




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (11): 173-181.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2022.0496
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles
Lu ZHANG1( ), Lei ZHENG2, Siru LIU3, Zejiang CAI1(
), Lei ZHENG2, Siru LIU3, Zejiang CAI1( ), Nan SUN1, Qiang ZHANG2(
), Nan SUN1, Qiang ZHANG2( ), Minggang XU1,3
), Minggang XU1,3
Received:2022-06-04
Accepted:2022-08-29
Online:2023-11-15
Published:2023-11-20
Contact:
Zejiang CAI,Qiang ZHANG
张璐1( ), 郑磊2, 刘思汝3, 蔡泽江1(
), 郑磊2, 刘思汝3, 蔡泽江1( ), 孙楠1, 张强2(
), 孙楠1, 张强2( ), 徐明岗1,3
), 徐明岗1,3
通讯作者:
蔡泽江,张强
作者简介:张璐E-mail:zhanglu01@caas.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Lu ZHANG, Lei ZHENG, Siru LIU, Zejiang CAI, Nan SUN, Qiang ZHANG, Minggang XU. Soil Initial Available Phosphorus and Exchangeable Magnesium Shaping the Response of Wheat Growth to pH[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(11): 173-181.
张璐, 郑磊, 刘思汝, 蔡泽江, 孙楠, 张强, 徐明岗. 土壤初始有效磷和交换性镁含量改变了小麦生长对pH的响应[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(11): 173-181.
土壤母质 Soil parent material | pH | 有机质 Organic matter/(g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Available nitrogen/(mg·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus/(mg·kg-1) | 有效钾 Available potassium/(mg·kg-1) | 交换性氢 Exchangeable hydrogen/(cmol+·kg-1) | 交换性铝 Exchangeable aluminum/(cmol+·kg-1) | 交换性镁 Exchangeable magnesium/(cmol+·kg-1) | 交换性钙 Exchangeable calcium/(cmol+·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
板页岩 Plate shale | 5.93 | 23.3 | 120.1 | 30.4 | 81.3 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 1.35 | 6.80 |
