




















中国农业科技导报 ›› 2024, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (6): 22-29.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0012
刘忠祥( ), 周文期, 李永生, 王晓娟, 杨彦忠, 连晓荣, 何海军, 周玉乾(
), 周文期, 李永生, 王晓娟, 杨彦忠, 连晓荣, 何海军, 周玉乾( )
)
收稿日期:2023-01-04
接受日期:2023-03-07
出版日期:2024-06-15
发布日期:2024-06-12
通讯作者:
周玉乾
作者简介:刘忠祥 E-mail: lzhxiang@sina.com;
基金资助:
Zhongxiang LIU( ), Wenqi ZHOU, Yongsheng LI, Xiaojuan WANG, Yanzhong YANG, Xiaorong LIAN, Haijun HE, Yuqian ZHOU(
), Wenqi ZHOU, Yongsheng LI, Xiaojuan WANG, Yanzhong YANG, Xiaorong LIAN, Haijun HE, Yuqian ZHOU( )
)
Received:2023-01-04
Accepted:2023-03-07
Online:2024-06-15
Published:2024-06-12
Contact:
Yuqian ZHOU
摘要:
矮秆资源是农作物矮化育种的物质基础,发掘矮秆基因资源对培育矮秆新品种具有重要作用。为了明确252CF裂变快中子辐射诱变玉米自交系KWS49筛选得到的矮秆突变体20F421的遗传特性和矮化机理,以20F421为材料分别与玉米自交系PH6WC、B73、Mo17及KWS49杂交构建F1和F2分离群体,分析矮秆性状的遗传模式,并以(20F421/B73)F2为定位群体,采用混池转录组测序(bulked segregant RNA-seq,BSR-seq)方法初步定位突变基因。结果表明,与KWS49相比,20F421的植株高度为95.2 cm,降低47.89%;穗位高度为23.9 cm,降低64.54%;茎秆节间长度显著缩短、叶片较直立密生,自交结实良好。遗传分析表明,F2分离群体野生型(高秆)与突变型(矮秆)植株性状分离比例符合3∶1,表明该突变体受单个核隐性基因控制;BSR-seq结果将突变基因定位在1号染色体177~255 Mb之间。通过与B73参考基因组进行比对发现,该区间内含有矮秆基因Br2,将20F421与br2突变体杂交进行等位性检测,F1和F2的株高均没有发生性状分离,表现为突变体20F421和br2表型,推测20F421的矮秆突变基因为矮秆基因Br2的等位突变。研究结果为进一步精细定位、克隆突变基因奠定基础,也为解析玉米矮化机理和培育矮秆玉米新品种提供重要基因资源和理论支撑。
中图分类号:
刘忠祥, 周文期, 李永生, 王晓娟, 杨彦忠, 连晓荣, 何海军, 周玉乾. 玉米矮秆突变体20F421的表型鉴定及遗传分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(6): 22-29.
Zhongxiang LIU, Wenqi ZHOU, Yongsheng LI, Xiaojuan WANG, Yanzhong YANG, Xiaorong LIAN, Haijun HE, Yuqian ZHOU. Phenotypic Identification and Genetic Analysis of a Dwarf Mutant 20F421 inMaize[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(6): 22-29.
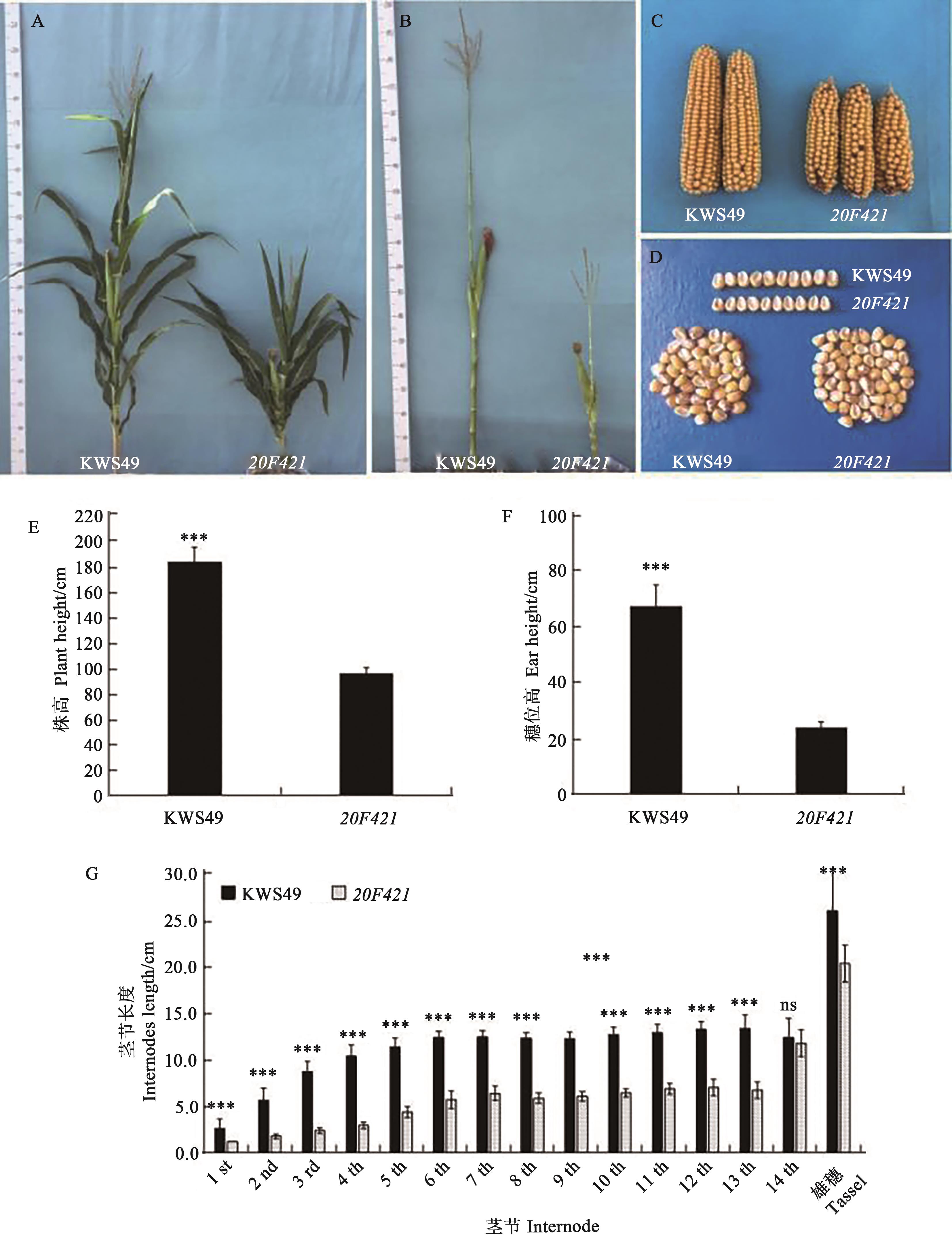
图1 玉米矮秆突变体20F421田间表型性状A:成株期表型;B:茎节表型;C:果穗;D:籽粒;E:株高;F:穗位高;G:茎节长度。 ***表示与20F421相比差异在P<0.001水平显著,ns表示差异不显著
Fig. 1 Phenotypes of dwarf mutant 20F421 in maizeA: Phenotypesat adult stage; B: Internode phenotypes at adult stage; C: Ear phenotypes; D: Grain; E: Plant height; F: Ear height; G: Internode length. *** indicates significant difference compared with 20F421 at P<0.001 level, ns indicates no significant difference
