




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (4): 36-44.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0876
• BIOTECHNOLOGY & LIFE SCIENCE • Previous Articles Next Articles
ling QIN( ), Yanke WANG, Erying CHEN, Yanbing YANG, Feifei LI, Mengyuan ZHANG, Yanan GUAN(
), Yanke WANG, Erying CHEN, Yanbing YANG, Feifei LI, Mengyuan ZHANG, Yanan GUAN( )
)
Received:2023-11-30
Accepted:2024-03-04
Online:2025-04-15
Published:2025-04-15
Contact:
Yanan GUAN
秦岭( ), 王艳珂, 陈二影, 杨延兵, 黎飞飞, 张梦媛, 管延安(
), 王艳珂, 陈二影, 杨延兵, 黎飞飞, 张梦媛, 管延安( )
)
通讯作者:
管延安
作者简介:秦岭 E-mail: qinling1021@163.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
ling QIN, Yanke WANG, Erying CHEN, Yanbing YANG, Feifei LI, Mengyuan ZHANG, Yanan GUAN. Analysis of Physiological Characteristics About ABA Alleviating Foxtail Millet Seedling Stage Under Drought Stress[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(4): 36-44.
秦岭, 王艳珂, 陈二影, 杨延兵, 黎飞飞, 张梦媛, 管延安. ABA缓解谷子幼苗干旱胁迫生理特性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(4): 36-44.
胁迫时间 Stress time/d | 济谷22 Jigu 22 | 鲁谷1号 Lugu 1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | PEG | PEG+ABA | CK | PEG | PEG+ABA | |
| 1 | 17.38±0.29 a | 17.30±0.64 a | 17.34±0.70 a | 19.60±1.01 a | 19.01±1.06 a | 19.16±0.87 a |
| 4 | 25.13±1.27 a | 20.48±1.17 c | 21.27±1.22 b | 28.61±0.97 a | 22.45±0.79 c | 23.45±0.94 b |
| 7 | 31.05±1.58 a | 21.23±1.12 b | 22.14±0.77 b | 33.48±1.02 a | 22.85±0.91 c | 23.97±1.04 b |
Table 1 Height of foxtail millet seedlings under different treatments
胁迫时间 Stress time/d | 济谷22 Jigu 22 | 鲁谷1号 Lugu 1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | PEG | PEG+ABA | CK | PEG | PEG+ABA | |
