




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (9): 69-78.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0222
• BIOTECHNOLOGY & LIFE SCIENCE • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jie LIU1( ), Bin WANG2, Jingjing HOU2, Bing WU1(
), Bin WANG2, Jingjing HOU2, Bing WU1( ), Li ZHAO1(
), Li ZHAO1( )
)
Received:2024-03-22
Accepted:2024-08-28
Online:2025-09-15
Published:2025-09-24
Contact:
Bing WU,Li ZHAO
刘杰1( ), 王斌2, 侯静静2, 吴兵1(
), 王斌2, 侯静静2, 吴兵1( ), 赵利1(
), 赵利1( )
)
通讯作者:
吴兵,赵利
作者简介:刘杰 E-mail:1280334764@qq.com
CLC Number:
Jie LIU, Bin WANG, Jingjing HOU, Bing WU, Li ZHAO. Analysis of Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Flax Local Varieties in Gansu[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(9): 69-78.
刘杰, 王斌, 侯静静, 吴兵, 赵利. 甘肃胡麻地方品种遗传多样性和群体结构分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(9): 69-78.
序号 Code | 名称 Name | 来源 Source | 序号 Code | 名称 Name | 来源 Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 灵台什字 Lingtaishenzi | 平凉 Pingliang | 9 | 静宁红 Jingninghong | 平凉 Pingliang |
| 2 | 灵台五星 Lingtaiwuxing | 平凉 Pingliang | 10 | 华亭 Huating | 平凉 Pingliang |
| 3 | 静宁选1 Jingningxuan 1 | 平凉 Pingliang | 11 | 庄浪红 Zhuanglanghong | 平凉 Pingliang |
| 4 | 灵台上良 Lingtaishangliang | 平凉 Pingliang | 12 | 静宁老 Jingninglao | 平凉 Pingliang |
| 5 | 庄浪小红 Zhuanglangxiaohong | 平凉 Pingliang | 13 | 静宁选3 Jingningxuan 3 | 平凉 Pingliang |
| 6 | 静宁选2 Jingningxuan 2 | 平凉 Pingliang | 14 | 庄浪胡麻 Zhuanglanghuma | 平凉 Pingliang |
| 7 | 平凉红 Pinglianghong | 平凉 Pingliang | 15 | 崇信二混子 Chongxingerhunzi | 平凉 Pingliang |
| 8 | 崇信红 Chongxinhong | 平凉 Pingliang | 16 | 庆阳老 Qingyanglao | 庆阳 Qingyang |
| 17 | 镇原 Zhenyuan | 庆阳 Qingyang | 38 | 舟曲除瓦 Zhouquchuwa | 甘南 Gannan |
| 18 | 合水红 Heshuihong | 庆阳 Qingyang | 39 | 定西红1 Dingxihong 1 | 定西 Dingxi |
| 19 | 环县胡麻 Huanxianhuma | 庆阳 Qingyang | 40 | 漳县红 Zhangxianhong | 定西 Dingxi |
| 20 | 庆阳 Qingyang | 庆阳 Qingyang | 41 | 定西红2 Dingxihong 2 | 定西 Dingxi |
| 21 | 宕昌高脚 Dangchanggaojiao | 陇南 Longnan | 42 | 陇西白 Longxibai | 定西 Dingxi |
| 22 | 西和老 Xihelao | 陇南 Longnan | 43 | 渭源胡麻 Weiyuanhuma | 定西 Dingxi |
| 23 | 武都 Wudu | 陇南 Longnan | 44 | 尧甸白 Yaodianbai | 定西 Dingxi |
| 24 | 礼县胡麻 Lixianhuma | 陇南 Longnan | 45 | 通渭白 Tongweibai | 定西 Dingxi |
| 25 | 礼县罗坝 Lixianluoba | 陇南 Longnan | 46 | 陇西红 Longxihong | 定西 Dingxi |
| 26 | 礼县白 Lixianbai | 陇南 Longnan | 47 | 通渭老红 Tongweilaohong | 定西 Dingxi |
| 27 | 西和红 Xihehong | 陇南 Longnan | 48 | 岷县胡麻 Mingxianhuma | 定西 Dingxi |
| 28 | 礼县高脚 Lixiangaojiao | 陇南 Longnan | 49 | 定西红 Dingxihong | 定西 Dingxi |
| 29 | 宕昌长脚 Dangchangchangjiao | 陇南 Longnan | 50 | 尧甸高杆 Yaodiangaogan | 定西 Dingxi |
| 30 | 宕昌短脚 Dangchangduanjiao | 陇南 Longnan | 51 | 渭源本地 Weiyuanbendi | 定西 Dingxi |
| 31 | 礼县低脚 Lixiandijiao | 陇南 Longnan | 52 | 定西红中川 Dingxihongzhongchuan | 定西 Dingxi |
| 32 | 天水渭南 Tianshuiweinan | 天水 Tianshui | 53 | 临夏尕红 Lingxiagahong | 临夏 Linxia |
| 33 | 清水老 Qingshuilao | 天水 Tianshui | 54 | 康乐白花 Kanglebaihua | 临夏 Linxia |
| 34 | 天水白 Tianshuibai | 天水 Tianshui | 55 | 东乡红 Dongxianghong | 临夏 Linxia |
| 35 | 天水渭南1 Tainshuiweinan 1 | 天水 Tianshui | 56 | 临夏尕胡麻 Linxiagahuma | 临夏 Linxia |
| 36 | 天水红 Tianshuihong | 天水 Tianshui | 57 | 临夏白 Linxiabai | 临夏 Linxia |
| 37 | 清水胡麻 Qingshuihuma | 天水 Tianshui | 58 | 康乐2 Kangle 2 | 临夏 Linxia |
