




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (6): 30-44.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0900
鲁一薇1( ), 夏雪岩1(
), 夏雪岩1( ), 赵宇1, 崔纪菡1, 刘猛1, 黄玫红1, 褚程1, 刘建军2, 李顺国1(
), 赵宇1, 崔纪菡1, 刘猛1, 黄玫红1, 褚程1, 刘建军2, 李顺国1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-12-07
接受日期:2024-03-04
出版日期:2024-06-15
发布日期:2024-06-12
通讯作者:
夏雪岩,李顺国
作者简介:鲁一薇E-mail: 1604425941@qq.com基金资助:
Yiwei LU1( ), Xueyan XIA1(
), Xueyan XIA1( ), Yu ZHAO1, Jihan CUI1, Meng LIU1, Meihong HUANG1, Cheng CHU1, Jianjun LIU2, Shunguo LI1(
), Yu ZHAO1, Jihan CUI1, Meng LIU1, Meihong HUANG1, Cheng CHU1, Jianjun LIU2, Shunguo LI1( )
)
Received:2023-12-07
Accepted:2024-03-04
Online:2024-06-15
Published:2024-06-12
Contact:
Xueyan XIA,Shunguo LI
摘要:
钾是作物生长不可缺少的元素,挖掘提高作物钾吸收能力的基因,增强作物对缺钾的耐受性具有重要的意义。以‘冀谷45’为供试材料,幼苗长至6叶期时进行缺钾胁迫7 d,通过农艺指标及转录组分析挖掘缺钾胁迫的相关基因。结果表明,缺钾胁迫影响谷子的生长发育,株高、叶宽、叶长、茎粗、苗期地上部干重及叶绿素含量低于CK,而根长、根表面积显著增加。转录组分析显示,缺钾胁迫后217个基因表达上调,38个基因表达下调。GO功能富集发现,差异表达基因主要富集于核糖体的结构成分、有机氮化合物代谢过程、蛋白质代谢过程、细胞蛋白质代谢过程、无膜细胞器等类别。KEGG功能富集结果表明,差异表达基因主要富集于核糖体、植物激素信号转导、谷胱甘肽代谢等19个通路。进而筛选出35个与激素表达显著相关的基因,19个氧化应激相关差异表达基因,10个转录因子家族及11个与转导信号相关的基因,1个与氨基酸及核苷酸的糖代谢相关的基因。候选基因Seita.9G193900属于CYP45084A亚家族,调控S型木质素合成的关键酶;Seita.5G365500属于WRKY家族,调控抗病响应基因PAD3等基因的表达;Seita.3G216900是RNA聚合酶Ⅱ转录亚基37E相关介质——HSPA1s辅助蛋白;Seita.4G286000为几丁内质内切酶基因CHIB,调控糖的合成与酵解。以上结果初步揭示了谷子缺钾胁迫相关基因的转录调控,为谷子耐缺钾相关基因的克隆与功能验证奠定基础。
中图分类号:
鲁一薇, 夏雪岩, 赵宇, 崔纪菡, 刘猛, 黄玫红, 褚程, 刘建军, 李顺国. 缺钾胁迫下谷子转录组分析及相关基因挖掘[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 30-44.
Yiwei LU, Xueyan XIA, Yu ZHAO, Jihan CUI, Meng LIU, Meihong HUANG, Cheng CHU, Jianjun LIU, Shunguo LI. Transcriptome Profiling and Gene Mining of Millet Response to Potassium Deficiency Stress[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(6): 30-44.
| 成分Component | 对照 Control | 缺钾 Potassium deficiency |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 mol·L-1 Ca(NO3)2·4H2O | 5 | 5 |
| 1.0 mol·L-1 KNO3 | 5 | — |
| 1 mol·L-1 NaH2PO4 | — | 1 |
| 1.0 mol·L-1 NaNO3 | — | 5 |
| 1.0 mol·L-1 MgSO4·7H2O | 2 | 2 |
| 1.0 mol·L-1 KH2PO4 | 1 | — |
| 0.5% Fe-EDTA | 1 | 1 |
微量元素母液 Trace element mother liquor | 1 | 1 |
| ddH2O | 985 | 985 |
总体积 Total volume | 1 000 | 1 000 |
表1 不同处理营养液配方 (mL)
Table 1 Nutrient solution formula for nitrogen deficiency treatment
| 成分Component | 对照 Control | 缺钾 Potassium deficiency |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 mol·L-1 Ca(NO3)2·4H2O | 5 | 5 |
| 1.0 mol·L-1 KNO3 | 5 | — |
| 1 mol·L-1 NaH2PO4 | — | 1 |
| 1.0 mol·L-1 NaNO3 | — | 5 |
| 1.0 mol·L-1 MgSO4·7H2O | 2 | 2 |
| 1.0 mol·L-1 KH2PO4 | 1 | — |
| 0.5% Fe-EDTA | 1 | 1 |
微量元素母液 Trace element mother liquor | 1 | 1 |
| ddH2O | 985 | 985 |
总体积 Total volume | 1 000 | 1 000 |
引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5'-3 ') |
|---|---|
| Seita.9G193900-F2 | ATGTTTGGCGGGACGGAGAC |
| Seita.9G193900-R2 | CCGATGGCCCAGACGTTGA |
| Seita.5G299700-F | GCGGGAGGACTTCGTGATGC |