| 1 | 17.38±0.29 a | 17.30±0.64 a | 17.34±0.70 a | 19.60±1.01 a | 19.01±1.06 a | 19.16±0.87 a |
| 4 | 25.13±1.27 a | 20.48±1.17 c | 21.27±1.22 b | 28.61±0.97 a | 22.45±0.79 c | 23.45±0.94 b |
| 7 | 31.05±1.58 a | 21.23±1.12 b | 22.14±0.77 b | 33.48±1.02 a | 22.85±0.91 c | 23.97±1.04 b |
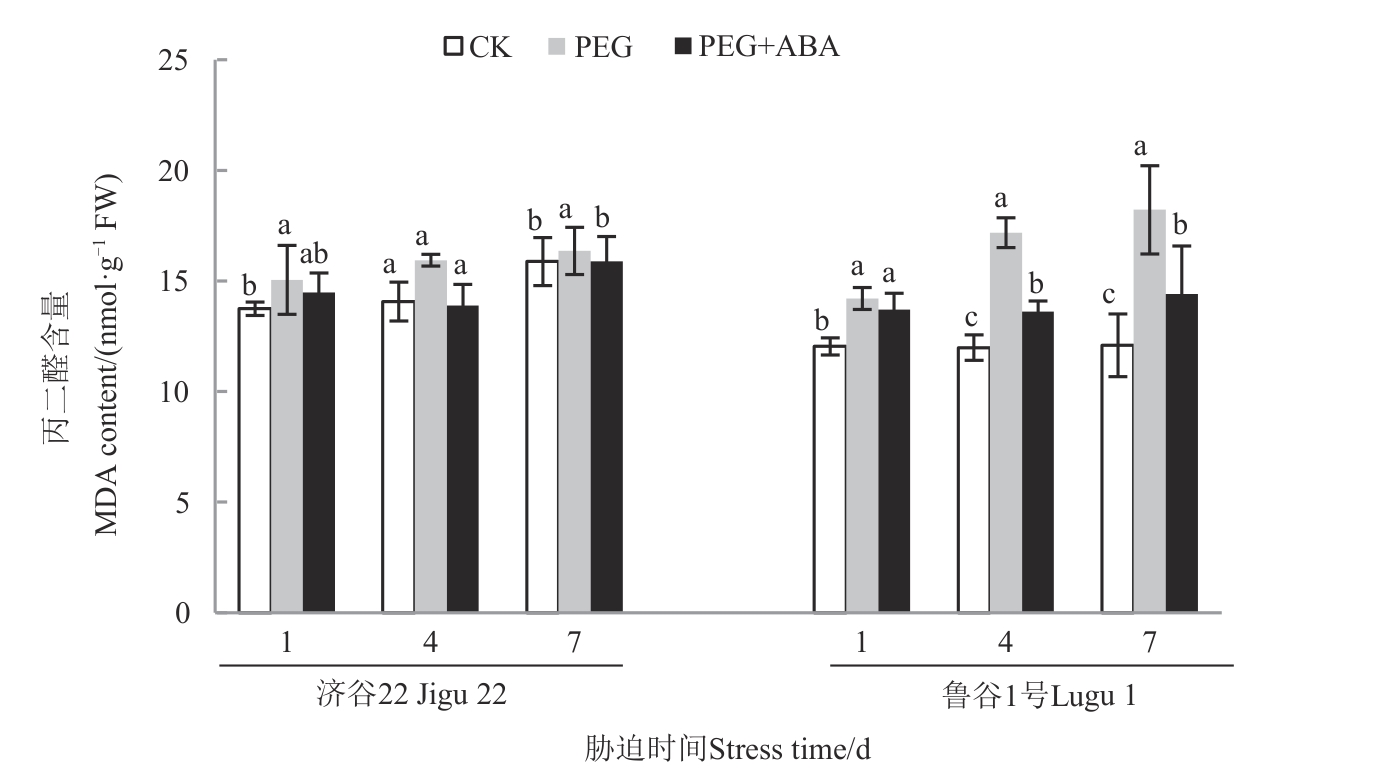
Fig. 2 Malondialdehyde content of 2 foxtail millet varieties under different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters in same stress time indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
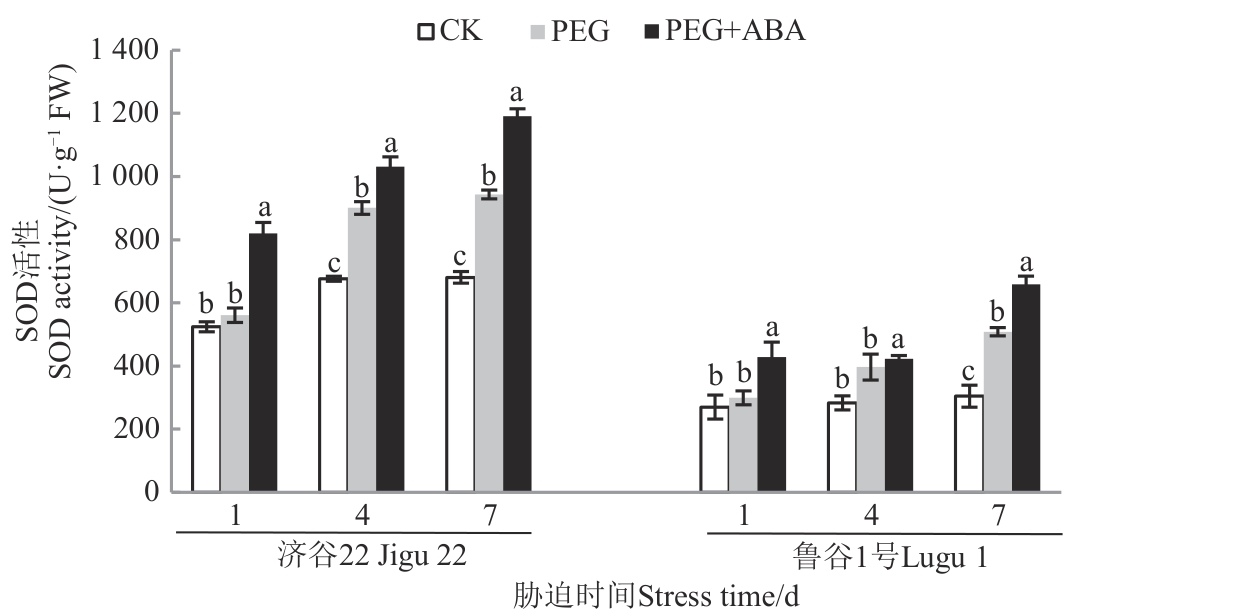
Fig. 3 SOD activity of 2 foxtail millet varieties under different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters in same stress time indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
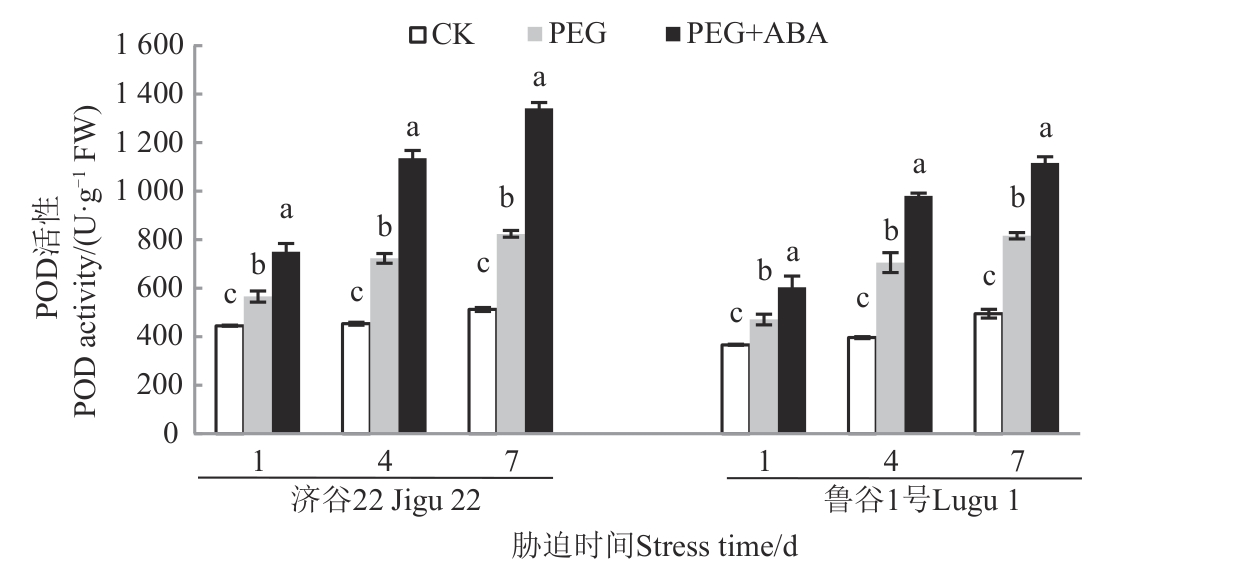
Fig. 4 POD activity of 2 foxtail millet varieties under different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters in same stress time indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
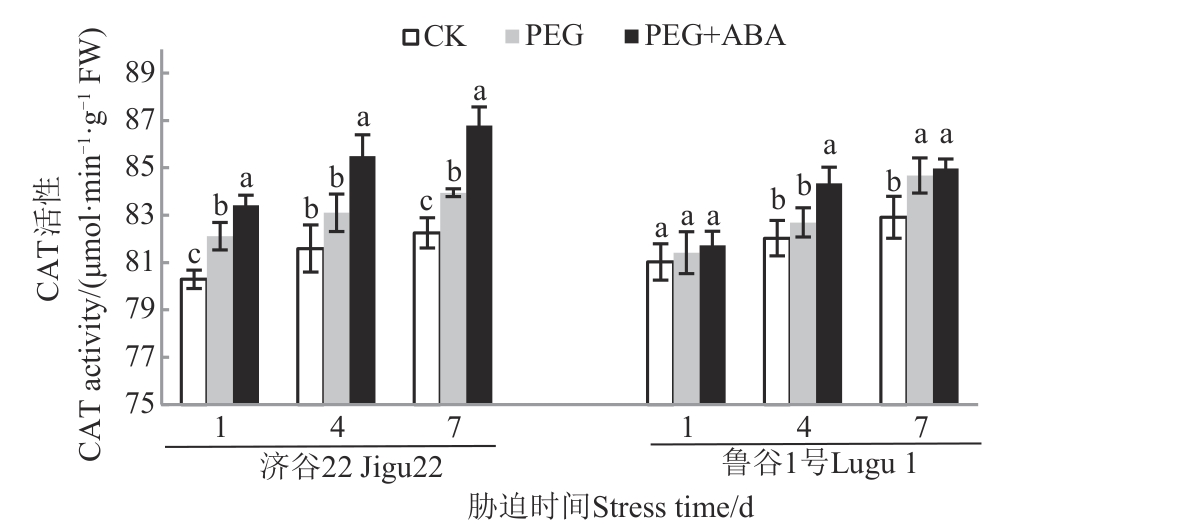
Fig. 5 CAT activity of 2 foxtail millet varieties under different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters in same stress time indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
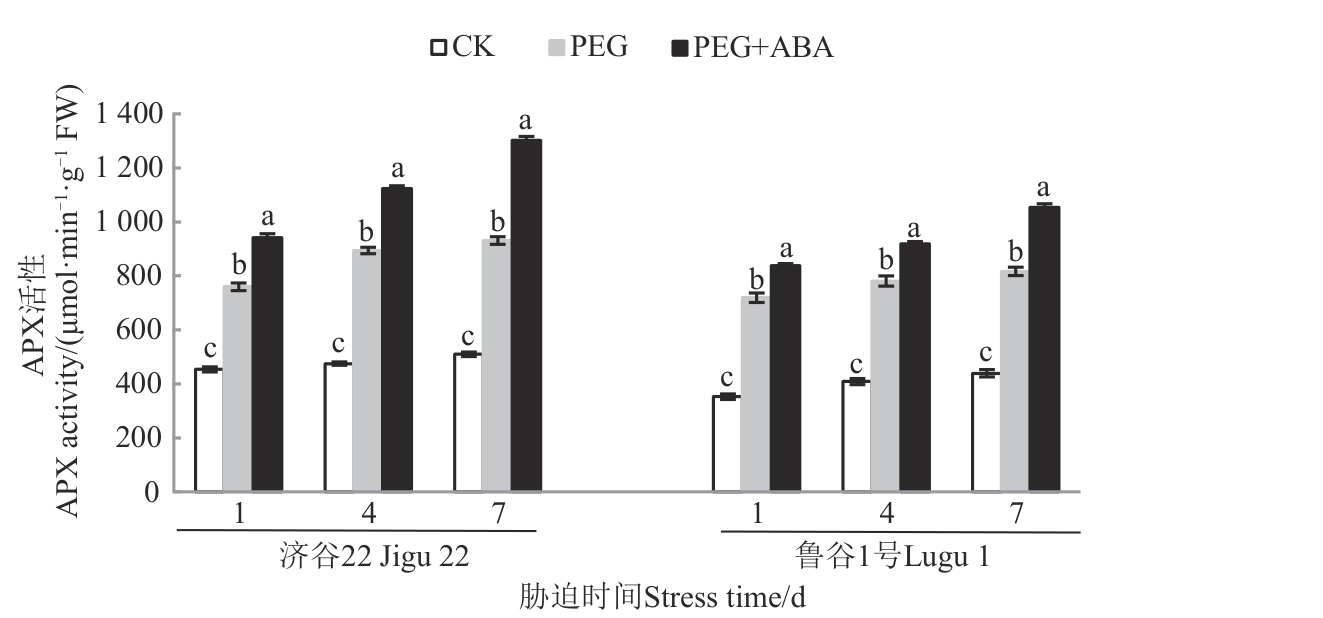
Fig. 6 APX activity of 2 foxtail millet varieties under different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters in same stress time indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
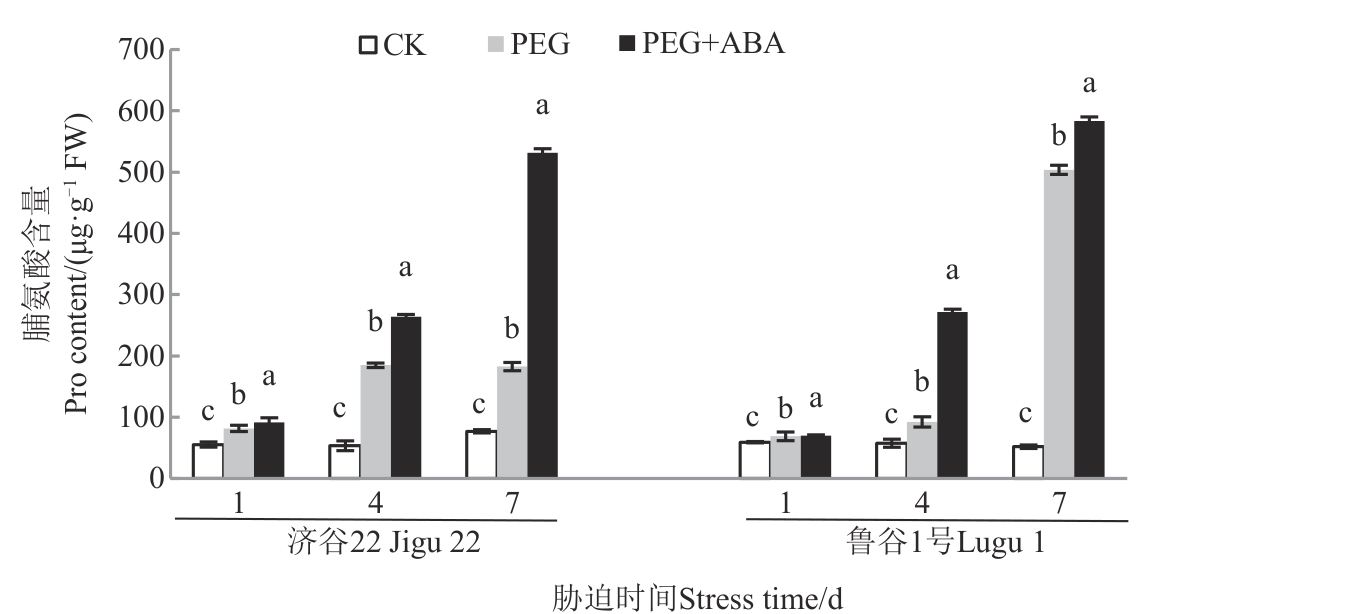
Fig. 7 Pro content of 2 foxtail millet varieties under different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters in same stress time indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
