




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (8): 51-62.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0311
• BIOTECHNOLOGY & LIFE SCIENCE • Previous Articles Next Articles
Fulin ZHANG1,2( ), Rui XI1,2, Yuxiang LIU1,2, Zhaolong CHEN1,2, Qinghui YU1, Ning LI1(
), Rui XI1,2, Yuxiang LIU1,2, Zhaolong CHEN1,2, Qinghui YU1, Ning LI1( )
)
Received:2023-04-19
Accepted:2023-08-25
Online:2024-08-15
Published:2024-08-12
Contact:
Ning LI
张福林1,2( ), 奚瑞1,2, 刘宇翔1,2, 陈兆龙1,2, 余庆辉1, 李宁1(
), 奚瑞1,2, 刘宇翔1,2, 陈兆龙1,2, 余庆辉1, 李宁1( )
)
通讯作者:
李宁
作者简介:张福林E-mail:18095998056@163.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Fulin ZHANG, Rui XI, Yuxiang LIU, Zhaolong CHEN, Qinghui YU, Ning LI. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Tomato BURP Structural Domain Gene Family[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(8): 51-62.
张福林, 奚瑞, 刘宇翔, 陈兆龙, 余庆辉, 李宁. 番茄BURP结构域基因家族全基因组鉴定及表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 51-62.
处理 Treatment | 试剂 Reagent |
|---|---|
| CK | 蒸馏水Distilled water |
| EBR0.05 | 0.05 mg·L-1 EBR |
| EBR0.10 | 0.10 mg·L-1 EBR |
| EBR0.20 | 0.20 mg·L-1 EBR |
| MT50 | 50 μmol·L-1 MT |
| MT100 | 100 μmol·L-1 MT |
| MT150 | 150 μmol·L-1 MT |
| NAA10 | 10 mg·L-1 NAA |
| NAA20 | 20 mg·L-1 NAA |
| NAA30 | 30 mg·L-1 NAA |
Table 1 Treatments with different concentration of plant growth regulators
处理 Treatment | 试剂 Reagent |
|---|---|
| CK | 蒸馏水Distilled water |
| EBR0.05 | 0.05 mg·L-1 EBR |
| EBR0.10 | 0.10 mg·L-1 EBR |
| EBR0.20 | 0.20 mg·L-1 EBR |
| MT50 | 50 μmol·L-1 MT |
| MT100 | 100 μmol·L-1 MT |
| MT150 | 150 μmol·L-1 MT |
| NAA10 | 10 mg·L-1 NAA |
| NAA20 | 20 mg·L-1 NAA |
| NAA30 | 30 mg·L-1 NAA |
基因名称 Gene name | 正向引物序列 Forward primer sequence (5’-3’) | 反向引物序列 Reverse primer sequence (5’-3’) |
|---|---|---|
| SlBURP2 | GCGGAGGCAATGCTTGATT | GCCACCATCTTGGGAGTTTCTA |
| SlBURP3 | CGGTGTTGATGGAACTAAGGTG | TGACAAATAGAGGGAGCACCAG |
| SlBURP5 | ACAGAGGAAGAGATTCGTGAGC | GAAGGGAATGGTTGATTGGC |
| SlBURP6 | GCAATGCGTGGCGTCTATT | TGATTTCGTCACTCTTCCGC |
| SlBURP7 | GGCAATACGCCTGTCCAAA | GACCAGCATTTCCATCGTTTC |
| SlBURP8 | GGTCGTAATGTGGTGGTTCG | CGCTTCGTAGACTCGGACTTT |
| SlBURP9 | GGTGAGACGAAACGATGTGTT | CCACCGTTGATTCCTTTGACT |
| SlBURP10 | AGACGGTGTTGTTCCTGAGC | GTATCGTTGGGATGCTTGAGTT |
| SlBURP11 | TCAAGCCAAGGTCTATCCAGC | AATGAGCGATGAGGGAACG |
| SlBURP12 | GTTGGAGGCAATAAAGGCG | AACAAACGGTGAGGGTCCA |
| SlActin | CAGGGTGTTCTTCAGGAGCAA | GGTGTTATGGTCGGAATGGG |
Table 2 Primers sequences used for RT-qPCR
基因名称 Gene name | 正向引物序列 Forward primer sequence (5’-3’) | 反向引物序列 Reverse primer sequence (5’-3’) |
|---|---|---|
| SlBURP2 | GCGGAGGCAATGCTTGATT | GCCACCATCTTGGGAGTTTCTA |
| SlBURP3 | CGGTGTTGATGGAACTAAGGTG | TGACAAATAGAGGGAGCACCAG |
