




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (5): 1-10.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0305
• AGRICULTURAL INNOVATION FORUM •
Yan CAO( ), Yantao YANG(
), Yantao YANG( ), Guogang WANG
), Guogang WANG
Received:2023-04-17
Accepted:2023-08-25
Online:2024-05-15
Published:2024-05-14
Contact:
Yantao YANG
通讯作者:
杨艳涛
作者简介:曹炎 E-mail:cyjy3020000@163.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yan CAO, Yantao YANG, Guogang WANG. Spatial-temporal Pattern Evolution and Matching Analysis of Maize Production and Consumption in China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(5): 1-10.
曹炎, 杨艳涛, 王国刚. 我国玉米生产与消费时空格局演变及匹配性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 1-10.

Fig. 1 Moving trajectory of maize production center of gravity in ChinaNote: The map is based on the standard map of GSGS(2019)1822 downloaded from the standard map service website of the Map Technology Review Center of the Ministry of Natural Resources, and the base map is not modified.
年份 Year | 生产重心 Production gravity center | 移动距离 Movement distance/km | 移动方向 Moving direction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
经度 Longitude/(°) | 纬度 Latitude/(°) | 年际 Interannual | 东西向 East-west | 南北向 North-south | ||
| 1999 | 115.34 | 38.16 | — | — | — | — |
| 2000 | 114.18 | 37.16 | 169.55 | 128.89 | 110.17 | 西南Southwest |
| 2001 | 114.90 | 37.68 | 98.92 | 80.33 | 57.72 | 东北Northeast |
| 2002 | 115.04 | 38.01 | 39.79 | 15.44 | 36.67 | 东北Northeast |
| 2003 | 115.03 | 38.19 | 19.42 | 1.22 | 19.38 | 西北Northwest |
| 2004 | 115.13 | 38.21 | 11.28 | 11.00 | 2.51 | 东南Southeast |
| 2005 | 115.08 | 38.17 | 6.59 | 5.22 | 4.02 | 东北Northeast |
| 2006 | 115.66 | 38.62 | 81.14 | 64.44 | 49.30 | 东北Northeast |
| 2007 | 115.30 | 38.45 | 44.30 | 40.11 | 18.80 | 西南Southwest |
| 2008 | 115.46 | 38.77 | 39.75 | 18.00 | 35.44 | 东北Northeast |
| 2009 | 115.03 | 38.58 | 52.69 | 48.44 | 20.73 | 西南Southwest |
| 2010 | 115.18 | 38.89 | 37.70 | 16.78 | 33.77 | 东北Northeast |
| 2011 | 115.56 | 39.18 | 53.35 | 42.22 | 32.61 | 东北Northeast |
| 2012 | 115.49 | 39.25 | 10.25 | 7.11 | 7.38 | 西北Northwest |
| 2013 | 115.53 | 39.51 | 29.69 | 3.67 | 29.47 | 东北Northeast |
| 2014 | 115.44 | 39.49 | 9.97 | 9.67 | 2.46 | 东南Southeast |
| 2015 | 115.57 | 39.56 | 16.41 | 14.22 | 8.19 | 东北Northeast |
| 2016 | 115.77 | 39.33 | 34.64 | 23.00 | 25.90 | 西北Northwest |