| Seita.5G299700-R | CGGTGACGGGAATGCTGGA |
| Seita.5G365500-F1 | CGGCCCTCCTCACCTCCAGTAT |
| Seita.5G365500-R1 | CGCGTCCATGCCTTGTTGC |
| Seita.3G216900-F | ACCCGTCCGTGCAGAGTGA |
| Seita.3G216900-R | GGCAGTGGGCTCGTTGATT |
| Seita.7G222200-F1 | GGTGGTGGAGGTCTTCGTC |
| Seita.7G222200-R1 | TGTTGCCACTGTGCTTGATG |
| Seita.4G286000-F2 | GACGCCACCATCGCCTTCA |
| Seita.4G286000-R2 | GTTGGACCCGTAGCTGACCC |
| Seita.2G285600-F | TGCACGTCCACTGCCACATC |
| Seita.2G285600-R | CACGAACGCCTTCAGAACCAC |
| SiActin-F | GGCAAACAGGGAGAAGATGA |
| SiActin-R | GAGGTTGTCGGTAAGGTCACG |
表 2 谷子差异表达基因 qRT-PCR 引物信息
Table 2 Information of primers used in qRT-PCR of differentially expressed genes in foxtail millet
引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5'-3 ') |
|---|---|
| Seita.9G193900-F2 | ATGTTTGGCGGGACGGAGAC |
| Seita.9G193900-R2 | CCGATGGCCCAGACGTTGA |
| Seita.5G299700-F | GCGGGAGGACTTCGTGATGC |
| Seita.5G299700-R | CGGTGACGGGAATGCTGGA |
| Seita.5G365500-F1 | CGGCCCTCCTCACCTCCAGTAT |
| Seita.5G365500-R1 | CGCGTCCATGCCTTGTTGC |
| Seita.3G216900-F | ACCCGTCCGTGCAGAGTGA |
| Seita.3G216900-R | GGCAGTGGGCTCGTTGATT |
| Seita.7G222200-F1 | GGTGGTGGAGGTCTTCGTC |
| Seita.7G222200-R1 | TGTTGCCACTGTGCTTGATG |
| Seita.4G286000-F2 | GACGCCACCATCGCCTTCA |
| Seita.4G286000-R2 | GTTGGACCCGTAGCTGACCC |
| Seita.2G285600-F | TGCACGTCCACTGCCACATC |
| Seita.2G285600-R | CACGAACGCCTTCAGAACCAC |
| SiActin-F | GGCAAACAGGGAGAAGATGA |
| SiActin-R | GAGGTTGTCGGTAAGGTCACG |
性状 Trait | 对照 Control | 缺钾 Potassium deficiency |
|---|---|---|
株高 Plant height /cm | 12.43 | 9.36* |
倒一叶叶宽 Top 1 leaf width /cm | 0.80 | 0.67 |
倒一叶叶长 Top 1 leaf length /cm | 20.75 | 17.75* |
倒二叶叶宽 Top 2 leaf width /cm | 0.80 | 0.67 |
倒二叶叶长 Top 2 leaf length/ cm | 19.63 | 19.50 |
倒三叶叶宽 Top 3 leaf width/cm | 0.80 | 0.60 |
倒三叶叶长 Top 3 leaf length /cm | 18.05 | 16.55* |
茎宽 Stem width /cm | 3.31 | 2.51 |
苗期地上部干重 Seedling stage aboveground dry weight/g | 0.07 | 0.06 |
苗期地下部干重 Seedling stage underground dry weight /g | 0.01 | 0.02 |
表3 缺钾胁迫谷子幼苗农艺性状的差异分析
Table 3 Analysis of differences in agronomic traits of millet seedlings under potassium deficiency stress
性状 Trait | 对照 Control | 缺钾 Potassium deficiency |
|---|---|---|
株高 Plant height /cm | 12.43 | 9.36* |
倒一叶叶宽 Top 1 leaf width /cm | 0.80 | 0.67 |
倒一叶叶长 Top 1 leaf length /cm | 20.75 | 17.75* |
倒二叶叶宽 Top 2 leaf width /cm | 0.80 | 0.67 |
倒二叶叶长 Top 2 leaf length/ cm | 19.63 | 19.50 |
倒三叶叶宽 Top 3 leaf width/cm | 0.80 | 0.60 |
倒三叶叶长 Top 3 leaf length /cm | 18.05 | 16.55* |
茎宽 Stem width /cm | 3.31 | 2.51 |
苗期地上部干重 Seedling stage aboveground dry weight/g | 0.07 | 0.06 |
苗期地下部干重 Seedling stage underground dry weight /g | 0.01 | 0.02 |
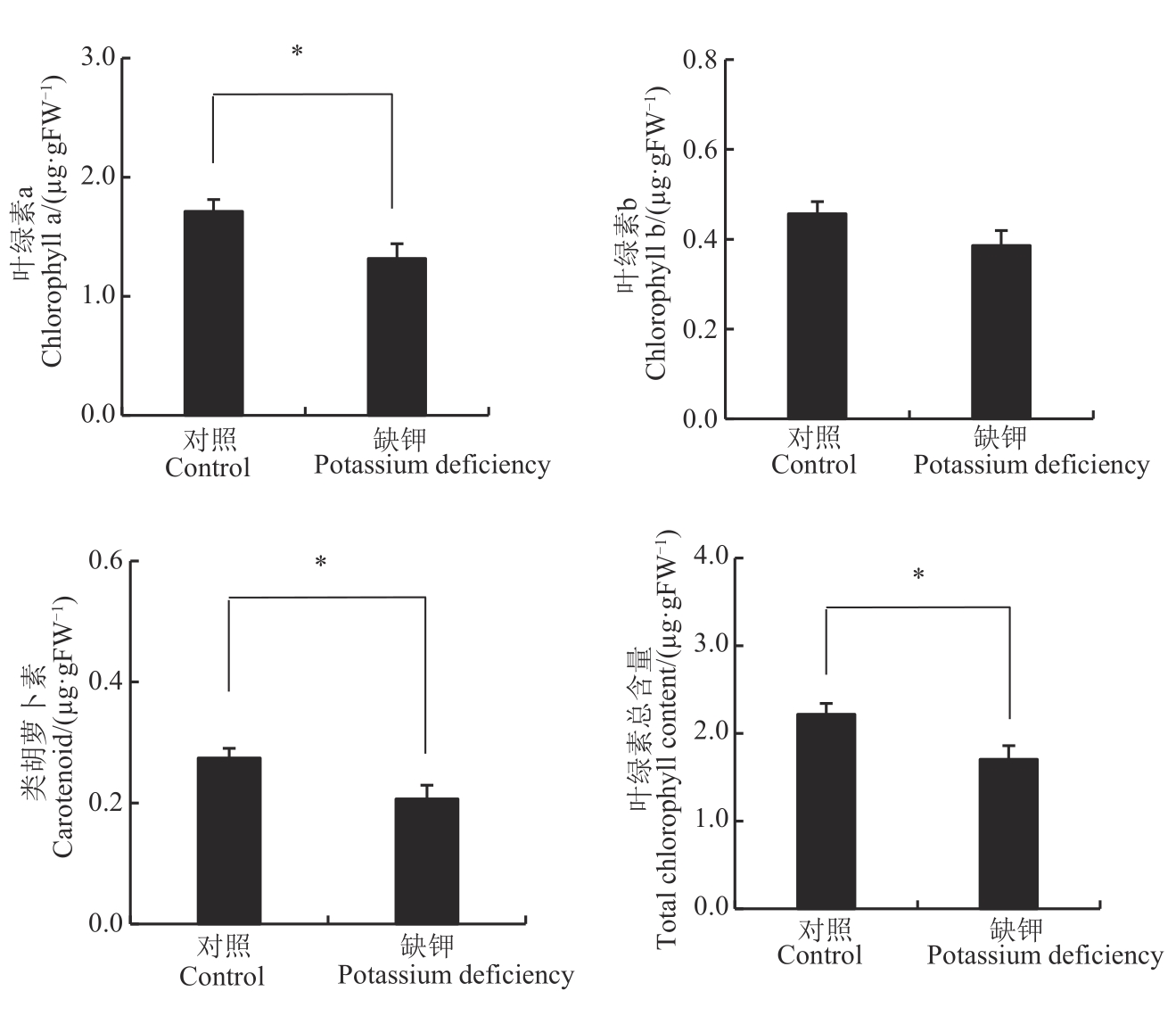
图2 缺钾胁迫对谷子幼苗叶绿素含量的影响注:*表示差异在P<0.05 水平显著。
Fig. 2 Effect of potassium deficiency stress on chlorophyll content in millet seedlingsNote: * means significant difference at P<0.05 level.
