




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (8): 223-233.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0942
• 生物制造 资源生态 • 上一篇
刘霏霏1( ), 何万荣1, 孙强2, 席琳乔1(
), 何万荣1, 孙强2, 席琳乔1( ), 廖结安3, 韩路4
), 廖结安3, 韩路4
收稿日期:2022-11-01
接受日期:2023-02-21
出版日期:2024-08-15
发布日期:2024-08-12
通讯作者:
席琳乔
作者简介:刘霏霏 E-mail:13239995801@163.com;
基金资助:
Feifei LIU1( ), Wanrong HE1, Qiang SUN2, Linqiao XI1(
), Wanrong HE1, Qiang SUN2, Linqiao XI1( ), Jiean LIAO3, Lu HAN4
), Jiean LIAO3, Lu HAN4
Received:2022-11-01
Accepted:2023-02-21
Online:2024-08-15
Published:2024-08-12
Contact:
Linqiao XI
摘要:
为探讨南疆干旱荒漠区苹果园种植覆盖作物苜蓿对果园土壤细菌群落结构与功能的影响,以苹果园间作苜蓿绿肥为处理(GMA)、清耕(CT)为对照,分别对0—20、20—40、40—60 cm土壤微生物16S rDNA 基因组采用Illumina MiSeq高通量测序技术和PICRUSt基因预测分析,比较不同处理下果园不同耕层土壤细菌群落结构、多样性及代谢功能变化。结果表明,苹果园间作苜蓿绿肥显著影响园区土壤细菌群落多样性,细菌拷贝数、丰富度指数(Chao1、ACE指数)及多样性指数(Shannon指数)均显著提高。其中,GMA处理下变形菌门(Proteobacteria)、放线菌门(Actinobacteria)和拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)的相对丰度分别为10.15%、64.97%和82.31%,较CT显著提高。通过PICRUSt功能预测,间作苜蓿绿肥明显提高了果园0—20 cm土层细菌功能的相对丰度,其中在7和9月提升最为显著,主要提高了土壤细菌对异物的生物降解能力,增强了土壤碳代谢、氮代谢相关功能菌的丰度。相关性分析表明,土壤细菌优势菌门与土壤全氮、总碳、碱解氮和有效钾含量呈显著正相关,与pH呈显著负相关。综上所述,苹果园种植苜蓿绿肥能显著改善土壤微生物群落组成,提高土壤细菌丰富度、多样性和拷贝数,显著提高土壤微生物功能,对果园土壤熟化、促进物质代谢及培肥地力具有重要作用。
中图分类号:
刘霏霏, 何万荣, 孙强, 席琳乔, 廖结安, 韩路. 苜蓿绿肥对塔里木盆地苹果园土壤细菌多样性和功能的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 223-233.
Feifei LIU, Wanrong HE, Qiang SUN, Linqiao XI, Jiean LIAO, Lu HAN. Effect of Alfalfa Green Manure on Diversity and Function of Soil Bacteria in Apple Orchards in Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(8): 223-233.