突变体20F421 Mutant20F421 | 野生型KWS49 Wild type KWS49 | P值 P value | 样本容量 Sample size(20F421/KWS49) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height/cm | 95.2±4.3 | 182.7±11.0 | 2.600 142×10-8 | 21/20 |
| 穗位Ear height/cm | 23.9±1.9 | 67.4±7.5 | 4.371 427×10-10 | 21/20 |
| 穗长Ear length/cm | 12.3±0.7 | 14.5±1.4 | 0.055 606 | 21/20 |
| 穗粗Ear diameter/cm | 3.7±0.2 | 3.9±0.2 | 0.849 836 | 21/20 |
| 穗行数 Row number per ear | 13.6±1.0 | 14.3±1.0 | 1.000 000 | 21/20 |
| 行粒数 Kernels per row | 19.3±2.8 | 30.1±12.1 | 0.005 992 | 21/20 |
| 秃尖长Rare ear length/cm | 1.4±0.6 | 1.2±0.4 | 0.122 239 | 21/20 |
| 雄穗长 Tassel length/cm | 27.0±2.3 | 32.2±2.4 | 0.037 186 | 21/20 |
| 雄穗分枝数 Number of tassel branches | 4.0±1.9 | 4.9±1.9 | 0.302 534 | 21/20 |
| 叶片数 Number of leaves | 13.5±0.6 | 13.5±0.7 | 0.343 959 | 21/20 |
| 倒3叶长Length of the third leaf/cm | 42.0±6.5 | 48.1±3.7 | 0.257 108 | 21/20 |
| 倒3叶宽 Width of the third leaf/cm | 6.4±0.5 | 6.7±0.7 | 0.979 684 | 21/20 |
表1 矮秆突变体20F421和野生型KWS49的农艺性状
Table 1 Agronomic traits of dwarf mutant 20F421 and wild type KWS49
突变体20F421 Mutant20F421 | 野生型KWS49 Wild type KWS49 | P值 P value | 样本容量 Sample size(20F421/KWS49) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height/cm | 95.2±4.3 | 182.7±11.0 | 2.600 142×10-8 | 21/20 |
| 穗位Ear height/cm | 23.9±1.9 | 67.4±7.5 | 4.371 427×10-10 | 21/20 |
| 穗长Ear length/cm | 12.3±0.7 | 14.5±1.4 | 0.055 606 | 21/20 |
| 穗粗Ear diameter/cm | 3.7±0.2 | 3.9±0.2 | 0.849 836 | 21/20 |
| 穗行数 Row number per ear | 13.6±1.0 | 14.3±1.0 | 1.000 000 | 21/20 |
| 行粒数 Kernels per row | 19.3±2.8 | 30.1±12.1 | 0.005 992 | 21/20 |
| 秃尖长Rare ear length/cm | 1.4±0.6 | 1.2±0.4 | 0.122 239 | 21/20 |
| 雄穗长 Tassel length/cm | 27.0±2.3 | 32.2±2.4 | 0.037 186 | 21/20 |
| 雄穗分枝数 Number of tassel branches | 4.0±1.9 | 4.9±1.9 | 0.302 534 | 21/20 |
| 叶片数 Number of leaves | 13.5±0.6 | 13.5±0.7 | 0.343 959 | 21/20 |
| 倒3叶长Length of the third leaf/cm | 42.0±6.5 | 48.1±3.7 | 0.257 108 | 21/20 |
| 倒3叶宽 Width of the third leaf/cm | 6.4±0.5 | 6.7±0.7 | 0.979 684 | 21/20 |
群体 Population | 观察值Observed values | 期望值Expected values | 卡方 χ2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 野生型Wild type | 突变体Mutant | 野生型Wild type | 突变体Mutant | ||
| (PH6WC×20F421) F2 | 85 | 36 | 90.75 | 30.25 | 1.215 |
| (B73×20F421) F2 | 357 | 104 | 345.75 | 115.25 | 1.337 |