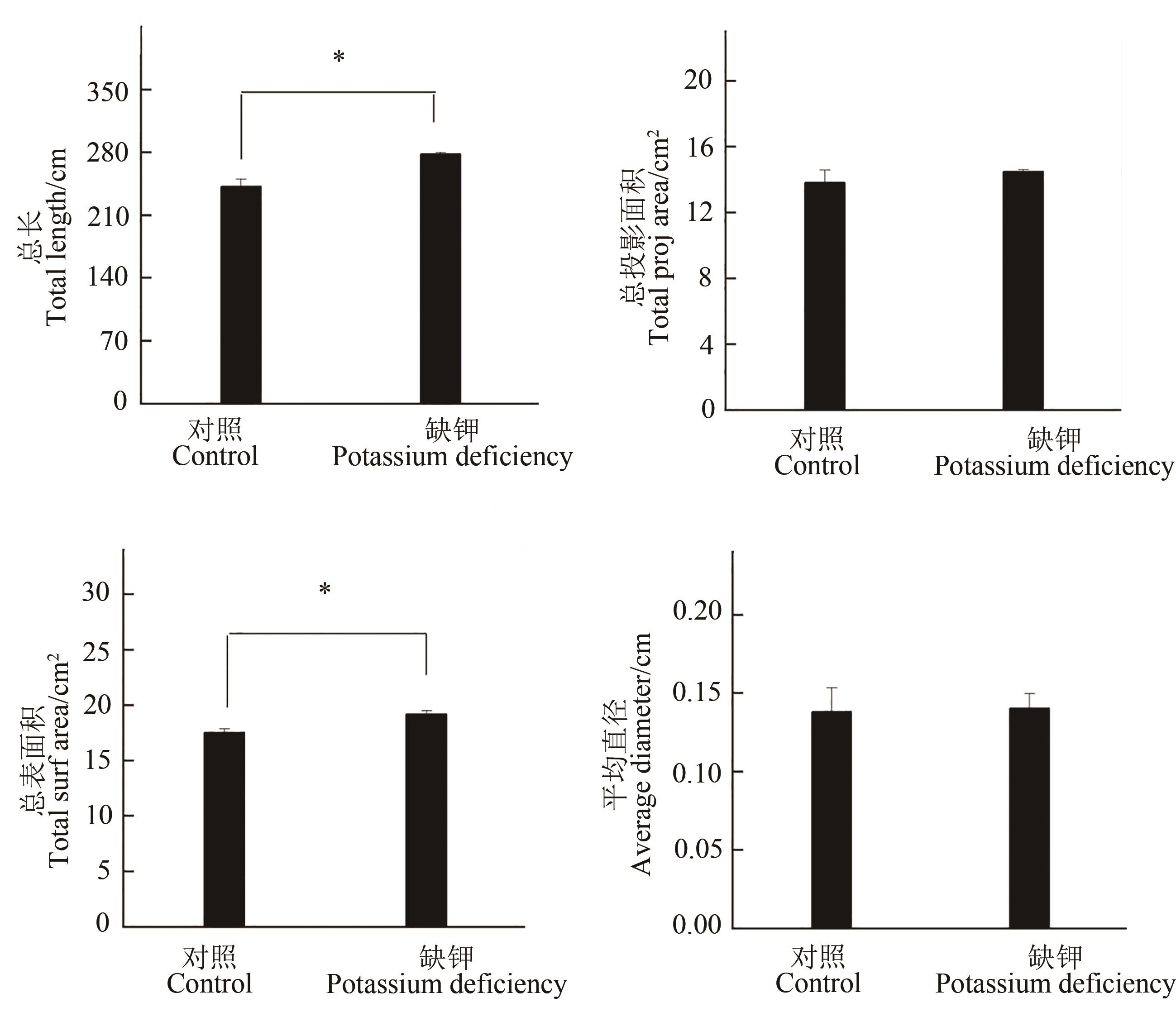
图3 缺钾胁迫对谷子幼苗根系性状的影响注:*表示差异在P<0.05水平显著。
Fig. 3 Effects of potassium deficiency stress on root traits of millet seedlingsNote: * means significant difference at P<0.05 level.
