




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (5): 24-33.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0062
• BIOTECHNOLOGY & LIFE SCIENCE • Previous Articles Next Articles
Chen CHEN( ), Ke SHI, Changwei ZHU, Guiying JIANG(
), Ke SHI, Changwei ZHU, Guiying JIANG( ), Lan LUO, Weiwei MENG, Fang LIU, Fengmin SHEN, Shiliang LIU(
), Lan LUO, Weiwei MENG, Fang LIU, Fengmin SHEN, Shiliang LIU( )
)
Received:2022-01-23
Accepted:2022-06-21
Online:2023-05-20
Published:2023-07-13
Contact:
Guiying JIANG,Shiliang LIU
陈琛( ), 石柯, 朱长伟, 姜桂英(
), 石柯, 朱长伟, 姜桂英( ), 罗澜, 孟威威, 刘芳, 申凤敏, 刘世亮(
), 罗澜, 孟威威, 刘芳, 申凤敏, 刘世亮( )
)
通讯作者:
姜桂英,刘世亮
作者简介:陈琛 E-mail: 1048778349@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Chen CHEN, Ke SHI, Changwei ZHU, Guiying JIANG, Lan LUO, Weiwei MENG, Fang LIU, Fengmin SHEN, Shiliang LIU. Effects of Planting Density and Nitrogen Application Rate on Wheat Photosynthetic Characteristics, Yield, and Soil Nitrogen Content in Fluvo-aquic Soil in Northern Henan Province[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(5): 24-33.
陈琛, 石柯, 朱长伟, 姜桂英, 罗澜, 孟威威, 刘芳, 申凤敏, 刘世亮. 种植密度和施氮量对豫北潮土区小麦光合特性和产量及土壤氮素的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(5): 24-33.
| 处理 Treatment | 小麦播量 Wheat seeding rate | N | P2O5 | K2O | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基施 Base application | 追施 Topdressing | ||||