| (MO17×20F421) F2 | 328 | 107 | 326.25 | 108.75 | 0.019 |
| (KWS49×20F421) F2 | 56 | 25 | 60.75 | 20.25 | 1.189 |
表2 F2分离群体中的目标性状分离和卡方测验
Table 2 Segregation analysis and Chi?square test of F2 segregating plants
群体 Population | 观察值Observed values | 期望值Expected values | 卡方 χ2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 野生型Wild type | 突变体Mutant | 野生型Wild type | 突变体Mutant | ||
| (PH6WC×20F421) F2 | 85 | 36 | 90.75 | 30.25 | 1.215 |
| (B73×20F421) F2 | 357 | 104 | 345.75 | 115.25 | 1.337 |
| (MO17×20F421) F2 | 328 | 107 | 326.25 | 108.75 | 0.019 |
| (KWS49×20F421) F2 | 56 | 25 | 60.75 | 20.25 | 1.189 |
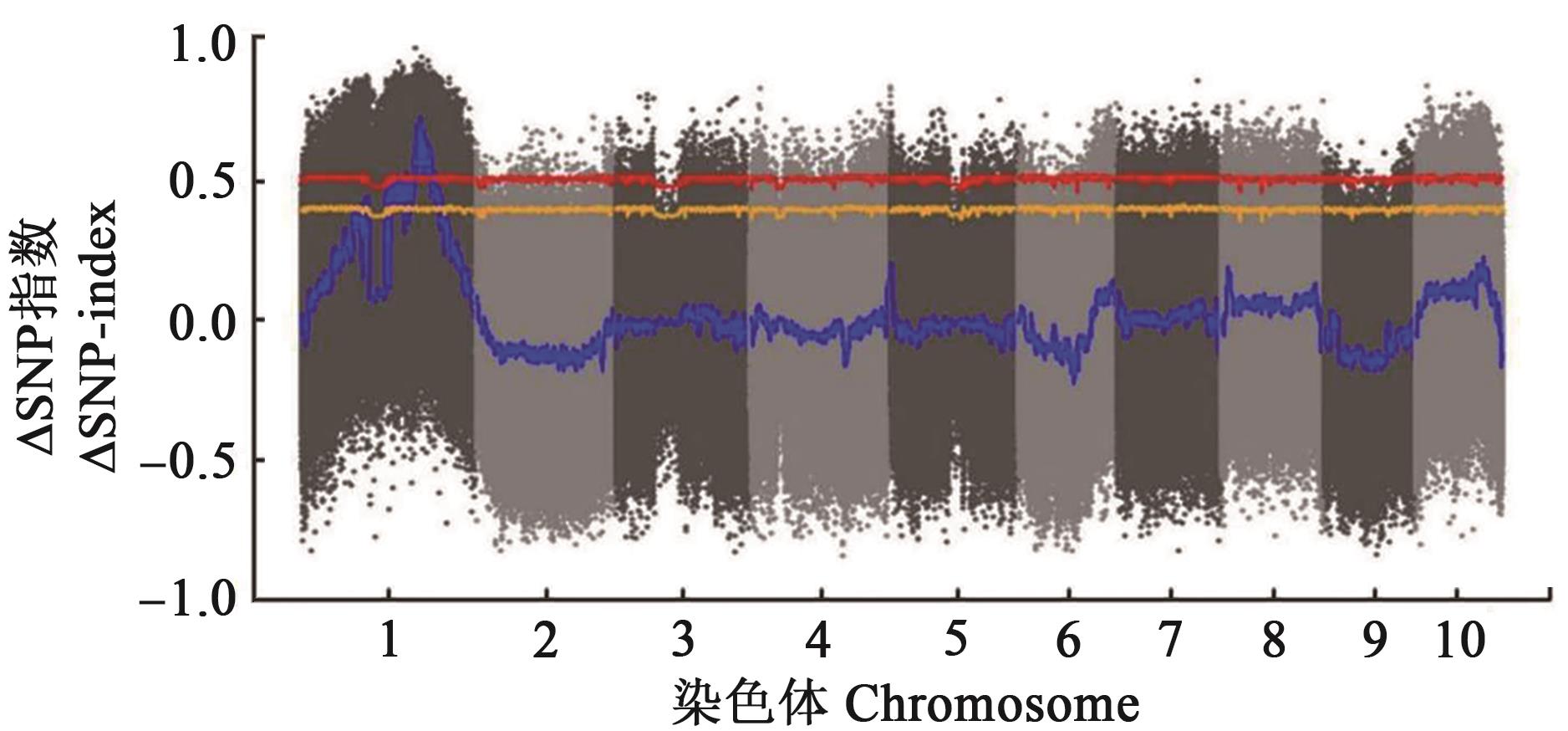
图2 玉米矮秆突变体20F421基因初步定位注:蓝色线表示2个混池SNP-index的差值;红色线表示99%置信区间;黄色线表示95%置信区间。
Fig. 2 Initial mapping of a dwarf mutant 20F421 in maizeNote:The blue line indicates the difference of SNP-index between two mixed pools; the red line represents 99% confidence interval; the yellow line indicates 95% confidence interval.
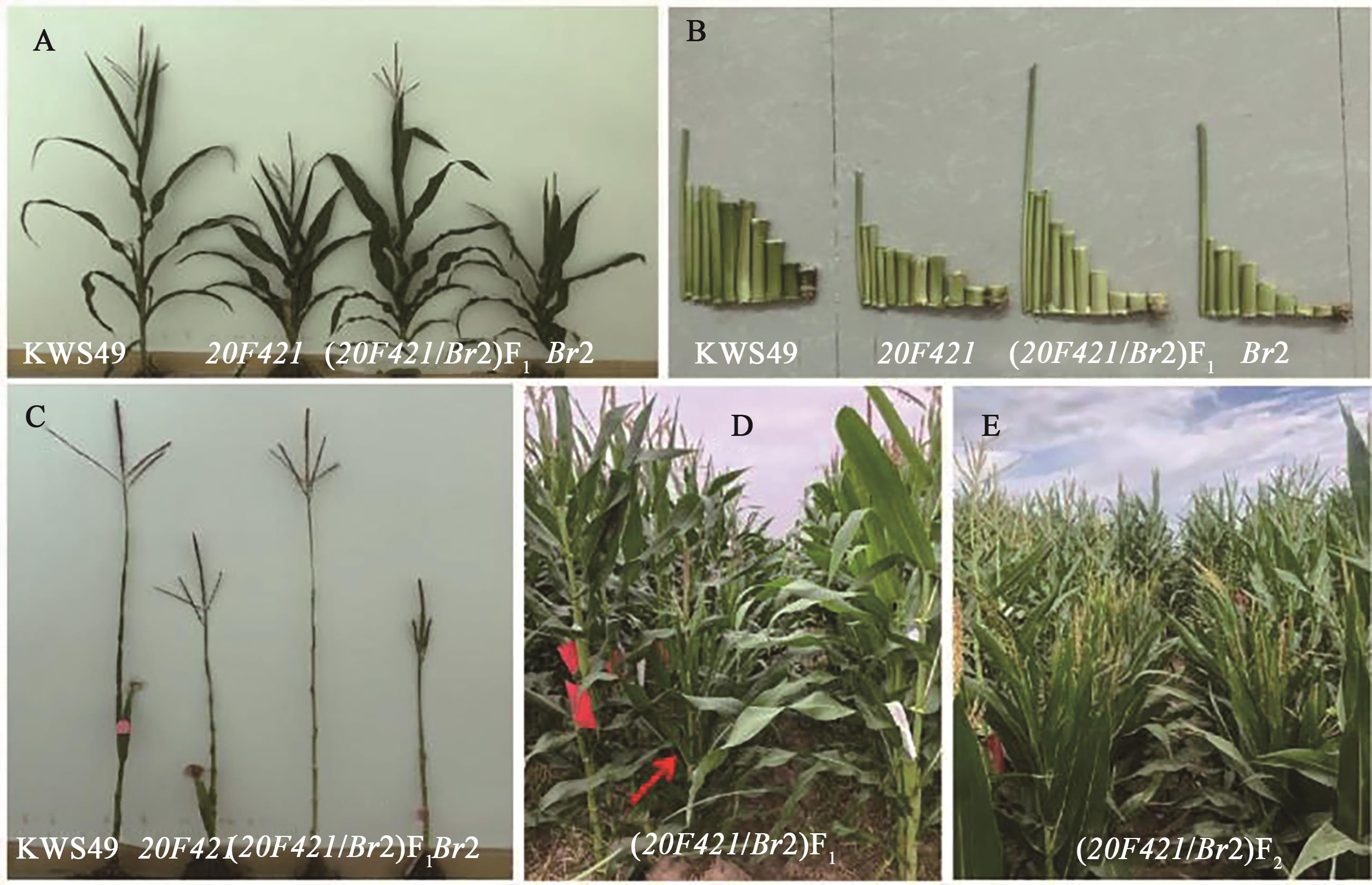
图3 玉米矮秆突变体20F421与br2的等位检测A: KWS49、20F421、(20F421×br2)F1、br2成株期表型;B: KWS49、20F421、(20F421×br2)F1、br2茎节长度表型;C: KWS49、20F421、(20F421×br2) F1、br2茎节数表型;D:(20F421×br2) F1田间表型;E:(20F421×br2) F2田间表型
Fig. 3 Allelic detection of a dwarf mutant 20F421 and br2 in maizeA: Phenotypes of KWS49,20F421,(20F421×br2) F1 and br2 at adult stage; B:Internode length of KWS49, 20F421,(20F421×br2)F1and br2; C: Internode phenotypes of KWS49, 20F421,(20F421×br2) F1and br2; D: Phenotypes of(20F421×br2) F1 in the field; E:Phenotypes of (20F421×br2) F2 in the field
| 1 | TENG F, ZHAI L H, LIU R X, et al.. ZmGA3ox2, a candidate gene for a major QTL, qPH3.1, for plant height in maize [J]. Plant J., 2013, 73: 405-416. |
| 2 | 刘忠祥. 玉米株高主效QTL定位研究综述[J].甘肃农业科技, 2018 (9): 62-69. |
| LIU Z X. A review of research on major QTL mapping for plant height in corn [J]. Gansu Agric. Sci. Technol., 2018 (9): 62-69. | |
| 3 | 宋朝玉, 张继余, 张清霞, 等. 玉米倒伏的类型、原因及预防治理措施[J]. 作物杂志, 2006(5): 36-38. |
| 4 | 勾玲, 黄建军, 张宾, 等. 群体密度对玉米茎秆抗倒力学和农艺性状的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2007, 33(10): 1688-1695. |
