




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (3): 71-82.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0591
刘金仙1,2( ), 王丽娟2(
), 王丽娟2( ), 刘杰2, 傅仙玉1,2, 武广珩3
), 刘杰2, 傅仙玉1,2, 武广珩3
收稿日期:2023-08-08
接受日期:2023-10-18
出版日期:2025-03-15
发布日期:2025-03-14
通讯作者:
刘金仙
作者简介:刘金仙 E-mail:liujinxian@163.com基金资助:
Jinxian LIU1,2( ), Lijuan WANG2(
), Lijuan WANG2( ), Jie LIU2, Xianyu FU1,2, Guangheng WU3
), Jie LIU2, Xianyu FU1,2, Guangheng WU3
Received:2023-08-08
Accepted:2023-10-18
Online:2025-03-15
Published:2025-03-14
Contact:
Jinxian LIU
摘要:
为了解茶树钙调蛋白结合转录激活因子(calmodulin-binding transcription activator,CAMTA)家族成员的功能,探究其表达特性,利用生物信息学方法在茶树全基因组中鉴定CsCAMTAs基因,并对其理化性质、基因结构、结构域、保守基序、系统进化、顺式作用元件进行分析,利用qRT-PCR技术分析CsCAMTAs在不同组织、不同激素处理和病菌胁迫下的表达情况。结果表明,在茶树全基因组中共鉴定出10个CsCAMTAs成员,共包含10个motifs,分布在6条染色体,均定位于细胞核。不同CsCAMTAs基因差异较大,氨基酸数目为124~1 419个,编码蛋白等电点为4.976~9.820,除1个为弱疏水蛋白外,其他均为亲水蛋白。系统进化分析将茶树10个CsCAMTAs基因划分为4个类群,有4个同源基因对,同源基因对在基因结构、保守结构域、保守基序数量和相对位置等方面具有较高相似性。CsCAMTAs启动子区含有34个与光响应、激素诱导以及生物胁迫相关的顺式作用元件。表达分析结果显示,CsCAMTAs在不同组织的表达有明显差异,其中CsCAMTA1、3、4、7、8、10在老叶中的表达水平较高;除CsCAMTA5不受茉莉酸甲酯诱导外,其他CsCAMTAs基因均受茉莉酸甲酯、脱落酸、水杨酸及茶轮斑病菌诱导表达,由此说明CsCAMTAs不仅调控茶树生长发育,还参与茶树对病菌和激素的应答。
中图分类号:
刘金仙, 王丽娟, 刘杰, 傅仙玉, 武广珩. 茶树钙调蛋白结合转录激活因子(CAMTA)家族基因鉴定与表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(3): 71-82.
Jinxian LIU, Lijuan WANG, Jie LIU, Xianyu FU, Guangheng WU. Identification and Expression Analysis of Calmodulin-binding Transcription Activator (CAMTA) Family Genes in Tea Plants[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(3): 71-82.