| 指标Index | 5月May | 7月July | 9月September | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT | GMA | CT | GMA | CT | GMA | |
总碳含量 TC content/(g·kg-1) | 2.97±0.31 a | 3.10±0.30 a | 2.72±0.40 a | 2.90±0.39 a | 2.78±0.24 a | 2.88±0.25 a |
全氮含量 TN content/(g·kg-1) | 0.85±0.06 ab | 0.91±0.07 ab | 0.80±0.05 b | 0.91±0.04 a | 0.81±0.06 ab | 0.91±0.07 ab |
碱解氮含量 AN content/(mg·kg-1) | 38.92±9.82 a | 30.33±6.92 a | 4.78±4.77 b | 5.40±2.40 b | 1.15±0.19 b | 1.58±0.70 b |
速效磷含量 AP content/(mg·kg-1) | 9.91±3.97 b | 14.57±2.32 ab | 24.20±7.87 a | 20.65±3.58 ab | 23.72±2.49 a | 21.95±0.59 a |
速效钾含量 AK content/(mg·kg-1) | 136.77±38.50 a | 155.03±42.80 a | 123.67±6.28 a | 99.40±46.35 a | 120.27±45.91 a | 83.70±22.40 a |
| pH | 8.18±0.08 a | 7.91±0.05 c | 8.03±0.01 b | 7.94±0.05 c | 7.91±0.05 c | 7.81±0.02 d |
总盐含量 TS content/% | 0.35±0.15 b | 0.86±0.18 a | 0.86±0.18 a | 0.93±0.16 a | 0.67±0.19 ab | 0.86±0.33 a |
表1 不同处理下苹果园土壤的理化性质
Table1 Chemical properties of soil in apple orchard under different treatments
| 指标Index | 5月May | 7月July | 9月September | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT | GMA | CT | GMA | CT | GMA | |
总碳含量 TC content/(g·kg-1) | 2.97±0.31 a | 3.10±0.30 a | 2.72±0.40 a | 2.90±0.39 a | 2.78±0.24 a | 2.88±0.25 a |
全氮含量 TN content/(g·kg-1) | 0.85±0.06 ab | 0.91±0.07 ab | 0.80±0.05 b | 0.91±0.04 a | 0.81±0.06 ab | 0.91±0.07 ab |
碱解氮含量 AN content/(mg·kg-1) | 38.92±9.82 a | 30.33±6.92 a | 4.78±4.77 b | 5.40±2.40 b | 1.15±0.19 b | 1.58±0.70 b |
速效磷含量 AP content/(mg·kg-1) | 9.91±3.97 b | 14.57±2.32 ab | 24.20±7.87 a | 20.65±3.58 ab | 23.72±2.49 a | 21.95±0.59 a |
速效钾含量 AK content/(mg·kg-1) | 136.77±38.50 a | 155.03±42.80 a | 123.67±6.28 a | 99.40±46.35 a | 120.27±45.91 a | 83.70±22.40 a |
| pH | 8.18±0.08 a | 7.91±0.05 c | 8.03±0.01 b | 7.94±0.05 c | 7.91±0.05 c | 7.81±0.02 d |
总盐含量 TS content/% | 0.35±0.15 b | 0.86±0.18 a | 0.86±0.18 a | 0.93±0.16 a | 0.67±0.19 ab | 0.86±0.33 a |
土层 Soil layer/cm | 处理 Treatment | 5月 May | 7月 July | 9月 September |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—20 | CT | 1.36±0.27 b | 3.01±0.24 b | 2.80±0.30 b |
| GMA | 3.09±0.45 a | 9.45±1.29 a | 6.96±0.85 a | |
| 20—40 | CT | 0.98±0.16 bc | 1.35±0.17 c | 1.31±0.12 c |
| GMA | 1.61±0.33 b | 2.91±0.35 b | 1.28±0.17 c | |
| 40—60 | CT | 0.76±0.16 c | 0.92±0.21 c | 1.00±0.14 c |
| GMA | 1.03±0.23 bc | 0.95±0.34 c | 0.91±0.25 c |
表2 不同处理苹果园土壤细菌基因的拷贝数 (×109)
Table 2 Number of gene copies of soil bacteria relative indifferent in different treatments
土层 Soil layer/cm | 处理 Treatment | 5月 May | 7月 July | 9月 September |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—20 | CT | 1.36±0.27 b | 3.01±0.24 b | 2.80±0.30 b |