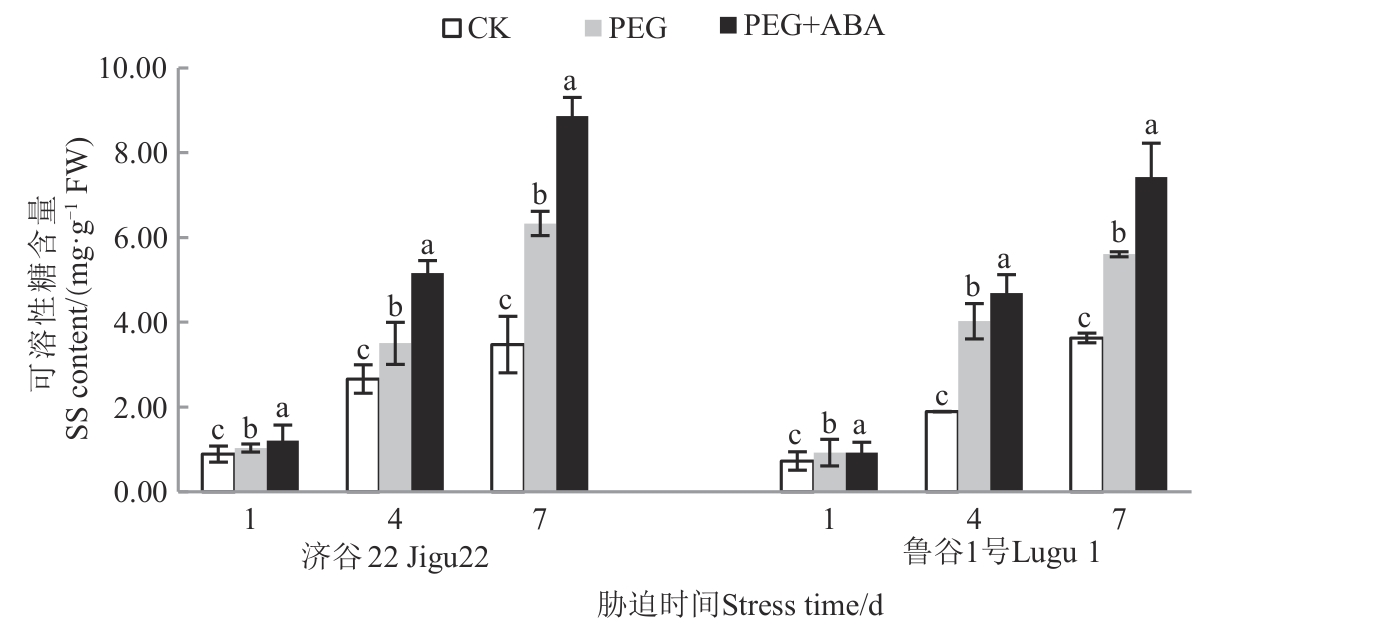
Fig. 8 SS content of 2 foxtail millet varieties under different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters in same stress time indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
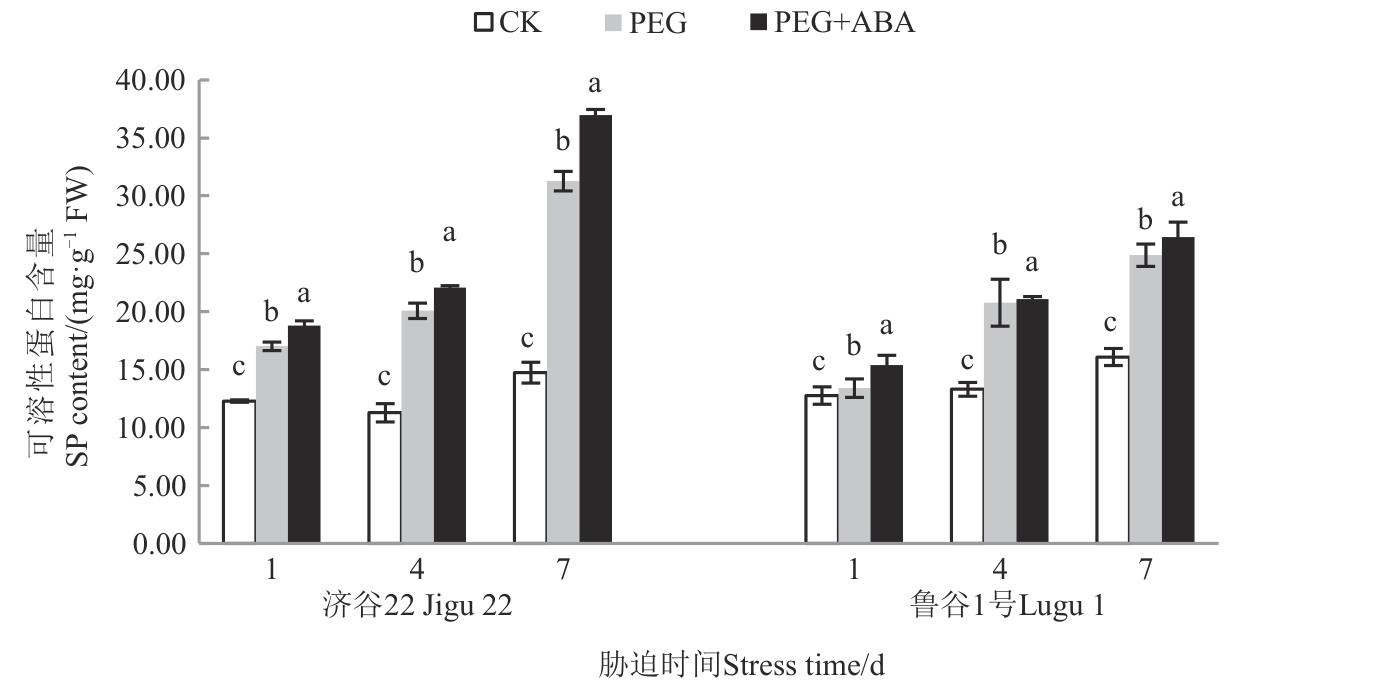
Fig. 9 SP content of 2 foxtail millet varieties under different treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters in same stress time indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 1 | 王忠.植物生理学[M].北京:中国农业出版社,1999:451-455. |
| 2 | 李昊文,赵军.非生物逆境信号转导的分子机制[J].中国农业科技导报,2008,10():1-6. |
| LI H W, ZHAO J. Molecular mechanism of abiotic stress signal transduction [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2008,10(S1):1-6. | |
| 3 | DIETZ K J, ZÖRB C, GEILFUS C M. Drought and crop yield [J]. Plant Biol., 2021,23(6):881-893. |
| 4 | ZHANG Y B, YANG S L, DAO J M,et al.. Drought-induced alterations in photosynthetic,ultrastructural and biochemical traits of contrasting sugarcane genotypes [J/OL].PLoS One,2020,15(7):e0235845 [2023-10-28]. . |
| 5 | SCHWARTZ S H, QINX Q, ZEEVAART J A. Elucidation of the indirect pathway of abscisic acid biosynthesis by mutants, genes, and enzymes [J]. Plant Physiol., 2003,131(4): 1591-601. |
| 6 | BECKER D, HOTH S, ACHE P, et al.. Regulation of the ABA-sensitive Arabidopsis potassium channel gene GORK in response to water stress [J]. FEBS Lett., 2003,554(1/2):119-126. |
| 7 | 郝格格,孙忠富,张录强,等.脱落酸在植物逆境胁迫研究中的进展[J].中国农学通报,2009,25(18):212-215. |
