




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (8): 18-27.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0328
刘之恩( ), 何勇, 王志成, 詹逍康, 王廷宝, 刘耀威, 田志宏(
), 何勇, 王志成, 詹逍康, 王廷宝, 刘耀威, 田志宏( )
)
收稿日期:2024-04-24
接受日期:2024-07-13
出版日期:2025-08-15
发布日期:2025-08-26
通讯作者:
田志宏
作者简介:刘之恩 E-mail:1874582018@qq.com;
基金资助:
Zhien LIU( ), Yong HE, Zhicheng WANG, Xiaokang ZHAN, Tingbao WANG, Yaowei LIU, Zhihong TIAN(
), Yong HE, Zhicheng WANG, Xiaokang ZHAN, Tingbao WANG, Yaowei LIU, Zhihong TIAN( )
)
Received:2024-04-24
Accepted:2024-07-13
Online:2025-08-15
Published:2025-08-26
Contact:
Zhihong TIAN
摘要:
生长调节因子(growth regulating factor,GRF)作为一种植物特有的转录因子,在植物生长发育过程中发挥重要作用。为鉴定水稻GRF基因家族成员,通过生物信息学方法对其蛋白的理化性质、二级结构、三级结构、亚细胞定位、基因结构、顺式作用元件、染色体定位、进化关系和共线性进行分析。结果表明,共鉴定出12个水稻GRF基因,其蛋白长度为211~456 aa,分子量为22.3~49.3 kD,等电点为4.78~9.85,亚细胞定位主要定位于细胞核;水稻GRF基因含有2~5个外显子,启动子顺式作用元件主要与激素调控、胁迫响应、光响应相关;12个GRF基因不均匀地分布在2、3、4、6、7、11、12号染色体上;水稻GRF基因与玉米亲缘关系较近,与番茄、拟南芥同源性较低;水稻GRF基因不存在串联重复事件,大片段重复是其主要扩张方式。以上研究结果为深入研究水稻GRF基因功能提供了理论依据。
中图分类号:
刘之恩, 何勇, 王志成, 詹逍康, 王廷宝, 刘耀威, 田志宏. 水稻生长调节因子GRF基因家族的鉴定及生物信息学分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(8): 18-27.
Zhien LIU, Yong HE, Zhicheng WANG, Xiaokang ZHAN, Tingbao WANG, Yaowei LIU, Zhihong TIAN. Identification and Bioinformatics Analysis of Growth Regulating Factor GRF Gene Family in Rice[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(8): 18-27.
基因ID Gene ID | 氨基酸长度 Amino acids length/aa | 分子量 Molecular weight/Da | 等电点 pI | 不稳定指数 Instability index | 脂肪酸指数 Aliphatic index | 平均亲水系数 GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Os02g0776900 | 397 | 43 565.42 | 7.10 | 58.65 | 45.21 | -0.817 |
| Os06g0204800 | 301 | 32 227.89 | 7.76 | 49.63 | 58.01 | -0.569 |
| Os04g0600900 | 384 | 41 286.02 | 6.41 | 51.04 | 61.64 | -0.428 |
| Os02g0701300 | 394 | 41 835.59 | 8.57 | 60.17 | 64.57 | -0.448 |
| Os06g0116200 | 348 | 37 814.97 | 8.56 | 57.48 | 55.34 | -0.665 |
| Os03g0729500 | 456 | 49 361.83 | 6.97 | 57.27 | 66.82 | -0.534 |
| Os12g0484900 | 413 | 44 171.36 | 9.25 | 50.44 | 70.17 | -0.499 |
| Os11g0551900 | 409 | 43 896.85 | 8.94 | 59.17 | 60.32 | -0.630 |
| Os03g0674700 | 426 | 47 852.03 | 9.30 | 58.65 | 57.11 | -0.816 |
| Os02g0678800 | 211 | 22 310.32 | 9.35 | 47.08 | 68.96 | -0.362 |
| Os07g0467500 | 269 | 28 000.97 | 4.78 | 63.81 | 59.55 | -0.645 |
| Os04g0574500 | 236 | 24 970.55 | 9.85 | 49.81 | 75.30 | -0.200 |
表1 水稻GRF基因编码蛋白的理化性质
Table 1 Physicochemical properties of proteins encoded by the GRF genes in rice
基因ID Gene ID | 氨基酸长度 Amino acids length/aa | 分子量 Molecular weight/Da | 等电点 pI | 不稳定指数 Instability index | 脂肪酸指数 Aliphatic index | 平均亲水系数 GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Os02g0776900 | 397 | 43 565.42 | 7.10 | 58.65 | 45.21 | -0.817 |
| Os06g0204800 | 301 | 32 227.89 | 7.76 | 49.63 | 58.01 | -0.569 |
| Os04g0600900 | 384 | 41 286.02 | 6.41 | 51.04 | 61.64 | -0.428 |
| Os02g0701300 | 394 | 41 835.59 | 8.57 | 60.17 | 64.57 | -0.448 |
| Os06g0116200 | 348 | 37 814.97 | 8.56 | 57.48 | 55.34 | -0.665 |
| Os03g0729500 | 456 | 49 361.83 | 6.97 | 57.27 | 66.82 | -0.534 |
| Os12g0484900 | 413 | 44 171.36 | 9.25 | 50.44 | 70.17 | -0.499 |
| Os11g0551900 | 409 | 43 896.85 | 8.94 | 59.17 | 60.32 | -0.630 |
| Os03g0674700 | 426 | 47 852.03 | 9.30 | 58.65 | 57.11 | -0.816 |