第四纪红土 Quaternary red earth | 4.60 | 16.1 | 76.7 | 5.7 | 87.5 | 0.72 | 4.61 | 0.26 | 1.52 |
河流冲积物 River alluvium | 5.39 | 17.8 | 105.9 | 15.4 | 50.0 | 0.25 | 0.62 | 0.52 | 3.73 |
红砂岩 Tertiary red sandstone | 4.45 | 30.6 | 175.4 | 9.7 | 68.8 | 0.24 | 7.76 | 0.23 | 0.72 |
花岗岩 Granite | 4.74 | 39.4 | 217.7 | 12.1 | 62.5 | 0.19 | 4.34 | 0.15 | 0.37 |
Table 1 Selected chemical properties of the soils as the initial conditions for the pot experiment in this study
土壤母质 Soil parent material | pH | 有机质 Organic matter/(g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Available nitrogen/(mg·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus/(mg·kg-1) | 有效钾 Available potassium/(mg·kg-1) | 交换性氢 Exchangeable hydrogen/(cmol+·kg-1) | 交换性铝 Exchangeable aluminum/(cmol+·kg-1) | 交换性镁 Exchangeable magnesium/(cmol+·kg-1) | 交换性钙 Exchangeable calcium/(cmol+·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
板页岩 Plate shale | 5.93 | 23.3 | 120.1 | 30.4 | 81.3 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 1.35 | 6.80 |
第四纪红土 Quaternary red earth | 4.60 | 16.1 | 76.7 | 5.7 | 87.5 | 0.72 | 4.61 | 0.26 | 1.52 |
河流冲积物 River alluvium | 5.39 | 17.8 | 105.9 | 15.4 | 50.0 | 0.25 | 0.62 | 0.52 | 3.73 |
红砂岩 Tertiary red sandstone | 4.45 | 30.6 | 175.4 | 9.7 | 68.8 | 0.24 | 7.76 | 0.23 | 0.72 |
花岗岩 Granite | 4.74 | 39.4 | 217.7 | 12.1 | 62.5 | 0.19 | 4.34 | 0.15 | 0.37 |
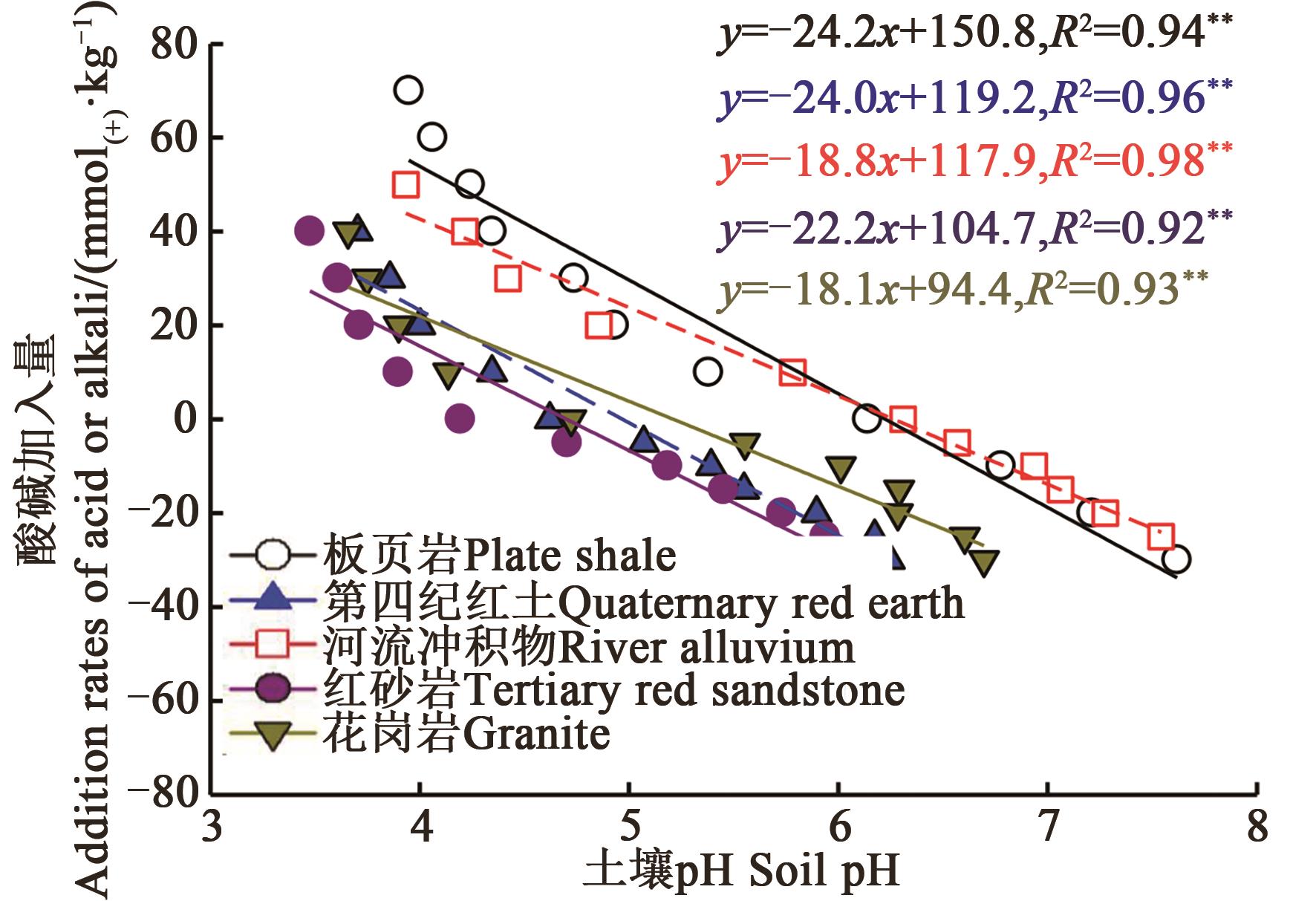
Fig. 1 pH buffering curve of soils derived from different parent materialsNote: >0 or <0 at y-axis represent acid or alkali addition rates, respectively;** indicates significant correlation at P<0.01 level.
