




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (8): 10-21.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0580
• 生物技术 生命科学 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2022-07-11
接受日期:2022-09-03
出版日期:2023-08-20
发布日期:2023-09-07
通讯作者:
黄五星
作者简介:杨丽莹 E-mail: yanglying@126.com;
基金资助:
Liying YANG( ), Mengya TAI, Yeyu ZHAI, Zicheng XU, Wuxing HUANG(
), Mengya TAI, Yeyu ZHAI, Zicheng XU, Wuxing HUANG( )
)
Received:2022-07-11
Accepted:2022-09-03
Online:2023-08-20
Published:2023-09-07
Contact:
Wuxing HUANG
摘要:
镉被联合国环境规划署列为具有全球意义的危害物质,土壤镉污染严重威胁植物生长并危害人体健康。外源硫影响植物对镉的吸收与积累,但不同形态和用量的硫对不同植物吸收积累镉的作用效果存在较大差异。综述了不同形态和用量硫对农作物(水稻、小麦、蔬菜、烟草)和镉富集植物(伴矿景天、龙葵)吸收积累镉的影响,从土壤镉的有效性(硫影响土壤pH和土壤对镉的吸附)、植物根系对镉的吸收(硫影响植物金属转运蛋白转录水平和根毛与铁膜的形成)和镉在植物内的分配积累(硫影响根细胞壁吸附和液泡区隔)3方面总结了其可能的作用机制,探讨了降低农作物和增加超富集植物镉吸收积累的施硫策略,以期为提高农作物安全性和修复土壤镉污染提供理论依据。
中图分类号:
杨丽莹, 邰孟雅, 翟夜雨, 许自成, 黄五星. 硫对植物吸收积累镉的影响及其作用机制研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 10-21.
Liying YANG, Mengya TAI, Yeyu ZHAI, Zicheng XU, Wuxing HUANG. Progress of Research on the Effect of Sulfur on Cadmium Uptake and Accumulation by Plants and Its Mechanism[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 10-21.
植物 Plant | 硫形态 Sulfur form | 硫处理水平 Sulfur treatment level | 镉处理水平 Cadmium treatment level | 处理时间 Treatment time | 结果 Result | 参考 文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
水稻 Oryza sativa | 元素硫/Na2SO4/ 巯基有机黏土 S(S0)/Na2SO4/ MP | 0、50、100 mg∙kg-1 | 1.14、1.99 mg∙kg-1 | 整个生育期 Whole growth period | 根Cd↓;地上部Cd,Cd向籽粒转移系数↑ Cd in roots↓; Cd in shoots,TF to grains↑ | |
| Na2S | 500 mg∙L-1 | 0.67 mg∙kg-1/0.0、0.2、0.5、1.0、2.0、 5.0 mg∙L-1 | 整个生育期 Whole growth period | 籽粒Cd,Cd向籽粒转移系数↓ Cd in grains, TF to grains↓ | ||
| K2SO4 | 0、10、40、80、 160 mg∙kg-1 | 0.79 mg∙kg-1 | 整个生育期 Whole growth period | 从根到茎以及从茎到籽粒的Cd转移系数↓ TF from roots to stems and TF from stems to grains↓ | ||
S0/石膏 S0/ gypsum | 0、150、300 mg∙kg-1 | 0、5 mg∙kg-1 | 整个生育期Whole growth period | 籽粒Cd,从根部到地上部的Cd转移系数↓ Cd in grains, TF from roots to shoots↓ | ||
| Na2SO4 | 0.00、1.75、3.50、 7.00 mmol∙ L-1 | 0.0、1.0 μmol∙L-1 | 7 d | 根Cd,叶Cd,从根部到地上部的Cd转移系数↓ Cd in roots, Cd in leaves, TF from roots to shoots↓ | ||
