




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (11): 49-57.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0625
• BIOTECHNOLOGY & LIFE SCIENCE • Previous Articles Next Articles
Da CHEN1( ), Jisheng JU1, Qi MA2, Shouzhen XU2, Juanjuan LIU1, Wenmin YUAN1, Jilian LI2, Caixiang WANG1, Junji SU1(
), Jisheng JU1, Qi MA2, Shouzhen XU2, Juanjuan LIU1, Wenmin YUAN1, Jilian LI2, Caixiang WANG1, Junji SU1( )
)
Received:2023-08-19
Accepted:2023-09-27
Online:2023-11-15
Published:2023-11-20
Contact:
Junji SU
陈炟1( ), 巨吉生1, 马麒2, 徐守振2, 刘娟娟1, 袁文敏1, 李吉莲2, 王彩香1, 宿俊吉1(
), 巨吉生1, 马麒2, 徐守振2, 刘娟娟1, 袁文敏1, 李吉莲2, 王彩香1, 宿俊吉1( )
)
通讯作者:
宿俊吉
作者简介:陈炟 E-mail: 3089781690@qq.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Da CHEN, Jisheng JU, Qi MA, Shouzhen XU, Juanjuan LIU, Wenmin YUAN, Jilian LI, Caixiang WANG, Junji SU. Effects of FeNPs on Cotton Roots Growth and Its Response to Drought Stress at Seedling Stage[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(11): 49-57.
