




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (2): 141-149.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0794
• 动植物健康 • 上一篇
金若珩( ), 李晓宇(
), 李晓宇( ), 姚经武, 王蓓蓓, 曹春霞(
), 姚经武, 王蓓蓓, 曹春霞( ), 黄大野(
), 黄大野( )
)
收稿日期:2023-10-31
接受日期:2024-01-18
出版日期:2025-02-15
发布日期:2025-02-14
通讯作者:
曹春霞,黄大野
作者简介:金若珩 E-mail:jinshirley@126.com基金资助:
Ruoheng JIN( ), Xiaoyu LI(
), Xiaoyu LI( ), Jingwu YAO, Beibei WANG, Chunxia CAO(
), Jingwu YAO, Beibei WANG, Chunxia CAO( ), Daye HUANG(
), Daye HUANG( )
)
Received:2023-10-31
Accepted:2024-01-18
Online:2025-02-15
Published:2025-02-14
Contact:
Chunxia CAO,Daye HUANG
摘要:
茶尺蠖(Ectropis obliqua)是茶叶上的重要害虫,给茶叶产业带来严重经济损失。苏云金芽孢杆菌(Bacillus thuringiensis, Bt)作为防治茶尺蠖的关键生物杀虫剂,在茶尺蠖的绿色防控中发挥重要作用。为明确Bt处理对茶尺蠖幼虫肠道菌群的影响,基于Illumina平台,采用16S rDNA高通量测序技术对不同水平Bt悬浮液处理的茶尺蠖幼虫肠道细菌的群落结构和种群多样性进行比较分析。结果表明,使用低剂量Bt处理茶尺蠖幼虫后,其肠道细菌组成与对照处理相比并未发生明显变化;但在较高剂量Bt处理下,茶尺蠖幼虫肠道细菌的群落多样性及丰度显著增加,表明茶尺蠖幼虫肠道细菌群落参与了对Bt侵染的响应。以上研究结果为深入探究Bt杀虫机制提供依据,并为提高Bt杀虫毒力提供新的思路。
中图分类号:
金若珩, 李晓宇, 姚经武, 王蓓蓓, 曹春霞, 黄大野. 苏云金芽孢杆菌对茶尺蠖肠道细菌多样性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(2): 141-149.
Ruoheng JIN, Xiaoyu LI, Jingwu YAO, Beibei WANG, Chunxia CAO, Daye HUANG. Effects of Bacillus thuringiensi on Intestinal Bacteria in Ectropis obliqua[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(2): 141-149.
