




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (3): 206-215.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0678
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
沈乐丞1( ), 温志刚1, 廖涵1, 刘贤标1, 蒋耀聪2, 张远聪1, 刘婷1, 王玫1(
), 温志刚1, 廖涵1, 刘贤标1, 蒋耀聪2, 张远聪1, 刘婷1, 王玫1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-09-13
接受日期:2023-11-22
出版日期:2025-03-15
发布日期:2025-03-14
通讯作者:
王玫
作者简介:沈乐丞 E-mail: shenlecheng@163.com;
基金资助:
Lecheng SHEN1( ), Zhigang WEN1, Han LIAO1, Xianbiao LIU1, Yaocong JIANG2, Yuancong ZHANG1, Ting LIU1, Mei WANG1(
), Zhigang WEN1, Han LIAO1, Xianbiao LIU1, Yaocong JIANG2, Yuancong ZHANG1, Ting LIU1, Mei WANG1( )
)
Received:2023-09-13
Accepted:2023-11-22
Online:2025-03-15
Published:2025-03-14
Contact:
Mei WANG
摘要:
为研究叶面喷施不同硒肥处理对水稻硒含量及硒形态和稻米组分的影响,选用晶两优1468进行田间试验,设置无机硒和纳米硒2个施硒处理,以喷施清水为对照(CK),测定并分析各处理间水稻各部位硒含量及硒形态差异,并对稻米的组分进行比较。结果表明,水稻各个部位对硒的积累存在显著差异,硒在水稻中的富集表现为根>茎叶>稻米>稻壳。喷施无机硒、纳米硒后,水稻稻米硒含量相较于CK分别上升93.4%、132.5%。成熟期水稻不同部位的硒形态存在差异,主要以有机硒的形态存在,其中硒代蛋氨酸(SeMet)占比最高,达47.0%~84.5%。喷施无机硒、纳米硒后,水稻稻米有机硒含量相较于CK分别显著上升84.0%、129.7%。相较于CK,2种硒对稻米的直链淀粉和蛋白质含量均无显著影响,而稻米中的砷含量分别降低56.9%、61.8%,汞含量分别降低79.7%、54.2%,铅含量分别降低25.0%、27.2%。综上可知,施用无机硒、纳米硒可以提高稻米中总硒含量及有机硒含量,相比无机硒,纳米硒处理可使稻米中含有更高比例的有机硒,且这2种施硒处理基本不影响稻米的直链淀粉和蛋白质含量,但有利于进一步降低稻米的砷、铅、汞含量,因此纳米硒在生产富硒大米中会产生更好的健康效应。研究结果为富硒大米生产实践提供了理论参考。
中图分类号:
沈乐丞, 温志刚, 廖涵, 刘贤标, 蒋耀聪, 张远聪, 刘婷, 王玫. 叶面喷施不同硒肥对水稻硒含量及硒形态和稻米组分的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(3): 206-215.