| HAO G G, SUN Z F, ZHANG L Q, et al.. A research overview of the plant resistance to adverse environment by using abscisic acid [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2009,25(18):212-215. | |
| 8 | KAUR M, GUPTA A K, ZHAWAR V K. Antioxidant response and Lea genes expression under exogenous ABA and water deficit stress in wheat cultivars contrasting in drought tolerance [J]. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol., 2014,23(1):18-30. |
| 9 | 阮英慧,董守坤,刘丽君,等.干旱胁迫下外源脱落酸对大豆花期生理特性的影响[J].大豆科学,2012,31(3):385-388, 394. |
| RUAN Y H, DONG S K, LIU L J, et al.. Effects of exogenous abscisic acid on physiological characteristics in soybean flowering under drought stress [J]. Soybean Sci., 2012,31(3):385-388, 394. | |
| 10 | 王芳,王铁兵,李鹏德.外源ABA对干旱胁迫下玉米幼苗氧化损伤的保护作用[J].草业科学, 2019, 36(11):2887-2894. |
| WANG F, WANG T B, LI P D. Protective effects of exogenous ABA on oxidative damage in maize seedlings under drought stress [J]. Pratac. Sci., 2019, 36(11):2887-2894. | |
| 11 | 李长宁,Manoj Kumar SRIVASTAVA,农倩,等.水分胁迫下外源ABA提高甘蔗抗旱性的作用机制[J].作物学报,2010,36(5):863-870. |
| LI C N, SRIVASTAVA M K, NONG Q, et al.. Mechanism of tolerance to drought in sugarcane plant enhanced by foliage dressing of abscisic acid under water stress [J].Acta Agron. Sin., 2010,36(5):863-870. | |
| 12 | 孙哲,范维娟,刘桂玲,等.干旱胁迫下外源ABA对甘薯苗期叶片光合特性及相关生理指标的影响[J].植物生理学报,2017,53(5):873-880. |
| SUN Z, FAN W J, LIU G L, et al.. Effects of exogenous ABA on leaf photosynthetic characteristics and associated physiological indexes of sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas) seedlings under drought stress [J]. Plant Physiol. J., 2017,53(5):873-880. | |
| 13 | 农倩,谢金兰,林丽,等.干旱胁迫下外源ABA对甘蔗幼苗生理特性和基因表达的影响[J].热带作物学报,2023,44(3):553-561. |
