




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (9): 69-82.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.1035
• BIOTECHNOLOGY & LIFE SCIENCE • Previous Articles Next Articles
Rui TIAN( ), Hua ZHANG, Meihong HUANG, Zhenqi SHAO, Xihuan LI(
), Hua ZHANG, Meihong HUANG, Zhenqi SHAO, Xihuan LI( ), Caiying ZHANG(
), Caiying ZHANG( )
)
Received:2022-11-27
Accepted:2022-12-26
Online:2023-09-15
Published:2023-09-28
Contact:
Xihuan LI,Caiying ZHANG
田蕊( ), 张华, 黄玫红, 邵振启, 李喜焕(
), 张华, 黄玫红, 邵振启, 李喜焕( ), 张彩英(
), 张彩英( )
)
通讯作者:
李喜焕,张彩英
作者简介:田蕊 E-mail:tianrui7726@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Rui TIAN, Hua ZHANG, Meihong HUANG, Zhenqi SHAO, Xihuan LI, Caiying ZHANG. Mining of Candidate Genes and Genetic Loci Conferring Drought Tolerance in Soybean[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 69-82.
田蕊, 张华, 黄玫红, 邵振启, 李喜焕, 张彩英. 大豆抗旱遗传位点及候选基因发掘[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 69-82.
环境 Environment | 均值 Mean | 标准差 SD | 最大值 Max. | 最小值 Min. | 变异系数 CV/% | 偏度 Skew. | 峰度 Kurt. | 显著性 Sig. | 遗传力 h2/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | 1.35 | 0.14 | 1.82 | 0.96 | 10.40 | 0.06 | 0.71 | ** | 81.44 |
| E2 | 1.47 | 0.17 | 2.11 | 1.07 | 11.64 | 0.43 | 0.94 | ** | |
| E3 | 1.48 | 0.12 | 1.68 | 0.98 | 8.71 | 0.14 | 0.21 | ** |
Table 1 Genetic variation analysis of drought resistance index in soybean natural population
环境 Environment | 均值 Mean | 标准差 SD | 最大值 Max. | 最小值 Min. | 变异系数 CV/% | 偏度 Skew. | 峰度 Kurt. | 显著性 Sig. | 遗传力 h2/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | 1.35 | 0.14 | 1.82 | 0.96 | 10.40 | 0.06 | 0.71 | ** | 81.44 |
| E2 | 1.47 | 0.17 | 2.11 | 1.07 | 11.64 | 0.43 | 0.94 | ** | |
| E3 | 1.48 | 0.12 | 1.68 | 0.98 | 8.71 | 0.14 | 0.21 | ** |
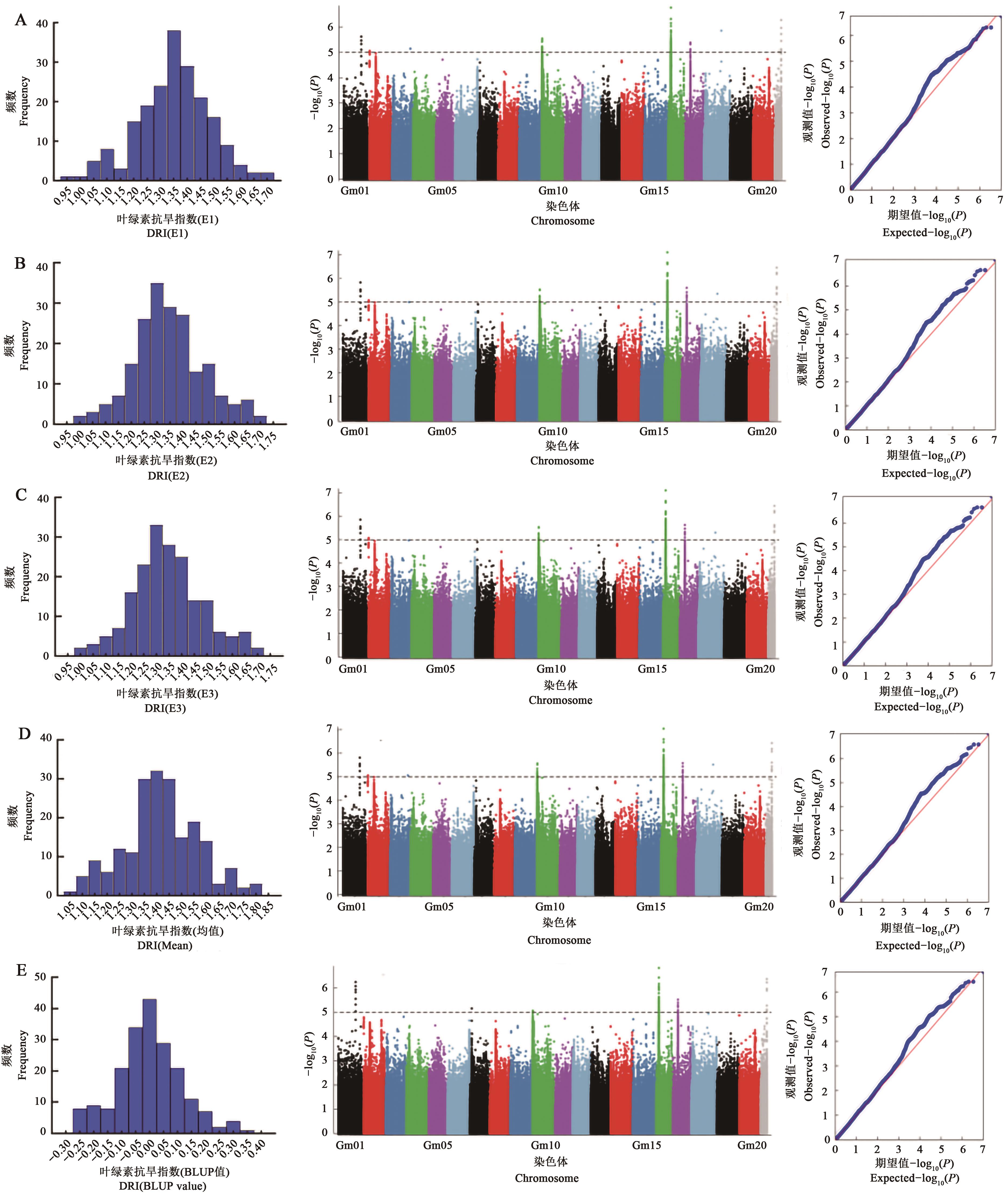
Fig. 1 Association analysis for chlorophyll drought resistance index in soybean populationA: Distribution, Manhattan and QQ plots of chlorophyll drought resistance index in E1; B: Distribution, Manhattan and QQ plots of chlorophyll drought resistance index in E2; C: Distribution, Manhattan and QQ plots of chlorophyll drought resistance index in E3; D: Distribution, Manhattan and QQ plots for mean values of chlorophyll drought resistance index; E: Distribution, Manhattan and QQ plots for BLUP values of chlorophyll drought resistance index
位点 Locus | 染色体 Chromosome | SNP区间 SNP interval/bp | SNP数目 SNP number | 最显著SNP Highest association SNP | -log10(P) | 环境 Environment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Locus 1 | Chr1 | 40 004 695~40 004 931 | 6 | Gm01:40004755 | 6.24 | Mean、BLUP、E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 2 | Chr2 | 687 623~688 028 | 5 | Gm02:687623 | 5.08 | Mean、E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 3 | Chr3 | 41 106 456 | 1 | Gm03:41106456 | 5.15 | Mean、E1 |
| Locus 4 | Chr7 | 4 696 623 | 1 | Gm07:4696623 | 5.16 | BLUP |
| Locus 5 | Chr10 | 348 939 | 1 | Gm10:348939 | 5.16 | Mean、BLUP、E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 6 | Chr10 | 656 486~694 780 | 5 | Gm10:656486 | 5.57 | Mean、BLUP、E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 7 | Chr10 | 703 703~707 681 | 15 | Gm10:703703 | 5.42 | Mean、E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 8 | Chr10 | 873 426 | 1 | Gm10:873426 | 5.07 | Mean、E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 9 | Chr10 | 987 325~1 087 932 | 5 | Gm10:1086041 | 5.20 | Mean、BLUP、E1 |
| Locus 10 | Chr16 | 5 831 709~5 931 196 | 3 | Gm16:5931196 | 5.38 | E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 11 | Chr16 | 6 226 168~6 321 014 | 62 | Gm16:6302330 | 5.81 | Mean、BLUP、E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 12 | Chr16 | 6 329 004~6 419 081 | 83 | Gm16:6353406 | 7.11 | Mean、BLUP、E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 13 | Chr16 | 6 438 949~6 534 022 | 27 | Gm16:6472037 | 6.23 | Mean、BLUP、E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 14 | Chr16 | 6 564 434~6 651 708 | 6 | Gm16:6564434 | 5.31 | Mean、BLUP、E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 15 | Chr17 | 11 692 552~11 760 989 | 9 | Gm17:11711567 | 5.64 | Mean、BLUP、E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 16 | Chr18 | 39 040 317 | 1 | Gm18:39040317 | 5.85 | Mean、E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 17 | scaffold | 58 888 | 1 | scaffold_82:58888 | 6.24 | Mean、BLUP、E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 18 | scaffold | 14 534~15 780 | 5 | scaffold_288:14774 | 6.46 | Mean、BLUP、E1、E2、E3 |
Table 2 Associated genetic loci for drought resistance index in soybean natural population