| CBCF | 232.50 | 150 | 69.0 | 120 | 120 |
| ZBCF | 302.25 | 150 | 69.0 | 120 | 120 |
| ZBJF | 302.25 | 120 | 55.2 | 120 | 120 |
| CBJF | 232.50 | 120 | 55.2 | 120 | 120 |
Table 1 Wheat seeding amount and fertilizer amount in each treatment
| 处理 Treatment | 小麦播量 Wheat seeding rate | N | P2O5 | K2O | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基施 Base application | 追施 Topdressing | ||||
| CBCF | 232.50 | 150 | 69.0 | 120 | 120 |
| ZBCF | 302.25 | 150 | 69.0 | 120 | 120 |
| ZBJF | 302.25 | 120 | 55.2 | 120 | 120 |
| CBJF | 232.50 | 120 | 55.2 | 120 | 120 |

Fig. 1 Net photosynthetic rates at different growth stages under different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters in same stage indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
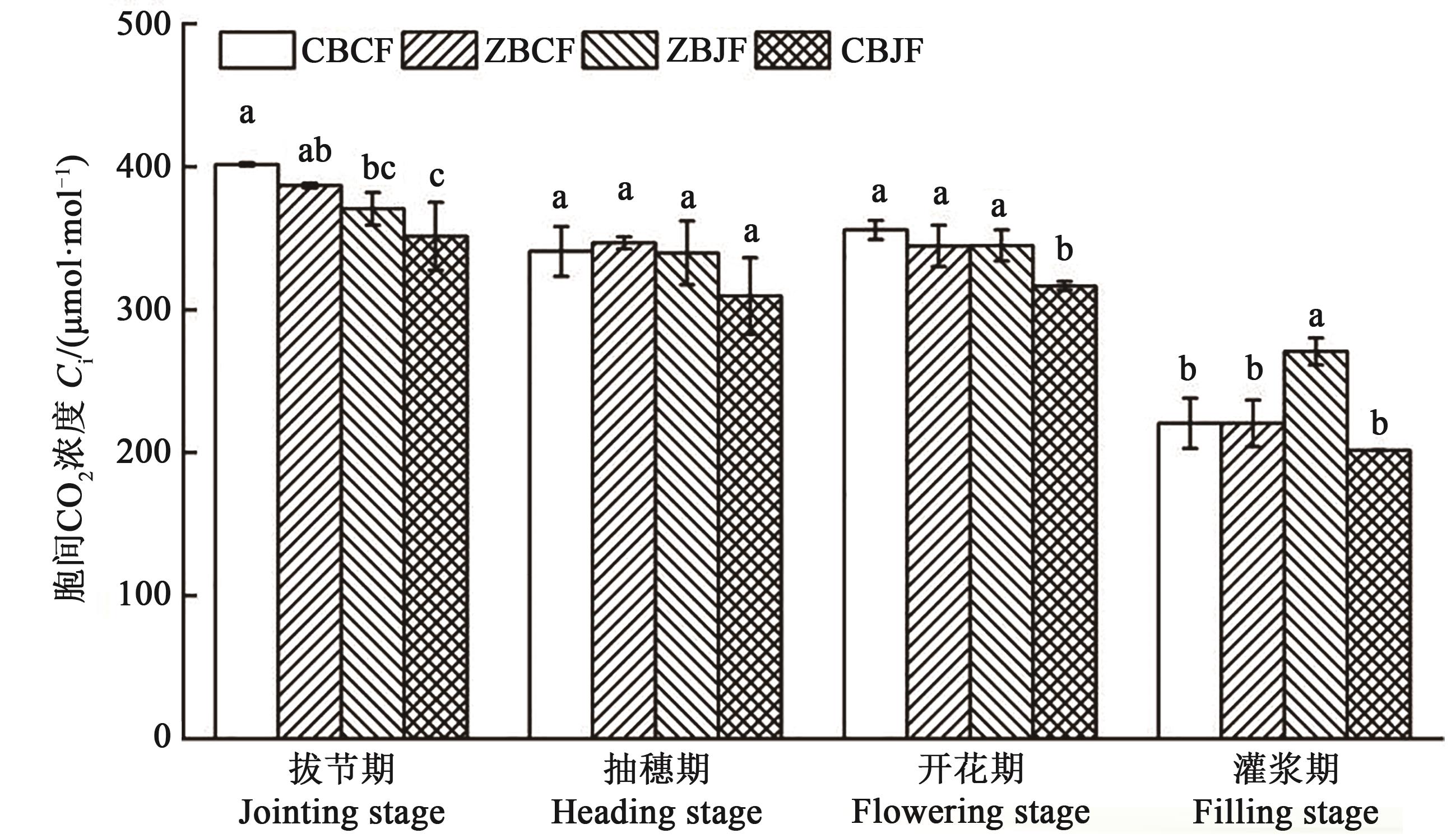
Fig. 2 Intercellular CO2 concentrations at different growth stages under different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters in same stage indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
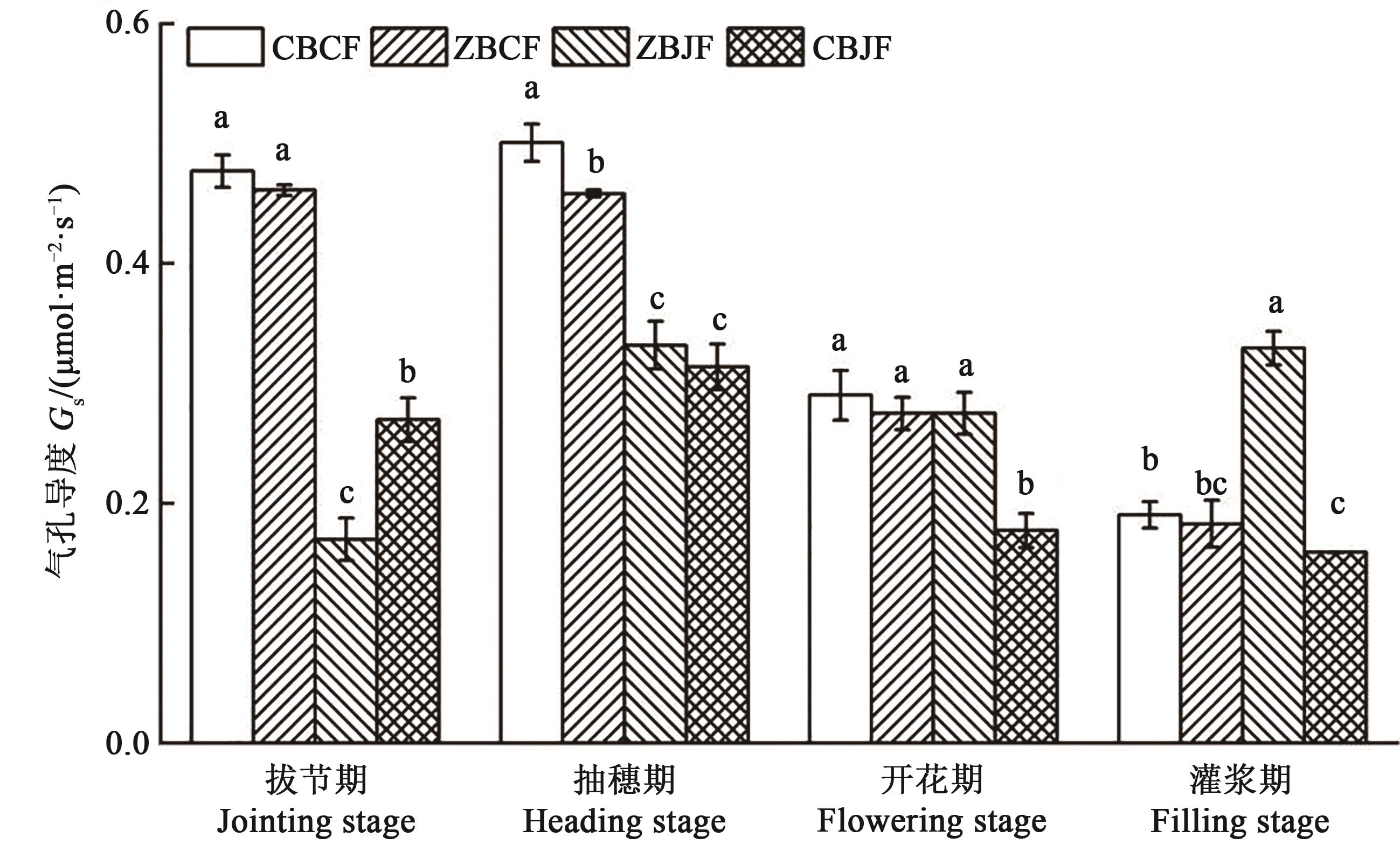
Fig. 3 Stomatal conductance at different growth stages under different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters in same stage indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.