基因 Gene | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5’-3’) |
|---|---|---|
| CsCAMAT10 | RT-CsCAMAT10-F | GCCATAGGAGCCTTAGCATA |
| RT-CsCAMAT10-R | CCAGGGCAAACTCAACAACT | |
| CsCAMAT9 | RT-CsCAMAT9-F | TGATCCTTTGGTGCAGAACG |
| RT-CsCAMAT9-R | CCAATCCAGCAACCATGTGA | |
| CsCAMAT8 | RT-CsCAMAT8-F | AGCATAATCTGGTCCGTTGG |
| RT-CsCAMAT8-R | CGTTCTTCTGTTTGCTTTCG | |
| CsCAMAT7 | RT-CsCAMAT7-F | GCCATAACTGGAGGAAGAAG |
| RT-CsCAMAT7-R | ATAGCTTCGCCTCTGGAAAT | |
| CsCAMAT6 | RT-CsCAMAT6-F | GCTGCTCGCATTCATCAAGT |
| RT-CsCAMAT6-R | GAATCCACGCAAACCACTCC | |
| CsCAMAT5 | RT-CsCAMAT5-F | GTCCGCAGATGTTACTGGCTAC |
| RT-CsCAMAT5-R | GCACTCAACTTGCTGGGATC | |
| CsCAMAT4 | RT-CsCAMAT4-F | AGGATGGCAAGACCGTCAAA |
| RT-CsCAMAT4-R | GTTCAAGGGCAACCGCACCA | |
| CsCAMAT3 | RT-CsCAMAT3-F | GTTCTCCCGTCACTCCTGTC |
| RT-CsCAMAT3-R | CCCTTCACGCTGATGATGTA | |
| CsCAMAT2 | RT-CsCAMAT2-F | TATGTTGTCTGGCTCCTCCC |
| RT-CsCAMAT2-R | CGGCTGATTACATCCTCCTC | |
| CsCAMAT1 | RT-CsCAMAT1-F | GGAAATTGTGAAATGGGCAGTC |
| RT-CsCAMAT1-R | TCCTCATCGTCATCGGCATC | |
| CsGAPDH | RT-CsGAPDH-F | TTGGCATCGTTGAGGGTCT |
| RT-CsGAPDH-R | CAGTGGGAACACGGAAAGC |
表1 CsCAMTAs基因qRT-PCR引物
Table 1 qRT-PCR primers of CsCAMTAs
基因 Gene | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5’-3’) |
|---|---|---|
| CsCAMAT10 | RT-CsCAMAT10-F | GCCATAGGAGCCTTAGCATA |
| RT-CsCAMAT10-R | CCAGGGCAAACTCAACAACT | |
| CsCAMAT9 | RT-CsCAMAT9-F | TGATCCTTTGGTGCAGAACG |
| RT-CsCAMAT9-R | CCAATCCAGCAACCATGTGA | |
| CsCAMAT8 | RT-CsCAMAT8-F | AGCATAATCTGGTCCGTTGG |
| RT-CsCAMAT8-R | CGTTCTTCTGTTTGCTTTCG | |