| 59 | 东乡高杆 Dongxianggaogan | 临夏 Linxia | 77 | 酒泉白 Jiuquanbai | 酒泉 Jiuquan |
| 60 | 康乐1 Kangle 1 | 临夏 Linxia | 78 | 敦煌白 Dunhuangbai | 酒泉 Jiuquan |
| 61 | 东乡白 Dongxiangbai | 临夏 Linxia | 79 | 武威红 Wuweihong | 武威 Wuwei |
| 62 | 和政紫 Hezhengzi | 临夏 Linxia | 80 | 黄羊白 Huangyangbai | 武威 Wuwei |
| 63 | 广河红 Guanghehong | 临夏 Linxia | 81 | 民勤胡麻 Minqinhuma | 武威 Wuwei |
| 64 | 景泰红 Jingtaihong | 白银 Baiyin | 82 | 永昌红 Yongchanghong | 金昌 Jinchang |
| 65 | 景泰白 Jingtaibai | 白银 Baiyin | 83 | 永昌 Yongchang | 金昌 Jinchang |
| 66 | 会宁大沟 Huiningdagou | 白银 Baiyin | 84 | 临泽小 Linzexiao | 张掖 Zhangye |
| 67 | 靖远红 Jingyuanhong | 白银 Baiyin | 85 | 张掖白 Zhangyebai | 张掖 Zhangye |
| 68 | 会宁红 Huininghong | 白银 Baiyin | 86 | 高台白 Gaotaibai | 张掖 Zhangye |
| 69 | 皋兰二混子 Gaolanerhunzi | 兰州 Lanzhou | 87 | 高台红 Gaotaihong | 张掖 Zhangye |
| 70 | 榆中红 Yuzhonghong | 兰州 Lanzhou | 88 | 民乐红 Minlehong | 张掖 Zhangye |
| 71 | 皋兰红 Ganlaohong | 兰州 Lanzhou | 89 | 临泽本地 Linzebendi | 张掖 Zhangye |
| 72 | 酒泉078 Jiuquan 078 | 酒泉 Jiuquan | 90 | 张掖红 Zhangyehong | 张掖 Zhangye |
| 73 | 安西红 Anxihong | 酒泉 Jiuquan | 91 | 肃南红 Sunanhong | 张掖 Zhangye |
| 74 | 酒泉红 Jiuquanhong | 酒泉 Jiuquan | 92 | 临泽白 Linzebai | 张掖 Zhangye |
| 75 | 酒泉小红 Jiuquan xiaohong | 酒泉 Jiuquan | 93 | 张掖混子 Zhangyehunzi | 张掖 Zhangye |
| 76 | 敦煌红 Dunhuanghong | 酒泉 Jiuquan | 94 | 民乐老胡麻 Minlelaohuma | 张掖 Zhangye |
Table 1 Information of 94 local germplasms in Gansu
序号 Code | 名称 Name | 来源 Source | 序号 Code | 名称 Name | 来源 Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 灵台什字 Lingtaishenzi | 平凉 Pingliang | 9 | 静宁红 Jingninghong | 平凉 Pingliang |
| 2 | 灵台五星 Lingtaiwuxing | 平凉 Pingliang | 10 | 华亭 Huating | 平凉 Pingliang |
| 3 | 静宁选1 Jingningxuan 1 | 平凉 Pingliang | 11 | 庄浪红 Zhuanglanghong | 平凉 Pingliang |
| 4 | 灵台上良 Lingtaishangliang | 平凉 Pingliang | 12 | 静宁老 Jingninglao | 平凉 Pingliang |
| 5 | 庄浪小红 Zhuanglangxiaohong | 平凉 Pingliang | 13 | 静宁选3 Jingningxuan 3 | 平凉 Pingliang |
| 6 | 静宁选2 Jingningxuan 2 | 平凉 Pingliang | 14 | 庄浪胡麻 Zhuanglanghuma | 平凉 Pingliang |
| 7 | 平凉红 Pinglianghong | 平凉 Pingliang | 15 | 崇信二混子 Chongxingerhunzi | 平凉 Pingliang |
| 8 | 崇信红 Chongxinhong | 平凉 Pingliang | 16 | 庆阳老 Qingyanglao | 庆阳 Qingyang |
| 17 | 镇原 Zhenyuan | 庆阳 Qingyang | 38 | 舟曲除瓦 Zhouquchuwa | 甘南 Gannan |
| 18 | 合水红 Heshuihong | 庆阳 Qingyang | 39 | 定西红1 Dingxihong 1 | 定西 Dingxi |
| 19 | 环县胡麻 Huanxianhuma | 庆阳 Qingyang | 40 | 漳县红 Zhangxianhong | 定西 Dingxi |
| 20 | 庆阳 Qingyang | 庆阳 Qingyang | 41 | 定西红2 Dingxihong 2 | 定西 Dingxi |
| 21 | 宕昌高脚 Dangchanggaojiao | 陇南 Longnan | 42 | 陇西白 Longxibai | 定西 Dingxi |
| 22 | 西和老 Xihelao | 陇南 Longnan | 43 | 渭源胡麻 Weiyuanhuma | 定西 Dingxi |
| 23 | 武都 Wudu | 陇南 Longnan | 44 | 尧甸白 Yaodianbai | 定西 Dingxi |
| 24 | 礼县胡麻 Lixianhuma | 陇南 Longnan | 45 | 通渭白 Tongweibai | 定西 Dingxi |
| 25 | 礼县罗坝 Lixianluoba | 陇南 Longnan | 46 | 陇西红 Longxihong | 定西 Dingxi |
| 26 | 礼县白 Lixianbai | 陇南 Longnan | 47 | 通渭老红 Tongweilaohong | 定西 Dingxi |
| 27 | 西和红 Xihehong | 陇南 Longnan | 48 | 岷县胡麻 Mingxianhuma | 定西 Dingxi |
| 28 | 礼县高脚 Lixiangaojiao | 陇南 Longnan | 49 | 定西红 Dingxihong | 定西 Dingxi |
| 29 | 宕昌长脚 Dangchangchangjiao | 陇南 Longnan | 50 | 尧甸高杆 Yaodiangaogan | 定西 Dingxi |
| 30 | 宕昌短脚 Dangchangduanjiao | 陇南 Longnan | 51 | 渭源本地 Weiyuanbendi | 定西 Dingxi |
| 31 | 礼县低脚 Lixiandijiao | 陇南 Longnan | 52 | 定西红中川 Dingxihongzhongchuan | 定西 Dingxi |