| NONG Q, XIE J L, LIN L, et al.. Effects of exogenous ABA on physiological characteristics and gene expression in sugarcane seedlings under drought stress [J]. Chin. J. Trop. Crops, 2023,44(3):553-561. | |
| 14 | 张笑,宋敏丽.外源脱落酸对干旱胁迫下谷子生长及生理特性的影响[J].太原师范学院学报(自然科学版),2020,19(4):91-96. |
| ZHANG X, SONG M L. Effects of exogenous abscisic acid on growth and physiological characteristicsof millet seedlings under drought stress [J]. J. Taiyuan Norm. Univ.(Nat.Sci.), 2020,19(4):91-96. | |
| 15 | TANG S, LI L, WANG Y Q,et al.. Genotype-specific physiological and transcriptomic responses to drought stress in Setaria italica (an emerging model for Panicoideae grasses) [J/OL].Sci.Rep.,2017,7:10009 [2023-10-28]. . |
| 16 | 秦岭, 陈二影, 杨延兵, 等.干旱和复水对不同耐旱型谷子品种苗期生理指标的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(3):146-151. |
| QIN L, CHEN E Y, YANG Y B, et al.. Effect of drought stress and rehydration on physiological characteristics of foxtail millet seedlings [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2019, 21(3):146-151. | |
| 17 | 王相敏,曹丽茹,鲁晓民.脱落酸对干旱胁迫下玉米幼苗生长和生理生化特性的影响[J].分子植物育种,2021,19(21):7193-7201. |
| WANG X M, CAO L R, LU X M. Effects of abscisic acid on growth and physiological and biochemical characteristics of maize seedlings under drought stress [J]. Mol. Plant Breed.,2021,19(21):7193-7201. | |
| 18 | GECHEV T S, HILLE J. Molecular basis of plant stress [J]. Cell. Mol. Life Sci.,2012,69(19):3161-3163. |
| 19 | DE SOUZA T C, MAGALHÃES P C, DE CASTRO E M, et al.. ABA application to maize hybrids contrasting for drought tolerance:changes in water parameters and in antioxidant enzyme activity [J]. Plant Growth Regul., 2014,73(3):205-217. |
