




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (9): 92-98.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0300
• BIOTECHNOLOGY & LIFE SCIENCE • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yueriyeti Sali( ), Nuerbiye Yisimayi, Aliya Waili, Lingna CHEN(
), Nuerbiye Yisimayi, Aliya Waili, Lingna CHEN( ), Yongkun CHEN(
), Yongkun CHEN( )
)
Received:2024-03-26
Accepted:2024-04-27
Online:2025-09-15
Published:2025-09-24
Contact:
Lingna CHEN,Yongkun CHEN
约日耶提·萨力( ), 努尔比耶·依斯马依, 阿丽亚·外力, 陈凌娜(
), 努尔比耶·依斯马依, 阿丽亚·外力, 陈凌娜( ), 陈永坤(
), 陈永坤( )
)
通讯作者:
陈凌娜,陈永坤
作者简介:约日耶提·萨力 E-mail:1960267580@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yueriyeti Sali, Nuerbiye Yisimayi, Aliya Waili, Lingna CHEN, Yongkun CHEN. Heterologous Expression of PaMT3-1 Gene from Phytolacca americana Enhances Salt and Osmotic Stress Tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(9): 92-98.
约日耶提·萨力, 努尔比耶·依斯马依, 阿丽亚·外力, 陈凌娜, 陈永坤. 异源表达垂序商陆PaMT3-1基因提高拟南芥盐和渗透胁迫抗性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2025, 27(9): 92-98.
