




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (3): 152-160.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0512
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles
Jiangang JIN1( ), Zaifang TIAN1, Minna ZHENG2, Jiahui KANG2
), Zaifang TIAN1, Minna ZHENG2, Jiahui KANG2
Received:2022-06-21
Accepted:2022-09-17
Online:2023-03-15
Published:2023-05-22
作者简介:靳建刚 E-mail:sxyyjjg@126.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Jiangang JIN, Zaifang TIAN, Minna ZHENG, Jiahui KANG. Effect of Different Fertilization Measures on the Diversity of Soil Bacteria Communities in Fed oats (Avena sativa L.)[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(3): 152-160.
靳建刚, 田再芳, 郑敏娜, 康佳惠. 不同施肥措施对饲用燕麦土壤细菌群落多样性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 152-160.
| 处理Treatment | CO(NH2)2/(kg·hm-2) | P2O5/(kg·hm-2) | K2O/(kg·hm-2) | 有机肥Organic fertilizer/(m3·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 |
| T2 | 180 | 90.0 | 90 | 0 |
| T3 | 162 | 84.9 | 81 | 18 |
| T4 | 144 | 79.8 | 72 | 36 |
| T5 | 126 | 74.7 | 63 | 54 |
| T6 | 108 | 69.6 | 51 | 72 |
| T7 | 90 | 64.5 | 45 | 90 |
Table 1 Specific information processed by the experiment
| 处理Treatment | CO(NH2)2/(kg·hm-2) | P2O5/(kg·hm-2) | K2O/(kg·hm-2) | 有机肥Organic fertilizer/(m3·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 |
| T2 | 180 | 90.0 | 90 | 0 |
| T3 | 162 | 84.9 | 81 | 18 |
| T4 | 144 | 79.8 | 72 | 36 |
| T5 | 126 | 74.7 | 63 | 54 |
| T6 | 108 | 69.6 | 51 | 72 |
| T7 | 90 | 64.5 | 45 | 90 |
处理 Treatment | 全氮 TN/% | 速效氮 AN/(mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 AK/(mg·kg-1) | 速效磷 AP/(mg·kg-1) | 有机碳SOC/(g·kg-1) | 可溶解性盐SS/(g·kg-1) | 株高 PH/cm | 干草产量 Y/(kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 3.10±0.22 a | 182.46±9.24 a | 189.36±21.02 c | 8.49±0.69 b | 32.18±0.12 a | 3.83±0.06 a | 89.36±4.35 c | 6 888.75±709.48 c |
| T2 | 3.25±0.21 a | 185.62±10.76 a | 219.34±45.36 bc | 9.88±0.25 b | 30.25±3.26 a | 2.63±0.05 b | 92.68±3.97 bc | 7 684.70±606.58 b |