| Os02g0678800 | 211 | 22 310.32 | 9.35 | 47.08 | 68.96 | -0.362 |
| Os07g0467500 | 269 | 28 000.97 | 4.78 | 63.81 | 59.55 | -0.645 |
| Os04g0574500 | 236 | 24 970.55 | 9.85 | 49.81 | 75.30 | -0.200 |

图2 水稻GRF蛋白的二级结构预测注:蓝色—α螺旋;红色—延伸链;绿色—β转角;紫色—无规则卷曲。
Fig. 2 Secondary structure prediction of GRF proteins in riceNote: Blue—Alpha helix; Red—Extended strand; Green—Beta turn; Purple—Random coil.
基因ID Gene ID | α螺旋 Alpha helix/% | 延伸链 Extended strand/% | β转角 Beta turn/% | 无规则卷曲 Random coil/% | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Os02g0776900 | 23.93 | 12.34 | 6.30 | 57.43 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Os06g0204800 | 28.90 | 4.98 | 2.99 | 63.12 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Os04g0600900 | 20.31 | 5.73 | 3.39 | 70.57 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Os02g0701300 | 22.59 | 7.87 | 3.30 | 66.24 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Os06g0116200 | 14.66 | 9.48 | 4.60 | 71.26 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Os03g0729500 | 19.96 | 10.53 | 1.97 | 67.54 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Os12g0484900 | 18.73 | 11.92 | 2.19 | 67.15 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Os11g0551900 | 19.07 | 13.45 | 6.60 | 60.88 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Os03g0674700 | 27.70 | 9.15 | 4.69 | 58.45 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Os02g0678800 | 30.33 | 8.53 | 3.79 | 57.35 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Os07g0467500 | 33.46 | 11.90 | 2.97 | 51.67 | 细胞核/叶绿体 Nucleus/chloroplast |
| Os04g0574500 | 19.49 | 14.83 | 7.20 | 58.47 | 叶绿体/线粒体 Chloroplast/mitochondrion |
表2 水稻GRF蛋白二级结构和亚细胞定位
Table 2 Secondary structure analysis and subcellular localization of GRF proteins in rice
基因ID Gene ID | α螺旋 Alpha helix/% | 延伸链 Extended strand/% | β转角 Beta turn/% | 无规则卷曲 Random coil/% | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Os02g0776900 | 23.93 | 12.34 | 6.30 | 57.43 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Os06g0204800 | 28.90 | 4.98 | 2.99 | 63.12 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Os04g0600900 | 20.31 | 5.73 | 3.39 | 70.57 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Os02g0701300 | 22.59 | 7.87 | 3.30 | 66.24 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Os06g0116200 | 14.66 | 9.48 | 4.60 | 71.26 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Os03g0729500 | 19.96 | 10.53 | 1.97 | 67.54 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Os12g0484900 | 18.73 | 11.92 | 2.19 | 67.15 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Os11g0551900 | 19.07 | 13.45 | 6.60 | 60.88 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Os03g0674700 | 27.70 | 9.15 | 4.69 | 58.45 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Os02g0678800 | 30.33 | 8.53 | 3.79 | 57.35 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Os07g0467500 | 33.46 | 11.90 | 2.97 | 51.67 | 细胞核/叶绿体 Nucleus/chloroplast |
| Os04g0574500 | 19.49 | 14.83 | 7.20 | 58.47 | 叶绿体/线粒体 Chloroplast/mitochondrion |

图3 水稻GRF蛋白的三级结构预测注:图中蛋白质三级结构按照氨基端-羧基端进行着色。
Fig. 3 Tertiary structure prediction of GRF proteins in riceNote: The protein tertiary structure in the figure is colored in the order of amino terminus to carboxyl terminus.

