




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (5): 193-202.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0960
赵昕1,2( ), 吴子龙1,2, 韩超1,2, 张浩1,2(
), 吴子龙1,2, 韩超1,2, 张浩1,2( ), 宋炜3, 李子怡1,2
), 宋炜3, 李子怡1,2
收稿日期:2023-12-27
接受日期:2024-04-22
出版日期:2025-05-15
发布日期:2025-05-20
通讯作者:
张浩
作者简介:赵昕 E-mail: zhaoxinmdj@126.com;
基金资助:
Xin ZHAO1,2( ), Zilong WU1,2, Chao HAN1,2, Hao ZHANG1,2(
), Zilong WU1,2, Chao HAN1,2, Hao ZHANG1,2( ), Wei SONG3, Ziyi LI1,2
), Wei SONG3, Ziyi LI1,2
Received:2023-12-27
Accepted:2024-04-22
Online:2025-05-15
Published:2025-05-20
Contact:
Hao ZHANG
摘要:
为研究丛枝菌根(arbuscular mycorrhizal,AM)真菌对重金属胁迫下植物生长的影响,在不同镉(Cd)水平(0 、10、30、50 mg·kg-1)下用AM真菌摩西斗管囊霉(Funneliformis mosseae)对狗尾草进行接种处理,探讨重金属污染对宿主与AM真菌共生的影响,以及AM真菌对狗尾草生长、光合特性和Cd吸收富集的影响。结果表明,同一Cd水平胁迫下,AM真菌显著提高了狗尾草的株高、叶绿素含量、净光合速率、蒸腾速率、气孔导度、表观量子效率和生物量。当Cd水平为50 mg·kg-1时,与未接种对照相比,接种AM处理的狗尾草株高、总叶绿素含量、净光合速率、蒸腾速率、气孔导度、表观量子效率和生物量分别显著提高51%、24%、33%、33%、26%、45%和51%(P<0.05)。同一Cd水平胁迫下,AM真菌显著增加了狗尾草根部Cd含量、地上部Cd富集量、根部Cd富集量及Cd富集系数(P<0.05)。当Cd为50 mg·kg-1时,与未接种对照相比,接种AM处理的狗尾草根部Cd含量、地上部Cd富集量、根部Cd富集量分别提高39%、18%、100%,显著促进了狗尾草对Cd的吸收和富集。研究结果为AM真菌-狗尾草联合修复Cd污染土壤提供参考。
中图分类号:
赵昕, 吴子龙, 韩超, 张浩, 宋炜, 李子怡. 丛枝菌根真菌对镉胁迫下狗尾草生长及镉富集的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(5): 193-202.
Xin ZHAO, Zilong WU, Chao HAN, Hao ZHANG, Wei SONG, Ziyi LI. Effects of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi on Growth and Cadmium Enrichment of Setaria viridis Under Cadmium Stress[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(5): 193-202.
处理 Treatment | 菌根侵染率 Mycorrhizal infection rate/% | 株高 Plant height/cm | 生物量/(g·盆-1) Biomass/(g·pot-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Cd处理前 Before Cd treatment | Cd处理后 After Cd treatment | 地上部 Aboveground | 根 Root | 全株 Whole plant | ||
| NM0 | 0.00±.0.00 | 0.00±0.00 d | 41.93±1.12 b | 19.40±0.62 b | 12.77±0.65 b | 32.17±1.26 b |
| NM10 | — | 0.00±0.00 d | 41.50±0.80 b | 18.57±0.57 b | 11.87±0.65 bc | 30.43±0.76 bc |
| NM30 | — | 0.00±0.00 d | 30.50±1.35 c | 10.47±0.40 d | 8.13±0.40 c | 18.60±0.80 c |
| NM50 | — | 0.00±0.00 d | 20.80± 0.56 d | 6.33± 0.06 e | 5.50±0.36 d | 11.83±0.42 d |
| AM0 | 43.80±1.87 | 53.70±1.28 a | 53.47±0.78 a | 26.50±1.59 a | 15.83±0.40 a | 42.33±1.96 a |
| AM10 | — | 52.60±0.82 a | 52.70±1.73 a | 25.30±1.31 a | 15.63±0.42 a | 40.93±1.42 a |
| AM30 | — | 38.80±1.59 b | 40.57±1.19 b | 17.13±0.85 c | 11.23±0.85 b | 28.37±1.68 c |