| Na2SO4 | 2、6、12 mmol∙L-1 | 0、10、100 μmol∙L-1 | 7 d | 叶Cd,Cd向叶转移系数↑ Cd in leaves, TF to leaves↑ | ||
小麦 Triticum aestivum | MgSO4+Na2SO4 | 2、6、9 mmol∙L-1 | 0.0、0.2、20.0、 40.0 μmol∙L-1 | 14 d | 地上部Cd,从根部到地上部的Cd转移系数↑ Cd in shoots, TF from roots to shoots↑ | |
| Na2SO4 | 0、30、60 mg∙kg-1 | 0.35、10.35 mg∙kg-1 | 整个生育期 Whole growth period | 籽粒Cd↑ Cd in grains↑ | ||
| MnSO4 | 0、500、1 000、 2 000 mg∙kg-1 | 1.98 mg∙kg-1 | 整个生育期Whole growth period | 根Cd,籽粒Cd,Cd向籽粒转移系数↓ Cd in roots, Cd in grains, TF to grains↓ | ||
S0/石膏 S0/ gypsum | 0、2 000、4 000、 8 000 mg∙kg-1 | 3.02 mg∙kg-1 | 整个生育期Whole growth period | 石膏处理各组织Cd↓, S0处理↑ Gypsum treatment Cd↓, S0 treatment Cd↑ | ||
| Na2SO4 | 0、60、120 mg∙kg-1 | 3.0 mg∙kg-1 | 整个生育期Whole growth period | 根Cd↑;籽粒Cd,Cd向籽粒转移系数↓ Cd in roots ↑;Cd in grains, TF to grains↓ | ||
小白菜 Brassica chinensis | Na2SO4 | -2、0、2 mmol∙L-1 (-2为缺S处理 -2 represents sulphur deficiency treatment) | 0、50 μmol∙L-1 | 7 d | 叶Cd↓ Cd in leaves ↓ | |
| Na2SO4/CaSO4 | 0、5 mmol∙L-1 | 0、20 μmol∙L-1 | 8 d | 叶Cd↓ Cdin leaves ↓ |
表1 不同形态和不同含量水平硫对植物吸收积累镉的影响
Table 1 Effect of different forms and content levels of sulfur on cadmium uptake and accumulation by plants
植物 Plant | 硫形态 Sulfur form | 硫处理水平 Sulfur treatment level | 镉处理水平 Cadmium treatment level | 处理时间 Treatment time | 结果 Result | 参考 文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
水稻 Oryza sativa | 元素硫/Na2SO4/ 巯基有机黏土 S(S0)/Na2SO4/ MP | 0、50、100 mg∙kg-1 | 1.14、1.99 mg∙kg-1 | 整个生育期 Whole growth period | 根Cd↓;地上部Cd,Cd向籽粒转移系数↑ Cd in roots↓; Cd in shoots,TF to grains↑ | |
| Na2S | 500 mg∙L-1 | 0.67 mg∙kg-1/0.0、0.2、0.5、1.0、2.0、 5.0 mg∙L-1 | 整个生育期 Whole growth period | 籽粒Cd,Cd向籽粒转移系数↓ Cd in grains, TF to grains↓ | ||
| K2SO4 | 0、10、40、80、 160 mg∙kg-1 | 0.79 mg∙kg-1 | 整个生育期 Whole growth period | 从根到茎以及从茎到籽粒的Cd转移系数↓ TF from roots to stems and TF from stems to grains↓ | ||
S0/石膏 S0/ gypsum | 0、150、300 mg∙kg-1 | 0、5 mg∙kg-1 | 整个生育期Whole growth period | 籽粒Cd,从根部到地上部的Cd转移系数↓ Cd in grains, TF from roots to shoots↓ | ||
| Na2SO4 | 0.00、1.75、3.50、 7.00 mmol∙ L-1 | 0.0、1.0 μmol∙L-1 | 7 d | 根Cd,叶Cd,从根部到地上部的Cd转移系数↓ Cd in roots, Cd in leaves, TF from roots to shoots↓ | ||
| Na2SO4 | 2、6、12 mmol∙L-1 | 0、10、100 μmol∙L-1 | 7 d | 叶Cd,Cd向叶转移系数↑ Cd in leaves, TF to leaves↑ | ||