| 20 | 谢静静,王笑,蔡剑,等.苗期外源脱落酸和茉莉酸缓减小麦花后干旱胁迫的效应及其生理机制[J].麦类作物学报,2018,38(2):221-229. |
| XIE J J, WANG X, CAI J, et al.. Effect of exogenous application of abscisic acid and jasmonic acid at seedling stage on post-anthesis drought stress and physiological mechanisms in wheat [J]. J. Triticeae Crops, 2018,38(2):221-229. | |
| 21 | 高爱丽, 赵秀梅, 秦鑫. 水分胁迫下小麦叶片渗透调节与抗旱性的关系[J]. 西北植物学报, 1991, 11(1):58-63 |
| GAO A L, ZHAO X M, QIN X. Relationship between osmotic and justment and drought resistance in wheat under water stress [J]. Acta Bot. Bor-Occid. Sin., 1991, 11(1):58-63. | |
| 22 | 周琳,徐辉,朱旭君,等.脱落酸对干旱胁迫下茶树生理特性的影响[J].茶叶科学,2014,34(5):473-480. |
| ZHOU L, XU H, ZHU X J,et al.. Effect of abscisic acid on physiological characteristics of tea plant under drought stress [J]. J. Tea Sci., 2014,34(5):473-480. |
| [1] | Shixu QU, Yu SUN, Yizhen SUO, Haipeng YUAN, Yuhong ZHANG. Effects of Exogenous Calcium on Physiological Characteristics and Secondary Metabolites of Cannabis sativa L. Under Salt Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(2): 80-88. |
| [2] | Zhichao REN, Yaohui MU, Xuyang YAO, Shue LI, Yongfeng ZHANG, Tianbao REN, Guoshun LIU, Quanyu YIN. Physiological Response of Tobacco Infected by Phytophthora to Trichoderma harzianum Inoculation Sequence [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(1): 155-164. |
| [3] | Zhenyu XUE, Kangkang ZHANG, Yuanyuan ZHANG, Qiangqiang YAN, Lirong YAO, Hong ZHANG, Yaxiong MENG, Erjing SI, Baochun LI, Xiaole MA, Huajun WANG, Juncheng WANG. Screening and Functional Gene Detection of High-quality and Drought-resistant Wheat Germplasms [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(1): 35-49. |