位点 Locus | 染色体 Chromosome | SNP区间 SNP interval/bp | SNP数目 SNP number | 最显著SNP Highest association SNP | -log10(P) | 环境 Environment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Locus 1 | Chr1 | 40 004 695~40 004 931 | 6 | Gm01:40004755 | 6.24 | Mean、BLUP、E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 2 | Chr2 | 687 623~688 028 | 5 | Gm02:687623 | 5.08 | Mean、E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 3 | Chr3 | 41 106 456 | 1 | Gm03:41106456 | 5.15 | Mean、E1 |
| Locus 4 | Chr7 | 4 696 623 | 1 | Gm07:4696623 | 5.16 | BLUP |
| Locus 5 | Chr10 | 348 939 | 1 | Gm10:348939 | 5.16 | Mean、BLUP、E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 6 | Chr10 | 656 486~694 780 | 5 | Gm10:656486 | 5.57 | Mean、BLUP、E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 7 | Chr10 | 703 703~707 681 | 15 | Gm10:703703 | 5.42 | Mean、E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 8 | Chr10 | 873 426 | 1 | Gm10:873426 | 5.07 | Mean、E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 9 | Chr10 | 987 325~1 087 932 | 5 | Gm10:1086041 | 5.20 | Mean、BLUP、E1 |
| Locus 10 | Chr16 | 5 831 709~5 931 196 | 3 | Gm16:5931196 | 5.38 | E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 11 | Chr16 | 6 226 168~6 321 014 | 62 | Gm16:6302330 | 5.81 | Mean、BLUP、E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 12 | Chr16 | 6 329 004~6 419 081 | 83 | Gm16:6353406 | 7.11 | Mean、BLUP、E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 13 | Chr16 | 6 438 949~6 534 022 | 27 | Gm16:6472037 | 6.23 | Mean、BLUP、E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 14 | Chr16 | 6 564 434~6 651 708 | 6 | Gm16:6564434 | 5.31 | Mean、BLUP、E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 15 | Chr17 | 11 692 552~11 760 989 | 9 | Gm17:11711567 | 5.64 | Mean、BLUP、E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 16 | Chr18 | 39 040 317 | 1 | Gm18:39040317 | 5.85 | Mean、E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 17 | scaffold | 58 888 | 1 | scaffold_82:58888 | 6.24 | Mean、BLUP、E1、E2、E3 |
| Locus 18 | scaffold | 14 534~15 780 | 5 | scaffold_288:14774 | 6.46 | Mean、BLUP、E1、E2、E3 |
| SNP | 石76368 Shi 76368 | 沧0719 Cang 0719 | 冀豆27 Jidou 27 | HN0906 | 石豆5号 Shidou 5 | HN1030 | 邯15-685 Han15-685 | 冀11B9 Ji 11B9 | 沧0627 Cang 0627 | 冀10B5 Ji 10B5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gm07:4696623 | AA | AA | AA | AA | AA | AA | — | |||
| Gm10:348939 | CC | CC | CC | — | CC | |||||
| Gm10:656486 | AA | AA | AA | AA | AA | |||||
| Gm10:703703 | CC | CC | CC | CC | CC | |||||
| Gm10:873426 | GG | GG | GG | GG | GG | |||||
| Gm10:1086041 | GG | GG | GG | GG | GG | GG | ||||
| Gm16:6302330 | TT | TT | TT | TT | TT | |||||
| Gm16:6353406 | AA | AA | AA | AA | AA | |||||
| Gm16:6564434 | GG | GG | GG | GG | GG | |||||
| Gm17:11711567 | CC | CC | CC | CC | CC | |||||
| scaffold_288:14774 | GG | — | GG | GG | GG | |||||
抗旱指数 Drought resistance index | 1.07 | 1.08 | 1.09 | 1.11 | 1.13 | 1.70 | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.81 | 1.83 |
优异等位变异数量 Number of elite allele | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 11 | 10 | 11 | 11 |
Table 3 Analysis of associated SNPs in different soybean accessions with different drought resistance index
| SNP | 石76368 Shi 76368 | 沧0719 Cang 0719 | 冀豆27 Jidou 27 | HN0906 | 石豆5号 Shidou 5 | HN1030 | 邯15-685 Han15-685 | 冀11B9 Ji 11B9 | 沧0627 Cang 0627 | 冀10B5 Ji 10B5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gm07:4696623 | AA | AA | AA | AA | AA | AA | — | |||
| Gm10:348939 | CC | CC | CC | — | CC | |||||
| Gm10:656486 | AA | AA | AA | AA | AA | |||||
| Gm10:703703 | CC | CC | CC | CC | CC | |||||
| Gm10:873426 | GG | GG | GG | GG | GG | |||||
| Gm10:1086041 | GG | GG | GG | GG | GG | GG | ||||
| Gm16:6302330 | TT | TT | TT | TT | TT | |||||
| Gm16:6353406 | AA | AA | AA | AA | AA | |||||
| Gm16:6564434 | GG | GG | GG | GG | GG | |||||
| Gm17:11711567 | CC | CC | CC | CC | CC | |||||
| scaffold_288:14774 | GG | — | GG | GG | GG | |||||
抗旱指数 Drought resistance index | 1.07 | 1.08 | 1.09 | 1.11 | 1.13 | 1.70 | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.81 | 1.83 |
优异等位变异数量 Number of elite allele | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 11 | 10 | 11 | 11 |
候选基因 Candidate gene | 基因注释 Annotation | 生物过程描述 Biological process description |
|---|---|---|
| Glyma.01G114050 | 驱动蛋白类蛋白KIN-14U Kinesin-like protein KIN-14U | 细胞脂质代谢过程 Cellular lipid metabolic process |
| Glyma.01G114300# | TIC蛋白Protein TIC | - |