| GMA | 3.09±0.45 a | 9.45±1.29 a | 6.96±0.85 a | |
| 20—40 | CT | 0.98±0.16 bc | 1.35±0.17 c | 1.31±0.12 c |
| GMA | 1.61±0.33 b | 2.91±0.35 b | 1.28±0.17 c | |
| 40—60 | CT | 0.76±0.16 c | 0.92±0.21 c | 1.00±0.14 c |
| GMA | 1.03±0.23 bc | 0.95±0.34 c | 0.91±0.25 c |
处理 Treatment | 月份 Month | 操作分类单元数 Number of OTUs | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | ACE指数 ACE index | Shannon指数 Shannon index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Coverage指数 Coverage index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT | 5 | 5 585 | 7 076.7±30.0 ab | 7 092.5±85.9 ab | 6.981 7±0.089 6 ab | 0.003 1±0.000 4 a | 0.985 2±0.000 4 ab |
| 7 | 5 228 | 6 587.7±344.0 ab | 6 547.8±304.4 ab | 6.868 6±0.169 6 ab | 0.005 3±0.004 5 a | 0.986 7±0.000 7 ab | |
| 9 | 5 203 | 6 494.3±55.0 b | 6 492.4±58.4 b | 6.917 4±0.092 0 ab | 0.003 9±0.001 9 a | 0.986 9±0.000 2 a | |
| GMA | 5 | 5 702 | 7 228.7±639.2 a | 7 235.8±638.6 a | 7.069 8±0.070 2 a | 0.002 4±0.000 2 a | 0.985 0±0.001 6 b |
| 7 | 5 526 | 7 037.7±493.8 ab | 6 985.4±438.0 ab | 7.071 7±0.062 0 a | 0.002 4±0.000 2 a | 0.985 6±0.001 0 ab | |
| 9 | 5 185 | 6 624.7±36.0 ab | 6 628.0±102.7 ab | 6.848 6±0.071 5 b | 0.003 4±0.000 6 a | 0.986 2±0.000 2 ab |
表3 不同处理下苹果园土壤细菌的多样性
Table 3 Soil bacterial diversity of apple orchard in different treatments
处理 Treatment | 月份 Month | 操作分类单元数 Number of OTUs | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | ACE指数 ACE index | Shannon指数 Shannon index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Coverage指数 Coverage index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT | 5 | 5 585 | 7 076.7±30.0 ab | 7 092.5±85.9 ab | 6.981 7±0.089 6 ab | 0.003 1±0.000 4 a | 0.985 2±0.000 4 ab |
| 7 | 5 228 | 6 587.7±344.0 ab | 6 547.8±304.4 ab | 6.868 6±0.169 6 ab | 0.005 3±0.004 5 a | 0.986 7±0.000 7 ab | |
| 9 | 5 203 | 6 494.3±55.0 b | 6 492.4±58.4 b | 6.917 4±0.092 0 ab | 0.003 9±0.001 9 a | 0.986 9±0.000 2 a | |
| GMA | 5 | 5 702 | 7 228.7±639.2 a | 7 235.8±638.6 a | 7.069 8±0.070 2 a | 0.002 4±0.000 2 a | 0.985 0±0.001 6 b |
| 7 | 5 526 | 7 037.7±493.8 ab | 6 985.4±438.0 ab | 7.071 7±0.062 0 a | 0.002 4±0.000 2 a | 0.985 6±0.001 0 ab | |
| 9 | 5 185 | 6 624.7±36.0 ab | 6 628.0±102.7 ab | 6.848 6±0.071 5 b | 0.003 4±0.000 6 a | 0.986 2±0.000 2 ab |
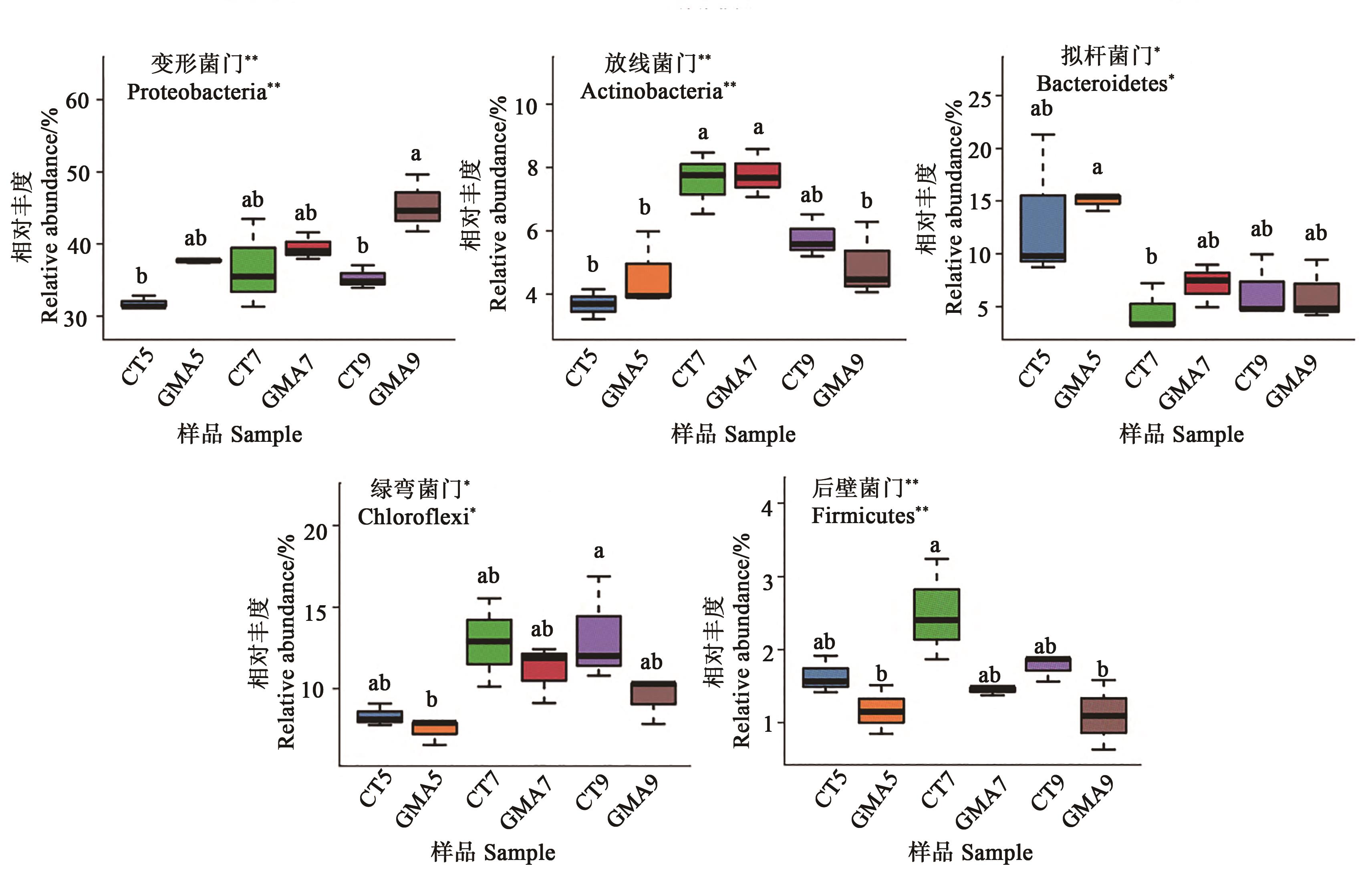
图2 5个细菌门在不同样品中的相对丰度注:不同小写字母表示不同样本间在P<0.05水平差异显著;*和**分别表示在P<0.05和P<0.01水平显著。