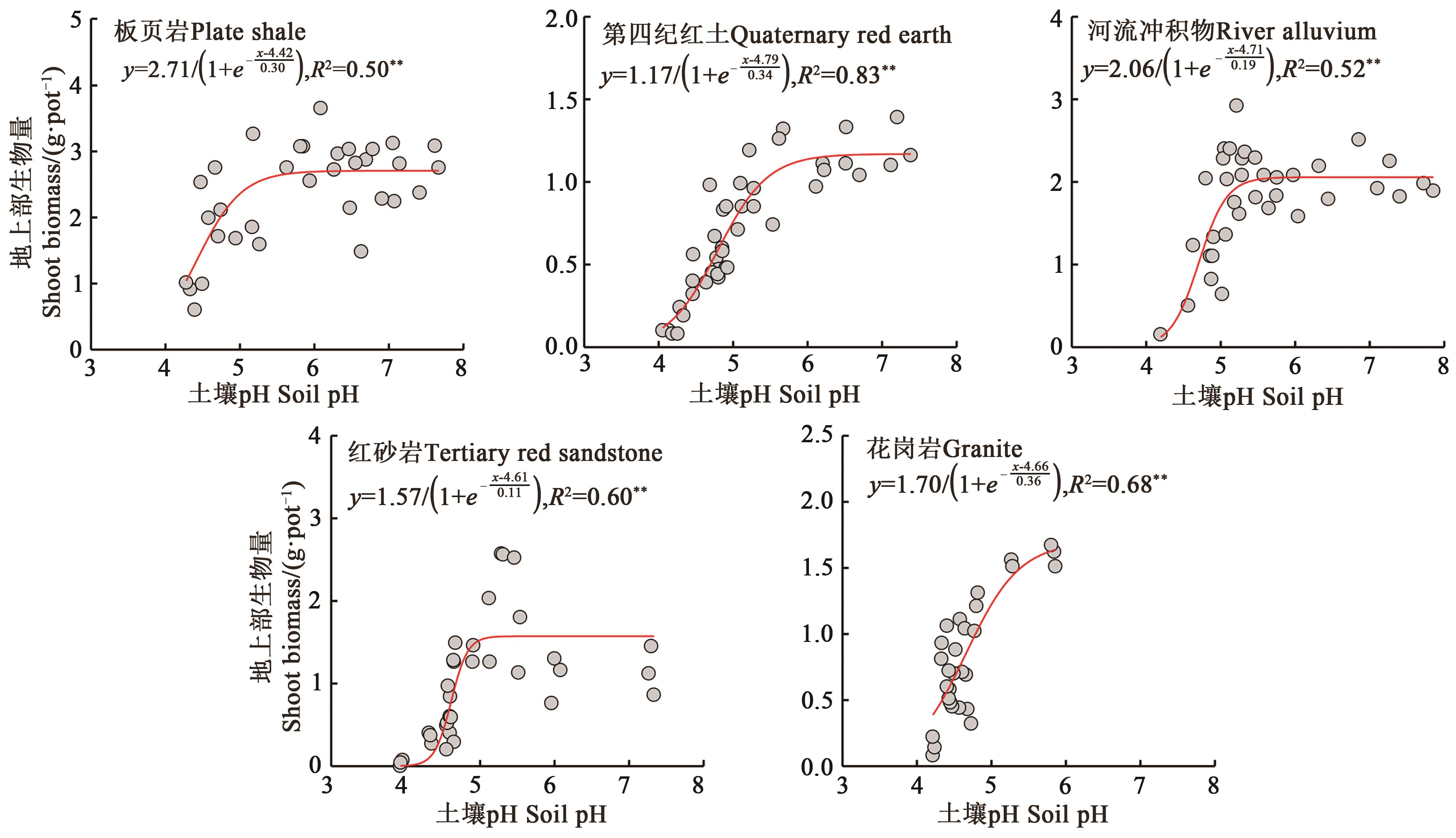
Fig. 2 Response of wheat shoot biomass to pH of soils derived from different parent materialsNote: ** indicates significant correlation at P<0.01 level.
