




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (7): 133-141.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0419
• 动植物健康 • 上一篇
杨艺帅1( ), 谭琳2, 牛丽1, 舒坪1, 史子涵1, 方洁2, 胡秋龙1(
), 谭琳2, 牛丽1, 舒坪1, 史子涵1, 方洁2, 胡秋龙1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-05-24
接受日期:2024-12-26
出版日期:2025-07-15
发布日期:2025-07-11
通讯作者:
胡秋龙
作者简介:杨艺帅E-mail:519414001@qq.com;
基金资助:
Yishuai YANG1( ), Lin TAN2, Li NIU1, Ping SHU1, Zihan SHI1, Jie FANG2, Qiulong HU1(
), Lin TAN2, Li NIU1, Ping SHU1, Zihan SHI1, Jie FANG2, Qiulong HU1( )
)
Received:2024-05-24
Accepted:2024-12-26
Online:2025-07-15
Published:2025-07-11
Contact:
Qiulong HU
摘要:
茶树根腐病常导致茶树整株枯死,极大地影响了茶产业的可持续发展。为明确茶树根腐病病原菌(Fusarium cugenangense)的生物学特性,筛选安全高效的杀菌剂,通过十字交叉法和血球计数法分别测定温度、pH、光照条件、碳源、氮源对其菌丝生长及产孢量的影响;利用菌丝生长速率法测定8种市售杀菌剂对菌丝生长的抑制作用,筛选并评估最佳抑菌药剂的室内毒力及其对菌丝生长及产孢量的影响。结果表明,Fusarium cugenangense菌丝在10~35 ℃、pH 5~12条件下均可生长,在15~35 ℃、pH 5~12条件下均可产孢。其中菌丝生长最适温度为25 ℃、产孢最适温度为30 ℃,菌丝生长最适pH为8、产孢最适pH为9,菌落生长的最适碳源为淀粉、产孢最适碳源为蔗糖,菌落生长和孢子产生的最适氮源均为蛋白胨,且光照能抑制菌丝生长及产孢量。此外,菌丝生长抑制率表明,噁霉灵的抑菌率最高,为80.97%,其有效抑制中浓度(EC50)为0.109 g·L-1,而氯溴异氰尿酸、氟菌·霜霉威抑菌率较低,分别为16.79%和9.71%。综上,温度、pH、光照条件、碳源、氮源等外界条件均能影响Fusarium cugenangense的生物学特性。此外,噁霉灵对Fusarium cugenangense具有较好的室内毒力。以上研究结果为有效控制茶树根腐病及其蔓延提供了理论依据。
中图分类号:
杨艺帅, 谭琳, 牛丽, 舒坪, 史子涵, 方洁, 胡秋龙. 茶树根腐病菌生物学特征及室内药剂筛选[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(7): 133-141.
Yishuai YANG, Lin TAN, Li NIU, Ping SHU, Zihan SHI, Jie FANG, Qiulong HU. Biological Characteristics and Fungicides Screening in Laboratory of Fusarium cugenangense Causing Camellia sinensis Root Rot[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(7): 133-141.