小麦 Triticum aestivum | MgSO4+Na2SO4 | 2、6、9 mmol∙L-1 | 0.0、0.2、20.0、 40.0 μmol∙L-1 | 14 d | 地上部Cd,从根部到地上部的Cd转移系数↑ Cd in shoots, TF from roots to shoots↑ | |
| Na2SO4 | 0、30、60 mg∙kg-1 | 0.35、10.35 mg∙kg-1 | 整个生育期 Whole growth period | 籽粒Cd↑ Cd in grains↑ | ||
| MnSO4 | 0、500、1 000、 2 000 mg∙kg-1 | 1.98 mg∙kg-1 | 整个生育期Whole growth period | 根Cd,籽粒Cd,Cd向籽粒转移系数↓ Cd in roots, Cd in grains, TF to grains↓ | ||
S0/石膏 S0/ gypsum | 0、2 000、4 000、 8 000 mg∙kg-1 | 3.02 mg∙kg-1 | 整个生育期Whole growth period | 石膏处理各组织Cd↓, S0处理↑ Gypsum treatment Cd↓, S0 treatment Cd↑ | ||
| Na2SO4 | 0、60、120 mg∙kg-1 | 3.0 mg∙kg-1 | 整个生育期Whole growth period | 根Cd↑;籽粒Cd,Cd向籽粒转移系数↓ Cd in roots ↑;Cd in grains, TF to grains↓ | ||
小白菜 Brassica chinensis | Na2SO4 | -2、0、2 mmol∙L-1 (-2为缺S处理 -2 represents sulphur deficiency treatment) | 0、50 μmol∙L-1 | 7 d | 叶Cd↓ Cd in leaves ↓ | |
| Na2SO4/CaSO4 | 0、5 mmol∙L-1 | 0、20 μmol∙L-1 | 8 d | 叶Cd↓ Cdin leaves ↓ |
植物 Plant | 硫形态 Sulfur form | 硫处理水平 Sulfur treatment level | 镉处理水平 Cadmium treatment level | 处理时间 Treatment time | 结果 Result | 参考 文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
小白菜 Brassica chinensis | Na2SO4 | 0、50 mg∙kg-1 | 0、1、5、25、50、 100 mg∙kg-1 | 30~35 d | 根Cd↑;叶Cd,Cd向叶片转移系数↓ Cd in roots ↑; Cd in leaves, TF to leaves↓ | |
菠菜 Ipomoea aquatica | Na2SO4 | 100、200 mg∙kg-1 | 0.24、2.50 mg∙kg-1 | 14 d | 根Cd↑;叶Cd↓,Cd向叶片转移系数↓ Cd in roots ↑; Cd in leaves, TF to leaves↓ | |
苋菜 Amaranshus mangostanus | S0/(NH4)2SO4/CaSO4 | 0、50 mg∙kg-1 | 15 mg∙kg-1 | 45 d | 根Cd,叶Cd↑ Cd in roots, Cd in leaves↑ | |
大白菜 Brassica campestris | S0/Na2SO4/Na2SO3 | 200 mg∙kg-1 | 2.3 mg∙kg-1 | 40 d | 根Cd,叶Cd↑ Cd in roots, Cd in leaves↑ | |
烟草 Nicotiana tabacum | K2SO4 | 0、130、105 mg∙kg-1 | 0、1、5 mg∙kg-1 | 20 d | 根Cd,叶Cd↓ Cd in roots, Cd in leaves↓ | |
| K2SO4 | 0、510、1 020 mg∙kg-1 | 9.4 mg∙kg-1 | 60 d | 根Cd,叶Cd,Cd向叶片转移系数↑ Cd in roots, Cd in leaves, TF to leaves↑ | ||
伴矿景天 Sedum plumbizincicola | S0 | 0~4 000 mg∙kg-1 | 1.33、4.44 mg∙kg-1 | 90 d | 根Cd,叶Cd↑ Cd in roots, Cd in leaves↑ | |
| S0/FeSO4 | 0~1 500 mg∙plant-1/0~ 1 200 mg∙plant-1 | 0.65 mg∙kg-1 | 60 d | 根Cd,叶Cd↑ Cd in roots, Cd in leaves↑ | ||
| S0 | 0、180、360、 720 g∙m-2 | 1.33 mg∙kg-1 | 150 d | 根Cd,叶Cd↑ Cd in roots, Cd in leaves↑ | ||