处理 Treatment | OTU数量 Number of OTU | 门 Phylum | 纲 Class | 目 Order | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种 Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 153 | 6.33 | 7.67 | 18.00 | 25.33 | 39.33 | 8.00 |
| Bt50 | 200 | 8.00 | 10.33 | 21.33 | 27.67 | 41.00 | 10.67 |
| Bt100 | 137 | 6.67 | 8.33 | 17.67 | 24.00 | 32.33 | 11.00 |
| Bt200 | 125 | 5.67 | 7.00 | 16.33 | 22.00 | 27.00 | 11.00 |
表1 不同 Bt处理下茶尺蠖幼虫肠道细菌的组成
Table 1 Composition of intestinal bacteria in E. oblique larvae under different Bt treatments
处理 Treatment | OTU数量 Number of OTU | 门 Phylum | 纲 Class | 目 Order | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种 Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 153 | 6.33 | 7.67 | 18.00 | 25.33 | 39.33 | 8.00 |
| Bt50 | 200 | 8.00 | 10.33 | 21.33 | 27.67 | 41.00 | 10.67 |
| Bt100 | 137 | 6.67 | 8.33 | 17.67 | 24.00 | 32.33 | 11.00 |
| Bt200 | 125 | 5.67 | 7.00 | 16.33 | 22.00 | 27.00 | 11.00 |
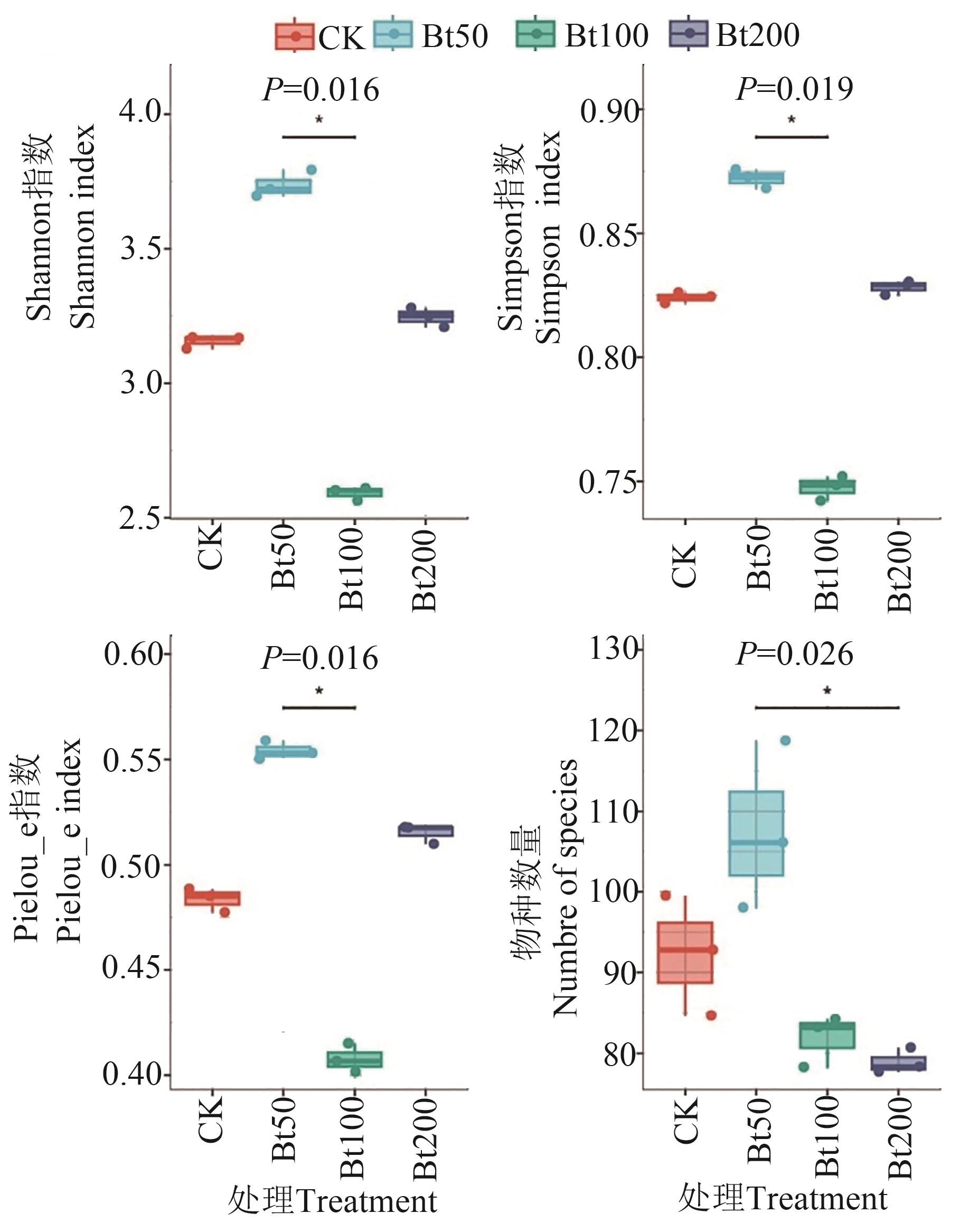
图3 不同处理茶尺蠖幼虫肠道细菌的Alpha多样性指数注:*表示在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 3 Alpha diversity of intestinal bacteria in of E. oblique larvae under different treatmentsNote: * indicates significant at P<0.05 level.

