




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (11): 70-79.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0271
收稿日期:2023-04-06
接受日期:2023-06-14
出版日期:2023-11-15
发布日期:2023-11-20
通讯作者:
王鸿
作者简介:张帆 E-mail: zhfan528@163.com;
基金资助:
Fan ZHANG( ), Hong WANG(
), Hong WANG( ), Xuebing ZHANG, Jianjun CHEN
), Xuebing ZHANG, Jianjun CHEN
Received:2023-04-06
Accepted:2023-06-14
Online:2023-11-15
Published:2023-11-20
Contact:
Hong WANG
摘要:
为研究NaCl胁迫下桃自根砧生长及生理生化指标变化,确定桃自根砧耐盐阈值,选择苗龄为1年的樱桃李(Prunus cerasifera Ehrhart)1号(李1)、樱桃李3号(李3)、樱桃李5号(李5)、RA (Prunus cerasifera Ehrhart)和GF677(Prunus dulcis Mill.×Prunus persica)桃砧木扦插苗为试材进行NaCl处理(质量体积分数0.2%、0.4%和0.6%NaCl)试验。结果表明,随着基质中NaCl含量的增加,5种桃砧木扦插苗的超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)活性和丙二醛(malondialdehyde,MDA)含量均呈上升趋势;过氧化物酶(peroxidase,POD)活性在李1、李3中先升后降,在李5、GF677中则相反,在RA中呈上升趋势;过氧化氢酶(catalase,CAT)活性在李1、李3、RA中呈上升趋势,在李5中呈下降趋势,在GF677则先升后降。脯氨酸(proline,Pro)含量在李1和RA中呈上升趋势,在李3和李5中先降后升,在GF677中先升后降。可溶性糖含量在李1、RA中先升后降,在李3和李5中呈上升趋势,在GF677中先降后升。相关性分析表明,Na+水平与基质中NaCl含量成正相关,而K+水平则与其呈负相关关系。李1的Na+/K+最大,GF677最小。在NaCl胁迫下,5种自根砧叶绿素合成明显受到抑制,荧光动力学参数以及光能吸收、捕获和传递参数均降低,快速叶绿素荧光诱导曲线(OJIP)发生变化,其中J、I、P 相降低,且ΔK小于0。以净光合速率为指标,李1、李3、李5、RA和GF677的耐盐性阈值分别为0.37%、0.43%、0.38%、0.46%和0.49% NaCl。综合隶属函数、耐盐系数及耐盐阈值,砧木耐盐性从高到低表现为GF677>RA>李3>李5>李1。综上所述,5种桃自根砧主要通过活性氧清除和渗透调节机制来适应盐胁迫,耐盐性高的砧木能较好地稳定光合反应中心,缓解盐胁迫对其光合系统的伤害。以上结果为揭示耐盐机理及桃耐盐砧木品种的筛选提供理论支撑。
中图分类号:
张帆, 王鸿, 张雪冰, 陈建军. 桃自根砧对NaCl生理生化响应及耐盐阈值分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(11): 70-79.
Fan ZHANG, Hong WANG, Xuebing ZHANG, Jianjun CHEN. Physiological and Biochemical Responses of Peach Self-rooted Rootstock to NaCl and Analysis of Salt Tolerance Threshold[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(11): 70-79.
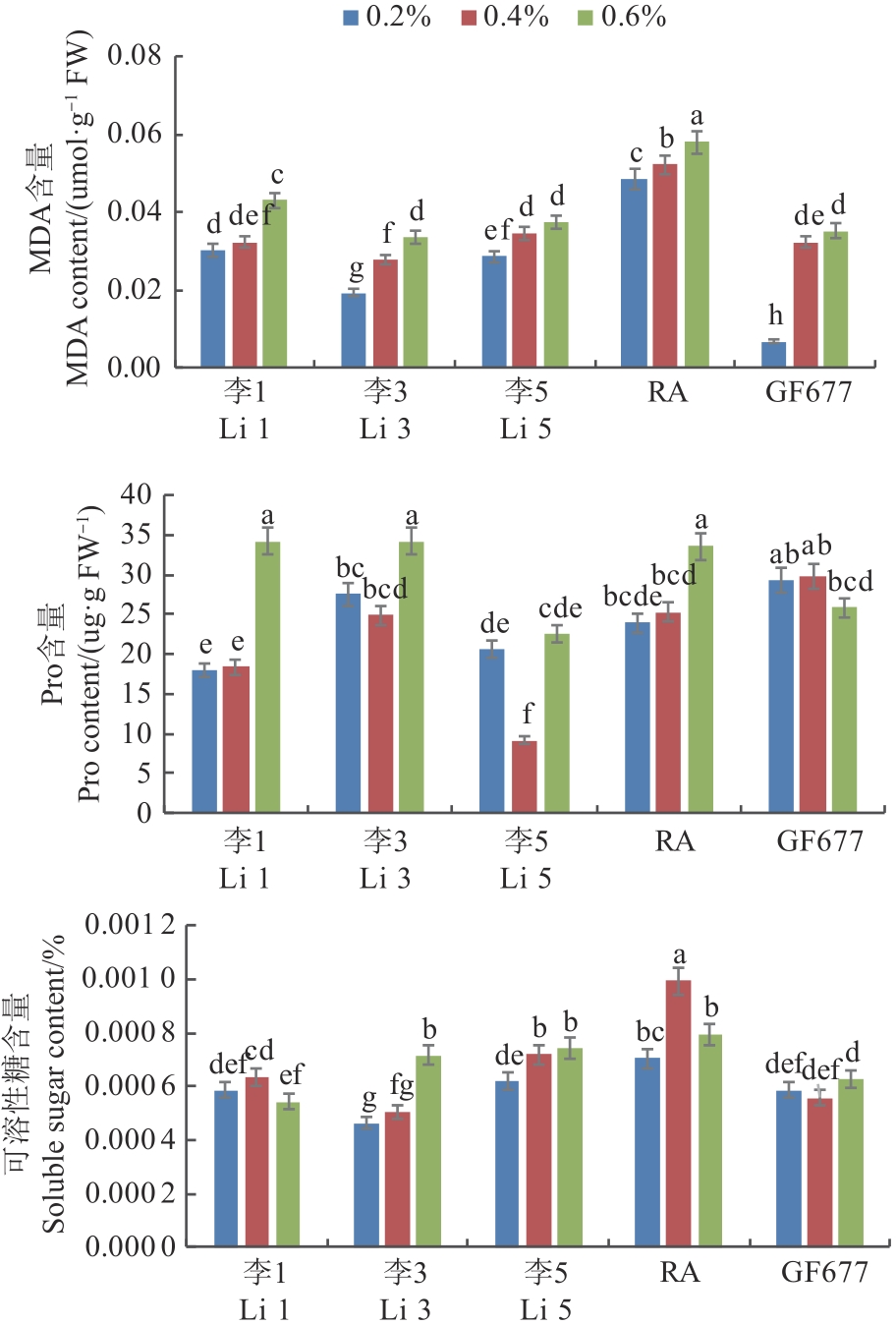
图1 盐胁迫下桃自根砧叶片的MDA、Pro和可溶性糖含量注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 Contents of MDA, Pro and soluble sugar in leaves of peach self-rooted rootstock under salt stressNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
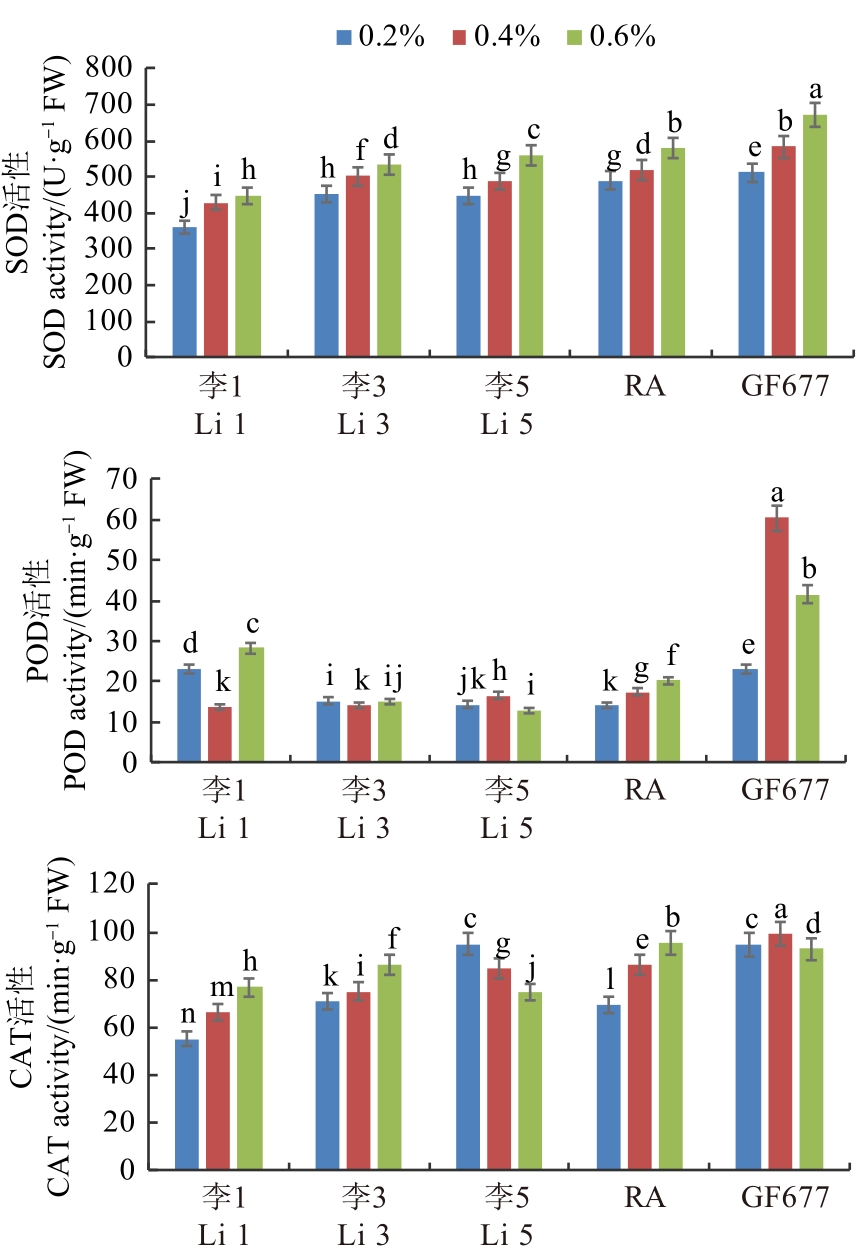