| GOU L, HUANG J J, ZHANG B, et al.. Effects of population density on stalk lodging resistant mechanism and agronomic characteristics of maize [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2007, 33(10): 1688-1695. | |
| 5 | 邱正高. 玉米矮秆突变体dm676的遗传分析及育种潜势研究[D]. 成都:四川农业大学, 2016. |
| QIU Z G. Study on genetic analysis and breeding potentially for maize dwarf mutant dm676 [D]. Chengdu: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2016. | |
| 6 | 徐敏, 石海春, 余学杰, 等. 一个玉米矮秆突变体K123d的遗传鉴定[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2017, 18(1): 155-163. |
| XU M, SHI H C, YU X J, et al.. Genetic identification of a dwarf mutant K123d in maize ( Zea mays L.) [J]. J. Plant Genet. Resour., 2017, 18(1): 155-163. | |
| 7 | 余传元. 论水稻新株型育种与绿色革命[J]. 江西农业学报, 1998, 10(1): 60-64. |
| YU C Y. Discussion on breeding for new plant type rice and green revolution [J]. Acta Agric. Jiangxi, 1998, 10(1): 60-64. | |
| 8 | MONNA L, KITAZAWA N, YOSHINO R, et al.. Positional cloning of rice semidwarfing gene, sd-1: rice ‘green revolution gene’encodes a mutant enzyme involved in gibberellin synthesis [J]. DNA Res., 2002, 9(1): 11-17. |
| 9 | SASAKI A, ASHIKARI M, UEGUCHI-TANAKA M, et al.. Green revolution: a mutant gibberellin-synthesis gene in rice [J]. Nature, 2002, 416 (6682): 701-702. |
| 10 | SPIELMEYER W F, ELLIS M H, CHANDLER P M, et al.. Semidwarf (sd-1), ‘green revolution’rice, contains a defective gibberellins 20-oxidase gene [J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2002, 99(13): 9043 -9048. |
| 11 | 周文期, 连晓荣, 刘忠祥, 等. 玉米株高和穗位高的调控机理研究[J]. 分子植物育种, 2021, 19(23): 7965-7976. |
| ZHOU W Q, LIAN X R, LIU Z X, et al.. Research progress on the mechanism of controlling maize plant height and ear height [J]. Mol. Plant Breeding, 2021, 19(23): 7965-7976. | |
| 12 | PENG J, RICHARDS D E, HARTLEY N M, et al.. ‘Green revolution’ genes encode mutant gibberellin response modulators [J]. Nature, 1999, 400(6741): 256-261. |
| 13 | 徐敏. 一个玉米矮秆突变体K123d的遗传鉴定[D]. 成都: 四川农业大学, 2016. |
| XU M. Genetic identification of a dwarf mutant K123d in maize (Zea mays L.) [D]. Chengdu: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2016. | |
| 14 | 王立静. 玉米矮秆基因Dt和坏死基因net⁃t的图位克隆与功能分析[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2012. |