| SlBURP5 | ACAGAGGAAGAGATTCGTGAGC | GAAGGGAATGGTTGATTGGC |
| SlBURP6 | GCAATGCGTGGCGTCTATT | TGATTTCGTCACTCTTCCGC |
| SlBURP7 | GGCAATACGCCTGTCCAAA | GACCAGCATTTCCATCGTTTC |
| SlBURP8 | GGTCGTAATGTGGTGGTTCG | CGCTTCGTAGACTCGGACTTT |
| SlBURP9 | GGTGAGACGAAACGATGTGTT | CCACCGTTGATTCCTTTGACT |
| SlBURP10 | AGACGGTGTTGTTCCTGAGC | GTATCGTTGGGATGCTTGAGTT |
| SlBURP11 | TCAAGCCAAGGTCTATCCAGC | AATGAGCGATGAGGGAACG |
| SlBURP12 | GTTGGAGGCAATAAAGGCG | AACAAACGGTGAGGGTCCA |
| SlActin | CAGGGTGTTCTTCAGGAGCAA | GGTGTTATGGTCGGAATGGG |
基因ID Gene ID | 基因名称 Gene name | 染色体 Chromosome | 氨基酸数量 Number of amino acids | 分子量 Molecular weight/Da | 等电点 pI | 脂肪指数 Aliphatic index | 亲水性 Hydrophilicity | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solyc01g004131.1 | SlBURP1 | 1 | 813 | 92 342.76 | 6.17 | 79.68 | -0.299 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Solyc01g004134.1 | SlBURP2 | 1 | 1 200 | 131 593.70 | 8.28 | 57.20 | -0.589 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Solyc02g000714.2 | SlBURP3 | 2 | 365 | 39 549.89 | 7.26 | 73.04 | -0.438 | 胞外Extracellular |
| Solyc02g000715.1 | SlBURP4 | 2 | 405 | 45 924.69 | 6.09 | 75.11 | -0.547 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| Solyc02g000716.1 | SlBURP5 | 2 | 264 | 30 034.04 | 7.10 | 87.54 | -0.031 | 胞外Extracellular |
| Solyc03g002688.1 | SlBURP6 | 3 | 322 | 36 324.05 | 8.54 | 84.72 | -0.248 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Solyc05g000048.2 | SlBURP7 | 5 | 337 | 38 173.93 | 7.65 | 84.69 | -0.217 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Solyc05g000050.1 | SlBURP8 | 5 | 325 | 37 217.51 | 6.05 | 76.46 | -0.303 | 胞外Extracellular |
| Solyc05g000051.1 | SlBURP9 | 5 | 611 | 66 805.31 | 6.16 | 51.72 | -0.689 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Solyc05g001003.1 | SlBURP10 | 5 | 629 | 69 069.40 | 7.93 | 58.46 | -0.632 | 胞外Extracellular |
| Solyc06g002169.1 | SlBURP11 | 6 | 693 | 76 193.18 | 9.22 | 61.07 | -0.470 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Solyc08g001592.1 | SlBURP12 | 8 | 408 | 45 869.40 | 9.02 | 76.45 | -0.262 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
Table 3 Identification and characteristics of the SlBURP gene family in tomato
基因ID Gene ID | 基因名称 Gene name | 染色体 Chromosome | 氨基酸数量 Number of amino acids | 分子量 Molecular weight/Da | 等电点 pI | 脂肪指数 Aliphatic index | 亲水性 Hydrophilicity | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solyc01g004131.1 | SlBURP1 | 1 | 813 | 92 342.76 | 6.17 | 79.68 | -0.299 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Solyc01g004134.1 | SlBURP2 | 1 | 1 200 | 131 593.70 | 8.28 | 57.20 | -0.589 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Solyc02g000714.2 | SlBURP3 | 2 | 365 | 39 549.89 | 7.26 | 73.04 | -0.438 | 胞外Extracellular |