| 32 | 天水渭南 Tianshuiweinan | 天水 Tianshui | 53 | 临夏尕红 Lingxiagahong | 临夏 Linxia |
| 33 | 清水老 Qingshuilao | 天水 Tianshui | 54 | 康乐白花 Kanglebaihua | 临夏 Linxia |
| 34 | 天水白 Tianshuibai | 天水 Tianshui | 55 | 东乡红 Dongxianghong | 临夏 Linxia |
| 35 | 天水渭南1 Tainshuiweinan 1 | 天水 Tianshui | 56 | 临夏尕胡麻 Linxiagahuma | 临夏 Linxia |
| 36 | 天水红 Tianshuihong | 天水 Tianshui | 57 | 临夏白 Linxiabai | 临夏 Linxia |
| 37 | 清水胡麻 Qingshuihuma | 天水 Tianshui | 58 | 康乐2 Kangle 2 | 临夏 Linxia |
| 59 | 东乡高杆 Dongxianggaogan | 临夏 Linxia | 77 | 酒泉白 Jiuquanbai | 酒泉 Jiuquan |
| 60 | 康乐1 Kangle 1 | 临夏 Linxia | 78 | 敦煌白 Dunhuangbai | 酒泉 Jiuquan |
| 61 | 东乡白 Dongxiangbai | 临夏 Linxia | 79 | 武威红 Wuweihong | 武威 Wuwei |
| 62 | 和政紫 Hezhengzi | 临夏 Linxia | 80 | 黄羊白 Huangyangbai | 武威 Wuwei |
| 63 | 广河红 Guanghehong | 临夏 Linxia | 81 | 民勤胡麻 Minqinhuma | 武威 Wuwei |
| 64 | 景泰红 Jingtaihong | 白银 Baiyin | 82 | 永昌红 Yongchanghong | 金昌 Jinchang |
| 65 | 景泰白 Jingtaibai | 白银 Baiyin | 83 | 永昌 Yongchang | 金昌 Jinchang |
| 66 | 会宁大沟 Huiningdagou | 白银 Baiyin | 84 | 临泽小 Linzexiao | 张掖 Zhangye |
| 67 | 靖远红 Jingyuanhong | 白银 Baiyin | 85 | 张掖白 Zhangyebai | 张掖 Zhangye |
| 68 | 会宁红 Huininghong | 白银 Baiyin | 86 | 高台白 Gaotaibai | 张掖 Zhangye |
| 69 | 皋兰二混子 Gaolanerhunzi | 兰州 Lanzhou | 87 | 高台红 Gaotaihong | 张掖 Zhangye |
| 70 | 榆中红 Yuzhonghong | 兰州 Lanzhou | 88 | 民乐红 Minlehong | 张掖 Zhangye |
| 71 | 皋兰红 Ganlaohong | 兰州 Lanzhou | 89 | 临泽本地 Linzebendi | 张掖 Zhangye |
| 72 | 酒泉078 Jiuquan 078 | 酒泉 Jiuquan | 90 | 张掖红 Zhangyehong | 张掖 Zhangye |
| 73 | 安西红 Anxihong | 酒泉 Jiuquan | 91 | 肃南红 Sunanhong | 张掖 Zhangye |
| 74 | 酒泉红 Jiuquanhong | 酒泉 Jiuquan | 92 | 临泽白 Linzebai | 张掖 Zhangye |
| 75 | 酒泉小红 Jiuquan xiaohong | 酒泉 Jiuquan | 93 | 张掖混子 Zhangyehunzi | 张掖 Zhangye |
| 76 | 敦煌红 Dunhuanghong | 酒泉 Jiuquan | 94 | 民乐老胡麻 Minlelaohuma | 张掖 Zhangye |
引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5’-3’) | |
|---|---|---|
| m10 | GGGATGCTGATGAGGAAG | GGAGGAGACAGAGGTGGA |
| LGM-61 | GCCTGCAGTTTAGTCGTTGG | CGGAAAGAACAATTCCAGCTC |
| LU28 | TCCCAGCGAGTTTGGTGAG | TGGAGGAACTAATTGTGGCAAG |
| LU3 | GCTCGTGATCTCCTTCATCC | AAAACCACGTCCAGATGCTC |
| LU7 | CATCCAACAAAGGGTGGTG | GGAACAAAGGGTAGCCATGA |
| LU8 | TCCCGTAATATTCTATGTTCTTCC | TGAGTTGGACCTTACAAGACTCA |
| LU15 | TGGACGACGATGAAGATGAA | CCGCCGGGTACACTACTACT |
| LU18 | AGAGGCGGAGGGCATTAC | TTGGAGAGTTGGAATCGAGA |
| 101 | AGGAAGAGGTAGCCCAGTCC | AGACTCACGGTGAAGGCAAC |
| 35L | ACGTCGAGGAGAAGGGAGAT | AATGTCCGTCTCCCACAAAC |
| SR3572 | TCTCGTAGCTAGGGAGATGG | AAAGCCGTCGTACTCACCAC |
| scaffold993 | CAGATCGATGAACTCCTCCTCA | GCTGCTTTTGTTGTTGTTGGAG |
| scaffold231 | TTGAGGTGCAGCTTAACAGAGC | AATGGGTTTCAGCAGCTTCTTC |
| sfd584 | TCATTTCTCCAACCAGCTGAAA | CAAATCTCCGGACCAGACTCTT |
| scaffold25 | TGGAGCTTCTTCATCTGCTTTG | GGATTCAACCGACTTGGGATAA |
| Lu291 | GGAAATTCCAAGTTCCCAGT | AGTTTCGCTATTCCGTCTGC |
| Lu672 | GGATTTGACGCTGGGTGTAG | GGATTTGACGCTGGGTGTAG |
| Lu836 | AAGATAGGGGGACGCAGAAT | AAGATAGGGGGACGCAGAAT |
| Lu2553 | TGGGAGAAATTATCCACTACGC | TGGGAGAAATTATCCACTACGC |
| Lu2565 | AACCAAGAGGCTTCATACGG | AACCAAGAGGCTTCATACGG |
| Lu2996 | GGCAGACTCTCGCTGGTTAG | GGCAGACTCTCGCTGGTTAG |
Table 2 SSR primer information
引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5’-3’) | |
|---|---|---|
| m10 | GGGATGCTGATGAGGAAG | GGAGGAGACAGAGGTGGA |
