




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (10): 35-44.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0280
收稿日期:2022-04-09
接受日期:2022-05-28
出版日期:2023-10-15
发布日期:2023-10-27
通讯作者:
张艳
作者简介:张曼 E-mail:zhangman920601@163.com;
基金资助:
Man ZHANG( ), Jin ZHANG, Xinyu ZHANG, Guoning WANG, Xingfen WANG, Yan ZHANG(
), Jin ZHANG, Xinyu ZHANG, Guoning WANG, Xingfen WANG, Yan ZHANG( )
)
Received:2022-04-09
Accepted:2022-05-28
Online:2023-10-15
Published:2023-10-27
Contact:
Yan ZHANG
摘要:
黄萎病是造成棉花品质与产量下降的重要原因之一,探索棉花抗病机制对推动生态农业的可持续发展具有深远意义。在黄萎病菌胁迫的陆地棉ND601根组织全长cDNA文库中,筛选到1个与黄萎病胁迫相关的植物特异NAC转录因子基因,将其命名为GhNAC1。该基因cDNA序列全长1 213 bp,开放阅读框840 bp,编码279个氨基酸。GhNAC1没有信号肽和跨膜结构,定位在细胞核。qRT-PCR分析结果表明,GhNAC1受黄萎病菌胁迫后在根部特异表达,显著上调,表达量在抗性品种中显著高于感病品种。GhNAC1沉默后棉花对黄萎病抗性降低,水杨酸路径标志基因(PAD4、NDR1、NPR1和PR1)表达量降低,以上结果表明GhNAC1可能通过调控水杨酸信号通道参与棉花黄萎病抗性。
中图分类号:
张曼, 张进, 张新雨, 王国宁, 王省芬, 张艳. 陆地棉GhNAC1基因的克隆及抗黄萎病功能分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(10): 35-44.
Man ZHANG, Jin ZHANG, Xinyu ZHANG, Guoning WANG, Xingfen WANG, Yan ZHANG. Cloning and Functional Analysis of GhNAC1 in Upland Cotton Involved in Verticillium Wilt Resistance[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(10): 35-44.
引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence(5’-3’) | 用途 Utilization |
|---|---|---|
| NAC1-F | ATGAGCTACCAATCAAACC | 基因克隆Gene cloning |
| NAC1-R | TTAAAAGTTGAGGATATTAGC | 基因克隆Gene cloning |
| NAC1-RT-F | GAACACATCTCTTCCTTCATCATCTT | 实时定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| NAC1-RT-R | AGTTGTCCCATATTTTCATTGCCTA | 实时定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| NAC1-V-F | GAATTCGGTTGAACTTCCTGGCTTTA | 载体构建Vector construction |