图2 盐胁迫下桃自根砧叶片的SOD、POD和CAT活性注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 Activities of SOD, POD and CAT in leaves of peach self-rooted rootstock under salt stressNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
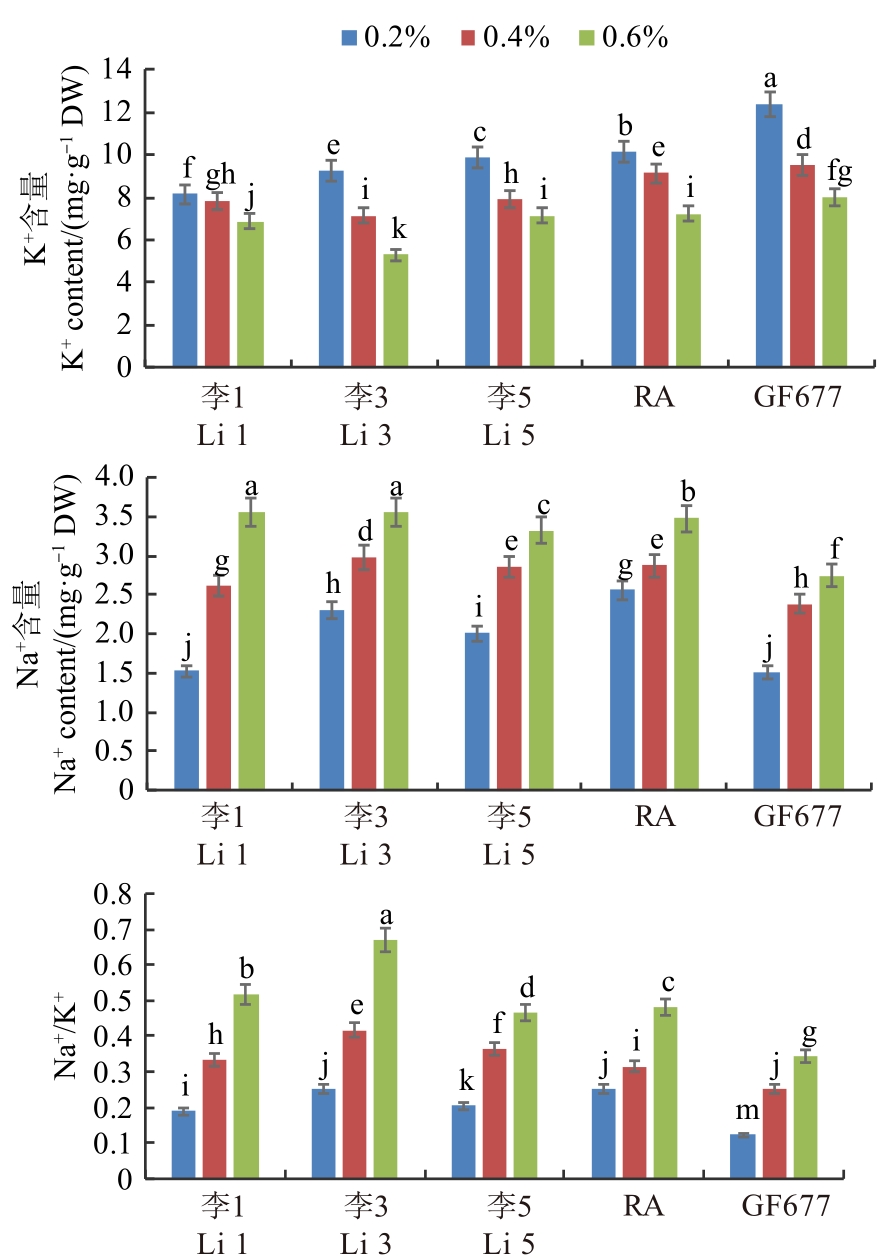
图3 盐胁迫下桃自根砧叶片的K+、Na+含量和Na+/K+注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 3 Contents of K+, Na+ and Na+/K+ ratio in leaves of peach self-rooted rootstock under salt stressNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
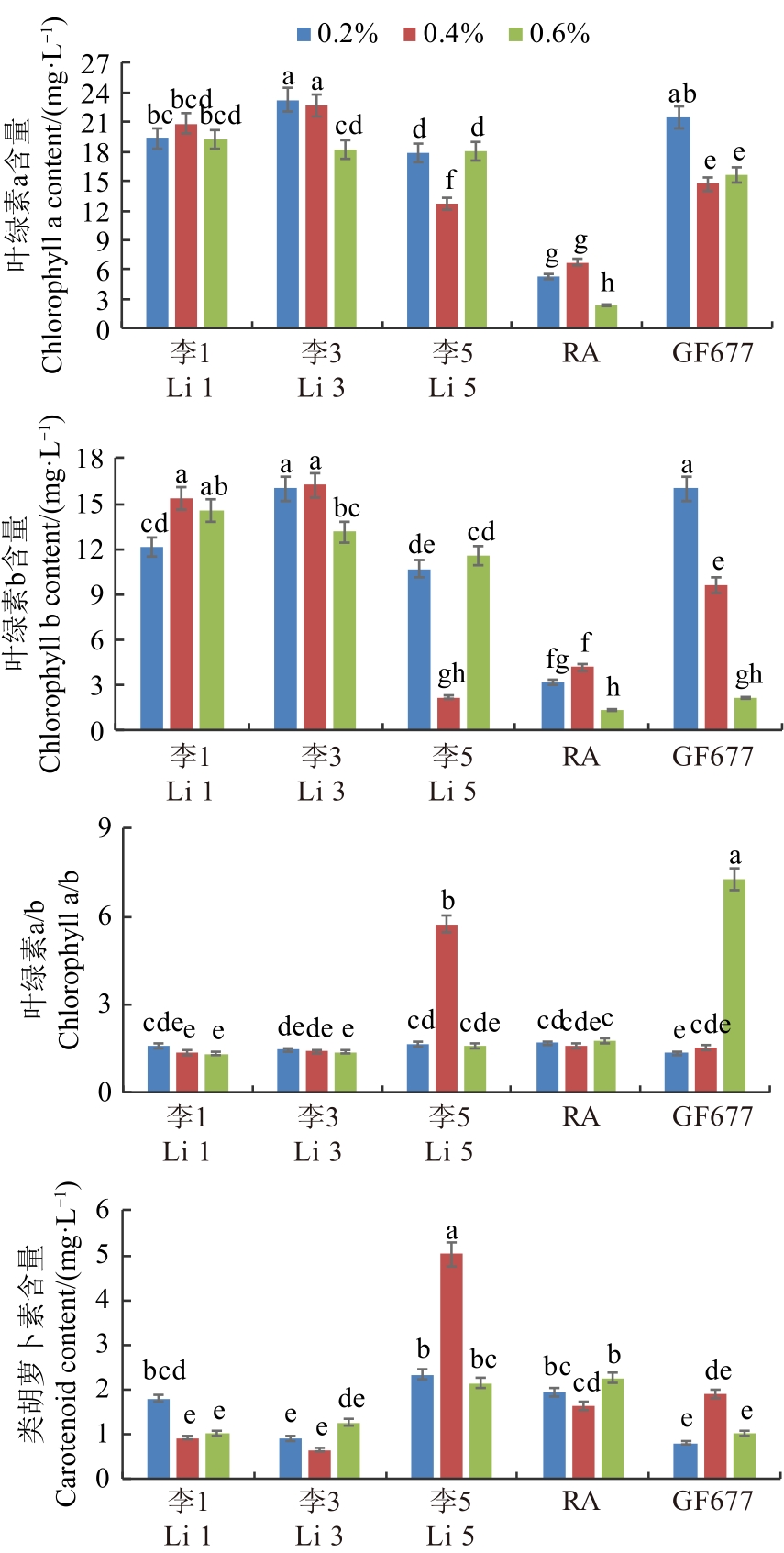
图4 盐胁迫下桃自根砧叶片的叶绿素a、叶绿素b、叶绿素a/b及类胡萝卜素含量注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 4 Contents of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, carotenoid and chlorophyll a/b value in leaves of peach self-rooted rootstock under salt stressNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 品种Variety | NaCl含量 NaCl content/% | Fv/Fm | φEo | φRo | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
李1 Li 1 | 0.2 | 0.829±0.011 abc | 1.959±0.331 b | 0.798±0.20 cdef | 1.221±0.168 ab | 0.401±0.035 efg |
| 0.4 | 0.671±0.032 e | 0.183±0.002 c | 0.195±0.001 ef | 0.898±0.068 bc | 0.459±0.040 ef | |
| 0.6 | 0.632±0.011 f | 0.008±0.001 c | 0.011±0.000 f | 0.284±0.005 d | 0.464±0.035 e | |
李3 Li 3 | 0.2 | 0.832±0.004 abc | 3.425±0.476 ab | 1.765±0.376 abc | 0.975±0.052 bc | 0.448±0.041 efg |
| 0.4 | 0.831±0.005 abc | 3.130±0.010 ab | 1.704±0.120 abcd | 1.196±0.041 b | 0.346±0.002 g | |
| 0.6 | 0.825±0.015 abc | 2.741±1.156 ab | 1.087±0.007 cde | 0.632±0.020 c | 0.503±0.035 de | |
李5 Li 5 | 0.2 | 0.810±0.040 bc | 1.995±0.366 b | 1.582±0.657 bcd | 0.883±0.078 bc | 0.351±0.023 fg |
| 0.4 | 0.805±0.003 c | 2.196±2.128 b | 0.957±0.999 cdef | 1.149±0.125 b | 0.570±0.113 cd | |
| 0.6 | 0.723±0.006 d | 2.694±0.621 ab | 0.701±0.139 def | 0.927±0.575 bc | 0.406±0.047 efg | |
| RA | 0.2 | 0.838±0.001 ab | 3.417±0.043 ab | 1.532±0.154 bcd | 1.222±0.196 ab | 0.668±0.078 c |
| 0.4 | 0.834±0.008 ab | 3.241±0.69 ab | 1.508±0.460 bcd | 1.096±0.052 b | 0.624±0.129 c | |
| 0.6 | 0.832±0.006 ab | 3.125±0.84 ab | 1.471±0.510 bcd | 0.897±0.268 bc | 0.622±0.023 c | |
| GF677 | 0.2 | 0.845±0.002 a | 4.364±1.06 a | 2.611±1.200 a | 1.539±0.015 a | 1.557±0.001 a |