土壤母质 Soil parent material | 稳定值 Stable value/(g·pot-1) | 阈值Critical value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH95% | pH50% | pH5% | ||
板页岩 Plate shale | 2.71 | 5.31 | 4.42 | 3.53 |
第四纪红土 Quaternary red earth | 1.17 | 5.79 | 4.79 | 3.80 |
河流冲积物 River alluvium | 2.06 | 5.25 | 4.71 | 4.16 |
红砂岩 Tertiary red sandstone | 1.57 | 4.94 | 4.61 | 4.29 |
花岗岩 Granite | 1.70 | 5.72 | 4.66 | 3.59 |
Table 2 Critical pH of wheat shoot biomass in soils derived from different parent materials
土壤母质 Soil parent material | 稳定值 Stable value/(g·pot-1) | 阈值Critical value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH95% | pH50% | pH5% | ||
板页岩 Plate shale | 2.71 | 5.31 | 4.42 | 3.53 |
第四纪红土 Quaternary red earth | 1.17 | 5.79 | 4.79 | 3.80 |
河流冲积物 River alluvium | 2.06 | 5.25 | 4.71 | 4.16 |
红砂岩 Tertiary red sandstone | 1.57 | 4.94 | 4.61 | 4.29 |
花岗岩 Granite | 1.70 | 5.72 | 4.66 | 3.59 |
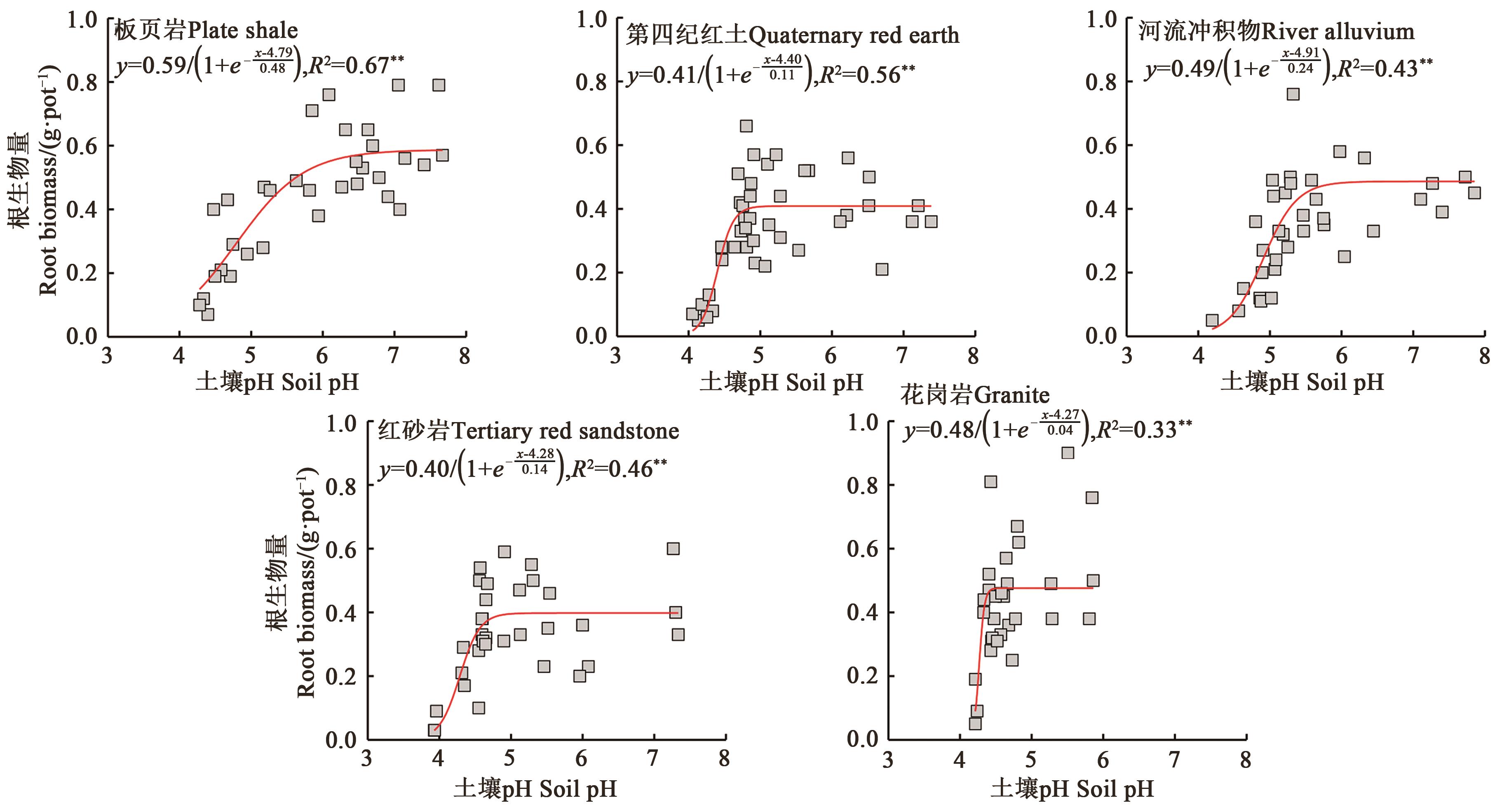
Fig. 3 Response of wheat root biomass to pH of soils derived from different parent materialsNote: ** indicates significant correlation at P<0.01 level.