| Solyc02g000715.1 | SlBURP4 | 2 | 405 | 45 924.69 | 6.09 | 75.11 | -0.547 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| Solyc02g000716.1 | SlBURP5 | 2 | 264 | 30 034.04 | 7.10 | 87.54 | -0.031 | 胞外Extracellular |
| Solyc03g002688.1 | SlBURP6 | 3 | 322 | 36 324.05 | 8.54 | 84.72 | -0.248 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Solyc05g000048.2 | SlBURP7 | 5 | 337 | 38 173.93 | 7.65 | 84.69 | -0.217 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Solyc05g000050.1 | SlBURP8 | 5 | 325 | 37 217.51 | 6.05 | 76.46 | -0.303 | 胞外Extracellular |
| Solyc05g000051.1 | SlBURP9 | 5 | 611 | 66 805.31 | 6.16 | 51.72 | -0.689 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Solyc05g001003.1 | SlBURP10 | 5 | 629 | 69 069.40 | 7.93 | 58.46 | -0.632 | 胞外Extracellular |
| Solyc06g002169.1 | SlBURP11 | 6 | 693 | 76 193.18 | 9.22 | 61.07 | -0.470 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Solyc08g001592.1 | SlBURP12 | 8 | 408 | 45 869.40 | 9.02 | 76.45 | -0.262 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |

Fig. 5 Interspecies colinearity analysis of BURP genesNote: At—Arabidopsis thaliana;Sl—Solanum lycopersicum;St—Solanum tuberosum;Os—Oryza sativa;Zm—Zea mays.
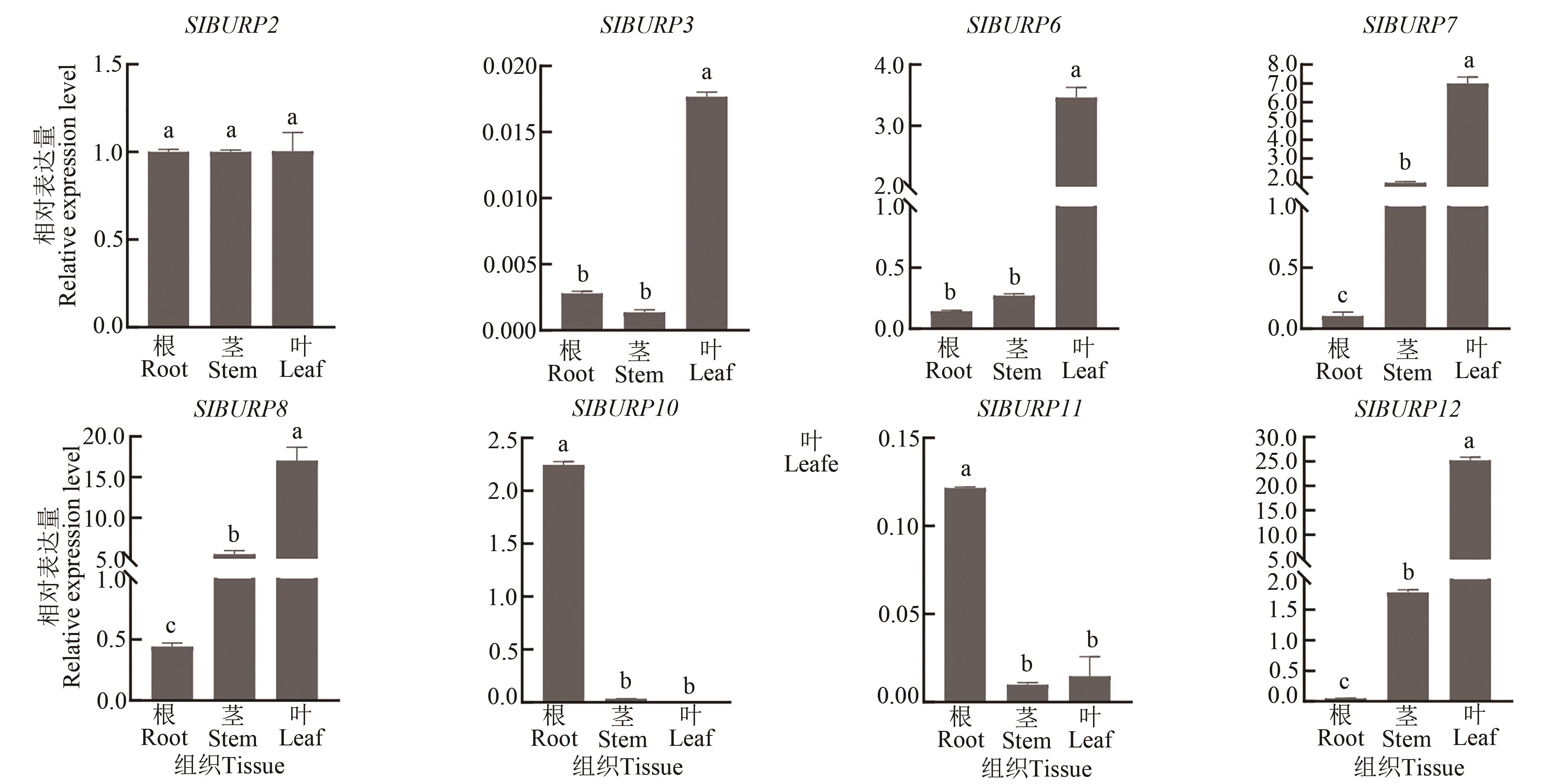
Fig. 6 Expression of SlBURPs gene in root, stem and leafNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different tissues at P<0.05 level.

Fig. 7 Expression analysis of SlBURP gene in leaves under salt stressNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at P<0.05 level.

Fig. 8 Expression of SlBURP gene during fruit development under plant growth regulators stressNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of same stage at P<0.05 level.
| 1 | PHILLIPS K, LUDIDI N. Drought and exogenous abscisic acid alter hydrogen peroxide accumulation and differentially regulate the expression of two maize RD22-like genes [J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2017, 7(1):8821 [2023-07-31]. . |
| 2 | VAN SON L, TIEDEMANN J, RUTTEN T, et al.. The BURP domain protein AtUSPL1 of Arabidopsis thaliana is destined to the protein storage vacuoles and overexpression of the cognate gene distorts seed development [J]. Plant Mol. Biol., 2009, 71(4):319-329. |
| 3 | JIN J, JEMAA E, XU Z, et al.. Arabidopsis ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE 3 directly regulates the expression of PG1β-like family genes in response to aluminum stress [J/OL]. J. Exp. Bot., 2022, 14:161 [2023-07-31]. . |
