clay content/% | 田间持水量 FC/% | 阳离子交换量 CEC/ (cmol·kg-1) | 土壤粘土矿物类型 Soil clay mineral type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 50.97 | 2.86 | 0.77 | 216.36 | 42.82 | 182.36 | 7.05 | 9.36 | 31.26 | 24.87 | 典型黑土(蒙脱石、伊利石) Typical black soil (montmorillonite, illite) |
| T2 | 28.50 | 1.68 | 0.50 | 168.51 | 45.53 | 147.25 | 6.98 | 23.00 | 28.96 | 19.64 | |
| T3 | 17.72 | 1.12 | 0.39 | 112.32 | 54.21 | 98.64 | 6.69 | 42.11 | 26.37 | 17.53 |
表1 3种不同农田黑土基础理化性质
Table 1 Basic physical and chemical properties of 3 different kinds of farmland black soil
| 处理 Treatment | 有机质 SOM/(g·kg-1) | 全氮 TN/ (g·kg-1) | P / (g·kg-1) 全磷 T | N / (mg·kg-1) 碱解氮 A | 速效磷 AP/ (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 AK/ (mg·kg-1) | pH | 粘粒含量 Clay content/% | 田间持水量 FC/% | 阳离子交换量 CEC/ (cmol·kg-1) | 土壤粘土矿物类型 Soil clay mineral type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 50.97 | 2.86 | 0.77 | 216.36 | 42.82 | 182.36 | 7.05 | 9.36 | 31.26 | 24.87 | 典型黑土(蒙脱石、伊利石) Typical black soil (montmorillonite, illite) |
| T2 | 28.50 | 1.68 | 0.50 | 168.51 | 45.53 | 147.25 | 6.98 | 23.00 | 28.96 | 19.64 | |
| T3 | 17.72 | 1.12 | 0.39 | 112.32 | 54.21 | 98.64 | 6.69 | 42.11 | 26.37 | 17.53 |
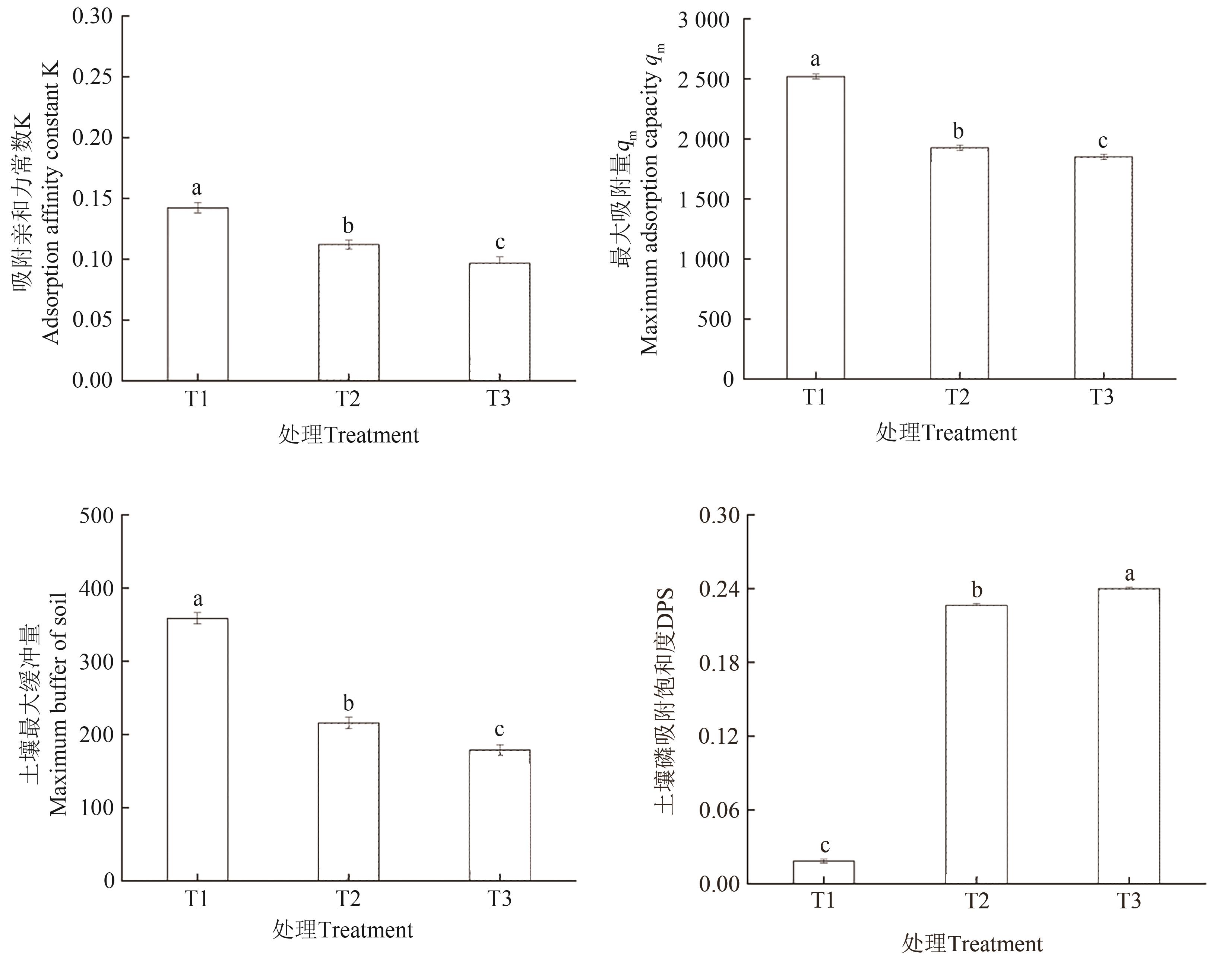
图1 不同有机质黑土磷吸附特性注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 Phosphorus adsorption characteristics of different organic black soilsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.