| NAC1-V-R | GGTACCGCAAAGTAGCATCAGGGAG | 载体构建Vector construction |
| NAC1-G-F | GGGGACAAGTTTGTACAAAAAAGCAGGCTTCATGA GCTACCAATCAAACC | 载体构建Vector construction |
| NAC1-G-R | GGGGACCACTTTGTACAAGAAAGCTGGGTGAAAGTT GAGGATATTAGC | 载体构建Vector construction |
| GhUBQ14-F | CAACGCTCCATCTTGTCCTT | 实时定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| GhUBQ14-R | TAGTCGTCTTTCCCGTAAGC | 实时定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| GhNDR1-F | CCCGTAACCAAGGAGGCTGT | 实时定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| GhNDR1-R | CTGCTAAGGGAAGGCAAGGATAG | 实时定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| GhNPR1-F | GTCTGGCTGATGTCAATCTGCG | 实时定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| GhNPR1-R | TCCTTCCCTTGCTCTGTCTTGG | 实时定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| GhPR1-F | GGCACAGAACTACGCTAATCAACG | 实时定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| GhPR1-R | GCTTTACCCTCTCACTAACCCACAT | 实时定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| GhPAD4-F | GGATGGAAGAATGGAAAGAAATGAA | 实时定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| GhPAD4-R | GAACTAGGAAAGCAGACTAAGGAACCA | 实时定量PCR Real-time PCR |
表1 试验所用引物序列
Table 1 Primers used in this experiment
引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence(5’-3’) | 用途 Utilization |
|---|---|---|
| NAC1-F | ATGAGCTACCAATCAAACC | 基因克隆Gene cloning |
| NAC1-R | TTAAAAGTTGAGGATATTAGC | 基因克隆Gene cloning |