| 4 | DING X P, HOU X, XIE K B, et al.. Genome-wide identification of BURP domain-containing genes in rice reveals a gene family with diverse structures and responses to abiotic stresses [J]. Planta, 2009, 230(1):149-163. |
| 5 | KOMATSU S, NANJO Y, NISHIMURA M. Proteomic analysis of the flooding tolerance mechanism in mutant soybean [J]. J. Proteomics, 2013, 79:231-250. |
| 6 | TANG Y L, LI X J, ZHONG Y T, et al.. Functional analysis of soybean SALI3-2 in yeast [J]. Shenzhen Univ. Sci. Eng., 2007, 24:324-330. |
| 7 | GAN D, JIANG H, ZHANG J, et al.. Genome-wide analysis of BURP domain-containing genes in maize and sorghum [J]. Mol. Biol. Rep., 2011, 38(7):4553-4563. |
| 8 | YU S W, ZHANG L D, ZUO K J, et al.. Isolation and characterization of a BURP domain-containing gene BnBDC1 from Brassica napus involved in abiotic and biotic stress [J]. Physiol. Plantarum, 2004, 122(2):210-218. |
| 9 | THAMMEGOWDA H V, LE V S, CHRISTIANE S, et al.. AtRD22 and AtUSPL 1, members of the plant-specific BURP domain family involved in Arabidopsis thaliana drought tolerance [J/OL]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(10):e110065 [2023-07-31]. . |
| 10 | TEERAWANICHPAN P, XIA Q, CALDWELL S J, et al.. Protein storage vacuoles of Brassica napus zygotic embryos accumulate a BURP domain protein and perturbation of its production distorts the PSV [J]. Plant Mol. Biol., 2009, 71(4):331-343. |
| 11 | WANG A M, XIA Q, XIE W S, et al.. The classical ubisch bodies carry a sporophytically produced structural protein (RAFTIN) that is essential for pollen development [J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2003, 100:14487-14492. |
| 12 | XU X Y, YANG H K, SINGH S P, et al.. Genetic manipulation of non-classic oilseed plants for enhancement of their potential as a biofactory for triacylglycerol production [J/OL]. Engineering, 2018, 4(4):11 [2023-07-31]. . |
| 13 | XU B, GOU J Y, LI F G, et al.. A cotton BURP domain protein interacts with α-expansin and their co-expression promotes plant growth and fruit production [J]. Mol. Plant, 2013, 6(3):945-958. |
| 14 | MATUS J T, AQUEA F, ESPINOZA C, et al.. Inspection of the grapevine BURP superfamily highlights an expansion of RD22 genes with distinctive expression features in berry development and ABA-mediated stress responses [J/OL]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(10):e110372 [2023-07-31]. . |
| 15 | 宋单单,史梦雪,高金汇,等.复配型转光棚膜光学性能及其对日光温室番茄生长及果实品质的影响[J].植物生理学报,2022,58(11):2218-2226. |
| SONG D D, SHI M X, GAO J H, et al.. Optical properties of complex-type of light conversion greenhouse films and their effects on the growth and fruit qualities of tomato in solar greenhouse [J]. J. Plant Physiol., 2022, 58(11):2218-2226. | |
| 16 | 刘向蕾,尹亚红,高玉迪,等.番茄SlNPF68基因参与缺氮条件下根系觅食反应[J].植物生理学报,2022,58(7):1212-1220. |