| 2017 | 115.71 | 39.25 | 11.02 | 7.22 | 8.32 | 西南Southwest |
| 2018 | 115.55 | 39.36 | 20.92 | 17.11 | 12.03 | 东南Southeast |
| 2019 | 115.68 | 39.45 | 16.79 | 13.89 | 9.43 | 东北Northeast |
| 2020 | 115.38 | 39.29 | 37.44 | 33.22 | 17.27 | 西南Southwest |
| 2021 | 115.56 | 39.57 | 37.04 | 20.33 | 30.96 | 东北Northeast |
| 2022 | 115.49 | 39.48 | 12.64 | 8.22 | 9.60 | 西南Southwest |
Table 1 Change in the production gravity center of maize in China from 1999 to 2022
年份 Year | 生产重心 Production gravity center | 移动距离 Movement distance/km | 移动方向 Moving direction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
经度 Longitude/(°) | 纬度 Latitude/(°) | 年际 Interannual | 东西向 East-west | 南北向 North-south | ||
| 1999 | 115.34 | 38.16 | — | — | — | — |
| 2000 | 114.18 | 37.16 | 169.55 | 128.89 | 110.17 | 西南Southwest |
| 2001 | 114.90 | 37.68 | 98.92 | 80.33 | 57.72 | 东北Northeast |
| 2002 | 115.04 | 38.01 | 39.79 | 15.44 | 36.67 | 东北Northeast |
| 2003 | 115.03 | 38.19 | 19.42 | 1.22 | 19.38 | 西北Northwest |
| 2004 | 115.13 | 38.21 | 11.28 | 11.00 | 2.51 | 东南Southeast |
| 2005 | 115.08 | 38.17 | 6.59 | 5.22 | 4.02 | 东北Northeast |
| 2006 | 115.66 | 38.62 | 81.14 | 64.44 | 49.30 | 东北Northeast |
| 2007 | 115.30 | 38.45 | 44.30 | 40.11 | 18.80 | 西南Southwest |
| 2008 | 115.46 | 38.77 | 39.75 | 18.00 | 35.44 | 东北Northeast |
| 2009 | 115.03 | 38.58 | 52.69 | 48.44 | 20.73 | 西南Southwest |
| 2010 | 115.18 | 38.89 | 37.70 | 16.78 | 33.77 | 东北Northeast |
| 2011 | 115.56 | 39.18 | 53.35 | 42.22 | 32.61 | 东北Northeast |
| 2012 | 115.49 | 39.25 | 10.25 | 7.11 | 7.38 | 西北Northwest |
| 2013 | 115.53 | 39.51 | 29.69 | 3.67 | 29.47 | 东北Northeast |
| 2014 | 115.44 | 39.49 | 9.97 | 9.67 | 2.46 | 东南Southeast |
| 2015 | 115.57 | 39.56 | 16.41 | 14.22 | 8.19 | 东北Northeast |
| 2016 | 115.77 | 39.33 | 34.64 | 23.00 | 25.90 | 西北Northwest |
| 2017 | 115.71 | 39.25 | 11.02 | 7.22 | 8.32 | 西南Southwest |
| 2018 | 115.55 | 39.36 | 20.92 | 17.11 | 12.03 | 东南Southeast |
| 2019 | 115.68 | 39.45 | 16.79 | 13.89 | 9.43 | 东北Northeast |
| 2020 | 115.38 | 39.29 | 37.44 | 33.22 | 17.27 | 西南Southwest |
| 2021 | 115.56 | 39.57 | 37.04 | 20.33 | 30.96 | 东北Northeast |
| 2022 | 115.49 | 39.48 | 12.64 | 8.22 | 9.60 | 西南Southwest |
年份 Year | 生产重心 Consumption gravity center | 移动距离 Movement distance/km | 移动方向 Moving direction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
经度 Longitude/(°) | 纬度 Latitude/(°) | 年际 Interannual | 东西向 East-west | 南北向 North-south | ||