| Glyma.01G114050 | 驱动蛋白类蛋白KIN-14U Kinesin-like protein KIN-14U | 细胞脂质代谢过程 Cellular lipid metabolic process |
| Glyma.02G006300# | AP2/ERF结构域蛋白 AP2/ERF domain-containing protein | 乙烯激活信号通路 Ethylene-activated signaling pathway |
| Glyma.03G188100∆ | C末端结构域蛋白 C-terminal domain-containing protein | 蛋白靶向膜 Protein targeting to membrane |
| Glyma.07G053900# | Dof型结构域蛋白 Dof-type domain-containing protein | 转录负调控 Negative regulation of transcription |
| Glyma.07G054000∆ | MYB转录因子 MYB transcription factor | 肉桂酸生物合成过程 Cinnamic acid biosynthetic process |
| Glyma.10G010700 | Fe2O G加双氧酶结构域蛋白 Fe2O G dioxygenase domain-containing protein | 赤霉素分解代谢过程 Gibberellin catabolic process |
| Glyma.10G010750 | - | - |
| Glyma.10G010902 | mRNA剪接因子 Probable pre-mRNA-splicing factor | mRNA加工 mRNA processing |
Table 4 Candidate genes of drought resistance index in soybean
候选基因 Candidate gene | 基因注释 Annotation | 生物过程描述 Biological process description |
|---|---|---|
| Glyma.01G114050 | 驱动蛋白类蛋白KIN-14U Kinesin-like protein KIN-14U | 细胞脂质代谢过程 Cellular lipid metabolic process |
| Glyma.01G114300# | TIC蛋白Protein TIC | - |
| Glyma.01G114050 | 驱动蛋白类蛋白KIN-14U Kinesin-like protein KIN-14U | 细胞脂质代谢过程 Cellular lipid metabolic process |
| Glyma.02G006300# | AP2/ERF结构域蛋白 AP2/ERF domain-containing protein | 乙烯激活信号通路 Ethylene-activated signaling pathway |
| Glyma.03G188100∆ | C末端结构域蛋白 C-terminal domain-containing protein | 蛋白靶向膜 Protein targeting to membrane |
| Glyma.07G053900# | Dof型结构域蛋白 Dof-type domain-containing protein | 转录负调控 Negative regulation of transcription |
| Glyma.07G054000∆ | MYB转录因子 MYB transcription factor | 肉桂酸生物合成过程 Cinnamic acid biosynthetic process |
| Glyma.10G010700 | Fe2O G加双氧酶结构域蛋白 Fe2O G dioxygenase domain-containing protein | 赤霉素分解代谢过程 Gibberellin catabolic process |
| Glyma.10G010750 | - | - |
| Glyma.10G010902 | mRNA剪接因子 Probable pre-mRNA-splicing factor | mRNA加工 mRNA processing |

Fig. 4 Identification of candidate gene Glyma.16G063600A:GWAS signal on chromosome 16 (top) in the region from 6.0~6.5 Mb and LD heatmap (bottom) for this region; B:Haplotypes of Glyma.16G063600 in soybean natural population, statistical significance is determined by a two-tailed t-test; C:Gene structure and encoding protein conserved domain of Glyma.16G063600. Black rectangle— Exon; White rectangle—5’UTR;White pentagon—3’UTR; Vertical red line—SNP mutation
候选基因 Candidate gene | 基因注释 Annotation | 生物过程描述 Biological process description |
|---|---|---|
| Glyma.10G011000 | PlsC结构域蛋白 PlsC domain-containing protein | CDP甘油二酯生物合成 CDP-diacylglycerol biosynthetic process |
| Glyma.10G011700∆ | EB_dh结构域蛋白 EB_dh domain-containing protein | - |
| Glyma.10G011600 | - | - |
| Glyma.10G003400# | VAN3结合蛋白 VAN3-binding protein | 韧皮部或木质部组织发生 Phloem or xylem histogenesis |
| Glyma.10G003500# | CCR4非转录复合亚族 CCR4-NOT transcription complex subunit | 生物过程 Biological process |
| Glyma.10G006600# | GmMYB29A1蛋白 GmMYB29A1 protein | 缺水反应 Response to water deprivation |
| Glyma.10G006700∆ | 大豆磷转运蛋白 Soybean phosphate transporter protein | 磷酸盐离子转运 Phosphate ion transport |
| Glyma.10G007000∆ # | AP2-EREBP转录因子 AP2-EREBP transcription factor | 乙烯激活信号通路 Ethylene-activated signaling pathway |
| Glyma.10G007100# | AP2/ERF结构域蛋白 AP2/ERF domain-containing protein | 乙烯激活信号通路 Ethylene-activated signaling pathway |
| Glyma.10G007200# | RING型结构域蛋白 RING-type domain-containing protein | 蛋白泛素化 Protein ubiquitination |
| Glyma.10G009000 | 果胶酯酶 Pectinesterase | 细胞壁修饰 Cell wall modification |
| Glyma.10G010400∆ # | MYB转录因子 MYB transcription factor | 缺水反应 Response to water deprivation |
| Glyma.10G010501 | 果胶酯酶结构域蛋白 Pectinesterase domain-containing protein | 细胞壁修饰 Cell wall modification |
| Glyma.16G059801# | 线粒体丙酮酸载体 Mitochondrial pyruvate carrier | 气孔运动的调节 Regulation of stomatal movement |
| Glyma.16G060800 | 萌发素类蛋白 Germin-like protein | 胁迫反应 Response to stress |
| Glyma.16G063600∆ # | F-box蛋白 F-box protein | 植物型过敏反应 Plant-type hypersensitive response |
| Glyma.16G063700 | Myb 原癌基因蛋白 Myb proto-oncogene protein | DNA结合转录因子 DNA-binding transcription factor activity |
| Glyma.16G063900∆ | 肽基丝氨酸-半乳糖转移酶 Peptidyl serine alpha-galactosyltransferase | 生物过程 Biological process |
| Glyma.16G064000 | WVD2蛋白 Protein WVD2 | 生物过程 Biological process |
| Glyma.16G064100# | 蛋白激酶结构域蛋白 Protein kinase domain-containing protein | 蛋白磷酸化 Protein phosphorylation |
Table 4 Candidate genes of drought resistance index in soybean
候选基因 Candidate gene | 基因注释 Annotation | 生物过程描述 Biological process description |
|---|---|---|
| Glyma.10G011000 | PlsC结构域蛋白 PlsC domain-containing protein | CDP甘油二酯生物合成 CDP-diacylglycerol biosynthetic process |