| CsCAMAT7 | RT-CsCAMAT7-F | GCCATAACTGGAGGAAGAAG |
| RT-CsCAMAT7-R | ATAGCTTCGCCTCTGGAAAT | |
| CsCAMAT6 | RT-CsCAMAT6-F | GCTGCTCGCATTCATCAAGT |
| RT-CsCAMAT6-R | GAATCCACGCAAACCACTCC | |
| CsCAMAT5 | RT-CsCAMAT5-F | GTCCGCAGATGTTACTGGCTAC |
| RT-CsCAMAT5-R | GCACTCAACTTGCTGGGATC | |
| CsCAMAT4 | RT-CsCAMAT4-F | AGGATGGCAAGACCGTCAAA |
| RT-CsCAMAT4-R | GTTCAAGGGCAACCGCACCA | |
| CsCAMAT3 | RT-CsCAMAT3-F | GTTCTCCCGTCACTCCTGTC |
| RT-CsCAMAT3-R | CCCTTCACGCTGATGATGTA | |
| CsCAMAT2 | RT-CsCAMAT2-F | TATGTTGTCTGGCTCCTCCC |
| RT-CsCAMAT2-R | CGGCTGATTACATCCTCCTC | |
| CsCAMAT1 | RT-CsCAMAT1-F | GGAAATTGTGAAATGGGCAGTC |
| RT-CsCAMAT1-R | TCCTCATCGTCATCGGCATC | |
| CsGAPDH | RT-CsGAPDH-F | TTGGCATCGTTGAGGGTCT |
| RT-CsGAPDH-R | CAGTGGGAACACGGAAAGC |
基因名称 Gene name | 基因ID Gene ID | 氨基酸 Amino acid/aa | 分子量 Molecular weight/kD | 等电点 pI | 亚细胞定位Subcellular prediction | 总平均疏水性Grand average hydropathicity | 信号肽预测 Singal petides |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CsCAMTA1 | TEA005634 | 124 | 14.29 | 9.811 | 细胞核Nucleus | -0.388 | 无No |
| CsCAMTA2 | TEA006574 | 984 | 109.83 | 6.153 | 细胞核Nucleus | -0.518 | 无No |
| CsCAMTA3 | TEA011186 | 953 | 107.62 | 6.828 | 细胞核Nucleus | -0.475 | 无No |
| CsCAMTA4 | TEA011489 | 155 | 17.63 | 9.515 | 细胞核Nucleus | -0.484 | 无No |
| CsCAMTA5 | TEA011490 | 864 | 97.26 | 6.028 | 细胞核Nucleus | -0.401 | 无No |
| CsCAMTA6 | TEA012477 | 1 419 | 157.99 | 6.669 | 细胞核Nucleus | -0.346 | 无No |
| CsCAMTA7 | TEA015813 | 139 | 16.33 | 8.722 | 细胞核Nucleus | -0.637 | 无No |