Lecheng SHEN, Zhigang WEN, Han LIAO, Xianbiao LIU, Yaocong JIANG, Yuancong ZHANG, Ting LIU, Mei WANG. Effects of Foliar Spraying of Different Selenium Fertilizers on Selenium Content, Selenium Speciation and Components in Rice[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(3): 206-215.
| 处理 Treatment | 根 Root | 茎叶 Stem and leaf | 稻壳 Rice husk | 稻米 Unpolished rice |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.631±0.119 b | 0.452±0.021 b | 0.184±0.001 c | 0.317±0.026 bc |
| IS | 0.692±0.073 b | 0.705±0.018 a | 0.420±0.021 b | 0.613±0.079 a |
| NS | 1.120±0.176 a | 0.752±0.164 a | 0.773±0.073 a | 0.737±0.014 a |
表1 水稻不同器官的硒含量 (mg·kg-1)
Table 1 Selenium content in different organs of rice
| 处理 Treatment | 根 Root | 茎叶 Stem and leaf | 稻壳 Rice husk | 稻米 Unpolished rice |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.631±0.119 b | 0.452±0.021 b | 0.184±0.001 c | 0.317±0.026 bc |
| IS | 0.692±0.073 b | 0.705±0.018 a | 0.420±0.021 b | 0.613±0.079 a |
| NS | 1.120±0.176 a | 0.752±0.164 a | 0.773±0.073 a | 0.737±0.014 a |
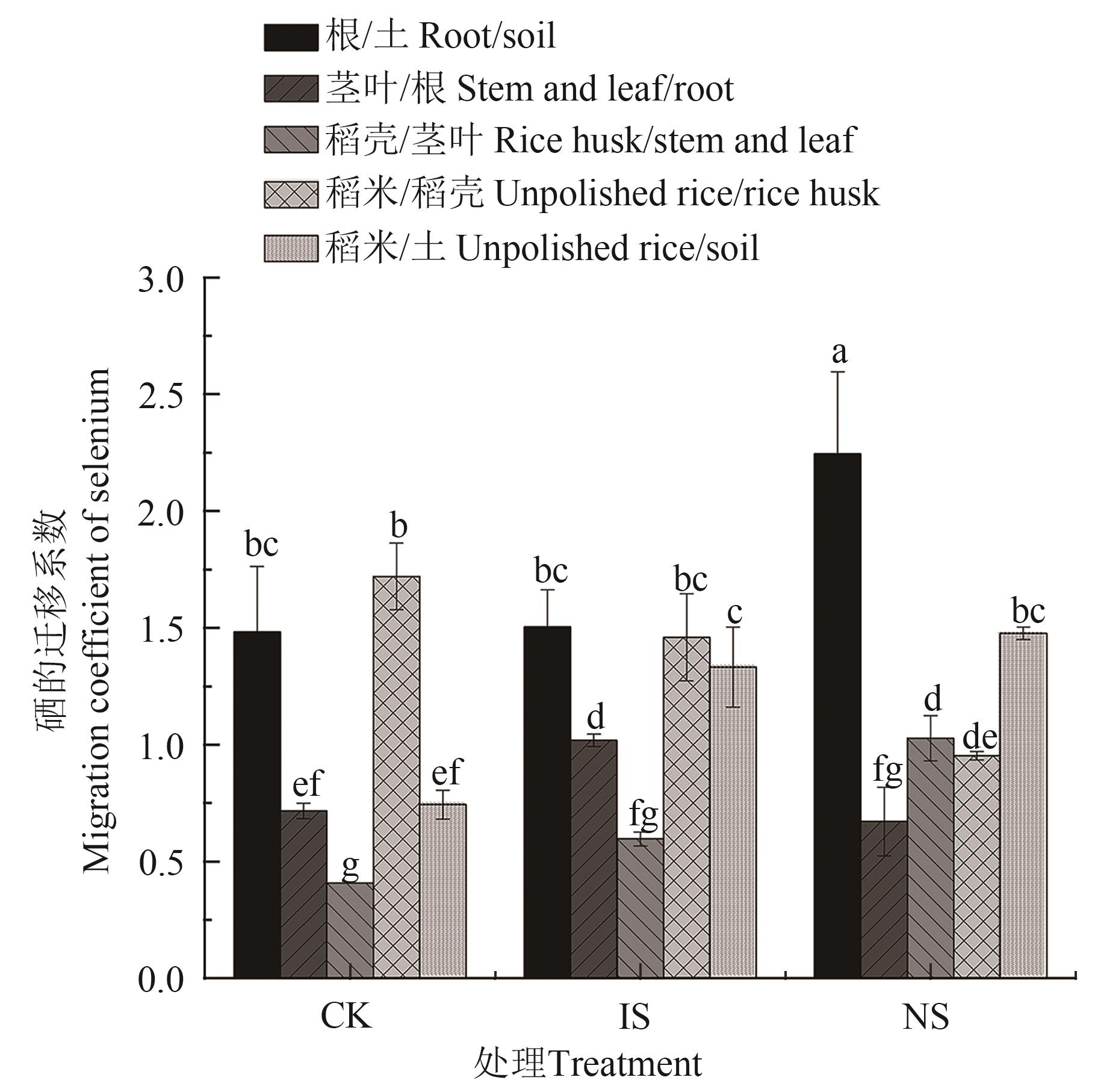
图1 水稻中不同器官硒的迁移系数注∶不同小写字母表示不同器官间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 Migration coefficient of selenium in different organs of riceNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different organs at P<0.05 level.
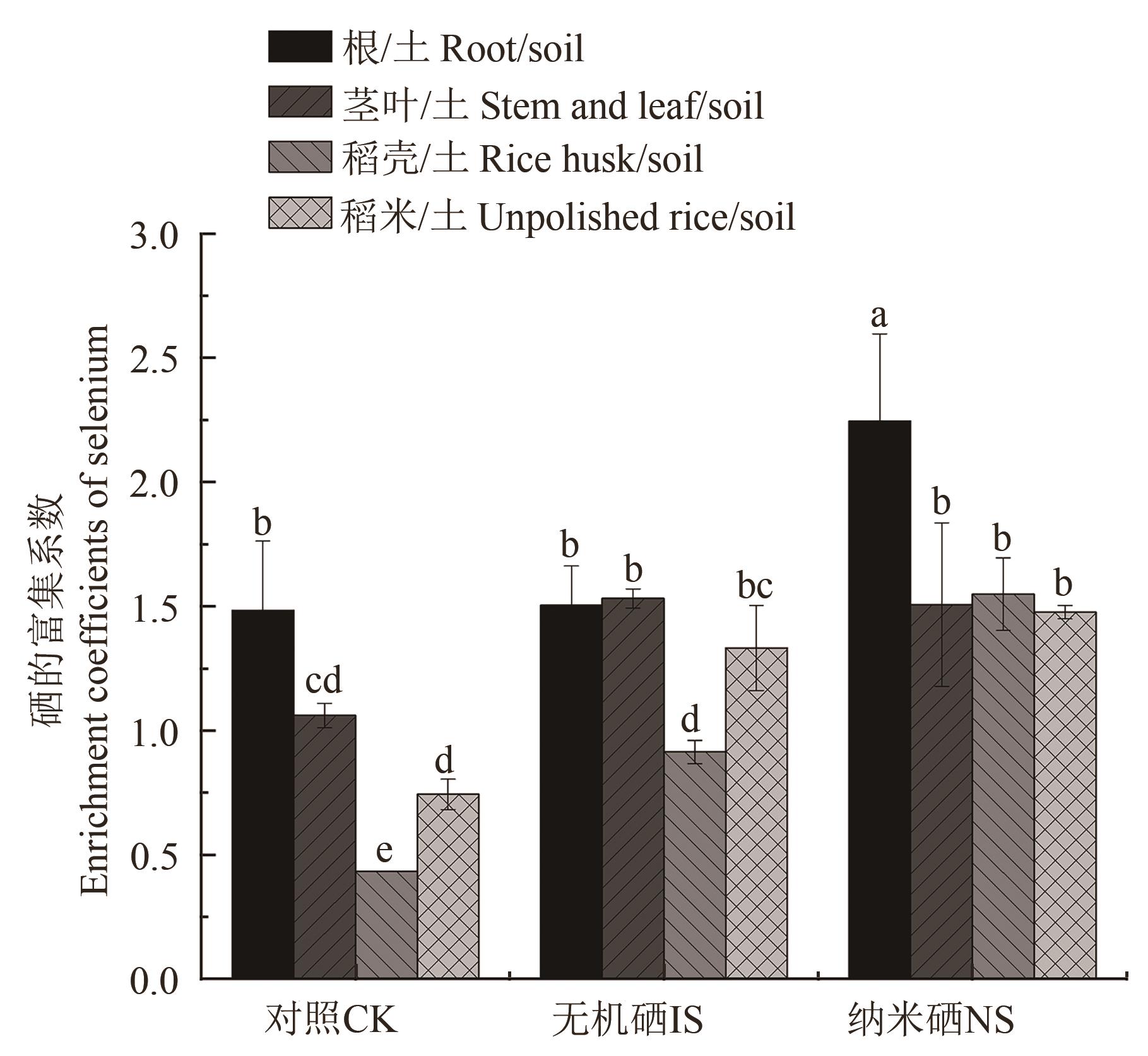
图 2 水稻中不同器官硒的富集系数注:不同小写字母表示不同器官间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 Enrichment coefficients of selenium in different organs of riceNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different organs at P<0.05 level.