| LGM-61 | GCCTGCAGTTTAGTCGTTGG | CGGAAAGAACAATTCCAGCTC |
| LU28 | TCCCAGCGAGTTTGGTGAG | TGGAGGAACTAATTGTGGCAAG |
| LU3 | GCTCGTGATCTCCTTCATCC | AAAACCACGTCCAGATGCTC |
| LU7 | CATCCAACAAAGGGTGGTG | GGAACAAAGGGTAGCCATGA |
| LU8 | TCCCGTAATATTCTATGTTCTTCC | TGAGTTGGACCTTACAAGACTCA |
| LU15 | TGGACGACGATGAAGATGAA | CCGCCGGGTACACTACTACT |
| LU18 | AGAGGCGGAGGGCATTAC | TTGGAGAGTTGGAATCGAGA |
| 101 | AGGAAGAGGTAGCCCAGTCC | AGACTCACGGTGAAGGCAAC |
| 35L | ACGTCGAGGAGAAGGGAGAT | AATGTCCGTCTCCCACAAAC |
| SR3572 | TCTCGTAGCTAGGGAGATGG | AAAGCCGTCGTACTCACCAC |
| scaffold993 | CAGATCGATGAACTCCTCCTCA | GCTGCTTTTGTTGTTGTTGGAG |
| scaffold231 | TTGAGGTGCAGCTTAACAGAGC | AATGGGTTTCAGCAGCTTCTTC |
| sfd584 | TCATTTCTCCAACCAGCTGAAA | CAAATCTCCGGACCAGACTCTT |
| scaffold25 | TGGAGCTTCTTCATCTGCTTTG | GGATTCAACCGACTTGGGATAA |
| Lu291 | GGAAATTCCAAGTTCCCAGT | AGTTTCGCTATTCCGTCTGC |
| Lu672 | GGATTTGACGCTGGGTGTAG | GGATTTGACGCTGGGTGTAG |
| Lu836 | AAGATAGGGGGACGCAGAAT | AAGATAGGGGGACGCAGAAT |
| Lu2553 | TGGGAGAAATTATCCACTACGC | TGGGAGAAATTATCCACTACGC |
| Lu2565 | AACCAAGAGGCTTCATACGG | AACCAAGAGGCTTCATACGG |
| Lu2996 | GGCAGACTCTCGCTGGTTAG | GGCAGACTCTCGCTGGTTAG |
| 引物Primer | Na | Ne | PIC | Ho | He | I | Fst | Nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m10 | 3 | 1.704 | 0.369 | 0.457 | 0.415 | 0.730 | 0.030 | 8.093 |
| LGM-61 | 2 | 1.353 | 0.227 | 0.309 | 0.262 | 0.430 | 0.014 | 17.634 |
| LU28 | 2 | 1.837 | 0.352 | 0.702 | 0.458 | 0.614 | 0.005 | 52.071 |
| LU3 | 2 | 1.826 | 0.350 | 0.692 | 0.455 | 0.627 | 0.011 | 23.148 |
| LU7 | 2 | 1.972 | 0.439 | 0.117 | 0.495 | 0.644 | 0.051 | 4.626 |
| LU8 | 3 | 2.305 | 0.522 | 0.400 | 0.569 | 0.645 | 0.010 | 25.916 |
| LU15 | 3 | 1.987 | 0.441 | 0.628 | 0.499 | 0.648 | 0.012 | 20.478 |
| LU18 | 2 | 1.732 | 0.333 | 0.606 | 0.425 | 0.654 | 0.046 | 5.150 |
| 101 | 2 | 1.929 | 0.366 | 0.809 | 0.484 | 0.675 | 0.008 | 30.151 |
| 35L | 2 | 1.937 | 0.367 | 0.819 | 0.486 | 0.677 | 0.006 | 41.212 |
| SR3572 | 2 | 1.996 | 0.375 | 0.511 | 0.502 | 0.692 | 0.007 | 34.529 |
| scaffold993 | 2 | 1.665 | 0.416 | 0.552 | 0.402 | 0.589 | 0.016 | 15.365 |
| scaffold231 | 2 | 1.996 | 0.375 | 0.958 | 0.502 | 0.692 | 0.002 | 151.690 |
| sfd584 | 2 | 1.209 | 0.158 | 0.192 | 0.174 | 0.316 | 0.060 | 3.943 |
| scaffold25 | 3 | 2.067 | 0.444 | 0.404 | 0.519 | 0.852 | 0.008 | 33.264 |
| Lu291 | 2 | 1.162 | 0.148 | 0.060 | 0.140 | 0.267 | 0.045 | 5.351 |
| Lu672 | 2 | 1.398 | 0.261 | 0.108 | 0.286 | 0.459 | 0.009 | 29.635 |
| Lu836 | 2 | 1.252 | 0.187 | 0.223 | 0.203 | 0.396 | 0.010 | 25.828 |
| Lu2553 | 2 | 1.858 | 0.355 | 0.170 | 0.464 | 0.855 | 0.007 | 34.298 |
| Lu2565 | 2 | 1.824 | 0.408 | 0.200 | 0.454 | 0.860 | 0.032 | 7.609 |
| Lu2996 | 2 | 1.586 | 0.301 | 0.489 | 0.372 | 0.556 | 0.030 | 8.038 |
Table 3 21 genetic diversity parameters for SSR primers
| 引物Primer | Na | Ne | PIC | Ho | He | I | Fst | Nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m10 | 3 | 1.704 | 0.369 | 0.457 | 0.415 | 0.730 | 0.030 | 8.093 |
| LGM-61 | 2 | 1.353 | 0.227 | 0.309 | 0.262 | 0.430 | 0.014 | 17.634 |
| LU28 | 2 | 1.837 | 0.352 | 0.702 | 0.458 | 0.614 | 0.005 | 52.071 |
| LU3 | 2 | 1.826 | 0.350 | 0.692 | 0.455 | 0.627 | 0.011 | 23.148 |
| LU7 | 2 | 1.972 | 0.439 | 0.117 | 0.495 | 0.644 | 0.051 | 4.626 |