土壤母质 Soil parent material | 稳定值 Stable value/(g·pot-1) | 阈值Critical value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH95% | pH50% | pH5% | ||
板页岩 Plate shale | 0.59 | 6.20 | 4.79 | 3.39 |
第四纪红土 Quaternary red earth | 0.41 | 4.73 | 4.40 | 4.07 |
河流冲积物 River alluvium | 0.49 | 5.60 | 4.91 | 4.21 |
红砂岩 Tertiary red sandstone | 0.40 | 4.70 | 4.28 | 3.87 |
花岗岩 Granite | 0.48 | 4.38 | 4.27 | 4.16 |
Table 3 Critical pH of wheat root biomass in soils derived from different parent materials
土壤母质 Soil parent material | 稳定值 Stable value/(g·pot-1) | 阈值Critical value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH95% | pH50% | pH5% | ||
板页岩 Plate shale | 0.59 | 6.20 | 4.79 | 3.39 |
第四纪红土 Quaternary red earth | 0.41 | 4.73 | 4.40 | 4.07 |
河流冲积物 River alluvium | 0.49 | 5.60 | 4.91 | 4.21 |
红砂岩 Tertiary red sandstone | 0.40 | 4.70 | 4.28 | 3.87 |
花岗岩 Granite | 0.48 | 4.38 | 4.27 | 4.16 |
土壤母质 Soil parent material | 稳定值 Stable value/cm | 阈值Critical value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH95% | pH50% | pH5% | ||
板页岩 Plate shale | 51.34 | 4.67 | 4.02 | 3.37 |
第四纪红土 Quaternary red earth | 34.76 | 5.17 | 4.36 | 3.56 |
河流冲积物 River alluvium | 53.40 | 5.09 | 4.32 | 3.55 |
红砂岩 Tertiary red sandstone | 42.43 | 5.01 | 4.31 | 3.61 |
花岗岩 Granite | 36.70 | 4.32 | 4.26 | 4.20 |
Table 4 Critical pH of wheat height in soils derived from different parent materials
土壤母质 Soil parent material | 稳定值 Stable value/cm | 阈值Critical value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH95% | pH50% | pH5% | ||
板页岩 Plate shale | 51.34 | 4.67 | 4.02 | 3.37 |
第四纪红土 Quaternary red earth | 34.76 | 5.17 | 4.36 | 3.56 |
河流冲积物 River alluvium | 53.40 | 5.09 | 4.32 | 3.55 |
红砂岩 Tertiary red sandstone | 42.43 | 5.01 | 4.31 | 3.61 |
花岗岩 Granite | 36.70 | 4.32 | 4.26 | 4.20 |
小麦生长 Wheat growth | 阈值 Critical value | 有机质 Organic matter | pH | 碱解氮 Available nitrogen | 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 有效钾 Available potassium | 交换性氢 Exchangeable hydrogen | 交换性铝 Exchangeable aluminum | 交换性镁 Exchangeable magnesium | 交换性钙 Exchangeable calcium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
地上部生物量 Shoot biomass | pH95% | -0.02 | -0.15 | -0.12 | -0.27 | 0.33 | 0.53 | -0.12 | -0.23 | -0.22 |
| pH50% | -0.25 | -0.65 | -0.22 | -0.89* | -0.16 | 0.79 | 0.35 | -0.80 | -0.67 | |
| pH5% | -0.20 | -0.40 | -0.07 | -0.46 | -0.46 | 0.12 | 0.42 | -0.42 | -0.33 | |
| 稳定值Stable value | -0.03 | 0.93* | -0.02 | 0.98** | -0.14 | -0.80 | -0.77 | 0.90* | 0.88* | |
根系生物量 Root biomass | pH95% | -0.51 | 0.95* | -0.50 | 0.87 | 0.04 | -0.44 | -0.83 | 0.94* | 0.99** |
| pH50% | -0.62 | 0.87* | -0.57 | 0.66 | -0.26 | -0.30 | -0.90* | 0.71 | 0.85 | |
| pH5% | 0.05 | -0.58 | 0.11 | -0.78 | -0.55 | 0.45 | 0.27 | -0.84 | -0.70 | |
| 稳定值Stable value | -0.02 | 0.94* | -0.06 | 0.95* | -0.02 | -0.67 | -0.85 | 0.88 | 0.86 | |
株高 Height | pH95% | -0.81 | -0.17 | -0.75 | -0.37 | 0.12 | 0.60 | 0.11 | -0.12 | 0.01 |
| pH50% | -0.12 | -0.79 | -0.07 | -0.95* | -0.27 | 0.68 | 0.57 | -0.90* | -0.79 | |
| pH5% | 0.80 | -0.48 | 0.78 | -0.40 | -0.36 | -0.09 | 0.35 | -0.63 | -0.69 | |
| 稳定值Stable value | -0.34 | 0.81 | -0.27 | 0.73 | -0.42 | -0.62 | -0.71 | 0.70 | 0.79 |
Table 5 Coefficient of correlation between critical pH of wheat and soil initial chemical properties
小麦生长 Wheat growth | 阈值 Critical value | 有机质 Organic matter | pH | 碱解氮 Available nitrogen | 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 有效钾 Available potassium | 交换性氢 Exchangeable hydrogen | 交换性铝 Exchangeable aluminum | 交换性镁 Exchangeable magnesium | 交换性钙 Exchangeable calcium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