| CsCAMTA8 | TEA015818 | 970 | 108.43 | 4.976 | 细胞核Nucleus | -0.587 | 无No |
| CsCAMTA9 | TEA025813 | 1 028 | 114.80 | 6.326 | 细胞核Nucleus | -0.512 | 无No |
| CsCAMTA10 | TEA028584 | 325 | 36.55 | 9.820 | 细胞核Nucleus | 0.006 | 无No |
表2 CsCAMTAs 基因的理化性质
Table 2 Physicochemical properties of CsCAMTAs genes
基因名称 Gene name | 基因ID Gene ID | 氨基酸 Amino acid/aa | 分子量 Molecular weight/kD | 等电点 pI | 亚细胞定位Subcellular prediction | 总平均疏水性Grand average hydropathicity | 信号肽预测 Singal petides |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CsCAMTA1 | TEA005634 | 124 | 14.29 | 9.811 | 细胞核Nucleus | -0.388 | 无No |
| CsCAMTA2 | TEA006574 | 984 | 109.83 | 6.153 | 细胞核Nucleus | -0.518 | 无No |
| CsCAMTA3 | TEA011186 | 953 | 107.62 | 6.828 | 细胞核Nucleus | -0.475 | 无No |
| CsCAMTA4 | TEA011489 | 155 | 17.63 | 9.515 | 细胞核Nucleus | -0.484 | 无No |
| CsCAMTA5 | TEA011490 | 864 | 97.26 | 6.028 | 细胞核Nucleus | -0.401 | 无No |
| CsCAMTA6 | TEA012477 | 1 419 | 157.99 | 6.669 | 细胞核Nucleus | -0.346 | 无No |
| CsCAMTA7 | TEA015813 | 139 | 16.33 | 8.722 | 细胞核Nucleus | -0.637 | 无No |
| CsCAMTA8 | TEA015818 | 970 | 108.43 | 4.976 | 细胞核Nucleus | -0.587 | 无No |
| CsCAMTA9 | TEA025813 | 1 028 | 114.80 | 6.326 | 细胞核Nucleus | -0.512 | 无No |
| CsCAMTA10 | TEA028584 | 325 | 36.55 | 9.820 | 细胞核Nucleus | 0.006 | 无No |
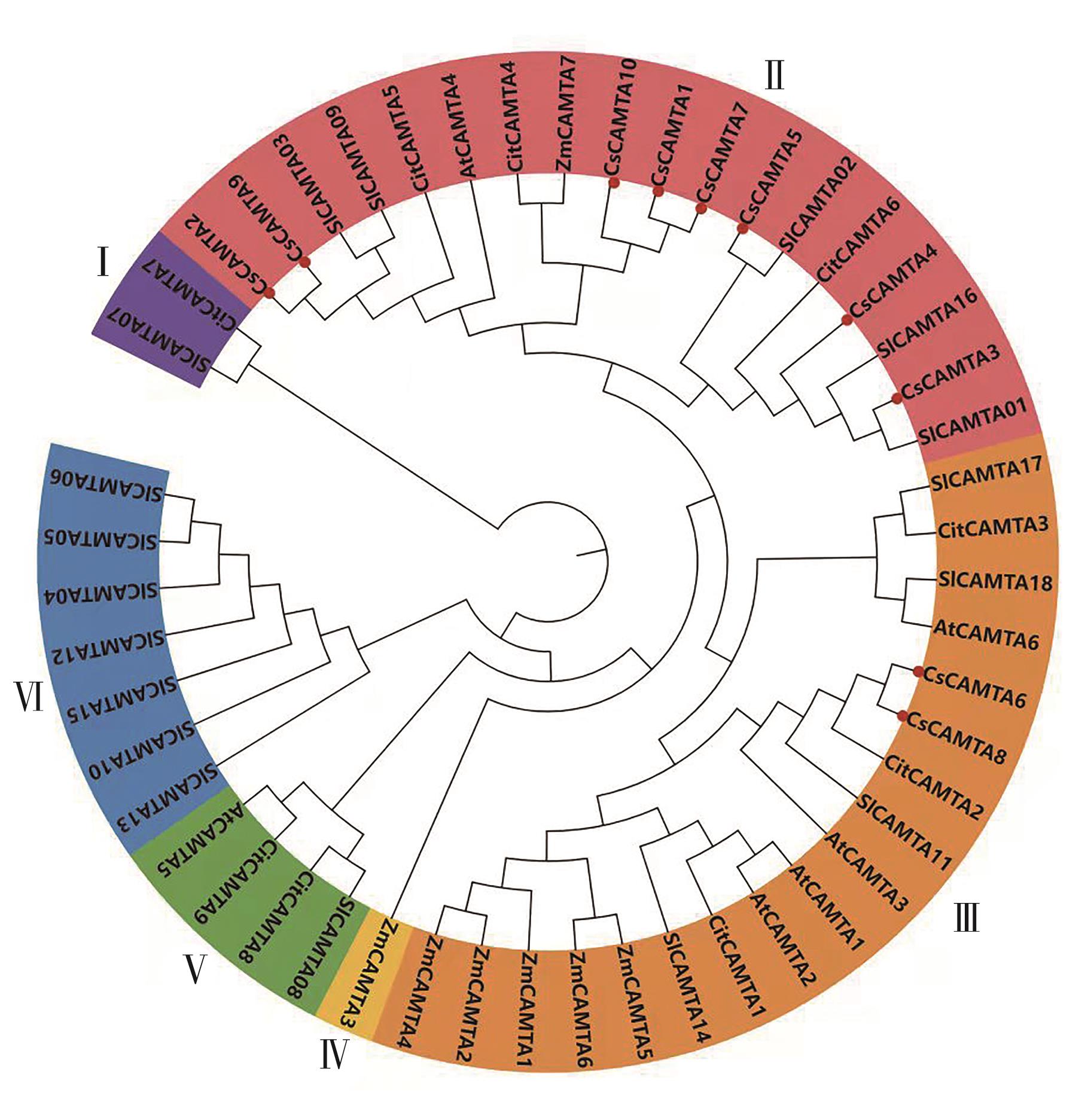
图6 不同来源CAMTA基因的系统进化树注:Cs—茶树;At—拟南芥;Sl—番茄;Zm—玉米;Cit—柑橘。
Fig. 6 Phylogenetic tree of CAMTA gene from different originNote:Cs—Camellia sinensis; At—Arabidopsis thaliana; Sl—Solanum lycopersicum; Zm—Zea mays; Cit—Citrus L.