| 0.4 | 0.843±0.007 a | 4.018±0.498 a | 2.125±0.499 ab | 1.159±0.010 b | 1.075±0.007 b | |
| 0.6 | 0.841±0.003 a | 4.023±0.414 a | 1.784±0.376 abc | 1.111±0.129 b | 0.616±0.083 c |
表1 盐胁迫对桃自根砧叶片的快速荧光动力学参数
Table 1 Fast fluorescence kinetic parameters of peach self-rooted rootstock leaves under salt stress
| 品种Variety | NaCl含量 NaCl content/% | Fv/Fm | φEo | φRo | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
李1 Li 1 | 0.2 | 0.829±0.011 abc | 1.959±0.331 b | 0.798±0.20 cdef | 1.221±0.168 ab | 0.401±0.035 efg |
| 0.4 | 0.671±0.032 e | 0.183±0.002 c | 0.195±0.001 ef | 0.898±0.068 bc | 0.459±0.040 ef | |
| 0.6 | 0.632±0.011 f | 0.008±0.001 c | 0.011±0.000 f | 0.284±0.005 d | 0.464±0.035 e | |
李3 Li 3 | 0.2 | 0.832±0.004 abc | 3.425±0.476 ab | 1.765±0.376 abc | 0.975±0.052 bc | 0.448±0.041 efg |
| 0.4 | 0.831±0.005 abc | 3.130±0.010 ab | 1.704±0.120 abcd | 1.196±0.041 b | 0.346±0.002 g | |
| 0.6 | 0.825±0.015 abc | 2.741±1.156 ab | 1.087±0.007 cde | 0.632±0.020 c | 0.503±0.035 de | |
李5 Li 5 | 0.2 | 0.810±0.040 bc | 1.995±0.366 b | 1.582±0.657 bcd | 0.883±0.078 bc | 0.351±0.023 fg |
| 0.4 | 0.805±0.003 c | 2.196±2.128 b | 0.957±0.999 cdef | 1.149±0.125 b | 0.570±0.113 cd | |
| 0.6 | 0.723±0.006 d | 2.694±0.621 ab | 0.701±0.139 def | 0.927±0.575 bc | 0.406±0.047 efg | |
| RA | 0.2 | 0.838±0.001 ab | 3.417±0.043 ab | 1.532±0.154 bcd | 1.222±0.196 ab | 0.668±0.078 c |
| 0.4 | 0.834±0.008 ab | 3.241±0.69 ab | 1.508±0.460 bcd | 1.096±0.052 b | 0.624±0.129 c | |
| 0.6 | 0.832±0.006 ab | 3.125±0.84 ab | 1.471±0.510 bcd | 0.897±0.268 bc | 0.622±0.023 c | |
| GF677 | 0.2 | 0.845±0.002 a | 4.364±1.06 a | 2.611±1.200 a | 1.539±0.015 a | 1.557±0.001 a |
| 0.4 | 0.843±0.007 a | 4.018±0.498 a | 2.125±0.499 ab | 1.159±0.010 b | 1.075±0.007 b | |
| 0.6 | 0.841±0.003 a | 4.023±0.414 a | 1.784±0.376 abc | 1.111±0.129 b | 0.616±0.083 c |
| 品种Variety | NaCl含量 NaCl content/% | ABC/CSm | TRo/CSm | ETO/CSm | RC/CSm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
李1 Li 1 | 0.2 | 1 969.00±26.664 ab | 1 479.00±158.072 ab | 746.00±94.000 ab | 275.33±10.682 abc |