地上部生物量 Shoot biomass | pH95% | -0.02 | -0.15 | -0.12 | -0.27 | 0.33 | 0.53 | -0.12 | -0.23 | -0.22 |
| pH50% | -0.25 | -0.65 | -0.22 | -0.89* | -0.16 | 0.79 | 0.35 | -0.80 | -0.67 | |
| pH5% | -0.20 | -0.40 | -0.07 | -0.46 | -0.46 | 0.12 | 0.42 | -0.42 | -0.33 | |
| 稳定值Stable value | -0.03 | 0.93* | -0.02 | 0.98** | -0.14 | -0.80 | -0.77 | 0.90* | 0.88* | |
根系生物量 Root biomass | pH95% | -0.51 | 0.95* | -0.50 | 0.87 | 0.04 | -0.44 | -0.83 | 0.94* | 0.99** |
| pH50% | -0.62 | 0.87* | -0.57 | 0.66 | -0.26 | -0.30 | -0.90* | 0.71 | 0.85 | |
| pH5% | 0.05 | -0.58 | 0.11 | -0.78 | -0.55 | 0.45 | 0.27 | -0.84 | -0.70 | |
| 稳定值Stable value | -0.02 | 0.94* | -0.06 | 0.95* | -0.02 | -0.67 | -0.85 | 0.88 | 0.86 | |
株高 Height | pH95% | -0.81 | -0.17 | -0.75 | -0.37 | 0.12 | 0.60 | 0.11 | -0.12 | 0.01 |
| pH50% | -0.12 | -0.79 | -0.07 | -0.95* | -0.27 | 0.68 | 0.57 | -0.90* | -0.79 | |
| pH5% | 0.80 | -0.48 | 0.78 | -0.40 | -0.36 | -0.09 | 0.35 | -0.63 | -0.69 | |
| 稳定值Stable value | -0.34 | 0.81 | -0.27 | 0.73 | -0.42 | -0.62 | -0.71 | 0.70 | 0.79 |
| 1 | 徐明岗, 文石林, 周世伟, 等. 南方地区红壤酸化及综合防治技术[J]. 科技创新与品牌, 2016 (7): 74-77. |
| XU M G, WEN S L, ZHOU S W, et al.. Acidification and integrated control techniques of red soil in southern China [J]. Sci. Technol. Innov., 2016(7): 74-77. | |
| 2 | GUO J H, LIU X J, ZHANG Y, et al.. Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands [J]. Science, 2010, 327(5968): 1008-1010. |
| 3 | 徐仁扣. 土壤酸化及其调控研究进展[J]. 土壤, 2015, 47(2): 238-244. |
| XU R K. Research progresses in soil acidification and its control [J]. Soils, 2015, 47(2): 238-244. | |
| 4 | CAI Z J, WANG B R, XU M G, et al.. Intensified soil acidification from chemical N fertilization and prevention by manure in an 18-year field experiment in the red soil of southern China [J]. J. Soil Sediment., 2015, 15(2): 260-270. |
| 5 | MULLEN C L, SCOTT B J, EVANS C M, et al.. Effect of soil acidity and liming on lucerne and following crops in central-western New South Wales [J]. Anim. Prod. Sci., 2006, 46(10): 1291-1300. |
| 6 | 蔡泽江, 孙楠, 王伯仁, 等. 长期施肥对红壤 pH、作物产量及氮、磷、钾养分吸收的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(1): 71-78. |
| CAI Z J, SUN N, WANG B R, et al.. Effects of long-term fertilization on pH of red soil crop yields and uptakes of nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium [J]. J. Plant Nutr. Fert., 2011, 17(1): 71-78. | |
| 7 | ZHU Q C, LIU X J, HAO T X, et al.. Cropland acidification increases risk of yield losses and food insecurity in China [J/OL]. Environ. Pollut., 2020, 256: 113145 [2022-05-12]. . |
| 8 | BAQUY M A, LI J Y, JIANG J, et al.. Critical pH and exchangeable Al of four acidic soils derived from different parent materials for maize crops [J]. J. Soil Sediment., 2018, 18:1490-1499. |
| 9 | 梁文君, 蔡泽江, 宋芳芳, 等. 不同母质发育红壤上玉米生长与土壤pH、交换性铝、交换性钙的关系[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2017, 36(8): 1544-1550. |
| LIANG W J, CAI Z J, SONG F F, et al.. Relationships between maize growth and the pH, exchangeable aluminum and calcium of red soils derived from different parent materials [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2017, 36(8): 1544-1550. | |
| 10 | BACHE B W, CROOKE W M. Interactions between aluminum, phosphorus and pH in the response of barley to soil acidity [J]. Plant Soil, 1981, 61(3): 365-375. |