| Glyma.10G011700∆ | EB_dh结构域蛋白 EB_dh domain-containing protein | - |
| Glyma.10G011600 | - | - |
| Glyma.10G003400# | VAN3结合蛋白 VAN3-binding protein | 韧皮部或木质部组织发生 Phloem or xylem histogenesis |
| Glyma.10G003500# | CCR4非转录复合亚族 CCR4-NOT transcription complex subunit | 生物过程 Biological process |
| Glyma.10G006600# | GmMYB29A1蛋白 GmMYB29A1 protein | 缺水反应 Response to water deprivation |
| Glyma.10G006700∆ | 大豆磷转运蛋白 Soybean phosphate transporter protein | 磷酸盐离子转运 Phosphate ion transport |
| Glyma.10G007000∆ # | AP2-EREBP转录因子 AP2-EREBP transcription factor | 乙烯激活信号通路 Ethylene-activated signaling pathway |
| Glyma.10G007100# | AP2/ERF结构域蛋白 AP2/ERF domain-containing protein | 乙烯激活信号通路 Ethylene-activated signaling pathway |
| Glyma.10G007200# | RING型结构域蛋白 RING-type domain-containing protein | 蛋白泛素化 Protein ubiquitination |
| Glyma.10G009000 | 果胶酯酶 Pectinesterase | 细胞壁修饰 Cell wall modification |
| Glyma.10G010400∆ # | MYB转录因子 MYB transcription factor | 缺水反应 Response to water deprivation |
| Glyma.10G010501 | 果胶酯酶结构域蛋白 Pectinesterase domain-containing protein | 细胞壁修饰 Cell wall modification |
| Glyma.16G059801# | 线粒体丙酮酸载体 Mitochondrial pyruvate carrier | 气孔运动的调节 Regulation of stomatal movement |
| Glyma.16G060800 | 萌发素类蛋白 Germin-like protein | 胁迫反应 Response to stress |
| Glyma.16G063600∆ # | F-box蛋白 F-box protein | 植物型过敏反应 Plant-type hypersensitive response |
| Glyma.16G063700 | Myb 原癌基因蛋白 Myb proto-oncogene protein | DNA结合转录因子 DNA-binding transcription factor activity |
| Glyma.16G063900∆ | 肽基丝氨酸-半乳糖转移酶 Peptidyl serine alpha-galactosyltransferase | 生物过程 Biological process |
| Glyma.16G064000 | WVD2蛋白 Protein WVD2 | 生物过程 Biological process |
| Glyma.16G064100# | 蛋白激酶结构域蛋白 Protein kinase domain-containing protein | 蛋白磷酸化 Protein phosphorylation |
候选基因 Candidate gene | 基因注释 Annotation | 生物过程描述 Biological process description |
|---|---|---|
| Glyma.16G064200∆ | 蛋白激酶结构域蛋白 Protein kinase domain-containing protein | 激素介导的信号途径 Hormone-mediated signaling pathway |
| Glyma.16G064300 | 驱动蛋白类蛋白KIN-4C Kinesin-like protein KIN-4C | 微管运动 Microtubule-based movement |
| Glyma.16G064401 | 蛋白激酶结构域蛋白 Protein kinase domain-containing protein | 激素介导的信号途径 Hormone-mediated signaling pathway |
| Glyma.16G064700# | 2-羧基-1,4萘醌转移酶 2-carboxy-1,4-naphthoquinone phytyltransferase | 光合电子传递 Photosynthetic electron transport |
| Glyma.16G064800 | 蛋白激酶结构域蛋白 Protein kinase domain-containing protein | 激素介导的信号途径 Hormone-mediated signaling pathway |
| Glyma.16G064900∆ | 蛋白激酶结构域蛋白 Protein kinase domain-containing protein | 激素介导的信号途径 Hormone-mediated signaling pathway |
| Glyma.16G065000 | 蛋白激酶结构域蛋白 Protein kinase domain-containing protein | 蛋白磷酸化 Protein phosphorylation |
| Glyma.16G065200∆ | 蛋白激酶结构域蛋白 Protein kinase domain-containing protein | 激素介导的信号途径 Hormone-mediated signaling pathway |
| Glyma.16G065300# | 蛋白Ycf2 Protein Ycf2 | 蛋白进入叶绿体基质 Protein import into chloroplast stroma |
| Glyma.16G065400∆ | 蛋白激酶结构域蛋白 Protein kinase domain-containing protein | 蛋白磷酸化 Protein phosphorylation |
| Glyma.16G065500∆ | LRRNT_2结构域蛋白 LRRNT_2 domain-containing protein | 蛋白磷酸化 Protein phosphorylation |
| Glyma.16G065600 | 蛋白激酶结构域蛋白 Protein kinase domain-containing protein | 激素介导信号途径 Hormone-mediated signaling pathway |
| Glyma.16G065900∆ | 胱氨酸 Cystinosin homolog | L-胱氨酸转运 L-cystine transport |
| Glyma.16G066200∆ | 琥珀酸脱氢酶[泛醌]铁硫 Succinate dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron-sulfur | 三羧酸循环 Tricarboxylic acid cycle |
| Glyma.16G066600 | 液泡加工酶 Vacuolar-processing enzyme | 液泡蛋白合成 Vacuolar protein processing |
| Glyma.16G067400 | - | - |
| Glyma.16G067500 | 水解酶_4结构域蛋白 Hydrolase_4 domain-containing protein | 生物过程 Biological process |
| Glyma.16G067600 | 未知蛋白 Uncharacterized protein | - |
| Glyma.16G067700 | 筛管封闭 Sieve element occlusion | 韧皮部发育 Phloem development |
Table 4 Candidate genes of drought resistance index in soybean
候选基因 Candidate gene | 基因注释 Annotation | 生物过程描述 Biological process description |
|---|---|---|
| Glyma.16G064200∆ | 蛋白激酶结构域蛋白 Protein kinase domain-containing protein | 激素介导的信号途径 Hormone-mediated signaling pathway |
| Glyma.16G064300 | 驱动蛋白类蛋白KIN-4C Kinesin-like protein KIN-4C | 微管运动 Microtubule-based movement |
| Glyma.16G064401 | 蛋白激酶结构域蛋白 Protein kinase domain-containing protein | 激素介导的信号途径 Hormone-mediated signaling pathway |
| Glyma.16G064700# | 2-羧基-1,4萘醌转移酶 2-carboxy-1,4-naphthoquinone phytyltransferase | 光合电子传递 Photosynthetic electron transport |
| Glyma.16G064800 | 蛋白激酶结构域蛋白 Protein kinase domain-containing protein | 激素介导的信号途径 Hormone-mediated signaling pathway |
