




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (12): 186-194.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0509
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles
Junyu ZHOU1( ), Yu GU1, Zhenqi TANG2, Haiyong WU1, Qiongfeng LIU1, Mingde LI1(
), Yu GU1, Zhenqi TANG2, Haiyong WU1, Qiongfeng LIU1, Mingde LI1( )
)
Received:2022-06-20
Accepted:2022-12-04
Online:2023-12-15
Published:2023-12-12
Contact:
Mingde LI
周峻宇1( ), 谷雨1, 唐珍琦2, 吴海勇1, 刘琼峰1, 李明德1(
), 谷雨1, 唐珍琦2, 吴海勇1, 刘琼峰1, 李明德1( )
)
通讯作者:
李明德
作者简介:周峻宇E-mail:zjy00001@126.com;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Junyu ZHOU, Yu GU, Zhenqi TANG, Haiyong WU, Qiongfeng LIU, Mingde LI. Effect of Compound Chelating Agent on Remediation of Cadmium Contaminated Farmland by Amaranthus hypochondriacus L.[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(12): 186-194.
周峻宇, 谷雨, 唐珍琦, 吴海勇, 刘琼峰, 李明德. 复合螯合剂对籽粒苋修复镉污染农田的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(12): 186-194.
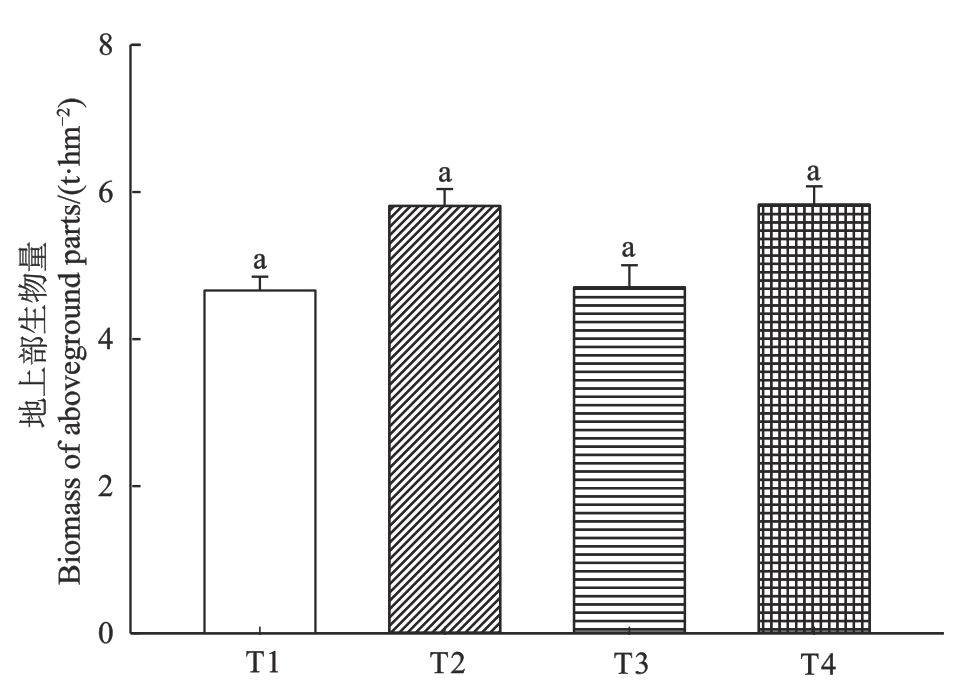
Fig. 1 Biomass of aboveground parts of Amaranthus hypochondriacus L. under different chelating agentsNote: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at P<0.05 level between different chelating agents treatments.