| 1 | KUDLA J, BATISTIC O, HASHIMOTO K. Calcium signals: the lead currency of plant information processing [J]. Plant Cell, 2010, 22(3):541-563 |
| 2 | DODD A N, KUDLA J, SANDERS D. The language of calcium signaling [J]. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol., 2010, 61 (1):593-620. |
| 3 | KIM Y, GILMOUR S J, CHAO L, et al.. Arabidopsis CAMTA transcription factors regulate pipecolic acid biosynthesis and priming of immunity genes [J]. Mol. Plant, 2019, 13(1):157-168. |
| 4 | LORENZO O. bZIP edgetic mutations: at the frontier of plant metabolism, development and stress trade-off [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2019, 70(20):5517-5520. |
| 5 | PEI J, FLIEDER D B, PATCHEFSKY A, et al.. Detecting MYB and MYBL1 fusion genes in tracheobronchial adenoid cystic carcinoma by targeted RNA-sequencing [J]. Mod. Pathol., 2019, 32(10):1416-1420. |
| 6 | ZHU D, HOU L X, XIAO P L, et al.. VvWRKY30, a grape WRKY transcription factor, plays a positive regulatory role under salinity stress [J]. Plant Sci., 2019, 280:132-142. |
| 7 | YANG Y, YOO C G, ROTTMANN W, et al.. PdWND 3A, NAC domain-containing proteinawood-associated, affects lignin biosynthesis and composition in populus [J/OL]. BMC Plant Biol., 2019, 19:486 [2023-07-05]. . |
| 8 | BOUCHE N, SCHARLAT A, SNEDDEN W, et al.. A novel family of calmodulin-binding transcription activators in multicellular organisms [J].J. Biol. Chem., 2002, 277 (24):21851-21861. |
| 9 | CHOI M S, KIM M C, YOO J H, et al.. Isolation of a calmodulin-binding transcription factor from rice (Oryza sativa L.) [J]. J. Biol. Chem., 2005, 280(49):40820-40831. |
| 10 | POOVAIAH B W, DU L Q, WANG H Z, et al.. Recent advances in calcium/calmodulin-mediated signaling with an emphasis on plant-microbe interactions [J]. Plant Physiol., 2013, 163 (2):531-542. |
| 11 | 李卉梓. SlGLRs 和SlCaMs 在调控番茄低温抗性中的机制研究[D].杭州:浙江大学, 2019. |
| LI H Z. Roles and mechanisms of SlGLRs and SlCaMs regulated cold tolerance in tomato [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2019. | |
| 12 | MEER L, MUMTAZ S, LABBO A M, et al.. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of calmodulin-binding transcription activator genes in banana under drought stress [J]. Sci. Hortic., 2019, 244:10-14. |
| 13 | NOMAN M, JAMEEL A, QIANG W D, et al.. Overexpression of GmCAMTA12 enhanced drought tolerance in Arabidopsis and soybean [J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2019, 20(19):4849 [2023-07-05]. . |
| 14 | PRASAD K V S K, ABDEL-HAMEED A A E, XING D H, et al.. Global gene expression analysis using RNA-seq uncovered a new role for SR1/CAMTA3 transcription factor in salt stress [J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2016, 6:27021 [2023-07-05]. . |
| 15 | 褚桂花.番茄SR/CAMTA 转录因子家族基因SlSR4的克隆与功能研究[D].重庆:重庆大学,2015. |
| CHU G H. Cloning and functional research of tomato SR/CAMTA family gene SlSR4 [D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2015. | |
| 16 | DOHERTY C J, VAN BUSKIRK H A, MYERS S J, et al.. Roles for Arabidopsis CAMTA transcription factors in cold regulated gene expression and freezing tolerance [J]. Plant Cell, 2009, 21(3):972-984. |
| 17 | 王晴晴.油菜CAMTA1参与冷胁迫应答的功能研究[D].武汉:华中师范大学,2013. |