| Glyma.16G064900∆ | 蛋白激酶结构域蛋白 Protein kinase domain-containing protein | 激素介导的信号途径 Hormone-mediated signaling pathway |
| Glyma.16G065000 | 蛋白激酶结构域蛋白 Protein kinase domain-containing protein | 蛋白磷酸化 Protein phosphorylation |
| Glyma.16G065200∆ | 蛋白激酶结构域蛋白 Protein kinase domain-containing protein | 激素介导的信号途径 Hormone-mediated signaling pathway |
| Glyma.16G065300# | 蛋白Ycf2 Protein Ycf2 | 蛋白进入叶绿体基质 Protein import into chloroplast stroma |
| Glyma.16G065400∆ | 蛋白激酶结构域蛋白 Protein kinase domain-containing protein | 蛋白磷酸化 Protein phosphorylation |
| Glyma.16G065500∆ | LRRNT_2结构域蛋白 LRRNT_2 domain-containing protein | 蛋白磷酸化 Protein phosphorylation |
| Glyma.16G065600 | 蛋白激酶结构域蛋白 Protein kinase domain-containing protein | 激素介导信号途径 Hormone-mediated signaling pathway |
| Glyma.16G065900∆ | 胱氨酸 Cystinosin homolog | L-胱氨酸转运 L-cystine transport |
| Glyma.16G066200∆ | 琥珀酸脱氢酶[泛醌]铁硫 Succinate dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron-sulfur | 三羧酸循环 Tricarboxylic acid cycle |
| Glyma.16G066600 | 液泡加工酶 Vacuolar-processing enzyme | 液泡蛋白合成 Vacuolar protein processing |
| Glyma.16G067400 | - | - |
| Glyma.16G067500 | 水解酶_4结构域蛋白 Hydrolase_4 domain-containing protein | 生物过程 Biological process |
| Glyma.16G067600 | 未知蛋白 Uncharacterized protein | - |
| Glyma.16G067700 | 筛管封闭 Sieve element occlusion | 韧皮部发育 Phloem development |
候选基因 Candidate gene | 基因注释 Annotation | 生物过程描述 Biological process description |
|---|---|---|
| Glyma.17G143800 | 鞘磷脂磷酸二酯酶 Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 4 | 生物过程 Biological process |
| Glyma.17G143900∆ # | AP2/ERF结构域蛋白 AP2/ERF domain-containing protein | 乙烯激活信号途径 Ethylene-activated signaling pathway |
| Glyma.17G144000 | 过氧化物酶体酰基辅酶A氧化酶 Peroxisomal acyl-coenzyme A oxidase | 茉莉酸生物合成 Jasmonic acid biosynthetic process |
| Glyma.17G144100# | HTH MYB型结构域蛋白 HTH MYB-type domain-containing protein | ABA反应 Response to abscisic acid |
| Glyma.17G144301 | Fe2O G加双氧酶结构域蛋白 Fe2O G dioxygenase domain-containing protein | - |
| Glyma.18G167700 | F-box结构域蛋白 F-box domain-containing protein | 生物过程 Biological process |
| Glyma.18G167833 | E1A结合蛋白 p400E1A-binding protein p400 | - |
| Glyma.U024802 | 含有蛋白激酶结构域的蛋质 Protein kinase domain-containing protein | 蛋白磷酸化 Protein phosphorylation |
| Glyma.U043000 | 未知蛋白 Uncharacterized protein | - |
Table 4 Candidate genes of drought resistance index in soybean
候选基因 Candidate gene | 基因注释 Annotation | 生物过程描述 Biological process description |
|---|---|---|
| Glyma.17G143800 | 鞘磷脂磷酸二酯酶 Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 4 | 生物过程 Biological process |
| Glyma.17G143900∆ # | AP2/ERF结构域蛋白 AP2/ERF domain-containing protein | 乙烯激活信号途径 Ethylene-activated signaling pathway |
| Glyma.17G144000 | 过氧化物酶体酰基辅酶A氧化酶 Peroxisomal acyl-coenzyme A oxidase | 茉莉酸生物合成 Jasmonic acid biosynthetic process |
| Glyma.17G144100# | HTH MYB型结构域蛋白 HTH MYB-type domain-containing protein | ABA反应 Response to abscisic acid |
| Glyma.17G144301 | Fe2O G加双氧酶结构域蛋白 Fe2O G dioxygenase domain-containing protein | - |
| Glyma.18G167700 | F-box结构域蛋白 F-box domain-containing protein | 生物过程 Biological process |
| Glyma.18G167833 | E1A结合蛋白 p400E1A-binding protein p400 | - |
| Glyma.U024802 | 含有蛋白激酶结构域的蛋质 Protein kinase domain-containing protein | 蛋白磷酸化 Protein phosphorylation |
| Glyma.U043000 | 未知蛋白 Uncharacterized protein | - |

Fig. 5 Identification of candidate gene Glyma.10G007000A:GWAS signal on chromosome 10 (top) in the region from 0.0~0.9 Mb and LD heatmap (bottom) for this region; B:Haplotypes of Glyma.10G007000 in soybean natural population, statistical significance is determined by a two-tailed t-test; C:Gene structure and encoding protein conserved domain of Glyma.10G007000. Black rectangle— Exon; White rectangle— 5’UTR; White pentagon—3’UTR; Vertical red line— SNP mutation
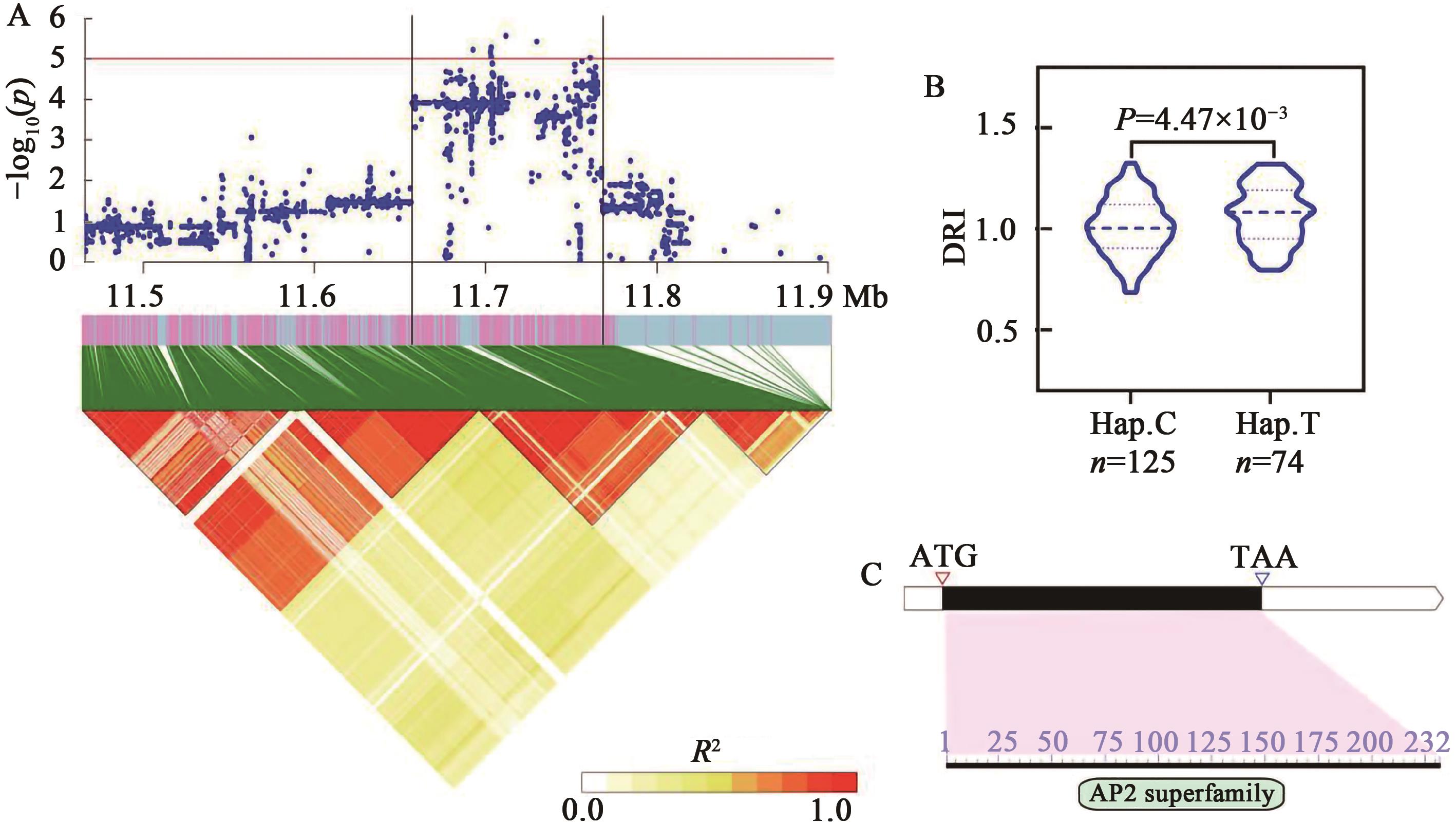
Fig. 6 Identification of candidate gene Glyma.17G143900A:GWAS signal on chromosome 17 (top) in the region from 11.5 ~11.9 Mb and LD heatmap (bottom) for this region; B:Haplotypes of Glyma.17G143900 in soybean natural population, statistical significance is determined by a two-tailed t-test; C:Gene structure and encoding protein conserved domain of Glyma.17G143900. Black rectangle—Exon; White rectangle—5’UTR; White pentagon—3’UTR; Vertical red line—SNP mutation
| 基因型Genotype | 品种数量Variety number | 抗旱指数Drought resistance index |
|---|---|---|
| 基因型Ⅰ (CCC)Genotype Ⅰ (CCC) | 70 | 0.97 d |
| 基因型Ⅱ (CCT)Genotype Ⅱ (CCT) | 36 | 1.03 c |
| 基因型Ⅲ (CAC)Genotype Ⅲ (CAC) | 17 | 1.10 abc |
| 基因型Ⅳ (CAT)Genotype Ⅳ (CAT) | 13 | 1.14 ab |