| WANG L J. Map-based cloning and functional analysis of dwarf gene Dt and necrotic gene nec⁃t in maize [D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2012. | |
| 15 | 王益军, 苗楠, 施亚婷, 等. 一份玉米显性矮杆突变体的遗传分析[J]. 华北农学报, 2010, 25(5) : 90-93. |
| WANG Y J, MIAO N, SHI Y T, et al.. Genetic analysis of a dominant dwarf mutant in maize [J]. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin., 2010, 25(5): 90-93. | |
| 16 | WANG Y I, DENG D X, DING H D, et al.. Gibberellin biosynthetic deficiency is responsible for maize dominant dwarf 11 ( D11 ) mutant phenotype: physiological and transcriptomic evidence [J/OL]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(6): e66466[2022-12-22]. . |
| 17 | CASSANI E, BERTOLINI E, BADONE F C, et al.. Characterization of the frst dominant dwarf maize mutant carrying a single amino acid insertion in the VHYNP domain of the dwarf 8 gene [J]. Mol. Breeding, 2009, 24: 375-385. |
| 18 | BENSEN R J, JOHAL G S, CRANE V C, et al.. Cloning and charac-terization of the maize An1 gene [J]. Plant Cell, 1995, 7(1): 75-84. |
| 19 | LAWIT S J, WYCH H M, XU D, et al.. Maize DELLA proteins dwarf plant 8 and dwarf plant 9 as modulators of plant development [J]. Plant Cell Physiol., 2010, 51(11): 1854-1868. |
| 20 | 樊景胜. 玉米矮生基因遗传及其利用[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 1999 (1) : 29-30. |
| 21 | 刘忠祥, 寇思荣, 连晓荣, 等. 玉米黄绿叶突变体表型鉴定及基因初步定位[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2020, 21(2): 452-458. |
| LIU Z X, KOU S R, LIAN X R, et al.. Phenotypic identification and low-resolution mapping of a yellow-green leaf mutant in maize [J]. J. Plant Genet. Resour., 2020, (21)2: 452-458. | |
| 22 | 王晓娟, 何海军, 刘忠祥,等. 一个玉米叶夹角突变体的表型鉴定及遗传分析[J].西北农业学报, 2019, 28(8): 1226-1231. |
| WANG X J, HE H J, LIU Z X, et al.. Phenotyping and genetic analysis of leaf angle mutant in maize(Zea mays L.) [J].Acta Agric. Bor-Occid. Sin., 2019, 28(8): 1226-1231. | |
| 23 | 刘忠祥, 何海军, 王晓娟, 等. 玉米叶夹角突变体 FU1603 的选育及遗传分析[J]. 甘肃农业科技,2019 (12): 1-4. |
| LIU Z X, HE H J, WANG X J, et al.. Breeding and genetic analysis of maize leaf angle mutant FU1603 [J]. Gansu Agric. Sci. Technol., 2019 (12): 1-4. | |
| 24 | 李玉荣. BSR-Seq方法定位玉米黄化突变基因[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2014. |