图6 不同物种GRF蛋白的系统进化树注:Os—粳稻;GRMZM—玉米;AT—拟南芥;Solyc—番茄;BG—籼稻。
Fig. 6 Phylogenetic tree of GRF proteins from different speciesNote: Os—Oryza sativa subsp. japonica; GRMZM—Zea mays; At—Arabidopsis thaliana; Solyc—Solanum lycopersicum; BG—Oryza sativa subsp. indica.
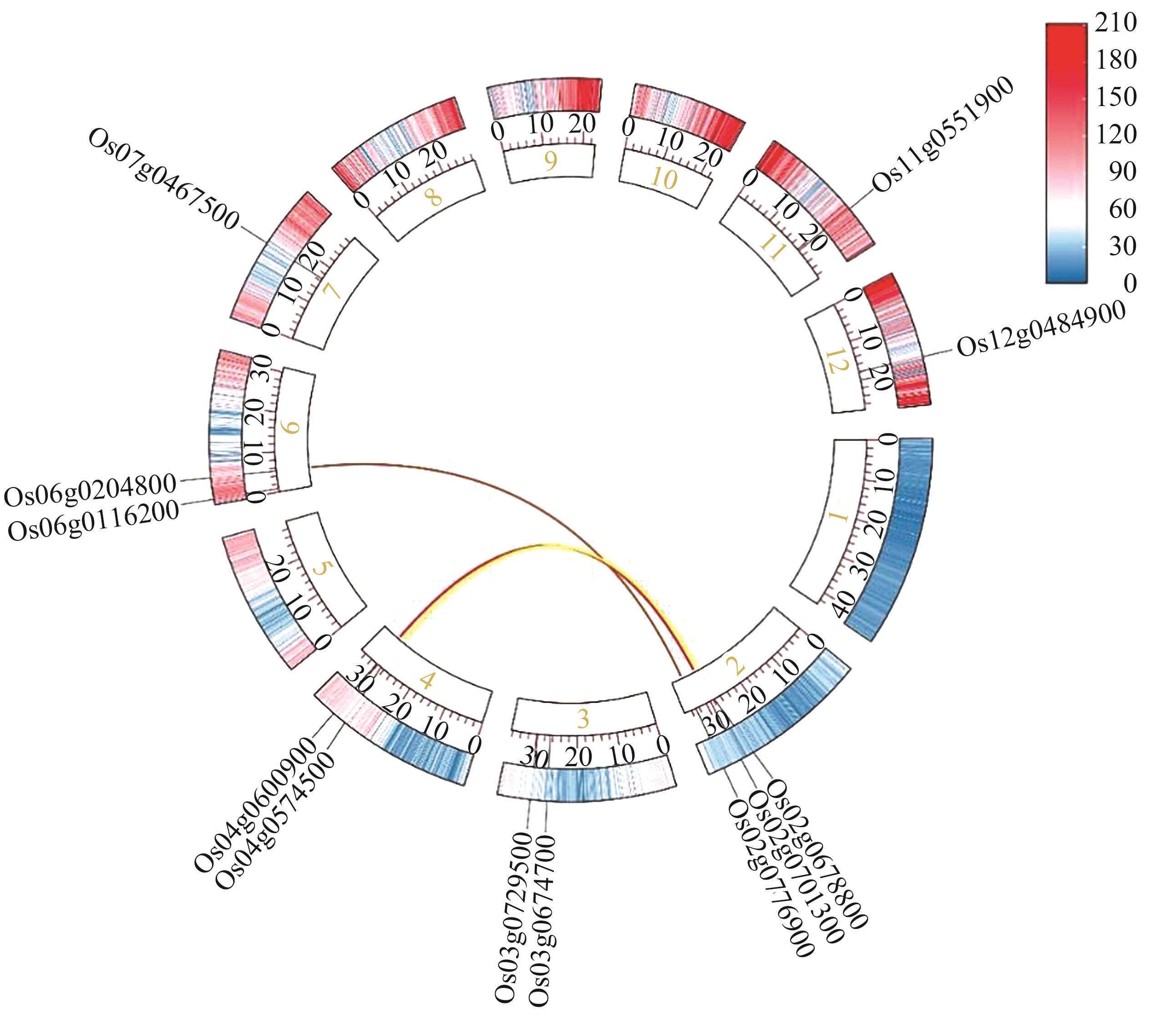
图8 水稻GRF基因的共线性分析注:右侧蓝色到红色刻度表示0.1 Mb范围内基因的数量。
Fig. 8 Collinearity analysis of GRF genes in riceNote: The blue to red scale on the right indicates the number of genes within 0.1 Mb.