陈炟, 巨吉生, 马麒, 徐守振, 刘娟娟, 袁文敏, 李吉莲, 王彩香, 宿俊吉. FeNPs对苗期棉花根系生长及其对干旱响应的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(11): 49-57.
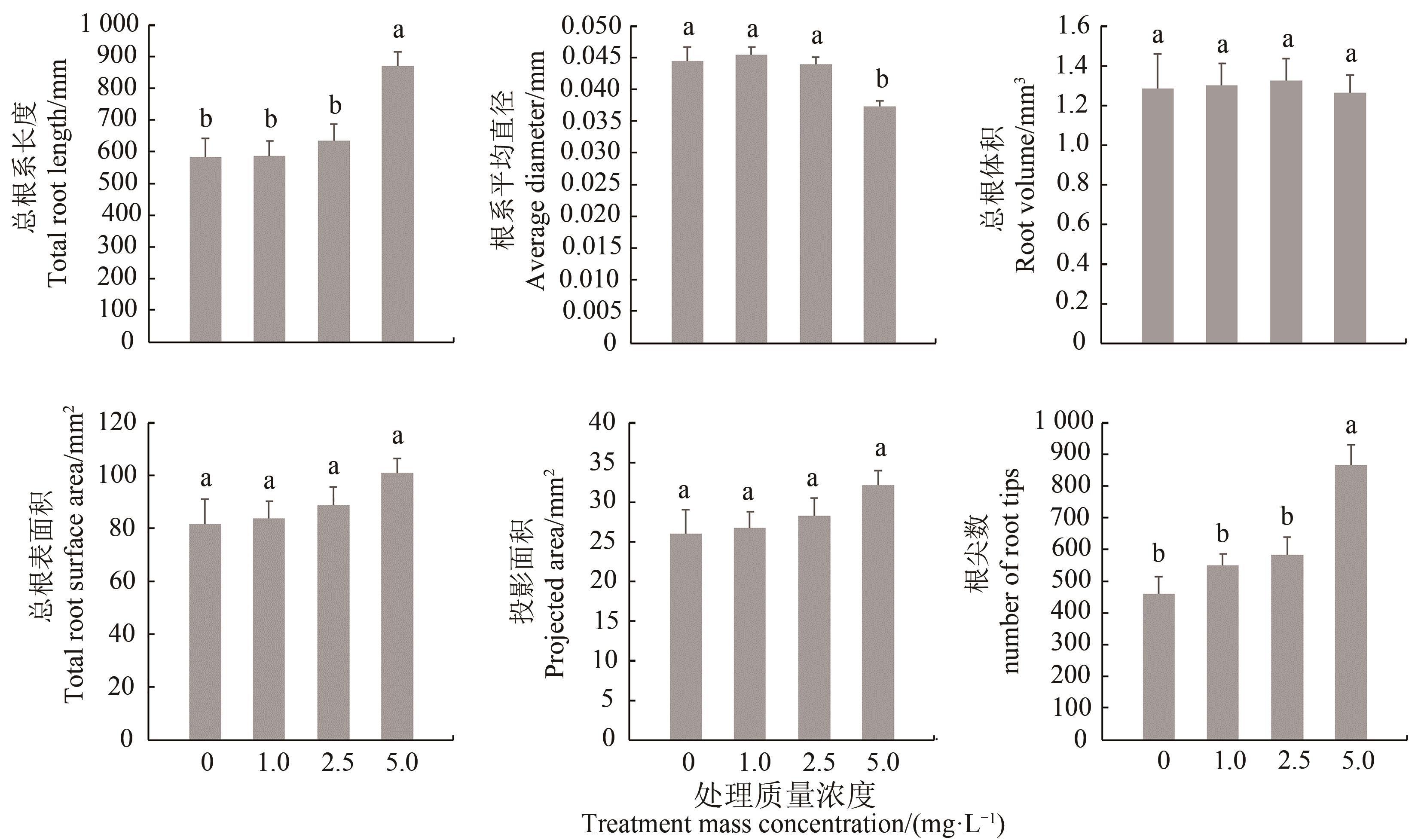
Fig. 1 Effects of different FeNPs levels on root related indexes of cotton.Note:Different letters in the figure mean significant difference at P<0.05 level.

Fig. 3 Effects of different FeNPs levels on plant height, main root length and dry matter accumulation in roots, stems and leaves of cottonNote:Different letters in the figure mean significant difference at P<0.05 level.
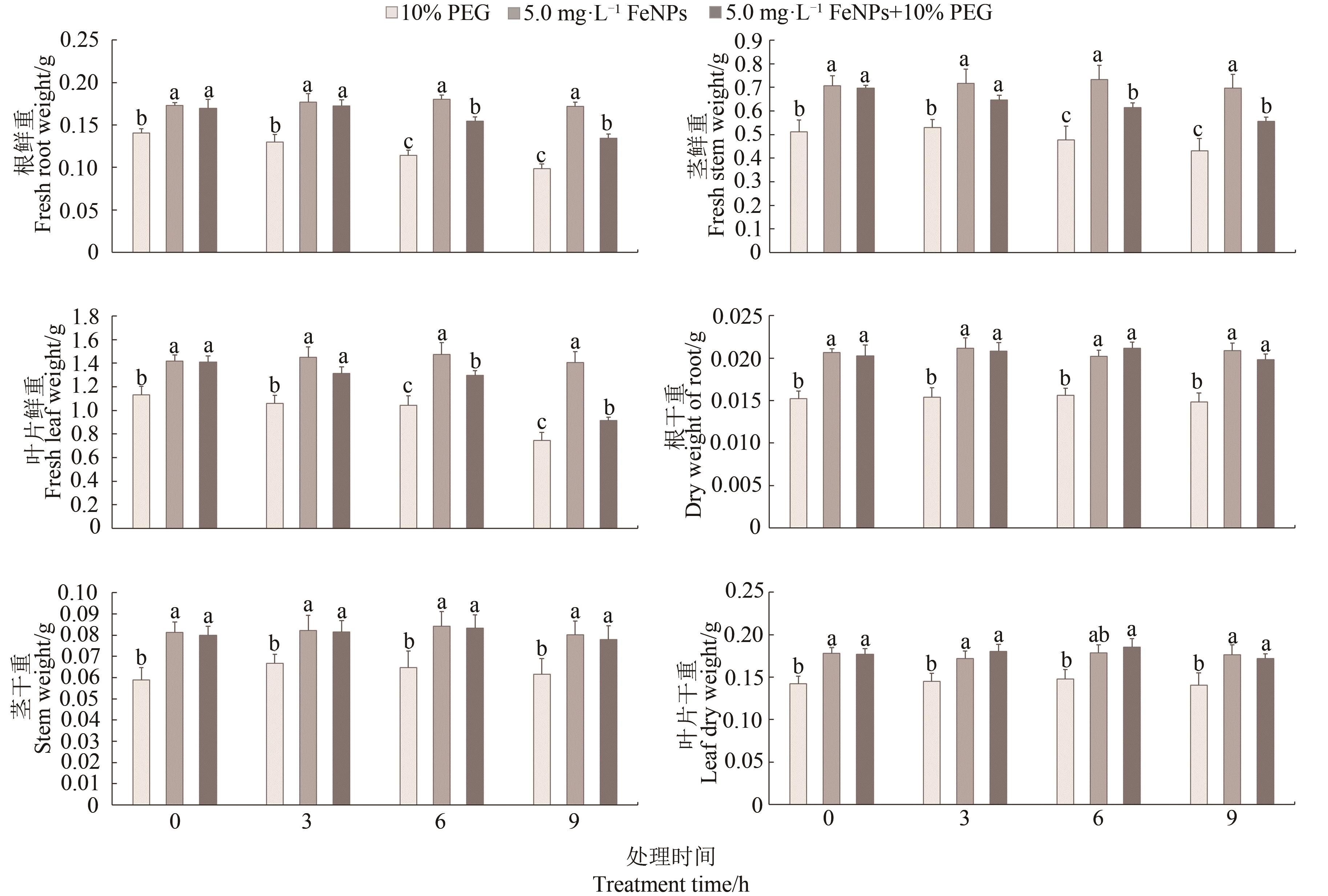
Fig. 4 Effects of the FeNPs on root, stem and leaf biomass of cotton under 10% PEG stress.Note:Different letters in the figure mean significant difference at P<0.05 level.