图5 不同Bt处理茶尺蠖肠道细菌种群的组成和丰度A~B:门水平;C~D:属水平
Fig. 5 Composition and abundance of intestinal bacterial populations in E. oblique under different treatmentsA~B: Phylum level; C~D: Genus level
| 1 | ENGEL P, MORAN N A. The gut microbiota of insects-diversity in structure and function [J]. FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 2013, 37(5):699-735. |
| 2 | PANG X J, XIAO X P, LIU Y, et al.. Mosquito C-type lectins maintain gut microbiome homeostasis [J/OL]. Nat. Microbiol., 2016, 1(5):16023 [2023-09-26]. . |
| 3 | PETERSON B F, SCHARF M E. Lower termite associations with microbes: synergy, protection, and interplay [J/OL]. Front. Microbiol., 2016, 7:422 [2023-09-26]. . |
| 4 | KIM J K, KIM N H, JANG H A, et al.. Specific midgut region controlling the symbiont population in an insect-microbe gut symbiotic association [J]. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2013, 79(23):7229-7233. |
| 5 | KURAISHI T, HORI A, KURATA S. Host-microbe interactions in the gut of Drosophila melanogaster [J/OL]. Front. Physiol., 2013, 4:375 [2023-09-26]. . |
| 6 | 黄云,詹先进,蓝家样,等.昆虫肠道微生物的研究进展[J].湖北农业科学,2009,48(11):2888-2890. |
| HUANG Y, ZHAN X J, LAN J Y, et al.. Research progress on intestinal tract microorganism of insect [J]. Hubei Agric. Sci., 2009, 48(11):2888-2890. | |
| 7 | 张振宇,圣平,黄胜威,等.昆虫肠道微生物的多样性、功能及应用[J].生物资源,2017,39(4):231-239. |
| ZHANG Z Y, SHENG P, HUANG S W, et al.. Diversity, function and application of insect gut microbiota [J]. Biotic Resour., 2017, 39(4):231-239. | |
| 8 | DOUGLAS A E. Multiorganismal insects: diversity and function of resident microorganisms [J]. Ann. Rev. Entomol., 2015, 60:17-34. |
| 9 | HAMMER T J, BOWERS M D. Gut microbes may facilitate insect herbivory of chemically defended plants [J]. Oecologia, 2015, 179(1):1-14. |
| 10 | DANTUR K I, ENRIQUE R, WELIN B, et al.. Isolation of cellulolytic bacteria from the intestine of Diatraea saccharalis larvae and evaluation of their capacity to degrade sugarcane biomass [J/OL]. AMB Express, 2015, 5:15 [2023-09-26]. . |
| 11 | MASON C J, LOWE-POWER T M, RUBERT-NASON K F, et al.. Interactions between bacteria and aspen defense chemicals at the phyllosphere-herbivore interface [J]. J. Chem. Ecol., 2016, 42(3):193-201. |
| 12 | 姚志超,白帅,张宏宇.昆虫肠道防御及微生物稳态维持机制[J].微生物学报,2018,58(6):1036-1048. |
| YAO Z C, BAI S, ZHANG H Y. Intestinal defense system and mechanism of maintenance of microbiota homeostasis in insects [J]. Acta Microbiol. Sin., 2018, 58(6):1036-1048. | |
| 13 | 王倩,刘玉升.蝗虫肠道微生物研究进展[J].微生物学通报,2023,50(7):3137-3145. |
| WANG Q, LIU Y S. Advances in locust gut microbiome [J]. Microbiology, 2023, 50(7):3137-3145. | |
| 14 | SCHNEPF E, CRICKMORE N, VAN RIE J, et al.. Bacillus thuringiensis and its pesticidal crystal proteins [J]. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 1998, 62(3):775-806. |
| 15 | 刘子铎,喻子牛.苏云金芽孢杆菌及其杀虫晶体蛋白作用机制的研究进展[J].昆虫学报,2000,43(2):207-213. |
| LIU Z D, YU Z N. Progress in the studies on the action mechanism of Bacillus thuringiensis and insecticidal crystal protein [J]. Acta Entomol. Sin., 2000, 43(2):207-213. | |
| 16 | ZHANG S, LUO J Y, JIANG W L, et al.. Response of the bacterial community of Propylea japonica (Thunberg) to Cry2Ab protein [J/OL]. Environ. Pollut., 2019, 254:113063 [2023-09-26]. . |
| 17 | 葛超美,殷坤山,唐美君,等.灰茶尺蠖的生物学特性[J].浙江农业学报,2016,28(3):464-468. |
| GE C M, YIN K S, TANG M J, et al.. Biological characteristics of Ectropis grisescens Warren [J]. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis, 2016, 28(3):464-468. | |