| 1999 | 114.23 | 34.06 | — | — | — | — |
| 2000 | 114.19 | 34.20 | 15.63 | 4.78 | 14.88 | 西北Northwest |
| 2001 | 114.25 | 34.32 | 15.66 | 6.78 | 14.12 | 东北Northeast |
| 2000 | 114.41 | 34.50 | 26.55 | 17.89 | 19.62 | 东北Northeast |
| 2003 | 114.55 | 34.66 | 23.46 | 15.44 | 17.66 | 东北Northeast |
| 2004 | 114.83 | 34.98 | 47.52 | 30.89 | 36.11 | 东北Northeast |
| 2005 | 114.90 | 35.11 | 15.73 | 8.11 | 13.48 | 东北Northeast |
| 2006 | 114.97 | 35.20 | 13.06 | 7.33 | 10.81 | 东北Northeast |
| 2007 | 115.02 | 34.79 | 45.79 | 6.11 | 45.38 | 东南Southeast |
| 2008 | 115.02 | 34.53 | 29.06 | 0.33 | 29.06 | 西南Southwest |
| 2009 | 115.10 | 34.56 | 9.54 | 8.89 | 3.47 | 东北Northeast |
| 2010 | 115.16 | 34.56 | 6.61 | 6.56 | 0.82 | 西北Northwest |
| 2011 | 115.16 | 34.39 | 18.94 | 0.44 | 18.93 | 东南Southeast |
| 2012 | 114.91 | 34.25 | 31.31 | 27.22 | 15.47 | 西南Southwest |
| 2013 | 114.63 | 34.07 | 36.73 | 31.11 | 19.53 | 西南Southwest |
| 2014 | 114.66 | 34.30 | 25.04 | 3.00 | 24.86 | 东北Northeast |
| 2015 | 114.63 | 34.35 | 6.38 | 2.67 | 5.80 | 东南Southeast |
| 2016 | 114.71 | 34.36 | 8.66 | 8.44 | 1.91 | 东北Northeast |
| 2017 | 114.78 | 34.38 | 8.41 | 8.22 | 1.77 | 东北Northeast |
| 2018 | 114.91 | 34.56 | 24.98 | 14.44 | 20.38 | 东北Northeast |
| 2019 | 114.91 | 34.79 | 25.61 | 0.44 | 25.61 | 东南Southeast |
| 2020 | 114.92 | 35.05 | 28.97 | 0.56 | 28.97 | 东北Northeast |
| 2021 | 114.92 | 35.01 | 4.55 | 0.33 | 4.53 | 西北Northwest |
| 2022 | 114.83 | 34.91 | 14.61 | 9.44 | 11.14 | 西南Southwest |
Table 2 Change in the consumption gravity center of maize in China from 1999 to 2022
年份 Year | 生产重心 Consumption gravity center | 移动距离 Movement distance/km | 移动方向 Moving direction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
经度 Longitude/(°) | 纬度 Latitude/(°) | 年际 Interannual | 东西向 East-west | 南北向 North-south | ||
| 1999 | 114.23 | 34.06 | — | — | — | — |
| 2000 | 114.19 | 34.20 | 15.63 | 4.78 | 14.88 | 西北Northwest |
| 2001 | 114.25 | 34.32 | 15.66 | 6.78 | 14.12 | 东北Northeast |
| 2000 | 114.41 | 34.50 | 26.55 | 17.89 | 19.62 | 东北Northeast |
| 2003 | 114.55 | 34.66 | 23.46 | 15.44 | 17.66 | 东北Northeast |
| 2004 | 114.83 | 34.98 | 47.52 | 30.89 | 36.11 | 东北Northeast |
| 2005 | 114.90 | 35.11 | 15.73 | 8.11 | 13.48 | 东北Northeast |
| 2006 | 114.97 | 35.20 | 13.06 | 7.33 | 10.81 | 东北Northeast |
| 2007 | 115.02 | 34.79 | 45.79 | 6.11 | 45.38 | 东南Southeast |
