




















Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology ›› 2023, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (10): 189-197.DOI: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2023.0023
• BIO-MANUFACTURING & RESOURCE AND ECOLOGY • Previous Articles
Hongyan WU( ), Miao YU, Jian FENG, Hui LIU
), Miao YU, Jian FENG, Hui LIU
Received:2023-01-06
Accepted:2023-07-31
Online:2023-10-15
Published:2023-10-27
作者简介:吴红艳 E-mail:lnwuhy@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Hongyan WU, Miao YU, Jian FENG, Hui LIU. Effect of Phosphorus Solubilizing Bio-fertilizer on Soil Phosphorus Availability and Pepper Yield in Greenhouse[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(10): 189-197.
吴红艳, 于淼, 冯健, 刘晖. 解磷生物肥对温室土壤磷有效性及辣椒产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(10): 189-197.
| 载体 Vector | 吸水性 Hygroscopy/mL | 有效菌体释放率 Effective thallus release rate/% |
|---|---|---|
| 腐殖酸 Humic acid | 6.4 | 72 |
| 蚯蚓粪 Wormcast | 8.1 | 59 |
| 鸡粪(腐熟) Chicken manure (decomposed) | 7.6 | 85 |
Table 1 Carrier hydroscopicity and effective cell release rate
| 载体 Vector | 吸水性 Hygroscopy/mL | 有效菌体释放率 Effective thallus release rate/% |
|---|---|---|
| 腐殖酸 Humic acid | 6.4 | 72 |
| 蚯蚓粪 Wormcast | 8.1 | 59 |
| 鸡粪(腐熟) Chicken manure (decomposed) | 7.6 | 85 |
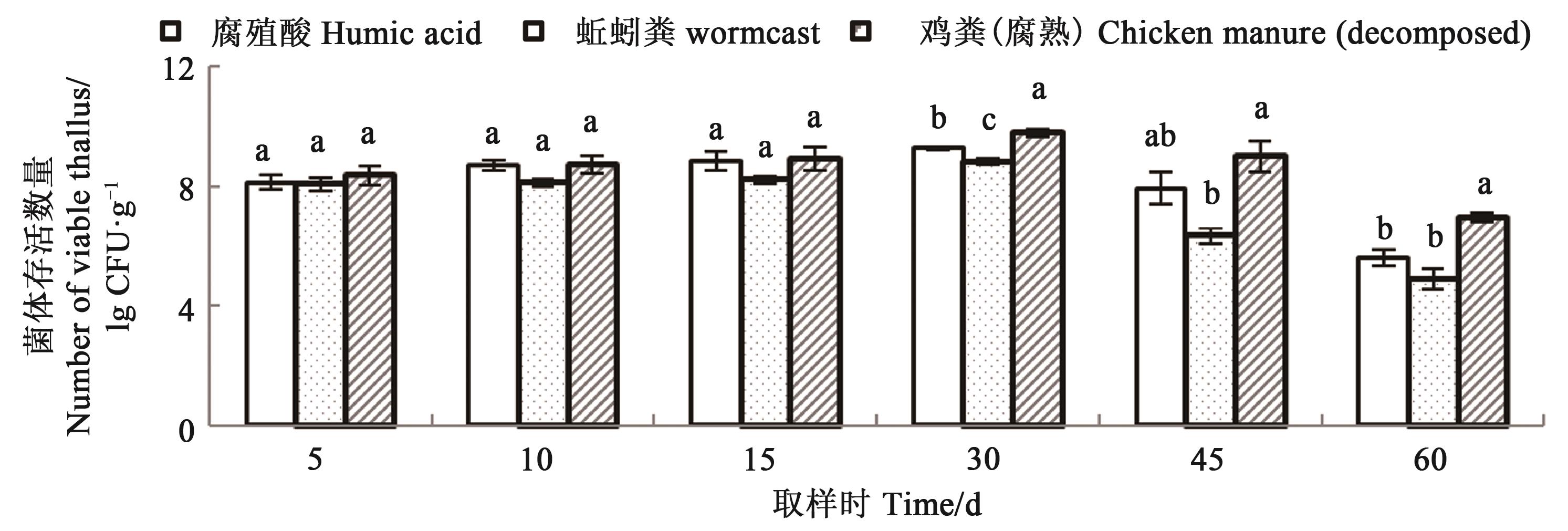
Fig. 1 Survival number of bacteria in different carriers at different timesNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference between treatments at P<0.05 level.