| WANG Q Q. Role of Brassica napus CAMTA1 protein in response to cold stress [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Normal University, 2013. | |
| 18 | KIM Y S, AN C, PARK S, et al.. CAMTA-mediated regulation of salicylic acid immunity pathway genes in Arabidopsis exposed to low temperature and pathogen infection [J]. Plant Cell, 2017, 29 (10):2465-2477. |
| 19 | PANDEY N, RANJAN A, PANT P, et al.. CAMTA1 regulates drought responses in Arabidopsis thaliana [J/OL]. BMC Genomics, 2013, 14: 216 [2023-07-05]. . |
| 20 | DU L Q, ALI G S, SIMONS K A, et al.. Ca2+/calmodulin regulates salicylic-acid-mediated plant immunity [J]. Nature, 2009, 457(7233):1154-1158. |
| 21 | YANG T, POOVAIAH B W. An early ethylene up-regulated gene encoding a calmodulin-binding protein involved in plant senescence and death [J]. J. Biol. Chem., 2000, 275(49):38467-38473. |
| 22 | GALON Y, ALONI R, NACHMIAS D, et al.. Calmodulin-binding transcription activator 1 mediates auxin signaling and responds to stresses in Arabidopsis [J]. Planta, 2010, 232(1):165-178. |
| 23 | GU J M, WANG C Y, WANG F, et al.. Roles of CAMTA/SR in plant growth and development and stress response [J]. Acta Hortic. Sin., 2021, 48(4):613-631. |
| 24 | BOUCHE N, SCHARLAT A, SNEDDEN W, et al.. A novel family of calmodulin-binding transcription activators in multicellular organisms [J]. J. Biol. Chem., 2002, 277(24):21851-21861. |
| 25 | WANG G P, ZENG H Q, HU X Y, et al.. Identification and expression analyses of calmodulin-binding transcription activator genes in soybean [J]. Plant Soil, 2015, 386:205-221. |
| 26 | YUE R Q, LU C X, SUN T, et al.. Identification and expression profiling analysis of calmodulin-binding transcription activator genes in maize (Zea mays L.) under abiotic and biotic stresses [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2015, 6:576 [2023-07-05]. . |
| 27 | 张静.柑橘CAMTA基因家族的鉴定与功能的初步研究[D].重庆:西南大学, 2019. |
| ZHANG J. Identification and functional analysis of citrus CAMTA genes [D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2019. | |
| 28 | 林显祖,肖小虎,阳江华,等.巴西橡胶树CAMTA 转录因子全基因组鉴定与表达分析[J].热带作物学报,2021,42(10): 2859-2868. |
| LIN X Z, XIAO X H, YANG J H, et al.. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the CAMTA family in rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis) [J]. Chin. J. Tropic. Crops, 2021, 42(10):2859-2868. | |
| 29 | LIVAK K J, SCHMITTGEN T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2- ΔΔCT method [J]. Methods, 2001, 25(4):402-408. |
| 30 | DEL CAMPO E M, CASANO L M, BARREO E. Evolutionary implications of intron-exon distribution and the properties and sequences of the RPL10A gene in eukaryotes [J]. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol., 2013, 66(3):857-867. |
| 31 | 王宝强,朱晓林,魏小红,等.番茄钙调蛋白结合转录因子CAMTA家族基因的鉴定及其低温胁迫下表达模式的分析[J].农业生物技术学报,2021,29(5):871-884. |
| WANG B Q, ZHU X L, WEI X H, et al.. Identification of calmodulin-binding transcription factor CAMTA gene family and its expression analysis under low-temperature stress in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) [J]. J. Agric. Biotechnol., 2021, 29(5):871-884. | |
| 32 | LI B, HE S, ZHENG Y Q, et al.. Genome-wide identifcation and expression analysis of the calmodulin-binding transcription activator (CAMTA) family genes in tea plant [J/OL]. BMC Genomics, 2022, 23:667 [2023-07-05]. . |