| AM50 | — | 25.40±0.89 c | 31.50±1.11 c | 10.00±0.36 d | 7.90± 0.46 c | 17.90±0.82 c |
| 菌根菌AM | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| 镉Cd | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| 菌根菌×镉AM×Cd | ** | ** | ns | ** | ns | * |
表1 不同处理下狗尾草菌根侵染率和生长情况
Table 1 Mycorrhizal infection rate and growth of Setaria viridis under different treatments
处理 Treatment | 菌根侵染率 Mycorrhizal infection rate/% | 株高 Plant height/cm | 生物量/(g·盆-1) Biomass/(g·pot-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Cd处理前 Before Cd treatment | Cd处理后 After Cd treatment | 地上部 Aboveground | 根 Root | 全株 Whole plant | ||
| NM0 | 0.00±.0.00 | 0.00±0.00 d | 41.93±1.12 b | 19.40±0.62 b | 12.77±0.65 b | 32.17±1.26 b |
| NM10 | — | 0.00±0.00 d | 41.50±0.80 b | 18.57±0.57 b | 11.87±0.65 bc | 30.43±0.76 bc |
| NM30 | — | 0.00±0.00 d | 30.50±1.35 c | 10.47±0.40 d | 8.13±0.40 c | 18.60±0.80 c |
| NM50 | — | 0.00±0.00 d | 20.80± 0.56 d | 6.33± 0.06 e | 5.50±0.36 d | 11.83±0.42 d |
| AM0 | 43.80±1.87 | 53.70±1.28 a | 53.47±0.78 a | 26.50±1.59 a | 15.83±0.40 a | 42.33±1.96 a |
| AM10 | — | 52.60±0.82 a | 52.70±1.73 a | 25.30±1.31 a | 15.63±0.42 a | 40.93±1.42 a |
| AM30 | — | 38.80±1.59 b | 40.57±1.19 b | 17.13±0.85 c | 11.23±0.85 b | 28.37±1.68 c |
| AM50 | — | 25.40±0.89 c | 31.50±1.11 c | 10.00±0.36 d | 7.90± 0.46 c | 17.90±0.82 c |
| 菌根菌AM | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| 镉Cd | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| 菌根菌×镉AM×Cd | ** | ** | ns | ** | ns | * |
处理 Treatment | 叶绿素a Chlorophyll a | 叶绿素b Chlorophyll b | 总叶绿素 Total chlorophyll | 类胡萝卜素 Carotenoids |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NM0 | 1.42±0.02 b | 0.29±0.01 ab | 1.71±0.03 c | 0.56±0.02 b |
| NM10 | 1.40±0.02 b | 0.28±0.01 b | 1.68±0.03 c | 0.54±0.01 b |
| NM30 | 1.22±0.04 c | 0.21±0.02 d | 1.43±0.05 d | 0.44±0.01 d |
| NM50 | 1.00±0.03 d | 0.13±0.02 e | 1.13±0.03 e | 0.36±0.02 e |
| AM0 | 1.75±0.02 a | 0.33±0.02 a | 2.08±0.02 a | 0.63±0.02 a |
| AM10 | 1.70±0.02 a | 0.31±0.01 ab | 2.01±0.02 b | 0.62±0.01 a |
| AM30 | 1.42±0.02 b | 0.26±0.01 c | 1.67±0.03 a | 0.55±0.01 ab |
| AM50 | 1.20±0.03 c | 0.19±0.02 d | 1.40±0.04 d | 0.47± 0.01 c |
| 菌根菌AM | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| 镉Cd | ** | ** | ** | ** |
菌根菌×镉 AM×Cd | ** | ns | ** | * |
表 2 不同处理下狗尾草的叶绿素含量 (mg·g-1)
Table 2 Chlorophyll content of Setaria viridis under different treatments