| LIU X L, YIN Y H, GAO Y D, et al.. SlNPF68 gene involved in root foraging response under nitrogen deficiency in tomato [J]. J. Plant Physiol., 2022, 58(7):1212-1220. | |
| 17 | 万玉通,裴茂松,韦同路,等.甲基化修饰影响果实生长发育的研究进展[J].植物生理学报,2022,57(3):531-541. |
| WAN Y T, PEI M S, WEI T L, et al.. Progress of methylation modification on fruit development [J]. J. Plant Physiol., 2022, 57(3):531-541. | |
| 18 | SUN H R, WEI H L, WANG H T, et al.. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the BURP domain-containing genes in Gossypium hirsutum [J/OL]. BMC Genomics, 2019, 20:558 [2023-07-31]. . |
| 19 | XU H, LI Y, YAN Y, et al.. Genome-scale identification of soybean BURP domain-containing genes and their expression under stress treatments [J]. BMC Plant Biol., 2010, 10(1):1-16. |
| 20 | JEONG H Y, NGUYEN H P, EOM S H, et al.. Integrative analysis of pectin methylesterase (PME) and PME inhibitors in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum): identification, tissue-specific expression, and biochemical characterization [J]. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 2018, 132:557-565. |
| 21 | XU Q, DUNBRACK R L. Assignment of protein sequences to existing domain and family classification systems: Pfam and the PDB [J]. Bioinformatics, 2012, 28(21):2763-2772. |
| 22 | SONNHAMMER E, EDDY S R, DURBIN R. Pfam: a comprehensive database of protein domain families based on seed alignments [J]. Proteins, 2015, 28(3):405-420. |
| 23 | SCHULTZ J, COPLEY R R, TOBIAS D, et al.. SMART: a web-based tool for the study of genetically mobile domains [J]. Nucl. Acids Res., 2000, 28:231-234. |
| 24 | ARTIMO P, JONNALAGEDDA M, ARNOLD K, et al.. ExPASy: SIB bioinformatics resource portal [J]. Nucl. Acids Res.. 2012, 40:597-603. |
| 25 | HORTON P, PARK K J, OBAYASHI T, et al.. WoLF PSORT: protein localization predictor [J]. Nucl. Acids Res., 2007, 35:585-587. |
| 26 | KUMAR S, STECHER G, TAMURA K. MEGA7 molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets [J]. Mol. Biol. Evol., 2015, 33:1870-1874. |
| 27 | CHEN C, CHEN H, ZHANG Y, et al.. TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data [J/OL]. Mol. Plant, 2020, 13(8):009 [2023-07-31] . |
| 28 | ROMBAUTS, DEHAIS, MONTAGU V, et al.. PlantCARE, a plant cis-acting regulatory element database [J]. Nucl. Acids Res., 1999, 27:295-296. |
| 29 | LIVAK K J, SCHMITTGEN T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2- ΔΔ CT [J]. Methods, 2001, 25:492-508. |
| 30 | 张中保,吴忠义,魏建华.玉米BURP家族基因的鉴定和分析[J].玉米科学,2014,22(3):36-42. |
| ZHANG Z B, WU Z Y, WEI J H. Genome-wide analysis and identification of ZmBURP genes family in maize [J]. J. Maize Sci., 2014, 22(3):36-42. | |