| LU8 | 3 | 2.305 | 0.522 | 0.400 | 0.569 | 0.645 | 0.010 | 25.916 |
| LU15 | 3 | 1.987 | 0.441 | 0.628 | 0.499 | 0.648 | 0.012 | 20.478 |
| LU18 | 2 | 1.732 | 0.333 | 0.606 | 0.425 | 0.654 | 0.046 | 5.150 |
| 101 | 2 | 1.929 | 0.366 | 0.809 | 0.484 | 0.675 | 0.008 | 30.151 |
| 35L | 2 | 1.937 | 0.367 | 0.819 | 0.486 | 0.677 | 0.006 | 41.212 |
| SR3572 | 2 | 1.996 | 0.375 | 0.511 | 0.502 | 0.692 | 0.007 | 34.529 |
| scaffold993 | 2 | 1.665 | 0.416 | 0.552 | 0.402 | 0.589 | 0.016 | 15.365 |
| scaffold231 | 2 | 1.996 | 0.375 | 0.958 | 0.502 | 0.692 | 0.002 | 151.690 |
| sfd584 | 2 | 1.209 | 0.158 | 0.192 | 0.174 | 0.316 | 0.060 | 3.943 |
| scaffold25 | 3 | 2.067 | 0.444 | 0.404 | 0.519 | 0.852 | 0.008 | 33.264 |
| Lu291 | 2 | 1.162 | 0.148 | 0.060 | 0.140 | 0.267 | 0.045 | 5.351 |
| Lu672 | 2 | 1.398 | 0.261 | 0.108 | 0.286 | 0.459 | 0.009 | 29.635 |
| Lu836 | 2 | 1.252 | 0.187 | 0.223 | 0.203 | 0.396 | 0.010 | 25.828 |
| Lu2553 | 2 | 1.858 | 0.355 | 0.170 | 0.464 | 0.855 | 0.007 | 34.298 |
| Lu2565 | 2 | 1.824 | 0.408 | 0.200 | 0.454 | 0.860 | 0.032 | 7.609 |
| Lu2996 | 2 | 1.586 | 0.301 | 0.489 | 0.372 | 0.556 | 0.030 | 8.038 |
| 来源地Source | 陇东LD | 陇南LN | 中部ZB |
|---|---|---|---|
| 陇南LN | 0.977 | ||
| 中部ZB | 0.984 | 0.991 | |
| 河西HE | 0.983 | 0.985 | 0.986 |
Table 4 Similarity coefficient between different sources of germplasms
| 来源地Source | 陇东LD | 陇南LN | 中部ZB |
|---|---|---|---|
| 陇南LN | 0.977 | ||
| 中部ZB | 0.984 | 0.991 | |
| 河西HE | 0.983 | 0.985 | 0.986 |
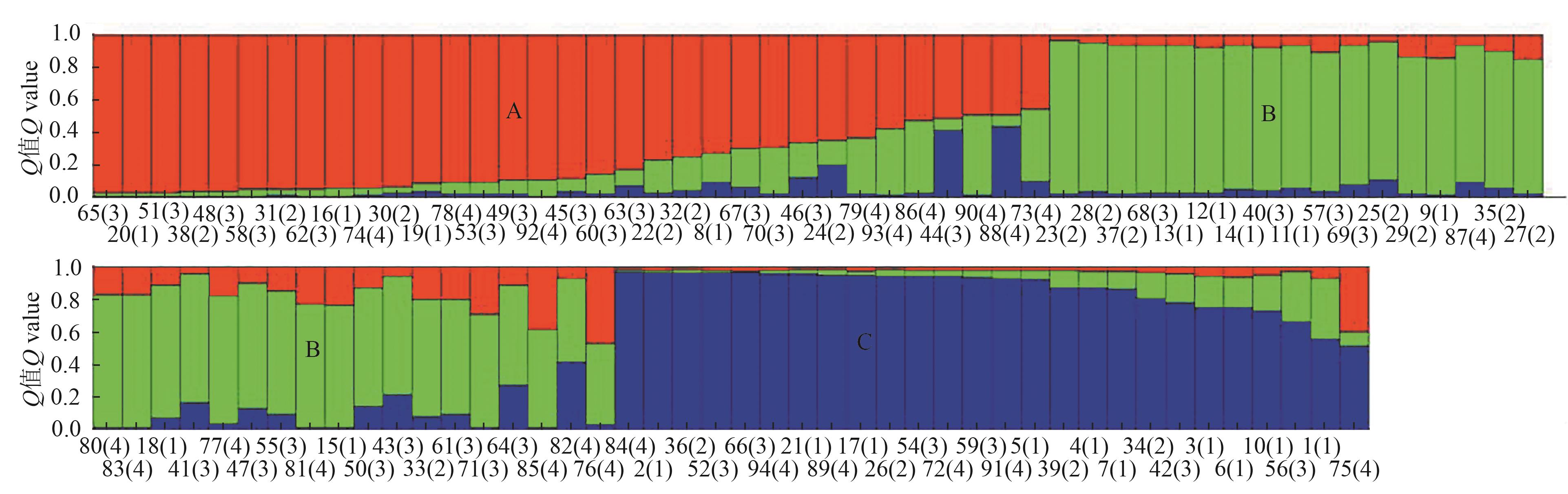
Fig. 2 Population structure of 94 flax local germplasmsNote: Code outside parentheses is code of 94 germplasms in Table 1; 1~4 in parentheses indicate LD, LN, ZB, HX.
| [1] | 马慧敏,任红燕,张振宇,等.山西胡麻产业高质量发展对策研究[J].山西农经,2024(5):152-156. |
| [2] | 崔翠,周清元,王利鹃,等.亚麻种质主要农艺性状主成分分析与综合评价[J].西南大学学报(自然科学版),2016,38(12):10-18. |
| CUI C, ZHOU Q Y, WANG L J, et al.. The cluster analysis and comprehensive evaluation of flax germplasm based on principal components of agronomic traits [J]. J. Southwest Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2016, 38(12): 10-18. | |
| [3] | 张丽丽,刘晶晶,乔海明,等.从俄罗斯引进亚麻种质资源的农艺性状评价[J].中国油料作物学报,2017,39(5):698-703. |
| ZHANG L L, LIU J J, QIAO H M, et al.. Evaluation of flax germplasm introduced from Russia by agronomic traits [J]. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci., 2017, 39(5): 698-703. | |
| [4] | HAO D M, QIU C S, LONG S H, et al.. An overview on molecular biology of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) in China [J]. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2016, 17(8):1767-1772. |
| [5] | 高凤云,斯钦巴特尔,周宇,等.基于SSR标记的胡麻粗脂肪及脂肪酸组分的关联分析[J].作物杂志,2022(1):44-49. |
| GAO F Y, Siqinbateer, ZHOU Y, et al.. Association analysis of crude fat and fatty acid components in flax based on SSR markers [J]. Crops, 2022(1):44-49. | |
| [6] | 潘慧云.亚麻表型性状与SSR标记的关联分析[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古大学,2019. |
| PAN H Y. Association analvsis of flax phenotypic traits using SSR markers [D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2019. | |
| [7] | 何东锋.亚麻RAPD和微卫星标记开发与遗传多样性分析[D].长沙:湖南农业大学,2009. |
| HE D F. Flax RAPD and microsatellite marker development and genetic diversity analysis [D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2009. | |