Fig. 6 Effects of FeNPs on antioxidant activity and MDA content in cotton leaves under 10% PEG stressNote:Different letters in the figure mean significant difference at P<0.05 level.
| 1 | JALALI M, GHANATI F, MODARRES-SANAVI A M, et al.. Physiological effects of repeated foliar application of magnetite nanoparticles on maize plants [J]. J. Agron. Crop Sci., 2017, 203(6): 593-602. |
| 2 | GATTULLO C E, YOURY P, ALLEGRETTA I, et al.. Iron mobilization and mineralogical alterations induced by iron-deficient cucumber plants (Cucumis sativus L.) in a calcareous soil [J]. Pedosphere, 2018, 28(1): 59-69. |
| 3 | MAZAHERI-TIRANI M, KASHANI A, KOOHI-DEHKORDI M. The role of iron nanoparticles on morpho-physiological traits and genes expression (IRT1 and CAT) in rue (Ruta graveolens) [J]. Plant Mol. Biol., 2022; 110(1-2): 147-160. |
| 4 | WANG Y, CHEN S, DENG C, et al.. Metabolomic analysis reveals dose-dependent alteration of maize (Zea mays L.) metabolites and mineral nutrient profiles upon exposure to zerovalent iron nanoparticles [J/OL]. NanoImpact, 2021, 23: 100336 [2023-08-18]. . |
| 5 | DOLA D B, MANNAN M A, SARKER U, et al.. Nano-iron oxide accelerates growth, yield, and quality of Glycine max seed in water deficits [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2022, 13: 992535 [2023-08-18]. . |
| 6 | FARAJOLLAHI Z, EISVAND H R, NAZARIAN-FIROUZABADI F, et al.. Nano-Fe nutrition improves soybean physiological characteristics, yield, root features and water productivity in different planting dates under drought stress conditions [J/OL]. Ind. Crop. Prod., 2023, 198: 116698 [2023-08-18]. . |
| 7 | 马扬旸,张辰弛,曹雪松,等.叶面喷施铁基纳米材料对大豆生长的影响及机制研究[J].农业资源与环境学报,2022,39(1):139-148. |
| MA Y Y, ZHANG C C, CAO X S, et al.. Mechanistic study on the effect of foliar-applied, iron-based nanomaterials on the growth of soybean [J]. J. Agric. Resour. Econ., 2022, 39(1): 139-148. | |
| 8 | MAHMOUD A W M, AYAD A A, ABDEL-AZIZ H S M, et al.. Foliar application of different iron sources improves morpho-physiological traits and nutritional quality of broad bean grown in sandy soil [J/OL]. Plants, 2022, 11(19): 2599 [2023-08-18]. . |
| 9 | 徐江兵,王艳玲,罗小三,等.纳米Fe3O4对生菜生长及土壤细菌群落结构的影响[J].应用生态学报,2017,28(9):3003-3010. |
| XU J B, WANG Y L, LUO X S, et al.. Influence of Fe3O4 nanoparticles on lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) growth and soil bacterial community structure [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2017, 28(9): 3003-3010. | |
| 10 | ADREES M, KHAN Z S, ALI S, et al.. Simultaneous mitigation of cadmium and drought stress in wheat by soil application of iron nanoparticles [J/OL]. Chemosphere, 2020, 238: 124681 [2023-08-18]. . |
| 11 | WANG Y, HU J, DAI Z, et al.. In vitro assessment of physiological changes of watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) upon iron oxide nanoparticles exposure [J]. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 2016, 108: 353-360. |
| 12 | YOSEFI A, MOZAFARI A A, Javadi T. In vitro assessment of strawberry (Fragaria ananassa Duch.) plant responses to water shortage stress under nano-iron application [J]. In Vitro Cell Dev-pl., 2022, 58(4): 499-510. |
| 13 | 龙瑶,宋玉兰.中国棉花补贴政策历史演变与未来趋势[J].中国棉花,2023,50(7):1-7. |