| 31 | SHAO Y H, WEI G, WANG L, et al.. Genome-wide analysis of BURP domain-containing genes in Populus trichocarpa [J]. J. Integr. Plant Biol., 2011, 53(9):743-755. |
| 32 | GRANGER C, CORYELL V, KHANNA A, et al.. Identification, structure, and differential expression of members of a BURP domain containing protein family in soybean [J/OL]. Genome, 2002, 45(4):693 [2023-07-31]. . |
| 33 | LI Y, CHEN X, CHEN Z, et al.. Identification and expression analysis of BURP domain-containing genes in Medicago truncatula [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2016, 7:485 [2023-07-31]. . |
| 34 | YU S W, ZHANG L D, ZUO K J, et al.. Isolation and characterization of a BURP domain-containing gene BnBDC1 from Brassica napus involved in abiotic and biotic stress [J]. Physiol. Plantarum, 2004, 100:210-218. |
| 35 | WANG H M, ZHOU L, FU Y P, et al.. Expression of an apoplast-localized BURP-domain protein from soybean (GmRD22) enhances tolerance towards abiotic stress [J]. Plant Cell Environ., 2012, 35(11):1932-4197. |
| 36 | 米子岚,钟活权,江年琼,等.BURP蛋白家族与植物对非生物胁迫的响应[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2015, 37(9):1302-1308. |
| MI Z L, ZHONG H Q, JIANG N Q, et al.. BURP Proteins Family and the Response of Plant to Abiotic Stress [J]. J. Cell Biol., 2015, 37(9):1302-1308. | |
| 37 | WANG L H, WU N N, ZHU Y, et al.. The divergence and positive selection of the plant-specific BURP-containing protein family [J]. Ecol. Evol., 2015, 5(22):5394-5412. |
| [1] | Junlei ZHANG, Xiaotong GE, Zhengting ZHAO, Di LIU, Jinfeng WANG, Ning JIANG, Yating LIU. Establishment and Optimization of RT-LAMP Assay System for Tobacco Tomato Spotted Wilt Virus [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(8): 140-150. |
| [2] | Zifan WANG, Yan LI, Qingyin ZHANG, Dandan WANG, Jianhua SHI, Xiaobin GENG, Dongliang TIAN, Zengming ZHONG, Xiaoming ZHAO, Lianfen QI. Effect of Microbicides on Main Diseases and Soil Microbial Communities of Tomatoes in Facilities [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(6): 102-112. |
| [3] | Mingbo LI, Yule LIU, Zhimin MU, Junwang GUO, Yong WEI, Dongyue REN, Jishen JIA, Zezhong WEI, Yuhong LI. Tomato Fruit Recognition Based on YOLOX-L-TN Model [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(4): 97-105. |
| [4] | Shuang LI, Aiying WANG, Zhen JIAO, Qing CHI, Hao SUN, Tao JIAO. Physiological and Chemical Characteristics and Transcriptome Analysis of Different Type of Wheat Seedlings Under Salt Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(2): 20-32. |
| [5] | Yurong DENG, Lian HAN, Jinlong WANG, Xinghan WEI, Xudong WANG, Ying ZHAO, Xiaohong WEI, Chaozhou LI. Identification of SOD Family Genes in Chenopodium quinoa and Their Response to Mixed Saline-alkali Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(1): 28-39. |