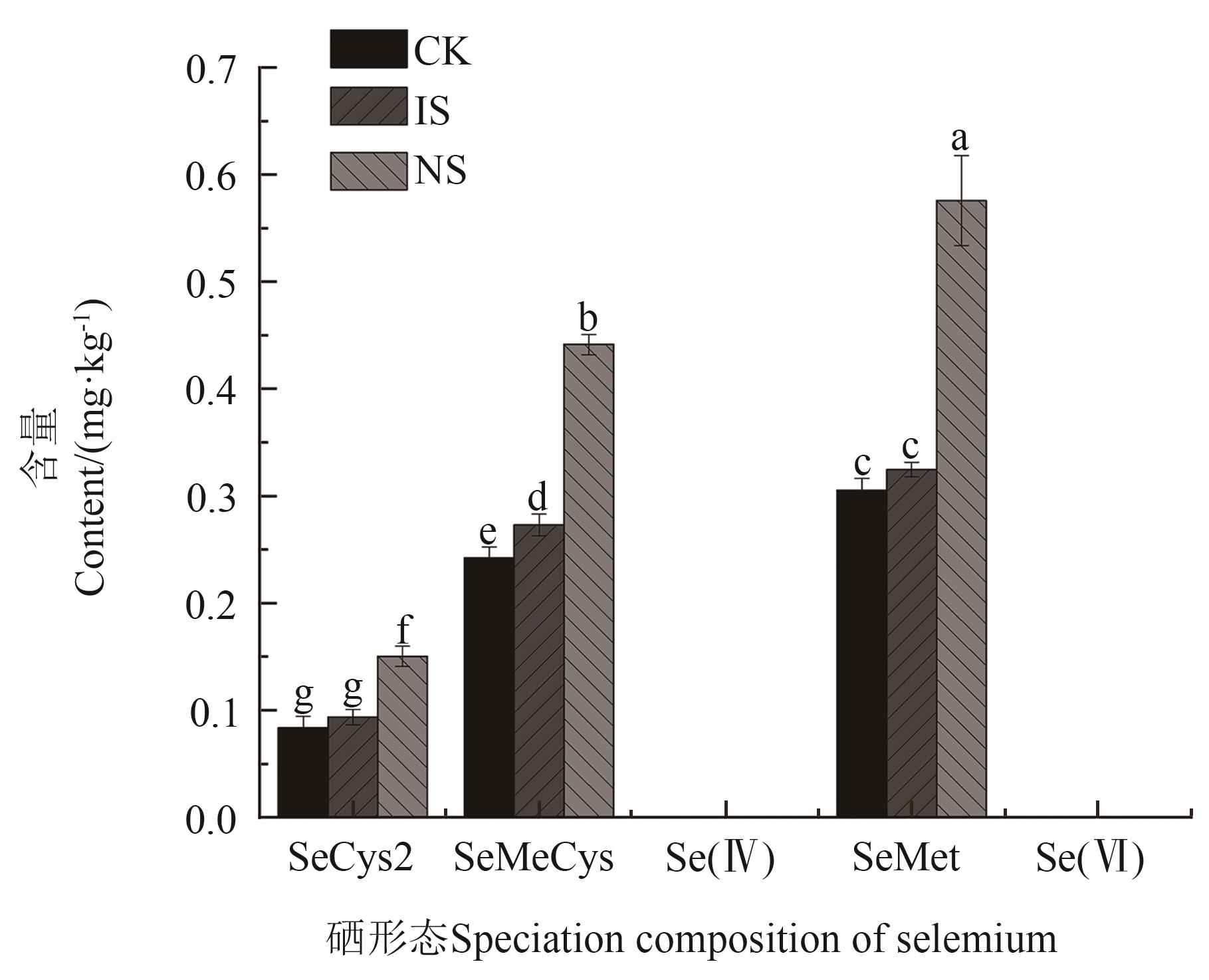
图3 水稻根系中的硒形态组成注:不同小写字母表示不同硒肥处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 3 Speciation composition of selenium in rice rootsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different selenium fertilizer treatments at P<0.05 level.