图2 不同水平有机质黑土的磷吸附-解吸量A:磷吸附;B:磷解吸。不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著
Fig. 2 Phosphorus adsorption-desorption capacity of different levels of organic black soilA:phosphorus adsorption; B: phosphorus desorption. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level
处理 Treatment | Langmuir拟合方程 Langmuir fitting equation | Freundlich拟合方程 Freundlich fitting equation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
最大吸附量 qm/(mg·g-1) | 常数KL Constant KL | 决定系数 R2 | 常数n Constant n | 常数KF Constant KF | 决定系数 R2 | ||
| T1 | 1.22 a | 0.052 a | 0.932** | 2.06 c | 0.030 c | 0.917** | |
| T2 | 1.14 b | 0.024 b | 0.916** | 2.56 b | 0.032 b | 0.893** | |
| T3 | 0.87 c | 0.025 b | 0.876** | 3.73 a | 0.034 a | 0.728** | |
表2 不同有机质农田黑土对磷吸附的Langmuir和Freundlich拟合方程
Table 2 Langmuir and Freundlich fitting equation for phosphorus adsorption in black soil ofdifferent organic matter
处理 Treatment | Langmuir拟合方程 Langmuir fitting equation | Freundlich拟合方程 Freundlich fitting equation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
最大吸附量 qm/(mg·g-1) | 常数KL Constant KL | 决定系数 R2 | 常数n Constant n | 常数KF Constant KF | 决定系数 R2 | ||
| T1 | 1.22 a | 0.052 a | 0.932** | 2.06 c | 0.030 c | 0.917** | |
| T2 | 1.14 b | 0.024 b | 0.916** | 2.56 b | 0.032 b | 0.893** | |
| T3 | 0.87 c | 0.025 b | 0.876** | 3.73 a | 0.034 a | 0.728** | |
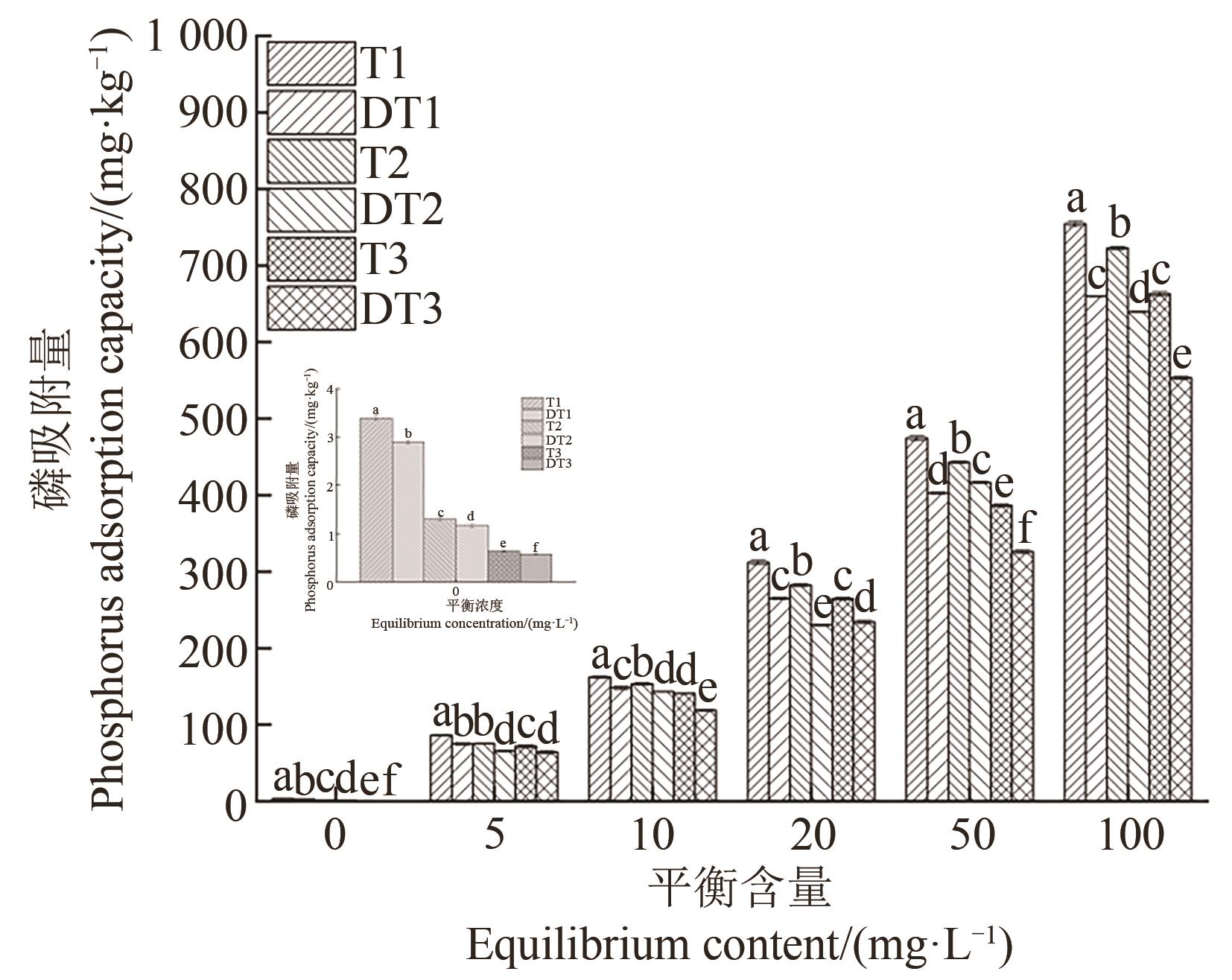
图3 去除有机质条件下不同黑土磷吸附量注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。图中小图代表平衡含量为0 mg·L-1时的吸附量。
Fig. 3 Phosphorus adsorption capacity of different black soils under organic matter removal conditionsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level. The small figure represents the adsorption capacity at 0 mg·L-1.
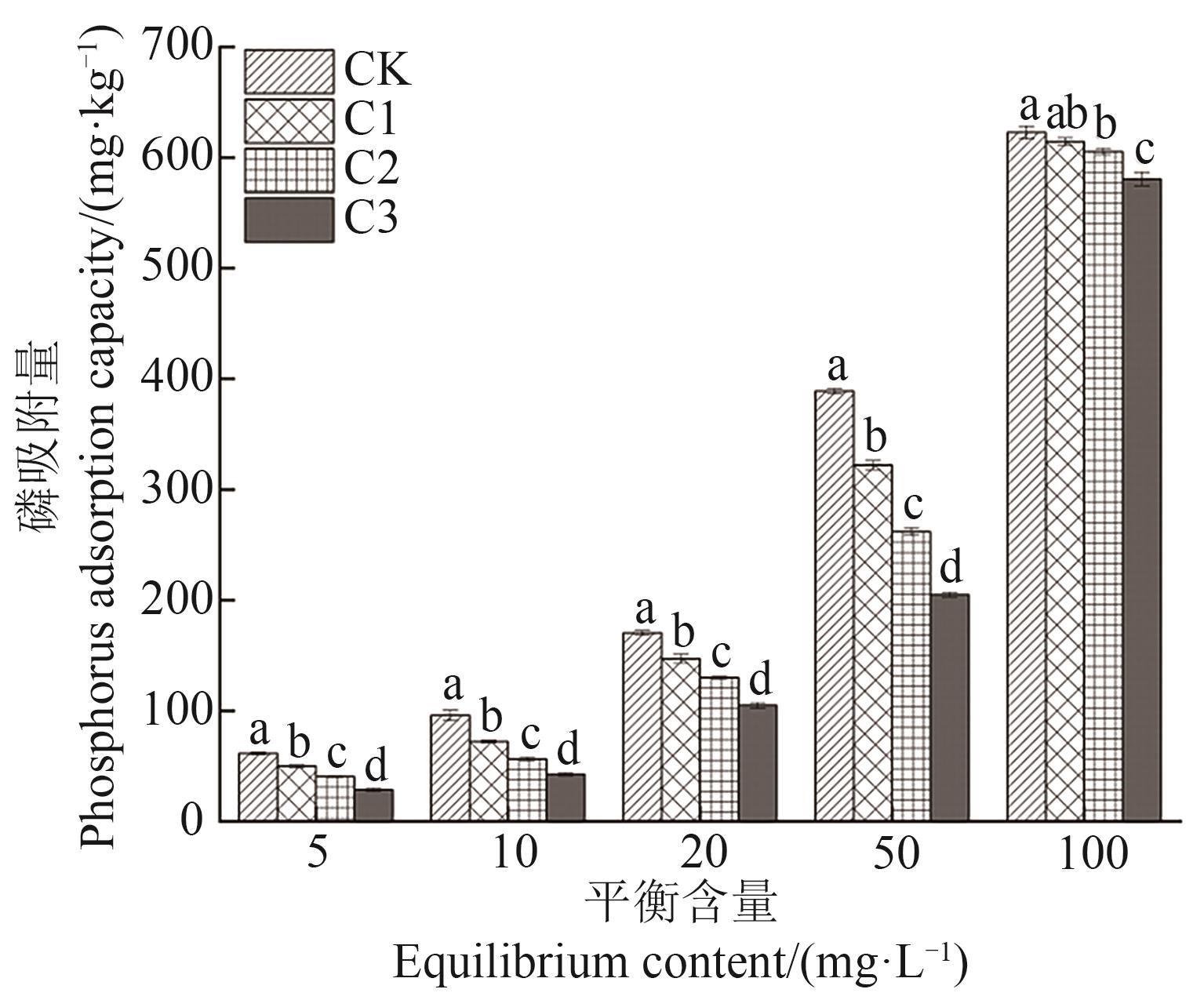
图4 添加不同剂量有机肥条件下高有机质黑土对磷的吸附量注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 4 Phosphorus adsorption capacity of high organic matter black soil with different dosage of organic fertilizerNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
处理 Treatment | Langmuir方程 Langmuir equation | Freundlich方程 Freundlich equation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大吸附量qm/(mg·g-1) | 常数KL Constant KL | 决定系数 R2 | 常数n Constant n | 常数KF Constant KF | 决定系数 R2 | ||