超积累型东南景天 Sedum alfredii Hance | K2SO4 | 0.00、0.75、1.50、 2.25 mmol∙L-1 | 0、10、100 μmol∙L-1 | 30 d | 根Cd,叶Cd↑ Cd in roots, Cd in leaves↑ | |
龙葵 Solanum nigrum | S0/石膏 S0/ gypsum | 0、100、50+ 50 mg∙kg-1 | 0、25、50 mg∙kg-1 | 70 d | 根Cd,叶Cd↑ Cd in roots, Cd in leaves↑ |
表1 不同形态和不同含量水平硫对植物吸收积累镉的影响 (续表Continued)
Table 1 Effect of different forms and content levels of sulfur on cadmium uptake and accumulation by plants
植物 Plant | 硫形态 Sulfur form | 硫处理水平 Sulfur treatment level | 镉处理水平 Cadmium treatment level | 处理时间 Treatment time | 结果 Result | 参考 文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
小白菜 Brassica chinensis | Na2SO4 | 0、50 mg∙kg-1 | 0、1、5、25、50、 100 mg∙kg-1 | 30~35 d | 根Cd↑;叶Cd,Cd向叶片转移系数↓ Cd in roots ↑; Cd in leaves, TF to leaves↓ | |
菠菜 Ipomoea aquatica | Na2SO4 | 100、200 mg∙kg-1 | 0.24、2.50 mg∙kg-1 | 14 d | 根Cd↑;叶Cd↓,Cd向叶片转移系数↓ Cd in roots ↑; Cd in leaves, TF to leaves↓ | |
苋菜 Amaranshus mangostanus | S0/(NH4)2SO4/CaSO4 | 0、50 mg∙kg-1 | 15 mg∙kg-1 | 45 d | 根Cd,叶Cd↑ Cd in roots, Cd in leaves↑ | |
大白菜 Brassica campestris | S0/Na2SO4/Na2SO3 | 200 mg∙kg-1 | 2.3 mg∙kg-1 | 40 d | 根Cd,叶Cd↑ Cd in roots, Cd in leaves↑ | |
烟草 Nicotiana tabacum | K2SO4 | 0、130、105 mg∙kg-1 | 0、1、5 mg∙kg-1 | 20 d | 根Cd,叶Cd↓ Cd in roots, Cd in leaves↓ | |
| K2SO4 | 0、510、1 020 mg∙kg-1 | 9.4 mg∙kg-1 | 60 d | 根Cd,叶Cd,Cd向叶片转移系数↑ Cd in roots, Cd in leaves, TF to leaves↑ | ||
伴矿景天 Sedum plumbizincicola | S0 | 0~4 000 mg∙kg-1 | 1.33、4.44 mg∙kg-1 | 90 d | 根Cd,叶Cd↑ Cd in roots, Cd in leaves↑ | |
| S0/FeSO4 | 0~1 500 mg∙plant-1/0~ 1 200 mg∙plant-1 | 0.65 mg∙kg-1 | 60 d | 根Cd,叶Cd↑ Cd in roots, Cd in leaves↑ | ||
| S0 | 0、180、360、 720 g∙m-2 | 1.33 mg∙kg-1 | 150 d | 根Cd,叶Cd↑ Cd in roots, Cd in leaves↑ | ||
超积累型东南景天 Sedum alfredii Hance | K2SO4 | 0.00、0.75、1.50、 2.25 mmol∙L-1 | 0、10、100 μmol∙L-1 | 30 d | 根Cd,叶Cd↑ Cd in roots, Cd in leaves↑ | |
龙葵 Solanum nigrum | S0/石膏 S0/ gypsum | 0、100、50+ 50 mg∙kg-1 | 0、25、50 mg∙kg-1 | 70 d | 根Cd,叶Cd↑ Cd in roots, Cd in leaves↑ |
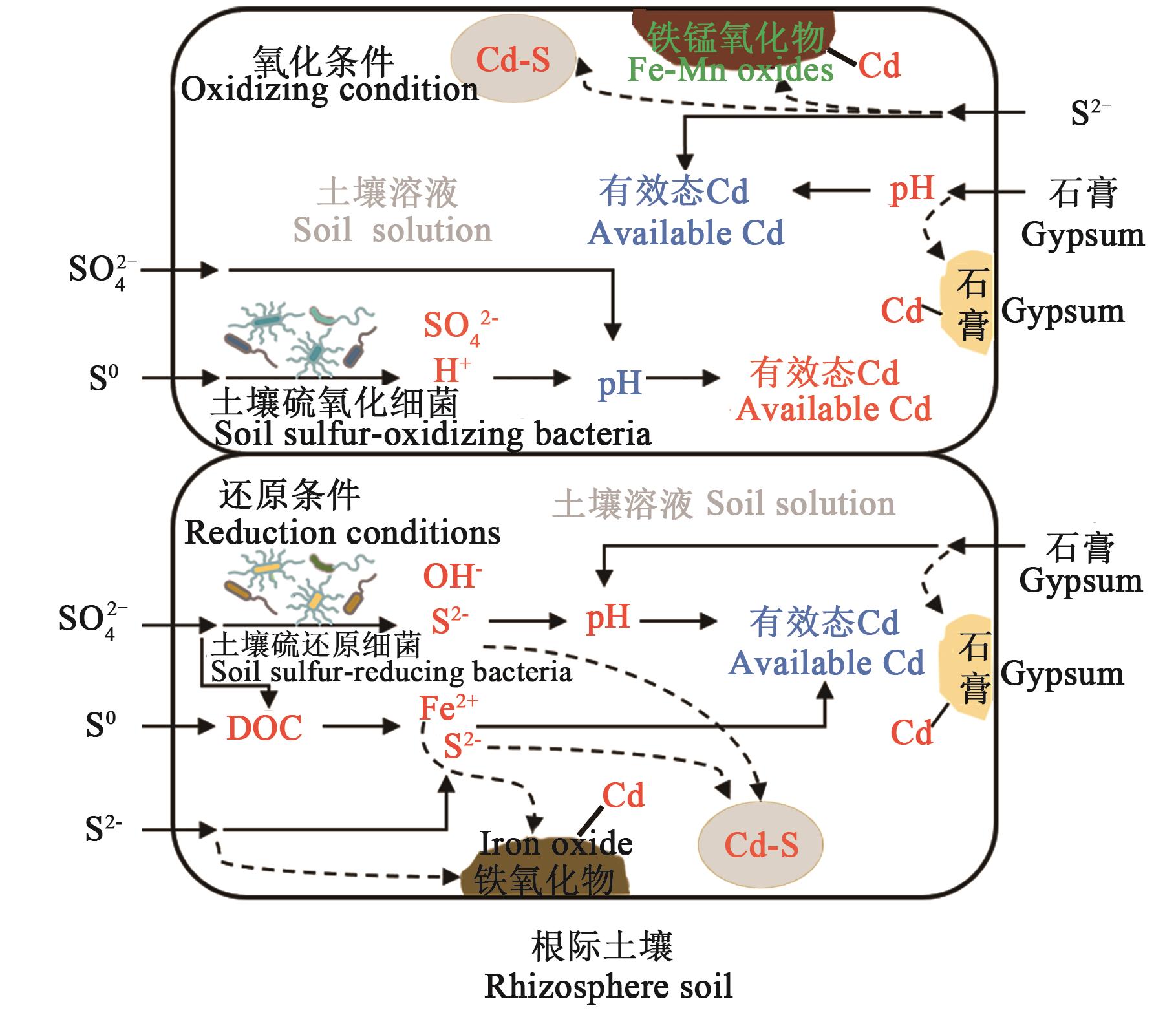
图1 硫对土壤镉有效性的影响注:红色字体表示增加,蓝色字体表示降低。
Fig. 1 Effect of sulfur on availability of cadmium in soilNote:Red font indicates an increase, blue font indicates a decrease.