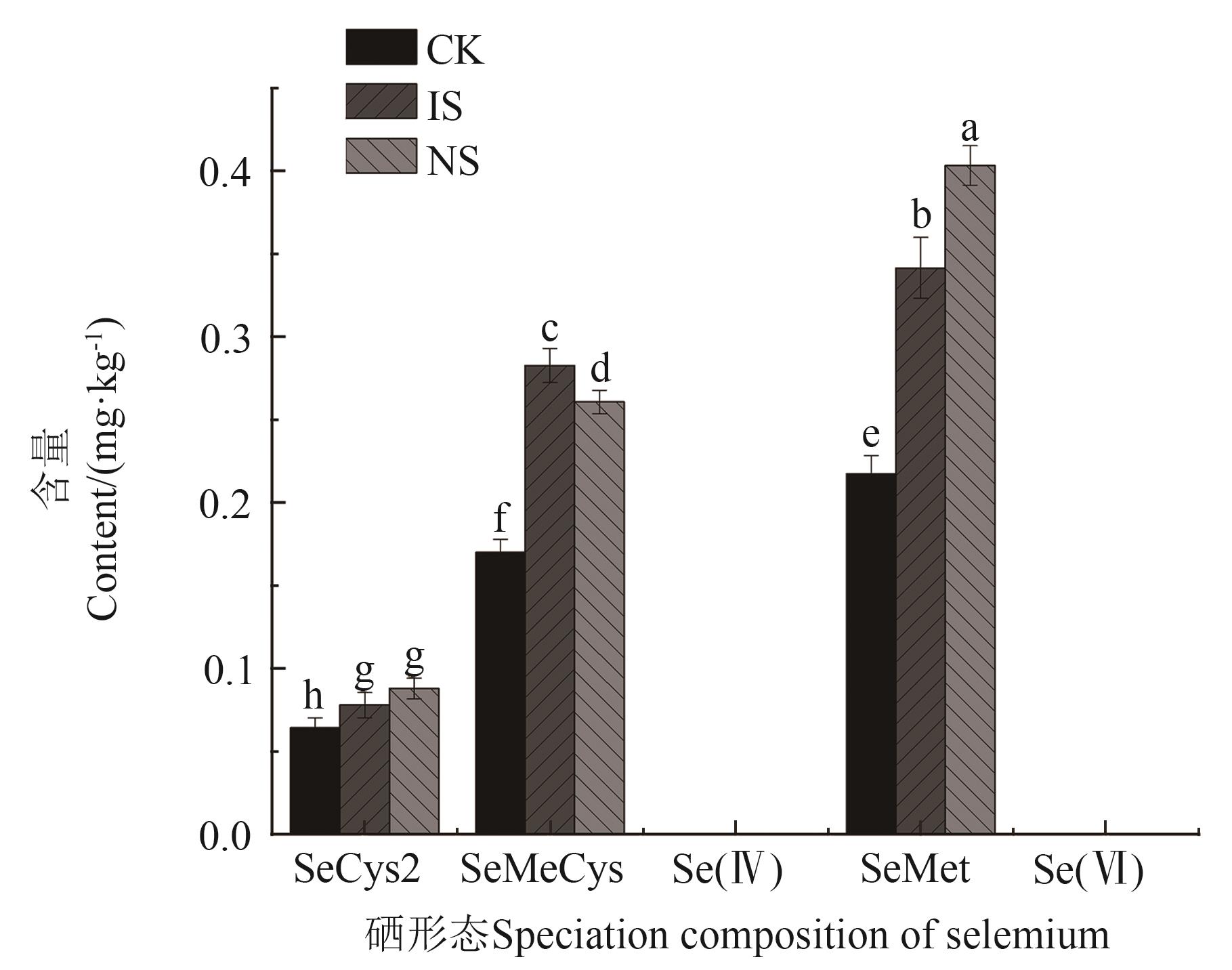
图4 水稻茎叶中的硒形态组成注:不同小写字母表示不同硒肥处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 4 Speciation composition of selenium in rice stems and leavesNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different selenium fertilizer treatments at P<0.05 level.
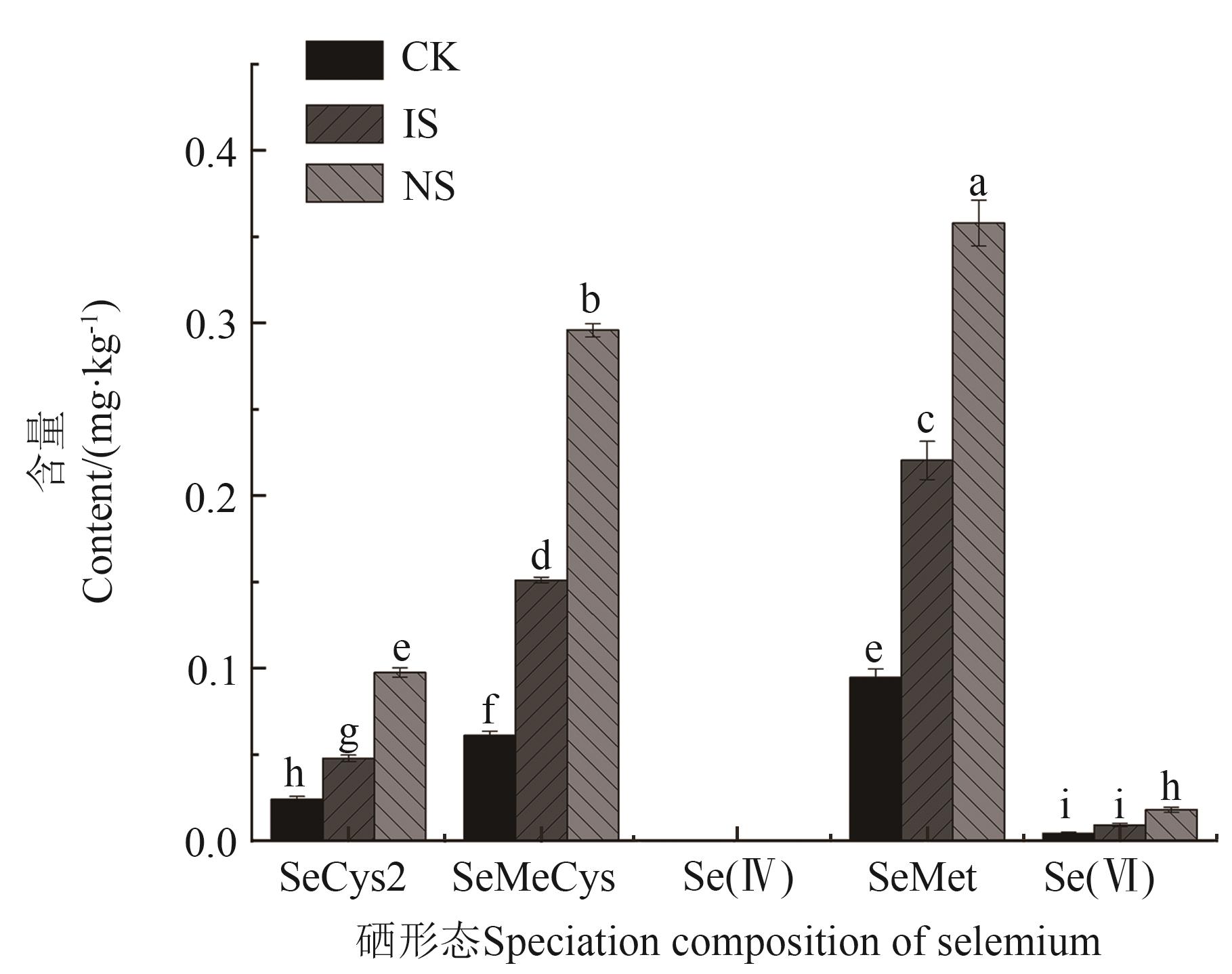
图5 水稻稻壳中的硒形态组成注:不同小写字母表示不同硒肥处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 5 Speciation composition of selenium in rice husksNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different selenium fertilizer treatments at P<0.05 level.