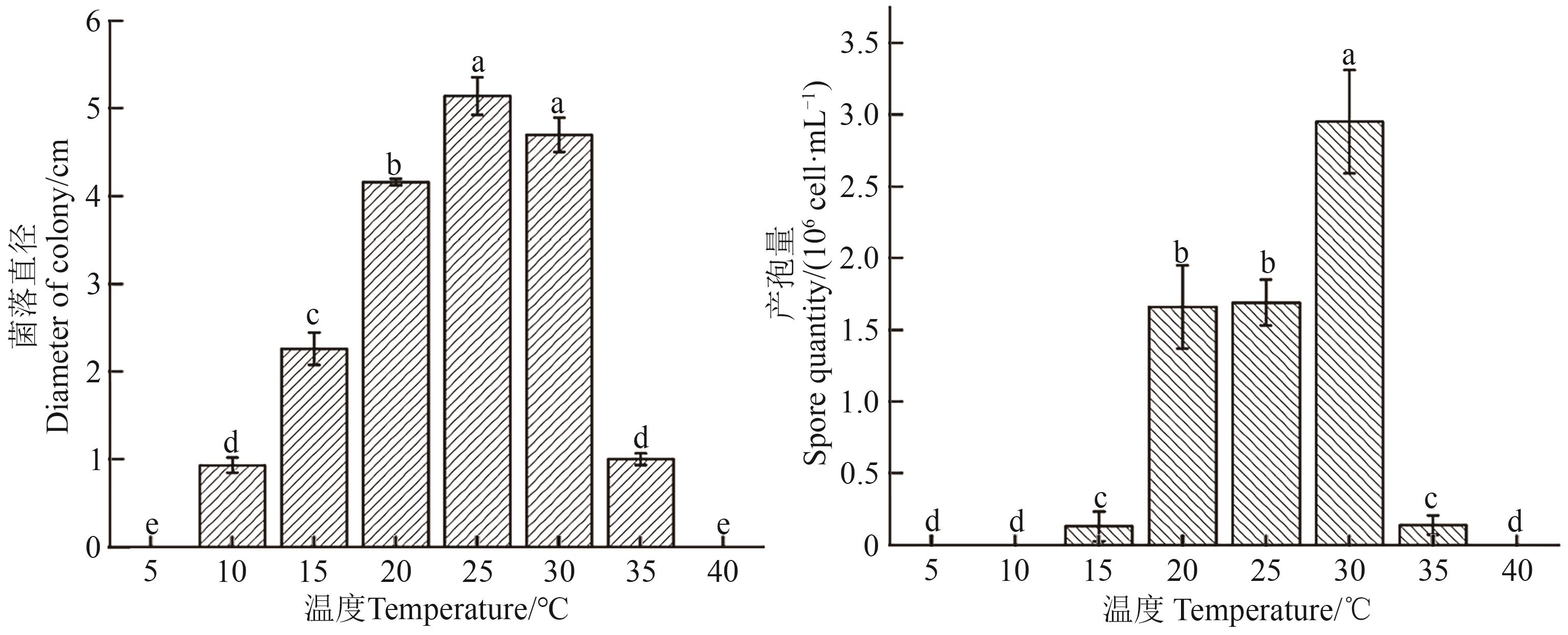
图1 不同温度下茶树根腐病病原菌菌丝的生长和产孢注:不同小写字母表示不同温度间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 1 Mycelial growth and sporulation of Fusarium cugenangense under different temperatureNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different temperatures at P<0.05 level.
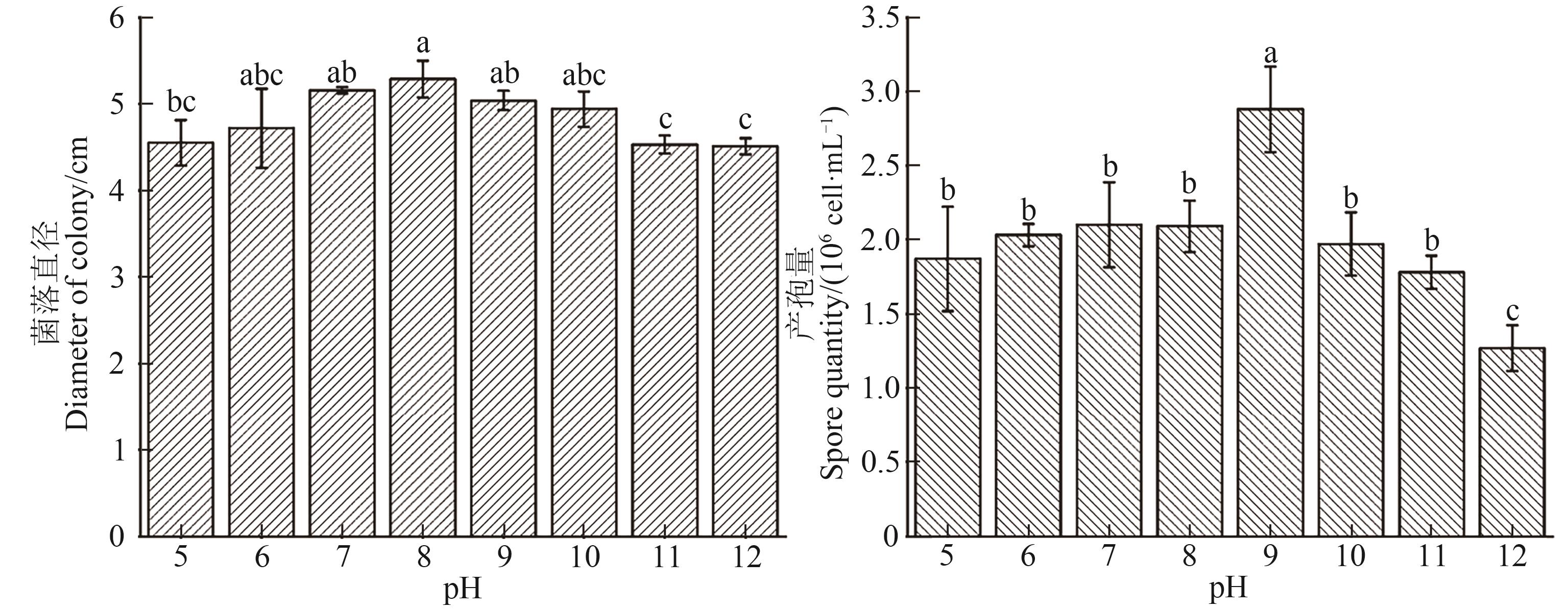
图2 不同pH下茶树根腐病病原菌菌丝的生长和产孢注:不同小写字母表示不同pH处理间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 2 Mycelial growth and sporulation of Fusarium cugenangense under different pH treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different pH treatments at P<0.05 level.

图3 不同光照条件下茶树根腐病病原菌菌丝的生长和产孢注:不同小写字母表示不同光照条件间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 3 Mycelial growth and sporulation of Fusarium cugenangense under different light conditionsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different light conditions at P<0.05 level.

图4 不同碳源下茶树根腐病病原菌菌丝的生长和产孢注:不同小写字母表示不同碳源间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 4 Mycelial growth and sporulation of Fusarium cugenangense under different carbon sourcesNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different carbon sources at P<0.05 level.
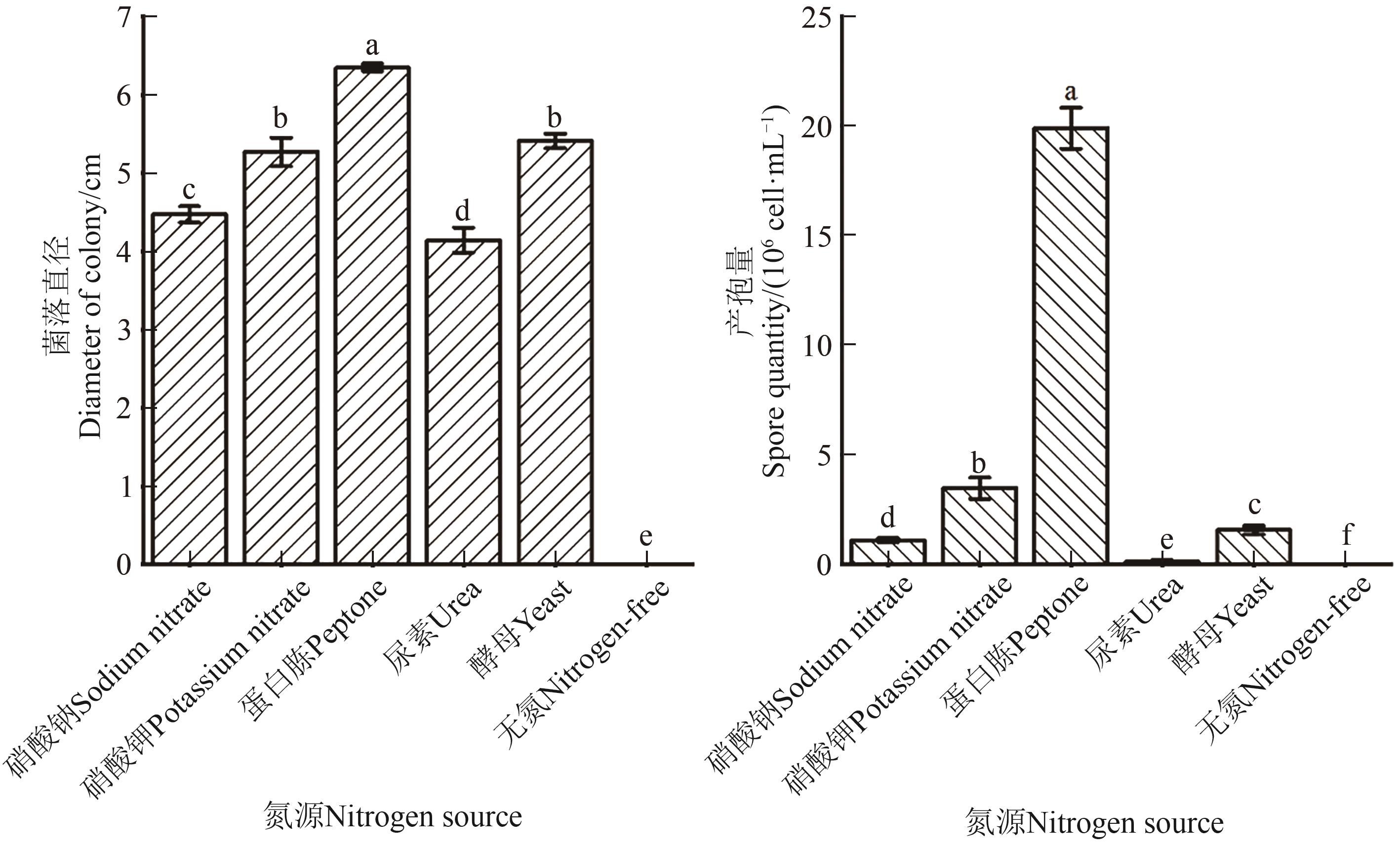
图5 不同氮源下茶树根腐病病原菌菌丝的生长和产孢注:不同小写字母表示不同氮源间在P<0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 5 Mycelial growth and sporulation of Fusarium cugenangense under different nitrogen resourcesNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different nitrogen sources at P<0.05 level.
| 药剂名称Agent name | 菌落直径Colony diameter/cm | 抑菌率Inhibition rate/% |
|---|---|---|
| 噁霉灵Hymexazol | 1.30±0.00 e | 80.97 a |
| 氟氯氰菊酯Cyfluthrin | 3.00±0.20 d | 56.08 b |
| 甲霜·噁霉灵Metalaxyl·hymexazol | 3.25±0.18 cd | 52.42 bc |
| 精甲·咯·嘧菌Metalaxyl-M·fludioxonil·azoxystrobin | 3.50±0.10 cd | 48.76 bc |