| NAC1-RT-F | GAACACATCTCTTCCTTCATCATCTT | 实时定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| NAC1-RT-R | AGTTGTCCCATATTTTCATTGCCTA | 实时定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| NAC1-V-F | GAATTCGGTTGAACTTCCTGGCTTTA | 载体构建Vector construction |
| NAC1-V-R | GGTACCGCAAAGTAGCATCAGGGAG | 载体构建Vector construction |
| NAC1-G-F | GGGGACAAGTTTGTACAAAAAAGCAGGCTTCATGA GCTACCAATCAAACC | 载体构建Vector construction |
| NAC1-G-R | GGGGACCACTTTGTACAAGAAAGCTGGGTGAAAGTT GAGGATATTAGC | 载体构建Vector construction |
| GhUBQ14-F | CAACGCTCCATCTTGTCCTT | 实时定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| GhUBQ14-R | TAGTCGTCTTTCCCGTAAGC | 实时定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| GhNDR1-F | CCCGTAACCAAGGAGGCTGT | 实时定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| GhNDR1-R | CTGCTAAGGGAAGGCAAGGATAG | 实时定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| GhNPR1-F | GTCTGGCTGATGTCAATCTGCG | 实时定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| GhNPR1-R | TCCTTCCCTTGCTCTGTCTTGG | 实时定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| GhPR1-F | GGCACAGAACTACGCTAATCAACG | 实时定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| GhPR1-R | GCTTTACCCTCTCACTAACCCACAT | 实时定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| GhPAD4-F | GGATGGAAGAATGGAAAGAAATGAA | 实时定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| GhPAD4-R | GAACTAGGAAAGCAGACTAAGGAACCA | 实时定量PCR Real-time PCR |

图2 GhNAC1蛋白结构分析A:GhNAC1信号肽预测结果;B:GhNAC1跨膜域预测结果;C:GhNAC1蛋白二级结构预测
Fig. 2 Structure analysis of GhNAC1 proteinA: Prediction result of GhNAC1 signal peptide; B: Prediction result of GhNAC1 transmembrane domain; C: Prediction of secondary structure of GhNAC1 protein