| 处理Treatment | Cd含量Cd content/(mg·kg-1) | 富集系数 Bioconcentration factor | 转运系数 Translocation factor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
地上部 Aboveground parts | 地下部 Underground parts | |||
| T1 | 10.14±1.64 b | 7.21±0.26 ab | 7.69±1.26 b | 1.40±0.21 b |
| T2 | 13.20±2.42 ab | 8.87±1.18 a | 9.35±1.15 ab | 1.49±0.17 ab |
| T3 | 10.24±3.42 b | 6.67±1.39 b | 8.41±3.28 ab | 1.52±0.30 ab |
| T4 | 14.84±1.37 a | 9.25±1.20 a | 10.83±0.85 a | 1.61±0.11 a |
Table 1 Cd content and bioconcentration and translocation factor under different chelating agents
| 处理Treatment | Cd含量Cd content/(mg·kg-1) | 富集系数 Bioconcentration factor | 转运系数 Translocation factor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
地上部 Aboveground parts | 地下部 Underground parts | |||
| T1 | 10.14±1.64 b | 7.21±0.26 ab | 7.69±1.26 b | 1.40±0.21 b |
| T2 | 13.20±2.42 ab | 8.87±1.18 a | 9.35±1.15 ab | 1.49±0.17 ab |
| T3 | 10.24±3.42 b | 6.67±1.39 b | 8.41±3.28 ab | 1.52±0.30 ab |
| T4 | 14.84±1.37 a | 9.25±1.20 a | 10.83±0.85 a | 1.61±0.11 a |
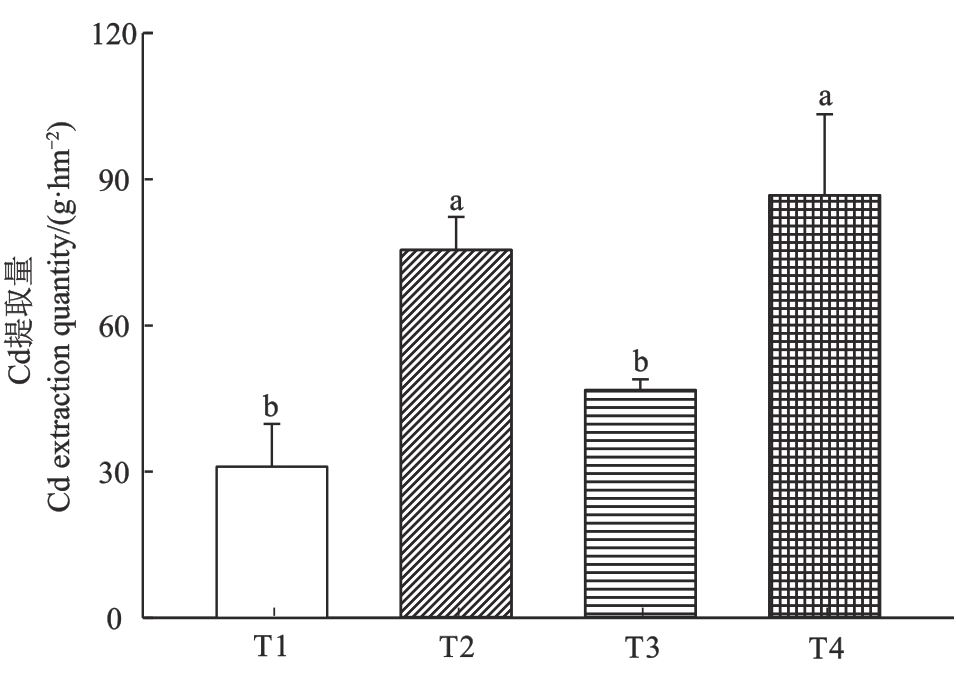
Fig. 2 Amount of Cd extracted by the aboveground parts of Amaranthus hypochondriacus L. under different chelating agentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at P<0.05 level between different chelating agents treatments.