| C1 | 1.65 a | 0.085 a | 0.948** | 1.62 c | 0.030 a | 0.893** | |
| C2 | -1.46 c | -0.048 b | 0.955** | 1.89 b | 0.027 ab | 0.741** | |
| C3 | -0.82 b | -0.098 c | 0.909** | 3.51 a | 0.019 c | 0.874** | |
表3 不同剂量有机肥处理下黑土磷吸附等温方程参数
Table 3 Parameters of phosphorus adsorption isothermal equation for black soil treated with different doses of organic fertilizer
处理 Treatment | Langmuir方程 Langmuir equation | Freundlich方程 Freundlich equation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大吸附量qm/(mg·g-1) | 常数KL Constant KL | 决定系数 R2 | 常数n Constant n | 常数KF Constant KF | 决定系数 R2 | ||
| C1 | 1.65 a | 0.085 a | 0.948** | 1.62 c | 0.030 a | 0.893** | |
| C2 | -1.46 c | -0.048 b | 0.955** | 1.89 b | 0.027 ab | 0.741** | |
| C3 | -0.82 b | -0.098 c | 0.909** | 3.51 a | 0.019 c | 0.874** | |
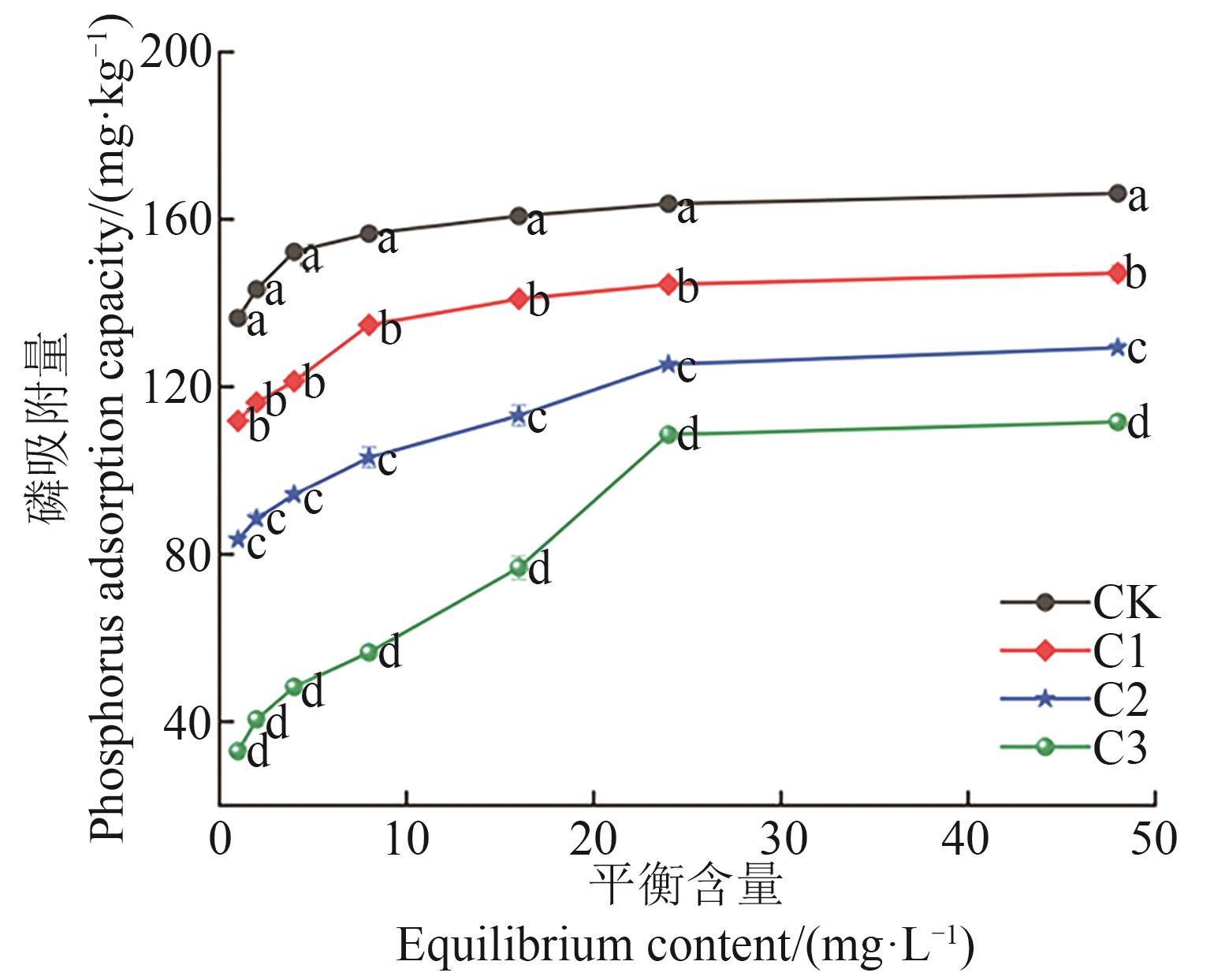
图5 添加不同剂量有机肥下高有机质黑土磷吸附量注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 5 Phosphorus adsorption capacity of high organic matter black soil with different dosage of organic fertilizerNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 处理 Treatment | 准一级动力方程 Pseudo-first-order kinetics equation | 准二级动力方程 Pseudo-second-order kinetics equation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
磷吸附总量 qe/(mg·g-1) | 常数k1 Constant k1 | 决定系数 R2 | 磷吸附总量 qe/(mg·g-1) | 常数k2 Constant k2 | 决定系数 R2 | ||
| C1 | 0.161 a | 0.058 a | 0.941** | 0.166 a | 0.005 b | 0.972** | |
| C2 | 0.148 b | 0.045 c | 0.944** | 0.151 b | 0.006 a | 0.965** | |
| C3 | 0.132 c | 0.054 b | 0.938** | 0.135 c | 0.006 a | 0.969** | |
表4 添加不同剂量有机肥高有机质农田土壤磷吸附动力学参数
Table 4 Kinetic parameters of phosphorus adsorption in high organic matter farmland soil with different doses of organic fertilizer were added
| 处理 Treatment | 准一级动力方程 Pseudo-first-order kinetics equation | 准二级动力方程 Pseudo-second-order kinetics equation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
磷吸附总量 qe/(mg·g-1) | 常数k1 Constant k1 | 决定系数 R2 | 磷吸附总量 qe/(mg·g-1) | 常数k2 Constant k2 | 决定系数 R2 | ||
| C1 | 0.161 a | 0.058 a | 0.941** | 0.166 a | 0.005 b | 0.972** | |
| C2 | 0.148 b | 0.045 c | 0.944** | 0.151 b | 0.006 a | 0.965** | |