| 多菌灵Sanmate | 4.53±0.25 c | 33.63 c |
| 宁南霉Ningnanmycin | 5.37±0.21 bc | 21.43 cd |
| 氯溴异氰尿酸Chloroisobromine cyanuric acid | 5.68±0.49 abc | 16.79 cd |
| 氟菌·霜霉威Fluomycetes downomycetes | 6.17±0.15 ab | 9.71 d |
| 对照Control | 6.83±0.15 a | — |
表1 供试药剂的抑菌率
Table 1 Inhibition rates of test agents
| 药剂名称Agent name | 菌落直径Colony diameter/cm | 抑菌率Inhibition rate/% |
|---|---|---|
| 噁霉灵Hymexazol | 1.30±0.00 e | 80.97 a |
| 氟氯氰菊酯Cyfluthrin | 3.00±0.20 d | 56.08 b |
| 甲霜·噁霉灵Metalaxyl·hymexazol | 3.25±0.18 cd | 52.42 bc |
| 精甲·咯·嘧菌Metalaxyl-M·fludioxonil·azoxystrobin | 3.50±0.10 cd | 48.76 bc |
| 多菌灵Sanmate | 4.53±0.25 c | 33.63 c |
| 宁南霉Ningnanmycin | 5.37±0.21 bc | 21.43 cd |
| 氯溴异氰尿酸Chloroisobromine cyanuric acid | 5.68±0.49 abc | 16.79 cd |
| 氟菌·霜霉威Fluomycetes downomycetes | 6.17±0.15 ab | 9.71 d |
| 对照Control | 6.83±0.15 a | — |
药剂名称 Agents name | 剂量 Dosage/(g·L-1) | 菌落直径 Colony diameter/cm | 抑菌率 Inhibition rate/% | 产孢数 Sporulation count/(cell·mL-1) | 毒力回归方程 Virulence regression equation | EC50/ (g·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
噁霉灵 Hymexazol | 0.1 | 3.45±0.15 | 49.12 | 2.75×107 | y=0.855x+0.889 | 0.109 |
| 0.2 | 2.88±0.09 | 57.52 | 2.23×107 | |||
| 0.3 | 2.23±0.06 | 67.11 | 1.87×107 | |||
| 0.4 | 2.13±0.09 | 68.58 | 1.26×107 | |||
| 0.5 | 1.89±0.08 | 72.12 | 5.12×106 | |||
氟氯氰菊酯 Cyfluthrin | 0.1 | 4.54±0.15 | 33.04 | 7.84×107 | y=0.659x+0.227 | 0.452 |
| 0.2 | 3.94±0.27 | 41.89 | 6.85×107 | |||
| 0.3 | 3.76±0.14 | 44.54 | 5.29×107 | |||
| 0.4 | 3.54±0.25 | 47.79 | 4.99×107 | |||
| 0.5 | 3.26±0.09 | 51.92 | 3.54×107 | |||
| 对照组Control | — | 6.78±0.08 | — | 1.23×108 | — | — |
表2 不同剂量噁霉灵、氟氯氰菊酯处理下的抑菌率
Table 2 Inhibition rate of oxamethrin and cyfluthrin at different dosages
药剂名称 Agents name | 剂量 Dosage/(g·L-1) | 菌落直径 Colony diameter/cm | 抑菌率 Inhibition rate/% | 产孢数 Sporulation count/(cell·mL-1) | 毒力回归方程 Virulence regression equation | EC50/ (g·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