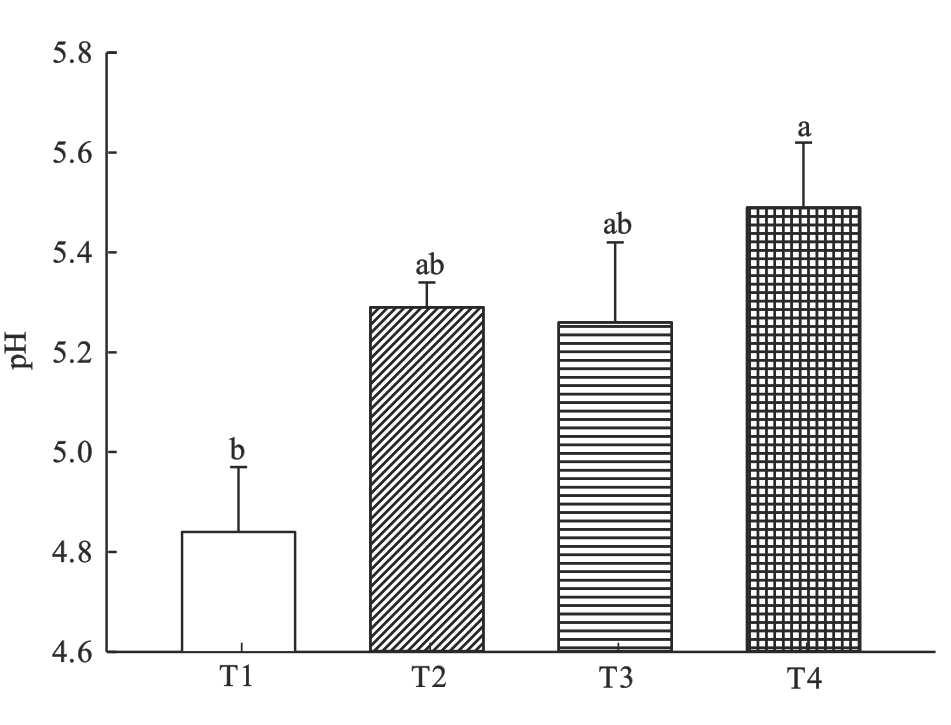
Fig. 3 Changes of soil pH under different chelating agentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at P<0.05 level between different chelating agents treatments.
指标 Index | 有机质 Organic matter | 土壤总镉 Soil total Cd | DTPA-Cd | 地上部生物量 Aboveground biomass | 地上部镉含量 Aboveground Cd content | 地上部镉提取量 Aboveground Cd extraction quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 0.503* | 0.755** | 0.307 | 0.567 | 0.132 | 0.457 |
| 有机质 Organic matter | 0.662** | 0.642** | -0.109 | 0.120 | 0.084 | |
| 土壤总镉 Soil total Cd | 0.573** | 0.461 | 0.457 | 0.616* | ||
| DTPA-Cd | -0.091 | -0.126 | -0.101 | |||
| 地上部生物量 Aboveground biomass | 0.356 | 0.832** | ||||
| 地上部镉含量 Aboveground Cd content | 0.796** |
Table 2 Pearson’s correlation coefficient between the soil physical and chemical properties and biomass, Cd uptake and accumulation in aboveground parts
指标 Index | 有机质 Organic matter | 土壤总镉 Soil total Cd | DTPA-Cd | 地上部生物量 Aboveground biomass | 地上部镉含量 Aboveground Cd content | 地上部镉提取量 Aboveground Cd extraction quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 0.503* | 0.755** | 0.307 | 0.567 | 0.132 | 0.457 |
| 有机质 Organic matter | 0.662** | 0.642** | -0.109 | 0.120 | 0.084 | |
| 土壤总镉 Soil total Cd | 0.573** | 0.461 | 0.457 | 0.616* | ||
| DTPA-Cd | -0.091 | -0.126 | -0.101 | |||
| 地上部生物量 Aboveground biomass | 0.356 | 0.832** | ||||
| 地上部镉含量 Aboveground Cd content | 0.796** |
| 1 | WANG G, ZHANG S, ZHONG Q, et al.. Feasibility of Chinese cabbage (Brassica bara) and lettuce (Lactuca sativa) cultivation in heavily metals-contaminated soil after washing with biodegradable chelators [J]. J. Clean. Prod., 2018, 197:479-490. |
| 2 | WANG G, ZHANG S, ZHONG Q, et al.. Effect of soil washing with biodegradable chelators on the toxicity of residual metals and soil biological properties [J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2018, 625:1021-1029. |
| 3 | WANG J, XING Y, LI P, et al.. Chemically-assisted phytoextraction from metal(loid)s-polluted soil at a typical carlin-type gold mining area in southwest China [J]. J. Clean. Prod., 2018, 189:612-619. |
| 4 | 湖南省发展和改革委员会.关于湖南省第二次土地调查主要数据成果的公报[R/OL]. (2014-03-07)[2022-05-20]. . |
| 5 | 黄道友,朱奇宏,朱捍华,等.重金属污染耕地农业安全利用研究进展与展望[J].农业现代化研究,2018,39(6):1030-1043. |
| HUANG D Y, ZHU Q H, ZHU H H, et al.. Advances and prospects of safety agro-utilization of heavy metal contaminated farmland soil [J]. Res. Agric. Modernization, 2018, 39(6):1030-1043. | |
| 6 | 谷雨,蒋平,谭丽,等.6种植物对土壤中镉的富集特性研究[J].中国农学通报,2019,35(30):119-123. |
| GU Y, JIANG P, TAN L, et al.. Enrichment characteristics of cadmium by six plants in soil [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2019, 35(30):119-123. | |
| 7 | 韩廿,黄益宗,魏祥东,等.螯合剂对油葵修复镉砷复合污染土壤的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2019,38(8):1891-1900. |
| HAN N, HUANG Y Z, WEI X D, et al.. Effect of chelating agents on remediation of cadmium and arsenic complex contaminated soil using oil sunflower [J]. J.Agro-Environ.Sci., 2019, 38(8): 1891-1900. | |
| 8 | NADGORSKA-SOCHA A, KANDZIORA-CIUPA M, TRZESICKI M, et al.. Air pollution tolerance index and heavy metal bioaccumulation in selected plant species from urban biotopes [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 183:471-482. |