| T3 | 3.51±0.09 a | 177.67±2.13 a | 205.34±25.31 bc | 9.34±1.36 b | 29.18±2.64 a | 2.40±0.03 b | 97.21±2.96 b | 7 729.66±883.55 b |
| T4 | 3.52±0.28 a | 194.32±14.32 a | 263.14±56.34 b | 11.09±0.96 a | 32.09±4.39 a | 1.62±0.35 c | 107.32±5.34 a | 9 245.55±992.84 a |
| T5 | 3.47±0.16 a | 187.26±3.69 a | 259.12±16.98 b | 10.23±0.98 ab | 32.34±1.28 a | 1.61±0.12 c | 101.25±6.78 ab | 8 976.04±712.23 ab |
| T6 | 3.56±0.26 a | 179.32±6.90 a | 229.41±15.24 bc | 9.21±1.24 b | 29.32±2.22 a | 1.54±0.01 c | 98.36±4.31 b | 8 706.09±785.26 ab |
| T7 | 3.40±0.17 a | 170.36±5.98 a | 298.99±30.67 a | 9.82±0.06 b | 30.11±4.35 a | 1.53±0.03 c | 98.45±2.57 b | 8 178.99±861.23 b |
Table 2 Physical and chemical properties of soil and biomass of oats under different treatments
处理 Treatment | 全氮 TN/% | 速效氮 AN/(mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 AK/(mg·kg-1) | 速效磷 AP/(mg·kg-1) | 有机碳SOC/(g·kg-1) | 可溶解性盐SS/(g·kg-1) | 株高 PH/cm | 干草产量 Y/(kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 3.10±0.22 a | 182.46±9.24 a | 189.36±21.02 c | 8.49±0.69 b | 32.18±0.12 a | 3.83±0.06 a | 89.36±4.35 c | 6 888.75±709.48 c |
| T2 | 3.25±0.21 a | 185.62±10.76 a | 219.34±45.36 bc | 9.88±0.25 b | 30.25±3.26 a | 2.63±0.05 b | 92.68±3.97 bc | 7 684.70±606.58 b |
| T3 | 3.51±0.09 a | 177.67±2.13 a | 205.34±25.31 bc | 9.34±1.36 b | 29.18±2.64 a | 2.40±0.03 b | 97.21±2.96 b | 7 729.66±883.55 b |
| T4 | 3.52±0.28 a | 194.32±14.32 a | 263.14±56.34 b | 11.09±0.96 a | 32.09±4.39 a | 1.62±0.35 c | 107.32±5.34 a | 9 245.55±992.84 a |
| T5 | 3.47±0.16 a | 187.26±3.69 a | 259.12±16.98 b | 10.23±0.98 ab | 32.34±1.28 a | 1.61±0.12 c | 101.25±6.78 ab | 8 976.04±712.23 ab |
| T6 | 3.56±0.26 a | 179.32±6.90 a | 229.41±15.24 bc | 9.21±1.24 b | 29.32±2.22 a | 1.54±0.01 c | 98.36±4.31 b | 8 706.09±785.26 ab |
| T7 | 3.40±0.17 a | 170.36±5.98 a | 298.99±30.67 a | 9.82±0.06 b | 30.11±4.35 a | 1.53±0.03 c | 98.45±2.57 b | 8 178.99±861.23 b |
处理 Treatment | 序列数 Raw read | OTU数量Number of OTUs | 覆盖度 Good’s coverage | Ace指数 Ace index | Shannon指数 Shannon index | Chao1指数 Chao l index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 777 095 | 1 533±35.23 b | 0.999 0±0.00 a | 820.16±36.21 c | 8.21±1.23 bcd | 858.71±12.31 d |