噁霉灵 Hymexazol | 0.1 | 3.45±0.15 | 49.12 | 2.75×107 | y=0.855x+0.889 | 0.109 |
| 0.2 | 2.88±0.09 | 57.52 | 2.23×107 | |||
| 0.3 | 2.23±0.06 | 67.11 | 1.87×107 | |||
| 0.4 | 2.13±0.09 | 68.58 | 1.26×107 | |||
| 0.5 | 1.89±0.08 | 72.12 | 5.12×106 | |||
氟氯氰菊酯 Cyfluthrin | 0.1 | 4.54±0.15 | 33.04 | 7.84×107 | y=0.659x+0.227 | 0.452 |
| 0.2 | 3.94±0.27 | 41.89 | 6.85×107 | |||
| 0.3 | 3.76±0.14 | 44.54 | 5.29×107 | |||
| 0.4 | 3.54±0.25 | 47.79 | 4.99×107 | |||
| 0.5 | 3.26±0.09 | 51.92 | 3.54×107 | |||
| 对照组Control | — | 6.78±0.08 | — | 1.23×108 | — | — |
| [1] | WEI C L, YANG H, WANG S B, et al.. Draft genome sequence of Camellia sinensis var. sinensis provides insights into the evolution of the tea genome and tea quality [J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2018, 115(18):4151-4158. |
| [2] | 黄华,张建,苏东,等.2017—2019年信阳市茶树病虫害发生种类调查及绿色防控技术探讨[J].中国植保导刊,2020,40(10):79-82. |
| [3] | 杨艺帅,杨学宇,王玉生,等.气候变化背景下茶角胸叶甲潜在适生区预测[J].湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版),2023,49(5):581-587. |
| YANG Y S, YANG X Y, WANG Y S, et al.. Prediction of the potential adaptive areas of Basilepta melanopus under climate change scenarios [J]. J. Hunan Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2023, 49(5):581-587. | |
| [4] | HU Y Q, ZHANG M T, LU M Q, et al.. Salicylic acid carboxyl glucosyl transferase UGT87E7 regulates disease resistance in Camellia sinensis [J]. Plant Physiol., 2021, 188(3):1507-1520. |
| [5] | LING H M, TANG X X, ZHENG C Q, et al.. First report of leaf spot caused by Clonostachys rosea on tea (Camellia sinensis) in China [J/OL]. Plant Dis., 2023, 107(8):2537 [2024-04-20]. . |
| [6] | WANG X, YIN Q X, JIANG S L, et al.. First report of Didymella bellidis causing tea leaf spot in China [J/OL]. Plant Dis., 2020, 104(4):1254 [2024-04-20]. . |