| [1] | 杨雪芮, 何沙娥, 陈少雄. GRF转录因子在植物中的研究进展[J]. 桉树科技, 2022, 39(3): 57-66. |
| YANG X R, HE S E, CHEN S X. Research progress of GRF transcription factors in plants [J]. Eucalypt Sci. Technol., 2022, 39(3): 57-66. | |
| [2] | WANG H Y, WANG H L, SHAO H B, et al.. Recent advances in utilizing transcription factors to improve plant abiotic stress tolerance by transgenic technology [J/OL]. Front.Plant Sci., 2016, 7:67 [2024-03-20]. . |
| [3] | 陈娜,迟晓元,程果,等.花生中低温胁迫相关转录因子基因的筛选[J].核农学报,2016,30(1):19-27. |
| CHEN N, CHI X Y, CHENG G, et al.. Profiling of genes encoding cold stress-related transcription factors in peanut [J]. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci., 2016, 30(1):19-27. | |
| [4] | VAN DER KNAAP E, KIM J H, KENDE H. A novel gibberellin-induced gene from rice and its potential regulatory role in stem growth [J]. Plant Physiol., 2000, 122(3): 695-704. |
| [5] | KIM J H, KENDE H. A transcriptional coactivator, AtGIF1, is involved in regulating leaf growth and morphology in Arabidopsis [J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2004, 101(36):13374-13379. |
| [6] | KIM J H, CHOI D, KENDE H. The AtGRF family of putative transcription factors is involved in leaf and Cotyledon growth in Arabidopsis [J]. Plant J., 2003, 36(1): 94-104. |
| [7] | FİLİZ E, KOÇ İ, TOMBULOĞLU H. Genome-wide identification and analysis of growth regulating factor genes in Brachypodium distachyon: in silico approaches [J]. Turk. J. Biol., 2014, 38:296-306. |
| [8] | JIN J P, ZHANG H, KONG L, et al.. PlantTFDB 3.0: a portal for the functional and evolutionary study of plant transcription factors [J]. Nucleic Acids Res., 2014, 42:1182-1187. |
| [9] | 马超,原佳乐,张苏,等. GRF转录因子对植物生长发育及胁迫响应调控的分子机制[J].核农学报,2017,31(11):2145-2153. |
| MA C, YUAN J L, ZHANG S, et al.. The molecular mechanisms of growth-regulating factors (GRFs) in plant growth,development and stress response [J]. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci., 2017, 31(11): 2145-2153. | |
| [10] | OMIDBAKHSHFARD M A, PROOST S, FUJIKURA U, et al.. Growth-regulating factors (GRFs): a small transcription factor family with important functions in plant biology [J]. Mol. Plant, 2015, 8(7):998-1010. |
| [11] | KIM J S, MIZOI J, KIDOKORO S, et al.. Arabidopsis growth-regulating factor7 functions as a transcriptional repressor of abscisic acid- and osmotic stress-responsive genes, including DREB2A [J]. Plant Cell, 2012, 24(8): 3393-3405. |
| [12] | LIU J, HUA W, YANG H L, et al.. The BnGRF2 gene (GRF2-like gene from Brassica napus) enhances seed oil production through regulating cell number and plant photosynthesis [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2012, 63(10):3727-3740. |
| [13] | WANG F D, QIU N W, DING Q, et al.. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the growth-regulating factor family in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis) [J]. BMC Genomics, 2014, 15(1): 807-816. |