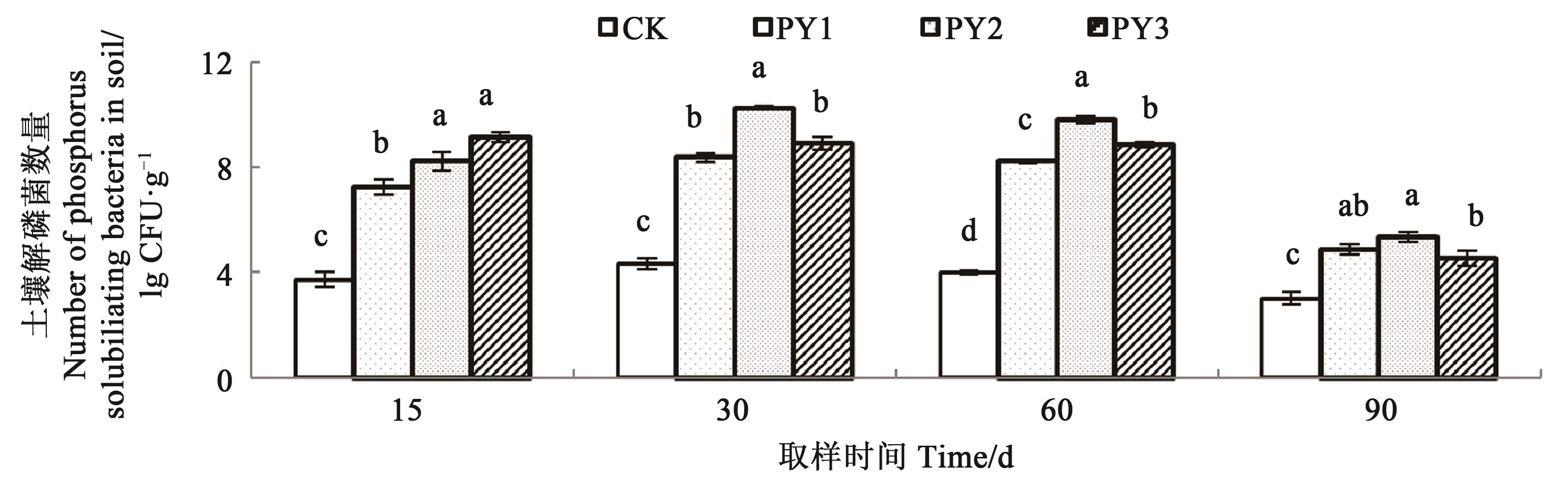
Fig. 2 Quantity of soil phosphorus solubilizing bacteria in different fertilization treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference between treatments at P<0.05 level.
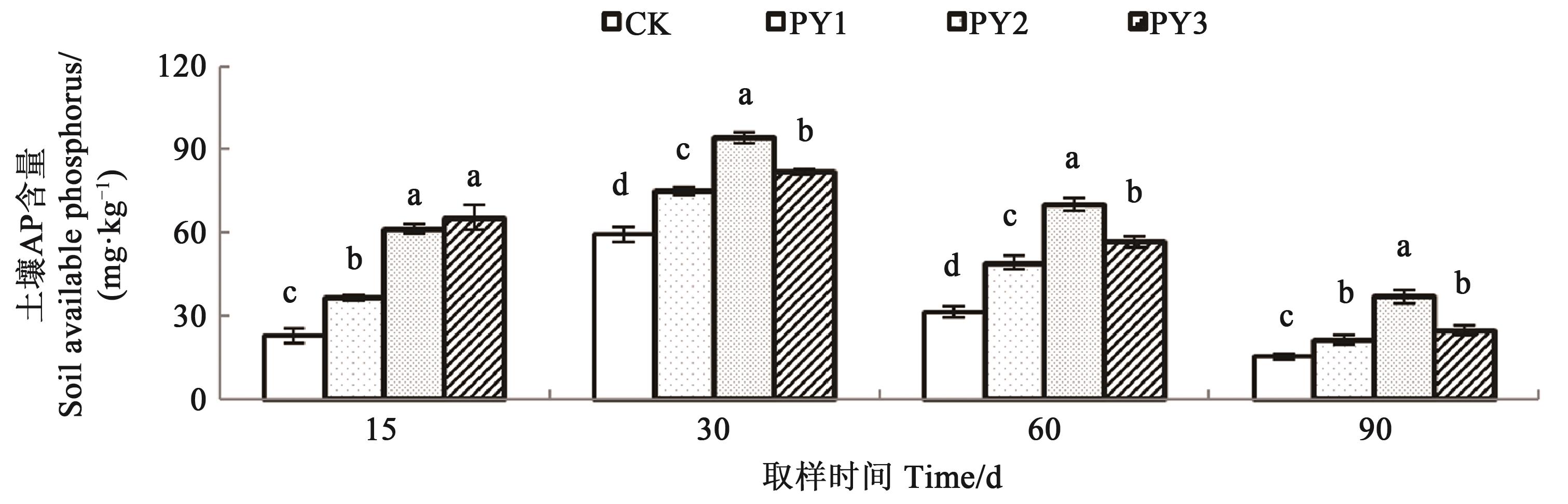
Fig. 3 Soil available phosphorus content under different fertilization treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference between treatments at P<0.05 level.