| 18 | 王业胜.茶叶害虫茶尺蠖的识别与防治[J].农业灾害研究,2015,5(8):6-8, 17. |
| WANG Y S. Study on identification and control method of tea pest Ectropis oblique hypulina Wehrli [J]. J. Agric. Catastrophol., 2015, 5(8):6-8, 17. | |
| 19 | 陈雨思,周孝贵,曾维健,等.不同茶园灰茶尺蠖和茶尺蠖对5种杀虫剂的抗药性监测[J].环境昆虫学报,2023,45(4):1103-1110. |
| CHEN Y S, ZHOU X G, ZENG W J, et al.. Resistance monitoring of two tea geometrid moths (Ectropis obliqua and E. grisescens) to five frequently used insecticides in different tea plantations [J]. J. Environ. Entomol., 2023, 45(4):1103-1110. | |
| 20 | 李红莉,崔宏春,余继忠.茶尺蠖生物学特性及防治技术研究现状[J].安徽农业科学,2017,45(19):150-151, 233. |
| LI H L, CUI H C, YU J Z. Research advances in biological characteristic and controlling of Ectropiso blique (Prout) [J]. J. Anhui Agric. Sci., 2017, 45(19):150-151, 233. | |
| 21 | 陈宗懋.茶园有害生物绿色防控技术发展与应用[J].中国茶叶,2022,44(1):1-6. |
| CHEN Z M. Development and application of green pest control technology in tea garden [J]. China Tea, 2022, 44(1):1-6. | |
| 22 | 李晓宇,黄大野,华登科,等.植保无人机喷施BT与藜芦碱混配药剂对灰茶尺蠖和小贯小绿叶蝉防治效果研究[J].现代农业科技,2021(20):89-91, 105. |
| LI X Y, HUANG D Y, HUA D K, et al.. Control effect of BT and veratrine mixture sprayed by plant protection UAV on Ectropis grisescens and Empoasca onukii [J]. Modern Agric. Sci. Technol., 2021(20):89-91, 105. | |
| 23 | 林荣华,倪珏萍,姜辉,等. 农药室内生物测定试验准则 杀虫剂第14部分:浸叶法: [S].北京:中国农业出版社,2008. |
| 24 | GUO Z M, JIN R H, GUO Z P, et al.. Insecticide susceptibility and mechanism of Spodoptera frugiperda on different host plants [J]. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2022, 70:11367-11376. |
| 25 | 姜玮瑜,梁革梅,林毅,等.对Bt蛋白抗性和敏感的棉铃虫中肠细菌群落的比较[J].微生物学报,2010,50(6):828-834. |
| JIANG W Y, LIANG G M, LIN Y, et al.. Comparison of midgut bacterial community between Bt resistant and sensitive Helicoverpa armigera [J]. Acta Microbiol. Sin., 2010, 50(6):828-834. | |
| 26 | 杨焊.四种鳞翅目害虫肠道细菌多样性分析[D].南京:南京农业大学,2012. |
| YANG H. Diversity of gut bacteria in larval of four Lepidopteran insect species [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricutural University, 2012. | |
| 27 | 吴丽红.寄主植物对草地贪夜蛾发育与繁殖、交配行为及肠道微生物的影响[D].贵阳:贵州大学,2022. |
| WU L H. Effects of host plants on the development, reproduction, mating behavior and gut microbiota of fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) [D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2022. | |
| 28 | 廖春丽,袁源,李绍冲,等.昆虫病原线虫共生菌NK杀虫蛋白处理后大蜡螟幼虫中肠细菌群落的变化[J].河南城建学院学报,2022,31(2):85-92. |
| LIAO C L, YUAN Y, LI S C, et al.. Change in diversity of bacterial community in larval midguts of Galleria mellonella after treatment with insecticidal proteins of symbiotic bacteria NK of entomopathogenic nematodes [J]. J. Henan Univ. Urban Construct., 2022, 31(2):85-92. | |
| 29 | BRODERICK N A, RAFFA K F, GOODMAN R M, et al.. Census of the bacterial community of the gypsy moth larval midgut by using culturing and culture-independent methods [J]. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2004, 70(1):293-300. |
| 30 | JOHNSTON P R, CRICKMORE N. Gut bacteria are not required for the insecticidal activity of Bacillus thuringiensis toward the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta [J]. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2009, 75(15):5094-5099. |
| 31 | 赵天宇.茶尺蠖幼虫肠道细菌与联苯菊酯抗药性间关系的研究[D].合肥:安徽农业大学,2020. |
| ZHAO T Y. Study on the relationship between gut bacteria of Ectropis obliqua larva and bifenthrin resistance [D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricutural University, 2020. | |
| 32 | WERREN J H. Biology of Wolbachia [J]. Annu. Rev. Entomol., 1997, 42:587-609. |