| 9 | DING P, ZHUANG P, LI Z, et al.. Accumulation and detoxification of cadmium by larvae of Prodenia litura (Lepidoptera: noctuidae) feeding on Cd-enriched amaranth leaves [J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 91 : 28-34. |
| 10 | 李晓宝,董焕焕,任丽霞,等.螯合剂修复重金属污染土壤联合技术研究进展[J].环境科学研究,2019,32(12):1993-2000. |
| LI X B, DONG H H, REN L X, et al.. Effects of chelating agent combination technologies on soil contaminated by heavy metals [J]. Res. Environ. Sci., 2019, 32(12):1993-2000. | |
| 11 | ASENSIO V G, FLORIDO F, RUIZ F, et al.. Screening of native tropical trees for phytoremediation in copper-polluted soils [J]. Int. J. Phytoremediation, 2018, 20(14): 1456-1463. |
| 12 | CHENG X, CHIQUAN H, SHI Z, et al.. Effect of spent mushroom substrate on strengthening the phytoremediation potential of Ricinus communis to Cd-and Zn-polluted soil [J]. Int. J. Phytoremediation, 2018, 20(14):1389-1399. |
| 13 | GUO H, SUN H, SU Z, et al.. Fe3O4@PAM@NTA-Ni2+ magnetic composite nanoparticles for highly specific separation of his-tagged proteins [J]. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol., 2018, 33(3):559-565. |
| 14 | GUO D, ALI A, REN C, et al.. EDTA and organic acids assisted phytoextraction of Cd and Zn from a smelter ontaminated soil by potherb mustard (Brassica juncea, Coss) and evaluation of its bioindicators [J]. Ecotox. Environ. Safe., 2019, 167:396-403. |
| 15 | SUBRAMANIAN B, CHRISTOU S Y, EFSTATHIOU A M, et al.. Regeneration of three-way automobile catalysts using biodegradable metal chelating agent-S, S-ethylenediamine disuccinic acid (S, S-EDDS) [J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2011, 186(2-3):999-1006. |
| 16 | 卫泽斌,陈晓红,吴启堂,等.可生物降解螯合剂GLDA诱导东南景天修复重金属污染土壤的研究[J].环境科学,2015,36(5):1864-1869. |
| WEI Z B, CHEN X H, WU Q T, et al.. Enhanced phytoextraction of heavy metals from contaminated soils using Sedum alfrediihance with biodegradable chelate GLDA [J]. Environ. Sci., 2015, 36(5):1864-1869. | |
| 17 | LIU X Y, MAO Y, ZHANG X Y, et al.. Effects of PASP/NTA and TS on the phytoremediation of pyrene-nickel contaminated soil by Bidens pilosa L. [J/OL]. Chemosphere, 2019:124502 [2022-05-20]. . |
| 18 | TANANONCHAI A, SANPANPANISH P, CHANPIWAT P, et al.. Effect of EDTA and NTA on cadmium distribution and translocation in Pennisetum purpureum Schum cv. Mott [J]. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 2019, 26(10):9851-9860. |
| 19 | SAMPANPANISH P, NANTHAVONG K. Effect of EDTA and NTA on arsenic bioaccumulation and translocation using phytoremediation by Mimosa pudica L. from contaminated soils [J]. Bull. Environ. Contam. Tox., 2019, 102(1):140-145. |
| 20 | WANG K, LIU Y, SONG Z, et al.. Chelator complexes enhanced Amaranthus hypochondriacus L. phytoremediation efficiency in Cd-contaminated soils [J/OL]. Chemosphere, 2019, 237:124480 [2022-05-20].. |
| 21 | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].三版.北京:中国农业出版社,2013:1-495. |
| 22 | 中华人民共和国环境保护部. 土壤和沉积物12种金属元素的测定 王水提取-电感耦合等离子体质谱法: [S].北京:中国环境科学出版社,2016. |
| 23 | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检测检疫总局. 土壤质量 有效态铅和镉的测定 原子吸收法: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2009. |
| 24 | GOTTLEIN A. Sampling of rhizosphere soil and collection of rhizosphere soil solution// LUSTERJ, FINLAYR, BRUNNERI. Handbook of Methods Used in Rhizosphere Research [M]. Birmensdorf: Swiss Federal Research Institute WSL, 2006: 25-29. |