| 基因型Ⅴ (ACC)Genotype Ⅴ (ACC) | 35 | 1.03 c |
| 基因型Ⅵ (ACT)Genotype Ⅵ (ACT) | 17 | 1.04 c |
| 基因型Ⅶ (AAT)Genotype Ⅶ (AAT) | 7 | 1.20 a |
| 基因型Ⅷ (AAC)Genotype Ⅷ (AAC) | 4 | 1.18 ab |
Table 5 Analysis of soybean natural population based on the allele variations of three selected causal genes
| 基因型Genotype | 品种数量Variety number | 抗旱指数Drought resistance index |
|---|---|---|
| 基因型Ⅰ (CCC)Genotype Ⅰ (CCC) | 70 | 0.97 d |
| 基因型Ⅱ (CCT)Genotype Ⅱ (CCT) | 36 | 1.03 c |
| 基因型Ⅲ (CAC)Genotype Ⅲ (CAC) | 17 | 1.10 abc |
| 基因型Ⅳ (CAT)Genotype Ⅳ (CAT) | 13 | 1.14 ab |
| 基因型Ⅴ (ACC)Genotype Ⅴ (ACC) | 35 | 1.03 c |
| 基因型Ⅵ (ACT)Genotype Ⅵ (ACT) | 17 | 1.04 c |
| 基因型Ⅶ (AAT)Genotype Ⅶ (AAT) | 7 | 1.20 a |
| 基因型Ⅷ (AAC)Genotype Ⅷ (AAC) | 4 | 1.18 ab |
| 1 | LI X H, TIAN R, SHAO Z Q, et al.. Genetic loci and causal genes for seed fatty acids accumulation across multiple environments and genetic backgrounds in soybean [J/OL]. Mol. Breeding, 2021, 41(5):31 [2022-10-26]. . |
| 2 | 郑巨云,桑志伟,王俊铎,等.棉花品种抗旱性相关指标分析与综合评价[J].中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(10):23-34. |
| ZHENG J Y, SANG Z W, WANG J D, et al.. Indexes analysis and comprehensive evaluation of drought resistance of cotton varieties [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2022, 24(10):23-34. | |
| 3 | 沈波,庄杰云,樊叶杨,等.不同供水条件下水稻叶绿素含量的QTL分析[J].浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2007, 33(4):400-406. |
| SHEN B, ZHUANG J Y, FAN Y Y, et al.. QTL analysis of chlorophyll contents in rice under different water supply [J]. J. Zhejiang Univ. (Agric. Life Sci.), 2007, 33(4):400-406. | |
| 4 | 胡颂平,梅捍卫,邹桂花,等.正常与水分胁迫下水稻叶片叶绿素含量的QTL分析[J].植物生态学报, 2006, 30(3):479-486. |
| HU S P, MEI H W, ZOU G H, et al.. Analysis of quantitative trait loci for chlorophyll content in rice leaves under drought stress [J]. Chin. J. Plant Ecol., 2006, 30(3):479-486. | |
| 5 | KUMAR S, SEHGAL S K, KUMAR U, et al.. Genomic characterization of drought tolerance-related traits in spring wheat [J]. Euphytica, 2012, 186:265-276. |
| 6 | PELEG Z, FAHIMA T, KRUGMAN T, et al.. Genomic dissection of drought resistance in durum wheat × wild emmer wheat recombinant inbreed line population [J]. Plant Cell Environ., 2009, 32(7):758-779. |
| 7 | 崔世友,喻德跃.大豆不同生育时期叶绿素含量QTL的定位及其与产量的关联分析[J].作物学报, 2007, 33(5):744-750. |
| CUI S Y, YU D Y. QTL mapping of chlorophyll content at various growing stages and its relationship with yield in soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2007, 33(5):744-750. | |
| 8 | FANG C, MA Y M, WU S W, et al.. Genome-wide association studies dissect the genetic networks underlying agronomical traits in soybean [J/OL]. Genome Biol., 2017, 18(1):161 [2022-10-26]. . |
| 9 | KATO K K, PALMER R G. Duplicate chlorophyll-deficient loci in soybean [J]. Genome, 2004, 47(1):190-198. |
| 10 | TIAN R, KONG Y B, SHAO Z Q, et al.. Discovery of genetic loci and causal genes for seed germination via deep re-sequencing in soybean [J/OL]. Mol. Breeding, 2022, 42(8):45 [2022-10-26]. . |
| 11 | 刘松涛. 玉米VT时期耐旱性遗传及重要基因发掘[D].保定: 河北农业大学, 2021. |
| LIU S T. Drought stress tolerance inheritance and important gene excavation in maize during the VT stage [D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2021. | |
| 12 | 刘过,刘松涛,董安忆,等.基于iTRAQ的玉米V12时期响应干旱胁迫的蛋白质组学分析[J].河北农业大学学报, 2020, 43(6):15-25. |
| LIU G, LIU S T, DONG A Y, et al.. Proteomic analysis of maize response to drought stress in the V12 stage based on iTRAQ technology [J]. J. Agric. Univ. Hehei, 2020, 43(6):15-25. | |
| 13 | HUO X B, LI X H, DU H, et al.. Genetic loci and candidate genes of symbiotic nitrogen fixation-related characteristics revealed by a genome-wide association study in soybean [J/OL]. Mol. Breeding, 2019, 39(9):127 [2022-10-26]. . |
| 14 | WEI W, LIANG D W, BIAN X H, et al.. GmWRKY54 improves drought tolerance through activating genes in abscisic acid and Ca2+ signaling pathways in transgenic soybean [J]. Plant J., 2019, 100(2):384-398. |
| 15 | XU K H, ZHAO Y, ZHAO Y, et al.. Soybean F-box-like protein GmFBL144 interacts with small heat shock protein and negatively regulates plant drought stress tolerance [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2022, 13:823529 [2022-10-26]. . |
| 16 | 赵利锋,柴团耀. AP2/EREBP转录因子在植物发育和胁迫应答中的作用[J].植物学通报, 2008, 25(1):89-101. |
| ZHAO L F, CHAI T Y. Roles of AP2/EREBP family of transcription factors in development and stress response of plant [J]. Chin. Bull. Bot., 2008, 25(1):89-101. | |
| 17 | 金梦娇,刘博,王抗抗,等.薇甘菊光能利用及叶绿素合成在不同光照强度下的响应[J].中国农业科学, 2022, 55(12):2347-2359. |