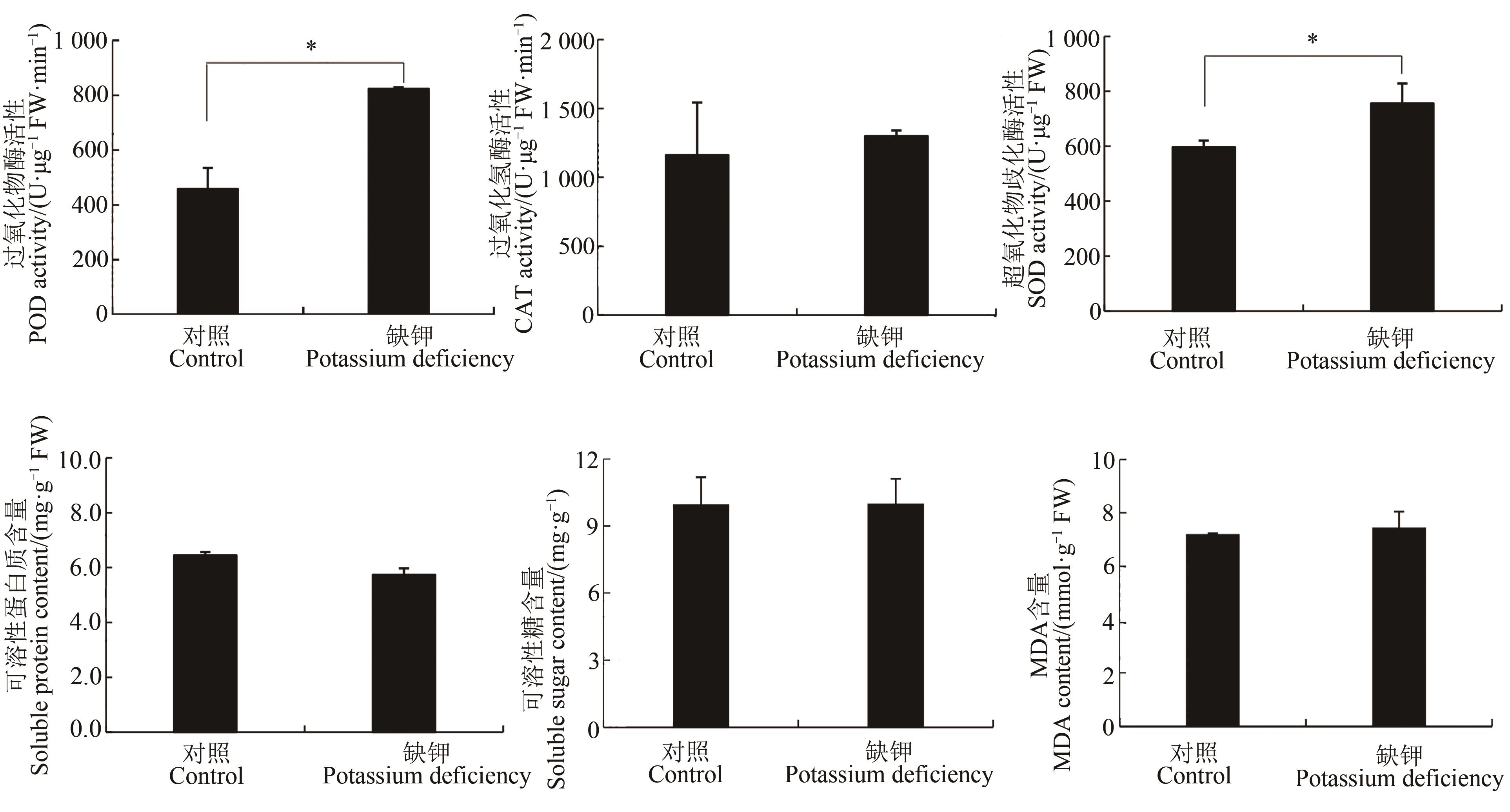
图4 缺钾胁迫对谷子幼苗叶片抗氧化指标的影响注:*表示差异在 P<0.05 水平显著。
Fig. 4 Effect of potassium deficiency stress on antioxidant indexes in leaves of foxtail millet seedlingsNote: * means significant difference at P<0.05 level.
样品 Sample | 原始读数 Raw reads | 过滤读数 Clean reads | 碱基含量 GC content/% | 多个映射 Multiple mapped | 唯一映射 Uniquely mapped | 映射比率 Mapping Ratio/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
对照 Control | CK-1 | 46 868 802 | 46 106 644 | 49.45 | 2 097 694 | 40 095 522 | 86.97 |
| CK-2 | 44 338 374 | 43 789 738 | 49.98 | 2 111 597 | 38 217 463 | 87.28 | |
| CK-3 | 45 196 350 | 44 462 108 | 50.03 | 2 855 499 | 37 291 700 | 83.88 | |
| 缺钾Potassium deficiency | QK-1 | 45 814 604 | 44 963 384 | 49.28 | 3 083 637 | 38 025 162 | 84.58 |
| QK-2 | 42 927 104 | 42 284 578 | 50.06 | 2 059 902 | 37 037 265 | 87.60 | |
| QK-3 | 51 831 874 | 51 061 668 | 56.00 | 2 097 363 | 45 595 390 | 89.30 | |
表4 测序数据质量评估
Table 4 Summary of the sequencing data quality
样品 Sample | 原始读数 Raw reads | 过滤读数 Clean reads | 碱基含量 GC content/% | 多个映射 Multiple mapped | 唯一映射 Uniquely mapped | 映射比率 Mapping Ratio/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
对照 Control | CK-1 | 46 868 802 | 46 106 644 | 49.45 | 2 097 694 | 40 095 522 | 86.97 |
| CK-2 | 44 338 374 | 43 789 738 | 49.98 | 2 111 597 | 38 217 463 | 87.28 | |
| CK-3 | 45 196 350 | 44 462 108 | 50.03 | 2 855 499 | 37 291 700 | 83.88 | |
| 缺钾Potassium deficiency | QK-1 | 45 814 604 | 44 963 384 | 49.28 | 3 083 637 | 38 025 162 | 84.58 |
| QK-2 | 42 927 104 | 42 284 578 | 50.06 | 2 059 902 | 37 037 265 | 87.60 | |
| QK-3 | 51 831 874 | 51 061 668 | 56.00 | 2 097 363 | 45 595 390 | 89.30 | |
途径 Pathway | 基因数量 Gene number |
|---|---|
| 核糖体Ribosome | 74 |
| 植物激素信号转导Plant hormone signal transduction | 35 |
| 谷胱甘肽代谢Glutathione metabolism | 28 |
| 信号通路-植物MAPK signaling pathway-plant MAPK | 27 |
| 丙氨酸天冬氨酸和谷氨酸代谢Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism | 15 |
| 丝氨酸甘氨酸和苏氨酸代谢Glycine, serine and threonine metabolism | 13 |
| 真核生物的核糖体合成Ribosome biogenesis in eukaryotes | 13 |
| 精氨酸生物合成Arginine biosynthesis | 10 |
| 苯丙氨酸、酪氨酸、色氨酸生物合成Phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis | 10 |
| 酪氨酸代谢Tyrosine metabolism | 10 |
| 苯丙胺酸代谢Phenylalanine metabolism | 9 |
| 异喹啉类生物碱的生物合成Isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis | 8 |
| 氮代谢Nitrogen metabolism | 8 |
| 玉米素生物合成Zeatin biosynthesis | 8 |
| 泛醌和其他萜醌的合成Ubiquinone and other terpenoid-quinone biosynthesis | 8 |
| 脂肪酸的降解Fatty acid degradation | 8 |
| 精氨酸和脯氨酸代谢Arginine and proline metabolism | 8 |
| 莨菪烷哌啶和吡啶碱的生物合成Tropane, piperidine and pyridine alkaloid biosynthesis | 7 |
| β-氨基丙酸代谢β-alanine metabolism | 7 |
表5 差异基因KEGG通路显著富集列表
Table 5 The significant enriched KEGG pathways of DEGs
途径 Pathway | 基因数量 Gene number |
|---|---|
| 核糖体Ribosome | 74 |
| 植物激素信号转导Plant hormone signal transduction | 35 |
| 谷胱甘肽代谢Glutathione metabolism | 28 |
| 信号通路-植物MAPK signaling pathway-plant MAPK | 27 |
| 丙氨酸天冬氨酸和谷氨酸代谢Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism | 15 |
| 丝氨酸甘氨酸和苏氨酸代谢Glycine, serine and threonine metabolism | 13 |
| 真核生物的核糖体合成Ribosome biogenesis in eukaryotes | 13 |
| 精氨酸生物合成Arginine biosynthesis | 10 |
| 苯丙氨酸、酪氨酸、色氨酸生物合成Phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis | 10 |
| 酪氨酸代谢Tyrosine metabolism | 10 |
| 苯丙胺酸代谢Phenylalanine metabolism | 9 |
| 异喹啉类生物碱的生物合成Isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis | 8 |
| 氮代谢Nitrogen metabolism | 8 |
| 玉米素生物合成Zeatin biosynthesis | 8 |
| 泛醌和其他萜醌的合成Ubiquinone and other terpenoid-quinone biosynthesis | 8 |
| 脂肪酸的降解Fatty acid degradation | 8 |
| 精氨酸和脯氨酸代谢Arginine and proline metabolism | 8 |
| 莨菪烷哌啶和吡啶碱的生物合成Tropane, piperidine and pyridine alkaloid biosynthesis | 7 |
| β-氨基丙酸代谢β-alanine metabolism | 7 |
激素种类 Hormone kind | 基因识别码 Gene identification code | 基因名称 Gene name | log2(FC) | 描述 Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
赤霉素 Gibberellin | Seita.3G246300 | GID1B | 1.11 | 赤霉素受体 Gibberellin receptor | |
生长素 Auxin | Seita.7G230900 | AUX | 2.20 | 生长素诱导的蛋白 Auxin induced like-protein | |
| Seita.1G252000 | AUX | 2.21 | 生长素调节的相关蛋白 Auxin-regulated protein-related | ||
| Seita.4G241400 | ARF | 7.17 | 生长素反应蛋白 Auxin responsive protein (auxin_inducible) | ||
| Seita.1G345400 | ARF | 2.36 | 生长素反应蛋白 Auxin responsive protein (auxin_inducible) | ||
| Seita.1G333600 | ARF | 1.59 | 生长素反应蛋白 Auxin responsive protein (auxin_inducible) | ||