| [8] | 李秋芝,宋鑫玲,曹洪勋,等.100份亚麻种质资源遗传多样性及亲缘关系的RAPD分析[J].现代农业科技,2015(24):65-67, 71. |
| LI Q Z, SONG X L, CAO H X, et al.. Genetic diversities and phylogenetic relationships of 100 flax germplasm resources based on RAPD [J]. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2015(24): 65-67, 71. | |
| [9] | 王斌.亚麻EST-SSR和SRAP标记研究[D].兰州:甘肃农业大学,2010. |
| WANG B. Studies on EST-SSR and SRAP markers in flax [D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2010. | |
| [10] | 李闻娟,齐燕妮,王利民,等.运用SRAP分子标记对胡麻杂交种纯度的鉴定研究[J].甘肃农业科技,2019(9):59-62. |
| [11] | 李丹丹.部分胡麻种质资源主要农艺性状和AFLP分子标记的遗传多样性分析[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学,2015. |
| LI D D. Genetic diversity of agronomic traits and aflp marker of flax germplasm [D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2015. | |
| [12] | SINGH N, AGARWAL N, YADAV H K. Genome-wide SNP-based diversity analysis and association mapping in linseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) [J/OL]. Euphytica, 2019, 215(8): 139 [2024-02-10]. . |
| [13] | 伊六喜,斯钦巴特尔,高凤云,等.内蒙古胡麻地方品种资源遗传多样性分析[J].作物杂志,2018,34(6):53-57. |
| YI L X, Siqinbateer, GAO F Y, et al.. Genetic diversity of flax germplasm resources in Inner Mongolia [J]. Crops, 2018, 34(6):53-57. | |
| [14] | 邓欣.亚麻分子标记的开发及产量相关性状的关联分析[D].北京:中国农业科学院,2013. |
| DENG X. Development of molecular markers and association analysis of yield related traits in flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2013. | |
| [15] | CLOUTIER S, NIU Z, DATLA R, et al.. Development and analysis of EST-SSRs for flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) [J]. Theor. Appl. Genet., 2009, 119(1): 53-63. |
| [16] | WU J, ZHAO Q, WU G, et al.. Development of novel SSR markers for flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) using reduced-representation genome sequencing [J]. Front. Plant Sci., 2017, 7(7): 22-30. |
| [17] | 李清超,张登峰,李春辉,等.西南地区玉米地方种质资源遗传多样性分析及综合评价[J].作物杂志,2024(4):24-32. |
| LI Q C, ZHANG D F, LI C H, et al.. Genetic diversity analysis and comprehensive evaluation of maize landraces in southwest China [J]. Crops, 2024(4): 24-32. | |
| [18] | 李荣华,夏岩石,刘顺枝,等.改进的CTAB提取植物DNA方法[J].实验室研究与探索,2009,28(9):14-16. |
| LI R H, XIA Y S, LIU S Z, et al.. CTAB-improved method of DNA extraction in plant [J]. Res. Explor. Lab., 2009, 28(9): 14-16. | |
| [19] | DENG X, LONG S H, HE D F, et al.. Isolation and characterization of polymorphic microsatellite markers from flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) [J]. Afr. J. Biotechnol., 2011, 10: 734-739. |
| [20] | SAHA D, RANA R S, DAS S, et al.. Genome-wide regulatory gene-derived SSRs reveal genetic differentiation and population structure in fiber flax genotypes [J]. J. Appl. Genet., 2019, 60(1): 13-25. |
| [21] | BICKEL C L, GADANI S, LUKACS M, et al.. SSR markers developed for genetic mapping in flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) [J]. Res. Reports Biol., 2011, 2: 23-29. |
| [22] | ROOSE-AMSALEG C, CARIOU-PHAM E, VAUTRIN D, et al.. Polymorphic microsatellite loci in Linum usitatissimum [J]. Mol. Ecol. Notes, 2006, 6(3): 796-799. |