处理 Treatment | 叶绿素a Chlorophyll a | 叶绿素b Chlorophyll b | 总叶绿素 Total chlorophyll | 类胡萝卜素 Carotenoids |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NM0 | 1.42±0.02 b | 0.29±0.01 ab | 1.71±0.03 c | 0.56±0.02 b |
| NM10 | 1.40±0.02 b | 0.28±0.01 b | 1.68±0.03 c | 0.54±0.01 b |
| NM30 | 1.22±0.04 c | 0.21±0.02 d | 1.43±0.05 d | 0.44±0.01 d |
| NM50 | 1.00±0.03 d | 0.13±0.02 e | 1.13±0.03 e | 0.36±0.02 e |
| AM0 | 1.75±0.02 a | 0.33±0.02 a | 2.08±0.02 a | 0.63±0.02 a |
| AM10 | 1.70±0.02 a | 0.31±0.01 ab | 2.01±0.02 b | 0.62±0.01 a |
| AM30 | 1.42±0.02 b | 0.26±0.01 c | 1.67±0.03 a | 0.55±0.01 ab |
| AM50 | 1.20±0.03 c | 0.19±0.02 d | 1.40±0.04 d | 0.47± 0.01 c |
| 菌根菌AM | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| 镉Cd | ** | ** | ** | ** |
菌根菌×镉 AM×Cd | ** | ns | ** | * |
处理 Treatment | 净光合速率 Pn/(μmol·m-2·s-1) | 蒸腾速率 Tr/(mmol·m-2·s-1) | 气孔导度 Gs/(mol·m-2·s-1) | 胞间CO2浓度 Ci/(μmol·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NM0 | 11.00±0.36 b | 1.70±0.04 b | 159.33±1.53 b | 257.33±1.53 d |
| NM10 | 10.63±0.15 bc | 1.66±0.03 b | 157.00±3.00 b | 260.67±2.52 d |
| NM30 | 9.43±0.50 c | 1.39±0.05 c | 132.33±3.06 c | 273.00±1.00 c |
| NM50 | 7.63±0.15 d | 1.06±0.04 d | 104.33±4.16 d | 313.33±4.16 a |
| AM0 | 12.97±0.60 a | 1.97±0.06 a | 181.67±6.03 a | 233.67±2.52 d |
| AM10 | 12.47±0.55 a | 1.92±0.05 a | 181.33±3.05 a | 238.67±2.08 d |
| AM30 | 11.10±0.26 b | 1.69±0.02 b | 153.00±4.00 b | 257.67±4.04 d |
| AM50 | 10.13±0.29 bc | 1.41±0.09 c | 131.77±4.73 c | 284.33±6.43 b |
| 菌根菌AM | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| 镉Cd | ** | ** | ** | ** |
菌根菌×镉 AM×Cd | ns | ns | ns | * |
表 3 不同处理下的狗尾草光合参数
Table 3 Photosynthetic parameter of Setaria viridis under different treatments
处理 Treatment | 净光合速率 Pn/(μmol·m-2·s-1) | 蒸腾速率 Tr/(mmol·m-2·s-1) | 气孔导度 Gs/(mol·m-2·s-1) | 胞间CO2浓度 Ci/(μmol·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NM0 | 11.00±0.36 b | 1.70±0.04 b | 159.33±1.53 b | 257.33±1.53 d |
| NM10 | 10.63±0.15 bc | 1.66±0.03 b | 157.00±3.00 b | 260.67±2.52 d |
| NM30 | 9.43±0.50 c | 1.39±0.05 c | 132.33±3.06 c | 273.00±1.00 c |
| NM50 | 7.63±0.15 d | 1.06±0.04 d | 104.33±4.16 d | 313.33±4.16 a |
| AM0 | 12.97±0.60 a | 1.97±0.06 a | 181.67±6.03 a | 233.67±2.52 d |
| AM10 | 12.47±0.55 a | 1.92±0.05 a | 181.33±3.05 a | 238.67±2.08 d |
| AM30 | 11.10±0.26 b | 1.69±0.02 b | 153.00±4.00 b | 257.67±4.04 d |
| AM50 | 10.13±0.29 bc | 1.41±0.09 c | 131.77±4.73 c | 284.33±6.43 b |