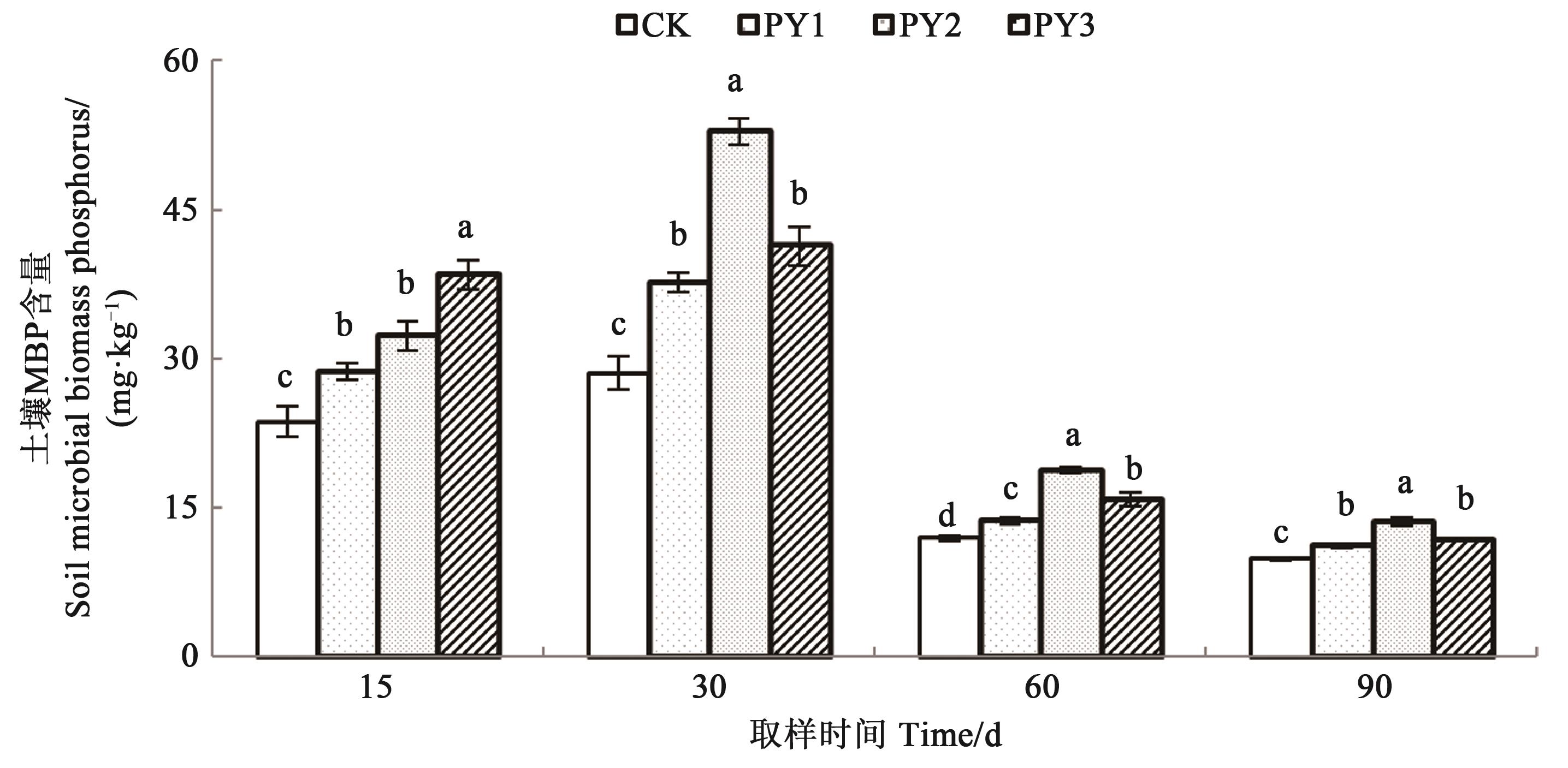
Fig. 4 Soil microbial biomass phosphorus content in different fertilization treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference between treatments at P<0.05 level.