Fig. 4 Transpiration rates at different growth stages under different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters in same stage indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
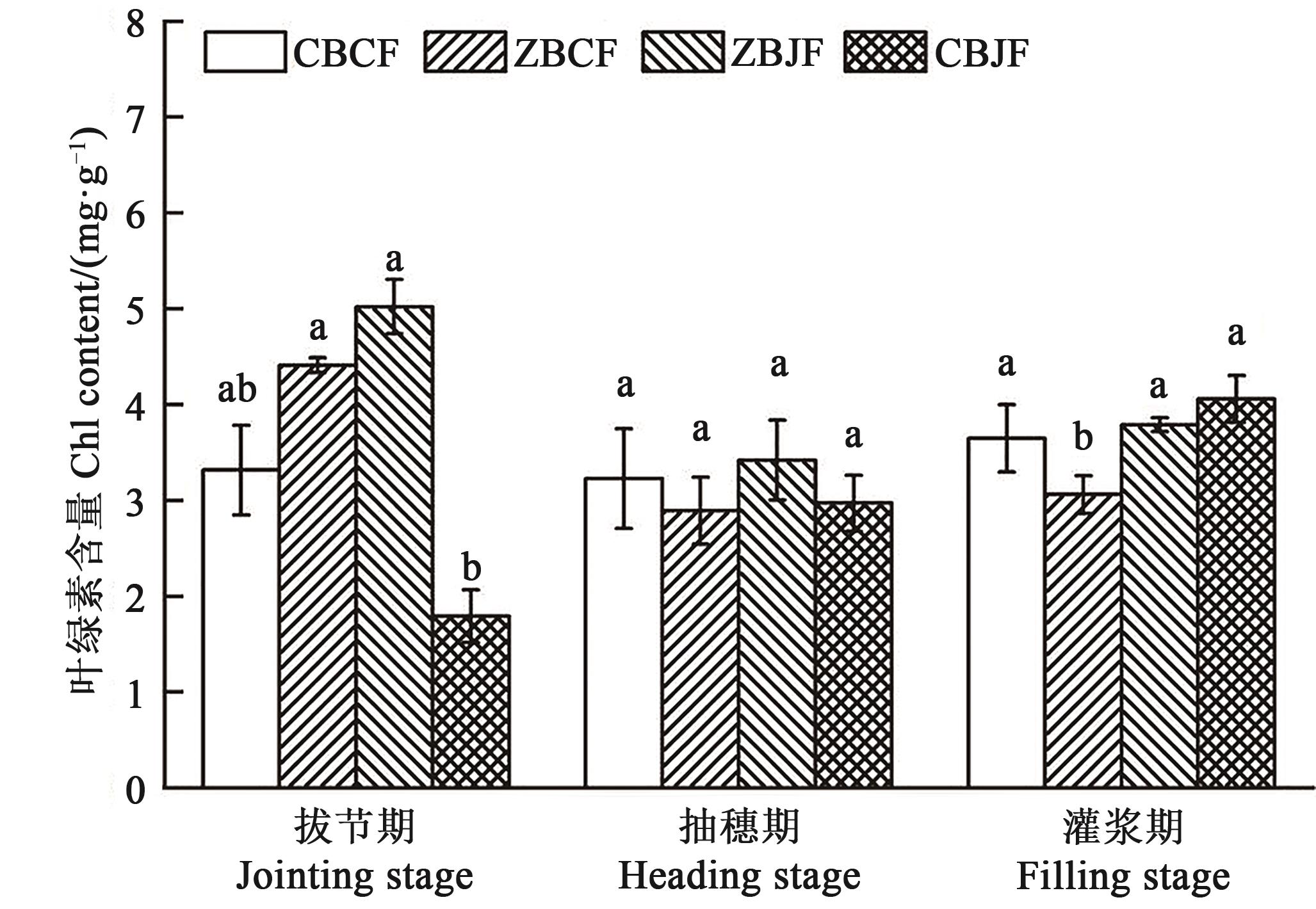
Fig. 5 Chlorophyll content at different growth stages under different treatmentsNote: Different lowercase letters in same stage indicate significant differences between different treatments at P<0.05 level.