| LONG Y, SONG Y L. China’s cotton subsidy policy: historical evolution and future trend [J] China Cotton, 2023, 50 (7): 1-7. | |
| 14 | 韩春丽.新疆棉花长期连作土壤养分时空变化及可持续利用研究[D].石河子:石河子大学,2010. |
| HAN C L. Temporal and spatial variation of soil nutrients of long-term monocultural cotton field and soil sustainable utilization in Xinjiang [D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2010. | |
| 15 | 李合生.植物生理生化实验原理和技术.北京:高等教育出版社,2000:164-165. |
| LI H S. Principles and Techniques of Plant Physiological and Biochemical Experiment [M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2000: 164-165. | |
| 16 | 陈刚,李胜.植物生理学实验.北京:高等教育出版社,2016:59-69. |
| CHEN G, LI S. Plant Physiology Experiment[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press., 2016: 59-69. | |
| 17 | 张丽,古超峰,王锐.叶面补铁对贺兰山东麓酿酒葡萄生理调节及品质提升的影响[J].中国土壤与肥料, 2021, (6): 233-238. |
| ZHANG L, GU C F, WANG R. Effects of foliar iron supplement on physiological regulation and quality improvement of wine grapes in eastern Helan Mountains [J]. Soil Fertil. Sci. China, 2021, (6): 233-238. | |
| 18 | 高洪波,陈贵林,章铁军,等.施铁对萝卜芽生长、产量及品质的影响[J].园艺学报,2006,33(5):1096-1098. |
| GAO H B, CHEN G L, ZHANG T J, et al.. Effect of iron application on growth, yield and quality in radish sprouts [J]. Acta Hortic. Sin., 2006, 33(5): 1096-1098. | |
| 19 | 张迎芳,李欣苗,李艳,等.螯合铁肥对艾生长及产量品质的影响[J].中国野生植物资源,2022,41(10):7-13. |
| ZHANG Y F, LI X M, LI Y, et al.. Effects of chelating iron fertilizer on growth, yield and quality of Artemisia argyi [J]. Chinese Wild Plant Resour., 2022, 41(10): 7-13. | |
| 20 | 胡华锋,介晓磊,郭孝,等.喷施硫酸亚铁对紫花苜蓿草产量、品质及矿质营养的影响[J].吉林农业大学学报,2009,31(3):291-296. |
| HU H F, JIE X L, GUO X, et al.. Effect of leaf surface spraying ferrous sulphate on herbage yield quality and mineral nutrition of alfalfa [J]. J. Jilin Agric. Univ., 2009, 31(3): 291-296. | |
| 21 | 周春涛,张茹艳,石铭福,等.铁肥形态对马铃薯块茎内源激素、产量及品质的影响[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2022,50(4):42-49. |
| ZHOU C T, ZHANG R Y, SHI M F, et al.. Effects of iron different forms of iron fertilizers on endogenous hormones, yield and quality of potato [J]. J. Northwest A&F Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.), 2022, 50(4): 42-49. | |
| 22 | 贾红霞,刘风珍,张秀荣,等.不同类型铁肥改善花生缺铁效果研究[J].花生学报,2021, 50(2):38-43+63. |
| JIA H X, LIU F Z, ZHANG X R, et al.. Effect of different types of iron fertilizer on alleviating iron deficiency of peanut [J]. J. Peanut Sci., 2021, 50(2): 38-43+63. | |
| 23 | 刘蓉,叶宇萍,海丹,等. 锌、铁微肥对夏玉米产量和品质的影响[J].西北农业学报,2017, 26(11):1598-1605. |
| LIU R, YE Y P, HAI D, et al.. Effects of zinc and iron micro-fertilizer on yield and quality of summer maize [J]. Acta Agric. Boreali-occidentalis Sin., 2017, 26(11): 1598-1605. | |
| 24 | 付力成,王人民,孟杰,等.叶面锌、铁配施对水稻产量、品质及锌铁分布的影响及其品种差异[J].中国农业科学,2010,43(24):5009-5018. |
| FU L C, WANG R M, MENG J, et al.. Effect of foliar application of zinc and iron fertilizers on distribution of zinc and iron,quality and yield of rice grain [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2010, 43(24): 5009-5018. | |
| 25 | 楚燕蒙,毛颖超,蔡剑,等.二氢卟吩铁对小麦渍水胁迫耐性的影响[J].中国农业科学,2023,56(10):1848-1858. |
| CHU Y M, MAO Y C, CAI J, et al.. Effect of Phytochlorin Iron on Stress Tolerance to Waterlogging in Wheat [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2023, 56 (10): 1848-1858. | |