| LI Y R. Etiolation mutant gene mapping via bulked segregant RNA-Seq(BSR-Seq) method in maize [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2014. | |
| 25 | 杨秀. 玉米矮生突变体das的鉴定和基因定位[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2019. |
| YING X. Characterization and gene mapping of das mutant in maize (Zea mays L.) [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2019. | |
| 26 | 岳洪. 新的玉米矮秆突变基因的鉴定与遗传分析[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2008. |
| YUE H. Identification and genetic analysis of a new dwarf mutant gene in maize [D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2008. | |
| 27 | 桑贤春, 杜川, 王晓雯, 等. 水稻矮秆脆性突变体dbc1的鉴定与基因定位[J]. 作物学报, 2013, 39(4): 626-631. |
| SANG X C, DU C, WANG X W, et al.. Identification and gene mapping of dwarf and brittle culm mutant dbc1 in Oryza sativa [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2013, 39(4): 626-63. | |
| 28 | SALVI S, CORNETI S, BELLOTTI M, et al.. Genetic dissection of maize phenology using an intraspecific introgression library [J/OL]. BMC Plant Biol., 2011, 11: 4 [2022-12-22]. . |
| 29 | LYU H, ZHENG J, WANG T, et al.. The maize d2003, a novel allele of VP8, is required for maize internode elongation [J]. Plant Mol. Biol., 2014, 84: 243-257. |
| 30 | 刘忠祥, 杨梅, 殷鹏程, 等. 玉米株高主效QTL qPH3.2 精细定位及遗传效应分析[J]. 作物学报, 2018, 44(9): 1357-1366 . |
| LIU Z X, YANG M, YIN P C, et al.. Fine mapping and genetic effect analysis of a major QTL qPH3.2 associated with plant height in maize (Zea mays L.) [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2018, 44(9): 1357-1366. | |
| 31 | MULTANI D S, BRIGGS S P, CHAMBERLIN M A, et al.. Loss of an MDR transporter in compact stalks of maize br2 and sorghum dw3 mutants [J]. Science, 2003, 302(5642): 81-84。 |
| 32 | 周文期,张贺通,何海军,等. 调控玉米株高和穗位高候选基因Zmdle1的定位[J]. 中国农业科学,2023, 56(5): 821-837. |
| ZHOU W Q, ZHANG H T, HE H J, et al.. Candidate gene localization of ZmDLE1 gene regulating plant height and ear height in maize [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2023, 56(5): 821-837. | |
| 33 | 蒋成功. 玉米矮杆突变体d12的表型分析及基因克隆[D]. 合肥:安徽农业大学,2020. |
| JIANG C G. Phenotyping and gene cloning of a dwarf mutant d12 in maize [D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2020. | |