| 2008 | 115.02 | 34.53 | 29.06 | 0.33 | 29.06 | 西南Southwest |
| 2009 | 115.10 | 34.56 | 9.54 | 8.89 | 3.47 | 东北Northeast |
| 2010 | 115.16 | 34.56 | 6.61 | 6.56 | 0.82 | 西北Northwest |
| 2011 | 115.16 | 34.39 | 18.94 | 0.44 | 18.93 | 东南Southeast |
| 2012 | 114.91 | 34.25 | 31.31 | 27.22 | 15.47 | 西南Southwest |
| 2013 | 114.63 | 34.07 | 36.73 | 31.11 | 19.53 | 西南Southwest |
| 2014 | 114.66 | 34.30 | 25.04 | 3.00 | 24.86 | 东北Northeast |
| 2015 | 114.63 | 34.35 | 6.38 | 2.67 | 5.80 | 东南Southeast |
| 2016 | 114.71 | 34.36 | 8.66 | 8.44 | 1.91 | 东北Northeast |
| 2017 | 114.78 | 34.38 | 8.41 | 8.22 | 1.77 | 东北Northeast |
| 2018 | 114.91 | 34.56 | 24.98 | 14.44 | 20.38 | 东北Northeast |
| 2019 | 114.91 | 34.79 | 25.61 | 0.44 | 25.61 | 东南Southeast |
| 2020 | 114.92 | 35.05 | 28.97 | 0.56 | 28.97 | 东北Northeast |
| 2021 | 114.92 | 35.01 | 4.55 | 0.33 | 4.53 | 西北Northwest |
| 2022 | 114.83 | 34.91 | 14.61 | 9.44 | 11.14 | 西南Southwest |
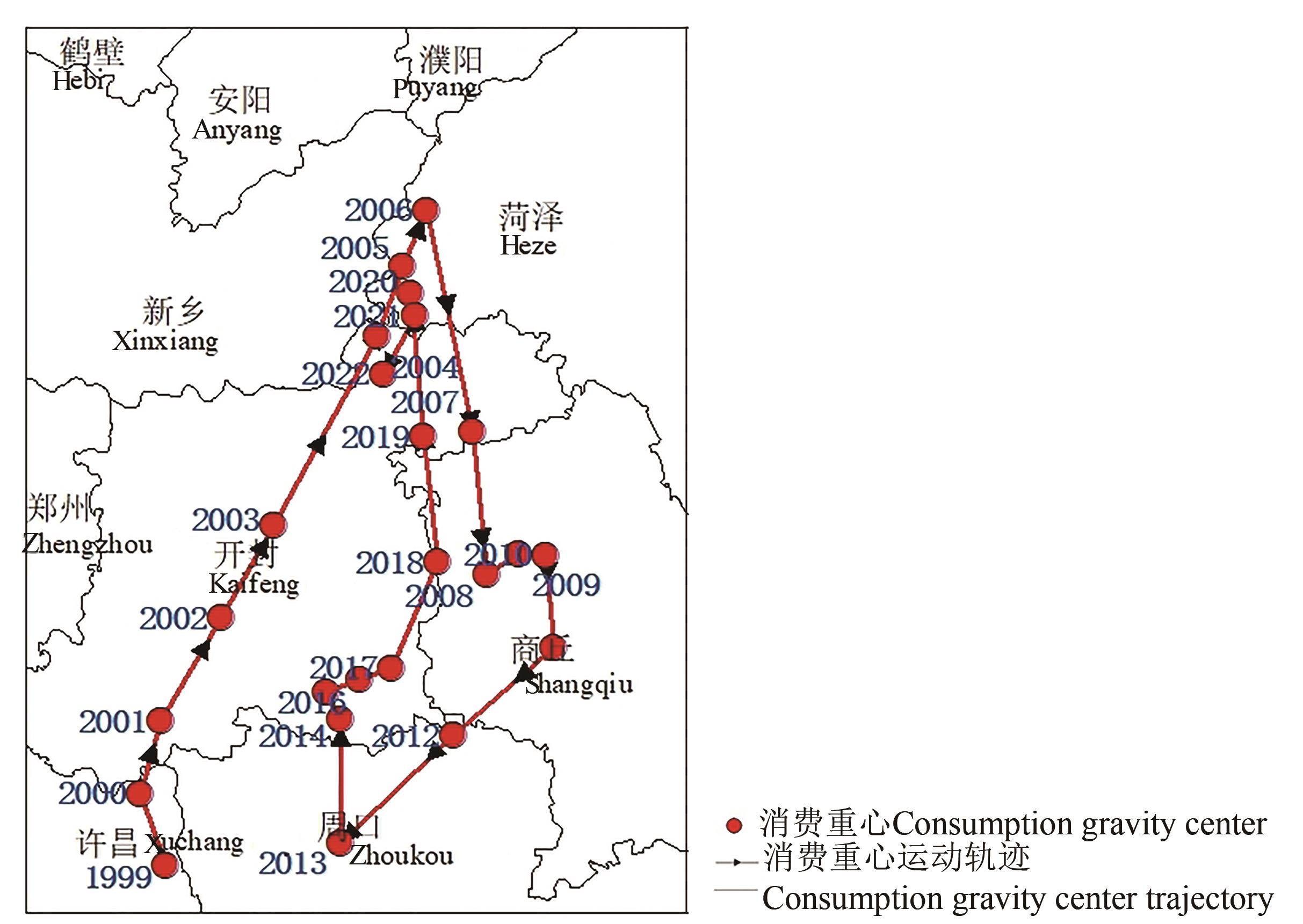
Fig. 2 Moving trajectory of maize consumption gravity center in ChinaNote: The map is based on the standard map of GSGS(2019)1822 downloaded from the standard map service website of the Map Technology Review Center of the Ministry of Natural Resources, and the base map is not modified.
| 1 | 华树春,钟钰.我国粮食区域供需平衡以及引发的政策启示[J].经济问题,2021(3):100-107. |
| HUA S C, ZHONG Y. Regional balance of grain supply and demand in China and the policy implications [J]. Econ. Problems, 2021(3):100-107. | |
| 2 | 乔颖丽,王艳华.中国玉米需求及供需平衡趋势分析[J].吉林农业科学,2013,38(3):81-85. |
| QIAO Y L, WANG Y H. Discussions on the trend of Chinese corn demand and supply-demand balance [J]. J. Jilin Agric. Sci., 2013, 38(3):81-85. | |
| 3 | 邓宗兵,封永刚,张俊亮,等.中国粮食生产空间布局变迁的特征分析[J].经济地理,2013,33(5):117-123. |
| DENG Z B, FENG Y G, ZHANG J L, et al.. Analysis on the characteristics and tendency of grain production’s spatial distribution in China [J]. Econ. Geography, 2013, 33(5):117-123. | |
| 4 | 何友,曾福生.中国粮食生产与消费的区域格局演变[J].中国农业资源与区划,2018,39(3):1-8. |
| HE Y, ZENG F S. The regional pattern evolution of China’s grain production and consumption [J]. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Regional Plan., 2018, 39(3):1-8. | |
| 5 | 杨艳涛,丁琪,王国刚.全球疫情下我国玉米供应链体系的风险问题与对策[J].经济纵横,2020(5):58-65. |
| YANG Y T, DING Q, WANG G G. Risk and countermeasures of corn supply chain system in China under global epidemic situation [J]. Econ. Rev. J., 2020(5):58-65. | |