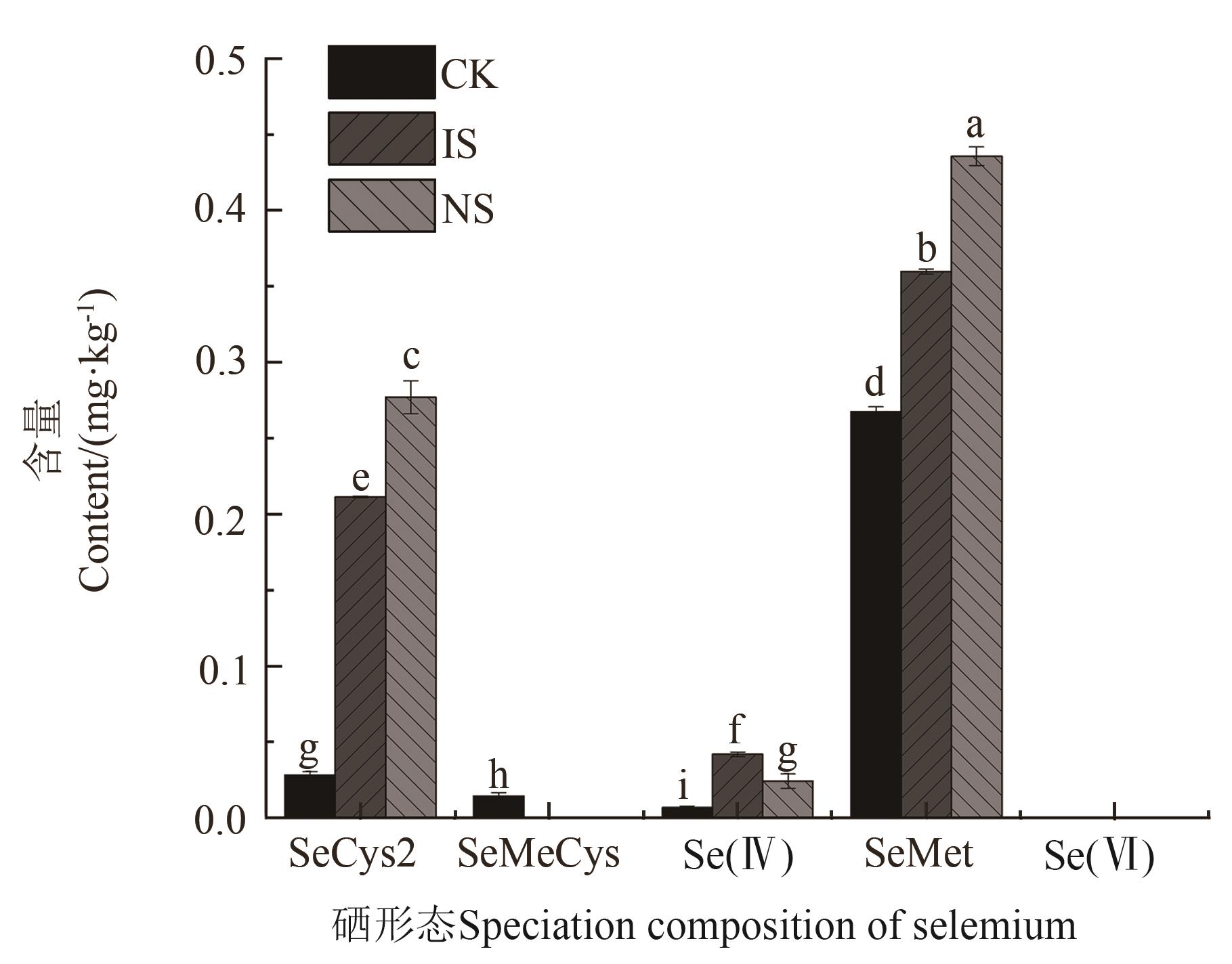
图6 水稻稻米中的硒形态组成注:不同小写字母表示不同硒肥处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 6 Speciation composition of selenium in riceNote:?Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different selenium fertilizer treatments at P<0.05 level.