| T2 | 77 453 | 1 748±38.96 a | 0.999 2±0.00 a | 996.07±38.22 c | 7.86±1.11 cd | 1 052.72±14.33 cd |
| T3 | 68 494 | 1 375±29.64 c | 0.999 8±0.01 a | 953.15±37.26 c | 8.26±1.20 bcd | 1 022.57±13.98 cd |
| T4 | 77 349 | 1 680±37.12 a | 0.999 4±0.01 a | 1 457.67±41.23 a | 8.36±1.19 bc | 1 485.35±15.94 a |
| T5 | 77 839 | 1 352±28.11 c | 0.996 5±0.00 a | 1 241.51±40.62 b | 7.76±1.05 d | 1 252.65±14.35 bc |
| T6 | 77 219 | 1 388±28.31 c | 0.999 0±0.00 a | 1 497.45±42.54 a | 8.93±1.15 a | 1 531.94±16.01 a |
| T7 | 78 013 | 1 213±26.86 c | 0.999 7±0.00 a | 1 360.74±41.78 ab | 8.64±1.12 ab | 1 431.60±15.87 ab |
Table 3 Bacterial sequencing and community α diversity index of soil treated with different improvement measures
处理 Treatment | 序列数 Raw read | OTU数量Number of OTUs | 覆盖度 Good’s coverage | Ace指数 Ace index | Shannon指数 Shannon index | Chao1指数 Chao l index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 777 095 | 1 533±35.23 b | 0.999 0±0.00 a | 820.16±36.21 c | 8.21±1.23 bcd | 858.71±12.31 d |
| T2 | 77 453 | 1 748±38.96 a | 0.999 2±0.00 a | 996.07±38.22 c | 7.86±1.11 cd | 1 052.72±14.33 cd |
| T3 | 68 494 | 1 375±29.64 c | 0.999 8±0.01 a | 953.15±37.26 c | 8.26±1.20 bcd | 1 022.57±13.98 cd |
| T4 | 77 349 | 1 680±37.12 a | 0.999 4±0.01 a | 1 457.67±41.23 a | 8.36±1.19 bc | 1 485.35±15.94 a |
| T5 | 77 839 | 1 352±28.11 c | 0.996 5±0.00 a | 1 241.51±40.62 b | 7.76±1.05 d | 1 252.65±14.35 bc |
| T6 | 77 219 | 1 388±28.31 c | 0.999 0±0.00 a | 1 497.45±42.54 a | 8.93±1.15 a | 1 531.94±16.01 a |
| T7 | 78 013 | 1 213±26.86 c | 0.999 7±0.00 a | 1 360.74±41.78 ab | 8.64±1.12 ab | 1 431.60±15.87 ab |
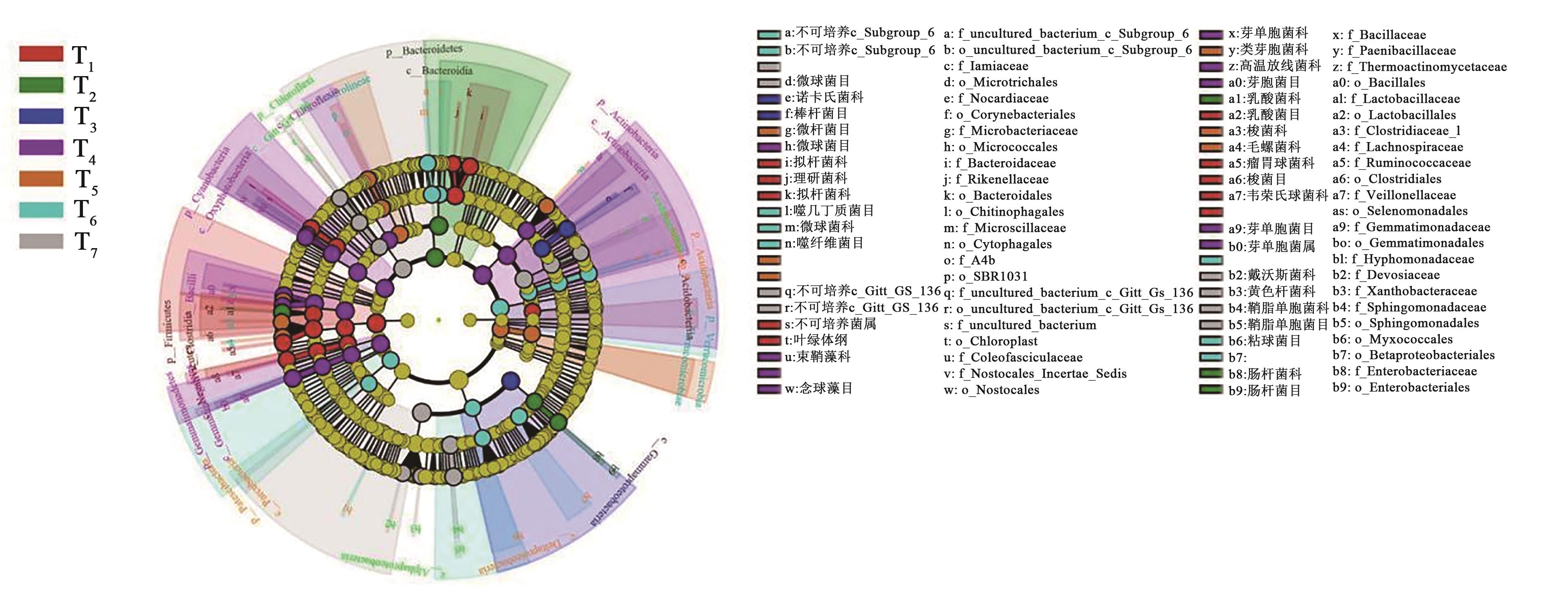
Fig. 3 Cladogram of soil bacterial community under different treatmentsNote: Each circle at a different classification level represents the classification at that level, yellow indicates no significant change in relative abundance, diameter of the circular indicates relative abundance.