| [7] | YIN Q X, AN X L, WU X, et al.. First report of Alternaria longipes causing leaf spot on tea in China [J/OL]. Plant Dis., 2021, 105(12):4167 [2024-04-20]. . |
| [8] | BAO X T, DHARMASENA D S P, LI D X, et al.. First report of Epicoccum sorghinum causing leaf spot on tea in China [J/OL]. Plant Dis., 2019, 103(12):3282 [2024-04-20]. . |
| [9] | TANG Z, ZHU J, SONG Q, et al.. Identification and pathogenicity of Fusarium spp . associated with tea wilt in Zhejiang province, China [J/OL]. BMC Microbiol., 2024, 24(1):38 [2024-04-20]. . |
| [10] | 叶正凡,张觉晚,钟世芳,等.湖南茶树病虫害防治研究的回顾与展望[J].茶叶通讯,1991(1):7-10. |
| [11] | 张觉晚,谭济才,袁通政,等.湖南茶园病虫区系特点及区域性防治[J].茶叶通讯,1998(3):21-23. |
| [12] | KOLANDASAMY M, PONNUSAMY P. Expression of phenolics and defence-related enzymes in relation to red root rot disease of tea plants [J]. Arch. Phytopathol., 2013, 46(4):451-462. |
| [13] | MORANG P, DEVI S P, JHA D K, et al.. Tea root brown-rot fungus disease reduction and yield recovery with rhizobacteria inoculation in both nursery and field trials [J]. Rhizosphere, 2018, 6:89-97. |
| [14] | SINNIAH G D, SENANAYAKE P D. Microbial technologies in pest and disease management of tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) //[M]. (1st Eds). BHATT P, GANGALA S, UDAYANGA D, et al.. Microbial Technology for Sustainable Environment. Singapore: Springer, 2021:325-345. |
| [15] | YANG Y S, YANG X Y, ZHANG Y D, et al.. First report of Fusarium cugenangense causing root rot of tea plants (Camellia sinensis) in China [J/OL]. Plant Dis., 2024, 108(1):214 [2024-04-20]. . |
| [16] | CHERUIYOT H. Armillaria root rot (Armillaria mellea) of tea: biology, pathogenicity, symptoms and control [J]. Tea, 2014, 35(3):7-30. |
| [17] | 赖宝春,姚锦爱.福建蜜柚炭疽病菌的生物学特性及高效防治药剂筛选[J].福建农业学报,2022,37(6):789-793. |