| [14] | WU L, ZHANG D F, XUE M, et al.. Overexpression of the maize GRF10, an endogenous truncated growth-regulating factor protein, leads to reduction in leaf size and plant height [J]. J. Integr. Plant Biol., 2014, 56(11):1053-1063. |
| [15] | MISTRY J, CHUGURANSKY S, WILLIAMS L, et al.. Pfam: The protein families database in 2021 [J]. Nucleic Acids Res., 2021, 49(D1):412-419. |
| [16] | LU S N, WANG J Y, CHITSAZ F, et al.. CDD/SPARCLE: the conserved domain database in 2020 [J]. Nucleic Acids Res., 2020, 48(D1):265-268. |
| [17] | DUVAUD S, GABELLA C, LISACEK F, et al.. Expasy, the Swiss Bioinformatics Resource Portal,as designed by its users [J]. Nucleic Acids Res., 2021, 49(W1):216-227. |
| [18] | KELLEY L A, MEZULIS S, YATES C M, et al.. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling,prediction and analysis [J]. Nat. Protoc., 2015, 10(6):845-858. |
| [19] | BAILEY T L, JOHNSON J, GRANT C E, et al.. The MEME suite [J]. Nucl. Acids Res., 2015, 43(W1):39-49. |
| [20] | CHEN C J, WU Y, LI J W, et al.. TBtools-II:a “one for all,all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining [J]. Mol. Plant, 2023, 16(11):1733-1742. |
| [21] | CHAO J T, KONG Y Z, WANG Q, et al.. MapGene2Chrom, a tool to draw gene physical map based on Perl and SVG languages [J]. Hereditas, 2015, 37(1):91-97. |
| [22] | TAMURA K, STECHER G, KUMAR S. MEGA11: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11 [J]. Mol. Biol. Evol., 2021, 38(7): 3022-3027. |
| [23] | THIJS G, MARCHAL K, LESCOT M, et al.. A Gibbs sampling method to detect overrepresented motifs in the upstream regions of coexpressed genes [J]. J. Comput. Biol., 2002, 9(2):447-464. |
| [24] | 阮先乐,王俊生,刘红占,等.油菜GRF基因家族的鉴定和基本特征分析[J].分子植物育种,2018,16(8):2420-2428. |
| RUAN X L, WANG J S, LIU H Z, et al.. Identification and basic characteristic analysis of GRF gene family in Brassica napus L [J]. Mol. Plant Breeding, 2018, 16(8):2420-2428. | |
| [25] | 陈俊, 屈志广, 方远鹏, 等. 高粱GRF基因家族鉴定及SbGRF4原核表达分析[J]. 植物保护学报, 2020, 47(4): 929-938. |
| CHEN J, QU Z G, FANG Y P, et al.. Identification of GRF gene family and prokaryotic expression analysis of SbGRF4 in sorghum [J]. J. Plant Prot., 2020, 47(4):929-938. | |
| [26] | 张立全,张浩林,李丛丛,等.谷子GRF基因家族鉴定与分析[J].西南农业学报,2021,34(11):2340-2347. |
| ZHANG L Q, ZHANG H L, LI C C, et al.. Genome-wide analysis and identification of GRF gene family in foxtail millet (Setaria italica) [J]. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci., 2021, 34(11):2340-2347. | |
| [27] | 阮诗雨,张智俊,陈家璐,等.毛竹GRF基因家族全基因组鉴定与表达分析[J].浙江农林大学学报,2021,38(4):792-801. |
| RUAN S Y, ZHANG Z J, CHEN J L, et al.. Genome identification and expression analysis of GRF gene family in Phyllostachys edulis [J]. J. Zhejiang Agric. For. Univ., 2021, 38(4):792-801. | |