| 1 | MAHDI R K, NAJI N M, AL-MAMOORI S O H, et al.. Effect cadmium on living organisms [J/OL]. IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci., 2021,735(1):012035 [2022-06-10]. . |
| 2 | MICHIEL H, ANN C, JANA D, et al.. Cadmium and plant development: an agony from seed to seed [J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2019,20(16):3971 [2022-06-10]. . |
| 3 | ALATAWI A, WANG X, MAQBOOL A, et al.. S-fertilizer (elemental sulfur) improves the phytoextraction of cadmium through Solanum nigrum L. [J/OL]. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 2022,19(3):1655 [2022-06-10]. . |
| 4 | LIANG J, SHOHAG M J I, YANG X, et al.. Role of sulfur assimilation pathway in cadmium hyperaccumulation by Sedum alfredii Hance [J]. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2014,100(2):159-165. |
| 5 | 鲍桐, 廉梅花, 孙丽娜, 等. 重金属污染土壤植物修复研究进展[J]. 生态环境,2008,17(2):858-865. |
| BAO T, LIAN M H, SUN L N, et al.. Research progress on the phytoremediation of soils contaminated by heavy metals [J]. Ecol. Environ., 2008,17(2):858-865. | |
| 6 | BROOKS R R, LEE J, REEVES R D, et al.. Detection of nickeliferous rocks by analysis of herbarium specimens of indicator plants [J]. J. Geochem. Explor., 1977,7(1):49-57. |
| 7 | WANG P, CHEN H P, PETER M K, et al.. Cadmium contamination in agricultural soils of China and the impact on food safety [J]. Environ. Pollut., 2019,249(6):1038-1048. |
| 8 | YANG Y, CHEN W P, WANG M E, et al.. Evaluating the potential health risk of toxic trace elements in vegetables: accounting for variations in soil factors [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2017,584-585:942-949. |
| 9 | GEORG E M, PENELOPE J E Q, EUNHA H, et al.. Tobacco smoke is a likely source of lead and cadmium in settled house dust [J/OL]. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol., 2021,63:126656 [2022-06-10]. . |
| 10 | KHAN M A, KHAN S, KHAN A, et al.. Soil contamination with cadmium, consequences and remediation using organic amendments [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2017,601-602:1591-1605. |
| 11 | BIAN R J, CHEN D, LIU X Y, et al.. Biochar soil amendment as a solution to prevent Cd-tainted rice from China: results from a cross-site field experiment [J]. Ecol. Eng., 2013,58(9):378-383. |
| 12 | 环境保护部. 环境保护部和国土资源部发布全国土壤污染状况调查公报 [R/OL]. (2014-04-17) [2022-06-10]. . |
| 13 | KHAN M I R, NAZIR F, ASGHER M, et al.. Selenium and sulfur influence ethylene formation and alleviate cadmium-induced oxidative stress by improving proline and glutathione production in wheat [J]. J. Plant Physiol., 2015,173(1):9-18. |
| 14 | 孙丽娟, 段德超, 彭程, 等. 硫对土壤重金属形态转化及植物有效性的影响研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 2014,25(7):2141-2148. |
| SUN L J, DUAN D C, PENG C, et al.. Influence of sulfur on the speciation transformation and phyto-availability of heavy metals in soil: a review [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2014,25(7):2141-2148. | |
| 15 | 彭鸥, 周靖恒, 喻崴伦, 等. 硅硫材料对复合污染土壤镉砷赋存形态的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020,39(2):294-303. |
| PENG O, ZHOU J H, YU W L, et al.. Effects of silicon-and sulfur-containing materials on the dynamics of cadmium and arsenic species in compound polluted soil [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2020,39(2):294-303. | |
| 16 | MUHAMMAD F Q, MUHAMMAD Z U R, SHAFAQAT A, et al.. Residual effects of monoammonium phosphate, gypsum and elemental sulfur on cadmium phytoavailability and translocation from soil to wheat in an effluent irrigated field [J]. Chemosphere, 2017,174(5):515-523. |
| 17 | ZHOU J, HAO M, LIU Y, et al.. Effects of exogenous sulfur on growth and Cd uptake in Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris spp. Pekinensis) in Cd-contaminated soil [J]. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int., 2018,25(16):15823-15829. |
| 18 | SHEN C, FU H, LIAO Q, et al.. Transcriptome analysis and physiological indicators reveal the role of sulfur in cadmium accumulation and transportation in water spinach (Ipomoea aquatica Forsk.) [J/OL]. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2021,225:112787 [2022-06-10]. . |
| 19 | 赵萌. 硫对水稻根区微界面有效态镉的影响及机制[D]. 北京:中国农业科学院, 2021. |
| ZHAO M. Effect of sulfur on labile cadmium at microinterface in rice root zone and its mechanism [D]. Beijing:Chinese Academy of Agricultural, 2021. | |
| 20 | 刘家豪, 赵龙, 孙在金, 等. 叶面喷施硫对镉污染土壤中水稻累积镉的机制研究[J]. 环境科学研究, 2019,32(12):2132-2138. |
| LIU J H, ZHAO L, SUN Z J, et al.. Protective effect of foliar application of sulfur on rice under the stress of Cd [J]. Res. Environ. Sci., 2019,32(12):2132-2138. | |
| 21 | ZHANG Q, CHEN H, HUANG D, et al.. Sulfur fertilization integrated with soil redox conditions reduces Cd accumulation in rice through microbial induced Cd immobilization [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ., 2022,824:153868 [2022-06-10]. . |
| 22 | ZHANG D X, DU G H, CHEN D, et al.. Effect of elemental sulfur and gypsum application on the bioavailability and redistribution of cadmium during rice growth [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2019,657:1460-1467. |