| JIN M J, LIU B, WANG K K, et al.. Light energy utilization and response of chlorophyll synthesis under different light intensities in Mikania micrantha [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2022, 55(12):2347-2359. | |
| 18 | 王晓通,陈鹏吉,熊宏,等.干旱胁迫对樟叶越桔叶片生理特性的影响[J/OL].东北农业科学,2022 [2022-10-26] . . |
| WANG X T, CHEN P J, XIONG H, et al.. Effect of drought stress on physiological characteristics of Vaccinium dunalianum wight leaves [J]. J. Northeast Agric. Sci., 2022 [2022-10-26]. . | |
| 19 | 王建伟,周凌云.土壤水分变化对金银花叶片生理生态特征的影响[J].土壤, 2007, 39(3):479-482. |
| WANG J W, ZHOU L Y. Effects of soil moisture content on physio-ecological characteristics of Lonicera japonica thunb leaves [J]. Soils, 2007, 39(3):479-482. | |
| 20 | 于永涛,刘成,吕玲,等.玉米品种耐旱性评价及相关鉴定指标的研究[J].作物杂志, 2008(4):55-58. |
| YU Y T, LIU C, LYU L, et al.. Studies on evaluation index of drought tolerance in maize [J]. Crops, 2008 (4):55-58. | |
| 21 | 刘桂茹,张荣芝,卢建祥,等.小麦品种抗旱性鉴定指标与产量性状关系的探讨[J].河北农业大学学报, 1995, 18(1):10-14. |
| LIU G R, ZHANG R Z, LU J X, et al.. Relationship between yield and indices determining drought-resistance in winter wheat [J]. J. Agric. Univ. Hebei, 1995, 18(1):10-14. | |
| 22 | 杨玉敏,杨武云,陈尚洪,等.不同基因型小麦抗旱性评价指标筛选[J].西南农业学报, 2016, 29(10):2284-2289. |
| YANG Y M, YANG W Y, CHEN S H, et al.. Drought resistance index and morphological index of drought resistance identification in wheat [J]. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci., 2016, 29(10):2284-2289. | |
| 23 | 王辉,曹立勇,郭玉华,等.水稻生理特性与抗旱性的相关分析及QTL定位[J].中国水稻科学, 2008, 22(5):477-484. |
| WANG H, CAO L Y, GUO Y H, et al.. Correlation analysis and QTL mapping of some physiological traits related to drought resistance in rice [J]. Chin. J. Rice Sci., 2008, 22(5):477-484. | |
| 24 | 王娇.水稻抗旱性相关性状的QTL定位分析[D]. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2015. |
| WANG J. QTL mapping analysis for rice drought resistant related traits [D]. Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2015. | |
| 25 | 张维军,袁汉民,陈东升,等.小麦抗旱性生理生化机制及QTL研究进展[J].干旱地区农业研究, 2015, 33(6):139-148. |
| ZHANG W J, YUAN H M, CHEN D S, et al.. Advances in studies on physiological and biochemical indexes and QTL for drought resistance in wheat [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2015, 33(6):139-148. | |
| 26 | 郑福兴.基于多光谱无人机水旱条件下小麦叶绿素含量全基因组关联分析[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆农业大学, 2021. |
| ZHENG F X. Genome-wide association studies of chlorophyll content in wheat under flood and drought conditions based on multi-spectral unmanned aerial vehicle [D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2021. | |
| 27 | 李广军,李河南,程利国,等.大豆叶绿素含量动态表达的QTL分析[J].作物学报, 2010, 36(2):242-248. |
| LI G J, LI H N, CHENG L G, et al.. QTL analysis for dynamic expression of chlorophyll content in soybean (Glycine max L. Merri.) [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2010, 36(2):242-248. | |
| 28 | DU W, WANG M, FU S, et al.. Mapping QTLs for seed yield and drought susceptibility index in soybean (Glycine max L.) across different environments [J]. J. Genet. Genomics, 2009, 36(12):721-731. |
| 29 | CARPENTIERI-PIPOLO V, PIPOLO A E, ABDEL-HALEEM H, et al.. Identification of QTLs associated with limited leaf hydraulic conductance in soybean [J]. Euphytica, 2012, 186(3):679-686. |
| 30 | SHI X L, YAN L, YANG C Y, et al.. Identification of a major quantitative trait locus underlying salt tolerance in ‘Jidou 12’ soybean cultivar [J/OL]. BMC Res. Notes, 2018, 11(1):95 [2022-10-26]. . |
| 31 | LI Q X, WANG W Q, WANG W L, et al.. Wheat F-box protein gene TaFBA1 is involved in plant tolerance to heat stress [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2018, 9:521 [2022-10-26]. . |
| 32 | ZHANG Y, ZHANG J, GUO J, et al.. F-box protein RAE1 regulates the stability of the aluminum-resistance transcription factor STOP1 in Arabidopsis [J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2019, 116:319-327. |
| 33 | QU L N, SUN M S, LI X M, et al.. The Arabidopsis F-box protein FOF2 regulates ABA-mediated seed germination and drought tolerance [J/OL]. Plant Sci., 2020, 301:110643 [2022-10-26]. . |
| 34 | LIM J, LIM C W, LEE S C. Functional analysis of pepper F-box protein CaDIF1 and its interacting partner CaDIS1: modulation of ABA signaling and drought stress response [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2019, 10:1365 [2022-10-26]. . |
| 35 | ZHANG Y L, ZHANG C L, WANG G L, et al.. Apple AP2/EREBP transcription factor MdSHINE2 confers drought resistance by regulating wax biosynthesis [J]. Planta, 2019, 249(3):1627-1643. |