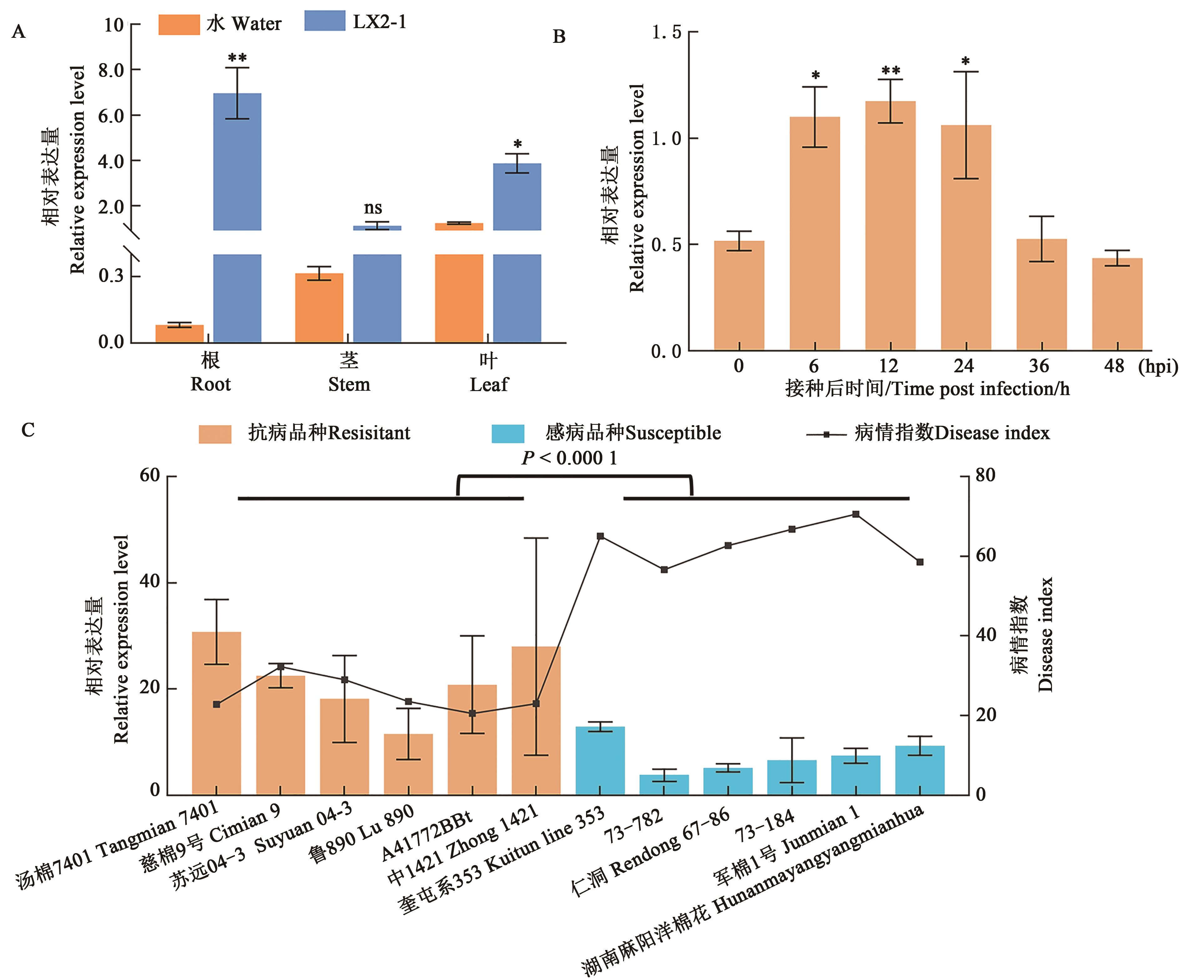
图3 GhNAC1的表达模式A:农大601不同组织器官中GhNAC1的表达;B:黄萎病菌胁迫下GhNAC1在ND601根部的表达;C:黄萎病菌胁迫下GhNAC1在12个不同抗性品种根部的表达及病情指数;*和**分别表示与0 h相比在P < 0.05和P < 0.01水平差异显著
Fig. 3 Expression pattern of GhNAC1A: Expression analysis of GhNAC1 in different tissues and organs of ND601; B: Expression analysis of GhNAC1 in ND601 roots under Verticillium wilt stress; C: Expression analysis of GhNAC1 in roots of 12 different resistant cultivars under Verticillium wilt stress; * and ** indicate significant differences compared with 0 h at P < 0.05 and P < 0.01 levels, respectively

图4 沉默GhNAC1降低了棉花对大丽轮枝菌的抗性A:棉花CLA1基因沉默后的叶片白化现象作为阳性对照;B:侵染7 d后野生型对照和沉默植株GhNAC1表达水平;C:20 dpi对照植株与沉默植株病害表现;D:病情指数;E:茎部病菌侵染表型。CK表示对照组,VIGS表示沉默组;**表示与CK相比在 P < 0.01水平差异显著
Fig. 4 Silencing GhNAC1 reduced the resistance to V. dahliae in cottonA: CLA1 gene was used as a positive control with an albino phenotype on leave after VIGS in cotton; B: Relative expression levels of GhNAC1 in WT and GhNAC1-silenced plants 7 d after hand-infiltration; C: Disease manifestations of control plants and silent plants at 20 dpi; D: Disease index; E: Phenotype of stem infected by V. dahliae. CK stands for control group, VIGS stands for silent group; ** indicates significant difference compared with CK at P < 0.01 level
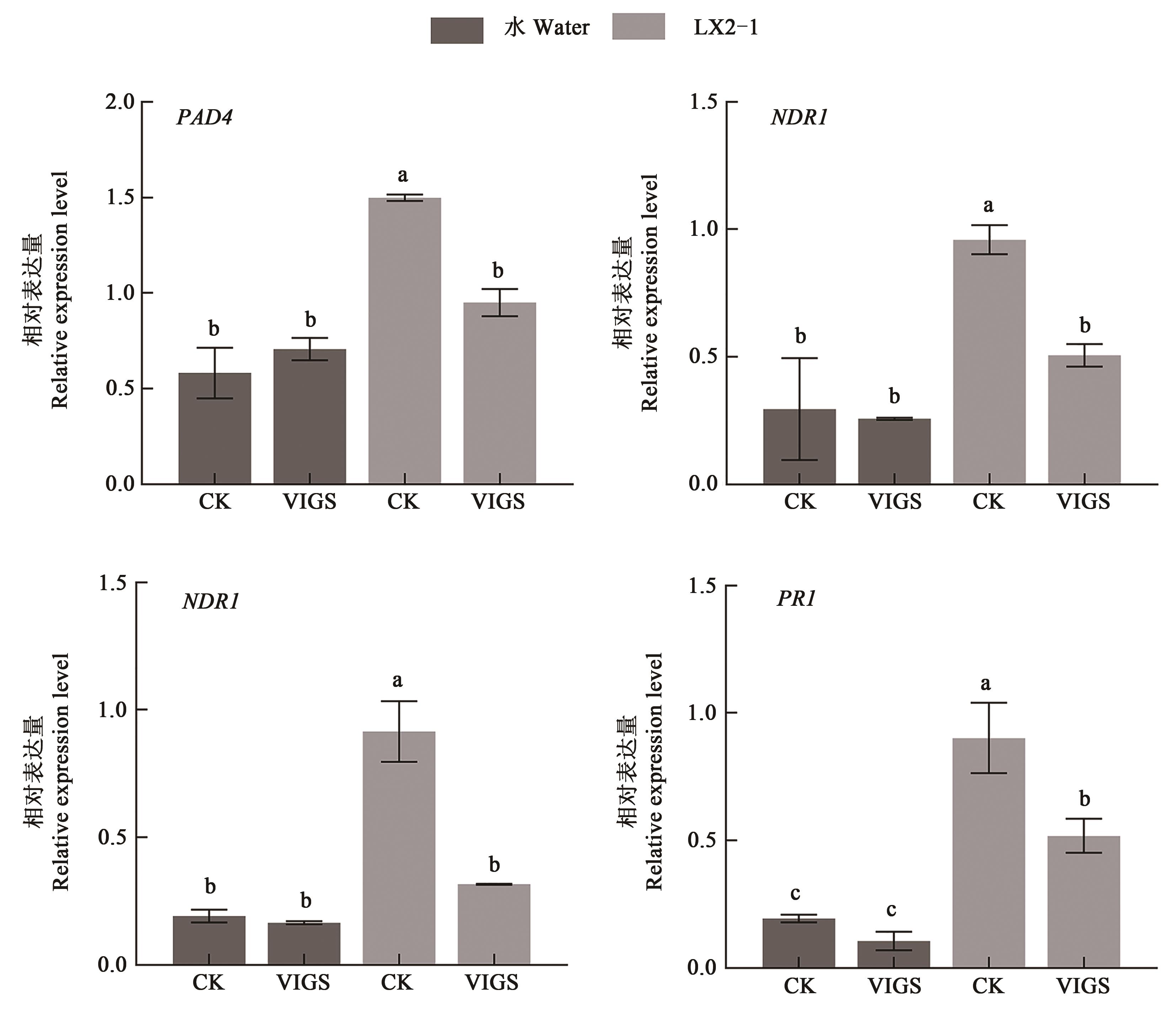
图5 GhNAC1沉默棉花接菌后水杨酸途径基因表达分析注:不同小写字母表示在P < 0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 5 Analysis of gene expression of salicylic acid pathway in GhNAC1 silenced cotton after inoculationNote:Different lowercase letters represent significant differences at P < 0.05 level.