| 23 | WU Z Y, NAVEED S, ZHANG C H, et al.. Adequate supply of sulfur simultaneously enhances iron uptake and reduces cadmium accumulation in rice grown in hydroponic culture [J/OL]. Environ. Pollut., 2020,262:114327 [2022-06-10]. . |
| 24 | 安志装, 王校常, 严蔚东, 等. 镉硫交互处理对水稻吸收累积镉及其蛋白巯基含量的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2004,41(5):728-734. |
| AN Z Z, WANG X C, YAN W D, et al.. Effects of sulfate and cadmium interaction on cadmium accumulation and content of nonprotein thiols in rice seedling [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2004,41(5):728-734. | |
| 25 | MATRASZEK-GAWRON R, HAWRYLAK-NOWAK B. Sulfur nutrition level modifies the growth, micronutrient status, and cadmium distribution in cadmium-exposed spring wheat [J]. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants, 2019,25(2):421-432. |
| 26 | HUANG L J, HANSEN H C B, WANG H H, et al.. Effects of sulfate on cadmium uptake in wheat grown in paddy soil-pot experiment [J]. Plant Soil Environ., 2019,65(12):602-608. |
| 27 | WANG Y, XU Y, LIANG X, et al.. Soil application of manganese sulfate could reduce wheat Cd accumulation in Cd contaminated soil by the modulation of the key tissues and ionomic of wheat [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ., 2021,770:145328 [2022-06-10]. . |
| 28 | SHI G L, LU H Y, LIU H, et al.. Sulfate application decreases translocation of arsenic and cadmium within wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) plant [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ., 2020,713:136665 [2022-06-10]. . |
| 29 | LI H L, PU P, LI X R, et al.. Sulfur application reduces cadmium uptake in edible parts of pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) by cadmium chelation and vacuolar sequestration [J]. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2020,194:110402 [2022-06-10]. . |
| 30 | HUANG Y F, CHEN J H, SUN Y M, et al.. Mechanisms of calcium sulfate in alleviating cadmium toxicity and accumulation in pak choi seedlings [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ., 2022,805:150115 [2022-06-10]. . |
| 31 | 杜小平, 康靖全, 吕金印. 镉低积累青菜品种筛选及硫对镉胁迫下青菜镉含量和品质影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018,37(8):1592-1601. |
| DU X P, KANG J Q, LYU J Y. Selection for low-Cd-accumulating cultivars of pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.), effects of sulfur on Cd content, and quality characters under Cd stress [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2018,37(8):1592-1601. | |
| 32 | 梁泰帅, 刘昌欣, 康靖全, 等. 硫对镉胁迫下小白菜镉富集、光合速率等生理特性的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2015,34(8):1455-1463. |
| LIANG T S, LIU C X, KANG J Q, et al.. Effects of sulfur on cadmium accumulation, photosynthesis and some other physiological characteristics of pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) under cadmium stress [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2015,34(8):1455-1463. | |
| 33 | 邹茸, 王秀斌, 迟克宇, 等. 不同品种硫肥对苋菜镉累积的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018,37(10):2135-2141. |
| ZOU R, WANG X B, CHI K Y, et al.. Effects of different sulfur fertilizers on cadmium accumulation in Amaranshus mangostanus L. [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2018,37(10):2135-2141. | |
| 34 | FENG X, LIU W, SEHAR S, et al.. Application of sulfur fertilizer reduces cadmium accumulation and toxicity in tobacco seedlings (Nicotiana tabacum) [J]. Plant Growth Regul., 2018,85(1):165-170. |
| 35 | LI X Z, YU H, SUN X W, et al.. Effects of sulfur application on cadmium bioaccumulation in tobacco and its possible mechanisms of rhizospheric microorganisms [J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2019,368(4):308-315. |
| 36 | WU G M, HU P J, ZHOU J W, et al.. Sulfur application combined with water management enhances phytoextraction rate and decreases rice cadmium uptake in a Sedum plumbizincicola-Oryza sativa rotation [J]. Plant Soil, 2019,440(1-2):539-549. |
| 37 | 吴佳玲, 陈喆, 游少鸿, 等. 硫肥对伴矿景天修复镉污染土壤的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2022,41(6):1241-1250. |
| WU J L, CHEN Z, YOU S H, et al.. Phytoremediation efficiency of cadmium-contaminated arable land by planted Sedum plumbizincicola with sulfur fertilization [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2022,41(6):1241-1250. | |
| 38 | 吴广美, 王青玲, 胡鹏杰, 等. 镉污染中性土壤伴矿景天修复的硫强化及其微生物效应[J]. 土壤, 2020,52(5):920-926. |
| WU G M, WANG Q L, HU P J, et al.. Sulfur assisted cadmium phytoextraction by Sedum plumbizincicola and its effect on microbial community in neutral paddy soil [J]. Soils, 2020,52(5):920-926. | |
| 39 | 李会合, 杨肖娥. 硫对超积累东南景天镉累积、亚细胞分布和化学形态的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2009,15(2):395-402. |
| LI H H, YANG X E. Effects of sulfur on accumulation, subcellular distribution and chemical forms of cadmium in hyperaccumulator-Sedum alfredii hance [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2009,15(2):395-402. | |
| 40 | HUANG Y, FEI G, YU S, et al.. Molecular and biochemical mechanisms underlying boron-induced alleviation of cadmium toxicity in rice seedlings [J/OL]. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2021,225:112776 [2022-06-10]. . |