Fig. 2 Relative abundance of 5 bacteria phylums in different samplesNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different samples at P<0.05 level;* and ** indicate significant differences at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels, respectively.

图6 土壤细菌门和土壤化学性质的相关性分析注:*和**分别表示在P<0.05和P<0.01水平相关显著。
Fig. 6 Correlation analysis between soil bacterial phylum and soil chemical propertiesNote: * and ** indicate significant correlations at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels respectively.
| 1 | 高卫红,杨磊.新疆统计年鉴_农业_第十二篇_[M].乌鲁木齐:中国统计出版社,2018:1-358. |
| 2 | 陈久红,马建江,李永丰,等.行间生草对‘库尔勒香梨’果园小气候、光合特性及果实品质的影响[J].北方园艺,2019(22):49-59. |
| CHEN J H, MA J J, LI Y F, et al.. Effects of herbage on ecological environment and photosynthetic characteristics fruits quality of ‘Korla Fragrant Pear’ [J]. Northern Hortic., 2019(22):49-59. | |
| 3 | 寇建村,杨文权,程国亭,等.行间种植不同草种对幼龄苹果园土壤特性的影响[J].干旱地区农业研究,2012,30(4):145-152. |
| KOU J C, YANG W Q, CHENG G T, et al.. Effects of different grasses between rows of apple trees on soil characteristics of 1-year-old orchard [J]. Agric. Res. Arid Areas, 2012, 30(4):145-152. | |
| 4 | 万华,雍明海.行间种植不同草种对幼龄苹果园土壤特性的影响对比分析[J].现代园艺,2017(24):9. |
| 5 | 王林娜.枣林间作牧草品种筛选及综合评价[D].阿拉尔:塔里木大学,2017. |
| WANG L N. Screening and evaluation forages under jujube forest [D]. Alar: Tarim University, 2017. | |
| 6 | 高明霞,孙瑞,崔全红,等.长期施用化肥对塿土微生物多样性的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2015,21(6):1572-1580. |
| GAO M X, SUN R, CUI Q H, et al.. Effect of long-term chemical fertilizer application on soil microbial diversity in anthropogenic loess soil [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2015, 21(6):1572-1580. | |
| 7 | 陈法霖,郑华,欧阳志云,等.土壤微生物群落结构对凋落物组成变化的响应[J].土壤学报,2011,48(3):603-611. |
| CHEN F L, ZHENG H, OUYANG Z Y, et al.. Responses of microbial community structure to the leaf litter composition [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2011, 48(3):603-611. | |
| 8 | 惠竹梅,李华,龙妍,等.葡萄园行间生草体系中土壤微生物数量的变化及其与土壤养分的关系[J].园艺学报,2010,37(9):1395-1402. |
| HUI Z M, LI H, LONG Y, et al.. Variation of soil microbial populations and relationships between microbial factors and soil nutrients in cover cropping system of vineyard [J]. Acta Hortic Sin., 2010, 37(9):1395-1402. | |
| 9 | 吴家森,张金池,钱进芳,等.生草提高山核桃林土壤有机碳含量及微生物功能多样性[J].农业工程学报,2013,29(20):111-117. |
| WU J S, ZHANG J C, QIAN J F, et al.. Intercropping grasses improve soil organic carbon content and microbial community functional diversities in Chinese hickory stands [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2013, 29(20):111-117. | |
| 10 | 薛泉宏,沈建伟,汤莉.钾细菌对土娄土养分活化作用的研究[J].西北农业学报,2000,9(3):67-71. |