| C3 | 0.132 c | 0.054 b | 0.938** | 0.135 c | 0.006 a | 0.969** | |
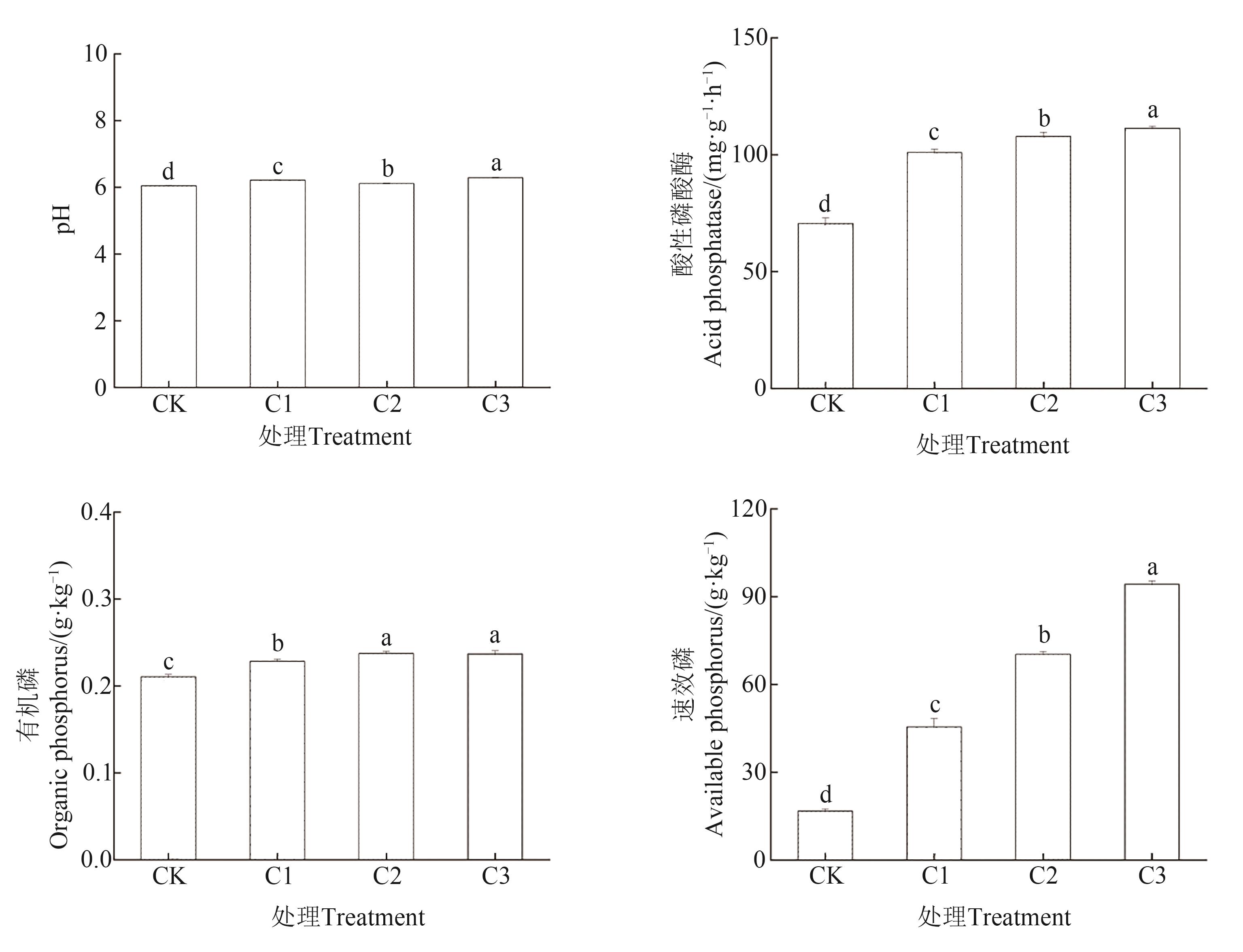
图6 添加不同剂量有机肥条件下土壤理化指标注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 6 Soil physical and chemical indexes under different levels of organic fertilizerNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 1 | LIU S N, MENG J, JIANG L L,et al.. Rice husk biochar impacts soil phosphorous availability,phosphatase activities and bacterial community characteristics in three different soil types [J]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2017,116:12-22. |
| 2 | 展晓莹,任意,张淑香,等.中国主要土壤有效磷演变及其与磷平衡的响应关系[J].中国农业科学,2015,48(23):4728-4737. |
| ZHAN X Y, REN Y, ZHANG S X,et al.. Changes in olsen phosphorus concentration and its response to phosphorus balance in the main types of soil in China [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2015,48(23):4728-4737. | |
| 3 | 张宝贵, 李贵桐. 土壤生物在土壤磷有效化中的作用[J]. 土壤学报, 1998, 38(1): 104-111. |
| ZHANG B G, LI G T. Roles of soil organisms on the enhancement of plant availability of soil phosphorus [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 1998, 38(1): 104-111. | |
| 4 | DOU Z X, RAMBERG C F, TOTH J D, et al.. Phosphorus speciation and sorption-desorption characteristics in heavily manured soils [J]. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J., 2009, 73(1): 93-101. |
| 5 | ZHANG S L, HUFFMAN T, ZHANG X Y,et al.. Spatial distribution of soil nutrient at depth in black soil of Northeast China:a case study of soil available phosphorus and total phosphorus [J]. J. Soils Sediments, 2014,14(11):1775-1789. |
| 6 | DEBICKA M, KOCOWICZ A, WEBER J, et al.. Organic matter effects on phosphorus sorption in sandy soils [J]. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci., 2016,62: 840-855. |
| 7 | DU Z Y, WANG Q H, LIU F C,et al.. Movement of phosphorus in a calcareous soil as affected by humic acid [J]. Pedosphere, 2013,23(2):229-235. |
| 8 | HIRADATE S, UCHIDA N. Effects of soil organic matter on pH-dependent phosphate sorption by soils [J]. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr., 2004, 50: 665-675. |