| 26 | 张士荣,白灯莎·买买提艾力,冯固.新疆棉花幼叶黄化现象及其铁锌含量差异分析[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2007,(4):745-748. |
| ZHANG S R, MAIMAITIELI B, FENG G. The phenomenon of chlorosis and analysis of difference in Fe and Zn content of cotton in Xinjiang [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2007, (4): 745-748. | |
| 27 | KAH M, KOOKANA R S, GOGOS A, et al.. A critical evaluation of nanopesticides and nanofertilizers against their conventional analogues [J]. Nat. Nanotechnol., 2018, 13(8): 677-684. |
| 28 | ASKARY M, AMIRJANI M R, SABERI T. Comparison of the effects of nano-iron fertilizer with iron-chelate on growth parameters and some biochemical properties of Catharanthus roseus [J]. J. Plant Nutr., 2017, 40(7): 974-982. |
| 29 | GUHA T, GOPAL G, CHATTERJEE R, et al.. Differential growth and metabolic responses induced by nano-scale zero valent iron in germinating seeds and seedlings of Oryza sativa L. cv. Swarna [J/OL]. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2020, 204: 111104 [2020-08-10]. . |
| 30 | 徐江兵,王艳玲,罗小三,等.纳米Fe3O4对生菜生长及土壤细菌群落结构的影响[J].应用生态学报,2017,28(9):3003-3010. |
| XU J B, WANG Y L, LUO X S, et al.. Influence of Fe3O4 nanoparticles on lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) growth and soil bacterial community structure [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2017, 28(9): 3003-3010. | |
| 31 | 孟令煜,杨涛,王引权,等.叶面喷施纳米铁对当归生理生化特性及药材产量、品质的影响[J].时珍国医国药,2022, 33(10):2497-2501. |
| MENG L Y, YANG T, WANG Y Q, et al.. Effects of spraying nano iron on physiological and biochemical characteristics of Angelica sinensis and its yield and quality [J]. Lishizhen Medicine Materia Medica Res., 2022, 33(10): 2497-2501. | |
| 32 | 杨涛,赵疆,闫鹏勋,等.纳米铁和褪黑素对驯化栽培条件下甘肃贝母产量和品质的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2021,27(7):144-150. |
| YANG T, ZHAO J, YAN P X, et al.. Effect of zero-valent iron nanoparticles and melatonin on yield and quality of fritillaria przewalskii in domesticated cultivation conditions [J]. Chin. J. Exp. Traditional Med. Formulae, 21, 27(7): 144-150. | |
| 33 | RUI M, MA C, HAO Y, et al.. Iron oxide nanoparticles as a potential iron fertilizer for peanut (Arachis hypogaea) [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2016, 7: 815 [2023-08-18]. . |
| 34 | NEMATI LAFMEJANI Z, JAFARI A A, MORADI P, et al.. Impact of foliar application of iron-chelate and iron nano particles on some morpho-physiological traits and rssential oil composition of peppermint (Mentha piperita L.) [J]. J. Essent. Oil Bear. Pl., 2018, 21(5): 1374-1384. |
| [1] | Wei WANG, Qiang ZHAO, Abuduaini Munire·, Alimu·Amuli, Xinxin LI, Yangqing TIAN. Effects of Different Exogenous Substances on Chemical Capping and Yield and Quality of Cotton [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 57-68. |
| [2] | Pengfei LIU, Xiaoshuang LU, Dilimurat Reheman, Tangnur Slay, Yanying QU, Quanjia CHEN, Xiaojuan DENG. Genetic Variation Analysis of Main Quality Traits and Agronomic Traits in Upland Cotton Seed [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 22-32. |
| [3] | Shijian BAI, Jinge HU, Jiuyun WU, Wen ZHANG, Hui XIE, Ronghua ZHAO, Guang CHEN, Junshe CAI. Effects of Rootstocks on the Growth Characteristics and Fruit Quality of ‘Crimson Seedless’ Grapes in Turpan Region [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 76-87. |