| Seita.9G194600 | ARF | 1.93 | 生长素反应蛋白 Auxin responsive protein (auxin_inducible) | ||
| Seita.2G375300 | GH3.2 | 4.78 | 吲哚-3-乙酸酰胺合成酶 Indole-3-acetic acid-amido synthetase | ||
| Seita.1G075600 | ARF | 2.50 | 生长素反应蛋白 Auxin responsive protein (auxin_inducible) | ||
| Seita.7G182000 | AUX | 2.95 | 生长素调节的相关蛋白Auxin-regulated protein-related | ||
表6 缺钾胁迫响应的激素信号相关基因差异表达分析及注释
Table 6 Analysis and annotation of the hormone signal-related DEGs response to potassium-deficiency
激素种类 Hormone kind | 基因识别码 Gene identification code | 基因名称 Gene name | log2(FC) | 描述 Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
赤霉素 Gibberellin | Seita.3G246300 | GID1B | 1.11 | 赤霉素受体 Gibberellin receptor | |
生长素 Auxin | Seita.7G230900 | AUX | 2.20 | 生长素诱导的蛋白 Auxin induced like-protein | |
| Seita.1G252000 | AUX | 2.21 | 生长素调节的相关蛋白 Auxin-regulated protein-related | ||
| Seita.4G241400 | ARF | 7.17 | 生长素反应蛋白 Auxin responsive protein (auxin_inducible) | ||
| Seita.1G345400 | ARF | 2.36 | 生长素反应蛋白 Auxin responsive protein (auxin_inducible) | ||
| Seita.1G333600 | ARF | 1.59 | 生长素反应蛋白 Auxin responsive protein (auxin_inducible) | ||
| Seita.9G194600 | ARF | 1.93 | 生长素反应蛋白 Auxin responsive protein (auxin_inducible) | ||
| Seita.2G375300 | GH3.2 | 4.78 | 吲哚-3-乙酸酰胺合成酶 Indole-3-acetic acid-amido synthetase | ||
| Seita.1G075600 | ARF | 2.50 | 生长素反应蛋白 Auxin responsive protein (auxin_inducible) | ||
| Seita.7G182000 | AUX | 2.95 | 生长素调节的相关蛋白Auxin-regulated protein-related | ||
基因识别码 Gene identification code | 差异倍数 log2 (FC) | 描述 Description |
|---|---|---|
| Seita.5G155100 | 3.76 | 过氧化物酶Peroxidase |
| Seita.7G180100 | 2.09 | 细胞色相关B561 Cytochrome B561-related |
| Seita.9G173500 | 5.14 | 细胞色素P450 85A1相关Cytochrome P450 85A1-related |
| Seita.5G064800 | 2.68 | 细胞色素P450家族成员Cytochrome P450 family member |
| Seita.4G077800 | 1.93 | 相关的NADH氧化还原酶NADH oxidoreductase-related |
| Seita.3G298400 | 4.71 | 细胞色素P450 CYP2亚家族Cytochrome P450 CYP2 subfamily |
| Seita.9G545600 | 3.39 | 细胞色素P450 CYP4/CYP19/CYP26亚家族Cytochrome P450 CYP4/CYP19/CYP26 subfamilies |
| Seita.9G342600 | 2.54 | 氧化还原酶Oxidoreductase |
| Seita.3G260700 | 3.27 | 细胞色素P450 CYP4/CYP19/CYP26亚家族Cytochrome P450 CYP4/CYP19/CYP26 subfamilies |
| Seita.9G081400 | 4.02 | 过氧化物酶/乳过氧化物酶Peroxidase / Lactoperoxidase |
| Seita.5G235200 | 1.23 | 细胞色素P450家族成员Cytochrome P450 family member |
| Seita.2G004800 | 2.65 | 过氧化物酶35相关Peroxidase 35-related |
| Seita.9G199900 | 1.09 | 细胞色素B561相关Cytochrome B561-related |
| Seita.1G117500 | 3.12 | 过氧化氢酶Catalase |
| Seita.1G042800 | 2.82 | 细胞色素P450家族成员Cytochrome P450 family member |
| Seita.3G226600 | 1.85 | 氧化还原酶Oxidoreductase |
| Seita.9G193900 | 4.77 | 细胞色素P450 84A1相关Cytochrome P450 84A1-related |
| Seita.5G010100 | 1.87 | 细胞色素P450 CYP2亚家族Cytochrome P450 CYP2 subfamily |
| Seita.9G444200 | 1.69 | L-抗坏血酸过氧化物酶L-ascorbate peroxidase |
表7 缺钾胁迫下抗氧化相关基因的表达差异分析及注释
Table 7 Analysis and annotation of the ex antioxidant related DEGs in response to potassium-deficiency
基因识别码 Gene identification code | 差异倍数 log2 (FC) | 描述 Description |
|---|---|---|
| Seita.5G155100 | 3.76 | 过氧化物酶Peroxidase |
| Seita.7G180100 | 2.09 | 细胞色相关B561 Cytochrome B561-related |
| Seita.9G173500 | 5.14 | 细胞色素P450 85A1相关Cytochrome P450 85A1-related |
| Seita.5G064800 | 2.68 | 细胞色素P450家族成员Cytochrome P450 family member |
| Seita.4G077800 | 1.93 | 相关的NADH氧化还原酶NADH oxidoreductase-related |
| Seita.3G298400 | 4.71 | 细胞色素P450 CYP2亚家族Cytochrome P450 CYP2 subfamily |
| Seita.9G545600 | 3.39 | 细胞色素P450 CYP4/CYP19/CYP26亚家族Cytochrome P450 CYP4/CYP19/CYP26 subfamilies |
| Seita.9G342600 | 2.54 | 氧化还原酶Oxidoreductase |
| Seita.3G260700 | 3.27 | 细胞色素P450 CYP4/CYP19/CYP26亚家族Cytochrome P450 CYP4/CYP19/CYP26 subfamilies |
| Seita.9G081400 | 4.02 | 过氧化物酶/乳过氧化物酶Peroxidase / Lactoperoxidase |
| Seita.5G235200 | 1.23 | 细胞色素P450家族成员Cytochrome P450 family member |
| Seita.2G004800 | 2.65 | 过氧化物酶35相关Peroxidase 35-related |
| Seita.9G199900 | 1.09 | 细胞色素B561相关Cytochrome B561-related |
| Seita.1G117500 | 3.12 | 过氧化氢酶Catalase |
| Seita.1G042800 | 2.82 | 细胞色素P450家族成员Cytochrome P450 family member |
| Seita.3G226600 | 1.85 | 氧化还原酶Oxidoreductase |
| Seita.9G193900 | 4.77 | 细胞色素P450 84A1相关Cytochrome P450 84A1-related |
| Seita.5G010100 | 1.87 | 细胞色素P450 CYP2亚家族Cytochrome P450 CYP2 subfamily |
| Seita.9G444200 | 1.69 | L-抗坏血酸过氧化物酶L-ascorbate peroxidase |
转录因子基因 Transcription factor gene | 基因识别码 Gene identification code | 差异倍数 log2 (FC) |