| [6] | Xuemin JIANG, Xiangqian CHEN, Hongyan LI, Qiyan JIANG. Metabolomic Analysis of Wheat Response to Salt Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 43-56. |
| [7] | Dengyang LU, Xin WANG, Zhanghu TANG, Cuiyun WU, Yunfeng PU, Min YAN, Jingkai BAO, Xi JIANG. Phenolic Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Pear Species During Fruit Development Comparison [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 97-104. |
| [8] | Yulu WU, Jiaxin HU, Yuxi CHEN, Bingsong ZHENG, DaoLiang YAN. Effects of External Application of α-Ketoglutarate on Growth, Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus Accumulation and Their Stoichiometric Relationships in Kosteletzkya virginica Under Salt Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 170-177. |
| [9] | Zhonghua MA, Juan CHEN, Na WU, Benju MAN, Xiaogang WANG, Yongqing ZHE, Jili LIU. Effects of Salt Stress and Phosphorus Supply on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Total Biomass of Switchgrass at Seedling Stage [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(6): 190-200. |
| [10] | Fan ZHANG, Hong WANG, Xuebing ZHANG, Jianjun CHEN. Physiological and Biochemical Responses of Peach Self-rooted Rootstock to NaCl and Analysis of Salt Tolerance Threshold [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(11): 70-79. |
| [11] | Feng LI, Congpei YIN, Ran YIN, Fan WANG, Yongliang HAN, Zhimin YANG, Jiancheng LIU. Response of Rhizosphere Soil Bacterial Community Diversity to Salt Stress in Oat (Avena sativa L.) [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(1): 153-165. |
| [12] | Xiubo XIA, Tao LI, Shoujun CAO, Jiangang YAO, Hongyun WANG, Lili ZHANG. Effect of Liquid Organic Fertilizer Partial Replacing Chemical Fertilizer on Bacterial Community in Greenhouse Tomato Root Zone [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(7): 187-196. |
| [13] | Yanling HAO, Wei YAN. Effects of Mixed Salt Stress on Morphological and Physiological Indexes of Ulmus pumila Seedlings [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(7): 69-76. |
| [14] | Wengyou TIAN, Hao LIU, Chaolin GAN, Liufen WU, Ai LI, Lifang YANG, Ying GAO. Photosynthetic Response and Spectral Characteristics of Cherry Rootstocks Under Salt Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(3): 77-83. |
| [15] | Jinfeng ZHAO, Aili YU, Yanfang LI, Yanwei DU, Gaohong WANG, Zhenhua WANG. Response Characteristics of SiCBL3 to Abiotic Stresses in Foxtail Millet [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(11): 68-75. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号