| 34 | 陈华伟, 石海春, 余学杰, 等. 1份60Co γ射线诱变玉米雄性不育突变体的遗传分析[J]. 核农学报, 2016, 30(5): 829-834. |
| CHEN H W, SHI H C, YU X J, et al.. Genetic analysis of a maize male sterile mutant induced by 60Co-γ irradiation [J]. Nucl. Agric. Sci., 2016, 30(5): 829-834. | |
| 35 | 刘平, 杨慧, 孟雪, 等. 植物矮化研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2010, 38(27): 15442-15446. |
| LIU P, YANG H, MENG X . et al .. Research advance of plant dwarfing [J]. Anhui Agric., Sci., 2010, 38(27): 15442-15446. | |
| 36 | 张志胜, 谢利, 萧爱兴, 等. 秋水仙素处理兰花原球茎对其生长和诱变效应的影响[J]. 核农学报, 2005,19 (1): 19-23. |
| ZHANG Z S, XIE L, XIAO A X, et al.. Effects of colchicine treatment on growth differentiation and mutagenseis of protocorm-like-body(plb) of orchid [J]. Acta Agric. Nucl. Sin., 2005, 19(1): 19-23. | |
| 37 | 赵长云,白光庭,何少勇,等.玉米矮秆基因d15的克隆及表达分析[J].植物遗传资源学报, 2023,24(4):1141-1150. |
| ZHAO C Y, BAI G T, HE S Y, et al.. Cloning and expression analysis of dwarf gene d15 in maize [J]. J. Plant Genet. Resour., 2023,24(4):1141-1150. | |
| 38 | PILU R, CASSANI E, VILLA D, et al.. Isolation and characterization of a new mutant allele of brachytic2 maize gene [J]. Mol. Breeding, 2007, 20(2): 83-91. |
| 39 | WEI L, ZHANG X, ZHANG Z, et al.. A new allele of the Brachytic2 gene in maize can efficiently modify plant architecture [J]. Heredity, 2018, 121(1): 75-86. |
| 40 | 石云素, 于永涛, 宋燕春, 等. 一个新矮生玉米种质资源的发现与遗传鉴定[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2008, 9(4): 521-524. |
| SHI Y S, YU Y T, SONG Y C, et al.. Discovery and genetic identification of a new dwarf germplasm in maize [J]. J. Plant Genet. Resour., 2008, 9(4): 521-524. | |
| 41 | 石云素, 于永涛, 宋燕春, 等. 一个新矮生玉米种质资源矮生性状QTL的定位[J]. 作物学报, 2010, 36(2): 256-260. |
| SHI Y S, YU Y T, SONG Y C, et al.. QTL identification for plant height in a new dwarf germplasm of maize [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2010, 36(2): 256-260. | |
| 42 | ROBERTO P, ELENA C, DANIELE V, et al.. Isolation and characterization of a new mutant allele of brachytic 2 maize gene [J]. Mol. Breeding, 2007, 20: 83-91. |
| 43 | CASSANI E, VILLA D, DURANTE M, et al.. The brachytic 2 and 3 maize double mutant shows alterations in plant growth and embryo development [J]. Plant Growth Regul., 2011, 64(2):185-192. |