| 6 | 刘玉,王国刚,高秉博,等.中国粮食生产的区域格局变化研究—基于1998—2010年的数据实证分析[J].农业现代化研究,2007,33(6):673-677. |
| LIU Y, WANG G G, GAO B B, et al.. Spatio-temporal analysis of grain production at different levels in China—based on statistical data from 1998 to 2010 [J]. Res. Agric. Mod., 2007, 33(6):673-677. | |
| 7 | QI X X, VITOUSEK P M, LIU L M. Provincial food security in China: a quantitative risk assessment based on local food supply and demand trends [J]. Food Security, 2015,7(3):621-632. |
| 8 | 杨艳昭,梁玉斌,封志明,等.中国玉米生产消费的时空格局及供需平衡态势[J].农业现代化研究,2016,37(5):817-823. |
| YANG Y Z, LIANG Y B, FENG Z M, et al..Temporal and spatial patterns of corn production, consumption and the balance of supply and demand in China [J]. Res. Agric. Mod., 2016, 37(5):817-823. | |
| 9 | 吴建寨,张建华,孔繁涛.中国粮食生产与消费的空间格局演变[J].农业技术经济,2015(11):46-52. |
| 10 | 陈秧分,李先德.中国粮食产量变化的时空格局与影响因素[J].农业工程学报,2013,29(20):1-10. |
| CHEN Y F, LI X D. Spatial-temporal characteristics and influencing factors of grain yield change in China [J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2013, 29(20):1-10. | |
| 11 | 李欠男.中国玉米生产空间布局变化及其驱动因素的实证研究[D].武汉:华中农业大学,2015. |
| LI Q N. An empirical study on the change of corn production and its driving [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2015. | |
| 12 | 杨宗辉,蔡鸿毅,陈珏颖,等.我国玉米生产空间布局变迁及其影响因素分析[J].中国农业资源与区划,2018,39(12):169-176. |
| YANG Z H, CAI H Y, CHEN Y Y, et al.. Analysis on the change of maize production spatial layout and its influencing factors [J]. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Region. Plan., 2018, 39(12):169-176. | |
| 13 | 卢丽琴.中国生猪养殖布局及其影响因素研究[D].南昌:江西农业大学,2016. |
| LU L Q. Study on the distribution of pig breeding and its influencing factors in China [D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2016. | |
| 14 | 仇焕广,李新海,余嘉玲.中国玉米产业:发展趋势与政策建议[J].农业经济问题,2021(7):4-16. |
| QIU H G, LI X H, YU J L. China maize industry: development trends and policy suggestions [J]. Issu. Agric. Econ., 2021(7):4-16. | |
| 15 | 陈印军,王琦琪,向雁.我国玉米生产地位、优势与自给率分析[J].中国农业资源与区划,2019,40(1):7-16. |
| CHEN Y J, WANG Q Q, XIANG Y. Analysis on the status,superiority and self-sufficiency ratio of maize in China [J]. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Region. Plan., 2019, 40(1):7-16. | |
| 16 | 张诗靓,文浩楠,杨艳涛.新形势下稳定中国玉米供给的影响因素研究——基于东北地区动态面板数据的实证分析[J].中国农业资源与区划,2019,40(12):214-219. |