| LAI B C, YAO J A. Biological characteristics of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides and fungicides for disease control on honey pomelo in Fujian [J]. Fujian J. Agric. Sci., 2022, 37(6):789-793. | |
| [18] | 黄玉凤,李菲,汪汉成,等.烟草镰刀菌根腐病病原生物学特性及其优势种的代谢表型特征[J].江苏农业科学,2024,52(7):124-132. |
| [19] | 代毅,杨文睿,吐逊艾力·艾孜提力,等.新疆甘草根腐病病原鉴定及生物学特性测定[J].北方园艺,2021(20):111-118. |
| DAI Y, YANG W R, Aizitili Tusunaili, et al.. Pathogen identification and biological characteristics of licorice root rot in Xinjiang [J]. Northern Hortic., 2021 (20):111-118. | |
| [20] | 张海珊.麦冬炭疽菌的生物学特性及有效药剂筛选[D].合肥:安徽农业大学,2009. |
| ZHANG H S. Biological characteristics and effective fungicide selection of anthracnose pathogen of Ophiopogon japonicus [D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2009. | |
| [21] | 王美琴,陈俊美,李新凤.不同碳、氮源对番茄两种内生真菌菌丝生长的影响研究[J].山西农业科学,2008 (11):75-77. |
| WANG M Q, CHEN J M, LI X F. Study on mycelia growth of two tomato endophytic fungi in different carbon and nitrogen medium [J]. J. Shanxi Agric. Sci., 2008(11):75-77. | |
| [22] | 周利,郭明明.茶园农药的合理选用和使用[J].中国茶叶,2022,44(9):1-7. |
| ZHOU L, GUO M M. Rational selection and application of pesticides in tea gardens [J]. China Tea, 2022, 44(9):1-7. | |
| [23] | LEON M E, SCHINASI L H, LEBAILLY P, et al.. Pesticide use and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoid malignancies in agricultural cohorts from France, Norway and the USA: a pooled analysis from the AGRICOH consortium [J]. Int. J. Epidemiol., 2019, 48(5):1519-1535. |
| [24] | 张志鹏,程庆华,谢靖康,等.小檗碱对不同茶树炭疽菌的抑菌活性及作用机制[J].茶叶科学,2022,42(3):367-375. |
| ZHANG Z P, CHEN Q H, XIE J K, et al.. The antifungal effect and mechanism of berberine on different Colletotrichum species causing tea brown blight disease [J]. J. Tea Sci., 2022, 42(3):367-375. | |