| 44 | 戴景瑞. 玉米的矮生基因及其遗传效应[J]. 遗传, 1979, 1 (5) :40-43. |
| 45 | TOMOYA N K, TAKAAKI N, MASAYOSKI N, et al.. Production of dwarf lettuce by overexpressing a pumpkin gibberellin 20-oxidase gene [J]. Plant Physiol., 2001, 126: 965-972. |
| [1] | 曹炎, 杨艳涛, 王国刚. 我国玉米生产与消费时空格局演变及匹配性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 1-10. |
| [2] | 高思琦, 杨新建, 朱德琪, 关明玮, 寇云婷, 满程, 焦健. 抗菌肽PAJE对金黄色葡萄球菌及其SCVs的杀菌作用机制研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 156-166. |
| [3] | 徐佳睿, 王逸茹, 赵绍赓, 李坤, 郑军. 玉米木质素合成途径基因ZmCCoAOMT1功能研究及转录组分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(5): 30-43. |
| [4] | 安东升, 严程明, 刘洋, 赵宝山, 孔冉, 苏俊波, 徐志军. 甘蔗间作系统生产力分析及适宜品种筛选[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(4): 37-45. |
| [5] | 赵亚凤, 王孟雪, 王德帅, 王冬冬, 李园, 胡峻峰. 基于CP-DeepLabv3+的玉米根系图像分割[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 110-116. |
| [6] | 吴占清, 陈威, 赵展, 许海良, 李豪远, 彭星星, 陈东旭, 张明月. 玉米GRAS基因家族的全基因组鉴定及生物信息学分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 15-25. |
| [7] | 曾建光, 刘桃李, 孙林娟, 袁定阳, 黄钰博, 金晨钟, 谭炎宁. 水稻矮秆迟抽穗突变体d534的性状及其对赤霉素的敏感性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(3): 7-14. |
| [8] | 丛文成, 袁立敏, 蒙仲举, 杨宇. 玉米芯颗粒对风沙土毛管水运移和蒸发特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(2): 198-207. |
| [9] | 王韵弘, 苗琪, 李俊超, 王红叶, 张济世, 崔振岭. 田间管理措施对滨海盐渍地区中低产田生产力的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(1): 163-172. |
| [10] | 姚建民, 马俊奎, 王忠祥, 毕昕媛, 李瑞珍, 杨瑞平, 刘钊, 郭丰辉. 全生物降解渗水地膜在大豆-玉米带状复合种植中的应用效果研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(9): 178-185. |
| [11] | 孟亚轩, 马玮, 姚旭航, 孙颖琦, 钟鑫, 黄山, 瓮巧云, 刘颖慧, 袁进成. 玉米产量对氮肥的响应因素研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 153-160. |
| [12] | 苑雅俊, 冯家兴, 杨启帆, 白雪, PUSHPA R A J, 边大红, 崔彦宏. 黄淮海平原北部不同熟性夏玉米品种抗倒伏能力研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(7): 21-28. |
| [13] | 张盼盼, 李川, 张美微, 赵霞, 牛军, 乔江方. 氮肥减施下添加硝化抑制剂对夏玉米氮素累积转运和产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 181-189. |
| [14] | 赵威, 马睿, 王佳, 郭宏杰, 许金普. 基于果穗图像的玉米品种分类识别[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 97-106. |
| [15] | 周宇, 李佳玉, 王乐, 贾晓爽, 高思琦, 王潇, 焦健. 金黄色葡萄球菌小菌落突变体诱导筛选及特性研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 147-157. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号