| 25 | 金鹏康,刘柯君,王先宝.慢速可生物降解有机物的转化特性及利用[J].环境工程学报,2016,10(5):2168-2174. |
| JIN P K, LIU K J, WANG X B. Conversion and utilization of slowly biodegradable organic matter [J]. Chin. J. Environ. Eng., 2016, 10(5):2168-2174. | |
| 26 | DAI S, LI H, YANG Z, et al.. Effects of biochar amendments on speciation and bioavailability of heavy metals in coal-mine-contaminated soil [J]. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess., 2018, 24(7):1887-1900. |
| 27 | HOU S, ZHENG N, TANG L, et al.. Effect of soil pH and organic matter content on heavy metals availability in maize (Zea mays L.) rhizospheric soil of non-ferrous metals smelting area [J/OL]. Environ. Monit. Assess., 2019, 191(10):634 [2022-05-20]. . |
| 28 | LUO C, SHEN Z, LI X, et al.. Enhanced phytoextraction of Pb and other metals from artificially contaminated soils through the combined application of EDTA and EDDS [J]. Chemosphere, 63(10):1773-1784. |
| 29 | 周宽,皇甫卓曦,钟承韡,等.可生物降解螯合剂GLDA诱导葎草修复镉污染土壤[J].环境工程,2021,39(5):165-170, 79. |
| ZHOU K, HUANGFU Z X, ZHONG C W, et al.. Biodegradable chelate glda enhanced phytoextraction forcadmium-contaminated soil [J]. Environ. Eng., 2021, 39(5):165-170, 79. | |
| 30 | MOHAMED M A, EFLIGENIR A, HUSSON J, et al.. Extraction of heavy metals from a contaminated soil by reusing chelating agent solutions [J]. J. Environ. Chem. Eng., 2013, 1(3):363-368. |
| 31 | 覃建军,唐盛爽,蒋凯,等.螯合剂GLDA对象草修复镉污染农田的影响[J].环境科学,2020,41(8):3862-3869. |
| QIN J J, TANG S S, JIANG K, et al.. Effects of chelate GLDA on the remediation of cadmium contaminated farmland by pennisetum purpureum schum [J]. Environ. Sci., 2020, 41(8):3862-3869. | |
| 32 | 李非里,邵鲁泽,吴兴飞,等.植物修复重金属强化技术和间套种研究进展[J].浙江工业大学学报,2021,49(3):345-354. |
| LI F L, SHAO L Z, WU X F, et al.. Research progress of enhanced phytoremediation for heavy metals and intercropping technique [J]. J. Zhejiang Univ. Technol., 2021, 49(3):345-354. | |
| 33 | GHNAVA T, ZAIER H, BAIOUI R, et al.. Implication of organic acids in the long-distance transport and the accumulation of lead in Sesuvium portulacastrum and Brassica juncea [J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 90(4):1449-1454. |
| 34 | 梅闯,王衡,蔡昆争,等.生物炭对土壤重金属化学形态影响的作用机制研究进展[J]. 生态与农村环境学报,2021,37(4):421-429. |
| MEI C, WANG H, CAI K Z, et al.. Advances of effects and mechanisms of biochar on chemical forms of heavy metals in contaminated soil [J]. J. Ecol. Rural Environ., 2021, 37(4):421-429. | |
| 35 | 陈春乐,杨婷,邹县梅,等.可生物降解螯合剂亚氨基二琥珀酸和谷氨酸N, N-二乙酸对重金属污染土壤的淋洗修复及动力学特征[J].生态与农村环境学报,2021,37(3):394-401. |
| CHEN C L, YANG T, ZOU X M, et al.. Remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil by biodegradable chelating agents of ids and glda washing and their washing kinetics characteristics [J]. J. Ecol. Rural Environ., 2021, 37(3):394-401. | |
| 36 | 陈雅慧,杨轶雄,李宁锋,等.复合螯合剂对铺地竹铅富集及土壤环境的影响[J].环境科学与技术,2021,44(4):140-148. |
| CHEN Y H, YANG Y X, LI N F, et al.. Effect of compound chelating agent on the accumulation of Pb in Sasa argenteostriata E.G. Camus and soil environment [J]. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2021, 44(4):140-148. | |
| 37 | WANG G, ZHANG S, XU X, et al.. Heavy metal removal by GLDA washing: optimization, redistribution, recycling, and changes in soil fertility [J]. Sci. Total Environ.,2016, 569-570(1):557-568. |