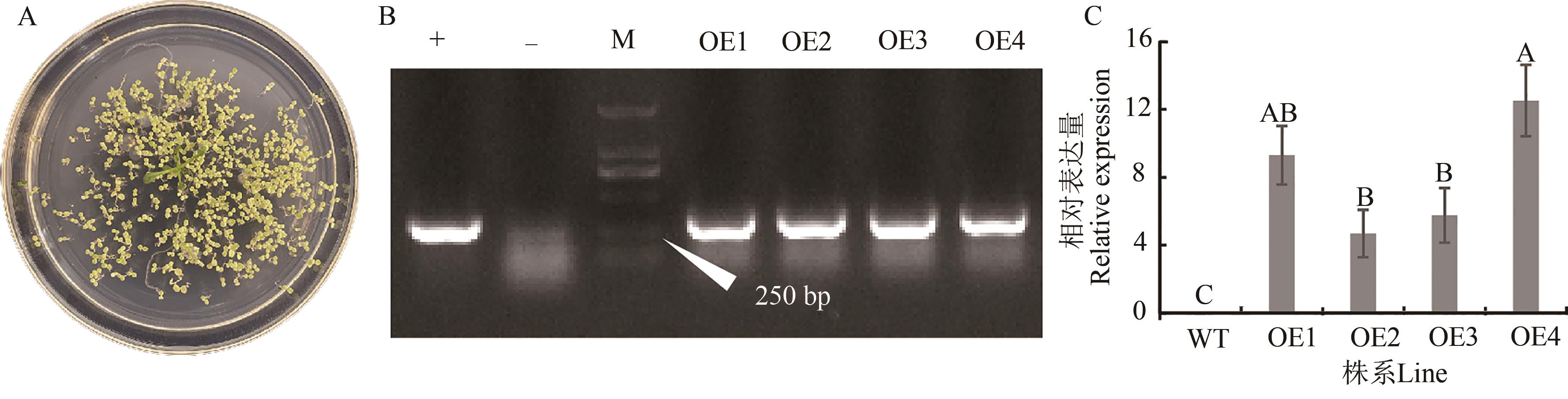
Fig. 2 Screening of Arabidopsis seeds with the PaMT3-1 gene and identification of transgenic linesA: Seed resistance screening; B: PCR detection, M—DNA molecular weight ladder DL2000, +—Positive control,-—Negative control, OE1~OE4—Transgenic lines; C: Expression level of PaMT3-1 gene, different capital letters indicate significant differences between different lines at P<0.01 level
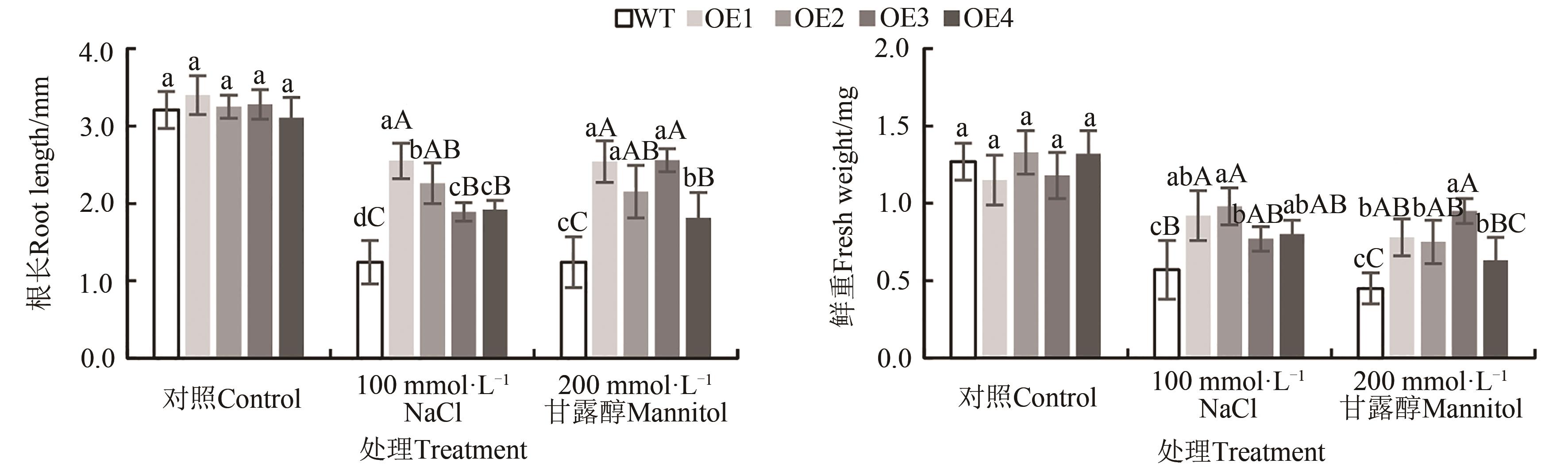
Fig. 3 Root length and fresh weight of transgenic Arabidopsis under salt and osmotic stressNote: Different capital and lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different lines at P<0.01 and P<0.05 levels, respectively.

Fig. 5 Physiological indices of stress resistance in WT and PaMT3-1 overexpressed Arabidopsis under salt and osmotic stressNote: Different capital and lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different lines at P<0.01 and P<0.05 levels, respectively.