| 0.4 | 1 725.33±5.131 b | 1 433.33±1.527 ab | 696.67±185.403 ab | 201.33±74.865 cde | |
| 0.6 | 1 705.33±5.231 b | 1 410.67±431.430 ab | 678.67±397.945 ab | 155.33±1.763 e | |
李3 Li 3 | 0.2 | 1 846.67±89.001 ab | 1 674.906±128 ab | 882.67±64.663 ab | 276.50±6.639 abc |
| 0.4 | 1 961.00±1.000 ab | 1 583.33±0.577 ab | 841.00±61.991 ab | 247.33±0.333 abcd | |
| 0.6 | 1 846.50±100.500 ab | 1 524.50±110.500 ab | 831.00±73.000 ab | 215.00±23.094 bcde | |
李5 Li 5 | 0.2 | 2 000.00±85.422 ab | 1 654.67±1.527 ab | 772. 00±59.000 ab | 209.00±38.214 bcde |
| 0.4 | 1 816.33±51.286 ab | 1 510.00±43.863 ab | 707.00±35.552 ab | 183.33±4.484 de | |
| 0.6 | 1 778.33±106.800 ab | 1 398.67±216.705 abc | 591.33±366.444 b | 148.00±0.577 e | |
| RA | 0.2 | 1 903.00±1.000 ab | 1 677.00±87.298 ab | 890.67±7.094 ab | 290.67±27.088 abc |
| 0.4 | 1 755.67±188.797 ab | 1 658.33±34.789 ab | 823.00±2.000 ab | 280.33±20.177 abc | |
| 0.6 | 1 896.00±140.000 ab | 1 574.00±136.000 ab | 791. 00±2.000 ab | 275.33±35.025 bcd | |
| GF677 | 0.2 | 2 028.67±6.806 a | 1 693.33±7.2342 a | 961.00±1.000 a | 329.33±14.858 a |
| 0.4 | 1 972.00±48.692 ab | 1 562.50±77.500 ab | 920.33±94.659 a | 321.33±28.309 a | |
| 0.6 | 1 862.50±78.500 ab | 1 658.33±39.106 ab | 866. 33±4.932 ab | 296.50±17.031 ab |
表2 盐胁迫下桃自根砧叶片的光能吸收、捕获和传递
Table 2 Light energy absorption, capture and transmission of peach self-rooted rootstock leaves under salt stress
| 品种Variety | NaCl含量 NaCl content/% | ABC/CSm | TRo/CSm | ETO/CSm | RC/CSm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
李1 Li 1 | 0.2 | 1 969.00±26.664 ab | 1 479.00±158.072 ab | 746.00±94.000 ab | 275.33±10.682 abc |
| 0.4 | 1 725.33±5.131 b | 1 433.33±1.527 ab | 696.67±185.403 ab | 201.33±74.865 cde | |
| 0.6 | 1 705.33±5.231 b | 1 410.67±431.430 ab | 678.67±397.945 ab | 155.33±1.763 e | |
李3 Li 3 | 0.2 | 1 846.67±89.001 ab | 1 674.906±128 ab | 882.67±64.663 ab | 276.50±6.639 abc |
| 0.4 | 1 961.00±1.000 ab | 1 583.33±0.577 ab | 841.00±61.991 ab | 247.33±0.333 abcd | |
| 0.6 | 1 846.50±100.500 ab | 1 524.50±110.500 ab | 831.00±73.000 ab | 215.00±23.094 bcde | |