| 36 | CHEN M, WANG Q Y, CHENG X G, et al.. GmDREB2, a soybean DRE-binding transcription factor, conferred drought and high-salt tolerance in transgenic plants [J]. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Co., 2007, 353(2):299-305. |
| 37 | COMINELLI E, GALBIATI M, VAVASSEUR A, et al.. A guard-cell-specific MYB transcription factor regulates stomatal movements and plant drought tolerance [J]. Curr. Biol., 2005, 15(13):1196-1200. |
| 38 | MA J, XU Z S, WANG F, et al.. Genome-wide analysis of HSF family transcription factors and their responses to abiotic stresses in two Chinese cabbage varieties [J]. Acta Physiol. Plant, 2014, 36(2):513-523. |
| 39 | LI X P, GAN R, LI P L, et al.. Identification and functional characterization of a leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase gene that is involved in regulation of soybean leaf senescence [J]. Plant Mol. Biol., 2006, 61(6):829-844. |
| [1] | Jianmin YAO, Junkui MA, Zhongxiang WANG, Xinyuan BI, Ruizhen LI, Ruiping YANG, Zhao LIU, Fenghui GUO. Application Effect of Full Biodegradable Water Permeable Plastic Film in Soybean-Maize Belt Composite Planting [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 178-185. |
| [2] | Chenyang ZHANG, Minggang XU, Fei WANG, Ran LI, Nan SUN. Effects of Manure Application on Soybean Yield and Soil Nutrients in China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 148-156. |
| [3] | Yancheng WANG, Jiyue ZHANG, Shuaiqi FENG, Xue LIANG, Zhen ZHANG, Weiwei DONG, Wenxiu JI. Effects of Exogenous PGPR Combined with Organic Fertilizers on Soil Properties and Stress Resistance of Ginseng Under Drought Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 196-202. |
| [4] | Boyang KE, Wenlong LI, Caiying ZHANG. Expressions of SWEET Genes During Pod and Seed Developments and Under Different Stress Conditions in Soybean [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 33-52. |
| [5] | Yaqian SUN, Shiliang CHEN, Jiahao CHU, Xihuan LI, Caiying ZHANG. Mining of QTLs and Candidate Genes for Pod and Seed Traits via Combining BSA-seq and Linkage Mapping in Soybean [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 29-42. |
| [6] | Shuang WANG, Yixing HOU, Linjiao FENG, Qianqian LU, Long ZHOU. Effect of Drought Stress on Anatomical Structure of Leaves in Table Grape Varieties [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(6): 40-49. |
| [7] | Yilong ZHANG, Xiaofan SUN, Shuo LI, Peiying LI, Zongjiu SUN. Physiological Response of Different Drought-resistant Cynodon dactylon Germplasm to Drought [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(6): 59-70. |
| [8] | Jian HU, Gang CHE, Lin WAN, Huiru ZHOU, Guang LI. Study of Soybean Row Line Extraction Method Under High Light Conditions [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(5): 106-111. |
| [9] | Zhanwu YANG, Hui DU, Xinzhu XING, Wenlong LI, Youbin KONG, Xihuan LI, Caiying ZHANG. Functional Analysis of Cytochrome P450 Family GmCYP78A71 in Soybean Nodulation [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(1): 50-57. |
| [10] | Qing LU, Ting LIANG, Weiwei WANG, Dezhou WANG, Xian WU, Xiaoyan WANG, Yimiao TANG. Cloning and Expression Analysis of Wheat Heat Shock Protein Gene TaHSP90-1 [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(8): 44-54. |
| [11] | Zhenxiang TIAN, Wei DING, Zhuo CHENG, Hangyu DAI. Isolation of Endophytic Bacteria in Soybean and Its Action Effect [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(6): 47-57. |
| [12] | Lili WANG, Congpei YIN, Feng LI, Zhimin YANG, Fangming LIU, Baisong LIN, Xiaojing LIU, Haijun LIU, Jing SUN, Dongdong SHAN, Jianghui CUI, Zhenqing ZHANG. Microbial Community Structure of Potato Rhizosphere Soil and Its Response to Drought Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(6): 58-69. |
| [13] | Kuiyuan CHEN, Hui LIU, Wei DING. Effect of Glyphosate on Soil Nutrient and the Functional Enzyme Activities in Soybean Fields [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(5): 180-188. |
| [14] | Fangling WANG, Mingyue ZHANG, Yaru ZHOU, Qinglin GUAN, Xinyan LI, Qiu ZHONG, Mingqin ZHAO. Effect of TS-PAA Water Retaining Agent on Growth and Photosynthetic Characteristics of Cigar under Drought Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(4): 162-172. |
| [15] | Ning QIN, Junru LI, Rui TIAN, Zhenqi SHAO, Xihuan LI, Caiying ZHANG. Mining of Genetic Loci and Screening of Candidate Genes for Seed Tocopherol Content in Soybean [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(3): 48-56. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号