| [1] | COBBETT C, GOLDSBROUGH P. Phytochelatins and metallothioneins:roles in heavy metal detoxification and homeostasis [J]. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol., 2002, 53(1):159-182. |
| [2] | NIELSON K B, WINGE D R. Order of metal binding in metallothionein [J]. J. Biol. Chem., 1983, 258(21):13063-13069. |
| [3] | GAUTAM N, TIWARI M, KIDWAI M, et al.. Functional characterization of rice metallothionein OsMT-I-Id: insights into metal binding and heavy metal tolerance mechanisms [J/OL]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2023, 458(15):131815 [2024-03-10]. . |
| [4] | KININGHAM K, KASARSKIS E. Antioxidant function of metallothioneins [J]. J. Trace Elem. Exp. Med., 1998, 11(2‐3):219-226. |
| [5] | GHUGE S A, NIKALJE G C, KADAM U S, et al.. Comprehensive mechanisms of heavy metal toxicity in plants, detoxification, and remediation [J/OL]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2023, 450:131039 [2024-03-10]. . |
| [6] | SEKHAR K, PRIYANKA B, REDDY V D, et al.. Metallothionein 1 (CcMT1) of pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan L.) confers enhanced tolerance to copper and cadmium in Escherichia coli and Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Environ. Exp. Bot., 2011, 72(2):131-139. |
| [7] | XIA Y, QI Y, YUAN Y X, et al.. Overexpression of Elsholtzia haichowensis metallothionein 1 (EhMT1) in tobacco plants enhances copper tolerance and accumulation in root cytoplasm and decreases hydrogen peroxide production [J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2012, 233(9):65-71. |
| [8] | 贾鹏,王媛,陈涛,等.苦荞MT2基因的克隆及其对铜胁迫的响应[J].农业生物技术学报,2017,25(6):874-883. |
| JIA P, WANG Y, CHEN T, et al.. Cloning of MT2 from tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum) and its response to Cu2+ stress [J]. J. Agric. Biotechnol., 2017, 25(6):874-883. | |
| [9] | LI R, YANG Y, CAO H, et al.. Heterologous expression of the tobacco metallothionein gene NtMT2F confers enhanced tolerance to Cd stress in Escherichia coli and Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Plant Physiol. Bioch., 2023, 195:247-255. |
| [10] | GU C S, LIU L, ZHAO Y H, et al.. Overexpression of Iris. lactea var. chinensis metallothionein IlMT2a enhances cadmium tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety, 2014, 105(7):22-28. |
| [11] | CHEN Y K, ZHI J K, LI X Y, et al.. Diversity in cadmium accumulation and resistance associated with various metallothionein genes (type Ⅲ) in Phytolacca americana L. [J]. Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2018, 108:704-709. |
| [12] | ZHI J K, LIU X, YIN P, et al.. Overexpression of the metallothionein gene PaMT3-1 from Phytolacca americana enhances plant tolerance to cadmium [J]. Plant Cell Tiss. Org., 2020, 143(1):211-218. |
| [13] | DUBEY A K, KUMAR A, KUMAR N, et al.. Over-expression of chickpea metallothionein 1 gene confers tolerance against major toxic heavy metal stress in Arabidopsis [J]. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants, 2021, 27:2665-2678. |
| [14] | KUMAR G, KUSHWAHA H R, PANJABI-SABHARWAL V, et al.. Clustered metallothionein genes are co-regulated in rice and ectopic expression of OsMT1e-P confers multiple abiotic stress tolerance in tobacco via ROS scavenging [J/OL]. BMC Plant Biol., 2012, 12:107 [2024-03-10]. . |
| [15] | YU X Z, LIN Y J, ZHANG Q. Metallothioneins enhance chromium detoxification through scavenging ROS and stimulating metal chelation in Oryza sativa [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 220(4):300-313. |
| [16] | CHOUDHURY F K, RIVERO R M, BLUMWALD E, et al.. Reactive oxygen species, abiotic stress and stress combination [J]. Plant J., 2017, 90(5):856-867. |