|---|---|---|
| ERF | Seita.5G280700 | 2.19 |
| WRKY | Seita.2G433600 | 4.98 |
| Seita.5G365500 | 3.31 | |
| NAC | Seita.3G225400 | 4.91 |
| Seita.5G391200 | 1.15 |
表8 缺钾胁迫响应的转录因子基因表达差异分析及注释
Table 8 Analysis and annotation of the transcription factor-related DEGs in response to potassium-deficiency
转录因子基因 Transcription factor gene | 基因识别码 Gene identification code | 差异倍数 log2 (FC) |
|---|---|---|
| ERF | Seita.5G280700 | 2.19 |
| WRKY | Seita.2G433600 | 4.98 |
| Seita.5G365500 | 3.31 | |
| NAC | Seita.3G225400 | 4.91 |
| Seita.5G391200 | 1.15 |
基因识别码 Gene identification code | 差异倍数 log2(FC) | 描述 Description |
|---|---|---|
| Seita.3G216900 | 1.87 | RNA聚合酶Ⅱ转录亚基37E相关介质 Mediator of RNA polymeraseⅡtranacription subunit 37E-realated |
| Seita.9G536800 | -2.03 | Armadillo重复含驱动蛋白样蛋白2 Armadillo repeat-containing kinesin-like protein 2 |
| Seita.2G212100 | -1.79 | SF71-磷脂酶D SF71-phospholipase D |
| Seita.1G047800 | 1.07 | SF245-ADP-核糖基化因子GTPASE激活蛋白AGD12相关 SF245-ADP-ribosylation factor GTPASE-activating protein AGD12-related |
| Seita.2G044300 | 1.66 | 小核核糖核蛋白相关蛋白B和N Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein-associated protein B and N |
| Seita.3G065200 | 1.49 | 小核核糖核蛋白SM D2 Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein SM D2 |
| Seita.5G376100 | 2.21 | RNA聚合酶Ⅱ转录亚基37E相关介质 Mediator of RNA polymeraseⅡtranacription subunit 37E-realated |
| Seita.9G367700 | 1.05 | SF9-小核核糖核蛋白 SF9-Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein |
| Seita.2G402800 | 1.37 | RNA结合蛋白RBM8/Tsunagi(RRM超家族) RNA-binding protein RBM8/Tsunagi (RRM superfamily) |
| Seita.5G092600 | 2.88 | SF141&小分子热休克蛋白HSP20家族 SF141-Small heat-shock protein HSP20 family |
| Seita.J011800 | 1.27 | SF17-BCR相关蛋白 SF17-BCR-associated protein,BAP |
| Seita.4G286000 | 6.66 | SF34-碱性内切酶 B SF34-basic endochitinase B |
表9 缺钾胁迫下转导信号与糖代谢相关基因的表达分析及注释
Table 9 Analysis and annotation of the transduction signal related genes in response to potassium-deficiency
基因识别码 Gene identification code | 差异倍数 log2(FC) | 描述 Description |
|---|---|---|
| Seita.3G216900 | 1.87 | RNA聚合酶Ⅱ转录亚基37E相关介质 Mediator of RNA polymeraseⅡtranacription subunit 37E-realated |
| Seita.9G536800 | -2.03 | Armadillo重复含驱动蛋白样蛋白2 Armadillo repeat-containing kinesin-like protein 2 |
| Seita.2G212100 | -1.79 | SF71-磷脂酶D SF71-phospholipase D |
| Seita.1G047800 | 1.07 | SF245-ADP-核糖基化因子GTPASE激活蛋白AGD12相关 SF245-ADP-ribosylation factor GTPASE-activating protein AGD12-related |
| Seita.2G044300 | 1.66 | 小核核糖核蛋白相关蛋白B和N Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein-associated protein B and N |
| Seita.3G065200 | 1.49 | 小核核糖核蛋白SM D2 Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein SM D2 |
| Seita.5G376100 | 2.21 | RNA聚合酶Ⅱ转录亚基37E相关介质 Mediator of RNA polymeraseⅡtranacription subunit 37E-realated |
| Seita.9G367700 | 1.05 | SF9-小核核糖核蛋白 SF9-Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein |
| Seita.2G402800 | 1.37 | RNA结合蛋白RBM8/Tsunagi(RRM超家族) RNA-binding protein RBM8/Tsunagi (RRM superfamily) |
| Seita.5G092600 | 2.88 | SF141&小分子热休克蛋白HSP20家族 SF141-Small heat-shock protein HSP20 family |
| Seita.J011800 | 1.27 | SF17-BCR相关蛋白 SF17-BCR-associated protein,BAP |
| Seita.4G286000 | 6.66 | SF34-碱性内切酶 B SF34-basic endochitinase B |
| 1 | 刁现民.禾谷类杂粮作物耐逆和栽培技术研究新进展[J].中国农业科学, 2019, 52(22): 3943-3949. |
| DIAO X M. Progresses in stress tolerance and field cultivation studies of orphan cereals in China [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2019, 52(22): 3943-3949. | |
| 2 | 王海岗,温琪汾,穆志新,等.山西谷子核心资源群体结构及主要农艺性状关联分析[J].中国农业科学, 2019, 52(22): 4088-4099. |
| WANG H G, WEN Q F, MU Z X, et al.. Population structure and association analysis of main agronomic traits of Shanxi core collection in foxtail millet [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2019, 52(22): 4088-4099. | |
| 3 | 刁现民.中国谷子产业与产业技术体系[M].北京:中国农业科学技术出版社,2011: 1-3. |
| DIAO X M. Millet industry and industrial technology system in China [M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2011: 1-3. | |
| 4 | 张亚琦.氮、钾肥对杂交谷子产量及耗水规律的影响研究[D].保定:河北农业大学,2014. |
| ZHANG Y Q. Study on the effects of nitrogen and potassium fertilizer on yield and water consumption pattern of hybrid millet [D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2014. | |
| 5 | PETTIGEEW W T. Potassium influences on yield and quality production for maize, wheat, soybean and cotton [J]. Physiol. Plantarum., 2008,133(4):670-681. |