| ZHANG S L, WEN H N, YANG Y T. study on the factors affecting stabilizing china’s maize supply under the new situation—an empirical analysis based on dynamic panel data in northeast China [J]. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Region. Plan., 2019, 40(12):214-219. | |
| 17 | 赵静,于卓,刘增金.中国饲料粮生产布局时空变迁及影响因素研究[J].世界农业,2023(4):71-83. |
| ZHAO J, YU Z, LIU Z J. Study of the spatial and temporal changes in the layout of feed grain production in China and the factors influencing it [J]. World Agric., 2023(4):71-83. | |
| 18 | 李姿.饲料加工业集群与玉米产业带的空间布局协调发展研究[D].长沙:湖南科技大学,2015. |
| LI Z. Research on the coordinated development between feed industry clusters and space layout of corn industry [D]. Changsha: Hunan University of Science and Technology, 2015. | |
| 19 | 陈印军.我国粮食安全形势分析[J].中国农业综合开发,2020(11):11-14. |
| 20 | 刘长全,韩磊,李婷婷,等.大食物观下中国饲料粮供给安全问题研究[J].中国农村经济,2023(1):33-57. |
| LIU C Q, HAN L, LI T T, et al.. The security of feed grains supply in China from the perspective of a big food concept [J]. Chin. Rural Econ.. 2023(1):33-57. |
| [1] | Yafeng ZHAO, Mengxue WANG, Deshuai WANG, Dongdong WANG, Yuan LI, Junfeng HU. Maize Root Image Segmentation Based on CP-DeepLabv3+ [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(3): 110-116. |
| [2] | Zhanqing WU, Wei CHEN, Zhan ZHAO, Hailiang XU, Haoyuan LI, Xingxing PENG, Dongxu CHEN, Mingyue ZHANG. Genome-wide Identification and Bioinformatics Analysis of GRAS Gene Family in Maize [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(3): 15-25. |
| [3] | Yunhong WANG, Qi MIAO, Junchao LI, Hongye WANG, Jishi ZHANG, Zhenling CUI. Effect of Comprehensive Management Measures on Productivity of Medium and Low Yield Farmland in Coastal Saline Areas [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(1): 163-172. |
| [4] | Jianmin YAO, Junkui MA, Zhongxiang WANG, Xinyuan BI, Ruizhen LI, Ruiping YANG, Zhao LIU, Fenghui GUO. Application Effect of Full Biodegradable Water Permeable Plastic Film in Soybean-Maize Belt Composite Planting [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 178-185. |
| [5] | Yaxuan MENG, Wei MA, Xuhang YAO, Yingqi SUN, Xin ZHONG, Shan HUANG, Qiaoyun WENG, Yinghui LIU, Jincheng YUAN. Study on the Response Factors of Maize Yield to Nitrogen Fertilizer [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 153-160. |
| [6] | Yajun YUAN, Jiaxing FENG, Qifan YANG, Xue BAI, R A J PUSHPA, Dahong BIAN, Yanhong CUI. Lodging-resistance Comparison Among Sumer Maize Varieties with Different Growth Period in North of Huang-Huai-Hai Plain [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 21-28. |