处理 Treatment | 成穗数 Spike number/ (×104·hm-2) | 穗粒数 Grains per spike | 千粒重 1 000-grain weight/g | 产量 Yield/(kg·hm-2) | 氮肥偏生产力 Nitrogen fertilizer partial productivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBCF | 538±7 c | 28±3 ab | 39.91±0.53 a | 5 296±317 b | 24.18±1.45 b |
| ZBCF | 554±11 c | 27±4 ab | 41.05±2.46 a | 5 535±295 b | 25.27±1.35 b |
| ZBJF | 573±7 b | 29±2 a | 41.28±1.31 a | 6 292±268 a | 35.91±1.53 a |
| CBJF | 619±4 a | 26±0 b | 40.09±1.00 a | 6 181±257 a | 35.28±1.46 a |
Table 2 Wheat yield and its components under different treatments
处理 Treatment | 成穗数 Spike number/ (×104·hm-2) | 穗粒数 Grains per spike | 千粒重 1 000-grain weight/g | 产量 Yield/(kg·hm-2) | 氮肥偏生产力 Nitrogen fertilizer partial productivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBCF | 538±7 c | 28±3 ab | 39.91±0.53 a | 5 296±317 b | 24.18±1.45 b |
| ZBCF | 554±11 c | 27±4 ab | 41.05±2.46 a | 5 535±295 b | 25.27±1.35 b |
| ZBJF | 573±7 b | 29±2 a | 41.28±1.31 a | 6 292±268 a | 35.91±1.53 a |
| CBJF | 619±4 a | 26±0 b | 40.09±1.00 a | 6 181±257 a | 35.28±1.46 a |
土层 Soil layer/cm | 处理 Treatment | 全氮 Total nitrogen/(g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Available nitrogen/ (mg·kg-1) | 硝态氮 Nitrate nitrogen/(mg·kg-1) | 铵态氮 Ammoniacal nitrogen/ (mg·kg-1) | 微生物量氮 Microbial biomass nitrogen/(mg·kg-1) | 可溶性有机氮 Dissolved organic nitrogen/(mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—10 | CBCF | 0.97±0.04 a | 71.43±1.71 a | 39.63±2.18 a | 15.18±0.97 a | 61.28±7.83 a | 42.41±4.70 a |
| ZBCF | 0.84±0.06 b | 71.38±0.94 a | 35.29±2.90 b | 12.06±1.43 bc | 51.69±8.36 ab | 37.68±4.75 ab | |
| ZBJF | 0.94±0.03 ab | 72.37±1.16 a | 31.69±1.20 c | 10.44±0.68 c | 47.34±4.87 b | 36.28±2.00 ab | |
| CBJF | 0.96±0.07 a | 67.92±1.60 b | 33.94±0.15 bc | 12.65±0.54 b | 47.74±4.61 b | 33.65±3.71 b | |
| 10—20 | CBCF | 0.87±0.03 a | 61.06±4.74 a | 31.05±5.17 a | 15.08±2.01 a | 46.43±5.49 a | 39.43±0.14 a |
| ZBCF | 0.80±0.00 b | 56.15±0.41 a | 19.37±1.35 c | 10.05±2.60 b | 45.77±3.00 a | 37.16±1.33 a | |
| ZBJF | 0.81±0.00 b | 57.18±2.81 a | 21.00±1.39 bc | 10.49±1.73 b | 34.69±4.85 b | 27.30±1.75 b | |
| CBJF | 0.77±0.01 c | 46.38±1.09 b | 24.44±0.60 b | 9.73±0.57 b | 35.27±4.01 b | 26.33±3.25 b | |
| 20—30 | CBCF | 0.47±0.02 a | 39.02±3.11 a | 21.00±0.05 a | 9.51±1.17 a | 34.45±2.35 a | 25.51±1.37 a |
| ZBCF | 0.48±0.01 a | 35.83±3.09 ab | 13.46±1.68 b | 7.25±2.04 a | 33.04±2.53 ab | 19.84±2.23 b | |
| ZBJF | 0.47±0.01 a | 31.60±2.62 b | 14.43±2.50 b | 7.97±1.34 a | 27.70±4.11 b | 21.18±3.34 ab | |
| CBJF | 0.45±0.01 a | 22.42±1.22 c | 15.75±3.02 b | 7.63±1.11 a | 29.91±3.81 ab | 18.59±1.01 b |
Table 3 Contents of different soil nitrogen forms after wheat harvest under different treatments
土层 Soil layer/cm | 处理 Treatment | 全氮 Total nitrogen/(g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Available nitrogen/ (mg·kg-1) | 硝态氮 Nitrate nitrogen/(mg·kg-1) | 铵态氮 Ammoniacal nitrogen/ (mg·kg-1) | 微生物量氮 Microbial biomass nitrogen/(mg·kg-1) | 可溶性有机氮 Dissolved organic nitrogen/(mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—10 | CBCF | 0.97±0.04 a | 71.43±1.71 a | 39.63±2.18 a | 15.18±0.97 a | 61.28±7.83 a | 42.41±4.70 a |
| ZBCF | 0.84±0.06 b | 71.38±0.94 a | 35.29±2.90 b | 12.06±1.43 bc | 51.69±8.36 ab | 37.68±4.75 ab | |
| ZBJF | 0.94±0.03 ab | 72.37±1.16 a | 31.69±1.20 c | 10.44±0.68 c | 47.34±4.87 b | 36.28±2.00 ab | |
| CBJF | 0.96±0.07 a | 67.92±1.60 b | 33.94±0.15 bc | 12.65±0.54 b | 47.74±4.61 b | 33.65±3.71 b | |
| 10—20 | CBCF | 0.87±0.03 a | 61.06±4.74 a | 31.05±5.17 a | 15.08±2.01 a | 46.43±5.49 a | 39.43±0.14 a |
| ZBCF | 0.80±0.00 b | 56.15±0.41 a | 19.37±1.35 c | 10.05±2.60 b | 45.77±3.00 a | 37.16±1.33 a | |