李5 Li 5 | 0.2 | 2 000.00±85.422 ab | 1 654.67±1.527 ab | 772. 00±59.000 ab | 209.00±38.214 bcde |
| 0.4 | 1 816.33±51.286 ab | 1 510.00±43.863 ab | 707.00±35.552 ab | 183.33±4.484 de | |
| 0.6 | 1 778.33±106.800 ab | 1 398.67±216.705 abc | 591.33±366.444 b | 148.00±0.577 e | |
| RA | 0.2 | 1 903.00±1.000 ab | 1 677.00±87.298 ab | 890.67±7.094 ab | 290.67±27.088 abc |
| 0.4 | 1 755.67±188.797 ab | 1 658.33±34.789 ab | 823.00±2.000 ab | 280.33±20.177 abc | |
| 0.6 | 1 896.00±140.000 ab | 1 574.00±136.000 ab | 791. 00±2.000 ab | 275.33±35.025 bcd | |
| GF677 | 0.2 | 2 028.67±6.806 a | 1 693.33±7.2342 a | 961.00±1.000 a | 329.33±14.858 a |
| 0.4 | 1 972.00±48.692 ab | 1 562.50±77.500 ab | 920.33±94.659 a | 321.33±28.309 a | |
| 0.6 | 1 862.50±78.500 ab | 1 658.33±39.106 ab | 866. 33±4.932 ab | 296.50±17.031 ab |
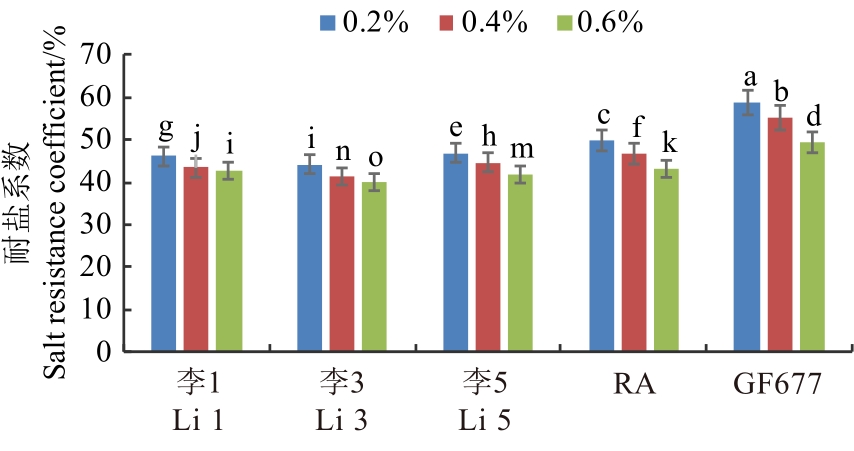
图6 盐胁迫下桃自根砧叶片的耐盐系数注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 6 Tolerance coefficient of leaves in peach self-rooted rootstock under salt stressNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 品 种Variety | 叶绿素Chlorophyll | 丙二醛MDA | 脯氨酸Pro | 可溶性糖Soluble sugar | 超氧化物歧化酶SOD | 过氧化物酶POD | 过氧化氢酶CAT | Na+ | K+ | 均值Mean | 排序Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 李1 Li 1 | 0.84 | 0.57 | 0.54 | 0.38 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 0.32 | 0.42 | 5 |
| 李3 Li 3 | 0.91 | 0.39 | 0.61 | 0.34 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 0.50 | 0.68 | 0.27 | 0.51 | 3 |
| 李5 Li 5 | 0.67 | 0.50 | 0.24 | 0.44 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.67 | 0.58 | 0.42 | 0.49 | 4 |
| RA | 0.12 | 0.90 | 0.59 | 0.72 | 0.54 | 0.54 | 0.65 | 0.69 | 0.5 | 0.58 | 2 |
| GF677 | 0.91 | 0.51 | 0.62 | 0.41 | 0.73 | 0.73 | 0.92 | 0.33 | 0.66 | 0.66 | 1 |
表3 不同桃自根砧品种抗盐指标的隶属度分析
Table 3 Membership analysis of salt resistance indexes of different peach self-rooted rootstock
| 品 种Variety | 叶绿素Chlorophyll | 丙二醛MDA | 脯氨酸Pro | 可溶性糖Soluble sugar | 超氧化物歧化酶SOD | 过氧化物酶POD | 过氧化氢酶CAT | Na+ | K+ | 均值Mean | 排序Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 李1 Li 1 | 0.84 | 0.57 | 0.54 | 0.38 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 0.32 | 0.42 | 5 |