| [4] | Tingting LIU, Xiyu HAO, Hui WANG, Jingwen LENG, Shihang GONG, Wei LIU. Correlation Analysis Between Yield and Agronomical Traits of Different Foxtail Millet Varieties in Semi-arid Area of Western Jilin Province [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(1): 50-60. |
| [5] | Hongshuo ZHAO, Hongyu CAO, Guanglei GAO, Zhe SUN, Ying ZHANG, Guodong DING. Effects of Sand Fixation Using Microbially Induced Carbonate Precipitation on Leaf Traits and Physiological Characteristics of Typical Psammophytes [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(6): 170-182. |
| [6] | Qianya WEI, Xinqi LIN, Lamei LIANG, Zhongwei QIN, Yingzhi LI. Effects of Melatonin on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Chaotian Pepper Under Drought Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(4): 46-57. |
| [7] | Yuan HE, Xiaotong GU, Liqing FENG, Huijun DUAN, Yongsheng TAO. Screening and Evaluation of Drought Resistance Index for Maize Hybrids During Seedling and Germination Stages [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(10): 30-40. |
| [8] | Shengmei LI, Bo PANG, Shiwei GENG, Wu SONG, Hongmei LI, Maosen MA, Ru ZHANG, Xinyan WANG, Wenwei GAO. Photosynthetic and Physiological Characteristics of Gossypium hirsutum L. × Gossypium barbadense L. Backross Populations in Full Boll Stage [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(1): 40-51. |
| [9] | Rui TIAN, Hua ZHANG, Meihong HUANG, Zhenqi SHAO, Xihuan LI, Caiying ZHANG. Mining of Candidate Genes and Genetic Loci Conferring Drought Tolerance in Soybean [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 69-82. |