| [17] | XUE T, LI X, ZHU W, et al.. Cotton metallothionein GhMT3a, a reactive oxygen species scavenger, increased tolerance against abiotic stress in transgenic tobacco and yeast [J]. J. Exp. Bot., 2009, 60(1):339-349. |
| [18] | YANG M, ZHANG F, WANG F, et al.. Characterization of a type 1 metallothionein gene from the stresses-tolerant plant Ziziphus jujuba [J]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2015, 16(8):16750-16762. |
| [19] | 徐畅,何好,李国良,等.紫花苜蓿1型金属硫蛋白基因的表达及抗逆性分析[J].草业学报,2018,27(4):89-97. |
| XU C, HE H, LI G L, et al.. Expression of type 1 metallothionein gene from Medicago sative and analysis of its function in stress tolerance [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2018, 27(4):89-97. | |
| [20] | LAL S, KUMAR V, GUPTA U, et al.. Overexpression of the chickpea metallothionein 1 (MT1) gene enhances drought tolerance in mustard (Brassica juncea L.) [J/OL]. Plant Cell Tiss. Org., 2024, 157(1):6 [2024-03-10]. . |
| [21] | ZHAO L, SUN Y L, CUI S X, et al.. Cd-induced changes in leaf proteome of the hyperaccumulator plant Phytolacca americana [J]. Chemosphere, 2011, 85(1):56-66. |
| [22] | FU X, DOU C, CHEN Y, et al.. Subcellular distribution and chemical forms of cadmium in Phytolacca americana L. [J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2011, 186(1):103-107. |
| [23] | CHEN Y, ZHI J, ZHANG H, et al.. Transcriptome analysis of Phytolacca americana L. in response to cadmium stress [J/OL]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(9):e0184681 [2024-03-10]. . |
| [24] | SCHMITTGEN T D, LIVAK K J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method [J]. Nat. Protoc., 2008, 3(6):1101-1108. |
| [25] | CHEN Y K, LIU Y X, DING Y N, et al.. Overexpression of PtPCS enhances cadmium tolerance and cadmium accumulation in tobacco [J]. Plant Cell Tiss. Org., 2015, 121:389-396. |
| [26] | 帖建科,李令媛,茹炳根,等.金属硫蛋白清除自由基及其对自由基引起的核酸损伤保护作用的研究[J].生物物理学报,1995,11(2):276-282. |
| TIE J K, LI L Y, RU B G, et al.. Fere radical scavenging and DNA damage protection by metallothionein [J]. Acta Biophys. Sin., 1995,11(2):276-282. | |
| [27] | HASSINEN V H, TERVAHAUTA A I, SCHAT H, et al.. Plant metallothioneins-metal chelators with ROS scavenging activity? [J]. Plant Biol., 2011, 13(2):225-232. |
| [28] | 美合日班·阿卜力米提,王艳.植物金属硫蛋白的金属结合及解毒研究进展[J].生物学杂志,2021,38(6):104-110. |
| Ablimit Mehriban, WANG Y. Research advance of plant metallothioneins in metal ion combination and detoxification [J]. J. Biol., 2021, 38(6):104-110. | |
| [29] | 刘阳,彭翠,吴彦辰,等.盐穗木金属硫蛋白HcMT的体外自由基清除活性及抗氧化能力[J].中国生物工程杂志,2022, 42(9):17-26. |
| LIU Y, PENG C, WU Y C, et al.. Free radical scavenging activity and antioxidant capacity of metallothionein HcMT from Halostachys capsica in vitro [J]. China Biotechnol., 2022, 42(9):17-26. | |
| [30] | WANG D, GAO Y, SUN S, et al.. Effects of salt stress on the antioxidant activity and malondialdehyde, solution protein, proline, and chlorophyll contents of three Malus species [J/OL]. Life, 2022, 12(11):1929 [2024-03-10]. . |
| [31] | YANG Z, WU Y R, LI Y, et al.. OsMT1a, a type 1 metallothionein, plays the pivotal role in zinc homeostasis and drought tolerance in rice [J]. Plant Mol. Biol., 2009, 70:219-229. |
| [32] | JAMPEETONG A, BRIX H. Effects of NaCl salinity on growth, morphology, photosynthesis and proline accumulation of Salvinia natans [J]. Aquat. Bot., 2009, 91(3):181-186. |
| [33] | TALEISNIK E, RODRÍGUEZ A A, BUSTOS D, et al.. Leaf expansion in grasses under salt stress [J]. J. Plant Physiol., 2009, 166(11):1123-1140. |
| [1] | Hao JIA, Hongzhe WANG, Zhengwen SUN, Qishen GU, Dongmei ZHANG, Xingyi WANG, Yan ZHANG, Huaiyu LU, Zhiying MA, Xingfen WANG. Genome-wide Identification of VOZ Genes Family in Cotton and Study on Salt Tolerance Function of GhVOZ1 [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(9): 58-68. |