| 李3 Li 3 | 0.91 | 0.39 | 0.61 | 0.34 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 0.50 | 0.68 | 0.27 | 0.51 | 3 |
| 李5 Li 5 | 0.67 | 0.50 | 0.24 | 0.44 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.67 | 0.58 | 0.42 | 0.49 | 4 |
| RA | 0.12 | 0.90 | 0.59 | 0.72 | 0.54 | 0.54 | 0.65 | 0.69 | 0.5 | 0.58 | 2 |
| GF677 | 0.91 | 0.51 | 0.62 | 0.41 | 0.73 | 0.73 | 0.92 | 0.33 | 0.66 | 0.66 | 1 |
| 1 | 马翠兰,刘星辉,陈中海.果树对盐胁迫的反应及耐盐性鉴定的研究进展[J].福建农业大学学报,2000(2):161-166. |
| MA C L, LIU X H, CHEN Z H. Advances in response of fruit trees to salt stress and their salt-tolerance identification [J]. J. Fujian Agric. For. Univ., 2000(2):161-166. | |
| 2 | 郭天文,郭全恩,王益权,等.钠盐胁迫对苹果树体内钠累积的影响[J].核农学报,2009,23(2):354-357, 184. |
| GUO T W, GUO Q E, WANG Y Q, et al.. Effect of sodic salinity stress on sodium accumulation in trees [J]. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci., 2009, 23(2):354-357, 184. | |
| 3 | 郁万文,蔡金峰,高长忠.不同桃砧类型对盐胁迫的生理响应及耐盐性评价[J].北方园艺,2016(12):1-6. |
| YU W W, CAI J F, GAO C Z. Physiological responsesof different peach rootstocks salt stressand and their salt tolerance evaluation [J]. Northern Hortic., 2016(12):1-6. | |
| 4 | 张帆,王鸿, 张雪冰,等.干旱胁迫及复水对不同桃自根砧生理特性影响[J].植物生理学报,2022,58(4):767-776. |
| ZHANG F, WANG H, ZHANG X B, et al.. ffects of drought stress and rehydration on physiological characteristics of different peach rootstocks [J]. Plant Physiol. J., 2022, 58(4):767-776. | |
| 5 | 张帆,王鸿.基质和激素对桃砧木GF677硬枝扦插生根的影响[J].林业科技通讯,2018(12):53-56. |
| ZHANG F, WANG H. Effects of substrates and hormones on rooting of peach rootstock GF677 hardwood cutting [J]. For. Sci. Tech. Comm., 2018(12):53-56. | |
| 6 | 宋海岩,陈栋,李靖,等.碱性土上GF677与毛桃叶片叶绿素合成及叶绿体结构差异性研究[J].西南农业学报,2018,31(12):2630-2637. |
| SONG H Y, CHEN D, LI J, et al.. Chlorophyll synthesis and chloroplast structure comparison research between GF677 and wild peach on alkaline soil [J]. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci., 2018, 31(12):2630-2637. | |
| 7 | 朱炜,龚林忠,王富荣,等.5个桃砧木品种对淹水胁迫的生理响应及耐涝性评价[J].南方农业学报,2022,53(10):2937-2945. |