| [23] | SOTO-CERDA B J, CARRASCO R A, ARAVENA G A, et al.. Identifying novel polymorphic microsatellites from cultivated flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) following data mining [J]. Plant Mol. Biol. Report., 2011, 29(3): 753-759. |
| [24] | SOTO-CERDA B J, CLOUTIER S. Outlier loci and selection signatures of simple sequence repeats (SSRs) in flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) [J]. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep., 2013, 31(4): 978-990. |
| [25] | 樊文强,盖红梅,孙鑫,等.SSR数据格式转换软件DataFormater [J].分子植物育种,2016,14(1):265-270. |
| FAN W Q, GAI H M, SUN X, et al.. DataFormater, a software for SSR data formatting to develop population genetics analysis [J]. Mol. Plant Breeding, 2016, 14(1): 265-270. | |
| [26] | YAN W, KARIKARI B, CHANG F, et al.. Genome-wide association study to map genomic regions related to the initiation time of four growth stage traits in soybean [J/OL]. Front. Genet., 2021, 12: 715529 [2024-02-10]. . |
| [27] | HIETER P A, HOLLIS G F, KORSMEYER S J, et al.. Clustered arrangement of immunoglobulin lambda constant region genes in man [J]. Nature, 1981, 294(5841): 536-540. |
| [28] | 汤存伟,余雄,刘武军,等.新疆13个绵羊群体遗传多样性及遗传分化的研究[J].家畜生态学报,2011,32(1):13-19. |
| TANG C W, YU X, LIU W J, et al.. Stndy on genetic diversity and genetic differentiation of 13 sheep populations in Xinjiang uygur autonomous region [J]. J. Domest. Anim. Ecol., 2011, 32(1): 13-19. | |
| [29] | WRIGHT S. Variability within and among Natural Populations [M]. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1978:1-256. |
| [30] | 黄燕,朱振东,段灿星,等.灰葡萄孢蚕豆分离物的遗传多样性[J].中国农业科学,2014,47(12):2335-2347. |
| HUANG Y, ZHU Z D, DUAN C X, et al.. Genetic diversity of Botrytis cinerea isolates from broad bean [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2014, 47(12): 2335-2347. | |
| [31] | 穆小婷,廖侦成,凌彩金,等.基于SSR标记的55份清远野生茶树种质资源遗传多样性和亲缘关系分析[J].中国茶叶,2023, 45(2): 36-43. |
| MU X T, LIAO Z C, LING C J, et al.. Genetic diversity and relationship analysis of 55 wild tea germplasm from Qingyuan based on SSR markers [J]. China Tea, 2023, 45(2): 36-43. | |
| [32] | 罗凯, 卢会翔, 吴正丹,等.中国西南地区甘薯主要育种亲本的遗传多样性及群体结构分析[J].中国农业科学,2016,49(3):593-608. |
| LUO K, LU H X, WU Z D, et al.. Genetic diversity and population structure analysis of main sweet potato breeding parents in southwest China [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2016, 49(3): 593-608. | |
| [33] | 王欣,李强,曹清河,等.中国甘薯产业和种业发展现状与未来展望[J].中国农业科学,2021,54(3):483-492. |
| WANG X, LI Q, CAO Q H, et al.. Current status and future prospective of sweetpotato production and seed industry in China [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2021, 54(3): 483-492. |
| [1] | Li ZHAO, Jingjing HOU, Bin WANG, Minglu YUAN, Jie LIU. Dynamic Change of Important Traits During the Development of Flax Seed [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(9): 25-33. |
| [2] | Shan GAO, Xiaocui YAN, Nan WANG, Mengjie ZHANG, Youpeng LI, Wenda DIAO, Huijun DUAN. Genetic Diversity Analysis of 255 Maize Germplasm Resources Based on 10K SNP Chip [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(8): 20-33. |
| [3] | Hui ZHAO, Chenhua JIN, Weihong XUAN, Haisheng XU. Research Status and Development Prospects of Cement-based Composite Materials with Flax Fiber [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(4): 153-163. |