| ZBJF | 0.81±0.00 b | 57.18±2.81 a | 21.00±1.39 bc | 10.49±1.73 b | 34.69±4.85 b | 27.30±1.75 b | |
| CBJF | 0.77±0.01 c | 46.38±1.09 b | 24.44±0.60 b | 9.73±0.57 b | 35.27±4.01 b | 26.33±3.25 b | |
| 20—30 | CBCF | 0.47±0.02 a | 39.02±3.11 a | 21.00±0.05 a | 9.51±1.17 a | 34.45±2.35 a | 25.51±1.37 a |
| ZBCF | 0.48±0.01 a | 35.83±3.09 ab | 13.46±1.68 b | 7.25±2.04 a | 33.04±2.53 ab | 19.84±2.23 b | |
| ZBJF | 0.47±0.01 a | 31.60±2.62 b | 14.43±2.50 b | 7.97±1.34 a | 27.70±4.11 b | 21.18±3.34 ab | |
| CBJF | 0.45±0.01 a | 22.42±1.22 c | 15.75±3.02 b | 7.63±1.11 a | 29.91±3.81 ab | 18.59±1.01 b |
| 1 | 王秀英.氮添加对小麦光合特性及产量的影响[J].江苏农业科学,2015,43(2):77-81. |
| WANG X Y. Effects of nitrogen addition on photosynthetic characteristics and yield of wheat [J]. Jiangsu Agric. Sci., 2015, 43(2):77-81. | |
| 2 | 吴永成,周顺利,王志敏.氮肥运筹对华北平原限水灌溉冬小麦产量和水氮利用效率的影响[J].麦类作物学报,2008,28(6):1016-1020. |
| WU Y C, ZHOU S L, WANG Z M. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer applications on yield, water and nitrogen use efficiency under limited irrigation of winter wheat in north China plain [J]. J. Triticeae Crops, 2008, 28(6):1016-1020. | |
| 3 | ADONIS M, LARISSA A C M, GOTZ S, et al.. Effect of nitrogen, row spacing, and plant density on yield, yield components, and plant physiology in soybean wheat intercropping [J]. Int. J. Res. Agron., 2015, 107(6):2162-2170. |
| 4 | ZHANG Y, DAI X L, JIA D Y, et al.. Effects of plant density on grain yield, protein size distribution, and bread making quality of winter wheat grown under two nitrogen fertilization rates [J]. Eur. J. Agron., 2016, 73:1-10. |
| 5 | 张福锁,王激清,张卫峰,等.中国主要粮食作物肥料利用率现状与提高途径[J].土壤学报,2008(5):915-924. |
| ZHANG F S, WANG J Q, ZHANG W F, et al.. Nutrient use efficiencies of major cereal crops in China and measures for improvement [J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2008(5):915-924. | |
| 6 | 朱倩,朱伟,闫向泉,等.减氮结合宽窄行种植对小麦光合特性及产量的影响[J].山东农业科学,2021,53(12):96-101. |
| ZHU Q, ZHU W, YAN X Q, et al.. Effects of nitrogen reduction combined with wide-narrow row planting on photosynthetic characteristics and yield of wheat [J]. Shandong Agric. Sci., 2021, 53(12):96-101. | |
| 7 | 李欣欣,石祖梁,王久臣,等.施氮量和种植密度对稻茬晚播小麦干物质积累及光合特性的影响[J].华北农学报,2020,35(5):140-148. |
| LI X X, SHI Z L, WANG J C, et al.. Effects of nitrogen application amount and planting density on dry matter accumulation and flag leaf photosynthetic characteristics for late-sowing wheat in rice-wheat rotation [J]. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin., 2020, 35(5):140-148. | |
| 8 | 马静丽,方保停,乔亚伟,等.减氮对豫北限水灌溉冬小麦冠层结构和光合特性的影响[J].麦类作物学报,2019,39(3):346-355. |
| MA J L, FANG B T, QIAO Y W, et al.. Effect of lower nitrogen application on canopy structure and photosynthesis of winter wheat grown under limited irrigation in northern Henan province [J]. J. Triticeae Crops, 2019, 39(3):346-355. | |
| 9 | 聂胜委,张巧萍,何宁,等.立式旋耕方式下氮肥不同减施水平对小麦品质的影响[J].农业资源与环境学报,2021,38(3):442-447. |
| NIE S W, ZHANG Q P, HE N, et al.. The effect of vertical rotary tillage and reduced N levels of nitrogen fertilizer application on wheat grain quality characteristics [J]. J. Agric. Res. Environ., 2021, 38(3):442-447. | |
| 10 | 苟志文,殷文,徐龙龙,等.绿洲灌区复种豆科绿肥条件下小麦稳产的减氮潜力[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2020,26(12):2195-2203. |
| GOU Z W, YIN W, XU L L, et al.. Potential of nitrogen reduction for maintaining wheat grain yield under multiple cropping with leguminous green manure in irrigated oasis [J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2020, 26(12):2195-2203. | |
| 11 | 张娟,武同华,代兴龙,等.种植密度和施氮水平对小麦吸收利用土壤氮素的影响[J].应用生态学报,2015,26(6):1727-1734. |