| 菌根菌AM | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| 镉Cd | ** | ** | ** | ** |
菌根菌×镉 AM×Cd | ns | ns | ns | * |
处理 Treatment | 表观量子效率 AQY | 暗呼吸速率 Rd/(μmol·m-2·s-1) | 最大净光合速率 Pmax/(μmol·m-2·s-1) | 光补偿点 LCP/(μmol·m-2·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NM0 | 0.043±0.002 d | 1.367±0.080 c | 20.925±0.124 c | 32.024±0.866 c |
| NM10 | 0.041±0.004 d | 1.160±0.066 d | 23.311±0.486 b | 28.162±2.374 cd |
| NM30 | 0.040±0.005 d | 1.870±0.088 b | 19.878±0.791 c | 46.591±3.281 b |
| NM50 | 0.038±0.003 d | 2.792±0.130 a | 13.325±0.316 d | 74.192±1.520 a |
| AM0 | 0.084±0.009 a | 0.788±0.158 e | 31.566±0.778 a | 9.326±0.904 d |
| AM10 | 0.079±0.007 a | 0.705±0.066 e | 31.690±0.435 a | 8.966±0.125 d |
| AM30 | 0.065±0.005 b | 1.841±0.160 b | 24.448±0.601 b | 28.445±0.683 cd |
| AM50 | 0.055±0.002 c | 2.601±0.022 a | 15.512±0.276 e | 47.216±3.385 b |
| 菌根菌AM | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| 镉Cd | ** | ** | ** | ** |
菌根菌×镉 AM×Cd | ** | ** | ** | ** |
表4 不同处理下的狗尾草净光合速率光响应曲线模拟参数
Table 4 Parameters of net photosynthetic rate and light response curve of Setaria viridis under different treatments
处理 Treatment | 表观量子效率 AQY | 暗呼吸速率 Rd/(μmol·m-2·s-1) | 最大净光合速率 Pmax/(μmol·m-2·s-1) | 光补偿点 LCP/(μmol·m-2·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NM0 | 0.043±0.002 d | 1.367±0.080 c | 20.925±0.124 c | 32.024±0.866 c |
| NM10 | 0.041±0.004 d | 1.160±0.066 d | 23.311±0.486 b | 28.162±2.374 cd |
| NM30 | 0.040±0.005 d | 1.870±0.088 b | 19.878±0.791 c | 46.591±3.281 b |
| NM50 | 0.038±0.003 d | 2.792±0.130 a | 13.325±0.316 d | 74.192±1.520 a |
| AM0 | 0.084±0.009 a | 0.788±0.158 e | 31.566±0.778 a | 9.326±0.904 d |
| AM10 | 0.079±0.007 a | 0.705±0.066 e | 31.690±0.435 a | 8.966±0.125 d |
| AM30 | 0.065±0.005 b | 1.841±0.160 b | 24.448±0.601 b | 28.445±0.683 cd |
| AM50 | 0.055±0.002 c | 2.601±0.022 a | 15.512±0.276 e | 47.216±3.385 b |
| 菌根菌AM | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| 镉Cd | ** | ** | ** | ** |
菌根菌×镉 AM×Cd | ** | ** | ** | ** |
处理 Treatment | 地上部Cd含量 Aboveground Cd content | 根部Cd含量 Cd content in root | 全株Cd含量Cd content in plant | 土壤Cd含量 Cd content in soil | 地上部Cd富集量 Aboveground Cd enrichment/mg | 根部Cd富集量 Root Cd enrichment/mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NM0 | 0.02±0.01 f | 0.06±0.01 g | 0.04±0.00 g | 0.05±0.01 g | 0.45±0.10 h | 0.72±0.05 g |