| [4] | Liting CHEN, Yuanyuan YAN. Investigation of Regulatory Mechanism of Floral Integrators in Upland Cotton [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(6): 11-21. |
| [5] | Zhengran SUN, Cuiping ZHANG, Jinli ZHANG, Hao WU, Xiuyan LIU, Zhenkai WANG, Yuzhen YANG, Daohua HE. Effects of Chemical Detopping on Cotton Plant Growth in Guanzhong Cotton Region [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(4): 167-177. |
| [6] | Man ZHANG, Jin ZHANG, Xinyu ZHANG, Guoning WANG, Xingfen WANG, Yan ZHANG. Cloning and Functional Analysis of GhNAC1 in Upland Cotton Involved in Verticillium Wilt Resistance [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(10): 35-44. |
| [7] | Guoqing LU, Caixia MA, Guoqing SUN, Huiming GUO, Hongmei CHENG. Molecular Characterization and Inheritance Stability Analysis of Herbicide-resistant Cotton GV-2 [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(1): 42-49. |
| [8] | Yan LIU, Hongshuai BAO, Hongyan SHANG, Guoning WANG, Yan ZHANG, Xingfen WANG, Zhiying MA, Jinhua WU. Selection of Cotton Fusarium Wilt and Culture Conditions [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(8): 124-132. |
| [9] | Ling LI, Helin DONG, Pengcheng LI, Liwen TIAN, Chunmei LI, Yunzhen MA, Na ZHANG, Fang WANG, Wenxiu XU. Effects of Machine Harvesting Planting Methods on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Dry Matter Accumulation of Different Plant Types of Cotton [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(8): 172-181. |
| [10] | Zhengwen SUN, Qishen GU, Yan ZHANG, Xingfen WANG, Zhiying MA. Research Progress on Cotton Gene Discovery and Molecular Breeding [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(7): 32-38. |
| [11] | Chengchuan YAN, Qingtao ZENG, Qin CHEN, Jincheng FU, Tingwei WANG, Quanjia CHEN, Yanying QU. Screening and Evaluation of Drought Resistance Indicators at Flowering and Boll Stage of Upland Cotton [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(7): 46-57. |
| [12] | Lijuan ZHANG, Yukun QIN, Huihuang CHENG, Yongqi LI, Haihua LUO. Research on Characteristics of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Loss from Surface Runoff of Cotton Field in Northern Jiangxi Province of Poyang Lake Region [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(6): 166-175. |
| [13] | Nan WU, Jun YANG, Yan ZHANG, Zhengwen SUN, Dongmei ZHANG, Lihua LI, Jinhua WU, Zhiying MA, Xingfen WANG. Overexpression of a Cotton Glucuronokinase Gene GbGlcAK Promotes Cell Elongation in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(6): 36-46. |
| [14] | Yajie HUANG, Dan REN, Shengmei LI, Jinxin CUI, Tao YANG, Jiaojiao REN, Wenwei GAO. Evaluation and Screening of Salt and Alkali Tolerance Indices of Upland Cotton Seedlings [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(5): 46-55. |
| [15] | Yuqing ZHOU, Yongfei YANG, Changwei GE, Qian SHEN, Siping ZHANG, Shaodong LIU, Huijuan MA, Jing CHEN, Ruihua LIU, Shicong LI, Xinhua ZHAO, Cundong LI, Chaoyou PANG. Identification of Cold-related Co-expression Modules in Cotton Cotyledon by WGCNA [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(4): 52-62. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号