| [7] | Panpan ZHANG, Chuan LI, Meiwei ZHANG, Xia ZHAO, Jun NIU, Jiangfang QIAO. Effect of Nitrification Inhibitor Application on Nitrogen Accumulation and Transportation and Grain Yield of Summer Maize Under Reduced Nitrogen [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(6): 181-189. |
| [8] | Hailong WEI, Yi CHENG, Bi SONG, Jun ZOU, Jin ZUO, Lei LI, Jun ZHANG, Dailing LIU, Tao ZENG, Jingfeng FU, Sheng WEI. Grain Filling Characteristics of Fresh Waxy Maize at Different Sowing Dates and Its Relationship with Meteorological Factors [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(4): 45-55. |
| [9] | Yunzhu ZHENG, Shuchen SUN. Effects of Straw Biochar and Straw on Soil Nutrients and Crop Yield in Wheat-Maize Rotation System [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(2): 152-162. |
| [10] | Shengwei GUO, Siwen BIAN, Jianwen DING, Xiaochen ZHANG, Xing YANG, Jin DU, Chunyang XIANG. Comprehensive Evaluation of Low Temperature Tolerance of Waxy Maize Varieties at Germination Stage [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(2): 38-47. |
| [11] | Shiya WANG, Xinyi WANG, Ying LIU, Huiying HU, Haiyan SUN, Wei GUO. Effect of Graphene on Soil Nutrient Transformation and Root Growth of Maize Seedlings [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(11): 192-206. |
| [12] | Weixin DONG, Dongxiao LI, Yuechen ZHANG. Effects of Different Nitrogen Levels on Physiological Parameters, Yield and Quality of Maize [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(1): 142-152. |
| [13] | Qian YANG, Na WU, Cong ZHAO, Yu HAN, Zhonghua MA, Yongsen YANG, Jili LIU. Effects of Zinc Fertilizer Application on Physiological Characteristics and Grain Zn Content of Maize in Saline-alkali Soil [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(9): 166-176. |
| [14] | Shuai WANG, Wei SONG, Ronghuan WANG, Jiuran ZHAO. Progress of Maize Biology Research in China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(7): 23-31. |
| [15] | Ming CHENG, Ying ZHU, Xiaonan WANG, Ping LUO, Yong CHEN, Zhuanfang HAO, Zhangying XI. Drought Resistance Regulated by Allelic Variations of ZmSNAC13 in Maize [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(5): 24-31. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号