处理 Treatment | 硒 Se/(mg·kg-1) | 硒代胱氨酸SeCys2/ (mg·kg-1) | 甲基硒代半胱氨酸 SeMeCys/ (mg·kg-1) | 亚硒酸盐Se(IV)/ (mg·kg-1) | 硒代蛋氨酸SeMet/ (mg·kg-1) | 亚硒酸盐 Se(VI)/ (mg·kg-1) | 有机硒Organic selenium | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
含量 Content/ (mg·kg-1) | 占比 Proportion/% | |||||||
| CK | 0.317±0.026 c | 0.028±0.003 c | 0.014±0.002 | 0.007±0.001 c | 0.267±0.003 c | 0 | 0.310±0.001 c | 97.87±0.38 a |
| IS | 0.613±0.079 b | 0.211±0.001 b | 0 | 0.042±0.002 a | 0.360±0.002 b | 0 | 0.571±0.002 b | 93.17±0.26 c |
| NS | 0.737±0.014 a | 0.277±0.011 a | 0 | 0.024±0.005 b | 0.436±0.006 a | 0 | 0.713±0.005 a | 96.71±0.65 b |
表2 不同硒肥处理下稻米硒含量及硒形态
Table 2 Selenium content and selenium speciation in rice under different selenium fertilizer treatments
处理 Treatment | 硒 Se/(mg·kg-1) | 硒代胱氨酸SeCys2/ (mg·kg-1) | 甲基硒代半胱氨酸 SeMeCys/ (mg·kg-1) | 亚硒酸盐Se(IV)/ (mg·kg-1) | 硒代蛋氨酸SeMet/ (mg·kg-1) | 亚硒酸盐 Se(VI)/ (mg·kg-1) | 有机硒Organic selenium | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
含量 Content/ (mg·kg-1) | 占比 Proportion/% | |||||||
| CK | 0.317±0.026 c | 0.028±0.003 c | 0.014±0.002 | 0.007±0.001 c | 0.267±0.003 c | 0 | 0.310±0.001 c | 97.87±0.38 a |
| IS | 0.613±0.079 b | 0.211±0.001 b | 0 | 0.042±0.002 a | 0.360±0.002 b | 0 | 0.571±0.002 b | 93.17±0.26 c |
| NS | 0.737±0.014 a | 0.277±0.011 a | 0 | 0.024±0.005 b | 0.436±0.006 a | 0 | 0.713±0.005 a | 96.71±0.65 b |
处理 Treatment | 水分 Moisture | 灰分 Ash | 蛋白质 Protein | 脂肪 Fat | 淀粉 Starch | 直链淀粉 Amylose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 11.300±0.100 a | 1.197±0.012 c | 8.227±0.091 a | 2.657±0.047 b | 74.467±0.306 b | 12.400±0.889 a |
| IS | 11.200±0.100 a | 1.273±0.012 b | 8.283±0.064 a | 2.843±0.076 a | 76.800±0.200 a | 12.867±0.551 a |
| NS | 11.133±0.058 a | 1.397±0.015 a | 8.213±0.095 a | 2.887±0.031 a | 76.833±0.115 a | 12.933±0.723 a |
表3 不同硒肥处理下稻米宏量营养素含量 (%)
Table 3 Macro nutrient content of rice under different selenium fertilizer treatments
处理 Treatment | 水分 Moisture | 灰分 Ash | 蛋白质 Protein | 脂肪 Fat | 淀粉 Starch | 直链淀粉 Amylose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 11.300±0.100 a | 1.197±0.012 c | 8.227±0.091 a | 2.657±0.047 b | 74.467±0.306 b | 12.400±0.889 a |
| IS | 11.200±0.100 a | 1.273±0.012 b | 8.283±0.064 a | 2.843±0.076 a | 76.800±0.200 a | 12.867±0.551 a |
| NS | 11.133±0.058 a | 1.397±0.015 a | 8.213±0.095 a | 2.887±0.031 a | 76.833±0.115 a | 12.933±0.723 a |
处理 Treatment | 钼Mo | 锌Zn | 钙Ca | 砷As | 镉Cd | 铅Pb | 铬Cr | 汞Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.746±0.070 b | 20.867±0.252 a | 163.667±4.726 a | 0.408±0.022 a | 0.065±0.006 a | 0.232±0.033 a | 0.285±0.032 a | 0.0059±0.0007 a |
| IS | 0.717±0.014 b | 19.000±2.000 ab | 130.667±3.512 c | 0.176±0.013 b | 0.069±0.008 a | 0.174±0.041 b | 0.394±0.081 a | 0.0012±0.0001 b |
| NS | 1.683±0.031 a | 17.900±0.300 b | 141.333±3.055 b | 0.156±0.030 b | 0.073±0.006 a | 0.169±0.017 b | 0.318±0.048 a | 0.0027±0.0012 b |
表4 不同硒肥处理下水稻稻米微量元素含量及重金属含量 (mg·kg-1)
Table 4 Trace element content and heavy metal content of rice under different selenium fertilizer treatments
处理 Treatment | 钼Mo | 锌Zn | 钙Ca | 砷As | 镉Cd | 铅Pb | 铬Cr | 汞Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.746±0.070 b | 20.867±0.252 a | 163.667±4.726 a | 0.408±0.022 a | 0.065±0.006 a | 0.232±0.033 a | 0.285±0.032 a | 0.0059±0.0007 a |
| IS | 0.717±0.014 b | 19.000±2.000 ab | 130.667±3.512 c | 0.176±0.013 b | 0.069±0.008 a | 0.174±0.041 b | 0.394±0.081 a | 0.0012±0.0001 b |
| NS | 1.683±0.031 a | 17.900±0.300 b | 141.333±3.055 b | 0.156±0.030 b | 0.073±0.006 a | 0.169±0.017 b | 0.318±0.048 a | 0.0027±0.0012 b |
| 1 | LYONS G, STANGOULIS J, GRAHAM R. High-selenium wheat:biofortification for better health [J]. Nutr. Res. Rev.,2003,16(1):45-60. |
| 2 | 徐琴, 王孟, 谢义梅, 等. 施硒对水稻外观品质及籽粒硒、镉和砷含量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(5): 135-140. |
| XU Q, WANG M, XIE Y M, et al.. Effect of selenium application on appearance quality, grain selenium, cadmium and arsenic content in rice [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2019, 21(5): 135-140. | |
| 3 | TAN J A, ZHU W Y, WANG W Y, et al.. Selenium in soil and endemic diseases in China [J]. Sci. Total Environ.,2002,284(1):227-235. |
| 4 | MUTHAYYA S, RAH J H, SUGIMOTO J D, et al.. The global hidden hunger indices and maps:an advocacy tool for action [J/OL].PLoS One,2013,8(6):e67860 [2023-08-16]. . |
| 5 | LIU H, YU F F, SHAO W Z,et al.. Associations between selenium content in hair and kashin-beck disease/Keshan disease in children in northwestern China:a prospective cohort study [J]. Biol. Trace Elem. Res., 2018,184(1):16-23. |
| 6 | DINH Q T, CUI Z W, HUANG J, et al.. Selenium distribution in the Chinese environment and its relationship with human health:a review [J]. Environ. Int., 2018,112:294-309. |
| 7 | RAYMAN M P.The use of high-selenium yeast to raise selenium status:how does it measure up? [J]. Brit. J. Nutr., 2004,92(4):557-573. |