| 38 | 吴仁杰,陈银萍,曹雯婕,等.营养元素与螯合剂强化植物修复重金属污染土壤研究进展[J].中国土壤与肥料,2021(5):328-337. |
| WU R J, CHEN Y P, CAO W J, et al.. Research advances in phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil strengthened by chelating agents and nutrient elements [J]. Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2021(5):328-337. | |
| 39 | 史广宇,余志强,施维林.植物修复土壤重金属污染中外源物质的影响机制和应用研究进展[J].生态环境学报,2021,30(3):655-666. |
| SHI G Y, YU Z Q, SHI W L. Research progress on mechanism and application of exogenous substances in phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil [J]. Ecol. Environ. Sci., 2021, 30(3):655-666. | |
| 40 | 王凯.复合蝥合剂强化籽粒苋修复Cd污染土壤效果研究[D]. 武汉:华中农业大学,2019. |
| WANG K. Chelator complexes enhanced phytoremediation of Cd contaminated soils with Amaranthus hypochondriacus L. [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2019. | |
| 41 | 宋波,张云霞,田美玲,等.应用籽粒苋修复镉污染农田土壤的潜力[J].环境工程学报,2019,13(7):1711-1719. |
| SONG B, ZHANG Y X, TIAN M L, et al.. Potential for cadmium contaminated farmland remediation with Amaranthus hypochondriacus L. [J]. Chin. J. Environ. Eng., 2019, 13(7):1711-1719. | |
| 42 | 景琪.螯合剂强化超富集植物修复重金属污染土壤的研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学,2014. |
| JING Q. Study on chelator-enhanced remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil by hyperaccumulator [D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2014. | |
| 43 | ZHANG X, ZHONG B, SHAFI M, et al.. Effect of EDTA and citric acid on absorption of heavy metals and growth of Moso bamboo [J]. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int., 2018, 25(19):18846-18852. |
| 44 | 谢斯扬,凌定勋,王平,等. PASP和NAA组配调控生物质高粱萃取镉效果研究[J].中南林业科技大学学报,2022,42(6):144-151. |
| XIE S Y, LING D X, WANG P, et al.. Effect of PASP and NAA coupling on extraction of cadmium from Sorghum dochna (Forssk.) Snowden [J]. J. Central South Univ. For. Technol.,2022, 42(6):144-151. | |
| 45 | 卫泽斌,郭晓方,吴启堂,等.混合螯合剂的不同施加方式对重金属污染土壤套种修复效果的影响[J].华南农业大学学报,2016,37(1):29-34. |
| WEI Z B, GUO X F, WU Q T, et al.. Effects of different application methods of mixed chelators on remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil in interplanting system [J]. J. South China Agric. Univ., 2016, 37(1):29-34. | |
| 46 | 谷雨,黄铁平,唐珍琦,等.籽粒苋修复土壤重金属污染研究进展[J].农学学报,2020,10(10):41-45. |
| GU Y, HUANG T P, TANG Z Q, et al.. Remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil by Amaranthus hypochondriacus: research progress [J]. J. Agric., 2020, 10(10):41-45. | |
| 47 | 王正,孙兆军, Sameh Mohamed, 等. 胺鲜酯与螯合剂GLDA联合强化柳枝稷吸收积累镉效果[J].环境科学,2020,41(12):5589-5599. |
| WANG Z, SUN Z J, SAMEH M, et al.. DA-6 and GLDA enhanced Pancium virgatum L.to phytoextract Cd from contaminated soils [J]. Environ. Sci., 2020, 41(12):5589-5599. | |
| 48 | 贺玉龙,余江,谢世前,等. 可生物降解螯合剂GLDA强化三叶草修复镉污染土壤[J].环境科学,2020,41(2):979-985. |
| HE Y L, YU J, XIE S Q, et al.. Enhanced phytoextraction of Cadmium contaminated soil by Trifolium repens with biodegradable chelate GLDA [J]. Environ. Sci., 2020, 41(2):979-985. |
| [1] | Lu ZHANG, Lei ZHENG, Siru LIU, Zejiang CAI, Nan SUN, Qiang ZHANG, Minggang XU. Soil Initial Available Phosphorus and Exchangeable Magnesium Shaping the Response of Wheat Growth to pH [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(11): 173-181. |
| [2] | Ruiting JIA, Limin YUAN, Zhongju MENG. Effects of Plant Measures on Soil Improvement of Desert Photovoltaic Power Station [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(10): 182-188. |