| 33 | WERREN J H, WINDSOR D M. Wolbachia infection frequencies in insects: evidence of a global equilibrium? [J]. The Royal Soc. Proc. B, 2000,267(1450):1277-1285. |
| 34 | BI J, WANG Y F. The effect of the endosymbiont Wolbachia on the behavior of insect hosts [J]. Insect Sci., 2020, 27(5):846-858. |
| 35 | BOURTZIS K, PETTIGREW M M, O'NEILL S L. Wolbachia neither induces nor suppresses transcripts encoding antimicrobial peptides [J]. Insect Mol. Biol., 2000, 9(6):635-639. |
| 36 | RAINEY S M, SHAH P, KOHL A, et al.. Understanding the Wolbachia mediated inhibition of arboviruses in mosquitoes: progress and challenges [J]. J. Gen. Virol., 2014, 95:517-530. |
| 37 | 郎晓磊.肠道菌对苏云金芽胞杆菌家蚕杀虫活性的作用[D].武汉:华中农业大学,2010. |
| LANG X L. Effects of gut bacteria to the insecticidal activity of Bacillus thuringiensis toward silkworm larvae [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricutural University, 2010. | |
| 38 | RAYMOND B, JOHNSTON P R, WRIGHT D J, et al.. A mid-gut microbiota is not required for the pathogenicity of Bacillus thuringiensis to diamondback moth larvae [J]. Enviorn. Microbiol., 2009, 11:2556-2563. |
| 39 | 朱翔宇,尤士骏,刘天生,等.节肢动物内共生菌Wolbachia的研究进展[J].昆虫学报,2020,63(7):889-901. |
| ZHU X Y, YOU S J, LIU T S, et al.. Research progress on Wolbachia endosymbionts in arthropods [J]. Acta Entomol. Sin., 2020, 63(7):889-901. | |
| 40 | GONG J T, LI Y, LI T P, et al.. Stable introduction of plant-virus-inhibiting Wolbachia into planthoppers for rice protection [J]. Curr. Biol., 2020, 30(24):4837-4845. |
| 41 | XIAO Y, CHEN H, WANG H, et al.. Structural and mechanistic insights into the complexes formed by Wolbachia cytoplasmic incompatibility factors [J/OL]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2021, 118(41):e2107699118 [2023-09-26]. . |
| [1] | 季梦婷, 陈长江, 罗流河, 林志坚, 詹梦琳, 杨丙烨, 胡方平, 蔡学清. 福建猕猴桃细菌性枯萎病的病原菌鉴定[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(4): 144-152. |
| [2] | 危潇, 曹春霞, 黄大野, 姚经武, 袁勤峰. 木霉菌生防作用机制及协同防病的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(11): 126-135. |
| [3] | 常峻嘉, 盖佳鑫, 陶刚, 莫转龙海. 哈茨木霉菌对烟草的促生及其黑胫病的诱导抗性评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(10): 168-176. |
| [4] | 冯雪莹, 王路宽, 黄玉翠, 杨春萍, 徐海云. 发育高温对烟粉虱及其优势寄生蜂适合度和同步性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 131-138. |
| [5] | 金辉, 王伟, 颜尘栋, 王薇, 李熙英. 水稻纹枯病生防木霉菌分离鉴定及适应性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(9): 139-148. |
| [6] | 林志坚, 陈长江, 周挺, 顾钢, 胡方平, 李春英, 蔡学清. 青枯菌噬菌体RPZH6株系对烟草青枯病的生防效果及全基因组测序分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(10): 133-142. |
| [7] | 赵兴丽1,陶刚2,3*,娄璇4,顾金刚5*. 钩状木霉在辣椒根际定殖动态及其对辣椒疫病的生物防治[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(5): 106-114. |
| [8] | 周红姿1,周方园1,赵晓燕1,吴翠霞2,张广志1,苑伟伟3,吴晓青1,谢雪迎1,范素素1,张新建1*. 小麦赤霉病生防菌的筛选及其田间防效研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(1): 67-77. |
| [9] | 路露1,2,张孟丽2,狄怡琳2,朱凯1*,石宝俊2*. 百里香酚对不同时期秀丽线虫杀虫效果探究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(9): 97-103. |
| [10] | 吴晓青1,赵晓燕1,徐元章2,王加宁1,周方园1,周红姿1,张广志1,谢雪迎1,颜坤3,张新建1*. 植物生物防治精准化施药技术的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(3): 13-21. |
| [11] | 曾俊棋,岳万福*. 454焦磷酸测序技术对不同猪种肠道菌群差异的分析(英文)[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2015, 17(6): 44-49. |
| [12] | 程亮1,2,郭青云1,2*. 燕麦镰刀菌GD\|2菌株作为生物除草剂的潜力研究(英文)[J]. , 2014, 16(3): 70-80. |
| [13] | 宋培勇,郑亚强,李斌,肖仲久. 赤水河流域土壤放线菌及其拮抗活性研究[J]. , 2013, 15(1): 136-143. |
| [14] | 王友娟,李荣峰,李华,李强,徐祥. 辽宁地区养殖淡水鱼感染嗜水气单胞菌的流行病学调查[J]. , 2012, 14(4): 128-134. |
| [15] | 邱德文. 生物农药与生物防治发展战略浅谈[J]. , 2011, 13(5): 88-92. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号