| [2] | Jilin SUN, Jiaqi ZHANG, Fansen MENG, Silong SUN. Genome-wide Identification and Tissue Expression Pattern Analysis of HSP70 Gene Family in Thinopyrum elongatum [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(6): 28-38. |
| [3] | Zhiduo DONG, Qiuping FU, Jian HUANG, Tong QI, Yanbo FU, Kuerban Kaisaier. Analysis of Salt Tolerance Capacity of Xinjiang Cotton Guring Germination [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(4): 57-67. |
| [4] | Tingting MA, Yanrong ZHAO, Yuqing WEI, Yuejuan WANG, Xuefei WANG, Erdong ZHANG. Dynamic Characteristics of Stem Growth and Sugar Accumulation of Sweet Sorghum at Late Growth Stage Under Soil Salt Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(2): 42-50. |
| [5] | Shixu QU, Yu SUN, Yizhen SUO, Haipeng YUAN, Yuhong ZHANG. Effects of Exogenous Calcium on Physiological Characteristics and Secondary Metabolites of Cannabis sativa L. Under Salt Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(2): 80-88. |
| [6] | Xuewen XU, Xingpeng WANG, Hongbo WANG, Zhenxi CAO. Physiological Regulation of Growth of Cotton Seedlings Under Salt Stress by Rhamnolipids [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2025, 27(1): 72-79. |
| [7] | Fulin ZHANG, Rui XI, Yuxiang LIU, Zhaolong CHEN, Qinghui YU, Ning LI. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Tomato BURP Structural Domain Gene Family [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(8): 51-62. |
| [8] | Shuang LI, Aiying WANG, Zhen JIAO, Qing CHI, Hao SUN, Tao JIAO. Physiological and Chemical Characteristics and Transcriptome Analysis of Different Type of Wheat Seedlings Under Salt Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(2): 20-32. |
| [9] | Xuemin JIANG, Xiangqian CHEN, Hongyan LI, Qiyan JIANG. Metabolomic Analysis of Wheat Response to Salt Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 43-56. |
| [10] | Yulu WU, Jiaxin HU, Yuxi CHEN, Bingsong ZHENG, DaoLiang YAN. Effects of External Application of α-Ketoglutarate on Growth, Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus Accumulation and Their Stoichiometric Relationships in Kosteletzkya virginica Under Salt Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 170-177. |
| [11] | Zhonghua MA, Juan CHEN, Na WU, Benju MAN, Xiaogang WANG, Yongqing ZHE, Jili LIU. Effects of Salt Stress and Phosphorus Supply on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Total Biomass of Switchgrass at Seedling Stage [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(6): 190-200. |
| [12] | Jing XU, Xiufen WANG, Xiaoyan LIU. Comparative Study on Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitory Activity and Antioxidant Activity of Gingerol Before and After Purification [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(5): 96-105. |
| [13] | Fan ZHANG, Hong WANG, Xuebing ZHANG, Jianjun CHEN. Physiological and Biochemical Responses of Peach Self-rooted Rootstock to NaCl and Analysis of Salt Tolerance Threshold [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(11): 70-79. |
| [14] | Juanjuan GUO, Shan WANG, Haoan LUAN, Han LI, Suping GUO, Guohui QI, Xuemei ZHANG. Effects of Microbial Inoculum on Red Raspberry Growth, Fruit Quality and Activating Soil Phosphorus and Potassium [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(10): 198-209. |
| [15] | Feng LI, Congpei YIN, Ran YIN, Fan WANG, Yongliang HAN, Zhimin YANG, Jiancheng LIU. Response of Rhizosphere Soil Bacterial Community Diversity to Salt Stress in Oat (Avena sativa L.) [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(1): 153-165. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号