| 8 | 刘梦兰.两种不同硒肥对水稻籽粒硒积累及品质相关性状的影响[D].扬州:扬州大学,2021. |
| LIU M L. Effects of two different selenium fertilizers on grain selenium accumulation and quality-related traits of rice [D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2021. | |
| 9 | 王玮, 杨万仁, 王锐. 纳米硒对水稻产量与品质的影响[J]. 安徽农学通报, 2022, 28(4): 77-78. |
| WANG W, YANG W R, WANG R. Effect of selenium-enriched fertilizer on rice quality and yield [J]. Anhui Agric. Sci. Bull., 2022, 28 (4): 77-78. | |
| 10 | 开建荣,王彩艳,李冬.外源硒对稻谷、糙米和精米吸收累积矿质元素及重金属的影响[J].宁夏农林科技,2020,61(3):52-56, 31. |
| KAI J R, WANG C Y, LI D. Effects of exogenous selenium on the accumulation of mineral elements and heavy metals in paddy,brown rice and polished rice [J]. Ningxia J. Agric. For. Sci. Technol., 2020,61(3):52-56, 31. | |
| 11 | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会,国家食品药品监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准 食品中硒的测定: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2017. |
| 12 | 曹赵云,毛雪飞,王世成,等. 粮谷中硒代半胱氨酸和硒代蛋氨酸的测定 液相色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱法: [S].北京:中国农业出版社,2020. |
| 13 | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会,国家食品药品监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准 食品中蛋白质的测定: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2016. |
| 14 | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会,国家食品药品监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准 食品中脂肪的测定: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2016. |
| 15 | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 食品安全国家标准 食品中水分的测定: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2016. |
| 16 | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 食品安全国家标准 食品中水分的测定: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2016. |
| 17 | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会,国家食品药品监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准 食品中淀粉的测定: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2016. |
| 18 | 熊宁,刘坚, 袁建,等. 大米 直链淀粉含量的测定: [S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. |
| 19 | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会,国家食品药品监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准 食品中多元素的测定: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2016. |
| 20 | 顾涛, 赵信文, 雷晓庆, 等. 珠江三角洲崖门镇地区水稻田土壤-作物系统中硒元素分布特征及迁移规律研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(5): 545-555. |
| GU T, ZHAO X W, LEI X Q, et al.. Distribution and migration characteristics of selenium in the soil-plant system of paddy fields in the pearl river delta, yamen town [J]. J. Rock Miner. Test., 2019, 38(5): 545-555. | |
| 21 | 陈锦平,刘永贤,潘丽萍,等.浔郁平原不同作物的硒富集特征及其影响因素[J].土壤,2018,50(6):1155-1159. |
| CHEN J P, LIU Y X, PAN L P, et al.. Selenium accumulation characteristics and influential factors of different crops in Xunyu Plain [J]. Soils, 2018,50(6):1155-1159. | |
| 22 | 陈松灿,孙国新,陈正,等.植物硒生理及与重金属交互的研究进展[J].植物生理学报,2014,50(5):612-624. |
| CHEN S C, SUN G X, CHEN Z, et al.. Progresses on selenium metabolism and interaction with heavy metals in higher plants [J].Plant Physiol. J., 2014,50(5):612-624. | |
| 23 | THIRY C, RUTTENS A, TEMMERMAN L D, et al.. Current knowledge in species-related bioavailability of selenium in food [J]. Food Chem., 2012, 130(4): 767-784. |
| 24 | TIWARY A K, STEGELMEIER B L, PANTER K E,et al..Comparative toxicosis of sodium selenite and selenomethionine in lambs [J]. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest.,2006,18(1):61-70. |
| 25 | 王智.硒-甲基硒代半胱氨酸诱导肝癌SMMC-7721细胞株的凋亡及机制探讨[J].江苏医药,2012,38(11):1263-1266, 1365. |
| WANG Z.A study on Se-methylseienocysteine inducing hepatocellular carcinoma cell apoptosis and its mechanism [J].Jiangsu Med. J., 2012,38(11):1263-1266, 1365. | |
| 26 | GASHU D, NALIVATA P C, AMEDE T, et al.. The nutritional quality of cereals varies geospatially in Ethiopia and Malawi [J].Nature,2021,594:71-76. |
| 27 | 王茂辉,李珂清,萧洪东,等.喷施不同硒肥对水稻生长及硒富集的影响[J].南方农业,2022,16(13):82-85. |
| 28 | 方勇.外源硒在水稻籽中的生物强化和化学形态研究[D].南京:南京农业大学,2010. |
| FANG Y. Studies on selenium biofortification and chemical speciation in rice seeds [D]. Nanjing:Nanjing Agricultural University, 2010. | |
| 29 | SUN G X, LIU X, WILLIAMS P N,et al.. Distribution and translocation of selenium from soil to grain and its speciation in paddy rice (Oryza sativa L.) [J].Environ. Sci. Technol., 2010,44(17):6706-6711. |
| 30 | 姜超强,沈嘉,祖朝龙.水稻对天然富硒土壤硒的吸收及转运[J].应用生态学报,2015,26(3):809-816. |
| JIANG C Q, SHEN J, ZU C L. Selenium uptake and transport of rice under different Se-enriched natural soils [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2015,26(3):809-816. | |
| 31 | 钟松臻.外源硒对土壤-水稻系统硒形态的影响[D].南昌:南昌大学,2017. |
| ZHONG S Z. Effects of exogenous selenite on the Se speciation in soil-rice system [D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2017. | |
| 32 | 郑雄伟,魏鸿,谭园.洪湖市中北部地区土壤硒元素分布特征[J].华东地质,2017,38(1):66-73. |