| ZHANG J, WU T H, DAI X L, et al.. Effects of plant density and nitrogen level on nitrogen uptake and utilization of winter wheat [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2015, 26(6):1727-1734. | |
| 12 | 石柯,董士刚,申凤敏,等.小麦播量与减氮对潮土微生物量碳氮及土壤酶活性的影响[J].中国农业科学,2019,52(15):2646-2663. |
| SHI K, DONG S G, SHENG F M, et al.. Effects of wheat seeding rate with nitrogen fertilizer application reduction on soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen and enzyme activities in fluvo-aquic soil in Huang-Huai Plain [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2019, 52(15):2646-2663. | |
| 13 | 叶盛嘉,郑晨萌,张影,等.氮肥减量配施有机肥对豫中地区冬小麦-夏玉米轮作生产力和土壤性质的影响[J/OL].中国生态农业学报,2022:900-912 [2022-01-02]. . |
| YE S J, ZHENG C M, ZHANG Y, et al.. Effects of reduced chemical nitrogen input combined with organic fertilizer application on the productivity of winter wheat and summer maize rotation and soil properties in central Henan province [J/OL]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2022:658 [2022-01-02].. | |
| 14 | ARNON D I. Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris [J]. Plant Physiol., 1949, 24:1-15. |
| 15 | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].3版.北京:中国农业出版社,2002:25-113. |
| 16 | 钟珍梅,杨庆,游小凤,等.圆叶决明添加量对红壤可溶性氮及酶活性的影响[J].草地学报,2022,30(3):622-630. |
| ZHONG Z M, YANG Q, YOU X F, et al.. Effects of additions of Chamaecrista rotundifolia on the soluble nitrogen and enzyme activity of red soil [J]. Acta Agrestia Sin., 2022, 30(3):622-630. | |
| 17 | 吕盛,王子芳,高明,等.秸秆不同还田方式对紫色土微生物量碳、氮、磷及可溶性有机质的影响[J].水土保持学报,2017,31(5):266-272. |
| LYU S, WANG Z F, GAO M, et al.. Effects of different straw returning methods on soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen,phosphorus and soluble organic matter in purple soil [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2017, 31(5):266-272. | |
| 18 | 王之杰,郭天财,王化岑,等.种植密度对超高产小麦生育后期光合特性及产量的影响[J].麦类作物学报,2001,21(3):64-67. |
| WANG Z J, GUO T C, WANG H C, et al.. Effect of planting density on photosynthetic characteristics and grain yield of super-high-yield winter wheat at late growth stages [J]. J. Triticeae Crops, 2001,21(3):64-67. | |
| 19 | 张永丽,肖凯,李雁鸣.种植密度对杂种小麦C6-38/Py85-1旗叶光合特性和产量的调控效应及其生理机制[J].作物学报,2005,31(4):498-505. |
| ZHANG Y L, XIAO K, LI Y M. Effects and physiological mechanism of planting densities on photosynthesis characteristics of flag leaf and grain yield in wheat hybrid C6-38/Py85-1 [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2005,31(4):498-505. | |
| 20 | 曹倩,贺明荣,代兴龙,等.氮密互作对小麦花后光合特性及籽粒产量的影响[J].华北农学报,2012,27(4):206-212. |
| CAO Q, HE M R, DAI X L, et al.. Effects of interaction between nitrogen and density on photosynthetic characteristics after anthesis and grain yield of winter wheat [J]. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin., 2012, 27(4):206-212. | |
| 21 | 张向前,刘良柏,乔玉强,等.多穗型品种华成3366减氮增密绿色增产稳产技术研究[J].华北农学报,2018,33(4):181-188. |
| ZHANG X Q, LIU L B, QIAO Y Q, et al.. Research on increasing and maintaining yield from reducing N application rate and enhancing planting density by using multiple spike cultivar of Huacheng 3366 [J]. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin., 2018, 33(4):181-188. | |
| 22 | 于振文,岳松涛,沈成国,等.不同密度对冬小麦开花后叶片衰老和粒重的影响[J].作物学报,1995,21(4):412-418. |
| YU Z W, YUE S T, SHEN C G, et al.. Effects of different density on leaf senescence and grain weight after anthesis of winter wheat [J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 1995,21(4):412-418. | |
| 23 | 陈根云,陈娟,许大全.关于净光合速率和胞间CO2浓度关系的思考[J].植物生理学通讯,2010,46(1): 64-66. |
| CHEN G Y, CHEN J, XU D Q. Thinking about the relationship between net photosynthetic rate and intercellular CO2 concentration [J]. Plant Physiol. Commun., 2010, 46(1):64-66. | |