| 41 | ZHANG Q, CHEN H F, HUANG D Y, et al.. Sulfur fertilization integrated with soil redox conditions reduces Cd accumulation in rice through microbial induced Cd immobilization [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ., 2022,824:153868 [2022-06-10]. . |
| 42 | 官迪, 吴家梅, 刘昭兵, 等. 外源硫化钠对土壤-水稻体系中镉迁移积累的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2021,40(7):1460-1469. |
| GUAN D, WU J M, LIU Z B, et al.. Effects of exogenous sodium sulfide on cadmium migration and accumulation in soil and rice plant systems [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2021,40(7):1460-1469. | |
| 43 | ZHAO M, LIU X W, LI Z T, et al.. Inhibition effect of sulfur on Cd activity in soil-rice system and its mechanism [J/OL]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2021,407:124647 [2022-06-10]. . |
| 44 | LIU T T, HUANG D Y, ZHU Q H, et al.. Increasing soil moisture faciliates the outcomes of exogenous sulfate rather than element sulfur in reducing cadmium accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) [J/OL]. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2020,191:110200 [2022-06-10]. . |
| 45 | ZHENG H, WANG M, CHEN S B, et al.. Sulfur application modifies cadmium availability and transfer in the soil-rice system under unstable pe+pH conditions [J/OL]. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2020,191:110200 [2022-06-10]. . |
| 46 | SUN L J, SONG K, SHI L Z, et al.. Impact of sulfur (S) fertilization in paddy soils on copper (Cu) accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) plants under flooding conditions [J]. Biol. Fertil. Soils, 2016,52(1):31-39. |
| 47 | LI X F, ZHOU D M. A meta-analysis on phenotypic variation in cadmium accumulation of rice and wheat: implications for food cadmium risk control [J]. Pedosphere, 2019, 29(5): 545-553. |
| 48 | YANG J L, CANG L, WANG X, et al.. Field survey study on the difference in Cd accumulation capacity of rice and wheat in rice-wheat rotation area [J]. J. Soil Sediment, 2020, 20(4): 2082-2092. |
| 49 | MATRASZEK-GAWRON R, HAWRYLAK-NOWAK B. Sulfur nutrition level modifies the growth, micronutrient status, and cadmium distribution in cadmium-exposed spring wheat [J]. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants, 2019,25(2):421-432. |
| 50 | 翁南燕, 周东美, 汪鹏, 等. 铜镉复合胁迫下硫素对小麦幼苗铜镉吸收、亚细胞分布及毒性的影响[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2011,6(1):87-93. |
| WENG N Y, ZHOU D M, WANG P, et al.. Influence of sulfur on subcellular distribution, uptake and toxicity of Cu and Cd to wheat seadlings [J]. Asian J. Ecotoxicol., 2011,6(1):87-93. | |
| 51 | 陶雪莹, 徐应明, 王林, 等. 喷施硫酸锰和硫酸锌对小麦籽粒镉锰锌生物可给性的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020,39(10):2181-2189. |
| TAO X Y, XU Y M, WANG L, et al.. Effects of foliar application of manganese sulfate and zinc sulfate on bioaccessibility of cadmium, manganese, and zinc in wheat grains [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2020,39(10):2181-2189. | |
| 52 | WANG J, HUANG F, YOU X, et al.. Molecular cloning, characterization and expression analysis of BcHHP3 under abiotic stress in Pak-choi (Brassica rapa ssp. Chinensis) [J/OL]. J. Plant Interact., 2019,14(1):1526981 [2022-06-10]. . |
| 53 | FAN H L, ZHOU W. Screening of amaranth cultivars (Amaranthus mangostanus L.) for cadmium hyperaccumulation [J]. Agric. Sci. China, 2009,8(3):342-351. |
| 54 | LI X, LI Y, ZHU X, et al.. Evaluation of the cadmium phytoextraction potential of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) and rhizosphere micro-characteristics under different cadmium levels [J/OL]. Chemosphere, 2022,286(P2):131714 [2022-06-10]. . |
| 55 | WANG H R, CHE Y H, WANG Z H, et al.. The multiple effects of hydrogen sulfide on cadmium toxicity in tobacco may be interacted with CaM signal transduction [J/OL]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2021,403:123651 [2022-06-10]. . |
| 56 | WU L H, LIU Y J, ZHOU S B, et al.. Sedum plumbizincicola X.H. Guo et S.B. Zhou ex L.H. Wu (Crassulaceae): a new species from Zhejiang province, China [J]. Plant Syst. Evol., 2013,299(3):487-498. |
| 57 | DENG L, LI Z, WANG J, et al.. Long-term field phytoextraction of zinc/cadmium contaminated soil by Sedum plumbizincicola under different agronomic strategies [J]. Int. J. Phytoremed., 2016,18(2):134-140. |
| 58 | WU L H, ZHOU J W, ZHOU T, et al.. Estimating cadmium availability to the hyperaccumulator Sedum plumbizincicola in a wide range of soil types using a piecewise function [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2018,637-638:1342-1350. |
| 59 | UDDIN I, BANO A, MASOOD S. Chromium toxicity tolerance of Solanum nigrum L. and Parthenium hysterophorus L. plants with reference to ion pattern, antioxidation activity and root exudation [J]. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2015,113(3):271-278. |
| 60 | HUSSAIN B, ASHRAF M N, SHAFEEQ-UR-RAHMAN, et al.. Cadmium stress in paddy fields: effects of soil conditions and remediation strategies [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ., 2021,754:142188 [2022-06-10]. . |