| [3] | Jing GAO, Minggang XU, Ran LI, Zejiang CAI, Nan SUN, Qiang ZHANG, Lei ZHENG. Effects of Biochar Application on Soil pH: A Meta-Analysis [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 186-196. |
| [4] | Huijun LI, Weijian ZHANG, Weijian WU, Gaoyang LI, Yijie CHEN, Fengcheng HUANG, Yongxiang HUANG, Zhong LIN, Zhen ZHEN. Effects of Sea Rice on Soil Chemical Properties and Microbial Community Structure in Coastal Solonchaks [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 147-156. |
| [5] | Caiyan DU, Haiyan LU, Yanzhu XIONG, Xi SUN, Xiumei SUN, Jixiong PU, Naiming ZHANG. Effects of Combined Application of Biogas Slurry and Chemical Fertilizer on Peach Growth and Soil Physical and Chemical Properties for Two Consecutive Years [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 165-175. |
| [6] | Yulu WU, Jiaxin HU, Yuxi CHEN, Bingsong ZHENG, DaoLiang YAN. Effects of External Application of α-Ketoglutarate on Growth, Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus Accumulation and Their Stoichiometric Relationships in Kosteletzkya virginica Under Salt Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 170-177. |
| [7] | Hongyuan LIU, Zhihua ZHOU, Guangxin ZHAO, Qinrui SHEN. Effects of Long-term Biochar Application on Greenhouse Gas Emission and Its Temporal Effect in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 178-186. |
| [8] | Xudong WANG, Xuebing REN, Shu TANG, Qin GUO, Mengyao XUE, Peng JIN, Yunhua ZHANG. Application of Sludge Biochar in Soil Improvement [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(6): 165-173. |
| [9] | PANG Zhe, WANG Qilong, LI Juan. Effects of Different Soil Amendments on Soil Physical and Chemical Properties, Rice Yield and Economic Benefits in Low-lying Saline Alkali Land in Northern Shaanxi [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(6): 174-180. |
| [10] | Hongyuan LIU, Zhihua ZHOU, Guangxin ZHAO, Yanjun WANG, Nana WANG. Effects of Modified Cellulose on Germination and Dryland Soil Physicochemical Properties of Upland Rice [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(5): 168-175. |
| [11] | Hairong XU, Lin WANG, Congmin WU, Yuanchun YU, Cheng DAI. Effects of Biogas Slurry Application on Green Pepper Growth and Soil Properties [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(10): 179-188. |
| [12] | Yue GU, Jinggui WU. Study on Dynamic Effects of Organic Materials on Soil Carbon, Nitrogen and Microbial Biomass [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(4): 126-133. |
| [13] | Zhenjia HE, Wangtao FAN, Yichun DU, Qilong WANG. Effects of Water and Fertilizer Coupling on the Physical and Chemical Properties of Rice Soil and Yield Based on Soil Organic Reconstruction [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(3): 176-185. |
| [14] | LI Shuang, ZHANG Wei, WANG Li, LI Xiaojun, CUI Juntao. Effect of Straw Returning on Fertility and Stem Rot of Black Soil with Different Land Fertility [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(8): 80-90. |
| [15] | JIA Jing\|dun, ZHANG Fu. Sustainable Utilization of Saline\|alkali Land Resources through Scientific and Technological Innovation in China [J]. , 2014, 16(5): 1-7. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号