| [25] | 张玉丹,谭琳,刘仲华,等.茶树炭疽病菌拮抗链霉菌的筛选及其抑菌特性研究[J].茶叶科学,2024, 44(2):283-298. |
| ZHANG Y D, TAN L, LIU Z H, et al.. Identification of antagonistic Streptomycetes against anthracnose pathogen of tea plants and determination of their inhibitory properties [J]. J. Tea Sci., 2024, 44(2):283-298. | |
| [26] | 王志坤.武夷菌素对茶树主要叶部病害的控制作用[D].重庆:西南大学,2008. |
| WANG Z K. Suppression effects of wuyiencin on tea foliar diseases and their pathogens [D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2008. | |
| [27] | MYRESIOTIS K, KARAOGLANIDIS G S, VRYZAS Z, et al.. Evaluation of plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria, acibenzolar-S-methyl and hymexazol for integrated control of Fusarium crown and root rot on tomato [J]. Pest Manag. Sci., 2012, 68(3):404-411. |
| [28] | ROBERTS T R, HUSTSON D H. Metabolic pathways of agrochemicals. part 2: insecticides and fungicides [J/OL]. R. Soc. Chem. 1999, 13:75 [2024-04-20]. . |
| [29] | FAN Y, GAO R H, XIAO X, et al.. Inclusion complexes of hymexazol with three different cucurbit[n]uril: preparation, and physicochemical and antifungal characterization [J]. Israel J. Chem., 2018, 58:466-471. |
| [30] | 焦鹏,贾变桃,孙颖,等.6种杀菌剂对兰花枯萎病菌抑制作用比较[J].山西农业大学学报(自然科学版),2012,32(2):154-157. |
| JIAO P, YAO B T, SUN Y, et al.. Conparison of inhibition of six fungicides against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Cattleyae [J]. J. Shanxi Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2012, 32(2):154-157. | |
| [31] | 李艳春,陈志鹏,林伟伟,等.茶树连作障碍形成机制及调控措施研究进展[J].生态科学,2019,38(5):225-232. |
| LI Y C, CHEN Z P, LIN W W, et al.. Research advances in mechanisms and preventions of continuous cropping obstacles of tea plants [J]. Ecol. Sci., 2019, 38(5):225-232. |
| [1] | 张波, 罗阳欢, 李浪, 梁恒飞, 胡家敏. 贵州茶树春季低温灾害气候风险评估与区划[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(4): 230-238. |