| [4] | Ziwen KONG, Ruxia TIAN, Ruyi MIAO, Yanping LIANG. Analysis of Agronomic Traits and Genetic Diversity of 60 Screw Pepper Germplasm Resources [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(3): 40-47. |
| [5] | Boyan XIE, Lijing KONG, Yubin ZHANG, Chenglong SUN, Siyuan ZHAO, Minghui ZHANG, Shengci FAN, Zengxu XIANG, Jinshuang ZHENG. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure Analysis of Atractylodes chinensis [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(12): 39-49. |
| [6] | Nali XU, Huixia YU, Mingming YAO, Yanqing WANG, Qingfeng LI, Caixia LIU, Gang SUN, Jiajing CHEN, Jiaohui LONG, Zhangjun WANG. Analysis of Genetic Diversity Based on SSR and SRAP Markers and Agronomic Traits of Wheat Resources [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(3): 30-46. |
| [7] | Xingfu WU, Fangchan JIAO, Xuejun CHEN, Zhiyu FANG, Guanghai ZHANG, Yihan ZHANG, Yongping LI. Phenotypic Genetic Diversity Analysis of Leaf Shrinkage and Economic Traits of Flue-cured Tobacco for Germplasm Resources [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(10): 54-64. |
| [8] | Shengchuan LIU, Yingfen XU, Jie WEI, Donghai YAN, Zhixiong CHEN, lin XU, Yan LIU, Yufeng ZHOU. Analysis of Genetic Diversity of Albino Tea Cultivars (Strains) Using 2b-RAD Technology [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(8): 65-73. |
| [9] | Liuxi YI, Rula SA, Xin FAN, Can ZHAO, Ru LI, Bateer SIQIN. Evaluation of Flax Germplasm Phenotype [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(5): 56-67. |
| [10] | Chenke CUI, Tao LIN, Yanbo AN, Peng CUI. Genetic Diversity Analysis of Different Characteristics of Sweetpotato Varieties by ISSR Molecular Marker [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(5): 68-75. |
| [11] | Xixi ZUO, Yingjie SONG, Xinyan MA, Yunhui YANG, Yifei WANG, Zeguang GUO, Xiongzhi ZHU, Yue LIU. Mining SSR Loci and Analysis the Genetic Diversity of Tartary Buckwheat Based on the Whole Genome Sequence [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(4): 38-51. |
| [12] | Peng ZHONG, Lili MIAO, Jie LIU, Jianli WANG, Haiyan LU, Hongjiu YU, Nan ZHANG. Effect of Different Planting Densities and Patterns on Population Structure and Yield of Cyperusesculentus [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(3): 186-196. |
| [13] | YU Haitian, LYU Meiyuan, WAN Shuwei, YANG Feng, HU Chaoqin, YANG Xin, ZHANG Xiaoyan, WANG Yubao, HE Chunhua, LIN Deming, WANG Liping. Genetic Diversity Analysis of Indian Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) Resources and Screening of Excellent Germplasm [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(7): 54-64. |
| [14] | WANG Liguang§, YE Chunlei§, CHEN Jun, LI Jinjing, LUO Junjie. Effects of Intercropping and Rotation Between Oil Flax and Wheat on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Growth of Oil Flax [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(12): 161-171. |
| [15] | LI Danyang, SUN Lingwei, WU Caifeng, ZHANG Shushan, ZHANG Defu, DAI Jianjun. SSR Genetic Diversity Analysis of Yangtze River Delta White Goats from Conservation Populations [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(10): 74-81. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号