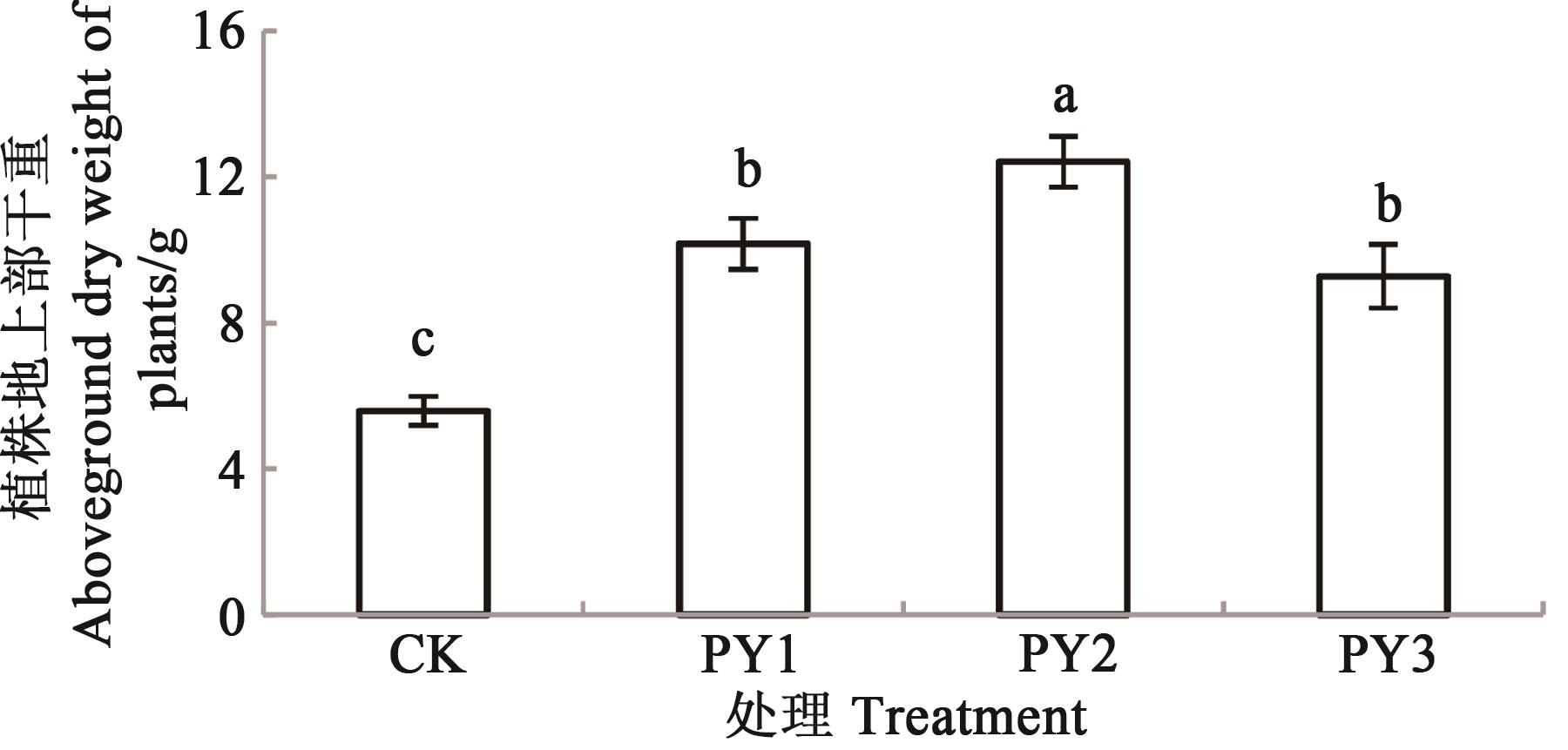
Fig. 5 Aboveground dry weight of pepper under different fertilization treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference between treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 根系 Root system | CK | PY1 | PY2 | PY3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 整根干重 Whole root dry weight/g | 4.213 5±0.167 2 c | 5.436 8±0.079 3 b | 6.826 9±0.101 3 a | 4.420 1±0.203 2 c |
| 根长度 Root length/cm | 24.533 6±1.469 0 c | 25.314 2±1.053 7 bc | 29.300 4±0.516 6 a | 28.466 7±1.215 5 ab |
| 主根直径 Taproot diameter/mm | 7.936 7±0.365 8 c | 8.916 2±0.116 1 b | 9.996 3±0.133 7 a | 8.663 9±0.307 2 bc |
Table 2 Whole root dry weight, length and taproot diameter of pepper under different fertilization treatments
| 根系 Root system | CK | PY1 | PY2 | PY3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 整根干重 Whole root dry weight/g | 4.213 5±0.167 2 c | 5.436 8±0.079 3 b | 6.826 9±0.101 3 a | 4.420 1±0.203 2 c |
| 根长度 Root length/cm | 24.533 6±1.469 0 c | 25.314 2±1.053 7 bc | 29.300 4±0.516 6 a | 28.466 7±1.215 5 ab |
| 主根直径 Taproot diameter/mm | 7.936 7±0.365 8 c | 8.916 2±0.116 1 b | 9.996 3±0.133 7 a | 8.663 9±0.307 2 bc |
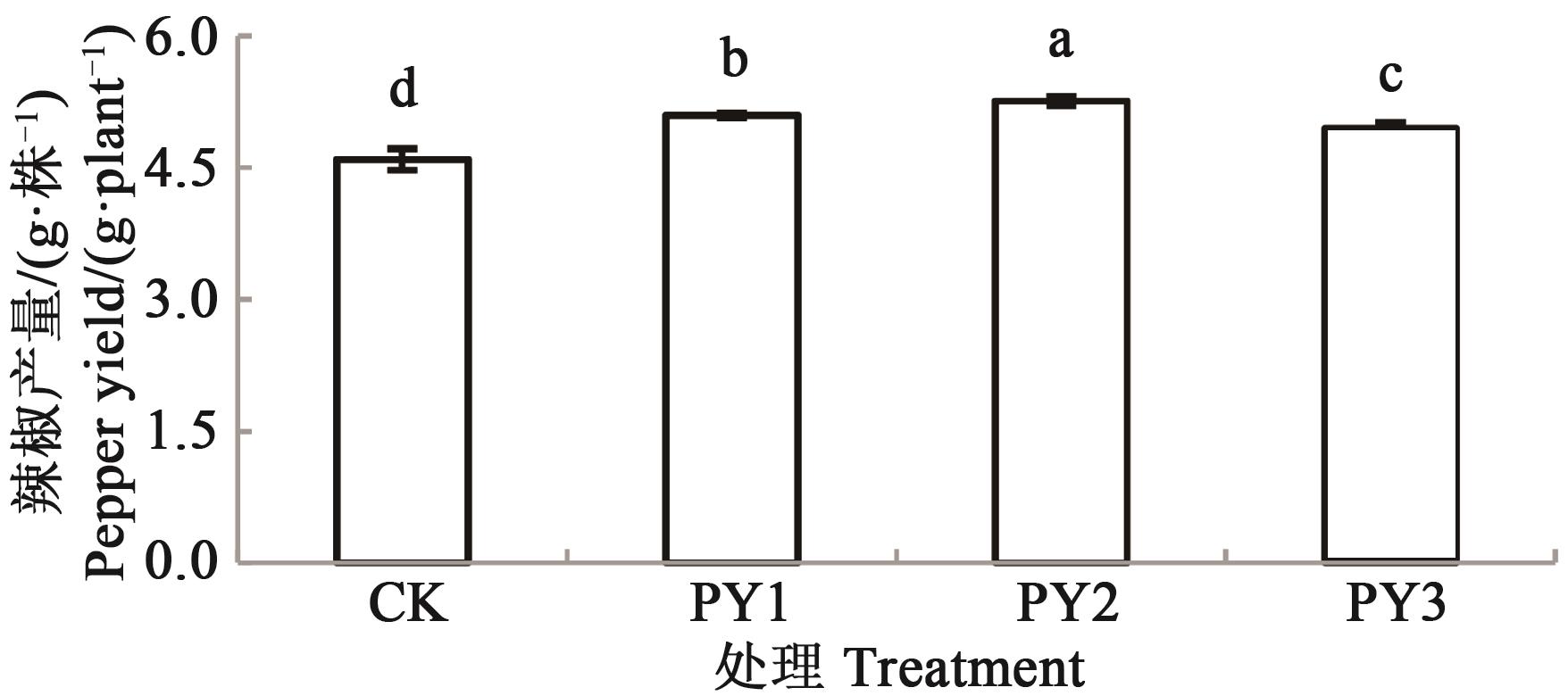
Fig. 6 Pepper yield under different fertilization treatmentsNote:Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference between treatments at P<0.05 level.
| 指标 Index | 土壤有效磷 Soil AP | 辣椒地上部干重 Aboveground dry weight | 辣椒产量 Pepper yield | 土壤解磷菌数量 Soil phosphorus solubiliating bacteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 辣椒地上部干重 Aboveground dry weight | 0.759** | |||
| 辣椒产量 Pepper yield | 0.791** | 0.921** | ||
| 土壤解磷菌数量 Poil phosphorus solubiliating bacteria | 0.799** | 0.814** | 0.924** | |
| 土壤微生物量磷 Soil MBP | 0.927** | 0.899** | 0.860** | 0.787** |
Table 3 Correlation analysis between number of soil phosphorus solubilizing bacteria, soil MBP, plant dry weight, pepper yield and soil AP
| 指标 Index | 土壤有效磷 Soil AP | 辣椒地上部干重 Aboveground dry weight | 辣椒产量 Pepper yield | 土壤解磷菌数量 Soil phosphorus solubiliating bacteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 辣椒地上部干重 Aboveground dry weight | 0.759** | |||
| 辣椒产量 Pepper yield | 0.791** | 0.921** | ||
| 土壤解磷菌数量 Poil phosphorus solubiliating bacteria | 0.799** | 0.814** | 0.924** | |
| 土壤微生物量磷 Soil MBP | 0.927** | 0.899** | 0.860** | 0.787** |
| 1 | 王孝忠. 我国蔬菜生产的环境代价、减排潜力与调控途径[D].北京:中国农业大学,2018. |
| WANG X Z. Environmental impacts,mitigation potentials and management approaches in Chinese vegetable production system [D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University,2018. | |
| 2 | 王连林,张志成,商立军,等.新型微生物功能菌剂的筛选与功能菌肥的研制[J].化肥工业,2019,46( 3): 6-9. |
| WANG L L, ZHANG Z C, SHANG L J,et al.. Screening of new microbial functional bacterial agents and development of functional bacterial fertilizer [J]. Chem. Fert. Ind., 2019,46(3): 6-9. | |