| 9 | YANG X Y, CHEN X W, YANG X T. Effect of organic matter on phosphorus adsorption and desorption in a black soil from Northeast China [J]. Soil Till. Res., 2019,187:85-91. |
| 10 | YAO Q, LIU J J, YU Z H,et al.. Three years of biochar amendment alters soil physiochemical properties and fungal community composition in a black soil of Northeast China [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2017,110:56-67. |
| 11 | ZHOU J, GUAN D W, ZHOU B K,et al..Influence of 34-years of fertilization on bacterial communities in an intensively cultivated black soil in Northeast China [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2015,90:42-51. |
| 12 | WU Q H, ZHANG S X, ZHU P,et al.. Characterizing differences in the phosphorus activation coefficient of three typical cropland soils and the influencing factors under long-term fertilization [J/OL].PLoS One,2017,12(5):e0176437 [2023-01-22]. . |
| 13 | 杨云辉, 焦亚, 杨柱琼, 等. 白魔芋芋鞭不同剂量有机肥试验初探[J].农业开发与装备, 2019 (11): 126. |
| 14 | YAN J L, JIANG T, YAO Y,et al.. Preliminary investigation of phosphorus adsorption onto two types of iron oxide-organic matter complexes [J]. J. Environ. Sci., 2016,42:152-162. |
| 15 | HAFIZ N, ADITY S M, MITU S F, et al.. Effect of manure types on phosphorus sorption characteristics of an agricultural soil in Bangladesh [J]. Cogent Food Agric., 2016, 2 (1): 127-160. |
| 16 | 乔德波. 施用有机肥对设施菜地土壤养分、重金属含量及其分布特征的影响[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2014. |
| QIAO D B. Effects of organic fertilizer application on soil nutrient and heavy metal contents and their distribution characteristics in vegetable fields [D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2014. | |
| 17 | KAISER K, GUGGENBERGER G. Mineral surfaces and soil organic matter [J]. Eur. J. Soil Sci., 2010, 54 (2): 219-236. |
| 18 | 李悦.不同有机质含量黑土磷吸附-解吸特性的研究[D].哈尔滨:东北农业大学,2018. |
| LI Y. Study on adsorption-desorption properties of different organic matter black soil phosphorus [D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2018. | |
| 19 | 夏瑶, 娄运生, 杨超光, 等. 几种水稻土对磷的吸附与解吸特性研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 2002, 35(11):1369-1374. |