| [2] | 杨冰. 大豆疫霉菌的致病机制及寄主分子响应和防控方法研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(3): 133-142. |
| [3] | 刘金仙, 王丽娟, 刘杰, 傅仙玉, 武广珩. 茶树钙调蛋白结合转录激活因子(CAMTA)家族基因鉴定与表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(3): 71-82. |
| [4] | 母时风, 温晓蕾, 冯丽娜, 赵德轩, 高素红, 高朋, 齐慧霞. 一种引起板栗内腐病的果生炭疽菌鉴定及其生物学特性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(9): 122-128. |
| [5] | 杨娅琳, 吴峰婧琳, 陈健鑫, 武自强, 刘丽, 张东华, 马焕成, 伍建榕. 油茶根腐病根际土壤、根系内真菌群落结构和多样性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(7): 121-135. |
| [6] | 卢登洋, 童盼盼, 闫敏, 鲍荆凯, 刘鸣哲, 夏怡蕾, 吴翠云. 库尔勒香梨大果芽变的鉴定与评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 52-64. |
| [7] | 石玉涛, 谢惠珍, 郑淑琳, 羽观华, 王飞权, 李力, 张渤, 李远华, 罗盛财. 武夷山地方茶树种质生化特性和茶多糖清除超氧阴离子自由基活性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 65-76. |
| [8] | 郑德有, 左东云, 王巧莲, 吕丽敏, 程海亮, 顾爱星, 宋国立. 氟节胺与杀菌剂复配防治棉花枯萎病的增效药剂筛选[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 119-124. |
| [9] | 方泰军, 侯璐, 白露超. 柴达木地区患根腐病枸杞根际土壤微生物多样性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 133-139. |
| [10] | 周世莹, 刘晏辰, 张洋, 杨雪松, 关伟军, 高扬. 大耳白兔骨髓间充质干细胞的分离培养与生物学鉴定[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 96-105. |
| [11] | 王鑫慈, 李军乔, 李晨芹, 田甜, 曲俊儒. 一株乳突赤壳属蕨麻致病菌的鉴定及生物学特性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 87-95. |
| [12] | 栗佳宁, 李爱霞, 霍佳欢, 冯丽娜, 郭思柔, 王建华, 温晓蕾, 孙伟明, 齐慧霞. 几种板栗品种对链格孢菌的室内抗性比较及防治药剂筛选[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 123-131. |
| [13] | 郑淑琳, 石玉涛, 王飞权, 吴邦强, 李远华, 张渤, 叶乃兴. 不同茶树种质资源花器矿质元素含量分析与综合评价[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 178-188. |
| [14] | 许鑫, 孟昆, 蔡红英, 杨培龙, 蒋显仁. 乳酸菌在猪生产中的应用研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(2): 19-26. |
| [15] | 杨克泽, 吴芳, 魏玉杰, 汪亮芳, 常浩, 吴之涛, 杨宪忠. 河西冷凉地区芍药根腐病病原鉴定及室内药剂筛选[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(10): 144-151. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号