| 24 | FARQUHAR G D, SHARKEY T D. Stomatal conductance and photosynthesis [J]. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol., 1982, 33(1):317-345. |
| 25 | 张黛静,马雪,王晓东,等.品种与密度对豫中地区小麦光合生理特性及光能利用率的影响[J].麦类作物学报,2014,34(3):388-394. |
| ZHANG D J, MA X, WANG X D, et al.. Effects of variety and density on photosynthetic traits and light utilization efficiency of wheat in middle Henan province [J]. J. Triticeae Crops., 2014, 34(3):388-394 | |
| 26 | 王鑫炜,任爱霞,孙敏,等.播量对宽幅条播冬小麦群体结构和干物质积累分配的影响[J].麦类作物学报,2021,41(10):1272-1280. |
| WANG X W, REN A X, SUN M, et al.. Effect of sowing rate on population structure and dry matter accumulation,distribution of winter wheat sowing in wide strip [J]. J. Triticeae Crops, 2021, 41(10):1272-1280. | |
| 27 | 殷复伟,王文鑫,谷淑波,等.株行距配置对宽幅播种小麦产量形成的影响[J].麦类作物学报,2018,38(6):710-717. |
| YI F W, WANG W X, GU S B, et al.. Effect of planting distance configuration repression on wheat yield formation with wide planting [J]. J. Triticeae Crops, 2018, 38(6):710-717. | |
| 28 | 黄波,张妍,孙建强,等.氮密互作对淮北砂姜黑土区冬小麦冠层光合特性和产量的影响[J].麦类作物学报,2019,39(8):994-1002. |
| HUANG B, ZHANG Y, SUN J Q, et al.. Effects of nitrogen-dense interaction on canopy photosynthetic characteristics and yield of winter wheat in the black soil area of concretion and concretion in Huaibei [J]. J. Triticeae Crops, 2019, 39(8):994-1002. | |
| 29 | 张均华,刘建立,吕菲,等.施氮对稻麦轮作区小麦地上器官干物质及氮素累积运转的影响[J].麦类作物学报,2009,29(5):892-896. |
| ZHANG J H, LIU J L, LYU F, et al.. Effect of nitrogen application on accumulation and transportation of matter and nitrogen in above-ground organs of wheat in rice-wheat rotation area [J]. J. Triticeae Crops, 2009, 29(5):892-896. | |
| 30 | 孟维伟,张正,徐杰,等.不同施氮量对玉米花生间作下茬小麦干物质积累及产量构成的影响[J].华北农学报,2018,33(4):175-180. |
| MENG W W, ZHANG Z, XU J, et al.. Effect of nitrogen fertilization on dry matter accumulation and yield components of following wheat which planted after maize peannt intercropping [J]. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin., 2018, 33(4):175-180. | |
| 31 | 马尚宇,王艳艳,刘雅男,等.播期、播量和施氮量对小麦干物质积累、转运和分配及产量的影响[J].中国生态农业学报,2020,28(3):375-385. |
| MA S Y, WANG Y Y, LIU Y N, et al.. Effect of sowing date, planting density, and nitrogen application on dry matter accumulation, transfer, distribution, and yield of wheat [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2020, 28(3):375-385. | |
| 32 | 薛金元,许芳芳,王娟娟,等.减氮增密对水稻产量、氮素吸收及土壤剖面养分分布的影响[J].河南农业科学,2021,50(6):82-90. |
| XUE J Y, XU F F, WANG J J, et al.. Effects of nitrogen reducing and density increasing on rice yield, nitrogen uptake and nutrient distribution in soil profile [J]. J. Henan Agric. Sci., 2021, 50(6):82-90. | |
| 33 | 胡岗,刘桂华,范成五,等.控氮对黄壤坡耕地小麦-玉米轮作土壤氮素分布特征的影响[J].西南农业学报,2018,31(10):2146-2151. |
| HU G, LIU G H, FANG C W, et al.. Effects of nitrogen control on soil nitrogen and crop yield of wheat and maize crop rotation system in sloping cropland with yellow soil [J]. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci., 2018, 31(10):2146-2151. | |
| 34 | 骆晓声,寇长林,王小非,等.施氮量对潮土区冬小麦-夏玉米轮作农田氮磷淋溶的影响[J].中国生态农业学报,2021,29(1):29-37. |
| LUO X S, KOU C L, WANG X F, et al.. Effects of nitrogen application on nitrogen and phosphorus leaching in fluvo-aquic soil on a winter wheat-summer maize rotation farmland [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2021, 29(1):29-37. |
| [1] | Yanjun KE, Yumeng ZHANG, Yanjie GUO, Lijuan ZHANG, Zitao ZHANG, Yanzhi JI. Effects of Bio-organic Fertilizer Combined with Subsoiling on Farmland Soil Fertility and Crop Yield [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(4): 157-166. |