| 1 | KLOSTERMAN S J, ATALLAH Z K, VALLAD G E, et al.. Diversity, pathogenicity and management of Verticillium species [J]. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol., 2009, 47(1): 39-62. |
| 2 | VALLAD G E, SU B B, ARAO K V. Colonization of resistant and susceptible lettuce cultivars by a green fluorescent protein-tagged isolate of Verticillium dahliae [J/OL]. Phytopathology, 2008, 98(8): 871 [2022-03-19]. . |
| 3 | CHEN J Y, KLOSTERMAN S J, HU X P, et al.. Key insights and research prospects at the dawn of the population genomics era for Verticillium dahliae [J]. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol., 2021, 59(1): 31-51. |
| 4 | SONG R, LI Y S, XIE H Y, et al.. An overview of the molecular genetics of plant resistance to the Verticillium wilt pathogen Verticillium dahliae [J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2020, 21(3): 1120 [2022-03-21]. . |
| 5 | 朱荷琴,李志芳,冯自力,等.我国棉花黄萎病研究十年回顾及展望[J].棉花学报, 2017, 29(z1): 37-50. |
| ZHU H Q, LI Z F, FENG Z L, et al.. Review and prospect of cotton Verticillium wilt research in ten years in China [J]. Cotton Sci., 2017, 029(z1): 37-50. | |
| 6 | GAO W, LONG L, ZHU L F, et al.. Proteomic and virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) analyses reveal that gossypol, brassinosteroids, and jasmonic acid contribute to the resistance of cotton to Verticillium dahliae [J]. Mol. Cell Proteomics, 2013, 12(12): 3690-3703. |
| 7 | YANG J, MA Q, ZHANG Y, et al.. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of GbRVd, a gene in Gossypium barbadense that plays an important role in conferring resistance to Verticillium wilt [J]. Gene, 2016, 575(2): 687-694. |
| 8 | ZHANG Y, WU L, WANG X, et al.. The cotton laccase gene GhLAC15 enhances Verticillium wilt resistance via an increase in defence-induced lignification and lignin components in the cell walls of plants [J]. Mol. Plant Pathol., 2019, 20(3): 309-322. |
| 9 | CHEN B, ZHANG Y, YANG J, et al.. The G-protein α subunit GhGPA positively regulates Gossypium hirsutum resistance to Verticillium dahliae via induction of SA and JA signaling pathways and ROS accumulation [J]. Crop J., 2021, 9(4): 823-833. |
| 10 | CHEN B, ZHANG Y, SUN Z W, et al.. Tissue-specific expression of GhnsLTPs identified via GWAS sophisticatedly coordinates disease- and insect-resistance by regulating metabolic flux redirection in cotton [J]. Plant J., 2021, 107(3): 831-846. |
| 11 | 安汶铠,常丹,杨艺,等.利用VIGS技术沉默GhBES1基因对棉花幼苗生理指标的影响[J].分子植物育种, 2016, 14(9): 1055-1061. |
| AN W K, CHANG D, YANG Y, et al.. Effects of GhBES1 gene silencing by VIGS technique on physiological indexes of cotton seedlings [J]. Mol. Plant Breeding, 2016, 14(9): 1055-1061. | |
| 12 | AIDA M, ISHIDA T, FUKAKI H, et al.. Genes involved in organ separation in Arabidopsis: an analysis of the cup-shaped cotyledon mutant [J]. Plant Cell, 1997, 9(6): 841-857. |