| NM10 | 0.82±0.04 e | 1.05±0.03 f | 0.91± 0.02 f | 0.94±0.02 e | 15.18± 1.22 f | 12.51±1.04 e |
| NM30 | 8.51±0.55 c | 10.17±0.04 d | 9.24±0.31 d | 9.41±0.16 c | 89.03±6.57 d | 82.73±3.80 c |
| NM50 | 24.64±2.10 a | 35.34±1.09 b | 29.62±1.58 b | 35.00±0.43 a | 156.05±13.20 b | 194.38±14.36 b |
| AM0 | 0.03±0.01 f | 0.09±0.01 g | 0.05± 0.01 g | 0.05±0.01 g | 0.88± 0.12 g | 1.37±0.07 f |
| AM10 | 0.72±0.04 e | 1.68±0.07 e | 1.09±0.05 e | 0.78±0.04 f | 18.31±1.46 e | 26.23±1.70 d |
| AM30 | 6.36±0.16 d | 16.72±0.29 c | 10.46±0.07 c | 7.99±0.08 d | 108.88±2.66 c | 187.90±16.86 b |
| AM50 | 18.47± 0.24 b | 49.17±0.51 a | 32.02±0.18 a | 23.61± 0.46 b | 184.69±4.92 a | 388.49± 23.91 a |
| 菌根菌AM | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| 镉Cd | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
菌根菌×镉 AM×Cd | ** | ** | ns | ** | ns | ns |
表5 不同处理下的狗尾草Cd富集 (mg·g-1)
Table 5 Cd enrichment of Setaria viridis under different treatments
处理 Treatment | 地上部Cd含量 Aboveground Cd content | 根部Cd含量 Cd content in root | 全株Cd含量Cd content in plant | 土壤Cd含量 Cd content in soil | 地上部Cd富集量 Aboveground Cd enrichment/mg | 根部Cd富集量 Root Cd enrichment/mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NM0 | 0.02±0.01 f | 0.06±0.01 g | 0.04±0.00 g | 0.05±0.01 g | 0.45±0.10 h | 0.72±0.05 g |
| NM10 | 0.82±0.04 e | 1.05±0.03 f | 0.91± 0.02 f | 0.94±0.02 e | 15.18± 1.22 f | 12.51±1.04 e |
| NM30 | 8.51±0.55 c | 10.17±0.04 d | 9.24±0.31 d | 9.41±0.16 c | 89.03±6.57 d | 82.73±3.80 c |
| NM50 | 24.64±2.10 a | 35.34±1.09 b | 29.62±1.58 b | 35.00±0.43 a | 156.05±13.20 b | 194.38±14.36 b |
| AM0 | 0.03±0.01 f | 0.09±0.01 g | 0.05± 0.01 g | 0.05±0.01 g | 0.88± 0.12 g | 1.37±0.07 f |
| AM10 | 0.72±0.04 e | 1.68±0.07 e | 1.09±0.05 e | 0.78±0.04 f | 18.31±1.46 e | 26.23±1.70 d |
| AM30 | 6.36±0.16 d | 16.72±0.29 c | 10.46±0.07 c | 7.99±0.08 d | 108.88±2.66 c | 187.90±16.86 b |
| AM50 | 18.47± 0.24 b | 49.17±0.51 a | 32.02±0.18 a | 23.61± 0.46 b | 184.69±4.92 a | 388.49± 23.91 a |
| 菌根菌AM | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| 镉Cd | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
菌根菌×镉 AM×Cd | ** | ** | ns | ** | ns | ns |
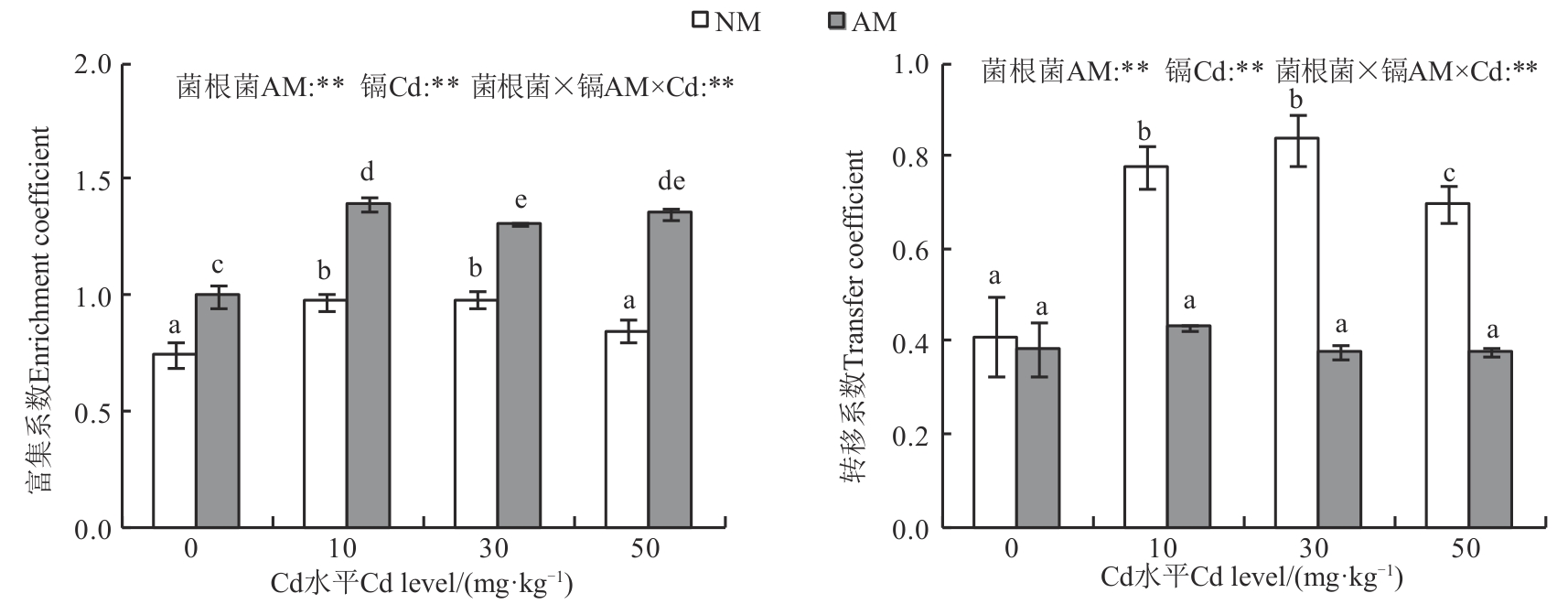
图2 Cd胁迫下AM真菌对狗尾草Cd富集特性的影响注:不同小写字母表示在P<0.05水平差异显著;**代表在P<0.01水平显著。
Fig. 2 Effects of AMF on Cd enrichment characteristics in Setaria viridis under Cd stressNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at P<0.05 level; ** indicates significant at P<0.01 level.