| 33 | ZHOU Q Y, ZHAO M W, XING F, et al.. Identification and expression analysis of CAMTA Genes in tea plant reveal their complex regulatory role in stress responses [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2022, 13:910768 [2023-07-05]. . |
| 34 | 吴娴.小麦CAMTA基因家族鉴定及TaCAMTA1b-B .1功能验证[D].荆州:长江大学,2022. |
| WU X. Genome-wide identification of CAMTA gene families in wheat (Triticum asetivum L.) and functional analysis of TaCAMTA1b-B.1 [D]. Jingzhou:Yangtze University, 2022. | |
| 35 | SHANGGUAN L F, WANG X M, LENG X P, et al.. Identification and bioinformatic analysis of signal responsive/calmodulin-binding transcription activators gene models in Vitis vinifera [J]. Mol. Biol. Rep., 2014, 41(5):2937-2949. |
| 36 | MEER L, MUMTAZ S, LABBO A M, et al.. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of calmodulin-binding transcription activator genes in banana under drought stress [J]. Sci. Hortic., 2019, 244:10-14. |
| 37 | BOUCHE N, SCHARLAT A, SNEDDEN W, et al.. A novel family of calmodulin-binding transcription activators in multicellular organisms [J]. J. Biol. Chem., 2002, 277(24):21851-21861. |
| 38 | CHOI M S, KIM M C, YOO J H, et al.. Isolation of a calmodulin-binding transcription factor from rice (Oryza sativa L.) [J]. J. Biol. Chem., 2005, 280(49):40820-40831. |
| 39 | 刘志鑫,孙宇,叶子,等.杧果钙调蛋白转录激活因子基因家族的鉴定及分析[J].果树学报,2021,38(8):1252-1263. |
| LIU Z X, SUN Y, YE Z, et al.. Identification and analysis of calmodulin-binding transcription activator gene family in mango [J]. J. Fruit Sci., 2021, 38(8):1252-1263. | |
| 40 | RAHMAN H, XU Y P, ZHANG X R, et al.. Brassica napus genome possesses extraordinary high number of CAMTA genes and CAMTA3 contributes to pamp triggered immunity and resistance to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum [J/OL]. Front. Plant. Sci., 2016, 7:581 [2023-07-05]. . |
| 41 | KAKAR K U, NAWAZ Z, CUI Z Q, et al.. Evolutionary and expression analysis of CAMTA gene family in Nicotiana tabacum yielded insights into their origin, expansion and stress responses [J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2018, 8(1):10322 [2023-07-05]. . |
| 42 | YANG F, DONG F S, HU F H,et al.. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the calmodulin-binding transcription activator (CAMTA) gene family in wheat(Triticum aestivum L.) [J/OL]. BMC Genetics, 2020, 21:105 [2023-07-05]. . |
| 43 | WEI M, XU X M, LI C H. Identification and expression of CAMTA genes in Populus trichocarpa under biotic and abiotic stress [J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2017, 7(1): 17910 [2023-07-05]. . |
| 44 | CHANG Y L, BAI Y J, WEI Y X, et al.. CAMTA3 negatively regulates disease resistance through modulating immune response and extensive transcriptional reprogramming in cassava [J]. Tree Physiol., 2020, 40(11):1520-1533. |
| 45 | RAHMAN H, YANG J, XU Y P, et al.. Phylogeny of plant CAMTAs and role of AtCAMTAs in nonhost resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2016, 7:177 [2023-07-05]. . |
| 46 | SCHWEIGHOFER A, HIRT H, MESKIENE I. Plant PP2C phos-phatases: emerging functions in stress signaling [J].Trends Plant Sci., 2004, 9(5):236-243. |
| 47 | 刘文宇,杜何为,黄敏.玉米CAMTA基因家族的全基因组分析[J].分子植物育种,2021,19(11):3499-3505. |