| 环境因子 Environmental factor | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient | P值P value |
|---|---|---|
| 全氮TN | 0.213 4 | 0.004 |
| 速效氮AN | 0.413 6 | 0.004 |
| 速效钾AK | 0.483 2 | 0.050 |
| 速效磷AP | 0.589 6 | 0.001 |
| 有机碳SOC | 0.493 1 | 0.003 |
| 可溶解性盐SS | 0.096 7 | 0.050 |
Table 4 Correlation analysis between bacterial communities and environmental factors at the genus level
| 环境因子 Environmental factor | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient | P值P value |
|---|---|---|
| 全氮TN | 0.213 4 | 0.004 |
| 速效氮AN | 0.413 6 | 0.004 |
| 速效钾AK | 0.483 2 | 0.050 |
| 速效磷AP | 0.589 6 | 0.001 |
| 有机碳SOC | 0.493 1 | 0.003 |
| 可溶解性盐SS | 0.096 7 | 0.050 |
| 1 | 陈宝书.牧草饲料作物栽培学[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2001:10-23. |
| CHEN B S. Forage and Forage Crop Cultivation Studies [M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2001:10-23. | |
| 2 | 赵秀芳,戎郁萍,赵来喜.我国燕麦种质资源的收集和评价[J].草业科学,2007,24(3)36-40. |
| ZHAO X F, RONG Y P, ZHAO L X. The collection of oat (Avena sativa) in China [J]. Pratac. Sci., 2007, 24(3):36-40. | |
| 3 | 李刚,郑敏娜,李荫藩.饲用燕麦品种在晋北农牧交错区的生产性能和营养价值研究[J].中国农业科技导报,2021,23(12):42-53. |
| LI G, ZHENG M N, LI Y F. Study on the production performance and nutritional value of fed oat varieties in northern Shanxi province [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2021, 23(12):42-53. | |
| 4 | 侯龙鱼,朱泽义,杨杰,等.我国饲草用燕麦现状、问题和潜力[J].西南民族大学学报(自然科学版),2019,45(3):248-253. |
| HOU L Y, ZHU Z Y, YANG J, et al.. Current status, problems and potentials of forage oat in China [J]. J. Southwest Univ. Nat. (Nat. Sci.), 2019, 45(3):248-253. | |
| 5 | 李生仪,孙延亮,赵俊威,等.施氮对苜蓿根际土壤微生物数量、酶活性及干草产量的影响[J].中国草地学报,2022, 44(4):113-119. |
| LI S Y, SUN Y L, ZHAO J W, et al.. Effect of nitrogen application on microbial quantity, enzyme activity and hay yield in alfalfa rhizosphere [J]. Chin. J. Grassland, 2022, 44(4):113-119. | |
| 6 | VOURLITIS G L, ZORBA G, PASQUINII S C, et al.. Chronic nitrogen deposition enhances nitrogen mineralization potential of semiarid shrubland soils [J]. Soil Sci. Soc. J., 2007, 123(1):836-842. |
| 7 | ZEGLIN L H, STURSOVA M, SINSABAUGH R L, et al.. Microbial responses to nitrogen addition in three contrasting grassland ecosystems [J]. Oecologia, 2007, 154(2):349-359. |
| 8 | 郑敏娜,梁秀芝,韩志顺,等.不同改良措施对盐碱土土壤细菌群落多样性的影响[J].草地学报,2021,29(6):1200-1210. |
| ZHENG M N, LIANG X Z, HAN Z S, et al.. Effects of different improvement measures on the diversity of soil bacteria communities in salt-alkali soil [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2021, 29(6):1200-1210. | |
| 9 | 商丽荣,万里强,李向林.有机肥对羊草草原土壤细菌群落多样性的影响[J].中国农业科学,2020,53(13):2614-2624. |
| SHANG L R, WAN L Q, LI X L. Effects of organic fertilizer on soil bacterial community diversity in Leymus chinensis steppe [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2020, 53(13):2614-2624. | |
| 10 | 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2001:1-495. |
| 11 | WU M, QIN H, CHEN Z, et al.. Effect of long-term fertilization on bacterial composition in rice paddy soil [J]. Biol. Fert. Soils, 2011, 47:397-405. |
| 12 | DAQUIADO A R, KUPPUSAMY S, KIM S Y, et al.. Pyrosequencing analysis of bacterial community diversity in long-term fertilized paddy field soil [J]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2016, 108:84-91. |
| 13 | ZHONG W H, GU T, WANG W, et al.. The effects of mineral fertilizer and organic manure on soil microbial community and diversity [J]. Plant Soil, 2010, 326(1/2):511-522. |
| 14 | 樊晓刚,金轲,李兆君,等.不同施肥和耕作制度下土壤微生物多样性研究进展[J].植物营养与肥料学报, 2010,16(3) :744-751. |