| 1 | 王雪蓉,梁如玉,王玉龙, 等. 重金属胁迫下丛枝菌根真菌对白茅生长和生理生态特征的影响[J]. 山西大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 46(2): 439-448. |
| WANG X R, LIANG R Y, WANG Y L, et al.. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth and ecophysiological characteristics of Imperata cylindrica under heavy metal stress [J]. J. Shanxi Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2023, 46(2): 439-448. | |
| 2 | 何红君. 丛枝菌根真菌接种对Cd胁迫下芹菜生长、生理及富集特征的影响[J]. 东北农业科学, 2020, 45(3): 70-75. |
| HE H J. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculation on the growth, physiology and accumulation characteristics of celery (Apium graveolens L.) under cadmium stress [J]. J. Northeast Agric. Sci.,2020, 45(3): 70-75. | |
| 3 | VECCHIA F D, ROCCA N L, MORO I, et al.. Morphogenetic, ultra structural and physiological damages suffered by submerged leaves of Elodea canadensis exposed to cadmium [J]. Plant Sci., 2005, 168(2): 329-338. |
| 4 | EDELSTEIN M, BEN-HUR M. Heavy metals and metalloids: sources, risks and strategies to reduce their accumulation in horticultural crops [J]. Sci. Hortic.,2018, 234(4): 431-444. |
| 5 | 赖秋羽, 魏树和, 代惠萍, 等. 番茄光合荧光特性及其镉吸收对土壤镉污染的响应[J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(11): 4737-4742. |
| LAI Q Y, WEI S H, DAI H P, et al.. Response of photosynthetic characteristics and fluorescence parameters of tomato to Cd in soil [J]. China Environ. Sci., 2019, 39(11): 4737-4742 | |
| 6 | 黄蕊, 辛建攀, 田如男. 镉胁迫下大薸生长的变化及镉积累、分布特征[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2022,41(9): 2033-2042. |
| HUANG R, XIN J P, TIAN R N. Growth changes and characteristics of cadmium accumulation and distribution in Pistia stratiotes under cadmium stress [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2022, 41(9): 2033-2042. | |
| 7 | 徐金玉, 王伟伟, 王惠, 等. 铜污染土壤的生物修复研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2020, 36(3): 471-480. |
| XU J Y, WANG W W, WANG H, et al.. Progress in bioremediation of copper-contaminated soils [J]. Chin. J. Biotechnol.,2020, 36(3): 471-480. | |
| 8 | 李琋, 王雅璇, 罗廷, 等. 利用生物炭负载微生物修复石油烃-镉复合污染土壤[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15 (2): 677-687. |
| LI X, WANG Y X, LUO T, et al.. Remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon-cadmium co-contaminated soil by biochar loaded microorganisms [J]. Chin. J. Environ. Eng.,2021, 15(2): 677-687. | |
| 9 | GONZÁLEZ-CHÁVEZ M D C A, CARRILLO-GONZÁLEZ R, CUELLAR-SÁNCHEZ A, et al.. Phytoremediation assisted by mycorrhizal fungi of a mexican defunct lead-acid battery recycling site [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2019, 650: 3134- 3144. |
| 10 | ZHANG X Y, ZHANG H J, ZHANG Y X, et al.. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi alter carbohydrate distribution and amino acid accumulation in Medicago truncatula under lead stress [J/OL]. Environ. Exp. Bot., 2020,171:103950 [2023-11-26]. . |
| 11 | BEGUM N, AHANGER M A, ZHANG L X. AMF inoculation and phosphorus supplementation alleviates drought induced growth and photosynthetic decline in Nicotiana tabacum by up-regulating antioxidant metabolism and osmolyte accumulation [J/OL]. Environ. Exp. Bot., 2020, 176:104088 [2023-11-26].. |
| 12 | CROSSAY T, CAVALOC Y, MAJOREL C, et al.. Combinations of different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi improve fitness and metal tolerance of sorghum in ultramafic soil [J/OL]. Rhizosphere, 2020, 14:100204 [2023-11-26]. . |
| 13 | 许隽, 胡浩, 曾艳, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌对镉胁迫水稻秧苗生长发育的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 49(10):30-35, 45. |
| XU J, HU H, ZENG Y, et al.. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the growth and development of rice seedings under cadmium stress [J]. J. Northwest A&F Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2021, 49(10): 30-35, 45. | |