| XUE Q H, SHEN J W, TANG L. Effect of the K bacteria on nutrients activation in Lou soil [J]. Acta Agric Bor-Occid. Sin., 2000, 9(3):67-71. | |
| 11 | 孙波,赵其国,张桃林,等.土壤质量与持续环境──Ⅲ.土壤质量评价的生物学指标[J].土壤,1997,29(5):225-234. |
| SUN B, ZHAO Q G, ZHANG T L, et al.. Soil quality and sustainable environment Ⅲ. biological indicators for soil quality assessment [J]. Soil, 1997, 29(5):225-234. | |
| 12 | 唐玉姝,魏朝富,颜廷梅,等.土壤质量生物学指标研究进展[J].土壤,2007,39(2):157-163. |
| TANG Y S, WEI C F, YAN T M, et al.. Biological indicator of soil quality: a review [J]. Soils, 2007, 39(2):157-163. | |
| 13 | 哈斯亚提·托逊江,刘晨,哈丽代·热合木江,等.苏丹草套种红枣和核桃对其产量及土壤水分含量的影响[J].新疆农业科学,2013,50(12):2241-2245. |
| Tuoxunjiang Hasiyati, LIU C, Rehemujiang Halidai,et al.. Effect of intercropping Sudan grass in fruit trees on herbage yield and soil moisture counted [J]. Xinjiang Agric. Sci., 2013, 50(12):2241-2245. | |
| 14 | 刘晨,哈斯亚提·托逊江,艾比布拉·伊马木.新疆环塔里木稀植果林间套种牧草生产初步研究[J].广东农业科学,2014,41(18):132-135. |
| LIU C, Tuoxunjiang Hasiyati, Yimamu Aibibula. Preliminary study on forage grass production by interplanting in sparse planting orchard in Tarim Basin of Xinjiang [J]. Guangdong Agric. Sci., 2014, 41(18):132-135. | |
| 15 | WEI Z, YANG T, FRIMAN V, et al.. Trophic network architecture of root-associated bacterial communities determines pathogen invasion and plant health [J/OL]. Nat. Comm., 2015, 6:8413 [2022-10-03]. . |
| 16 | DOU R, SUN J, DENG F, et al.. Contamination of pyrethroids and atrazine in greenhouse and open-field agricultural soils in China [J/OL]. Sci. Total Environ., 2020, 701: 134916 [2022-10-03]. . |
| 17 | SATAPUTE P, KAMBLE M V, ADHIKARI S S, et al.. Influence of triazole pesticides on tillage soil microbial populations and metabolic changes [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2019, 651(PT.2):2334-2344. |
| 18 | 张博岩,窦森,张笑唯. 不同种植年限榛地土壤基本理化性质及腐殖物质组成[J].吉林农业大学学报, 2022,44(3):345-351. |
| ZHANG B Y, DOU S, ZHANG X W. Effects of different planting years of hazelnut on basic physical and chemical properties of soil and humus composition [J]. J. Jilin Agric. Univ., 2022, 44(3):345-351. | |
| 19 | 周泉,张小短,马淑敏,等.间作绿肥对油菜根际土壤碳氮及根际微生物的影响[J].生态学报,2017,37(23):7965-7971. |
| ZHOU Q, ZHANG X D, MA S M, et al.. Effects of intercropping green manure on soil carbon, nitrogen and soil microbial in rapeseed rhizosphere [J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2017, 37(23):7965-7971. | |
| 20 | LONGA C M O, NICOLA L, ANTONIELLI L, et al.. Soil microbiota respond to green manure in organic vineyards [J]. J. Appl. Microbiol., 2017, 123(6):1547-1560. |