| [28] | 薛正刚, 王树杰, 杨永乾, 等. 大麦GRF家族的基因组鉴定及生物信息学分析[J]. 分子植物育种, 2021, 19(6): 1750-1757. |
| XUE Z G, WANG S J, YANG Y Q, et al.. Genome-wide identification and bioinformatics analysis of growth regulating factor (GRF) family in barley [J]. Mol. Plant Breeding, 2021, 19(6):1750-1757. | |
| [29] | HUSON D H, BRYANT D. Application of phylogenetic networks in evolutionary studies [J]. Mol. Biol. Evol., 2006, 23(2):254-267. |
| [30] | CAO F Y, YOSHIOKA K, DESVEAUX D. The roles of ABA in plant-pathogen interactions [J]. J.Plant Res., 2011, 124(4):489-499. |
| [31] | 黄俊宝, 陈立才,曹中盛,等.茉莉酸甲酯对水稻纹枯病的诱导抗性及防御酶活性影响的研究[J].江西农业学报,2023,35(8):82-87. |
| HUANG J B, CHEN L C, CAO Z S, et al.. Effect of methyl jasmonate on rice induced resistance to sheath blight and activity of related defense enzymes [J]. Acta Agric. Jiangxi, 2023, 35(8): 82-87. |
| [1] | 邵丽华, 李鹏. 水稻对恶苗病菌侵染响应的蛋白质组分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(6): 126-135. |
| [2] | 沈乐丞, 温志刚, 廖涵, 刘贤标, 蒋耀聪, 张远聪, 刘婷, 王玫. 叶面喷施不同硒肥对水稻硒含量及硒形态和稻米组分的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(3): 206-215. |
| [3] | 杨大兵, 胡亮, 杜雪树, 万丙良, 夏明元, 戚华雄, 李进波. CRISPR/Cas9基因编辑技术创制水稻雄性不育系的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(3): 24-34. |
| [4] | 刘金仙, 王丽娟, 刘杰, 傅仙玉, 武广珩. 茶树钙调蛋白结合转录激活因子(CAMTA)家族基因鉴定与表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(3): 71-82. |
| [5] | 熊橙梁, 张庆富, 姚未远, 夏滔, 许庆平, 周喜新, 张毅, 陈丽鹃, 杨柳. 添加不同类型水稻秸秆对植烟连作土壤微生物群落的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 233-240. |
| [6] | 李贤国, 戴麒, 王泽鹏, 陈兆龙, 闫会转, 李宁. 番茄CCCH类锌指蛋白家族的鉴定及其表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 80-95. |
| [7] | 魏荣华, 尹明, 王文生, 崔彦茹. 基于BSA-seq发掘水稻抽穗期相关QTLs及候选基因[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(9): 12-24. |
| [8] | 郭肖蓉, 刘颖, 樊佳珍, 黄涛, 周荣. 猪CREBRF基因生物信息学和表达规律分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(9): 44-53. |
| [9] | 孙亮, 徐益, 蔡沁, 郭靖豪, 赵灿, 郭保卫, 邢志鹏, 霍中洋, 张洪程, 胡雅杰. 中微量元素对水稻产量和品质的影响研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 9-19. |
| [10] | 刘大为, 秦锋, 廖骞, 王修善, 谢方平, 李铁辉. 南方籼稻热风干燥特性及其工艺参数优化[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 93-102. |
| [11] | 鲍新跃, 陈红敏, 王伟伟, 唐益苗, 房兆峰, 马锦绣, 汪德州, 左静红, 姚占军. 小麦TaCOBL-5基因克隆及表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 11-21. |
| [12] | 岳伟, 王晖, 陈曦, 占新春, 阮新民. 安徽省稻米品质综合评价方法研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 141-147. |
| [13] | 陈明迪, 胡桂花, 张海文, 王旺田. 水稻RR基因家族生物信息学及表达模式分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 20-29. |
| [14] | 吴占清, 陈威, 赵展, 许海良, 李豪远, 彭星星, 陈东旭, 张明月. 玉米GRAS基因家族的全基因组鉴定及生物信息学分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 15-25. |
| [15] | 曾建光, 刘桃李, 孙林娟, 袁定阳, 黄钰博, 金晨钟, 谭炎宁. 水稻矮秆迟抽穗突变体d534的性状及其对赤霉素的敏感性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 7-14. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号