| 14 | 王立, 安广楠, 马放, 等. AMF 对镉污染条件下水稻抗逆性及根际固定性的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2014, 33(10): 1882-1889. |
| WANG L, AN G N, MA F, et al.. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on cadmium tolerance and rhizospheric fixation of rice [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2014, 33(10): 1882-1889. | |
| 15 | 田野,张会慧,孟祥英, 等. 镉(Cd)污染土壤接种丛枝菌根真菌(Glomus mosseae)对黑麦草生长和光合的影响[J]. 草地学报, 2013, 21(1):135-141. |
| TIAN Y, ZHANG H H, MENG X Y, et al.. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (Glomus mosseae) on growth and photosynthesis characteristics of Lolium perenne L. under Cd contaminated soil [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2013, 21(1):135-141. | |
| 16 | BRUTNELL T P, BENNETZEN J L, VOGEL J P. Brachypodium distachyon and Setaria viridis: model genetic systems for the grasses [J]. Ann. Rev. Plant Biol., 2015, 66: 465-485. |
| 17 | BRUTNELL T P. Model grasses hold key to crop improvement [J/OL]. Nat. Plants, 2015, 1: 15062 [2023-11-26]. . |
| 18 | KAZNINA N M, TITOV A F, LAIDINEN G F, et al. Setaria viridis tolerance of high zine concentrations [J]. Biol. Bull., 2009, 36(11):575-580. |
| 19 | 王振艳, 丁军, 孙向辉, 等. 七种本土植物对土壤中镉的富集效果比较研究[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2020, 59(12): 61-64. |
| WANG Z Y, DING J, SUN X H, et al.. Comparative study on the soil cadmium enrichment effects of seven indigenous plant species [J]. Hubei Agric. Sci., 2020, 59(12): 61-64. | |
| 20 | 张丽, 彭重华, 王莹雪, 等. 14种植物对土壤重金属的分布、富集及转运特性[J]. 草业科学, 2014, 31(5): 833- 838. |
| ZHANG L, PENG C H, WANG Y X, et al.. Heavy metal distribution bioaccumulation and translocation characteristics of fourteen plants [J]. Pratac. Sci., 2014, 31(5): 833- 838. | |
| 21 | GIOVANNETTI M, MOSSE B. An evalution of technique for measuring vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal infection in root [J]. New Phytol., 1980, 84(3): 489-500. |
| 22 | PIRIE A, MULLINS M G. Changes in anthocyanin and phenolics content of grapevine leaf and fruit tissues treated with sucrose, nitrate, and abscisic acid [J]. Plant Physiol., 1976, 58(4): 468-472. |
| 23 | 张中峰, 尤业明, 黄玉清, 等. 模拟岩溶水分供应分层的干旱胁迫对青冈栎光合特性和生长的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2012, 31(9):2197-2202. |
| ZHANG Z F, YOU Y M, HUANG Y Q, et al.. Effects of drought stress on the photosynthesis and growth of Cyclobalanopsis glauca seedlings: a study with simulated hierarchical karst water supply [J]. Chin. J. Ecol., 2012, 31(9):2197-2202. | |
| 24 | 肖华, 周宁波, 陶贤蛟. 新墙河区草本植物重金属含量的测定[J]. 分析科学学报, 2010, 26(1): 119-121. |
| XIAO H, ZHOU N B, TAO X J. Determination of heavy metals in herbs in the Xinqiang river [J]. J. Anal. Sci., 2010, 26(1): 119-121. | |
| 25 | 贺金明. 微波消解-石墨炉原子吸收光谱法测定土壤中铅和镉的方法研究[J]. 华南预防医学, 2017, 43(1): 75-77. |
| 26 | 冯鹏, 孙力, 申晓慧, 等. 多年生黑麦草对Pb、Cd胁迫的响应及富集能力研究[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(1): 153-162. |
| FENG P, SUN L, SHEN X H, et al.. Response and enrichment ability of perennial ryegrass under lead and cadmium stresses [J]. Acta Partac. Sin., 2016, 25(1): 153-162. | |
| 27 | 吴燕玉, 周启星, 田均良. 制定我国土壤环境标准(汞、镉、铅和砷)的探讨[J]. 应用生态学报, 1991, 2(4): 344-349. |
| WU Y Y, ZHOU Q X, TIAN J L. An approach to the enactment of soil-environmental standards (Hg, Cd, Pb and As) in China [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 1991, 2(4): 344-349. | |
| 28 | SEREGIN I V, IVANOV V B. Physiological aspects of cadmium and lead toxic effects on higher plants [J]. Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2001, 48(4): 523-544. |
| 29 | 滕秋梅, 张中锋, 李红艳, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌对镉胁迫下芦竹生长、光合特性和矿质营养的影响[J]. 土壤, 2020, 52 (6): 1212-1221. |
| TENG Q M, ZHANG Z F, LI H Y, et al.. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth, photosynthesis characteristics and mineral nutrition of arundo donax under Cd stress [J]. Soils, 2020, 52 (6): 1212-1221. | |