| LIU W Y, DU H W, HUANG M. Genome-wide analysis of the CAMTA gene family in maize (Zea mays L.) [J]. Mol. Plant Breeding, 2021, 19(11):3499-3505. | |
| 48 | YANG T B, PENG H, WHITAKER B D, et al.. Characterization of a calcium/calmodulin-regulated SR/CAMTA gene family during tomato fruit development and ripening [J/OL]. BMC Plant Biol., 2012, 12:19 [2023-07-05]. . |
| 49 | YANG Y J, SUN T, XU L Q, et al.. Genome-wide identification of CAMTA gene family members in Medicago truncatula and their expression during root nodule symbiosis and hormone treatments [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2015, 6:459 [2023-07-05]. . |
| 50 | IQBAL Z, IQBAL M S, SINGH S P, et al.. Ca2+/calmodulin complex triggers CAMTA transcriptional machinery under stress in plants: signaling cascade and molecular regulation [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2020, 11:598327 [2023-07-05]. . |
| 51 | REDDY A S N, ALI G S, CELESNIK H, et al.. Coping with stresses:roles of calcium- and calcium/calmodulin-regulated gene expression[J]. Plant Cell, 2011, 23(6):2010-2032. |
| 52 | DU L Q, ALI G S, SIMONS K A, et al.. Ca2+/calmodulin regulates salicylic-acid-mediated plant immunity [J]. Nature, 2009, 457(7233):1154-1158. |
| [1] | 李贤国, 戴麒, 王泽鹏, 陈兆龙, 闫会转, 李宁. 番茄CCCH类锌指蛋白家族的鉴定及其表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(1): 80-95. |
| [2] | 郭肖蓉, 刘颖, 樊佳珍, 黄涛, 周荣. 猪CREBRF基因生物信息学和表达规律分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(9): 44-53. |
| [3] | 张福林, 奚瑞, 刘宇翔, 陈兆龙, 余庆辉, 李宁. 番茄BURP结构域基因家族全基因组鉴定及表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 51-62. |
| [4] | 鲍新跃, 陈红敏, 王伟伟, 唐益苗, 房兆峰, 马锦绣, 汪德州, 左静红, 姚占军. 小麦TaCOBL-5基因克隆及表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 11-21. |
| [5] | 石玉涛, 谢惠珍, 郑淑琳, 羽观华, 王飞权, 李力, 张渤, 李远华, 罗盛财. 武夷山地方茶树种质生化特性和茶多糖清除超氧阴离子自由基活性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 65-76. |
| [6] | 刘博, 王旺田, 马骊, 武军艳, 蒲媛媛, 刘丽君, 方彦, 孙万仓, 张岩, 刘睿敏, 曾秀存. 白菜型油菜IPT基因家族鉴定及表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 56-66. |
| [7] | 张振伟, 董相书, 杨婧, 李学俊, 杞美军, 蒋快乐, 杨永林, 王步天, 施学东, 邱俊超, 陈治华, 葛宇. 小粒咖啡叶绿素合成基因CaPOR的全基因组鉴定及表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(10): 83-97. |
| [8] | 邓玉荣, 韩联, 王金龙, 韦兴翰, 王旭东, 赵颖, 魏小红, 李朝周. 藜麦SOD家族基因的鉴定及其对混合盐碱胁迫的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 28-39. |
| [9] | 郑淑琳, 石玉涛, 王飞权, 吴邦强, 李远华, 张渤, 叶乃兴. 不同茶树种质资源花器矿质元素含量分析与综合评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 178-188. |
| [10] | 张曼, 王志城, 刘正文, 王国宁, 王省芬, 张艳. 陆地棉BGLU基因家族成员的全基因组鉴定与表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 48-59. |
| [11] | 刘声传, 许应芬, 魏杰, 鄢东海, 陈智雄, 徐霖, 刘燕, 周玉锋. 基于2b-RAD技术分析白化茶树品种(系)遗传多样性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(8): 65-73. |
| [12] | 赵晋锋, 余爱丽, 李颜方, 杜艳伟, 王高鸿, 王振华. 谷子SiCBL3对非生物胁迫响应特征分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(11): 68-75. |
| [13] | 王琴琴, 陈修贵, 陆许可, 王帅, 张悦新, 范亚朋, 陈全家, 叶武威. 陆地棉GhPKE1的生物信息学分析及功能验证[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1): 38-45. |
| [14] | 刘正文, 王省芬, 孟成生, 张艳, 孙正文, 吴立强, 马峙英, 张桂寅. 海岛棉GH9基因家族成员鉴定及分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(9): 30-45. |
| [15] | 蒲全明, 杨鹏, 雍磊, 邓榆川, 何自涵, 林邦民, 施松梅, 向承勇, 方芳. 萝卜紫红叶色突变体的色素含量及光合特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(8): 45-54. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号