| 6 | 张亚琦,李淑文,杜雄,等.施钾对杂交谷子水分利用效率和产量的影响[J].河北农业大学学报, 2014, 37(6) :1-6. |
| ZHANG Y Q, LI S W, DU X, et al.. Effect of potassium fertilization on water use efficiency and yield of hybrid millet [J]. J. Hebei Agric. Univ., 2014, 37(6) :1-6. | |
| 7 | 张毓宜.钾素对谷子糖代谢及营养品质的影响[D].太谷:山西农业大学, 2021. |
| ZHANG Y Y. Effect of potassium on sugar metabolism and nutritional quality of millet [D]. Taigu: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2021. | |
| 8 | JIN C, LU C, QU H Y, et al.. Alteration of nutriental lacation and ransportergenes expression in rice under N, P, K and Mg deficiencies [J]. Acta Physiol. Plant, 2012,34(3):939-946. |
| 9 | VICENTE-AGULLO F, RIGAS S, DESBROSSES G, et al.. Potassium carrier TRH1 is required for auxin transport in Arabidopsis roots [J]. Plant J., 2004, 40(4):523-535. |
| 10 | 李艳芬,郑君岗,尹美强,等.低钾胁迫对谷子幼苗叶片光合作用的影响[J].西北植物学报, 2022,42(6): 1021-1024. |
| LI Y F, ZHENG J G, YIN M Q, et al.. Effect of low potassium stress on leaf photosynthesis of millet seedings [J]. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occidentalia Sin., 2022,42(6): 1021-1024. | |
| 11 | 何应对.香蕉幼苗根系对缺钾胁迫的响应及分子机制研究[D].武汉:华中农业大学, 2021. |
| HE Y D. Response of banana seedling roots to potassium deficiency stress and its molecular mechanism [D]. Wuhan:Huazhong Agricultural University, 2021. | |
| 12 | 黄文功,姜卫东,姚玉波,等.亚麻响应低钾胁迫转录谱分析[J].作物学报, 2021, 47(6):1070-1081. |
| HANG W G, JIANG W D, YAO Y B, et al.. Transcriptome profiling of flax (Linum usttatissimum L.) response to low potassium stress [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2021, 47(6):1070-1081. | |
| 13 | 王婉晶.TOR信号通路通过CIPK23调控马铃薯和拟南芥的钾离子吸收和生长[D].重庆:西南大学, 2017. |
| WANG W J. TOR signaling pathway regulated potassium absorption and growth via CIPK23 in potato and Arabidopsis [D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2017. | |
| 14 | GAMBALE F, UOZUMI N. Properties of shaker-type potassium channels in higher plants [J]. J. Membr. Biol., 2006,210(1):1-19. |
| 15 | LEBAUDY A, VERY A A, SENTENAC H. K+ channel activity in plants: genes, regulations and functions [J]. FEBS Lett., 2007, 581(12): 2357-2366. |
| 16 | 王学奎,黄见良.植物生理生化实验原理与技术[M].第3版.北京:高等教育出版社, 2015:1-324. |
| 17 | 王桂芹.硒和VitC对高氟所致氧化应激、DNA损伤及Bcl-2蛋白表达影响研究[D].广州: 广东药科大学, 2011. |
| WANG G Q. Studies on the influence of selenium and vitamin C on oxidative stress, DNA damage and Bcl-2 protein expression induced by high fluoride [D]. Guangzhou: Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, 2011. | |
| 18 | 邹琦.植物生理生化实验指导[M].北京:中国农业出版社, 2003:1-108. |
| 19 | 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M].北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000: 1-279. |
| 20 | 王岳.甘蓝型油菜pol CMS温度敏感性的分子机制研究[D]. 武汉:华中农业大学, 2018. |
| WANG Y. Molecular mechanism of temperature sensitivity of pol CMS in Brassica napus L. [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University,2018. | |
| 21 | 吴雪霞,朱月林,朱为民,等.外源一氧化氮对NaCl胁迫下番茄幼苗生理影响[J].中国农业科学, 2006, 39(3):575-581. |
| WU X X, ZHU Y L, ZHU W M,et al.. Physilolgical effects of exogenous nitric oxide in tomato seedings under NaCl stress [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2006, 39(3):575-581. | |
| 22 | 万凯旋.谷子耐低钾品种筛选及其生理生化研究[D].太谷:山西农业大学,2020. |
| WAN K X. Screening of foxtail foxtail millet varieties with tolerance to low-potassium and study on its physiological and biochemical mechanis [D]. Taigu:Shanxi Agricultural University, 2020. | |
| 23 | 董轲, 许亚萍, 崔冰, 等.盐胁迫下不同钾素水平对海滨锦葵生长和光合作用的影响[J]. 植物生理学报, 2015, 51(10):1649-1657. |
| DONG K, XU Y P, CUI B, et al.. Effects of different potassium levels on the growth and photosynthesis of Kostelezkya virginica under salt stress [J]. Plant Physiol. J., 2015, 51 (10): 1649-1657. | |
| 24 | HU W, JIANG N, YANG J S, et al.. Potassium (K) supply affects K accumulation and photosynthetic physiology in two cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) cultivars with different K sensitivities [J]. Field Crops Res., 2016, 196:51-63. |
| 25 | 杨然, 郭树勋, 杨小慧, 等.硅对低钾胁迫下番茄幼苗生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 山东农业科学, 2022, 54(9): 55-63. |
| YANG R, GUO S L, YANG X H, et al.. Effects of silicon on growth and physiological characteristics of tomato seedlings under low potassium stress [J]. Shandong Agric. Sci., 2022, 54(9): 55-63. | |
| 26 | 田晓莉, 王刚卫, 杨富强, 等.棉花不同类型品种耐低钾能力的差异[J]. 作物学报, 2008, 34(10): 1770-1780. |