| FAN X G, JIN K, LI Z J, et al.. Progress in soil microbial diversity under different fertilization and tillage systems [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2010, 16(3):744-751. | |
| 15 | ZHAO J, ZHANG R F, XUE C, et al.. Pyrosequencing reveals contrasting soil bacterial diversity and community structure of two main winter wheat cropping systems in China [J]. Microb. Ecol., 2014, 67: 443-453. |
| 16 | 苏贝贝,张英,道日娜.4种豆科栽培牧草根际土壤细菌群落分布特征研究[J].草地学报,2021,29(2):250-258. |
| SU B B, ZHANG Y, DAO R N. Distribution of bacterial communities in rhizosphere of four legume cultivated grasses [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2021, 29(2):250-258. | |
| 17 | SUN R, ZHANG X, GUO X, et al.. Bacterial diversity in soils subjected to long-term chemical fertilization can be more stably maintained with the addition of livestock manure than wheat straw [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2015, 88(9):9-18. |
| 18 | GE G, LI Z, FAN F, et al.. Soil biological activity and their seasonal variations in response to long-term application of organic and inorganic fertilizers [J]. Plant Soil, 2010, 326:31-44. |
| 19 | XU J, LIU S J, SONG S R, et al.. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi influence decomposition and the associated soil microbial community under different soil phosphorus availability [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2018, 20:181-190. |
| 20 | KOPECKY J, KYSELKOVA M, OMELKA M, et al.. Actinobacterial community dominated by a distinct clade in acidic soil of a waterlogged deciduous forest [J]. FEMS Microb. Ecol., 2011, 78(2):386-394. |
| 21 | SUN J, ZHANG Q, ZHOU J, et al.. Pyrosequencing technology reveals the impact of different manure doses on the bacterial community in apple rhizosphere soil [J]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2014, 78:28-36. |
| 22 | 卡着才让, 德科加, 徐成体.不同施肥时间及施氮水平对高寒草甸生物量和土壤养分的影响[J].草地学报, 2015, 23(4): 726-732. |
| KA Z C R, DE K J, XU C T, et al.. The effects of different fertilization time and nitrogen application levels on biomass and soil nutrients in Alpine meadow [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2015, 23(4): 726-732. | |
| 23 | CHEN X, JIANG N, CHEN Z H, et al.. Response of soil phoD phosphatase gene to long-term combined applications of chemical fertilizers and organic materials [J]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2017, 119(10):197-204. |
| 24 | LI M, JAIN S, DICK G J. Genomic and transcriptomic resolution of organic matter utilization among deep-sea bacteria in Guaymas basin hydrothermal plumes [J/OL]. Front. Microbiol., 2016, 7: 1125 [2022-05-10]. . |
| 25 | LINO T, MORI K, UCHINO Y, et al.. Ignavibacterium album gen. nov., sp. nov., a moderately thermophilic anaerobic bacterium isolated from microbial mats at a terrestrial hot spring and proposal of Ignavibacteria classis nov., for a novel lineage at the periphery of green sulfur bacteria [J]. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2010, 60(6):1376-1382. |
| 26 | XUN W B, HUANG T, ZHAO J, et al.. Environmental conditions rather than microbial inoculum composition determine the bacterial composition, microbial biomass and enzymatic activity of reconstructed soil microbial communities [J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2015, 90(11):10-18. |
| [1] | Jia YAO, Jiaxin LIU, Yan SU, Xiaojuan SU. Effects of Combined Application of Tobacco Stem Biochar and Nitrogen Fertilizers on Corn Growth and Soil Properties in Seeding Stage [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(3): 140-151. |
| [2] | Yunzhu ZHENG, Shuchen SUN. Effects of Straw Biochar and Straw on Soil Nutrients and Crop Yield in Wheat-Maize Rotation System [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(2): 152-162. |