| XIA Y, LOU Y S, YANG C G, et al.. Characteristics of phosphate adsorption and desorption in paddy soils [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2002, 35(11): 1369-1374. | |
| 20 | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].第3版.北京:中国农业出版社,2000: 25-114. |
| 21 | 程敏华,梁俭,蓝品滩,等.百色市不同土地利用类型土壤对磷吸附特性研究[J].山东化工,2018,47(24):190-192. |
| CHENG M H, LIANG J, LAN P T,et al.. Phosphorus adsorption characteristics of soil under different utilization ways in Baise [J].Shandong Chem. Ind.,2018,47(24):190-192. | |
| 22 | 韩旭,吴东洋,王新刚.不同土壤对磷的吸附特性研究[J].现代农业科技,2011(20):285-286. |
| 23 | 丁武泉,何家洪,刘新敏,等.有机质对三峡库区水体中土壤胶体颗粒凝聚影响机制研究[J].水土保持学报,2017,31(4):166-171. |
| DING W Q, HE J H, LIU X M, et al.. Effect of organic matter on aggregation of soil colloidal particles in water bodies of three gorge reservoir region [J].J. Soil Water Conserv., 2017,31(4):166-171. | |
| 24 | BORGGAARD O K, JDRGENSEN S S, MOBERG J P, et al.. Influence of organic matter on phosphate adsorption by aluminium and iron oxides in sandy soils [J]. Eur. J. Soil Sci., 1990, 41 (3): 443-449. |
| 25 | BORIE F, ZUNINO H, MARTANEZ L, et al.. Associations and inositol phosphates in some chilean volcanic soils of temperate regions [J]. Commun. Soil Sci. Plan., 2008, 20 (17-18): 1881-1894. |
| 26 | 罗安程, 章永松, 孙羲. 有机肥对大麦根系生理代谢和磷吸收的影响[J]. 西北农业学报, 1996, 5(3): 9-12. |
| LUO A C, ZHANG Y S, SUN X. Effect of organic manure on phosphate absorption and physiological metabolism of barley roots [J]. Acta Agric. Bor-Occid. Sin., 1996,5(3): 9-12. | |
| 27 | 田艳洪,赵晓锋,刘玉娥,等.不同有机肥用量对大豆植株生长及产量的影响[J].大豆科学,2018,37(4):578-584. |
| TIAN Y H, ZHAO X F, LIU Y E,et al.. Effects of different dosages of organic fertilizer on the growth and yield of soybean [J]. Soybean Sci., 2018,37(4):578-584. | |
| 28 | 闫金龙,吴文丽,江韬,等.土壤组分对磷形态和磷吸附-解吸的影响:基于三峡库区消落带落干期土壤[J].中国环境科学,2019,39(3):1124-1131. |
| YAN J L, WU W L, JIANG T, et al.. Effect of organic matter and iron oxides on phosphorus forms and adsorption-desorption on dry-period soils in the water-level-fluctuating zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir [J].China Environ. Sci.,2019,39(3):1124-1131. | |