| ZHU W, GONG L Z, WANG F R, et al.. Physiological responses and waterlogging tolerance evaluation of five peach rootstock varieties under waterlogging stress [J]. J. Southern Agric., 2022, 53(10):2937-2945. | |
| 8 | 李合生.植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2000. |
| 9 | 杜远鹏,晋学娟,郭淑华,等.不同盐碱类型胁迫对红地球/贝达葡萄植株离子分布的影响[J].应用生态学报,2015,26(6):1801-1806. |
| DU Y P, JIN X J, GUO S H, et al.. Effects of different salt alkali types of stress on ion distribution in red globe/beida grape plants [J]. J. Appl. Ecol., 2015, 26(6):1801-1806. | |
| 10 | 赵天然,车路平,谢会成,等.流苏树对NaCl的生理响应及耐盐阈值分析[J].植物生理学报,2022,58(10):1935-1945. |
| ZHAO T R, CHE L P, XIE H C, et al.. Physiological response and salt tolerance threshold analysis of tassel trees to NaCl [J]. Plant Physiol. J., 2022, 58(10):1935-1945. | |
| 11 | 张瑞,贾旭梅,朱祖雷,等.'烟富六号'苹果在不同砧木上响应盐碱胁迫的光合及生理特性[J].果树学报,2019,36(6):718-728. |
| ZHANG R, JIA X M, ZHU Z L, et al.. Photosynthesis and physiological characteristics of ‘Yanfu 6’ apple under saline-alkali stress on different rootstocks [J]. J. Fruit Sci., 2019, 36(6):718-728. | |
| 12 | 吴强盛,刘琴.果树对盐胁迫的响应和耐盐机制研究进展[J].长江大学学报(自科版),2007(4):9-12, 22. |
| WU Q S, LIU Q, Research progress on the response and salt tolerance mechanism of fruit trees to salt stress [J]. J. Changjiang Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2007(4):9-12, 22. | |
| 13 | 魏婧,徐畅,李可欣,等.超氧化物歧化酶的研究进展与植物抗逆性[J].植物生理学报,2020,56(12):2571-2584. |
| WEI J, XU C, LI K X, et al.. Research progress of superoxide dismutase and plant stressresistance [J]. Plant Physiol. J., 2020, 56(12):2571-2584. | |
| 14 | ZELM E V, ZHANG Y X, TESTERINK C. Salt tolerance mechanisms of plants [J]. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol., 2020, 71:403-433. |
| 15 | FRANCISCO G, NICOLAS D, ANA Q, et al.. Transcriptomic analysis reveals salt tolerance mechanisms present in date-plum persimmon rootstock (Diospyros lotus L) [J/OL]. Agronomy, 2020, 10:1703 [2023-03-02]. . |
| 16 | ANALIA L, MARÍA V P, CLAUDIA V, et al.. Molecular control to salt tolerance mechanisms of woody plants: recent achievements and perspectives [J/OL]. Ann. Forest Sci., 2021, 78:96 [2023-03-02]. . |