| ZHENG X W, WEI H, TAN Y. Distribution characteristics of selenium in the soils of the north central region of Honghu,Hubei province [J]. East China Geol., 2017,38(1):66-73. | |
| 33 | PICKERING I J, PRINCE R C, SALT D E, et al.. Quantitative,chemically specific imaging of selenium transformation in plants [J].Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA,2000,97(20):10717-10722. |
| 34 | 石吕, 薛亚光, 石晓旭, 等. 不同硒肥喷施时期对2种富硒土壤水稻产量、米质及硒吸收的影响[J]. 大麦与谷类科学, 2022, 39(3): 44-53. |
| SHI L, XUE Y G, SHI X X, et al.. Effects of the timing of spray-applying selenium fertilizer on rice yield,grain quality, and selenium absorption in two selenium-rich soils [J]. Barley Cereals Sci., 2022, 39(3): 44-53. | |
| 35 | CAREY A M, SCHECKEL K G, LOMBI E,et al..Grain accumulation of selenium species in rice (Oryza sativa L.) [J].Environ. Sci. Technol.,2012,46(10):5557-5564. |
| 36 | 尹雪斌,杨荣,杨枫,等. 中华人民共和国供销合作行业标准 富硒农产品: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2017. |
| 37 | 胡振瀛.硒强化对糙米营养组分的影响及其含硒蛋白磷酸化改性应用[D].南昌:南昌大学,2019. |
| HU Z Y. Effects of selenium biofortification on nutrient components and the utilization of se-containing protein modified by phosphorylation [D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2019. | |
| 38 | LIDON F C, OLIVEIRA K, RIBEIRO M M, et al.. Selenium biofortification of rice grains and implications on macronutrients quality [J]. J. Cereal Sci., 2018, 81: 22-29. |
| 39 | GAO M, ZHOU J, LIU H L, et al.. Foliar spraying with silicon and selenium reduces cadmium uptake and mitigates cadmium toxicity in rice [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2018,631:1100-1108. |
| 40 | KAUR S, SINGH D, SINGH K. Effect of selenium application on arsenic uptake in rice (Oryza sativa L.) [J/OL].Environ. Monit. Assess., 2017,189(9):430 [2023-08-16].. |
| 41 | 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会,国家市场监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准 食品中污染物限量: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2022. |
| 42 | LIAO G J, XU Y, CHEN C, et al.. Root application of selenite can simultaneously reduce arsenic and cadmium accumulation and maintain grain yields,but show negative effects on the grain quality of paddy rice [J]. J. Environ. Manage., 2016,183:733-741. |
| 43 | PEREZ-PUYANA V, OSTOS F J, LÓPEZ-CORNEJO P,et al.. Assessment of the denaturation of collagen protein concentrates using different techniques [J].Biol. Chem.,2019,400(12):1583-1591. |
| 44 | 马俊桃,周文,李静浩,等.外源硒调控植物重金属胁迫机制的研究进展[J].中国农业科技导报,2022,24(6):27-35. |
| MA J T, ZHOU W, LI J H, et al.. Research progress on the regulation mechanism of exogenous selenium on heavy metal stress in plants [J]. J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2022,24(6):27-35. | |
| 45 | YANG B B, YANG C, SHAO Z Y, et al.. Selenium (Se) does not reduce cadmium (Cd) uptake and translocation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) in naturally occurred Se-rich paddy fields with a high geological background of Cd [J]. Bull. Environ. Contam.Toxicol., 2019,103(1):127-132. |
| [1] | 熊橙梁, 张庆富, 姚未远, 夏滔, 许庆平, 周喜新, 张毅, 陈丽鹃, 杨柳. 添加不同类型水稻秸秆对植烟连作土壤微生物群落的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 233-240. |
| [2] | 魏荣华, 尹明, 王文生, 崔彦茹. 基于BSA-seq发掘水稻抽穗期相关QTLs及候选基因[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(9): 12-24. |
| [3] | 高阳, 李粤, 位士全, 黄椿, 吴紫晗, 魏晨辉, 黄麒润. 具有腐熟剂喷施装置的香蕉秸秆粉碎还田机的设计与试验[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(9): 93-104. |
| [4] | 孙亮, 徐益, 蔡沁, 郭靖豪, 赵灿, 郭保卫, 邢志鹏, 霍中洋, 张洪程, 胡雅杰. 中微量元素对水稻产量和品质的影响研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 9-19. |
| [5] | 刘大为, 秦锋, 廖骞, 王修善, 谢方平, 李铁辉. 南方籼稻热风干燥特性及其工艺参数优化[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 93-102. |
| [6] | 岳伟, 王晖, 陈曦, 占新春, 阮新民. 安徽省稻米品质综合评价方法研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 141-147. |
| [7] | 陈明迪, 胡桂花, 张海文, 王旺田. 水稻RR基因家族生物信息学及表达模式分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 20-29. |
| [8] | 曾建光, 刘桃李, 孙林娟, 袁定阳, 黄钰博, 金晨钟, 谭炎宁. 水稻矮秆迟抽穗突变体d534的性状及其对赤霉素的敏感性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 7-14. |
| [9] | 黄椿, 李粤, 位士全, 高阳, 吴紫晗, 黄麒润, 魏晨辉. 异向双轴香蕉秸秆粉碎还田机设计与试验[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(11): 97-106. |
| [10] | 张艺, 何军, 张宝龙, 张才军, 甘学华. 蓄雨型间歇灌溉模式下缓释肥对水稻生长、产量及水分利用的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(10): 195-205. |
| [11] | 钱政, 杨孙哲, 张国卿, 郭紫微, 张林朋, 万家兴, 杨红云. 基于卷积神经网络的水稻氮素营养诊断[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 113-121. |
| [12] | 李慧君, 张伟健, 吴伟健, 李高洋, 陈艺杰, 黄枫城, 黄永相, 蔺中, 甄珍. 种植海水稻对滨海盐土化学性质和微生物群落影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 147-156. |
| [13] | 邵社刚, 李婷, 柳勇, 林兰稳, 张东, 倪栋, 李俊杰, 朱立安. 外源菌剂对稻秆腐解及微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 166-177. |
| [14] | 单莉莉. 孕穗期低温对水稻叶片生理、产量的影响及外源褪黑素缓解效应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 23-33. |
| [15] | 张冬梦, 姚栋萍, 吴俊, 罗秋红, 庄文, 刘雄伦, 邓启云, 柏斌. 灌浆期田间自然低温对稻米蒸煮食味品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 144-153. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号