| 13 | 孙利军,李大勇,张慧娟,等.NAC转录因子在植物抗病和抗非生物胁迫反应中的作用[J].遗传, 2012, 34(8): 993-1002. |
| SUN L J, LI D Y, ZHANG H J, et al.. Functions of NAC transcription factors in biotic and abiotic stress responses in plants [J]. Hereditas, 2012, 34(8): 993-1002. | |
| 14 | ZHONG R, LEE C, HAGHIGHAT M, et al.. Xylem vessel-specific SND5 and its homologs regulate secondary wall biosynthesis through activating secondary wall NAC binding elements [J]. New Phytol., 2021, 231(4): 1496-1509. |
| 15 | FU B L, WANG W Q, LIU X F, et al.. An ethylene-hypersensitive methionine sulfoxide reductase regulated by NAC transcription factors increases methionine pool size and ethylene production during kiwifruit ripening [J]. New Phytol., 2021,231(1): 237-251. |
| 16 | 曲潇玲,焦裕冰,罗健达,等.本氏烟NbNAC062的克隆及对马铃薯Y病毒侵染的抑制作用[J].中国农业科学, 2021, 54(19):84-94. |
| QU X L, JIAO Y B, LUO J D, et al.. Cloning of tobacco NbNAC062 and its inhibition on potato virus Y infection [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2021, 54(19): 84-94. | |
| 17 | 叶鸿鹰,梅双双,戎伟. ATAF2正调控拟南芥对橡胶树白粉菌的抗病性[J].热带生物学报, 2020, 11(1): 61-65. |
| YE H Y, MEI S S, RONG W. ATAF2 positively contributes to the disease resistance against Oidium heveae in Arabidopsis [J]. J. Trop. Biol., 2020, 11(1): 61-65. | |
| 18 | CAI W, YANG S, WU R, et al.. Pepper NAC-type transcription factor NAC2c balances the trade-off between growth and defense responses [J]. Plant Physiol., 2021, 186(4): 4. |
| 19 | 王国宁,赵贵元,岳晓伟,等.河北省棉花黄萎病菌致病性与ISSR遗传分化[J].棉花学报, 2012, 24(4): 348-357. |
| WANG G N, ZHAO G Y, YUE X W, et al.. Pathogenicity and ISSR genetic differentiation of Verticillium dahliae isolates from cotton growing areas of Hebei province [J]. Cotton Sci., 2012, 24(4): 348-357. | |
| 20 | SPARKES I A, RUNIONS J, KEARNS A, et al.. Rapid, transient expression of fluorescent fusion proteins in tobacco plants and generation of stably transformed plants [J]. Nature Protoc., 2006, 1(4):2019-2025. |
| 21 | ZHANG M, WANG X F, YANG J, et al.. GhENODL6 isoforms from the phytocyanin gene family regulate Verticillium wilt resistance in cotton [J]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2022, 23(6):2913-2921. |
| 22 | ZHANG Y, WANG X F, DING Z G, et al.. Transcriptome profiling of Gossypium barbadense inoculated with Verticillium dahliae provides a resource for cotton improvement [J/OL]. BMC Genomics, 2013, 14(1): 637 [2022-03-21]. . |
| 23 | YANG J, MA Q, ZHANG Y, et al.. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of GbRvd, a gene in Gossypium barbadense that plays an important role in conferring resistance to Verticillium wilt [J]. Gene, 2016, 575(2016): 687-694. |
| 24 | 李宝笃,沈崇尧. Hoaglands营养液栽苗法快速鉴定甜椒疫霉病菌致病性及对杀菌剂敏性研究初报[J].植物病理学报, 1993, 23(3): 243-244. |
| LI B D, SHEN C Y. Preliminary report on the rapid identification of pathogenicity and fungicide sensitivity of phytophthora capsicum by Hoaglands nutrient solution seedling method [J]. Acta Phytopathol. Sin., 1993, 23(3): 243-244. | |