| 3 | 李夏夏,李春钢,姜雄,等.矿物微生物肥料的应用前景[J].化工矿物与加工,2018(6) :63-66. |
| LI X X, LI C G, JIANG X, et al.. Application prospect of mineral microbial fertilizer [J].Ind. Minerals Process., 2018(6): 63-66. | |
| 4 | 张胜男.颗粒微生物肥料的研制及其促生机理研究[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学,2017. |
| ZHANG S N. Development of granule microbial fertilizer and its effect and mechanism of plant growth-promoting [D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2017. | |
| 5 | 王应兰. 解磷微生物细菌的筛选、鉴定及其制备肥料的研究[D].贵阳:贵州大学,2020. |
| WANG Y L. Study on screening and identification of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria and preparation of fertilizers [D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2020. | |
| 6 | 杜雷,陈钢,王素萍,等.解磷菌剂对生菜根际土壤微生物数量和酶活性的影响[J].湖北农业科学,2019,58(11): 70-74. |
| DU L, CHEN G, WANG S P, et al.. Effects of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria on rhizosphere microorganism and enzyme activities of lettuce [J].Hubei Agric. Sci., 2019,58(11): 70-74. | |
| 7 | 胡英宏,任泽广,杨姝钰,等.生物有机肥对菠萝心腐病发生和土壤细菌群落结构的影响[J].应用与环境生物学报, 2022, 28(6): 1444-1451. |
| HU Y H, REN Z G, YANG S Y, et al.. Effects of bio-organic fertilizers on pineapple heart rot and bacterial community structure [J]. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol., 2022, 28(6): 1444-1451. | |
| 8 | 李玉奇,辛世杰,奥岩松.微生物菌肥对温室黄瓜生长、产量及品质的影响[J].中国农学通报,2012,28(1):259-263. |
| LI Y Q, XIN S J, AO Y S. Effects of microbial fertilizers on the growth, yield and quality of cucumber in greenhouse cultivation [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2012,28(1):259-263. | |
| 9 | 于会丽,徐变变,徐国益,等. 生物有机肥对苹果幼苗生长、生理特性以及土壤微生物功能多样性的影响[J].中国农学通报, 2022,38(1):32-38. |
| YU H L, XU B B, XU G Y, et al.. Effects of bio-organic fertilizer on growth, physiological characteristics of apple seedlings and soil microbial functional diversity [J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2022,38(1):32-38. | |
| 10 | 周通. 草莓枯萎病生防菌的筛选及其生物有机肥研究[D]. 大连:大连理工大学,2018. |
| ZHOU T. Isolation of antagonistic microbe for controlling fusarium wilt of strawberry and study on its fortified bio-organic fertilizer [D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology,2018. | |
| 11 | 谢东锋,王国强,谢荣,等.不同微生物菌肥处理连作土壤对黄瓜生长及防御性酶的影响[J].福建农业学报,2018,33(7):696-701. |
| XIE D F, WANG G Q, XIE R, et al.. Effects of microbial fertilizers on growth and defense-related enzymes of continuously cropped cucumbers [J]. Fujian J. Agric. Sci., 2018, 33(7):696-701. | |
| 12 | 苗天瑶.微生物菌剂与秸秆肥结合改良设施栽培土壤的研究[D].长春:吉林农业大学,2017. |
| MIAO T Y. Study on improvement of greenhouse soil by combination of microbial inoculum and straw fertilizer [D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2017. | |
| 13 | ZENG Q W, WU X Q, WEN X Y. Erratum to:identification and characterization of the rhizosphere phosphate-solubilizing bacterium Pseudomonas frederiksbergensis JW-SD2,and its plant growth-promoting effects on poplar seedlings [J]. Ann. Microbiol., 2017,67(3):1343-1354. |