| 17 | 李赵嘉,左永梅,宋明月,等.盐胁迫对大叶蒲公英生长生理指标及耐盐阈值的影响[J].中药材,2020,43(7):1558-1562. |
| LI Z J, ZUO Y M, SONG M Y, et al.. Effects of salt stress on physiological indicators and salt tolerance threshold of dandelion growth [J]. Chin. Med. Herbs, 2020, 43(7):1558-1562. |
| [1] | 高静娟, 朱晨宇, 柯玉琴, 郑朝元, 李春英, 李文卿. 烟稻轮作条件下有机肥施用时期对烤烟碳氮代谢的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 157-165. |
| [2] | 姜雪敏, 陈向前, 李红燕, 姜奇彦. 小麦盐胁迫响应的代谢组学分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 43-56. |
| [3] | 吴雨露, 扈嘉鑫, 陈宇熙, 郑炳松, 闫道良. 外施α-酮戊二酸对盐胁迫下海滨锦葵生长、碳氮磷养分积累及其计量关系的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 170-177. |
| [4] | 麻仲花, 陈娟, 吴娜, 满本菊, 王晓港, 者永清, 刘吉利. 盐胁迫与供磷水平对柳枝稷苗期光合特性与总生物量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 190-200. |
| [5] | 张一龙, 孙晓梵, 李硕, 李培英, 孙宗玖. 不同抗旱性狗牙根种质的抗旱生理响应差异分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 59-70. |
| [6] | 李峰, 殷丛培, 殷冉, 王凡, 韩永亮, 杨志敏, 刘建成. 燕麦根际土壤细菌多样性对盐胁迫的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(1): 153-165. |
| [7] | 郝艳玲, 闫伟. 混合盐胁迫对白榆幼苗形态及生理指标的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(7): 69-76. |
| [8] | 田翁由, 刘昊, 甘超林, 伍柳芬, 李爱, 杨丽芳, 高英. 盐胁迫下樱桃砧木的光合响应和光谱特性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(3): 77-83. |
| [9] | 李江艳, 张鲜花, 袁小强. 鸭茅种质资源苗期抗旱指标筛选及抗旱评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(3): 84-94. |
| [10] | 张胜珍, 马艳芝. 氯化钙对盐胁迫下荆芥种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响 [J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(7): 65-71. |
| [11] | 胡杨, 李钢铁, 李星, 贾守义. 干旱胁迫对细穗柽柳幼苗生长和生理生化指标的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(6): 43-50. |
| [12] | 孙艳, 蒲文宣, 吴长征, 黄平俊, 孙铭雪, 宋德安, 刘来华. 植物响应亚适低温的生长发育及分子机制研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(5): 18-26. |
| [13] | 李星, 胡杨, 马媛, 贾守义, 李钢铁. 细穗柽柳对3种单盐胁迫的生理响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(5): 52-60. |
| [14] | 张茂,徐彦红,席溢*,裴应杰,黄本用,杨克超,李金孟. 铅、锌、镉胁迫对多年生黑麦草生长及生理生化特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(3): 41-50. |
| [15] | 顾惠敏1,陈波浪1*,孙锦2. 菌根化育苗对盐胁迫下加工番茄生长和生理特征的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(3): 166-177. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号