| 25 | 唐永凯, 贾永义.荧光定量PCR数据处理方法的探讨[J].生物技术, 2008, 18(3): 91-93. |
| TANG Y K, JIA Y Y. Discussion on data processing method of fluorescence quantitative PCR [J]. Biotechnology, 2008, 18(3):91-93. | |
| 26 | ZHANG B, YANG Y, CHEN T, et al.. Island cotton Gbve1 gene encoding a receptor-like protein confers resistance to both defoliating and non-defoliating isolates of Verticillium dahliae [J/OL]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(12): e51091 [2022-03-21]. . |
| 27 | JYOTHISHWARAN G, KOTRESHA D, SELVARAJ T, et al.. A modified freeze-thaw method for efficient transformation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens [J]. Curr. Sci., 2007, 93(6): 770-772. |
| 28 | GAO X, BRITT R C, SHAN L, et al.. Agrobacterium-mediated virus-induced gene silencing assay in cotton [J/OL]. J. Vis. Exp., 2011, 54(54): e2938 [2022-03-21]. . |
| 29 | LOAKE G, GRANT M. Salicylic acid in plant defence-the players and protagonists [J]. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol., 2007, 10(5): 466-472. |
| 30 | MARQUES D N, REIS S D, SOUZA C D. Plant NAC transcription factors responsive to abiotic stresses [J]. Plant Gene, 2017, 11: 170-179. |
| 31 | PURANIK S, SAHU P P, SRIVASTAVA P S, et al.. NAC proteins: regulation and role in stress tolerance [J/OL]. Trends Plant Sci., 2012, 17(6): 369-381 [2022-03-21]. . |
| 32 | SHEN H, YIN Y, CHEN F, et al.. A bioinformatic analysis of NAC genes for plant cell wall development in relation to lignocellulosic bioenergy production [J/OL]. Bioenergy Res., 2009, 2(4): 217 [2022-03-21]. |
| 33 | WANG X, BASNAYAKE B, ZHANG H, et al.. The Arabidopsis ATAF1, a NAC transcription factor, is a negative regulator of defense responses against necrotrophic fungal and bacterial pathogens [J]. Mol. Plant Microbe., 2009, 22(10): 1227-1238. |
| 34 | NAKASHIMA K, TRAN L S P, NGUYEN D V, et al.. Functional analysis of a NAC-type transcription factor OsNAC6 involved in abiotic and biotic stress-responsive gene expression in rice [J]. Plant J., 2010, 51(4): 617-630. |
| 35 | SANG R P, KIM H S, LEE K S, et al.. Overexpression of rice NAC transcription factor OsNAC58 on increased resistance to bacterial leaf blight [J]. J. Plant Biochem. Biot., 2017, 44(2): 149-155. |
| 36 | ZHANG X M, ZHANG Q, PEI C L, et al.. TaNAC2 is a negative regulator in the wheat-stripe rust fungus interaction at the early stage [J]. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol., 2018, 102: 144-153. |
| 37 | LIU B, OUYANG Z, ZHANG Y, et al.. Tomato NAC transcription factor SlSRN1 positively regulates defense response against biotic stress but negatively regulates abiotic stress response [J]. PloS One, 2014, 9(7): e102067 [2022-03-21]. . |
| 38 | CHANG Y, YU R, FENG J, et al.. NAC transcription factor involves in regulating bacterial wilt resistance in potato [J]. Funct. Plant Biol., 2020, 47: 925-936. |