| 14 | 赵玥.芽孢杆菌的筛选及在复合菌肥中应用研究[D]. 长春:吉林农业大学,2020. |
| ZHAO Y. Screening of bacillus and its application in compound fertilizer [D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2020. | |
| 15 | 袁芳,张凯,马超,等.有机肥添加对不同磷肥用量新疆棉田磷素状况及棉花产量的影响[J].农业资源与环境学报,2022,39(1):118-128. |
| YUAN F, ZHANG K, MA C, et al.. Effects of organic fertilizer addition on field phosphorus status and yield under different amounts of phosphorus fertilization in cotton field in Xinjiang, China [J]. J. Agric. Resour. Environ., 2022, 39(1): 118-128. | |
| 16 | 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京:中国农业出版社,2000:14-243. |
| 17 | 吴金水,林先贵,贺前锋,等. 土壤微生物生物量的测定熏蒸提取法: [S].北京:中国标准出版社,2020. |
| 18 | 张博凯,郝鲜俊,高文俊,等. 不同有机肥及用量对矿区复垦土壤有效磷含量及供磷特性的影响[J]. 水土保持学报,2021,35(2):271-278. |
| ZHANG B K, HAO X J, GAO W J, et al.. Effects of different organic fertilizers and amounts on available phosphorus content and phosphorus supply characteristics in coal mining reclaimed soil [J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2021,35(2):271-278. | |
| 19 | 刘彦伶,李渝,张艳,等. 长期施用磷肥和有机肥黄壤微生物量磷特征[J].中国农业科学,2021,54(6):1188-1198. |
| LIU Y L, LI Y, ZHANG Y, et al.. Characteristics of microbial biomass phosphorus in yellow soil under long-term application of phosphorus and organic fertilizer [J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2021,54(6):1188-1198. | |
| 20 | 祁娟,姚拓,白小明,等. 复合菌肥替代部分磷肥对苜蓿草地生产力及土壤肥力的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2017,26(10):118-128. |
| QI J, YAO T, BAI X M, et al.. Impacts on alfalfa productivity and soil fertility of partially replacting phosphate fertilizers with microbial fertilizers [J]. Acta Pratac. Sin., 2017,26(10):118-128. | |
| 21 | 郑淇元,谢意太,卞海洋,等. 溶磷菌肥对红壤磷组分及土壤肥力的影响[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2022,44(1):233-244. |
| ZHENG Q Y, XIE Y T, BIAN H Y, et al.. Effects of phosphate solubilizing bio-fertilizer on phosphorus fractions and fertility of red soil [J]. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis, 2022,44(1):233-244. | |
| 22 | 方华舟,左雪枝.稻田固氮解磷解钾菌筛选及其复合菌剂对土壤培肥作用[J].中国土壤与肥料,2014(2): 82-87. |
| FANG H Z, ZUO X Z. Isolation and application of N-fixing,P-releasing and K-releasing bacteria from rice paddy [J].Soil Fert. Sci. China, 2014(2): 82-87. | |
| 23 | 滕艳敏,韩卉,郝梓依,等.不同蔬菜种植模式对土壤淋溶水总氮、总磷和COD的影响[J].中国生态农业学报,2017,25(5):759-768. |
| TENG Y M, HAN H, HAO Z Y, et al.. Effect of vegetable cropping system on total nitrogen, phosphorus and COD in farmland leachate [J]. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2017, 25(5): 759-768. | |
| 24 | GUIÑAZÚ L B, ANDRÉS J A, PAPA M F D. Response of alfalfa Medicago sativa L.to single and mixed inoculation with phosphate-solubilizing bacteria and Sinorhizobium meliloti [J]. Biol. Fert. Soils, 2010,46:185-190. |
| 25 | HAMEEDA B, HARINI G, RUPELA O P, et al.. Growth promotion of maize by phosphate-solubilizing bacteriaisolated from composts and macrofauna [J]. Microbiol. Res.,2008,163:234-242. |