| 11 | 成杰民, 胡光鲁, 潘根兴, 等. 用酸碱滴定曲线拟合参数表征土壤对酸缓冲能力的新方法[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2004, 23 (3): 569-573. |
| CHENG J M, HU G L, PAN G X, et al.. New method for evaluating buffering capacity and equilibrium pH of paddy soil with simulation parameter [J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2004, 23(3): 569-573. | |
| 12 | 汪吉东, 冯冰, 李传哲, 等. 中国几种典型土壤酸碱缓冲容量测定方法的比较[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2020, 36(6): 1452-1458. |
| WANG J D, FENG B, LI C Z, et al.. Comparative study on determination methods for acid buffering capacity of several typical soils in China [J]. Jiangsu J. Agric. Sci., 2020, 36(6): 1452-1458. | |
| 13 | 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000:1-495. |
| 14 | 王如月, 袁世力, 文武武, 等. 磷对铝胁迫紫花苜蓿幼苗根系生长和生理特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 53-62. |
| WANG R Y, YUAN S L, WEN W W, et al.. Effects of phosphorus on root growth and photosynthetic physiology of alfalfa seedlings under aluminum stress [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2021, 30(10): 53-62. | |
| 15 | 艾佐佐, 袁军, 黄丽媛, 等. 磷对铝胁迫下油茶幼苗根冠比及根系形态的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2017, 45(12): 106-108. |
| AI Z Z, YUAN J, HUANG L Y, et al.. Effects of phosphorus on root-shoot ratio and root morphology of camellia oleifera seedlings under aluminum stress [J]. Jiangsu Agric. Sci., 2017, 45(12): 106-108. | |
| 16 | 朱美红, 蔡妙珍, 吴韶辉, 等. 磷对铝胁迫下荞麦元素吸收与运输的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2009, 23(2): 183-187. |
| ZHU M H, CAI M Z, WU S H, et al.. Effect of phosphorus on element uptake and transportation in buckwheat under aluminum stress [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2009, 23(2): 183-187. | |
| 17 | 王宁, 郑怡, 王芳妹, 等. 铝毒胁迫下磷对荞麦根系铝形态和分布的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2011, 25(5): 168-171. |
| WANG N, ZHENG Y, WANG F M, et al.. Effect of phosphorus on speciation and distribution of aluminum in the roots of buckwheat under aluminum toxicity [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2011, 25(5): 168-171. | |
| 18 | 吴良泉. 科学施镁, 让土地“美”起来! [J]. 中国农资, 2018 (46): 24. |
| WU L Q. Let the land “beautiful” up by scientific applying magnesium [J]. China Agri-product. News, 2018(46): 24. | |
| 19 | 赵越, 杨金玲, 许哲, 等. 模拟酸雨淋溶下不同母质发育雏形土矿物风化中的盐基离子与硅计量关系[J/OL]. 土壤学报, 2022 [2022-05-12]. . |
| ZHAO Y, YANG J L, XU Z, et al.. Stoichiometry of base cations and silicon of cambosols derived from different parent materials as leached by simulated acid rain [J/OL]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2022 [2022-05-12]. . | |
| 20 | BOSSOLANI J W, CRUSCIOL C A C, MORETTI L G, et al.. Improving soil fertility with lime and phosphogypsum enhances soybean yield and physiological characteristics [J/OL]. Agron. Sustain. Dev., 2022, 42: 26 [2022-05-12].. |
| 21 | LAURICELLA D, BUTTERLY C R, CLARK G J, et al.. Effectiveness of innovative organic amendments in acid soils depends on their ability to supply P and alleviate Al and Mn toxicity in plants [J]. J. Soil Sediment., 2020, 20(11): 3951-3962. |
| [1] | Jingjuan GAO, Chenyu ZHU, Yuqin KE, Chaoyuan ZHENG, Chunying LI, Wenqing LI. Effects of Organic Fertilizer Application Period on Carbon and Nitrogen Metabolism in Flue-cured Tobacco Under Tobacco-Rice Rotation [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 157-165. |