| TIAN X L, WANG G W, YANG F Q, et al.. Differences in tolerance to low-potassium supply among different types of cultivars in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2008, 34(10): 1770-1780. | |
| 27 | 王鲲娇. 油菜响应缺钾胁迫的转录组分析及其CPA家族差异表达基因的鉴定[D].武汉:华中农业大学, 2021. |
| WANG K J. Transcriptome analysis of Oilseed rape in response to potassium deficiency stress and identification of diffentially express genes in the CPA family [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2021. | |
| 28 | QIAO J Y, JIANG H Z, LIN Y Q, et al.. A novel miR167a-OsARF6-OsAUX3 module regulates grain length and weight in rice [J]. Mol. Plant, 2021, 14(10): 1683-1698. |
| 29 | FAN L S, Li R L, PAN J W, et al.. Endocytosis and its regulation in plants[J]. Trends in Plant Sci.,2015,20(6):388-397. |
| 30 | REYNOLDS G D, WANG C, PAN J W, et al.. Inroads into internalization: five years of endocytic exploration[J]. Plant Physiol., 2018,176(1): 208-218. |
| 31 | HALUSKOVA L, VALENTOVICOVA K, HUTTOVA J, et al.. Effect of abiotic stresses on glutathione peroxidase and glutathione S-transferase activity in barley root tips [J]. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 2009, 47(11/12):1069-1074. |
| 32 | 王航辉. 小麦响应钾离子胁迫的转录组学分析及候选基因TaHAK25的功能鉴定[D].郑州:河南农业大学, 2022. |
| WANG H H. Transcriptome analysis of wheat in response to potassium stress and functional identification of the candidate gene TaHAK25 [D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2022. | |
| 33 | ZHANG X Q, JIANG H, WANG H, et al.. Transcriptome analysis of rice seedling roots in response to potassium deficiency [J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2017,7(1):5523 [2024-04-01]. . |
| 34 | THORNBURG T E, LIU J, LI Q, et al.. Potassium deficiency significantly affected plant growth and development as well as microRNA-mediated mechanism in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) [J/OL]. Front. Plant Sci., 2020, 11:1219 [2024-04-01]. . |
| 35 | BENCKE-MALATO M, CABREIRA C, WIEBKE-STROHM B, et al.. Genome-wide annotation of the soybean WRKY family and functional characterization of genes involved in response to Phakopsora pachyrhizi infection [J/OL]. BMC Plant Biol., 2014, 14: 236 [2024-04-01]. . |
| 36 | QIU J L, FIIl B K, PETERSEN K, et al.. Arabidopsis MAP kinase 4 regulates gene expression through transcription factor release in the nucleus [J]. EMBO J., 2008,27(16):2214-2221. |
| [1] | 徐佳睿, 王逸茹, 赵绍赓, 李坤, 郑军. 玉米木质素合成途径基因ZmCCoAOMT1功能研究及转录组分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 30-43. |
| [2] | 李双, 王爱英, 焦浈, 池青, 孙昊, 焦涛. 盐胁迫下不同抗性小麦幼苗生理生化特性及转录组分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 20-32. |
| [3] | 李相吴, 刘自扬, 徐玉俊, 祝建波, 吴燕民. 真菌诱导子调控紫草素合成的分子机制探究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 78-88. |
| [4] | 王潇然, 李笑语, 孙慧, 于海东, 石永春. 硼胁迫下烟草叶片转录组分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 53-64. |
| [5] | 王云胜, 陈银翠, 程在, 张锦, 张传博. 过表达veA基因对冠突散囊菌次级代谢的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 77-86. |
| [6] | 马蓝, 彭晴, 徐小轻, 杨硕, 张宇微, 田丹丹, 施琳波, 石波, 乔宇. 大肠杆菌O157∶H7生物被膜状态下基因表达分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 71-88. |
| [7] | 李瑞珍, 姚建民, 王忠祥, 高凤翔, 窦贵新, 杨瑞平, 刘钊, 张继, 张振宇. 全生物降解渗水地膜覆盖冬播谷子产量结构关系分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 185-191. |
| [8] | 张会, 王越越, 赵波, 张丽玲, 郄倩茹, 韩渊怀, 李旭凯. 基于WGCNA的谷子苗期冷胁迫应答基因网络构建与核心因子发掘[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(10): 22-34. |
| [9] | 焦雄飞, 于晋, 冯乐勇, 郭耀东, 樊丽生. 不同播期对谷子DUS测试性状的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(8): 55-64. |
| [10] | 周雨青, 杨永飞, 葛常伟, 沈倩, 张思平, 刘绍东, 马慧娟, 陈静, 刘瑞华, 李士丛, 赵新华, 李存东, 庞朝友. 基于WGCNA的棉花子叶抗冷相关共表达模块鉴定[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(4): 52-62. |
| [11] | 赵晋锋, 余爱丽, 李颜方, 杜艳伟, 王高鸿, 王振华. 谷子SiCBL3对非生物胁迫响应特征分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(11): 68-75. |
| [12] | 郭瑞锋, 任月梅, 杨忠, 刘贵山, 任广兵, 张绶, 朱文娟. 草甘膦铵盐诱导谷子雄性不育的转录组分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(10): 35-43. |
| [13] | 李舒欣, 张浩, 郑厚胜, 郑培和, 逄世峰, 许世泉. 转录组分析二马牙和长脖类型林下参表型差异[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(9): 56-68. |
| [14] | 鱼冰星, 王宏富, 王振华, 张鹏, 成锴, 余爱丽, 闫海丽, 鱼冰洁. 多效唑对谷子茎秆特征及抗倒性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(8): 37-44. |
| [15] | 刘源, 张秀妍, 徐妙云, 郑红艳, 邹俊杰, 张兰, 王磊. 水稻干旱胁迫的small RNA转录组分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(6): 23-32. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号