| 26 | 蒋欣梅,夏秀华,于锡宏,等. 微生物解磷菌肥对大棚茄子生长及土壤有效磷利用的影响[J]. 浙江大学学报(理学版), 2012, 39(6):685-688. |
| JIANG X M, XIA X H, DING X H, et al.. Effects of phosphorus-dissolving microbers fertilizer on growth of eggplant and utilization of available phosphorus in soil in the vinyl tunnel [J]. Acta Agric. Univ. Zhejiangensis (Sci.),2012,39(6):685-688. | |
| 27 | 王秀娟,韩瑛祚,何志刚,等. 微生物菌肥对设施番茄养分吸收与土壤氮磷累积的影响[J]. 北方园艺,2021(19):100-106. |
| WANG X J, HAN Y Z, HE Z G,et al.. Effcts of microbial fertilizer on nutrient uptake of tomato and soil nitrogen and phosphorus accumulation in facilities [J]. Northern Hortic., 2021(19):100-106. | |
| 28 | 苑伟伟,赵阳国,井永苹,等. 一种高效解磷复合菌剂的筛选与应用[J].山东农业科学,2016,48(12) : 86-90. |
| YUAN W W, ZHAO Y G, JING Y P, et al.. Screening and application of an efficient phosphate-solubilizing compound microbial inoculants [J]. Shandong Agric. Sci., 2016,48(12) : 86-90. | |
| 29 | 曾洪玉,李志勇,唐宝国,等. 不同磷肥用量对油菜产量、肥料利用率及土壤养分的影响[J]. 农学学报,2019,9(7):31-36. |
| ZENG H Y, LI Z Y, TANG B G, et al.. Effects of different amounts of phosphate fertilizer on rapeseed yield,fertilizer utilization and soil nutrients [J]. Agric. Sci., 2019,9(7):31-36. | |
| 30 | 任朝辉,田浩,廖卫琴,等. 磷肥不同施用量对辣椒生长农艺性状及产量的影响[J].辣椒杂志,2021(1):10-13. |
| REN C H, TIAN H, LIAO W Q,et al.. Effects of different applications of phosphate fertilizer on agronomic characters and yield of pepper [J]. J. China Capsicum,2021(1):10-13. | |
| 31 | 慧薇,李丽君, 王斌,等. 磷肥对藜麦生长及养分吸收的影响[J]. 山西农业科学,2021,49(4):444-448. |
| HUI W, LI L J, WANG B, et al. Effects of phosphate fertilizer on growth and nutrient accumulation of quinoa [J]. Shanxi Agric. Sci.,2021,49(4):444-448. |
| [1] | Yuanyuan DUAN, Xiaohong LIU, Tao TANG, Fanfan WANG, Jingmao YOU, Xiaoliang GUO, Jie GUO. Effects of Planting Density on Growth and Quality of Fritillaria hupehensis [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 197-206. |
| [2] | Ying ZHOU, Jingyong LI, Linxiu DAI, Dicai AO, Ziyi LI, Fan YANG, Junwei GU, Qiang XU, Zhi DOU, Hui GAO. Effect of Melatonin Spraying on Rice Yield Formation and Lodging Resistance Under Rice-Crayfish Coculture Mode [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 34-42. |
| [3] | Wei WANG, Qiang ZHAO, Abuduaini Munire·, Alimu·Amuli, Xinxin LI, Yangqing TIAN. Effects of Different Exogenous Substances on Chemical Capping and Yield and Quality of Cotton [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(9): 57-68. |
| [4] | Chenyang ZHANG, Minggang XU, Fei WANG, Ran LI, Nan SUN. Effects of Manure Application on Soybean Yield and Soil Nutrients in China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 148-156. |
| [5] | Zhigang ZHENG, Li XIANG, Gongyi LIU, Cai XU, Bin QIN, Weiqin WANG, Huabin ZHENG, Qiyuan TANG. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Density on Growth and Yield of Orderly Machine-thrown Early Rice [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 132-143. |