| [10] | Yancheng WANG, Jiyue ZHANG, Shuaiqi FENG, Xue LIANG, Zhen ZHANG, Weiwei DONG, Wenxiu JI. Effects of Exogenous PGPR Combined with Organic Fertilizers on Soil Properties and Stress Resistance of Ginseng Under Drought Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 196-202. |
| [11] | Yongyan LIU, Zhengxiong SONG, Jiawei JIN, Jing WANG, Min XU, Junxue ZHOU, Zhanmin LI, Shimin ZHAO, Yunpeng FU, Xiaoyan DAI. Effects of Molybdenum and Zinc Nutrition on Physiological Characteristics and Quality of Flue-cured Tobacco [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(6): 216-224. |
| [12] | Shuang WANG, Yixing HOU, Linjiao FENG, Qianqian LU, Long ZHOU. Effect of Drought Stress on Anatomical Structure of Leaves in Table Grape Varieties [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(6): 40-49. |
| [13] | Yilong ZHANG, Xiaofan SUN, Shuo LI, Peiying LI, Zongjiu SUN. Physiological Response of Different Drought-resistant Cynodon dactylon Germplasm to Drought [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(6): 59-70. |
| [14] | Hui ZHANG, Yueyue WANG, Bo ZHAO, Liling ZHANG, Qianru QIE, Yuanhuai HAN, Xukai LI. Identification of Co-expression Genes Related to Cold Stress in Foxtail Millet by WGCNA [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(10): 22-34. |
| [15] | Qian YANG, Na WU, Cong ZHAO, Yu HAN, Zhonghua MA, Yongsen YANG, Jili LIU. Effects of Zinc Fertilizer Application on Physiological Characteristics and Grain Zn Content of Maize in Saline-alkali Soil [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(9): 166-176. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号