| 61 | HOEFER C, SANTNER J, PUSCHENREITER M, et al.. Localized metal solubilization in the rhizosphere of Salix smithiana upon sulfur application [J]. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2015,49(7):4522-4529. |
| 62 | 刘同同. 不同水分管理模式下外源硫素对水稻吸收镉的调控效应[D]. 荆州:长江大学, 2020. |
| LIU T T. Effects of sulfur application on accumulation of cadmium in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under different soil moisture conditions [D]. Jingzhou:Yangtze University, 2020. | |
| 63 | 唐冰培, 杨世杰, 王代长, 等. 硫素对氧化还原条件下水稻土氧化铁和砷形态影响[J]. 环境科学, 2014,35(10):3851-3861. |
| TANG B P, YANG S J, WANG D Z, et al.. Effect of sulfur on the species of Fe and As under redox condition in paddy soil [J]. Environ. Sci., 2014,35(10):3851-3861. | |
| 64 | 张基茂, 黄运湘. 硫对水稻镉吸收的影响机理[J]. 作物研究, 2017,31(1):82-87. |
| ZHANG J M, HUANG Y X. Effect of sulfur on cadmium absorption of rice [J]. Crop Res., 2017,31(1):82-87. | |
| 65 | ZHU H H, CHEN C, XU C, et al.. Effects of soil acidification and liming on the phytoavailability of cadmium in paddy soils of central subtropical China [J]. Environ. Pollut., 2016,219(12):99-106. |
| 66 | 刘颖, 苏广权, 郭湘, 等. 不同形态硫对水稻吸收积累镉的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2021,40(6):1208-1218. |
| LIU Y, SU G Q, GUO X, et al.. Effects of different sulfur forms on cadmium uptake and accumulation in paddy rice [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2021,40(6):1208-1218. | |
| 67 | 王晓娟, 王文斌, 杨龙, 等. 重金属镉(Cd)在植物体内的转运途径及其调控机制[J]. 生态学报, 2015,35(23):7921-7929. |
| WANG X J, WANG W B, YANG L, et al.. Transport pathways of cadmium (Cd) and its regulatory mechanisms in plant [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2015,35(23):7921-7929. | |
| 68 | ADHIKARI S, GHOSH S, AZAHAR I, et al.. Sulfate improves cadmium tolerance by limiting cadmium accumulation, modulation of sulfur metabolism and antioxidant defense system in maize [J]. Environ. Exp. Bot., 2018,153:143-162. |
| 69 | BAHMANI R, KIM D G, KIM J A, et al.. The density and length of root hairs are enhanced in response to cadmium and arsenic by modulating gene expressions involved in fate determination and morphogenesis of root hairs in Arabidopsis [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2016,7:1763 [2022-06-10]. . |
| 70 | CUI J H, LIU T X, LI F B, et al.. Silica nanoparticles alleviate cadmium toxicity in rice cells: mechanisms and size effects [J]. Environ. Pollut., 2017,228(9):263-269. |
| 71 | WANG L, ZOU R, LI Y C, et al.. Effect of wheat-Solanum nigrum L. intercropping on Cd accumulation by plants and soil bacterial community under Cd contaminated soil [J/OL]. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2020,206:111383 [2022-06-10]. . |
| 72 | ZHAN J, HUANG H G, YU H Y, et al.. The combined effects of Cd and Pb enhanced metal binding by root cell walls of the phytostabilizer Athyrium wardii (Hook.) [J/OL]. Environ. Pollut., 2020,258:113663 [2022-06-10]. . |
| 73 | 魏帅. 硫肥对水稻—东南景天轮作系统中镉有效性及根际细菌群落特征的影响[D]. 杭州:浙江大学, 2019. |
| WEI S. Effect of sulfur on the bioavailability of cadmium and characteristics of rhizosphere bacterial community in rice-Sedum alfredii hance rotation system [D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University, 2019. |
| [1] | 吴香, 李娟, 曹艳, 程艳荣, 闫旭宇, 李玲. 植物根系分泌物响应镉胁迫的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 12-20. |
| [2] | 侯非凡, 张笑文, 王嘉琦, 张建珍, 李凯泉, 尹雪斌. 硒肥土施位置对小麦生理特性及硒积累的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 144-152. |
| [3] | 庞喆, 王启龙, 李娟. 不同土壤改良剂对陕北低洼盐碱地土壤理化性质及水稻产量和经济效益的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 174-180. |
| [4] | 孙鲁鹏, 杨洋, 王卫超, 傅廷栋, 周广生, 张凤华. 油菜苗期对盐碱胁迫的离子响应机制[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 46-54. |
| [5] | 孔令博, 林巧, 聂迎利, 王晶静, 魏虹. 中国农作物种业发展现状及对策分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 1-13. |
| [6] | 姚佳, 刘加欣, 苏焱, 苏小娟. 烟杆炭配施氮肥对玉米苗期生长及土壤特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 140-151. |
| [7] | 柴冠群, 王丽, 刘桂华, 罗沐欣键, 蒋亚, 梁红, 范成五. 3类朝天椒重金属健康风险评价与镉吸收累积差异[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 169-177. |
| [8] | 刘云飞, 韦凤杰, 夏茂林, 于兆锦, 夏昊, 衣春宇, 常剑波, 姬小明. 新型复合水凝胶对镉胁迫烟草幼苗的缓解效应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 188-197. |
| [9] | 陈军, 李静雯, 王立光, 朱天地, 陈琛, 包奇军, 欧巧明. 低醇溶蛋白转基因大麦氮素转移特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 47-56. |
| [10] | 吴长征, 蒲文宣, 盛崧, 向禹澄, 杨伟芹, 李文瑞, 黄平俊, 刘来华. 亚适低温影响植物生长及氮营养的分子生理机制研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(1): 16-25. |
| [11] | 褚志云, 祁惠, 李颖, 万一兵, 任志雨, 刘春, 袁素霞. 八仙花‘Bailmer’花萼和叶片内铝离子的动态变化[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(1): 65-71. |
| [12] | 郑龙. 小白菜镉含量基因型与环境效应研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(9): 58-65. |
| [13] | 贾睿琪, 郭子昂, 姚晨, 李璞, 腊贵晓, 陆夏梓, 郭虹妤, 李烜桢. 低磷胁迫对小麦镉吸收的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(8): 154-160. |
| [14] | 魏全全, 高英, 芶久兰, 张萌, 饶勇, 杨斌, 凡迪, 冯文豪, 肖华贵. 播种量和播种方式对冬油菜养分吸收利用及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(8): 182-191. |
| [15] | 马俊桃, 周文, 李静浩, 景艺卓, 韩丹, 邵惠芳. 外源硒调控植物重金属胁迫机制的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(6): 27-35. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号