| 21 | SARA E, KATARINA H, ANNA M. Soil enzyme activities, microbial community composition and function after 47 years of continuous green manuring [J]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2006, 35(3):610-621. |
| 22 | 李洁,孙寓姣,尹萌,等.永定河山峡与城市段微生物群落结构季节变化[J].北京师范大学学报(自然科学版),2020,56(2):257-264. |
| LI J, SUN Y J, YIN M, et al.. Seasonal variations in microbial community structure in Yongding river [J]. J. Beijing Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2020, 56(2):257-264. | |
| 23 | 彭晓邦,秦绍龙.黄芩种植地土壤微生物数量特征及土壤酶活性研究[J].陕西农业科学,2020,66(8):60-64. |
| PENG X B, QIN S L. Quantitative characteristics of soil microorganisms and soil enzyme activities in Scutellaria baicalensis cultivated land [J]. Shaanxi Agric. Sci., 2020,66(8):60-64. | |
| 24 | TODA M, UCHIDA Y. Long-term use of green manure legume and chemical fertiliser affect soil bacterial community structures but not the rate of soil nitrate decrease when excess carbon and nitrogen are applied [J]. Soil Res., 2017, 55(6):524-536. |
| 25 | 高嵩涓.冬绿肥-水稻模式下的土壤微生物特征及硝化作用调控机制[D].北京:中国农业大学,2018. |
| GAO S J. Soil microbial characteristics and nitrification regulation mechanism under the winter green manure-rice model [D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University,2018. | |
| 26 | 严海元,辜夕容,申鸿.森林凋落物的微生物分解[J].生态学杂志,2010,29(9):1827-1835. |
| YAN H Y, GU X R, SHEN H. Microbial decomposition of forest litter [J]. Chin. J. Ecol., 2010.29(9):1827-1835. | |
| 27 | 李文广,杨晓晓,黄春国,等.饲料油菜作绿肥对后茬麦田土壤肥力及细菌群落的影响[J].中国农业科学,2019,52(15):2664-2677. |
| LI W G, YANG X X, HUANG C G, et al.. Effects of rapeseed green manure on soil fertility and bacterial community in dryland wheat field [J]. Chin. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2019, 52(15):2664-2677. | |
| 28 | AJAY N, MATHIEU N. Soil microbial biomass, functional microbial diversity, and nematode community structure as affected by cover crops and compost in an organic vegetable production system [J]. Appl. Soil Ecol., 2012, 58:45-55. |
| 29 | 李丽娜,席运官,陈鄂,等.耕作方式与绿肥种植对土壤微生物组成和多样性的影响[J].生态与农村环境学报,2018,34(4):342-348. |
| LI L N, XI Y G, CHEN E, et al.. Effects of tillage and green manure crop on composition and diversity of soil microbial community [J]. J. Ecol. Rural Environ., 2018, 34(4):342-348. | |
| 30 | MKA A, ENOI J. The effects of crop rotation and nitrogen fertilization on soil chemical and microbial properties in a Guinea Savanna Alfisol of Nigeria [J]. Plant Soil, 2006, 281(1-2):234-245. |
| 31 | 秦杰,姜昕,周晶,等.长期不同施肥黑土细菌和古菌群落结构及主效影响因子分析[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2015,21(6):1590-1598. |