| [6] | Yaxuan MENG, Wei MA, Xuhang YAO, Yingqi SUN, Xin ZHONG, Shan HUANG, Qiaoyun WENG, Yinghui LIU, Jincheng YUAN. Study on the Response Factors of Maize Yield to Nitrogen Fertilizer [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 153-160. |
| [7] | Wen ZHOU, Xiaoheng GUO, Rui XU, Xiaoli WANG, Huiwei NIU, Dan HAN, Huifang SHAO. Effects of Intercropping Pinellia ternata on Growth, Yield and Quality of Flue-cured Tobacco [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(7): 161-169. |
| [8] | PANG Zhe, WANG Qilong, LI Juan. Effects of Different Soil Amendments on Soil Physical and Chemical Properties, Rice Yield and Economic Benefits in Low-lying Saline Alkali Land in Northern Shaanxi [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(6): 174-180. |
| [9] | Panpan ZHANG, Chuan LI, Meiwei ZHANG, Xia ZHAO, Jun NIU, Jiangfang QIAO. Effect of Nitrification Inhibitor Application on Nitrogen Accumulation and Transportation and Grain Yield of Summer Maize Under Reduced Nitrogen [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(6): 181-189. |
| [10] | Lu TIAN, Xiaoxia GUO, Wenbin SU, Chunyan HUANG, Zhi LI, Peng ZHANG, Caiyuan JIAN, Jia LIU, Dejuan KONG, Kang HAN. Effects of Microbial Fertilizer on Growth, Yield and Quality of Continuous Cropping Sugar Beet [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(5): 192-203. |
| [11] | Chen CHEN, Ke SHI, Changwei ZHU, Guiying JIANG, Lan LUO, Weiwei MENG, Fang LIU, Fengmin SHEN, Shiliang LIU. Effects of Planting Density and Nitrogen Application Rate on Wheat Photosynthetic Characteristics, Yield, and Soil Nitrogen Content in Fluvo-aquic Soil in Northern Henan Province [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(5): 24-33. |
| [12] | Yanjun KE, Yumeng ZHANG, Yanjie GUO, Lijuan ZHANG, Zitao ZHANG, Yanzhi JI. Effects of Bio-organic Fertilizer Combined with Subsoiling on Farmland Soil Fertility and Crop Yield [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(4): 157-166. |
| [13] | Zhengran SUN, Cuiping ZHANG, Jinli ZHANG, Hao WU, Xiuyan LIU, Zhenkai WANG, Yuzhen YANG, Daohua HE. Effects of Chemical Detopping on Cotton Plant Growth in Guanzhong Cotton Region [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(4): 167-177. |
| [14] | Wenjun ZHAO, Jizhou YANG, Mei YIN, Jianfeng CHEN, Kaizheng XUE, Baowen HU, Libo FU, Wei WANG, Zhiyuan WANG, Yanxian YANG, Hua CHEN. Effects of Combined Application of Green Manure with Reduced Nitrogen Fertilizer on Yield and Quality of Flue-cured Tobacco [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(4): 189-196. |
| [15] | Xiangdong WANG, Yue SONG, Yanzhi MA. Quality Comparison and Comprehensive Evaluation of Different Zingiber officinale Rosc. Varieties [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(4): 56-66. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802021197号
京公网安备11010802021197号