| [2] | Pan LIU, Shan GAO, Haoyu LI, Yi WANG, Baozhong YIN, Jinkao GUO, Wenchao ZHEN. Effects of Row Space Reduction and Plant Space Expansion on Tillers Number in Wheat and Its Physiological Mechanism [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(4): 32-44. |
| [3] | Nali XU, Huixia YU, Mingming YAO, Yanqing WANG, Qingfeng LI, Caixia LIU, Gang SUN, Jiajing CHEN, Jiaohui LONG, Zhangjun WANG. Analysis of Genetic Diversity Based on SSR and SRAP Markers and Agronomic Traits of Wheat Resources [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(3): 30-46. |
| [4] | Tongtong ZHENG, Wendi YANG, Ning WANG, Junjie MA, Long LIU, Qingyuan GUO. Morphological and Polygenetic Identification of Pathogen of Wheat Leaf Blight [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(2): 111-118. |
| [5] | Yunzhu ZHENG, Shuchen SUN. Effects of Straw Biochar and Straw on Soil Nutrients and Crop Yield in Wheat-Maize Rotation System [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(2): 152-162. |
| [6] | Ting LIANG, Jinghong ZUO, Qing LU, Dong YANG, Yimiao TANG, Chunman GUO, Dezhou WANG, Weiwei WANG. Identification and Expression Analysis Under Abiotic Stress of IQM Gene Family in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(2): 27-37. |
| [7] | Wenhao ZHAO, Jiangtao JI, Hao MA, Xin JIN, Xue LI, Haigang MA. Extraction of Winter Wheat Coverage Based on Improved K-means Algorithm [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(1): 83-91. |
| [8] | Ruiqi JIA, Ziang GUO, Chen YAO, Pu LI, Guixiao LA, Xiazi LU, Hongyu GUO, Xuanzhen LI. Effect of Low Phosphorus Stress on Cadmium Uptake in Wheat [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(8): 154-160. |
| [9] | Qing LU, Ting LIANG, Weiwei WANG, Dezhou WANG, Xian WU, Xiaoyan WANG, Yimiao TANG. Cloning and Expression Analysis of Wheat Heat Shock Protein Gene TaHSP90-1 [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(8): 44-54. |
| [10] | Wenqi ZHANG, Sheng WU, Xinyu GUO, Weiliang WEN, Xianju LU, Chunjiang ZHAO. Evaluation of Plant Self-rotation Multi-view Reconstruction Technique in 3D Phenotype Acquisition of Wheat Plants [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(8): 87-98. |
| [11] | Xuejing LIU, Xiaoyuan BAO, Xiaoyang HOU, Wenchao ZHEN. Dynamics of Soil Water Content and Yield Formation Characteristics of Winter Wheat Under Water Limited Irrigation in Spring in Haihe Plain [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(7): 167-176. |
| [12] | Tongmei GAO, Feng LI, Xiaoyu SU, Dongyong WANG, Yuan TIAN, Pengyu ZHANG, Tongke LI, Zihao YANG, Shuangling WEI. Effect of Nitrogen Reduction on Agronomic Trait, Photosynthetic Characteristics and Yield of Sesame [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(6): 176-188. |
| [13] | Xin WANG, Yuxia ZHANG, Weidong CHEN, Congying LIN, Wenhui HOU, Guleng SIRI, Baiming CONG. Effects of Nitrogen Topdressing on Yield and Photosynthetic Fluorescence Characteristics of Different Forage Oat Varieties [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(5): 170-179. |
| [14] | Yuan YI, Huiyun ZHANG, Liwei LIU, Jing WANG, Xuecheng ZHU, Na ZHAO, Guohua FENG. Effects of Slow-released Fertilizer Compound Humic Acid Instead of Urea on Grain Yield and Population Quality in Xumai New Varieties [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(4): 144-153. |
| [15] | Fangling WANG, Mingyue ZHANG, Yaru ZHOU, Qinglin GUAN, Xinyan LI, Qiu ZHONG, Mingqin ZHAO. Effect of TS-PAA Water Retaining Agent on Growth and Photosynthetic Characteristics of Cigar under Drought Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(4): 162-172. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号