| QIN J, JIANG X, ZHOU J, et al.. Characteristics and driving factors of soil bacterial and archaeal communities under long-term fertilization regimes in black soil [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2015, 21(6):1590-1598. | |
| 32 | 冯天祥,王玲,陈海敏,等.植物内生放线菌功能及生物活性物质研究进展[J].中国生物工程杂志,2015,35(4):98-106. |
| FENG T X, WANG L, CHEN H M, et al.. Research advanceson function and bioactive substances of endophytic actinomycetes [J]. Chin. Biotechnol., 2015, 35(4):98-106. | |
| 33 | 陈力力,刘金,李梦丹,等.水稻-油菜双序列复种免耕、翻耕土壤真菌多样性[J].激光生物学报,2018,27(1):60-68. |
| CHEN L L, LIU J, LI M D, et al.. Diversity of filamentous fungus community in paddy fields with different tillage methods [J]. Acta Laser Biol. Sin., 2018, 27(1):60-68. |
| [1] | 李海利, 徐引弟, 王治方, 朱文豪, 张立宪, 马春江. 一株多重耐药大肠杆菌全基因组测序及其耐药性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 113-121. |
| [2] | 季梦婷, 陈长江, 罗流河, 林志坚, 詹梦琳, 杨丙烨, 胡方平, 蔡学清. 福建猕猴桃细菌性枯萎病的病原菌鉴定[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(4): 144-152. |
| [3] | 李鹏声, 黄清泰, 范咏梅, 王萌, 杨叶. 海南省东方市甜瓜细菌性果斑病病原鉴定[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 117-123. |
| [4] | 张二豪, 刘盼盼, 何萍, 简阅, 徐雨婷, 陈诚欣, 禄亚洲, 兰小中, 索朗桑姆. 甘青青兰根际土壤理化性质及微生物群落结构特征分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 201-213. |
| [5] | 苗宇, 王婕, 赵尧尧, 张丽佳, 刘美君. 低温胁迫后紫花苜蓿叶片光合作用的恢复特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 80-89. |
| [6] | 方泰军, 侯璐, 白露超. 柴达木地区患根腐病枸杞根际土壤微生物多样性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 133-139. |
| [7] | 邵社刚, 李婷, 柳勇, 林兰稳, 张东, 倪栋, 李俊杰, 朱立安. 外源菌剂对稻秆腐解及微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 166-177. |
| [8] | 张庆昕, 张玉霞, 孙明雪, 夏全超, 王显国, 刘庭玉, 杜晓艳. 钾肥对苜蓿低温胁迫下抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 186-195. |
| [9] | 胡亚强, 苑亚, 杨鲁伟, 章学来, 邱少鹏, 于馨尧. 植入式苜蓿草捆热风干燥系统的研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 105-112. |
| [10] | 贾晶莹, 李雅辉, 伏兵哲, 马云, 蔡小艳. 苜蓿miRs表达谱分析及跨界潜力miRs初步筛选[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 43-53. |
| [11] | 靳建刚, 田再芳, 郑敏娜, 康佳惠. 不同施肥措施对饲用燕麦土壤细菌群落多样性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 152-160. |
| [12] | 赵柏霞, 闫建芳. 高通量技术分析‘砂蜜豆’甜樱桃不同组织内生细菌多样性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(3): 66-77. |
| [13] | 滕泽, 张玉霞, 陈卫东, 丛百明, 田永雷, 张庆昕, 张永亮, 王东儒. 壳聚糖对苜蓿抗寒性及抗寒保护物质含量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 192-198. |
| [14] | 申云鑫, 施竹凤, 韩天华, 周旭东, 贺彪, 赵文山, 和强, 马斌, 陈齐斌, 杨佩文. 土壤微生物多样性对有机碳源物料输入的响应特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(10): 221-233. |
| [15] | 夏秀波, 李涛, 曹守军, 姚建刚, 王虹云, 张丽莉. 液态有机肥部分替代化肥对设施番茄根区细菌群落的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 187-196. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号