| 29 | YANG W, GU S Y, XIN Y,et al..Compost addition enhanced hyphal growth and sporulation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi without affecting their community composition in the soil [J/OL].Front. Microbiol.,2018,9:169 [2023-01-22].. |
| 30 | DAVIS J A. Adsorption of natural dissolved organic matter at the oxide/water interface [J]. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1982, 46 (11):2381-2393. |
| 31 | 梁佳辉,张少良,穆林林,等.东北典型黑土区坡面土壤速效磷空间分布规律[J].水土保持研究,2017,24(1):90-95, 102. |
| LIANG J H, ZHANG S L, MU L L, et al.. Spatial heterogeneity of soil available phosphorus on typical slope in black soil of northeastern China [J]. Res. Soil Water Conserv., 2017,24(1):90-95, 102. | |
| 32 | 吕鉴于, 高文俊, 郝鲜俊, 等. 不同有机肥对矿区复垦土壤磷素矿化特征研究[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2020, 39 (4): 59-67. |
| LYU J Y, GAO W J, HAO X J, et al.. Study on phosphorus mineralization characteristics of reclaimed soil with different organic fertilizers [J]. J. Irrig. Drain., 2020, 39 (4): 59-67. | |
| 33 | 李清华.畜禽有机肥磷的形态、养分矿化及流失潜力评价研究进展[J].安徽农学通报,2013,19(3):73-75. |
| 34 | 王敏锋,严正娟,陈硕,等.施用粪肥和沼液对设施菜田土壤磷素累积与迁移的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2016,35(7):1351-1359. |
| WANG M F, YAN Z J, CHEN S,et al.. Effects of manure and biogas slurry applications on phosphorus accumulation and mobility in organic vegetable soil under greenhouse [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2016,35(7):1351-1359. | |
| 35 | 刘彦伶,李渝,张萌,等.长期不同施肥对黄壤磷素吸附-解吸特性的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2021,27(3):450-459. |
| LIU Y L, LI Y, ZHANG M, et al.. Effects of long-term fertilization on phosphorus adsorption and desorption characters in yellow soil [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert.,2021,27(3):450-459. | |
| 36 | GUO Y J, LI G D. Nitrogen leaching and phosphorus accumulation in a perennial pasture after composted goat manure was topdressed and incorporated in the Three Gorges Region [J]. J. Soils Sediments, 2012,12(5):674-682. |
| 37 | 杨燕玲.农田土壤对磷的吸附和解吸特性研究进展[J].安徽农业科学,2019,47(1):4-5, 16. |
| YANG Y L. Advances in phosphorus adsorption and desorption of farmland soils [J]. J. Anhui Agric. Sci., 2019,47(1):4-5, 16. | |