| [3] | Juxian GUO, Bishan OUYANG, Guihua LI, Mei FU, Wenlong LUO, Shanwei LUO, Meilian LU. Effect of Bio-organic Fertilizers on Quality and Soil of Continuous Crop Chinese Flowering Cabbage [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(2): 182-191. |
| [4] | Xin LUO, Yuekai WU, Niannian ZHANG, Jie XU, Zaihua YANG. Composition and Diversity of Fungal Community in Rhizosphere Soil of Camellia Oleifera [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(2): 199-210. |
| [5] | Xuejin YANG, Yuanyuan ZHOU, Xinyi PENG, Jianfeng LIU, Aimin ZHANG, Aiqin JING, Gangyong ZHAO, Dandan CAO. Comparative Analysis of Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Community Structure Between Root-knot Nematode Diseased and Healthy Cucumber [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(1): 109-118. |
| [6] | Xiaohu YANG, Manyu ZHANG, Haichang YANG, Fenghua ZHANG, Yilin JIANG, Xiaolan YI. Inversion of Soil Salinity in Farmland of Manas River Basin Based on Combined Model [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(1): 134-141. |
| [7] | Geng LI, Yuanyuan ZHAO, Yuyuan CHENG, Jiang WU, Weidong DUAN, Guangting YIN, Qian LI, Chen CHEN, Fei ZHENG, Yuan LIU, Hongzhi SHI. Effects of Different Organic-inorganic Nitrogen Ratios on Soil Carbon and Nitrogen and Upper Leaf Quality in Nanyang Tobacco Area [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(1): 175-186. |
| [8] | Chuang LU, Haitang HU, Yuan QIN, Heju HUAI, Cunjun LI. Delineating Management Zones in Spring Maize Field Based on UAV Multispectral Image [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(9): 106-115. |
| [9] | Guanqun CHAI, Guihua LIU, Wei ZHOU, Xiujin ZHANG, Longpin LI, Chengwu FAN. Evaluation of Pollution Risk and Source Analysis of Heavy Metals in Greenhouse Soils in Wumeng Mountain Area, Guizhou Province [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(8): 144-153. |
| [10] | Quanquan WEI, Ying GAO, Jiulan GOU, Meng ZHANG, Yong RAO, Bin YANG, Di FAN, Wenhao FENG, Huagui XIAO. Effects of Different Sowing Rates and Sowing Methods on the Nutrient Absorption, Utilization and Yield of Winter Rapeseed in Yellow Soil [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(8): 182-191. |
| [11] | Xuejing LIU, Xiaoyuan BAO, Xiaoyang HOU, Wenchao ZHEN. Dynamics of Soil Water Content and Yield Formation Characteristics of Winter Wheat Under Water Limited Irrigation in Spring in Haihe Plain [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(7): 167-176. |
| [12] | Ning YAN, Yu ZHAN, Xinyue MIAO, Ergang WANG, Changbao CHEN, Qiong LI. Effects of Reductive Soil Disinfestation on Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Soil Enzyme Activity in Continuous Cropping of Ginseng [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(6): 133-144. |
| [13] | Yaru HUANG, Yingbin MA, Yonghua LI, Xue DONG, Yuan LIU, Meng YU, Chunxia HAN, Kaimin JIAN, Haifeng MA. Relationships Between Soil Factors and Populus euphratica’s Sap Flow at Different Time Scales [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(6): 196-205. |
| [14] | Chenguang ZHAO, Siyun NIU, Xun CHEN, Li FANG, Haitao LI, Peixing WANG, Binbin SHEN, Yuanzhi SHI. Effects of Compound Fertilizer on Tea Yield, Quality and Fertility of Tea Garden Soil [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(6): 206-217. |
| [15] | Jie LI, Ying LIN, Meiyu XU, Fei WANG, Lingchuan XU. Sequencing Analysis of Fungal Diversity in Rhizosphere Soil of Cynanchum bungei Decne [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(6): 70-81. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号