| [2] | Shegang SHAO, Ting LI, Yong LIU, Lanwen LIN, Dong ZHANG, Dong NI, Junjie LI, Li’an ZHU. Effects of Exogenous Promoting Bacteria Agent on Decomposition Characteristics and Microbial Community Structure of Rice Straw [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 166-177. |
| [3] | Jing GAO, Minggang XU, Ran LI, Zejiang CAI, Nan SUN, Qiang ZHANG, Lei ZHENG. Effects of Biochar Application on Soil pH: A Meta-Analysis [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 186-196. |
| [4] | Yuanyuan DUAN, Xiaohong LIU, Tao TANG, Fanfan WANG, Jingmao YOU, Xiaoliang GUO, Jie GUO. Effects of Planting Density on Growth and Quality of Fritillaria hupehensis [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 197-206. |
| [5] | Lili SHAN. Effects of Low Temperature During Booting Stage on Rice Physiology and Alleviating Effect of Exogenous Melatonin [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 23-33. |
| [6] | Wei WANG, Qiang ZHAO, Abuduaini Munire·, Alimu·Amuli, Xinxin LI, Yangqing TIAN. Effects of Different Exogenous Substances on Chemical Capping and Yield and Quality of Cotton [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 57-68. |
| [7] | Rui TIAN, Hua ZHANG, Meihong HUANG, Zhenqi SHAO, Xihuan LI, Caiying ZHANG. Mining of Candidate Genes and Genetic Loci Conferring Drought Tolerance in Soybean [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 69-82. |
| [8] | Peng ZHONG, Lili MIAO, Jianli WANG, Jie LIU, Xiaolong WANG. Physiological Response and Cold Resistance Evaluation of Cyperus esculentus Germplasms Under Low Temperature Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 83-96. |
| [9] | Dengyang LU, Xin WANG, Zhanghu TANG, Cuiyun WU, Yunfeng PU, Min YAN, Jingkai BAO, Xi JIANG. Phenolic Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Pear Species During Fruit Development Comparison [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 97-104. |
| [10] | Yitong XIAO, Shuai LIU, Chenlian HOU, Qi LIU, Fuzhong LI, Wuping ZHANG. Organ Segmentation and Phenotypic Analysis of Soybean Plants Based on Three-dimensional Point Clouds [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 115-125. |
| [11] | Rui XIAO, Lu TAN, Liang WU, Hao ZHANG, Jiayuan GUO, Haijun YANG. Microbial Community Structure and Diversity in Rhizosphere and Non-rhizosphere Soil of Kochia scoparia Under Cd Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 203-215. |
| [12] | Dongdong ZHANG, Hongwei HAN, Zhenfan YU, Bin ZENG, Jiahui YANG, Wenwen GAO, Xintong MA. Codon Preference Analysis of Chloroplast Genome in 12 Rosaceae Plants [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 65-75. |
| [13] | Xiang WU, Juan LI, Yan CAO, Yanrong CHENG, Xuyu YAN, Ling LI. Research Advances on Plant Root Exudates in Response to Cadmium Stress [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 12-20. |
| [14] | Xingsheng YIN, Lingfeng BAO, Yongyu PU, Jiali SUN, Qing ZHANG, Haiping LI, Mingying YANG, Yueping LIN, Huaixin WANG, Yonghong HE, Peiwen YANG. Effects of Chemical Fertilizer Reduction Combined with Bio-organic Fertilization on Tobacco Soil Characteristics and Tobacco Bacterial Wilt Control [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 122-131. |
| [15] | Feifan HOU, Xiaowen ZHANG, Jiaqi WANG, Jianzhen ZHANG, Kaiquan LI, Xuebin YIN. Effect of Selenium Fertilizer Application Position on Physiological Characters and Selenium Accumulation in Wheat [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 144-152. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号