| 39 | SHIRASU K, NAKAJIMA H, LAMB D C, et al.. Salicylic acid potentiates an agonist-dependent gain control that amplifies pathogen signals in the activation of defense mechanisms [J]. Plant Cell, 1997, 9: 261-270. |
| 40 | LONG L, XU F C, ZHAO J R, et al.. GbMPK3 overexpression increases cotton sensitivity to Verticillium dahliae by regulating salicylic acid signaling [J/OL]. Plant Sci., 2020, 292: 110374 [2022-03-21]. . |
| 41 | MÉTRAUX J. Recent breakthroughs in the study of salicylic acid biosynthesis [J]. Trends Plant Sci., 2002, 7(8): 332-334. |
| 42 | CHEN Z, ZHENG Z, HUANG J, et al.. Biosynthesis of salicylic acid in plants [J]. Plant Signal. Behav., 2009, 4(6): 493-496. |
| 43 | ZHENG X Y, SPIVEY N, ZENG W, et al.. Coronatine promotes Pseudomonas syringae virulence in plants by activating a signaling cascade that inhibits salicylic acid accumulation [J]. Cell Host Microbe, 2012, 11(6): 587-596. |
| [1] | 王为, 赵强, 穆妮热·阿卜杜艾尼, 阿里木·阿木力null, 李欣欣, 田阳青. 烯效唑复配不同外源物质对棉花化学封顶及产量品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 57-68. |
| [2] | 孙正冉, 张翠萍, 张晋丽, 吴昊, 刘秀艳, 王振凯, 杨玉珍, 贺道华. 喷施化学打顶剂对关中棉区棉花植株生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 167-177. |
| [3] | 陆国清, 马彩霞, 孙国清, 郭惠明, 程红梅. 抗除草剂棉花GV-2的分子特征和遗传稳定性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(1): 42-49. |
| [4] | 刘艳, 鲍红帅, 尚红燕, 王国宁, 张艳, 王省芬, 马峙英, 吴金华. 棉花枯萎病菌及其培养条件筛选[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(8): 124-132. |
| [5] | 刘海涛, 韩鑫, 兰玉彬, 伊丽丽, 王宝聚, 崔立华. 基于YOLOv4网络的棉花顶芽精准识别方法[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(8): 99-108. |
| [6] | 孙正文, 谷淇深, 张艳, 王省芬, 马峙英. 棉花基因发掘与分子育种研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 32-38. |
| [7] | 闫成川, 曾庆涛, 陈琴, 付锦程, 王婷伟, 陈全家, 曲延英. 陆地棉花铃期抗旱指标筛选及评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 46-57. |
| [8] | 吴楠, 杨君, 张艳, 孙正文, 张冬梅, 李丽花, 吴金华, 马峙英, 王省芬. 过表达棉花葡萄糖醛酸激酶基因GbGlcAK促进拟南芥细胞伸长[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(6): 36-46. |
| [9] | 黄雅婕, 任丹, 李生梅, 崔进鑫, 杨涛, 任姣姣, 高文伟. 陆地棉苗期的耐盐碱性评价及鉴定指标筛选[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(5): 46-55. |
| [10] | 周雨青, 杨永飞, 葛常伟, 沈倩, 张思平, 刘绍东, 马慧娟, 陈静, 刘瑞华, 李士丛, 赵新华, 李存东, 庞朝友. 基于WGCNA的棉花子叶抗冷相关共表达模块鉴定[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(4): 52-62. |
| [11] | 张静, 郭思梦, 韩迎春, 雷亚平, 邢芳芳, 杜文丽, 李亚兵, 冯璐. 基于无人机RGB图像的棉花产量估算[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(11): 112-120. |
| [12] | 李娟, 闫旭宇, 吴香, 李玲. 纤维类作物对农田土壤镉污染修复的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(11): 171-178. |
| [13] | 柯会锋, 孙正文, 王国宁, 孟成生, 吴立强. 棉籽大小与形状关联标记发掘及候选基因筛选[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(11): 76-86. |
| [14] | 郝梦媛, 杭琦, 师恭曜. VIGS基因沉默技术在作物基因功能研究中的应用与展望[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 1-13. |
| [15] | 李生梅, 张大伟, 迪丽拜尔·迪力买买提, 魏鑫, 芮存, 杨涛, 耿世伟, 高文伟. 减量灌溉对转ScALDH21基因棉花农艺性状、产量和品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(9): 152-159. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号