| 30 | 毕银丽, 张延旭, 江彬, 等. 水分胁迫下AM 真菌与解磷细菌协同对玉米生长及土壤肥力的影响[J]. 煤炭学报, 2019, 44(12): 3655-3661. |
| BI Y L, ZHANG Y X, JIANG B, et al.. Effects of AM fungi and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria inoculation on maize growth and soil fertility under water stress [J]. J. China Coal Soc., 2019, 44(12): 3655-3661. | |
| 31 | 悦飞雪, 李继伟, 王艳芳, 等. 生物炭和AM真菌提高矿区土壤养分有效性的机理[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2019, 25(8): 1325-1334. |
| YUE F X, LI J W, WANG Y F, et al.. Mechanism of the improvement effect by biochar and AM fungi on the availability of soil nutrients in coal mining area [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2019, 25(8): 1325-1334. | |
| 32 | CHRISTOPHERSEN H M, SMITH F A, SMITH S E. Unraveling the influence of arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization on arsenic tolerance in Medicago: Glomus mosseae is more effective than G. intraradices, associated with lower expression of root epidermal Pi transporter genes [J/OL]. Front. Physiol., 2012, 3: 91 [2023-11-26]. . |
| 33 | PENG R N, SUN W Y, JIN X X, et al.. Analysis of 2,4-epibrassinolide created an enhancement tolerance on Cd toxicity in Solanum nigrum L. [J]. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 2020, 27(14):16784-16797. |
| 34 | 李明亮, 李欢, 王凯荣, 等. Cd 胁迫下丛枝菌根对花生生长、光合生理及 Cd 吸收的影响[J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35 (11): 2344-2352. |
| LI M L, LI H, WANG K R, et al.. Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizae on the growth,photosynthetic characteristics and cadmium uptake of peanut plant under cadmium stress [J]. Environ. Chem., 2016, 35 (11): 2344-2352. | |
| 35 | 韩玮. 丛枝菌根真菌对镉胁迫下黑麦草光合生理的响应[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2022(6): 204-212, 220. |
| HAN W. Response of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on photosynthetic physiology of Lolium perenne under Cd stress [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2022(6): 204-212, 220. |
| [1] | 王子豪, 周雪, 张冬寒, 梁红怡, 王岩, 赵子昂, 陈清. 含腐植酸水溶肥料对玉米苗生长及土壤改良的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(4): 209-220. |
| [2] | 陈小双, 徐兴倩, 赵熹, 屈新, 王海军, 彭光灿. 镉污染红黏土电阻率特性及其评价模型研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(4): 164-173. |
| [3] | 李双, 王爱英, 焦浈, 池青, 孙昊, 焦涛. 盐胁迫下不同抗性小麦幼苗生理生化特性及转录组分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 20-32. |
| [4] | 苗宇, 王婕, 赵尧尧, 张丽佳, 刘美君. 低温胁迫后紫花苜蓿叶片光合作用的恢复特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 80-89. |
| [5] | 蒲子天, 王菲, 李畅, 王鑫鑫. 丛枝菌根真菌影响植物氮素吸收和转运的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(11): 171-179. |
| [6] | 樊娅萍, 宋柏权, 王倡宪. 土壤灭菌与丛枝菌根真菌在缓解连作障碍中的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(10): 158-167. |
| [7] | 徐皖菁, 彭芳, 赵豆豆, 罗姣姣, 陶珊, 廖海浪, 毛常清, 吴宇, 朱秀, 徐正君, 张超. 基于转录组和代谢组解析川芎对镉胁迫的响应机制[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(10): 98-109. |
| [8] | 高静娟, 朱晨宇, 柯玉琴, 郑朝元, 李春英, 李文卿. 烟稻轮作条件下有机肥施用时期对烤烟碳氮代谢的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 157-165. |
| [9] | 杨丽莹, 邰孟雅, 翟夜雨, 许自成, 黄五星. 硫对植物吸收积累镉的影响及其作用机制研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 10-21. |
| [10] | 肖锐, 谭璐, 吴亮, 张皓, 郭佳源, 杨海君. 镉胁迫下地肤根际与非根际土壤微生物群落结构及多样性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 203-215. |
| [11] | 吴香, 李娟, 曹艳, 程艳荣, 闫旭宇, 李玲. 植物根系分泌物响应镉胁迫的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 12-20. |
| [12] | 王小婷, 张芃芃. 集胞藻6803中丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶系统发育和功能概述[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 66-76. |
| [13] | 孟璐, 范敬文, 赛欣娱, 曾路生, 宋祥云, 崔德杰. 石灰对苹果园土壤改良和植株生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 197-204. |
| [14] | 申海玉, 张浩, 吴子龙, 韩超, 宋炜, 马晓斐. 几种改良剂对煤矸石基质水分特征及狗尾草萌发的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 161-168. |
| [15] | 柴冠群, 王丽, 刘桂华, 罗沐欣键, 蒋亚, 梁红, 范成五. 3类朝天椒重金属健康风险评价与镉吸收累积差异[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 169-177. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号