| 38 | 蔡越桐.添加有机物料及解磷菌对黑土磷吸附性及其有效性的影响[D].哈尔滨:东北农业大学,2019. |
| CAI Y T. Effect of adding organic material and phosphorus solubilizing bacteria on phosphorus adsorption and availability of black soil [D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2019. |
| [1] | 王兴松, 王娜, 杜宇, 周鹏, 王戈, 贾孟, 徐照丽, 白羽祥. 有机肥对玉溪植烟土壤有机质组分和微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 201-212. |
| [2] | 王世芳, 宋海燕. 土壤有机质可见-近红外反射光谱特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(7): 183-188. |
| [3] | 韩秀丽, 李嘉伟, 张杰, 郭艳杰, 张丽娟, 吉艳芝. 生物有机肥替代化肥对葡萄生长与土壤肥力的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(4): 195-205. |
| [4] | 高静娟, 朱晨宇, 柯玉琴, 郑朝元, 李春英, 李文卿. 烟稻轮作条件下有机肥施用时期对烤烟碳氮代谢的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 157-165. |
| [5] | 张晨阳, 徐明岗, 王斐, 李然, 孙楠. 施用有机肥对我国大豆产量及土壤养分的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 148-156. |
| [6] | 王艳成, 张纪月, 冯帅奇, 梁雪, 张振, 董微巍, 姬文秀. 外源促生菌联合有机肥对干旱胁迫下参地土壤性状及人参抗逆性影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 196-202. |
| [7] | 尹兴盛, 包玲凤, 濮永瑜, 孙加利, 张庆, 李海平, 杨明英, 林跃平, 王怀鑫, 何永宏, 杨佩文. 减氮配施生物有机肥对植烟土壤特性及烟草青枯病的防效研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 122-131. |
| [8] | 侯非凡, 张笑文, 王嘉琦, 张建珍, 李凯泉, 尹雪斌. 硒肥土施位置对小麦生理特性及硒积累的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 144-152. |
| [9] | 可艳军, 张雨萌, 郭艳杰, 张丽娟, 张子涛, 吉艳芝. 生物有机肥配合深松对农田土壤肥力和作物产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 157-166. |
| [10] | 孟璐, 范敬文, 赛欣娱, 曾路生, 宋祥云, 崔德杰. 石灰对苹果园土壤改良和植株生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 197-204. |
| [11] | 靳建刚, 田再芳, 郑敏娜, 康佳惠. 不同施肥措施对饲用燕麦土壤细菌群落多样性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 152-160. |
| [12] | 郭巨先, 欧阳碧珊, 李桂花, 符梅, 罗文龙, 骆善伟, 陆美莲. 微生物有机肥对连作菜薹生长及土壤性质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 182-191. |
| [13] | 蒯雁, 苏欣悦, 王晋峰, 范志勇, 李建华, 孙楠, 张久权, 徐明岗. 大理典型烟区土壤有机质与全氮时空演变特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(12): 177-185. |
| [14] | 周婷, 孙松林, 朱海英, 彭才望. 含水率对黑水虻生物转化猪粪有机肥黏结流动的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(10): 126-136. |
| [15] | 吴红艳, 于淼, 冯健, 刘晖. 解磷生物肥对温室土壤磷有效性及辣椒产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(10): 189-197. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号